Circulation and Respiration
|
|
|
- Melvyn Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1. What can doctors do if a person s heart fails? 2. In this chapter, you will study all of the following systems EXCEPT a. the respiratory system. c. the cardiovascular system. b. the digestive system. d. the lymphatic system. What Do You Think? (p. 487) Answer these questions in your ScienceLog now. Then later, you ll have a chance to revise your answers based on what you ve learned. Investigate! (p. 487) 3. What causes the throbbing called a pulse? Section 1: The Cardiovascular System (p. 488) 4. The system that transports materials to and from your What Is Blood? (p. 488) 5. Your blood is a type of connective tissue. True or False? (Circle one.) is made up of blood, the, and blood. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 143
2 6. Which of the following make up the plasma? (Circle all that apply.) a. red blood cells e. minerals b. water f. white blood cells c. proteins g. nutrients d. platelets h. sugars 7. How does the shape of a red blood cell make it especially well suited for its job? Mark each of the following statements True or False. 8. Hemoglobin is a cell that helps to transport the oxygen you inhale to the rest of your body. 9. The bone marrow is where red blood cells are produced. 10. Red blood cells have a relatively short life span because they have no DNA and cannot make proteins. Answer questions after you finish reading about white blood cells on page 489. Choose the term in Column B that best matches the phrase in Column A, and write the corresponding letter in the space provided. Column A 11. a tiny particle that can make you sick 12. a chemical that some WBCs release to help fight intruders 13. formed in the bone marrow 14. where some WBCs mature 15. Which of the following statements are true of platelets? (Circle all that apply.) a. They last for 5 to 10 days. b. They pinch off fragments of themselves to form a blood clot. c. They are fragments of larger cells. d. They help reduce blood loss. Column B a. antibody b. pathogen c. white blood cell d. lymphatic organ 144 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
3 Have a Heart (p. 490) 16. Your heart is a four-chambered muscular organ about the size of your a. stomach. c. liver. b. nose. d. fist. 17. What causes the lub-dub sounds of your heartbeat? Use the diagram on page 490 to place the following steps of blood flow through the heart in the correct order. Write the appropriate number in the space provided. 18. Blood is squeezed into the ventricles when the atria contract. 19. Blood enters the atria. 20. Blood is pushed out of the heart when the atria relax and the ventricles contract. Blood Vessels (p. 491) 21. Look at Figure 8. Capillaries connect to. (large veins or small veins, large arteries or small arteries) Choose the type of blood vessel in Column B that best matches the description in Column A, and write the corresponding letter in the space provided. Blood vessels can be used more than once. Column A 22. smallest blood vessels in the body 23. direct blood away from the heart 24. many substances can diffuse through their walls 25. direct blood back to the heart 26. push blood with the help of skeletal muscles 27. very close to all living cells in the body 28. have thick walls to withstand pressure Column B a. arteries b. capillaries c. veins DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 145
4 Going with the Flow (p. 492) 29. Pulmonary circulation is the process during which blood obtains oxygen from the lungs. True or False? (Circle one.) 30. Systemic circulation is the circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs. True or False? (Circle one.) Use the diagram on page 492 to answer the following questions. Indicate whether each of the following statements is a part of pulmonary or systemic circulation. In the space provided, write P if it is part of pulmonary circulation and S if it is part of systemic circulation. 31. Oxygen-poor blood travels through arteries to the lungs. 32. Oxygen-poor blood is delivered to the right atrium of the heart by two large veins. 33. The blood releases carbon dioxide and absorbs oxygen. 34. Oxygen, nutrients, and water are delivered to the body s cells. 35. Oxygen-rich blood pumps from the left ventricle into arteries. Blood Flows Under Pressure (p. 493) 36. How is blood running through your veins like water running through a hose? 37. The units that blood pressure is reported in are. 38. Figure 10 shows a person getting his blood pressure checked. How might your blood pressure indicate a problem with your cardiovascular system? 146 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
5 39. In a normal blood pressure reading of 120/80, the number 80 stands for the pressure in the a. arteries when the ventricles relax. b. arteries when the ventricles contract. c. ventricles when the ventricles relax. d. ventricles when the ventricles contract. Exercise and Blood Flow (p. 493) Mark each of the following statements True or False. 40. When you exercise, blood flow is reduced to the brain, heart, and lungs so that more blood can go to the muscles. 41. Some of your organs, like your kidneys, do not need oxygen when you exercise. 42. When your heart beats faster, more oxygen and nutrients are being delivered to your muscles. 43. When all the water faucets in the body are open, the heart rate slows down. 44. Your brain directs blood flow. Review (p. 493) Now that you ve finished reading the first part of Section 1, review what you ve learned by answering the Review questions in your ScienceLog. What s Your Blood Type? (p. 494) 45. Is it safe to give a person blood of any type? Explain. 46. Everyone has type,,, or blood. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 147
6 Each of the following statements is false. Change the underlined word to make the statement true. Write the new word in the space provided. 47. Blood type is determined by the antibodies present on the surface of your red blood cells. 48. Type O blood has both A and B antigens. 49. Certain chemicals in plasma, called enzymes, can bind to RBCs and cause the RBCs to clump together. 50. Type O people are universal recipients. Cardiovascular Problems (p. 495) 51. Cardiovascular problems occur only in the heart. True or False? (Circle one.) 52. Cardiovascular problems affect the movement of through the body. 53. What is wrong with the blood vessel shown in Figure 12? 54. Which of the following statements is NOT true about hypertension? a. It is promoted by atherosclerosis. b. It weakens blood vessels. c. It is an abnormally low blood pressure. d. It can lead to a stroke. 148 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
7 55. List three things mentioned in the text that people can do to reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease. Review (p. 495) Now that you ve finished Section 1, review what you learned by answering the Review questions in your ScienceLog. Section 2: The Lymphatic System (p. 496) 1. Your cells are bathed in fluid. What happens to that fluid? 2. The lymphatic system and the cardiovascular system are both systems. Vessels of the Lymphatic System (p. 496) 3. Besides fluid, the lymph also contains that are too large to enter the blood capillaries. 4. Lymph is carried into lymphatic vessels by, the smallest vessels of the lymphatic system. 5. Lymph is not pushed through the lymphatic system by a pump. How does it move? DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 149
8 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1. What can doctors do if a person s heart fails? They can temporarily replace the heart with an artificial heart, which may be able to keep the patient alive for a short time. 2. In this chapter, you will study all of the following systems EXCEPT a. the respiratory system. c. the cardiovascular system. b. the digestive system. d. the lymphatic system. What Do You Think? (p. 487) Answer these questions in your ScienceLog now. Then later, you ll have a chance to revise your answers based on what you ve learned. Investigate! (p. 487) 3. What causes the throbbing called a pulse? The pulse is caused by blood vessels expanding and then returning to their original position with each heartbeat. Section 1: The Cardiovascular System (p. 488) 4. The system that transports materials to and from your cells heart vessels What Is Blood? (p. 488) 5. Your blood is a type of connective tissue. True or False? (Circle one.) is made up of blood, the, and blood. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 143
9 6. Which of the following make up the plasma? (Circle all that apply.) a. red blood cells e. minerals b. water f. white blood cells c. proteins g. nutrients d. platelets h. sugars 7. How does the shape of a red blood cell make it especially well suited for its job? The shape of a red blood cell gives it a large surface area to absorb and release oxygen. Mark each of the following statements True or False. 8. False Hemoglobin is a cell that helps to transport the oxygen you inhale to the rest of your body. 9. True The bone marrow is where red blood cells are produced. 10. True Red blood cells have a relatively short life span because they have no DNA and cannot make proteins. Answer questions after you finish reading about white blood cells on page 489. Choose the term in Column B that best matches the phrase in Column A, and write the corresponding letter in the space provided. b a c d Column A 11. a tiny particle that can make you sick 12. a chemical that some WBCs release to help fight intruders 13. formed in the bone marrow 14. where some WBCs mature 15. Which of the following statements are true of platelets? (Circle all that apply.) a. They last for 5 to 10 days. b. They pinch off fragments of themselves to form a blood clot. c. They are fragments of larger cells. d. They help reduce blood loss. Column B a. antibody b. pathogen c. white blood cell d. lymphatic organ 144 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
10 Have a Heart (p. 490) 16. Your heart is a four-chambered muscular organ about the size of your a. stomach. c. liver. b. nose. d. fist. 17. What causes the lub-dub sounds of your heartbeat? The lub-dub sounds of my heartbeat are caused by my heart valves closing. Use the diagram on page 490 to place the following steps of blood flow through the heart in the correct order. Write the appropriate number in the space provided Blood is squeezed into the ventricles when the atria contract Blood enters the atria Blood is pushed out of the heart when the atria relax and the ventricles contract. Blood Vessels (p. 491) 21. Look at Figure 8. Capillaries connect small veins small arteries. (large veins or small veins, large arteries or small arteries) Choose the type of blood vessel in Column B that best matches the description in Column A, and write the corresponding letter in the space provided. Blood vessels can be used more than once. b a b c c b a Column A 22. smallest blood vessels in the body 23. direct blood away from the heart 24. many substances can diffuse through their walls 25. direct blood back to the heart 26. push blood with the help of skeletal muscles 27. very close to all living cells in the body 28. have thick walls to withstand pressure to Column B a. arteries b. capillaries c. veins DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 145
11 Going with the Flow (p. 492) 29. Pulmonary circulation is the process during which blood obtains oxygen from the lungs. True or False? (Circle one.) 30. Systemic circulation is the circulation of blood between the heart and the lungs. True or False? (Circle one.) Use the diagram on page 492 to answer the following questions. Indicate whether each of the following statements is a part of pulmonary or systemic circulation. In the space provided, write P if it is part of pulmonary circulation and S if it is part of systemic circulation. 31. P Oxygen-poor blood travels through arteries to the lungs. 32. S Oxygen-poor blood is delivered to the right atrium of the heart by two large veins. 33. P The blood releases carbon dioxide and absorbs oxygen. 34. S Oxygen, nutrients, and water are delivered to the body s cells. 35. S Oxygen-rich blood pumps from the left ventricle into arteries. Blood Flows Under Pressure (p. 493) 36. How is blood running through your veins like water running through a hose? Water in the hose pushes against the inside of the hose and causes the hose to stiffen, similar to the way blood pushing on veins causes the veins to stiffen. 37. The units that blood pressure is reported in are mm Hg. 38. Figure 10 shows a person getting his blood pressure checked. How might your blood pressure indicate a problem with your cardiovascular system? If your blood pressure is consistently high or low, it might indicate that there is a problem with your cardiovascular system. 146 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
12 39. In a normal blood pressure reading of 120/80, the number 80 stands for the pressure in the a. arteries when the ventricles relax. b. arteries when the ventricles contract. c. ventricles when the ventricles relax. d. ventricles when the ventricles contract. Exercise and Blood Flow (p. 493) Mark each of the following statements True or False. 40. False When you exercise, blood flow is reduced to the brain, heart, and lungs so that more blood can go to the muscles. 41. False Some of your organs, like your kidneys, do not need oxygen when you exercise. 42. True When your heart beats faster, more oxygen and nutrients are being delivered to your muscles. 43. True When all the water faucets in the body are open, the heart rate slows down. 44. True Your brain directs blood flow. Review (p. 493) Now that you ve finished reading the first part of Section 1, review what you ve learned by answering the Review questions in your ScienceLog. What s Your Blood Type? (p. 494) 45. Is it safe to give a person blood of any type? Explain. No; it isn t safe to give someone blood of any type because mixing some blood types can cause a person s RBCs to clump together, forming a clot, which can block vessels and cause death. 46. Everyone has type A, B, AB, or O blood. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 147
13 Each of the following statements is false. Change the underlined word to make the statement true. Write the new word in the space provided. 47. Blood type is determined by the antibodies present on the surface of your red blood cells. antigens 48. Type O blood has both A and B antigens. Type AB 49. Certain chemicals in plasma, called enzymes, can bind to RBCs and cause the RBCs to clump together. antibodies 50. Type O people are universal recipients. donors Cardiovascular Problems (p. 495) 51. Cardiovascular problems occur only in the heart. True or False? (Circle one.) 52. Cardiovascular problems affect the movement of blood through the body. 53. What is wrong with the blood vessel shown in Figure 12? The blood vessel shown in Figure 12 has atherosclerosis, a cardiovascular problem in which fatty deposits build up inside the blood vessels. The deposits can block blood flow. 54. Which of the following statements is NOT true about hypertension? a. It is promoted by atherosclerosis. b. It weakens blood vessels. c. It is an abnormally low blood pressure. d. It can lead to a stroke. 148 HOLT SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
14 55. List three things mentioned in the text that people can do to reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease. Answers should include three of the following: never smoking; eating a diet low in animal fat, palm and coconut oils, and salt; eating many fruits, vegetables, and whole grains; and exercising regularly. Review (p. 495) Now that you ve finished Section 1, review what you learned by answering the Review questions in your ScienceLog. Section 2: The Lymphatic System (p. 496) 1. Your cells are bathed in fluid. What happens to that fluid? The fluid is either reabsorbed by the capillaries or collected by my lymphatic system and returned to my blood. 2. The lymphatic system and the cardiovascular system are both circulatory systems. Vessels of the Lymphatic System (p. 496) 3. Besides fluid, the lymph also contains particles that are too large to enter the blood capillaries. 4. Lymph is carried into lymphatic vessels by lymph capillaries, the smallest vessels of the lymphatic system. 5. Lymph is not pushed through the lymphatic system by a pump. How does it move? The squeezing of the skeletal muscles forces the lymph to move through the vessels. DIRECTED READING WORKSHEETS 149
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Circulatory System. The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is blood? What is blood pressure? What are blood types?
 CHAPTER 16 2 Blood SECTION Circulation and Respiration California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is
CHAPTER 16 2 Blood SECTION Circulation and Respiration California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is
How does the Circulatory System maintain
 How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
KS4 Biology. The Heart and Circulatory System. 1 of 49. Boardworks Ltd 2004
 1 of 49 KS4 Biology The Heart and Circulatory System 2 of 49 Contents The Heart and Circulatory System The circulatory system Structure of the heart Valves in the heart How the heart pumps blood Summary
1 of 49 KS4 Biology The Heart and Circulatory System 2 of 49 Contents The Heart and Circulatory System The circulatory system Structure of the heart Valves in the heart How the heart pumps blood Summary
The Body s Transportation System (pages )
 The Body s Transportation System (pages 100-106) Use the diagram to answer the following questions. Name Date Class Circulatory Packet 1. Draw arrows on the diagram to show the path of the blood flow throughout
The Body s Transportation System (pages 100-106) Use the diagram to answer the following questions. Name Date Class Circulatory Packet 1. Draw arrows on the diagram to show the path of the blood flow throughout
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body
 The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body (1) As you have already learned, there are muscles all over your body. All of them are important, but not all of them are vital. The muscle
The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body (1) As you have already learned, there are muscles all over your body. All of them are important, but not all of them are vital. The muscle
Circulatory System. Circulatory System
 Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
The Body s Transport System (pp )
 The Body s Transport System (pp. 538 547) This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete
The Body s Transport System (pp. 538 547) This section describes how the heart, blood vessels, and blood work together to carry materials throughout the body. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, complete
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation.
 As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 Chapter Test A Part A: Multiple Choice CHAPTER 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which is the
Chapter Test A Part A: Multiple Choice CHAPTER 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems In the space at the left, write the letter of the phrase that best answers each question. 1. Which is the
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
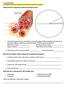 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
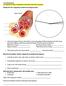 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1
 Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1 Which part of the brain controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, & digestion? A. Cerebellum B. Brain stem C. Cerebrum 0 0 0 10/1/2014 Nervous System 2 Cerebellum Brain
Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1 Which part of the brain controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, & digestion? A. Cerebellum B. Brain stem C. Cerebrum 0 0 0 10/1/2014 Nervous System 2 Cerebellum Brain
 Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
14-1: The Body s Transport System. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Circulatory System. Chapter 32
 Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Circulatory System. Date. Name Sunday, March 10. By Sharon Fabian
 Sunday, March 10 Circulatory System By Sharon Fabian Blood circulates through your body all the time through a complicated system of large and small pathways. Your heart pumps day and night to transport
Sunday, March 10 Circulatory System By Sharon Fabian Blood circulates through your body all the time through a complicated system of large and small pathways. Your heart pumps day and night to transport
By Semih. The first system is about the respiratory system. It provides our body with the oxygen it needs and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
 By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
Summary The Circulatory System Blood and the Lymphatic System. Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Summary 37-1 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together with the respiratory
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Summary 37-1 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together with the respiratory
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q.1 Choose the best answer. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) veins b) arteries
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Hierarchy of Biological Organization
 Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Some Fun Facts The left side of the heart contains oxygenated blood whereas the right side has de-oxygenated blood. One drop of blood has about 5 million red blood cells and 12 thousand
The Circulatory System Some Fun Facts The left side of the heart contains oxygenated blood whereas the right side has de-oxygenated blood. One drop of blood has about 5 million red blood cells and 12 thousand
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review
 Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
The circulatory system brings many different materials to all the cells of the body and picks up waste from the same cells.
 CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
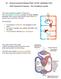 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System
 Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
Cells & Systems The Circulatory System The Circulatory System What does it do? Your body s transportation network Transports Oxygen (O) Transports Carbon Dioxide (CO 2 ) Removes Waste products Delivers
Identify and describe the circulation system that is missing from the organizer above.
 Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
One system involved in exercising is the respiratory system. The respiratory system includes three main parts breathing, lungs and blood.
 By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
The Circulatory System. Lesson 4. Quick Check. Trace the path of blood after it is pumped from the heart. 22. First
 Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38
 Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Functions of the Circulatory System
 Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
OB16 Demonstrate the effect of exercise and rest on pulse and breathing rate and appreciate that a balance of each promotes good health
 Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system.
 Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
Low Demand Questions QUESTIONSHEET 1 The list gives some structures in the blood and circulatory system. heart artery red blood cell ventricle capillary plasma vein white blood cell platelets Which of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Circulatory System. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted. Circulatory System 1
 Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
