JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 10 Page October 2016
|
|
|
- Corey Baldwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impact Factor Index Copernicus Value: ISSN (e) x ISSN (p) DOI: Ultrasound and CT Evaluation of Pleural Lesions Authors Dr Shivani Gogi 1, Dr M.Veena 2, Dr B. Sumithra 3, Dr N. Anil Kumar 4, Dr V. Shanthi Sree 5 1 Assistant Professor, Gandhi Hospital, Secunderabad, Telangana state, India dr_shivanigogi@yahoo.com 2 Assistant professor, Gandhi Hospital, Secunderabad, Telangana state, India 3 Resident, Gandhi hospital, Secunderabad, Telangana state, India sumithrabongu@gmail.com 4 Assistant professor, Gandhi hospital, Secunderabad, Telangana state, India nethikoppula@rediffmail.com 5 Associate professor, Gandhi hospital, Secunderabad, Telangana state, India drshanthisree@yahoo.com Corresponding Author Dr M.Veena Gandhi Hospital, Secunderabad, Telangana State, INDIA dr.rajveena@gmail.com, phone no Abstract Aims And Objectives: To assess the value of Ultrasonography and Computed Tomography in evaluation of pleural lesions. To determine the Sensitivity and Specificity of Ultrasound and CT in pleural lesions. Summary: The present study was aimed at assessing the value of Ultrasonography and CT in evaluating the pleural lesions. In our study, during the period of months 100 patients with pleural effusions were evaluated. The most common cause was transudates. Exudates consist of malignant and non malignant causes. Conclusion: The role of ultrasound and CT are complimentary, give high yield of positive results for pleural mass differentiation; useful for guided procedures, like pleural biopsy and pleural drainage. Combined study not only useful for localization of lesion but also gives information about the extent of disease and characterizing the tissue density by analysis of attenuation coefficient. Keywords: ultrasound, MDCT, pleural effusion, transudate and exudates. INTRODUCTION The pleura is derived embryologically from the mesenchyme (1). It serves an important role in lung function in that it acts as a cushion for the lungs and allows for smooth movement of the lungs within the chest cavity (2). A variety of imaging techniques can be used to evaluate the pleura and pleural space. Standard radiographs are the most commonly used, but difficult to differentiate the pleural collection from masses. Ultrasound is an effective, easily performed complimentary to chest radiograph in evaluation of puzzling areas of increased opacity Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page 918
2 in the chest. Ultrasound may provide useful information that eliminates the need for more invasive/expensive studies. Useful in differentiating pulmonary consolidation from lung masses and pleural lesions, which are main causes of increased opacity on chest radiograph. Ultrasound provides detailed information about nature of pleural fluid. It allows determining whether a fluid is amenable to aspiration. Hence initial screening with ultrasound to determine whether the lesion is solid or fluid filled (3) helps to limit the differential diagnosis. Chest CT scanning permits imaging of entire pleural space, pulmonary parenchyma and mediastinum simultaneously. CT reveals early stage of pleural abnormalities and contrast enhanced scan can depict multiple loculation and localizing effusion. Differentiate between lung consolidation Vs pleural effusion; cystic from solid lesion, necrotic areas, pleural thickening, nodules, masses or round atelectasis and peripheral lung abscess from lung empyema and tumoral extent. Helps in identifying benign Vs malignant involvement. MATERIALS AND METHODS The study was conducted in our hospital over a period of January 2015 to December It was a prospective study. A total of 100 patients with suspected pleural lesions on chest radiography were enrolled for this study. After obtaining relevant history and clinical data these cases were subjected to ultrasound (real time SS-D 1000 Aloka 5 MHz) and C.T (SEIMENS 16 SLICE). Subsequently the confirmed pleural lesions were subjected to pleurocentesis /FNAC/biopsy to know the nature of the lesion. A comparative study was done between USG and CT findings. Further, the pleural lesions were correlated with FNAC/biopsy (4). These observations were analyzed and statistical assessments were performed. LIST OF PLEURAL PATHOLOGIES Pleural Effusion Collection of fluid between the visceral and parietal pleura. Pleural effusion is classically divided into transudates and exudates (5). USG is useful in characterizing the nature of effusion. CT is of limited value in distinguishing transudate from exudates (6) depending on attenuation coefficient. (Higher density indicates exudates) (7). Empyema It is infected exudative pleural effusion when loculated it is lenticular shape making obtuse angle with chest wall. Split pleural sign : where the parietal and visceral pleura are split and show marked enhancement in empyema CT helps to differentiate effusion from ascites by 1. Displaced crus sign (8) 2. Diaphragm sign (9). 3. Interface sign (10). 4. Bare area sign. Focal Pleural Diseases Includes pleural thickening and pleural plaques affecting most commonly parietal pleura. It is seen on USG as homogenous echogenic layer adjacent to chest wall and on CT as soft tissue opacity. Pleural plaques ossify if it is due to asbestosis. Diffuse pleural diseases: Includes fibrothorax, malignant mesothelioma and metastatic carcinoma and lymphoma. Fibrothorax is characterized by pleural thickening more than 8 cm craniocaudally and 5cm laterally with thickness more than 3mm Malignant mesothelioma, highly malignant locally aggressive tumour of pleura caused due to exposure to asbestos with an average latent period of 35 yrs (11). CT appearance consists of pleural effusion with thickened irregular nodular pleura encasing the lung and extending into the pleural fissure. Occasionally only pleural effusion can be identified (, 13). Signs which indicate malignant pleural thickening are 1. Circumferential thickening Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page 919
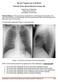
3 2. Nodularity 3. Parietal thickening >1cm 4. Involvement of mediastinal pleura. Metastasis to pleura occurs from bronchogenic carcinoma, breast cancer, lymphoma, ovarian and gastric cancer. CT findings include pleural nodule, extensive pleural thickening with contrast enhancement. Lymphoma shows characteristic CT appearance of pleural involvement, consists of localized broad based lymphomatous pleural plaques. Case 1: axial CECT image showing enhancing nodular pleural mass with exudative right pleural effusion and liver metastases. Case 2: axial CECT chest images of a patient with breast carcinoma in mediastinal and lung window showing bilateral pleural and mediastinal effusion and secondaries in lung. Case 3: chest x-ray, USG and axial CECT chest of a patient with Bronchogenic carcinoma with metastatic lymphadenopathy and pleural nodules. Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page 920
4 Case 4: chest x-ray, USG, axial CECT chest of a patient with pleural lymphoma showing left exudative pleural effusion and enhancing nodular pleural based mass. Case 5: X-ray chest and axial CT chest showing plaque like pleural calcifications. OBSERVATIONS AND RESULTS Table 1: Nature of pleural effusion: Nature of effusion No. Of patients Percentage (%) Transudate Exudate non malignant malignant Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page
5 Bar diagram representing sonographic pattern and nature of pleural effusion Table 2 showing sonographic pattern and nature of pleural effusions. Effusions Internal echogenecity Anechoic n=58 Complex nonseptated n=14 Complex septated n=24 Homogenously n=4 echogenic Transudate % Exudate a. Non malignant 20.68% % 50% 3 75% b. Malignant % % 50% 1 25% Bar diagram showing nature of pleural effusion and associated findings Table 3 showing thickened pleura and associated findings. Nature of effusion Thickened pleura n=23 Pleural nodule n=3 Parenchymal changes n=16 Transudate Exudate a) Nonmalignant b) malignant Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page 922
6 Table 4 showing etiology of pleural effusion. Transudate (n=28) No. Percentage a) Congestive heart failure b) Cirrhosis of liver c) Hypo albuminaemia d) others Exudate(n=72) 1) non-malignant(n=34) a) Tuberculosis b) Non tuberculous bacterial infections c) Empyema d) Pancreatitis 2) 2. Malignant (n=38) a) Bronchogenic carcinoma b) Breast carcinoma c) Lymphoma d) Ovarian and gastric e) unknown Table 5 showing CT findings in 72 exudates and 28 transudates. Group Parietal pleural thickening Extra pleural fat thickening Visceral thickening pleural Exudate n= Transudate n= Table 6 showing diffuse pleural disease n=38 Benign % 1) Empyema 2) Fibrothorax 3) Asbestosis % 38.8% 11.2% Malignant % 1) Metastasis 2) Mesothelioma 3) Lymphoma % 15% 5% Bar diagram showing characteristics of diffuse pleural diseases. Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page 923
7 Table 7 showing characteristics of diffuse pleural disease. Characteristic Mesothelioma (3) Metastasis (16) Lymphoma (1) Asbestosis (2) Fibrothorax (7) Empyema (9) 1. Nodularity Rind Thickness >1cm Calcifications Mediastinal pleural involvement Unilateral involvement Effusion Hilar adenopathy DISCUSSION The current study was undertaken to assess the evaluation of USG and CT in evaluation of pleural lesions. There have been few trials which have sought to determine the accuracy of USG and CT chest in these cases. Age and sex incidence: In our study on 100 patients, 59 were males (59%) and 41 were females (41%).According to Aquino SL webb et al 1994 male (68.75%) and females (31.25%), Yang et al 1992, males were (59%) and females were (41%). Between the age group of 2-80 yrs with mean age of 55 yrs. According to Yang et al 1992, mean age was 54 yrs, Aquino SL Webb et al 1994 it was 58 years. Nature of pleural effusion In our study transudate was 28% and exudates were 72% as compared to Aquino SL Webb et al 1994, transudate was 31.4% and exudates were 68.6%. Sonographic patterns of pleural effusion Pattern Present study Yang et al 1992 Anechoic 58% 53.75% Complex non septated 14% 15.62% Complex septated 24% 23.75% Homogenous echogenic 4% 6.87% Comparison table showing associated findings in pleural effusion Findings Present study Yang et al 1992 Thickened Pleura 23% 23.75% Pleural Nodule 3% 3.% Parenchymal changes 16% 16.87% Comparison of studies evaluating CT characteristics of diffuse pleural disease Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page 924
8 The characteristic findings on CT in our study showed specificities of - nodularity (88%), pleural thickening >1cm(94.4%), Rind sign (100%) and mediastinal pleural involvement (88.8%), whereas according to Leung et al 1990 specificities were nodularity (94%), pleural thickening >1cm (94%), Rind sign (100%) and mediastinal pleural involvement (88%). Comparison studies evaluating CT characteristics in malignant pleural disease Percentage Present study Fredrick Abraham et al Leung et al Specificity (%) Sensitivity (%) CONCLUSION The pattern of ultrasonography helps in differentiating the nature of effusion. In addition to the basic effusion patterns (anechoic, complex non septated, complex septated) a pleural effusion can be homogenously echogenic. Transudates are usually anechoic, whereas an anechoic effusion could be either a transudate or an exudate. Pleural effusion with complex septated, complex nonseptated or homogenously echogenic patterns are always exudates. The most common sonographic pattern in our study was anechoic which represented 58%. CT scan revealed very small effusion. For detecting exudative effusion by CT, the sensitivity was 61.11% and specificity was 96.44%.The CT features most helpful in distinguishing malignant from benign pleural disease are pleural rind, nodular pleural thickening, pleural thickening greater than 1cm and mediastinal pleural involvement. Overall, the sensitivity was 70% and the specificity was 83.33% for detecting malignant pleural disease in our study. Hence the role of ultrasound and CT are complimentary, giving high yield of positive results for pleural mass differentiation, useful for guided procedures like pleural biopsy and pleural drainage. Combined study not only useful for localization of lesion but also gives information about the extent of disease and characterizing the tissue density by analysis of attenuation coefficient. REFERENCES 1. M.C. Renda, A. Giambona, E. Fecarotta, F. Leto, G. Makrydimas, D. Renda, G. Damiani, M.C. Jakil, F. Picciotto, A. Piazza, M. Valtieri, A. MaggioEmbryofetal erythroid megaloblasts in the human coelomic cavity J. Cell. Physiol., 225 (2) (2010), pp Delrue L, Gosselin R, Ilsen B, Landeghem AV, de Mey J, and Duyck P. Difficulties in the interpretation of chest radiography. In: Coche EE et al., editors. Comparative interpretation of ct and standard radiography of the chest, medical radiology. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer- Verlag; p doi: / _2 3. N.J. Stephens, J.M. PilcherThe diagnostic role of ultrasound in the chest ultrasound, 15 (3) (2007), pp Lips Comb DJ Flower CDR.Ultrasound in diagnosis and management of pleural disease. BrJ Dis Chest 1980;74: Paddock FK. The diagnostic significance of serous fluids in disease N.Engl J Med 1940;223: D B Chang; P C Yang; K T Luh; S H Kuo; C J Yu Ultrasound guided pleural biopsy Chest 1991;100(5): NL Müller - Imaging of pleura Radiology, 1993;186: RJ Waite, RJ Carbonneau, JP Balikian,.,et al. Parietal pleural changes in Empyema: appearance at CT.Radiology 1990; 175: Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page 925
9 9. Dwyer A, The displaced crus: A sign for distinguishing between pleural fluid and ascites on computed tomography. J Comput Asst Tomogr 1978;2: ROBERT A. HALVORSEN, MD,*f PETER J. FEDYSHIN, MD.tt MELVYN KOROBKIN, MD,f AND WILLIAM M. THOMPSON, CT differentiation of ascites and pleural effusion invest radiology 1986:21: Hsu C Cytologic detector of malignancy in pleural effusions.a diagnosiss cytopathol 1987 Vol.3 issue 1,8-.. Kreel L. Computed tomography in Mesotheliomas. Semin Oncol 1981;8: Dr Shivani Gogi et al JMSCR Volume 04 Issue 10 October Page 926
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings
 Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
CT in Differential Diagnosis of Diffuse Pleural Disease
 487 0361-803x/9o/1 543-0487 American Roentgen Ray Society Ann N. Leung1 Nestor L. MUller1 Roberta R. Miller2 Received August 31, 1989; accepted after revision October 16, 1989. Department of Radiology,
487 0361-803x/9o/1 543-0487 American Roentgen Ray Society Ann N. Leung1 Nestor L. MUller1 Roberta R. Miller2 Received August 31, 1989; accepted after revision October 16, 1989. Department of Radiology,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Efficacy of ultrasonography and computed tomography in differentiating transudate from exudate in patients with pleural effusion
 Efficacy of ultrasonography and computed tomography in differentiating transudate from exudate in patients with pleural effusion Purpose: To evaluate USG and CT imaging findings in differentiating transudative
Efficacy of ultrasonography and computed tomography in differentiating transudate from exudate in patients with pleural effusion Purpose: To evaluate USG and CT imaging findings in differentiating transudative
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
CT Manifestations of Late Sequelae in Patients with Tuberculous Pleuritis
 CT Manifestations of Late Sequelae in Patients with Tuberculous Pleuritis T uberculous pleuritis remains one of the major causes of pleural effusion with an incidence ranging from as high as 86% in a population
CT Manifestations of Late Sequelae in Patients with Tuberculous Pleuritis T uberculous pleuritis remains one of the major causes of pleural effusion with an incidence ranging from as high as 86% in a population
Computed tomography features in malignant pleural mesothelioma and other commonly seen pleural diseases
 European Journal of Radiology 41 (2002) 1 9 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Computed tomography features in malignant pleural mesothelioma and other commonly seen pleural diseases Muzaffer Metintas a, *,
European Journal of Radiology 41 (2002) 1 9 www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Computed tomography features in malignant pleural mesothelioma and other commonly seen pleural diseases Muzaffer Metintas a, *,
Imaging of pleural masses: Which to choose? Republished article $
 Respiratory Medicine CME (2008) 1, 10 14 respiratory MEDICINE CME CME ARTICLE Imaging of pleural masses: Which to choose? Republished article $ Aaron S. Bruns, John G. Mastronarde Division of Pulmonary
Respiratory Medicine CME (2008) 1, 10 14 respiratory MEDICINE CME CME ARTICLE Imaging of pleural masses: Which to choose? Republished article $ Aaron S. Bruns, John G. Mastronarde Division of Pulmonary
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Malignant Effusions. Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital
 Malignant Effusions Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital Malignant Effusions Definition: Presence of malignant cells in the pleural space 75% are caused by
Malignant Effusions Anantham Devanand Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Singapore General Hospital Malignant Effusions Definition: Presence of malignant cells in the pleural space 75% are caused by
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Spectrum of Radiological Findings in Bronchogenic Carcinoma A Retrospective Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. VIII January. (2018), PP 43-59 www.iosrjournals.org Spectrum of Radiological Findings
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. VIII January. (2018), PP 43-59 www.iosrjournals.org Spectrum of Radiological Findings
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
MRI and CT in the Differential Diagnosis of Pleural Disease*
 MRI and CT in the Differential Diagnosis of Pleural Disease* Johannes Hierholzer, MD; Liangping Luo, MD; Roland C. Bittner, MD; Christian Stroszczynski, MD; Ralf-Jürgen Schröder, MD; Nicolas Schoenfeld,
MRI and CT in the Differential Diagnosis of Pleural Disease* Johannes Hierholzer, MD; Liangping Luo, MD; Roland C. Bittner, MD; Christian Stroszczynski, MD; Ralf-Jürgen Schröder, MD; Nicolas Schoenfeld,
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of CT imaging to evaluate solitary pulmonary nodule with extrapulmonary neoplasms
 Original Research Article Role of CT imaging to evaluate solitary pulmonary nodule with extrapulmonary neoplasms Anand Vachhani 1, Shashvat Modia 1*, Varun Garasia 1, Deepak Bhimani 1, C. Raychaudhuri
Original Research Article Role of CT imaging to evaluate solitary pulmonary nodule with extrapulmonary neoplasms Anand Vachhani 1, Shashvat Modia 1*, Varun Garasia 1, Deepak Bhimani 1, C. Raychaudhuri
ROLE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF ASCITES Ramesh Chander 1, Kamlesh Gupta 2, Arvinder Singh 3, V. K. Rampal 4, Mohit Khandelwal 5
 ROLE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF ASCITES Ramesh Chander 1, Kamlesh Gupta 2, Arvinder Singh 3, V. K. Rampal 4, Mohit Khandelwal 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ramesh Chander, Kamlesh Gupta, Arvinder
ROLE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF ASCITES Ramesh Chander 1, Kamlesh Gupta 2, Arvinder Singh 3, V. K. Rampal 4, Mohit Khandelwal 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ramesh Chander, Kamlesh Gupta, Arvinder
Respiratory Interactive Session. Elaine Borg
 Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Pleural effusions Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased
Pleural effusions Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased
Comparative Interpretation of CT and Standard Radiography of the Pleura
 Ilsen, B et al 2016 Comparative Interpretation of CT and Standard Radiography of the Pleura. Journal of the Belgian Society of Radiology, 100(1): 106, pp. 1 10, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5334/jbr-btr.1229
Ilsen, B et al 2016 Comparative Interpretation of CT and Standard Radiography of the Pleura. Journal of the Belgian Society of Radiology, 100(1): 106, pp. 1 10, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5334/jbr-btr.1229
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University
 objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
objectives Pitfalls and Pearls in PET/CT imaging Kevin Robinson, DO Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Michigan State University To determine the regions of physiologic activity To understand
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING EUROPEAN COLLEGE OF VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING
 EISAGOGIKO EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING EUROPEAN COLLEGE OF VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING ARISTOTLE UNIVERSITY OF THESSALONIKI SCHOOL OF VETERINARY MEDICINE SECTION OF RADIOLOGY
EISAGOGIKO EUROPEAN ASSOCIATION OF VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING EUROPEAN COLLEGE OF VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING ARISTOTLE UNIVERSITY OF THESSALONIKI SCHOOL OF VETERINARY MEDICINE SECTION OF RADIOLOGY
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
Thoracic Ultrasound in the diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Effusion
 Thorax Online First, published on October 13, 2008 as 10.1136/thx.2008.100545 Thoracic Ultrasound in the diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Effusion Authors: Nagmi R Qureshi FRCR 1* Najib M Rahman MRCP 2*
Thorax Online First, published on October 13, 2008 as 10.1136/thx.2008.100545 Thoracic Ultrasound in the diagnosis of Malignant Pleural Effusion Authors: Nagmi R Qureshi FRCR 1* Najib M Rahman MRCP 2*
CALGARY ZONE PULMONARY REFERRAL QUICK REFERENCE
 CALGARY ZONE PULMONARY REFERRAL QUICK REFERENCE EMERGENCY (Patient needs to be seen immediately) Hemoptysis (Active & 2 TBSP per day) Hypoxemia (if resting O2 SAT 85%) Pulmonary embolism (Acute - known
CALGARY ZONE PULMONARY REFERRAL QUICK REFERENCE EMERGENCY (Patient needs to be seen immediately) Hemoptysis (Active & 2 TBSP per day) Hypoxemia (if resting O2 SAT 85%) Pulmonary embolism (Acute - known
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia.
 Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Pleural Plaques: Appearances, Mimics and Clinical implications
 Pleural Plaques: Appearances, Mimics and Clinical implications Poster No.: P-0108 Congress: ESTI 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: D. J. Martin, K. J. Litton, H. Adams; Cardiff/UK Keywords: Occupational
Pleural Plaques: Appearances, Mimics and Clinical implications Poster No.: P-0108 Congress: ESTI 2014 Type: Educational Poster Authors: D. J. Martin, K. J. Litton, H. Adams; Cardiff/UK Keywords: Occupational
Radiological staging of lung cancer. Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh
 Radiological staging of lung cancer Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh Bronchogenic Carcinoma Accounts for 14% of new cancer diagnoses in 2012. Estimated to kill ~150,000
Radiological staging of lung cancer Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh Bronchogenic Carcinoma Accounts for 14% of new cancer diagnoses in 2012. Estimated to kill ~150,000
CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities
 Insights Imaging (2010) 1:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0039-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities Naim Ceylan & Selen Bayraktaroglu & Recep Savaş & Hudaver Alper
Insights Imaging (2010) 1:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s13244-010-0039-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW CT findings of high-attenuation pulmonary abnormalities Naim Ceylan & Selen Bayraktaroglu & Recep Savaş & Hudaver Alper
Solid Pleural Lesions
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Hussein-Jelen et al. Solid Pleural Lesions Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Tamara Hussein-Jelen 1,2 lexander. ankier 1 Ronald L. Eisenberg
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Hussein-Jelen et al. Solid Pleural Lesions Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Tamara Hussein-Jelen 1,2 lexander. ankier 1 Ronald L. Eisenberg
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis?
 Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
Intrathoracic extrapleural lesions: MDCT
 Intrathoracic extrapleural lesions: MDCT Poster No.: C-0994 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: S. S. Kim, Y. T. Kim, S. S. Jou, J. K. Han; Cheonan/KR Keywords: Thoracic
Intrathoracic extrapleural lesions: MDCT Poster No.: C-0994 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: S. S. Kim, Y. T. Kim, S. S. Jou, J. K. Han; Cheonan/KR Keywords: Thoracic
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria
 American College of Radiology ACR Criteria Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and Masses Variant 1: Middle-aged patient (35 60 years old) with an incidental 1.5-cm lung nodule. The lesion was smooth.
American College of Radiology ACR Criteria Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and Masses Variant 1: Middle-aged patient (35 60 years old) with an incidental 1.5-cm lung nodule. The lesion was smooth.
Pleural fluid analysis
 Pleural fluid analysis Dr Akash Verma Senior Consultant- Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore 308433 Adj A/Professor- Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine
Pleural fluid analysis Dr Akash Verma Senior Consultant- Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore 308433 Adj A/Professor- Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Pleural fluid A tiny amount of fluid in the pleural cavity is physiological.
Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Pleural fluid A tiny amount of fluid in the pleural cavity is physiological.
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Radiographic Manifestations of Pediatric TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR November 13, 2009 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD,
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Radiographic Manifestations of Pediatric TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR November 13, 2009 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD,
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (IV) No (I) January-June 2015 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Rushi Patel*, Viral Shah*, Deepali Kamdar** Abstract : Aim : Normally the pleural cavities contain
Original Article GCSMC J Med Sci Vol (IV) No (I) January-June 2015 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Rushi Patel*, Viral Shah*, Deepali Kamdar** Abstract : Aim : Normally the pleural cavities contain
PLEURAL DISEASES. (Pleural effusion & empyema) Menaldi Rasmin
 PLEURAL DISEASES (Pleural effusion & empyema) Menaldi Rasmin Department of Pulmonology & Respiratory Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia Introduction Pleural effusion is the most common
PLEURAL DISEASES (Pleural effusion & empyema) Menaldi Rasmin Department of Pulmonology & Respiratory Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia Introduction Pleural effusion is the most common
Lecture 3. Inflammatory Processes
 Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR October 14, 2013 Disclosures I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to report
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR October 14, 2013 Disclosures I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to report
Pulmonary Manifestations Of Skeletal Disorders
 Pulmonary Manifestations Of Skeletal Disorders U. A. Saeed, MBBS FCPS, J. Nair, MBBS MD, R. Khosla, MD FRCR, K. Sayegh, MD FRCPC, J. Kosiuk, MD FRCPC, J. Taylor, MD FRCPC; Department of Radiology, McGill
Pulmonary Manifestations Of Skeletal Disorders U. A. Saeed, MBBS FCPS, J. Nair, MBBS MD, R. Khosla, MD FRCR, K. Sayegh, MD FRCPC, J. Kosiuk, MD FRCPC, J. Taylor, MD FRCPC; Department of Radiology, McGill
Pleural Diseases. Dr Matthew J Knight Consultant Respiratory Physician
 Pleural Diseases Dr Matthew J Knight Consultant Respiratory Physician What do you need to know? What do you need to know? Pleura- normal anatomy and physiology Pleural effusions Causes and investigations
Pleural Diseases Dr Matthew J Knight Consultant Respiratory Physician What do you need to know? What do you need to know? Pleura- normal anatomy and physiology Pleural effusions Causes and investigations
Ovarian Lesion Benign vs Malignant?
 Ovarian Lesion Benign vs Malignant? Michele Keenan 1,2 Bernice Dunne 2 Mary Moran 1 Therese Herlihy 1 1. Radiography and Diagnostic Imaging, School of Medicine, University College Dublin, Ireland 2. Midland
Ovarian Lesion Benign vs Malignant? Michele Keenan 1,2 Bernice Dunne 2 Mary Moran 1 Therese Herlihy 1 1. Radiography and Diagnostic Imaging, School of Medicine, University College Dublin, Ireland 2. Midland
Table 2: Outcomes measured. Table 1: Intrapleural alteplase instillation therapy protocol
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Intrapleural F brinolytic Therapy with Alteplase in Empyema Thoracis in Children conducted in the Department of Pediatric critical care and Pulmonology unit at our institution
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Intrapleural F brinolytic Therapy with Alteplase in Empyema Thoracis in Children conducted in the Department of Pediatric critical care and Pulmonology unit at our institution
Normal Sonographic Anatomy
 hapter 2:The Liver DUNSTAN ABRAHAM Normal Sonographic Anatomy Homogeneous, echogenic texture (Figure 2-1) Measures approximately 15 cm in length and 10 12.5 cm anterior to posterior; measurement taken
hapter 2:The Liver DUNSTAN ABRAHAM Normal Sonographic Anatomy Homogeneous, echogenic texture (Figure 2-1) Measures approximately 15 cm in length and 10 12.5 cm anterior to posterior; measurement taken
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 복부질환초음파 이재영
 IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 2013-4-3 복부질환초음파 이재영 나는오늘누구를위하여 종을울리나? 전통적의료 의사 공학설계자 의사 최첨단진단장비들 USG, CT, MRI 환자 환자 현대의료 사용자중심의사고 US in the Abdomen Detection DDx Look Behavior Response by external stimuli Guiding Tool
IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 2013-4-3 복부질환초음파 이재영 나는오늘누구를위하여 종을울리나? 전통적의료 의사 공학설계자 의사 최첨단진단장비들 USG, CT, MRI 환자 환자 현대의료 사용자중심의사고 US in the Abdomen Detection DDx Look Behavior Response by external stimuli Guiding Tool
Diagnostic Correlation of Findings of Multidetector Computed Tomography and Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Lung Masses
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Diagnostic Correlation of Findings 10.5005/jp-journals-10057-0004 of MDCT and FNAC in Lung Masses Diagnostic Correlation of Findings of Multidetector Computed Tomography and Fine Needle
RESEARCH ARTICLE Diagnostic Correlation of Findings 10.5005/jp-journals-10057-0004 of MDCT and FNAC in Lung Masses Diagnostic Correlation of Findings of Multidetector Computed Tomography and Fine Needle
Resident Case Review CHEST. Daria Manos CAR 2016
 Resident Case Review CHEST CAR 2016 Daria Manos Disclosure Speakers bureau, Roche CAR 2016 Daria Manos 1. Recognize common and critical chest radiograph and computed tomography signs and use these clues
Resident Case Review CHEST CAR 2016 Daria Manos Disclosure Speakers bureau, Roche CAR 2016 Daria Manos 1. Recognize common and critical chest radiograph and computed tomography signs and use these clues
Let s Talk TB A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year
 A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Barry Rabinovitch, MD, FRCP(C) Author Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD co-author and Series Editor Barry Rabinovitch is an assistant
A Series on Tuberculosis, A Disease That Affects Over 2 Million Indians Every Year Barry Rabinovitch, MD, FRCP(C) Author Madhukar Pai, MD, PhD co-author and Series Editor Barry Rabinovitch is an assistant
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD:
 Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD: A Case Report 1 Ju Young Lee, M.D., In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Soo Kee Min, M.D. 3, Min-Jeong Kim, M.D., Sung Il Hwang, M.D., Yul Lee, M.D., Sang
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD: A Case Report 1 Ju Young Lee, M.D., In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Soo Kee Min, M.D. 3, Min-Jeong Kim, M.D., Sung Il Hwang, M.D., Yul Lee, M.D., Sang
Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month. Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA
 May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA Clinical History: A 32-year-old man presented for routine
May 2017 Imaging Case of the Month Prasad M. Panse, MD and Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, Arizona USA Clinical History: A 32-year-old man presented for routine
Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural
 Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural San José, Costa Rica Junio 29, 2017 Rodrigo Cartín Ceba, MD, MSc Consultant, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic 2010 MFMER
Manejo Práctico del Derrame Pleural San José, Costa Rica Junio 29, 2017 Rodrigo Cartín Ceba, MD, MSc Consultant, Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Associate Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic 2010 MFMER
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
Case 5 15-year-old male
 Case 5 15-year-old male Present illness: Six months ago, abnormality of ECG was incidentally detected by annual health check. His blood level of γ-gtp, HbA1c and norepinephrine were elevated; however,
Case 5 15-year-old male Present illness: Six months ago, abnormality of ECG was incidentally detected by annual health check. His blood level of γ-gtp, HbA1c and norepinephrine were elevated; however,
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Relative Survival Rate
 5X Su r vi val Th r ou gh Ear l y Det ect i on Cancer Stage I II III IV Relative Survival Rate 55,2% 28% 8% 2% 90% TIME AND COST IS W AITING IN LINE OBJ ECTIVES Reduce Screening Time By Reduce Screening
5X Su r vi val Th r ou gh Ear l y Det ect i on Cancer Stage I II III IV Relative Survival Rate 55,2% 28% 8% 2% 90% TIME AND COST IS W AITING IN LINE OBJ ECTIVES Reduce Screening Time By Reduce Screening
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL
 The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
The Various Methods to Biopsy the Lung PROF SHITRIT DAVID HEAD, PULMONARY DEPARTMENT MEIR MEDICAL CENTER, ISRAEL Conflict of Interest This presentation is supported by AstraZeneca Two main steps before
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
100 Chest X Rays for Study Group. by Dr. Suneet Khurana
 100 Chest X Rays for Study Group by Dr. Suneet Khurana Approach to - Chest X Ray (shadow of the viscera on a photographic plate) Gas appears Black Fat appears Dark Grey Water Appears as Light Grey Bone
100 Chest X Rays for Study Group by Dr. Suneet Khurana Approach to - Chest X Ray (shadow of the viscera on a photographic plate) Gas appears Black Fat appears Dark Grey Water Appears as Light Grey Bone
Role of MDCT in Diagnosis of Different Calcified Chest Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 1127-1131, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MDCT in Diagnosis of Different Calcified Chest Lesions YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; TAKEYA TAYMOUR,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 3, June: 1127-1131, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MDCT in Diagnosis of Different Calcified Chest Lesions YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.*; TAKEYA TAYMOUR,
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress
 A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS
 1 MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Adrenal masses!!!!!!! page 2 2. Liver Masses!!!!!!! page 3 3. Obstetric US Soft Markers for Aneuploidy!! pages 4-6 4. Ovarian and Adnexal Cysts!!!!! pages 7-10 5. Pancreatic
1 MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS 1. Adrenal masses!!!!!!! page 2 2. Liver Masses!!!!!!! page 3 3. Obstetric US Soft Markers for Aneuploidy!! pages 4-6 4. Ovarian and Adnexal Cysts!!!!! pages 7-10 5. Pancreatic
North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Mesothelioma
 THIS DOCUMENT IS North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Mesothelioma [Based on WOSCAN SCLC CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN] UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED Document
THIS DOCUMENT IS North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Mesothelioma [Based on WOSCAN SCLC CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN] UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED Document
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2
 Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2 The Committee for Management of CT-screening-detected Pulmonary Nodules 2009-2011 The Japanese Society of CT Screening
Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2 The Committee for Management of CT-screening-detected Pulmonary Nodules 2009-2011 The Japanese Society of CT Screening
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
International Journal of Current Medical Sciences- Vol. 6, Issue,, pp , June, 2016 A B S T R A C T
 ISSN: 2320-8147 International Journal of Current Medical Sciences- Vol. 6, Issue,, pp. 122-126, June, 2016 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN HEPATIC METASTASES Ananthakumar P and Adaikkappan M., Available online
ISSN: 2320-8147 International Journal of Current Medical Sciences- Vol. 6, Issue,, pp. 122-126, June, 2016 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN HEPATIC METASTASES Ananthakumar P and Adaikkappan M., Available online
Chief Complain. For chemotherapy
 Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
A case of pulmonary tuberculosis presenting as a large pseudo-tumour
 CASE REPORT A case of pulmonary tuberculosis presenting as a large pseudo-tumour Abdulhalim Ibrahim 1, Mozafar Khalid 2, Mohammed KM Ali 3 1. Manchester Royal infirmary, Manchester, UK. 2. North Tees University
CASE REPORT A case of pulmonary tuberculosis presenting as a large pseudo-tumour Abdulhalim Ibrahim 1, Mozafar Khalid 2, Mohammed KM Ali 3 1. Manchester Royal infirmary, Manchester, UK. 2. North Tees University
Collaborative Stage. Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG
 Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Slide 1 Collaborative Stage Site-Specific Instructions - LUNG In this presentation, we are going to review the AJCC Cancer Staging criteria for the lung primary site. Slide 2 Reading Assignments As each
Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition
 Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition Nodular thyroid is a common clinical entity. All patients were evaluated by grey
Role of ultrasonography in recognition of malignant potential of thyroid nodules on the basis of their internal composition Nodular thyroid is a common clinical entity. All patients were evaluated by grey
Chapter. Imaging of Pneumonia in Children. Introduction. Chest X-ray and Common Infective Agents. School Age Children
 content Chapter 11 Winnie CW Chu Introduction Chest X-ray and Common Infective Agents School Age Children Computed Tomography and Common Infective Agents Utility of Computed Tomography Evaluation of Persistent
content Chapter 11 Winnie CW Chu Introduction Chest X-ray and Common Infective Agents School Age Children Computed Tomography and Common Infective Agents Utility of Computed Tomography Evaluation of Persistent
Approach to Pulmonary Nodules
 Approach to Pulmonary Nodules Edwin Jackson, Jr., DO Assistant Professor-Clinical Director, James Early Detection Clinic Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and
Approach to Pulmonary Nodules Edwin Jackson, Jr., DO Assistant Professor-Clinical Director, James Early Detection Clinic Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, Critical Care and
PLEURAL EFFUSION. Prof. G. Zuliani
 PLEURAL EFFUSION Prof. G. Zuliani Anatomy of pleural membrane and pleural space Pleural membrane consists of parietal pleura and visceral pleura A space situated between parietal and visceral pleura is
PLEURAL EFFUSION Prof. G. Zuliani Anatomy of pleural membrane and pleural space Pleural membrane consists of parietal pleura and visceral pleura A space situated between parietal and visceral pleura is
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer
 Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
امعة زهر قسم ا مراض الصدریة
 Al- Azhar University Faculty of Medicine Department of Chest diseases امعة زهر كلیة الطب (بنين) قسم ا مراض الصدریة مقرر الصدریة ا مراض الدبلوم لطلبة COURSE of Chest diseases For Diploma Degree 2013-2014
Al- Azhar University Faculty of Medicine Department of Chest diseases امعة زهر كلیة الطب (بنين) قسم ا مراض الصدریة مقرر الصدریة ا مراض الدبلوم لطلبة COURSE of Chest diseases For Diploma Degree 2013-2014
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY Research Article Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Ehsan Shahverdi 1 *, Ashkan
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY Research Article Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Ehsan Shahverdi 1 *, Ashkan
GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer
 GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Cancer Imaging Cross-Cutting Group April 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This document is intended as a ready reference for
GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Cancer Imaging Cross-Cutting Group April 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This document is intended as a ready reference for
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
Pleural and pleural space diseases: a pictorial review
 Pleural and pleural space diseases: a pictorial review Poster No.: C-1950 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Mereu, E. Di Nicola, F. De Filippis, B. Feragalli, R. L. 1 3 2 3 1 3 2
Pleural and pleural space diseases: a pictorial review Poster No.: C-1950 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Mereu, E. Di Nicola, F. De Filippis, B. Feragalli, R. L. 1 3 2 3 1 3 2
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS:
 CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
CT EVALUATION OF GASTRIC LESIONS: Pictural essay Hasni Bouraoui I, Kahloun A, Jemni H, Elouni F, Moulahi H, Daadoucha A, Ben Ali A, Sriha B, Tlili Graies K Departments of Radiology, Gastro enterology,
Derivation and Validation of a CT Scan Scoring System for Discriminating Malignant From Benign Pleural Effusions
 [ Original Research Disorders of the Pleura ] Derivation and Validation of a CT Scan Scoring System for Discriminating Malignant From Benign Pleural Effusions José M. Porcel, MD, FCCP ; Marina Pardina,
[ Original Research Disorders of the Pleura ] Derivation and Validation of a CT Scan Scoring System for Discriminating Malignant From Benign Pleural Effusions José M. Porcel, MD, FCCP ; Marina Pardina,
Renal masses - the role of diagnostic imaging
 Renal masses - the role of diagnostic imaging Poster No.: C-2471 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Rai#; Bjelovar/HR Keywords: Cysts, Cancer, Structured reporting, Ultrasound, MR,
Renal masses - the role of diagnostic imaging Poster No.: C-2471 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Rai#; Bjelovar/HR Keywords: Cysts, Cancer, Structured reporting, Ultrasound, MR,
