Circulatory System. Date. Name Sunday, March 10. By Sharon Fabian
|
|
|
- Felix Nelson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Sunday, March 10 Circulatory System By Sharon Fabian Blood circulates through your body all the time through a complicated system of large and small pathways. Your heart pumps day and night to transport the blood on its nonstop journey. This is your circulatory system, and it is in constant motion for a very good reason. Your circulatory system is like the freight train that delivers essential supplies to wherever they are needed in your body. As blood travels to all parts of your body, it delivers food and oxygen to your cells. It removes carbon dioxide and other waste materials. Along the way, it also helps to regulate your body temperature. The center of your circulatory system is your heart. It is a hollow muscle with two side-by-side pumps. When you are resting, your heart pumps about 70 times each minute. When you are exercising, it pumps even more. The pump on the right side sends a supply of blood to your lungs. The pump on the left side sends blood to all other parts of your body. Another part of the system is blood vessels, the rubbery tubes that carry the blood from place to place. The three types of blood vessels are arteries, veins, and capillaries. Arteries carry blood from the heart; the main one is the aorta. Veins carry blood to the heart; the two main ones are called the vena cava. Capillaries are very tiny blood vessels that connect arteries to veins. The third part of the circulatory system is the blood itself. Blood is made up of a liquid called plasma and three types of particles called red cells, white cells, and platelets. An average sized adult has about 5 quarts of blood in his body. A child who weighs 80 pounds has about 2 1/2 quarts of blood. The circulatory system does its job by working together with other body systems. It works with your respiratory system to deliver oxygen. After your lungs take in a good breath of air, the oxygen passes into your blood stream. The blood travels to your heart, where it is pumped out the left side, through your aorta, to all parts of your body. Blood carries its supply of oxygen through your arteries, then through smaller capillaries, and finally delivers it through the capillary walls to wherever it is needed. Next, carbon dioxide, which you don't need, comes into the capillaries, passing right through the capillary walls just like the oxygen did. It flows through little capillaries, then through larger veins back to the heart through a main vein, the vena cava. The right side of your heart pumps this supply of blood, with its cargo of carbon dioxide, to your lungs, and you breathe out. One journey is finished! Your circulatory system works with your digestive system in much the same way that it works with your respiratory system. It carries digested food to everywhere it is needed. Food enters the blood stream the same way that oxygen does, right through the wall! Digested food passes through the wall from your small intestine into your capillaries. Your blood stream carries it on a complete path through your body, with a stopover at your liver. It delivers the nutrients, the good parts of the food, to the right places, and carries the waste products on to other places so they can be disposed of. Blood helps regulate your temperature too. When the weather is hot, lots of blood flows to your skin where it can release heat from inside your body. In cold weather, less blood flows to your skin, to keep more of your heat inside. Your heart, blood vessels, and blood make up a system that can do all kinds of useful things! In fact, they make up the best transportation system ever invented -- your circulatory system.
2 Sunday, March 10 Circulatory System Questions 1. The circulatory system. A. digests food B. includes all of the bones C. carries blood throughout the body D. includes muscles and tendons 2. The circulatory system. A. delivers supplies B. removes wastes C. regulates temperature D. all of the above 3. The parts of the circulatory system are. A. heart, blood vessels, blood B. blood vessels, blood, red cells C. heart, muscles, blood D. blood vessels, blood, oxygen 4. The liquid part of blood is. A. plasma B. platelets C. red cells D. white cells 5. Each system of the body can work independently, with no help from any other systems. A. false B. true 6. Arteries are. A. blood vessels that carry blood to the heart B. parts of the respiratory system C. the tiniest blood vessels D. blood vessels that carry blood from the heart 7. The body needs a supply of. A. oxygen B. nutrients C. both D. neither 8. If you are exercising outside on a hot day, your face gets red because. A. less blood flows to your skin B. you are breathing slower C. your heart pumps slower D. more blood flows to your skin
3 Monday, March 11 Red Blood Cells By Jennifer Kenny Red blood cells are one of the four main parts of blood. The other parts are white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Did you know that there are about twenty-five trillion red blood cells in an adult's body? Red blood cells are very tiny. One hundred twenty-five red blood cells placed end-to-end would only be one millimeter long. Red blood cells are shaped like a doughnut. They are round, but they look like their centers have been partially scooped out. Even though they are considered cells, they do not have a nucleus. They are soft and flexible so they can pass through the capillaries. They can't move on their own, though. Instead, the flow of blood carries them. Red blood cells are produced in bone marrow, the spongy part inside some of the bones. The mother cells in bone marrow can make over one hundred million red blood cells each minute. Red blood cells live for about four months. They become fragile as they get older and begin to lose their shape. When that happens, they are carried to the spleen or the liver where they are destroyed, but parts of them can be recycled into new blood cells. What is the main job of the red blood cells? They transport oxygen from the lungs to every other part of the body. They also collect carbon dioxide from the body and take it back to the lungs. There is a special protein in red blood cells called hemoglobin that helps them do this. Actually, each red blood cell contains over two hundred fifty million hemoglobin molecules. The hemoglobin makes the blood red. More importantly, though, the hemoglobin combines with the oxygen and carbon dioxide so it can be transported where it needs to go. Red Blood Cells Questions 1. The four main parts of blood are white blood cells, platelets, plasma, and. A. oxygen B. red blood cells C. bone marrow 2. There are about red blood cells in an adult's body. A. 25 trillion B. 125 C. 100 million 3. Red blood cells do not have a nucleus. A. False B. True 4. Red blood cells live for about 120 days. A. True B. False
4 Monday, March makes the blood red. 6. What is the main job of red blood cells? A. carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide B. fighting disease C. clotting blood 7. What do you think would happen if the red blood cells weren't doing their job correctly? Describe red blood cells to someone who has never heard of them.
5 Tuesday, March 12 Donating Blood By Cindy Grigg A blood bank is a place where blood is stored for emergency use. In the United States about every two seconds, someone needs blood. That's over 43,000 people every DAY. Not long ago, people with a bad wound might have bled to death. Today, blood is donated by people. The donated blood is stored in blood banks to keep it safe for emergency use. To donate blood, a person must be 17 years old and weigh at least 110 pounds. Adults have about 10 pints of blood in their bodies. When blood is donated, about one pint is taken. The process takes about 10 minutes. With the paperwork and recovery time afterwards, a person is usually in and out of the donation center in 45 minutes to one hour. January is National Volunteer Blood Donor Month. One pint of blood can save up to three lives. A pint of blood can be separated into its different parts: red blood cells, plasma, and platelets. Donated blood can be given to a person as whole blood. Or each part can be given to three different people. Red blood cells contain iron, and they carry oxygen in the blood. Platelets help blood to clot. Platelets are needed by people with leukemia and other cancers or patients having surgery. Plasma is a mixture of water, proteins, and salts. Plasma is needed to transport the other blood parts to all the body's cells. Plasma makes up more than half of the volume of blood. Plasma can be frozen and used up to a year later. Red blood cells can be stored for 42 days. Platelets can only be stored for 5 days. The American Red Cross urges people to donate blood so that many lives can be saved. Donating Blood Questions 1. If 43,200 people need blood each day, how many people need a blood donation in a year? 2. To donate blood, a person must be. A. 21 years old B. 35 years old C. 17 years old D. 18 years old 3. What is the job of red blood cells? A. Red blood cells contain iron and carry oxygen in the blood. B. Red blood cells help blood to clot. C. Red blood cells transport the other blood parts to all the body's cells. D. all of the above
6 Tuesday, March Whole blood can be separated into different parts. A. two B. ten C. three D. five 5. Plasma. A. is a mixture of water, proteins, and salts B. makes up more than half of the volume of blood C. can be frozen and used up to a year later D. all of the above 6. The author's main purpose for writing this story was to. A. persuade B. inform C. entertain D. express personal feelings Do you know anyone who has received a blood donation? If so, ask this person how he or she feels about the person who donated the blood. What would the person who received the blood like to say to the person who donated it? If you don't know anyone who has received blood, write a dialog that you think might take place between these two people.
7 Wednesday, March 13 White Blood Cells By Brandi Waters Caption: Frog blood cells; the white blood cells are the round, dark ones in the center of the picture. Red blood cells give your blood its red color. They carry oxygen from your lungs to all of the cells in your body. However, there is more to your blood than just red blood cells. More than half of your blood is made up of a liquid called plasma. It is mostly water, but it is very important. Plasma helps your blood to flow. It allows your heart to pump your blood through your blood vessels. Red blood cells make up most of the remaining part of your blood, but there are other important blood components. One of these is white blood cells. White blood cells may seem a little out of place in your blood. They have little in common with red blood cells. Their job has nothing to do with the heart or blood vessels. White blood cells are like soldiers. Their job is to protect you from invaders. White blood cells fight germs that try to enter your body. Germs can get into your body through the air that you breathe and through the things that you eat or drink. They can also get into your body through a cut on your skin. White blood cells are always looking out for germs. If they find a germ (or many germs), they can call for help and more white blood cells will come to help. If there is an accident and you have a cut, white blood cells can also help to prevent germs from getting inside your body. They move quickly to the area that is hurt. They help keep the area clean, help your body to heal, and kill germs. Normally, there are not very many white blood cells in your blood. If you need them, your body can make more. If you get a small cut on your knee, you will need a few more white blood cells to help the cut heal and to kill germs. If you get sick with the flu, you will need a lot more white blood cells. After the threat has passed, some white blood cells can remember what the invader looked like. These white blood cells can react very quickly if that type of germ ever returns. They can act so quickly that they can kill the germ before it can make you sick! White Blood Cells Questions 1. makes up more than half of your blood. A. White blood cells B. Red blood cells C. Plasma D. Platelets 2. White blood cells. A. carry oxygen to your cells B. fight germs C. help your blood flow D. all of the above
8 Wednesday, March What is the job of a white blood cell? 4. Your body makes more white blood cells. A. when you have a cut B. when you get sick C. when you need them D. all of the above 5. What can some white blood cells do that protects you from getting sick from the same type of germ a second time? Doctors can count the number of white blood cells in your blood to help them find out what is wrong with a patient. What does it mean if a patient has a large number of white blood cells in their blood? What does it mean if there are a small number of white blood cells in their blood?
9 Thursday, March 14 The Heart By Jennifer Kenny The heart is the strong muscle which pumps blood throughout your body. It is a hollow muscle, about the size and shape of a fist. It is actually made up of two separate pumps. It is called an involuntary muscle because it works without you ever having to think about it working. Isn't that amazing? You'd never get anything done if you always had to think about making your heart beat! The heart is located between the lungs and behind your rib cage. It is in a slanting position in the center of the chest. The pericardium is a covering that keeps the heart from rubbing against your lungs and chest wall. The heart has four chambers in it (right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle). The muscular wall called the septum divides the two sides of the heart. Blood can't pass from one side to the other. Each side of the heart has an upper chamber and a lower chamber. The upper chambers are called the atria. The atria are holding chambers for blood entering the heart from the veins. The ventricles are the lower chambers. They act like pumps. The walls of the ventricles are thick. During each heartbeat, the cardiac muscle squeezes hard, forcing blood into the pulmonary artery or aorta (the main artery). The right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs. The left side of the heart pumps blood away to the rest of the body. Valves in the heart control the flow of blood through the heart. Therefore, the blood can go in only one direction. The valves are called the tricuspid valve, the mitral valve, and the semilunar valves. Your heart continuously beats. For the average adult, the heart beats about seventy times a minute. That amounts to around forty million times a year. Isn't that hard to believe? The Heart Questions 1. The is the strong muscle which pumps blood throughout your body. 2. The heart is actually made of separate pumps. A. 3 B. 5 C. 4 D The heart is a voluntary muscle. A. True B. False
10 Thursday, March The is a protective covering which keeps the heart from rubbing against your lungs and chest wall. A. pericardium B. septum C. valve D. chamber 5. The muscular wall called the divides the two sides of the heart. A. valve B. pericardium C. chamber D. septum 6. The are the lower chambers of the heart. A. ventricles B. atria 7. The is the main artery. 8. On average, how many times a minute does the heart beat in an adult? A. 70 times B. 140 times C. 4 times D. 40,000 times
11 Friday, March 15 Keeping Your Circulatory System Healthy By Brandi Waters It is important to keep your circulatory system working at its best. Your heart pumps blood to every part of your body. It travels through thousands of miles of blood vessels! Blood carries oxygen from your lungs. If there is a problem with your blood, your heart, or your blood vessels, your whole body can suffer. If you don't get enough oxygen to your brain, you might not be able to think clearly. If your stomach isn't getting enough oxygen, it might be hard for you to digest your food. If there is a problem with one of your blood vessels, blood could stop flowing to a part of your body. Without it, those cells could die. What can you do to keep your circulatory system healthy? You can make sure that you are getting plenty of exercise. When you exercise, you heart beats faster. This makes your heart stronger. Your heart is a muscle. Just like the muscles in your arms and legs, your heart gets bigger and stronger the more that you use it. Exercise also helps to keep your blood vessels working properly. Go outside and play! Ride your bicycle. Go for a swim. Your body will thank you! Eat healthy foods. They will keep your circulatory system healthy. Iron-rich foods like beans, whole-grain breads and cereals, red meat, and green vegetables are good for your blood. Try to avoid fatty foods, especially fried foods and foods that contain a type of fat called trans fat. Eating too much fat can cause fat to build up in your blood vessels. This could cause a heart attack. Eating too much sugar can also be unhealthy. It causes inflammation, or swelling, inside your body, even in your blood vessels. One final thing that you can do to keep your circulatory system healthy is easy. Do not smoke. Smoking puts many dangerous chemicals in your body. It harms your blood vessels and heart. It also puts unhealthy gases into your blood. Your cells will get less oxygen. Saying no to smoking is the easiest way to do something good for your body. Keeping Your Circulatory System Healthy Questions 1. Which of the following is NOT a part of the circulatory system? A. blood B. blood vessels C. stomach D. heart 2. Exercise helps to keep your heart healthy because. A. your heart gets stronger when it beats faster B. your heart pumps less blood when you exercise C. you make new blood vessels when you exercise D. all of the above 3. Beans and green vegetables are a good source of, which is good for your blood. A. sodium B. iron C. vitamin C D. oxygen
12 Friday, March Explain how a problem with your circulatory system could affect your brain. 5. What is one thing that you should not do in order to keep your circulatory system healthy? Exercise is good for your heart. What is your favorite way to exercise? Explain what you like about it.
13 The Heart By Brandi Waters Saturday, March 16 Many people think of love when they think about their hearts. They might say, "I love you from the bottom of my heart." Sometimes people complain of having a broken heart when they are sad. A person who does something mean might be described as being heartless. Actually, your heart has nothing to do with your feelings. Your heart has a much more important job. Your heart is a big muscle. It is about the same size as your fist. Like all muscles, your heart can "flex." It makes a squeezing motion when it flexes. Your heart does this over and over again. This is your heartbeat. Your heart beats to move blood to all the parts of your body. This process is called circulation. It takes less than a minute to move blood to all of the cells in your body! Blood is pumped to your lungs where it picks up oxygen from the air you breathe. Next, the blood is pumped from the heart to other parts of your body. The blood delivers oxygen to all your cells. It also carries away waste that your cells don't need. This waste is carbon dioxide. Your heart keeps beating and carries the blood back to your lungs. There, your blood exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen. When you breathe out, or exhale, the carbon dioxide is removed from your body. Your heart carries oxygen to all the parts of your body. This is why your heart is so important. If your heart stops beating, your cells do not have oxygen. They stop working. Your body cannot survive for very long without oxygen. Your heart helps to keep you alive. The Heart Questions 1. Your heart. A. is a muscle B. carries carbon dioxide to your cells C. holds your emotions D. all of the above 2. Your heart's job is to. A. move blood to all the parts of your body B. help you breathe C. make you strong D. make heat to keep your body warm 3. Your heart and work together to supply your body with oxygen and to remove carbon dioxide from your body. A. brain B. fist C. stomach D. lungs
14 Saturday, March The process that moves to every part of your body is called circulation. 5. How big is your heart? Why do you think that people have associated the heart with feelings, especially feelings of love? Explain your reasoning.
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
The Circulatory System answers to worksheet will either be on the presentation or video By: Lanya King, Geianah Shaw,and Heidi Puerta The Functions of the Circulatory System Respiration- delivers oxygen
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
Circulation and Respiration
 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
 Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM VOCABULARY blood vessel - arteries veins capillaries blood plasma white blood cells red blood cells platelets WHAT IS CIRCULATION? What messenger makes trillions
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM VOCABULARY blood vessel - arteries veins capillaries blood plasma white blood cells red blood cells platelets WHAT IS CIRCULATION? What messenger makes trillions
The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body
 The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body (1) As you have already learned, there are muscles all over your body. All of them are important, but not all of them are vital. The muscle
The Human Heart: The Most Important Muscle in the Human Body (1) As you have already learned, there are muscles all over your body. All of them are important, but not all of them are vital. The muscle
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is blood? What is blood pressure? What are blood types?
 CHAPTER 16 2 Blood SECTION Circulation and Respiration California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is
CHAPTER 16 2 Blood SECTION Circulation and Respiration California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is
How does the Circulatory System maintain
 How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
The circulatory system brings many different materials to all the cells of the body and picks up waste from the same cells.
 CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
By Semih. The first system is about the respiratory system. It provides our body with the oxygen it needs and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
 By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
14-1: The Body s Transport System. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
7 th Grade Life Science Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system, also called circulatory system, is made of your heart blood vessels, and blood. It is like the network of highways on Earth, where
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
Heart Facts. The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime.
 Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
OB16 Demonstrate the effect of exercise and rest on pulse and breathing rate and appreciate that a balance of each promotes good health
 Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
Biology: 6. The Circulation System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier Syllabus OB13 Describe the function and composition of blood
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation.
 As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
As a courtesy to your fellow classmates please refrain from talking, beating, or snoring. And Now Our Feature Presentation. Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Functions of the Circulatory System
 Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Circulatory System. Circulatory System
 Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System. The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Circulatory System The circulatory system is actually two systems combined: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system Lymphatic System This is a group of organs and tissues that collect the fluid
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
One system involved in exercising is the respiratory system. The respiratory system includes three main parts breathing, lungs and blood.
 By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1
 Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1 Which part of the brain controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, & digestion? A. Cerebellum B. Brain stem C. Cerebrum 0 0 0 10/1/2014 Nervous System 2 Cerebellum Brain
Circulatory System 10/1/2014 1 Which part of the brain controls heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, & digestion? A. Cerebellum B. Brain stem C. Cerebrum 0 0 0 10/1/2014 Nervous System 2 Cerebellum Brain
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
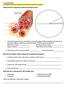 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Circulatory System. Chapter 32
 Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Some Fun Facts The left side of the heart contains oxygenated blood whereas the right side has de-oxygenated blood. One drop of blood has about 5 million red blood cells and 12 thousand
The Circulatory System Some Fun Facts The left side of the heart contains oxygenated blood whereas the right side has de-oxygenated blood. One drop of blood has about 5 million red blood cells and 12 thousand
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
Blood Vessels. veins. valve. to the heart. capillaries from the heart. arteries. Visual 25-1
 Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
Blood Vessels veins valve to the heart capillaries from the heart arteries Visual 25-1 Human Heart pulmonary arteries superior vena cava aorta pulmonary veins semilunar valves right atrium pulmonary arteries
 The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
The Circulatory System. Lesson 4. Quick Check. Trace the path of blood after it is pumped from the heart. 22. First
 Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
DAY ONE BLOOD. What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made?
 BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Topic Page: Circulatory system
 Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
Topic Page: Circulatory system Definition: circulatory system from Collins English Dictionary n 1 anatomy, zoology the system concerned with the transport of blood and lymph, consisting of the heart, blood
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review
 Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Lecture 8. Heart and Circulatory System. Lecture 8
 Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body.
 Circulatory System The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body. What does blood consist of? The blood consists
Circulatory System The circulatory system is a complex series of tubes that transports nutrient-rich blood and waste products throughout the entire body. What does blood consist of? The blood consists
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Thanks. Connect. You Might Also Like. Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback.
 Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Thanks Thank you for downloading my product. I truly appreciate your support and look forward to hearing your feedback. Connect You can connect with me and find many free activities and strategies over
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
MESA DAY CONTEST RULES
 FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
FOR CENTER DIRECTOR S USE ONLY ANSWERS MODEL SCIENCE THE HEART High School All Grades Students MUST be prepared to answer each question with a complete sentence or sentences. 1. What is the size of the
Respiration and Circulation
 Respiration and Circulation lood Functions of lood Have your ever had an injury that caused bleeding? lood is a red liquid that is a little thicker than water. You learned that your circulatory system
Respiration and Circulation lood Functions of lood Have your ever had an injury that caused bleeding? lood is a red liquid that is a little thicker than water. You learned that your circulatory system
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
LER Made of durable Soft Foam! Explore the human heart through hands-on investigation!
 LER 1902 Made of durable Soft Foam! Explore the human heart through hands-on investigation! The human heart is one of the most important parts of the body. It is responsible for moving blood and other
LER 1902 Made of durable Soft Foam! Explore the human heart through hands-on investigation! The human heart is one of the most important parts of the body. It is responsible for moving blood and other
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System. Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted. Circulatory System 1
 Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
Circulatory System Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 11 Illustrations 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. unless otherwise noted Circulatory System 1 Circulatory System Circulatory system = Cardiovascular system
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Cardiovascular System Facts The average person has nearly 100,000 km of blood vessels running through them. The larger the organism, the slower the heart beats (a woman s heart will
The Circulatory System Cardiovascular System Facts The average person has nearly 100,000 km of blood vessels running through them. The larger the organism, the slower the heart beats (a woman s heart will
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located
 How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD The circulatory system is a group of organs which carry food and oxygen to and remove waste from every cel l in the body. Arteries-Lead away from the heart Plasma - -+-- 55%
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM AND BLOOD The circulatory system is a group of organs which carry food and oxygen to and remove waste from every cel l in the body. Arteries-Lead away from the heart Plasma - -+-- 55%
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System
 NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
NOTEBOOK Table of Contents: #41: Comparative Circulatory System Assignment Page: #41: Monday January 9, 2017: Comparative Circulatory System Agenda: 1. Comparative Circulatory System (Notes with Handout)
