ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle
|
|
|
- Jonathan Austin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ACTIVITY: The Heart Cycle In this activity, you will follow the flow of blood through the heart. Your heart has two jobs to do, and its two sides have separate responsibilities: The left side pumps oxygen-enriched blood from your lungs to your body s cells, and the right side pumps oxygen-poor, waste-carrying blood back from your body s cells to your lungs. When blood has made one round trip, it has completed one heart cycle. Although this activity will guide you through the heart cycle by examining what happens in one chamber at a time, it is important for you to know that blood flows through both sides of the heart simultaneously. That is, when the right atrium contracts and pumps its blood, the left atrium contracts at the same time. The same is true for the ventricles both the right and left ventricles contract and pump blood at the same time. In biological drawings, it is standard to use blue to represent deoxygenated blood and red to represent oxygenated blood. (This practice is not just to make your drawing colorful; oxygen-rich blood actually looks bright red, and oxygen-poor blood looks bluish or purple.) You will, therefore, use blue circles to follow deoxygenated blood through the right side of the heart and red circles to follow oxygenated blood through the left side of the heart. Materials Needed: 10 blue circles & 10 red circles (use a hole punch and blue and red construction paper) colored pencils or markers heart diagrams Procedure: 1) Each stage will instruct you to place colored circles on the number diagram. Be sure to place the circles on the correct numbers and to use the correct color (red or blue). 2) On the heart sequence page, sketch and color the circles for each stage. 3) Before going to the next stage, remove the circles from the number diagram so that they can be reused for the next stage. The idea, of course, is to show the movement of the blood in successive stages. (OVER)
2 STAGE ONE: Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the superior and inferior venae cavae. Place BLUE circles on numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8. Sketch and color these circles on DIAGRAM A. STAGE TWO: When the right atrium is full, it contracts and forces blood through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle. Remove the blue circles from stage one and place them on numbers 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13. Sketch and color these colors on DIAGRAM B. STAGE THREE: After the blood passes into the right ventricle, the tricuspid valve slams shut. The muscular wall of the right atrium contracts, forcing the blood through the pulmonary artery and to the lungs. Remove the blue circles from stage two and place them on numbers 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, and 23. Sketch and color these circles on DIAGRAM C. STAGE FOUR: The blood returns from the lungs to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. While in the lungs, the red blood cells become saturated with oxygen and change from a bluish color to a bright red. Remove the circles from stage three. Place RED circles on numbers 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, and 31. Sketch and color these circles on DIAGRAM D. STAGE FIVE: When the left atrium is full, it contracts and forces blood through the bicuspid valve and into the left ventricle. Remove the red circles from stage four and place on numbers 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, and 38. Sketch and color these circles on DIAGRAM E. STAGE SIX: The last stage of the heart cycle occurs when the bicuspid valve slams shut and the oxygen-enriched blood is pumped out of the left ventricle through the aorta. From the aorta, the blood is directed to the body s cells. Remove the red circles from stage five and place them on numbers 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, and 47. Sketch and color these circles on DIAGRAM F. Answer the post-activity questions on the back of your colored heart cycle diagrams!
3
4 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name The Heart Cycle Activity
5 The Heart Cycle Questions: 1) Through which veins does deoxygenated blood enter the right atrium? 2) What structure must the blood pass through before it enters the right ventricle? 3) Where is the blood pumped after it leaves the right ventricle? 4) What is the job of the pulmonary veins? 5) What happens when the left atrium is full? 6) What structure must the blood pass through before it enters the left ventricle? 7) Where is the blood pumped after it leaves the left ventricle?
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
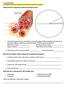 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
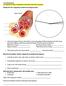 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Blood Vessels. veins. valve. to the heart. capillaries from the heart. arteries. Visual 25-1
 Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
(2) (1) (3) (4) BLOOD PATHWAY ASSESSMENT RUBRIC
 BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
CIRCULATORY WEBQUEST L.E. Biology (PART I: Introduction, Parts of the Heart, and Pathway of Blood)
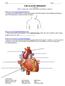 Name: Period: CIRCULATORY WEBQUEST L.E. Biology (PART I: Introduction, Parts of the Heart, and Pathway of Blood) http://www.smm.org/heart/heart/steth.htm 1. Where is your heart located? Use the stethoscope
Name: Period: CIRCULATORY WEBQUEST L.E. Biology (PART I: Introduction, Parts of the Heart, and Pathway of Blood) http://www.smm.org/heart/heart/steth.htm 1. Where is your heart located? Use the stethoscope
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD The circulatory system is a group of organs which carry food and oxygen to and remove waste from every cel l in the body. Arteries-Lead away from the heart Plasma - -+-- 55%
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD The circulatory system is a group of organs which carry food and oxygen to and remove waste from every cel l in the body. Arteries-Lead away from the heart Plasma - -+-- 55%
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection
 Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System
 NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT
 CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT Fahey/Insel/Roth, Fit & Well: Core Concepts and Labs in Physical Fitness and Wellness, Chapter 3 ANATOMY OF THE HEART O The heart is divided into right and left hand side
CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT Fahey/Insel/Roth, Fit & Well: Core Concepts and Labs in Physical Fitness and Wellness, Chapter 3 ANATOMY OF THE HEART O The heart is divided into right and left hand side
Identify and describe the circulation system that is missing from the organizer above.
 Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
PART I: HEART ANATOMY
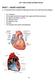 Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
Lab 7: Heart Sounds and Blood Pressure PART I: HEART ANATOMY a) You should be able to identify the following structures on an adult human heart diagram. the 4 chambers the bicuspid (mitral) and tricuspid
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT
 BOOK 4 HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT SECTION 3 EXERCISE AND FITNESS IN HUMANS THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The human nervous system consists of: the central nervous system (CNS) the brain and spinal
BOOK 4 HEALTH FITNESS AND SPORT SECTION 3 EXERCISE AND FITNESS IN HUMANS THE STRUCTURE OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The human nervous system consists of: the central nervous system (CNS) the brain and spinal
Danil Hammoudi.MD 1/12/2009
 Danil Hammoudi.MD Aorta the biggest and longest artery (a blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart) in the body. It carries oxygen rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.inferior
Danil Hammoudi.MD Aorta the biggest and longest artery (a blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart) in the body. It carries oxygen rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.inferior
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Cardiovascular System. Heart Anatomy
 Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
A. Incorrect! The left ventricle receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the left atrium.
 DAT Biology - Problem Drill 10: The Circulatory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. What is the flow of deoxygenated blood through the heart as it returns from the body? Question #01 (A) Vena cava; right ventricle;
DAT Biology - Problem Drill 10: The Circulatory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. What is the flow of deoxygenated blood through the heart as it returns from the body? Question #01 (A) Vena cava; right ventricle;
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Learners MUST KNOW R A G. Know the double- circulatory system (systemic and pulmonary)
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
End of chapter exercises
 End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
End of chapter exercises Problem 1: The following diagrams show the heart during the cardiac cycle. The arrows represent the flow of blood. Study the diagrams and answer the questions that follow: Figure
Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms?
 Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms? I.Transportthe absorption and circulation that allows substances to pass into or out of cells and move throughout the organism. A. absorptionsubstances
Aim: Transport- Why is it so important to multicellular organisms? I.Transportthe absorption and circulation that allows substances to pass into or out of cells and move throughout the organism. A. absorptionsubstances
OB16 Demonstrate the effect of exercise and rest on pulse and breathing rate and appreciate that a balance of each promotes good health
 Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
THE HEART. Structure & Function
 THE HEART Structure & Function SARAH JOHANSON BIOTECH ENGINEERING, 2015 Function of the Heart: The heart is muscular organ that sits centrally in the thorax region of the body, but is skewed and twisted
THE HEART Structure & Function SARAH JOHANSON BIOTECH ENGINEERING, 2015 Function of the Heart: The heart is muscular organ that sits centrally in the thorax region of the body, but is skewed and twisted
Heart and Lung Dissection
 Heart and Lung Dissection Name(s) Before you begin any work or dissection of your specimen, please try to identify the following. You will need to illustrate what you see, so make sure to note size, texture
Heart and Lung Dissection Name(s) Before you begin any work or dissection of your specimen, please try to identify the following. You will need to illustrate what you see, so make sure to note size, texture
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
THE HEART. Structure & Function
 THE HEART Structure & Function SARAH JOHANSON BIOTECH ENGINEERING, 2015 Function of the Heart: The heart is muscular organ that sits centrally in the thorax region of the body, but is skewed and twisted
THE HEART Structure & Function SARAH JOHANSON BIOTECH ENGINEERING, 2015 Function of the Heart: The heart is muscular organ that sits centrally in the thorax region of the body, but is skewed and twisted
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart
 Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
Human Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Worksheet 1- The Heart Name Date Period 1. The "double pump" function of the heart includes the right side, which serves as the circuit pump, while the left side
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Date :... Class: A1&2 Time Allowed: 40Minutes Maximum Marks: 25
 1 loomfield Hall School 1 Test (Unit 9) Name :... Paper: iolog y Date :... lass: 1& Time llowed: 40Minutes Maximum Marks: 5 TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks] Fig. 1.1 shows the changes in blood pressure
1 loomfield Hall School 1 Test (Unit 9) Name :... Paper: iolog y Date :... lass: 1& Time llowed: 40Minutes Maximum Marks: 5 TKheory Section: [Total 16 Marks] Fig. 1.1 shows the changes in blood pressure
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
The Cardiovascular. Parts and Functions
 The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
An Illustrated 1. Dissection Guide. To The... Mammalian. rr= Heart. Right ventricle+---, by David H. Hall
 An Illustrated 1. Dissection Guide. To The... Mammalian rr= Heart ventricle+---, by David H. Hall The Mam.malian Heart Because mammals are warm blooded (endothermic) and generally very active animals,
An Illustrated 1. Dissection Guide. To The... Mammalian rr= Heart ventricle+---, by David H. Hall The Mam.malian Heart Because mammals are warm blooded (endothermic) and generally very active animals,
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
9 Transport in animals
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Transport in animals Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 9 Transport
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Transport in animals Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Unit ooklet IGSE iology ambridge International Examinations 9 Transport
The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body.
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body. What does blood consist of? The blood consists
Circulatory System The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body. What does blood consist of? The blood consists
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38
 Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Read Me. covering the Heart Anatomy. Labs. textbook. use. car: you
 Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
Heart Anatomy Lab Pre-Lab Exercises Read Me These exercises should be done before coming to lab, after watching the videos covering the Heart Anatomy Labs. Answer the questions in this guide using the
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 32 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Textbook pages 82 95 Before You Read Section 2.3 Summary How do you think oxygen from the air you breathe gets into your
MESA DAY CONTEST RULES
 FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
Circulation and Respiration
 Circulation and Respiration Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Respiratory system moves O 2 into,
Circulation and Respiration Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Miller, Geoffrey. 2009. Spent: Sex, Evolution, and Consumer Behavior. Respiratory system moves O 2 into,
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART
 LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
One system involved in exercising is the respiratory system. The respiratory system includes three main parts breathing, lungs and blood.
 By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System
 AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Respiration & Circulation
 Respiration & Circulation Objectives Describe the purpose of the respiratory system List & describe the structures of the respiratory system Describe the respiratory cycle, frequency, and factors that
Respiration & Circulation Objectives Describe the purpose of the respiratory system List & describe the structures of the respiratory system Describe the respiratory cycle, frequency, and factors that
Contents. Page 1. Homework 11 Chapter Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11
 Page 1 Homework 11 Chapter 18-19 Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11 Contents When printing, make sure that you specify the page range that you want to print out! Learning objectives for Lecture 11:...pg
Page 1 Homework 11 Chapter 18-19 Blood Vessels Due: Week 6 Lec 11 Contents When printing, make sure that you specify the page range that you want to print out! Learning objectives for Lecture 11:...pg
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems
 Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Mammalian Transport and The Heart
 Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located
 How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
