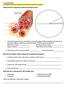
Identify and describe the circulation system that is missing from the organizer above.
|
|
|
- Rosamund Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions of the circulatory system. I. Cardiovascular system 1. Structures: blood, and blood vessels 2. Function: moves materials throughout the body 3 Circulation systems: flow of blood Identify and describe the circulation system that is missing from the organizer above. II. The Heart a. Describe the chambers of the heart: Watch the following: b. What are the structure(s) and function(s) of valves? III. Blood Vessels: tubes that carry blood to every part of the body 1
2 IV. Blood Pressure: force of blood on blood vessel walls 1. highest in and lowest in veins a. Systolic: ventricles contract = blood pushed out of heart b. Diastolic: relax and fill with blood V. Cardiovascular Disease: Leading cause of death in US 1. Atherosclerosis: a. can lead to heart 2. Hypertension: a. can be caused by atherosclerosis b. heart must work harder 3. What actions prevent against heart disease? VI. Summarize Visit the following link: Copy the Circulation diagram to the right and complete the following tasks: 1. Which letter best represents the capillaries? 2. Which letter best represents the left atrium? 3. Which letter best represents the pulmonary vein, which returns blood to the left side of the heart from the lungs? 4. Blood leaves the heart on the right side by way of the pulmonary artery. Which letter best represents the pulmonary artery, which carries blood to the lungs so that carbon dioxide can be exchanged for oxygen? 5. Which letter best represents the aorta, which carries blood to all body parts from the left side? 6. Copy and complete the flow chart. 2
3 Lesson 15.1 CLASSWORK: The Circulatory System Learning Target: I can identify structures and explain functions of the circulatory system. Vocabulary: pulmonary; systemic; coronary; chamber; valve; vein; artery; capillary; atherosclerosis; hypertension Warm Up: Complete Socrative Assessment. Copy errors and confusions. Teaching: Review LT; Vocabulary; Socrative Results Possible Misconceptions: What is the error about the heart diagram? Are heart beat and pulse rate the same? Can you use a stethoscope to take heart rate? How does an atria and artery compare? Task: 1. I can use a stethoscope to compare my heartbeats to my pulse measured in (bpm). A. Use a stethoscope, listen to your heart. Count the beats you hear in 15 seconds. Make a table to record your findings. Name(s); Heartbeat/15 seconds; Heartbeats/1 minute (n x = heartbeats/1 minute) B. Find your pulse at your wrist or neck. Count your pulse for 15 seconds. Make a table to record your findings. Name(s); Pulse/15 seconds; Pulse/1 minute (n x = Pulse/1 minute) C. What is the relationship between heartbeat and pulse? 2. Complete "Heart Label Lab" **See pages 4-5 of this document 3. Design a model that compares atherosclerosis with a healthy blood vessel. 4. Complete "Blood Pressure" Worksheet *See pages Enrichment: "Circulatory System Model" **See pages 8-9 of this document Summarize: Check your answers 3
4 Lab: Heart Structure LT: I can use text descriptions to label the parts of the heart. NOTE: Notice that Figure 2 shows the left and right sides of the heart reversed. The diagram actually shows the position of the heart in a person as it would appear if you were facing the person whose heart is shown. 1. The vena cava returns blood to the right side of the heart from body organs. Locate and label the vena cava. 2. The pulmonary vein returns the blood to the left side of the heart from the lungs. Locate and label the pulmonary vein. 3. Blood in veins enters the right and left atrium, two small chambers at the top of the heart. Locate and label the right atrium and left atrium. 4. Pumping action of the heart squeezes blood from the atria into the right and left ventricles, two large chambers at the bottom of the heart. Locate and label the right ventricle and the left ventricle. 5. Pumping action of the heart squeezes blood from the two ventricles. Blood leaves the heart on the left side by way of an artery called the aorta. Locate and label the aorta, which carries blood to all body parts. 6. Blood leaves the heart on the right side by way of another artery, the pulmonary artery. Locate and label the pulmonary artery, which carries blood to the lungs so that carbon dioxide can be exchanged for oxygen. 7. Locate and label the heart valves between the atria and ventricles. Valves keep blood flowing in one direction. 8. Locate and label the valves where the pulmonary artery and aorta are joined to the heart. 9. Use a blue pencil to color in the spaces on Figure 2 to show where deoxygenated blood would be. Blood returning to or pumped from the right side of the heart is deoxygenated. This means that the amount of oxygen in the blood is low. 10. Use a red pencil to color in the spaces on Figure 2 to show where oxygenated blood would be. Oxygenated blood contains a large amount of oxygen. Those vessels returning to or leaving the left side of the heart carry oxygenated blood. 4
5 Name: Date: Class: #: Data and Observations: Complete Table 1. Use the words oxygenated or deoxygenated to describe the condition of the blood in each part. If the part does not exist on the specified side, place an X in the box. (Example: the vena cava only exists on the right side, so place an X in the box on the left side vena cava section. Remember: Figure 2 shows the left and right sides of the heart reversed. Table 1 Part Right Side Left Side Atrium Ventricle Vena cava X Aorta Pulmonary Vein Pulmonary Artery Analysis Questions: 1. How does the left side of the heart compare to the right side of the heart? 2. Veins are blood vessels that carry blood to the heart and usually carry deoxygenated blood, (appearing blue). Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart and usually carry oxygenated blood, (appearing red). Why does the pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein not fully match this description? 5
6 Name: Date: Class: #: LT: I can read and interpret graphs in order to determine blood pressure readings. Blood Pressure Blood pressure is described by measuring two events: (a) Systolic pressure pressure when the ventricles of the heart contract and push blood into arteries (b) Diastolic pressure pressure when the ventricles relax and blood in the arteries is not being pushed. Blood pressure is a comparison of systolic to diastolic numbers, and is written as a fraction. The systolic number is written as the numerator and the diastolic number is written as the denominator. Figure 3 shows a person s blood pressures (measured in mm of mercury) as it changes from birth to age 60. For example, the systolic pressure for the child at 10 years old was 100 mm of mercury. The diastolic pressure for this child was 65 mm of mercury. Figure 4 1. a. What is the systolic pressure for this person at age 20? b. What is the diastolic pressure for this person at age 20? 2. From the graph, determine the blood pressure at the following ages: (to be written as a fraction) a. 15 years old: b. 30 years old: c. 40 years old: 6
7 For Numbers 3 and 4, show all work in the space provided. You will not earn credit without showing work. 3. a. How much change occurs in systolic pressure from age 0 to 60? b. How much change occurs in diastolic pressure from age 0 to 60? 4. Does systolic blood pressure change more from ages 0 to 20 or from ages 20 to 60? 5. a. At what age is there the greatest difference between systolic pressure and diastolic pressure? b. What is the blood pressure at this age? 6. At what age did the person have a systolic pressure of about 120 and diastolic pressure of about 75? A person is said to have high blood pressure if systolic and diastolic pressures are higher than normal. A person is said to have a low blood pressure if systolic and diastolic pressure are lower than normal. 1. Determine the person s blood pressure at each of the following ages (see Table 1 below). 2. Determine if the person has low, ideal (normal), pre-high, or high blood pressure by comparing the pressures in Table 1 with those in the graph in Figure 4. Using this blood pressure chart (Figure 4): To determine blood pressure readings, just find your top number (systolic) on the left side of the blood pressure chart and read across, and your bottom number (diastolic) on the bottom of the blood pressure chart. Your blood pressure is where the two points meet. Table 1: Blood Pressure Age Systolic Diastolic Pressure Work Show Here 7
8 Circulatory System Model LT: I can follow a procedure in order to model structures of the circulatory system. Introduction In this activity you will learn about all the parts of your circulatory system and what they do. Let's start by building a model that can serve as your guide to the parts of the circulatory system and how they fit together. Materials 4 Paper cups Tape 3 Lima beans 1 Straw Balloon (white) Scissors Glue Colored thread (blue and red) Ruler Ruler 2 Paper towels Blue and red pencils or pens 2 20cm pieces of blue yarn 2 20cm pieces of red yarn Procedure First, you are going to build a model heart. The heart has four chambers. In each side of the heart, blood enters the upper chamber and leaves the lower chamber. Now follow Steps 1 through 6 as you build your model heart. Step 1 Place the open ends of two paper cups together. Secure the cups together with tape. Do the same thing with the other two cups. Step 2 Stand the two sets of cups side by side. Each cup represents a heart chamber. Step 3 Carefully poke a hole in the side of each cup using a pencil. Step 4 Cut a straw into four equal pieces. Color or paint two of the pieces blue and the other two pieces red. Step 5 Insert and glue one of the blue straws into opening B. Insert and glue a red straw into opening C. Step 6 Stick a piece of blue yarn into the open end of the blue straw attached to the cups. Stick a piece of red yarn into the open end of the red straw attached to the cups. The straws and yarn represent blood vessels coming to and leaving the heart. The straws and yarn represent the system of blood vessels through which the heart pumps blood. This model resembles a figure eight. Half of the figure eight is the lung circuit where blood picks up oxygen. The other half of the figure eight is the body circuit where blood gives oxygen to all the cells of the body. Now you know the significance of the blue and red colors. Blue represents vessels carrying blood after it gives oxygen to cells. Red represents vessels carrying blood with a full load of oxygen. You can use this information in completing the following steps to finish your model. Step 7 Inflate a white balloon to about 10cm (4 inches) in diameter and tie it off. The balloon represents the lungs. Step 8 Glue blue and red threads on the surface of the inflated balloon. The threads (or colored lines) represent the tiniest blood vessels where the blood picks up oxygen and delivers carbon dioxide to the lungs. 8
9 Step 9 Glue the free ends of the blue yarn to the surface of the balloon that has the tiny blue vessels. Glue the free ends of the red yarn to the surface of the balloon that has the tiny red vessels. You have completed the part of the model that represents the pump that moves blood to your lungs and back to the heart. Step 10 Now finish your model of the heart by showing how blood moves to your body cells. Insert and glue the other red straw into opening D. Insert and glue the other blue straw into opening A. Step 11 Stick a piece of red yarn into the open end of the second red straw. Stick a piece of blue yarn into the open end of the second blue straw. Step 12 Obtain three or four lima beans to represent body cells. Cut about 10 to 12 pieces of thread, each about 3 centimeters long. Half of the pieces should be red. The other half should be blue. Glue one end of several red and blue threads on the surface of each bean. Step 13 Attach the free end of the red threads to the red yarn. Attach the free ends of the blue threads to the blue yarn. Step 14 Be sure you can explain to someone the path that a drop of blood would take in flowing through your model. End of Lab Task: 1. Draw a diagram of your completed model including labels for the following: a. What does the balloon represent? b. What do the beans represent? c. What do the cups represent? d. What do the different colored string and yarn represent? 2. Write an explanation of how blood would flow through your model. 9
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Circulatory System Heart Stations
 Circulatory System Heart Stations Standard Addressed: Life Science Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, lungs, and body and how carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and oxygen (O 2 ) are exchanged
Circulatory System Heart Stations Standard Addressed: Life Science Students know how blood circulates through the heart chambers, lungs, and body and how carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) and oxygen (O 2 ) are exchanged
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Body s Transport System (pp )
 The Body s Transport System (pp. 538 547) This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete
The Body s Transport System (pp. 538 547) This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38
 Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
TOPIC NFL PLAY 60 Kids Day Live Virtual Field Trip
 EDUCATOR COMPANION GUIDE TOPIC NFL PLAY 60 Kids Day Live Virtual Field Trip KEY LEARNING OBJECTIVES In the following activities students will: Model the functioning of the heart. Describe how the heart
EDUCATOR COMPANION GUIDE TOPIC NFL PLAY 60 Kids Day Live Virtual Field Trip KEY LEARNING OBJECTIVES In the following activities students will: Model the functioning of the heart. Describe how the heart
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Circulatory System Learning Outcomes State the type of tissue the heart is made of State the function of the heart State the number of chambers in the heart Know how the blood flows
The Circulatory System Circulatory System Learning Outcomes State the type of tissue the heart is made of State the function of the heart State the number of chambers in the heart Know how the blood flows
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
CIRCULATORY WEBQUEST L.E. Biology (PART I: Introduction, Parts of the Heart, and Pathway of Blood)
 Name: Period: CIRCULATORY WEBQUEST L.E. Biology (PART I: Introduction, Parts of the Heart, and Pathway of Blood) http://www.smm.org/heart/heart/steth.htm 1. Where is your heart located? Use the stethoscope
Name: Period: CIRCULATORY WEBQUEST L.E. Biology (PART I: Introduction, Parts of the Heart, and Pathway of Blood) http://www.smm.org/heart/heart/steth.htm 1. Where is your heart located? Use the stethoscope
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
KS4 Biology. The Heart and Circulatory System. 1 of 49. Boardworks Ltd 2004
 1 of 49 KS4 Biology The Heart and Circulatory System 2 of 49 Contents The Heart and Circulatory System The circulatory system Structure of the heart Valves in the heart How the heart pumps blood Summary
1 of 49 KS4 Biology The Heart and Circulatory System 2 of 49 Contents The Heart and Circulatory System The circulatory system Structure of the heart Valves in the heart How the heart pumps blood Summary
The Body s Transportation System (pages )
 The Body s Transportation System (pages 100-106) Use the diagram to answer the following questions. Name Date Class Circulatory Packet 1. Draw arrows on the diagram to show the path of the blood flow throughout
The Body s Transportation System (pages 100-106) Use the diagram to answer the following questions. Name Date Class Circulatory Packet 1. Draw arrows on the diagram to show the path of the blood flow throughout
ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle
 ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle In this activity, you will follow the flow of blood through the heart. Your heart has two jobs to do, and its two sides have separate responsibilities: The left side pumps oxygen-enriched
ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle In this activity, you will follow the flow of blood through the heart. Your heart has two jobs to do, and its two sides have separate responsibilities: The left side pumps oxygen-enriched
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body
 The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body (1) As you have already learned, there are muscles all over your body. All of them are important, but not all of them are vital. The muscle
The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body (1) As you have already learned, there are muscles all over your body. All of them are important, but not all of them are vital. The muscle
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Functions of the Circulatory System
 Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13}
 Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Ch.15 Cardiovascular System Pgs {15-12} {15-13} E. Skeleton of the Heart 1. The skeleton of the heart is composed of rings of dense connective tissue and other masses of connective tissue in the interventricular
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1 1. Moves nutrients to and waste from cells 2. Pathway for disease fighting agents and hormones 3. Control of body temperature homeostasis 2 The Circulatory
TRANSPORTATION AND CIRCULATION THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1 1. Moves nutrients to and waste from cells 2. Pathway for disease fighting agents and hormones 3. Control of body temperature homeostasis 2 The Circulatory
Circulation and Respiration
 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body.
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body. What does blood consist of? The blood consists
Circulatory System The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body. What does blood consist of? The blood consists
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Cardiovascular Learners MUST KNOW R A G. Know the double- circulatory system (systemic and pulmonary)
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection
 Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
Cardiovascular System BELLWORK: Define using technology angio hemo/hema cardio brady as in bradycardia tachy as in tachycardia Standards 8) Outline basic concepts of normal structure and function of all
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
OB16 Demonstrate the effect of exercise and rest on pulse and breathing rate and appreciate that a balance of each promotes good health
 Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
INVESTIGATING THE STRUCTURE OF THE HEART
 Luke Micallef name Heart Health: A Beginner s guide to cardiovascular disease Section INVESTIGATING THE STRUCTURE OF THE HEART Guide to Week 1 home practical Note: You will also need to download a copy
Luke Micallef name Heart Health: A Beginner s guide to cardiovascular disease Section INVESTIGATING THE STRUCTURE OF THE HEART Guide to Week 1 home practical Note: You will also need to download a copy
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4 The Circulatory System: The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) has 3 basic components:- *A muscular pump: heart *Interconnecting tubes: blood
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM : (circulatory system) Lab-4 The Circulatory System: The circulatory system (cardiovascular system) has 3 basic components:- *A muscular pump: heart *Interconnecting tubes: blood
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
Human Anatomy - Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 Human Anatomy - Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson Overview The circulatory and respiratory systems work together to pump blood and oxygen through the human body. Without these systems, the human
Human Anatomy - Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson Overview The circulatory and respiratory systems work together to pump blood and oxygen through the human body. Without these systems, the human
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Cardiovascular System. Heart Anatomy
 Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
THE HEART. Structure & Function
 THE HEART Structure & Function SARAH JOHANSON BIOTECH ENGINEERING, 2015 Function of the Heart: The heart is muscular organ that sits centrally in the thorax region of the body, but is skewed and twisted
THE HEART Structure & Function SARAH JOHANSON BIOTECH ENGINEERING, 2015 Function of the Heart: The heart is muscular organ that sits centrally in the thorax region of the body, but is skewed and twisted
Thanks. Connect. You Might Also Like. Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback.
 Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. in Exercise 10A you will learn how to measure blood pressure. 2. in
AP Biology Laboratory Date: Name and Period: AP Biology Lab 10 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM OVERVIEW In this lab you will: 1. in Exercise 10A you will learn how to measure blood pressure. 2. in
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Heart to Heart! Advance
 Heart to Heart! Lesson Concept Link The structure of the heart enables it to oxygenate and pump blood throughout the body. In the previous lesson, students investigated the structure and function of the
Heart to Heart! Lesson Concept Link The structure of the heart enables it to oxygenate and pump blood throughout the body. In the previous lesson, students investigated the structure and function of the
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
Heart and Lung Dissection
 Heart and Lung Dissection Name(s) Before you begin any work or dissection of your specimen, please try to identify the following. You will need to illustrate what you see, so make sure to note size, texture
Heart and Lung Dissection Name(s) Before you begin any work or dissection of your specimen, please try to identify the following. You will need to illustrate what you see, so make sure to note size, texture
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Blood Pressure Laboratory
 Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
Introduction The blood that circulates throughout the body maintains a flow and pressure. The nervous system can change the flow and pressure based on the particular needs at a given time. For example,
9 Transport in animals
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Transport in animals Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 9 Transport
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Transport in animals Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 9 Transport
A. Incorrect! The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium.
 DAT Biology - Problem Drill 10: The Circulatory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. What is the flow of deoxygenated blood through the heart as it returns from the body? Question #01 (A) Vena cava; right ventricle;
DAT Biology - Problem Drill 10: The Circulatory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. What is the flow of deoxygenated blood through the heart as it returns from the body? Question #01 (A) Vena cava; right ventricle;
Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy. Student Information Page 3A
 Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy Student Information Page 3A Activity Introduction: Once you get home from running around all day, your throat is probably a little dry. You go to your kitchen, get
Vessels by Design: Basic Vessel Anatomy Student Information Page 3A Activity Introduction: Once you get home from running around all day, your throat is probably a little dry. You go to your kitchen, get
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates
 LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM. NATURAL SCIENCE 2 nd ESO
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM NATURAL SCIENCE 2 nd ESO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The circulatory system is made up of: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM HEART BLOOD BLOOD VESSELS THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The heart pumps the blood
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM NATURAL SCIENCE 2 nd ESO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The circulatory system is made up of: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM HEART BLOOD BLOOD VESSELS THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The heart pumps the blood
Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. Name the 3 parts of a neuron and their function: a. b. c. 2. What is
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. Name the 3 parts of a neuron and their function: a. b. c. 2. What is
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System. Circulatory System
 Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
THE HEART. Structure & Function
 THE HEART Structure & Function SARAH JOHANSON BIOTECH ENGINEERING, 2015 Function of the Heart: The heart is muscular organ that sits centrally in the thorax region of the body, but is skewed and twisted
THE HEART Structure & Function SARAH JOHANSON BIOTECH ENGINEERING, 2015 Function of the Heart: The heart is muscular organ that sits centrally in the thorax region of the body, but is skewed and twisted
