STRUCTURE OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACTUS IN ARISTICHTHYS NOBILIS
|
|
|
- Cecil Montgomery
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lucrări ştiinţifice - vol. 51 seria Zootehnie STRUCTURE OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACTUS IN ARISTICHTHYS NOBILIS Gabriela VASILE, Gianina COMĂNESCU, Elena CIORNEA The paper presents some histological aspects of the digestive tractus in Aristichthys nobilis in its various segments (anterior post-oesophagian intestine, anterior distal intestine, median and posterior intestine), as correlated with both age and main type of food for the species under study. The digestive tube has been taken over form 5 Aristichthys nobilis individuals of various ages, namely: one- and four-old summer ones, the digestive tractus being unfolded along its whole length, after which rectangularly-shaped fragments were taken over and processed by methods of histological techniques; thus, the nuclei were colored with hemalaune, while the cytoplasm - with eosine. Thickness of the mucous and muscular tunics was measured by the micrometric method, with a micrometric objective thin plate lamina and an ocular micrometric lamina. The experimental results obtained put into evidence some variation in the form of the mucous folds (simpler in one summer-old individuals and more complex in the four summer-old ones), along with variations in the thickness of the mucous and muscles. For both categories of ages taken into study, the mucous and muscular tunics are more well-developed in the segment of the post-oesophagian anterior intestine than in the rest of the digestive tractus, which entitles one to consider this portion as a stomach, in spite of the typically intestinal aspect of the mucous tunic. MATERIALS AND METHOD As the studies devoted to the morpho-structural aspects of the digestive tractus in Asian cyprinids are quite few and very synthetic (BERRY and LOW, 1970; BREMER, 1978; TREVISAN, 1979; ATHIKESAVAN et al., 2006), the present investigation analyzes such aspects in bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) of various ages, i.e., one and four summer-old individuals, for evidencing some possible intraspecific (age-dependent) similarities or differences. The digestive tube has been taken over form five Aristichthys nobilis individuals of various ages, namely: one- and four-old summer ones, the digestive tractus being unfolded along its whole length, after which rectangularly-shaped fragments were taken over and processed by methods of histological techniques; thus, the nuclei were colored with hemalaune, while the cytoplasm - with eosine (HUMASON, 1962; MARTOJA and MARTOJA, 1967). Thickness of the mucous and muscular tunics was measured by the micrometric method, with a micrometric objective thin plate lamina and an ocular micrometric lamina (MUREŞAN et al., 1974)
2 Universitatea de Ştiinţe Agricole şi Medicină Veterinară Iaşi RESULTS AND DISCUSSION In one summer-old bighead carp representatives, one may observe that - in the post-oesophagian portion of the anterior intestine - the mucous tunic evidences a few folds with cylindroidal aspect, lying on the surface of the mucous tunic. Besides them, other smaller, conical-shaped folds may be observed, their axis evidencing the corione infiltrated with lymphocytes while, in the cylindroidal shaped folds, the corione hardly penetrates (Fig. 1). On its whole, the corione of the mucous tunic is totally infiltrated with lymphocytes - even some lymphatic follicles being observed in its thickness (Fig. 2). Fig.1. Cross-section through the anterior post-oesophagus intestine of one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (assembly; 100x) (original photo) Fig.2. Cross-section through the anterior post-oesophagus intestine of one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (detail: lymphatic follicle from the corione mucous thickness; 200x) (original photo) In this segment, the height of the mucous tunic is of µm. The mucous, calyx -shaped cells from the epithelium are not very numerous. As to the muscular tunic, both the circular and the longitudinal layers have a thickness of µm
3 Lucrări ştiinţifice - vol. 51 seria Zootehnie In four summer-old organisms, the portion of the anterior postoesophagian intestine is especially well-developed, the mucous tunic being high, with ample folds, most of them cylindroidal in shape, with a rich epithelium, high and rich in calyx-shaped cells in full activity. The corione of the mucous tunic is intensely impregnated with lymphocitary elements, which supports the idea that an intense immunitary activity is developing in this segment of the digestive tractus, probably determined by the type of food which - in the opinion of several authors - is constituted, predominantly, of zooplankton (LAZAREVA et al., 1977; MARCIAK and BOGDAN, 1979; CUI et al., 2005). As to the apical part of some of the mucous tunic's folds, it has been observed that, here and there, it is folded and eroded, the erosions evidencing some repression from the part of the intensely lymphocyte impregnated corione. Very well represented is also the muscular part of the mucous tunic, while the sub-mucous tunic is weakly evidenced (Figs. 3-4). On the whole, the thickness of the mucous tunic is of µm. As to the muscular tunic, it is wellevidenced at this level - especially the internal, circular layer - the thickness of this tunic being of 625 µm. Fig.3. Cross-section through the anterior post-oesophagus intestine of four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (assembly; 100x) (original photo) Fig.4. (Cross-section through the anterior post-oesophagus intestine of four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (detail: repression of the lymphocyte impregnated corione; 200x) (foto original)
4 Universitatea de Ştiinţe Agricole şi Medicină Veterinară Iaşi In the distal part of the anterior intestine, in one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis representatives, the mucous tunic is relatively high, with a thickness of 250 µm, evidencing folds of various shapes. The epithelium is extremely thin, while the calyxshaped cells are not visible. The corione is lax, with slight lymphocytary infiltrations. Again, at this level, a lymphocyte mass may be observed, migrating inside the lumen of the respective cavity; the muscular tunic is thin, of µm (Fig. 5). Fig.5. Cross-section through the anterior distal intestine of one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (assembly; 200x) (original photo) In four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis individuals, the distal segment of the anterior intestine evidences a very high mucous tunic, with folds of various shapes - some of them cylindrical, others conical and even trapezoidal - with a very high prismatic epithelium, very rich in calyx-shaped cells; the striated plateau of the epithelium is highly visible. In the axis of these folds, the corione is sufficiently well-represented, being strongly impregnated with lymphocytes. Such lymphocytary infiltrations penetrate the epithelium, as well, trying to reach the intestinal lumen. The presence of some lymphatic follicles may be also observed in the thickness of the corione (Figs. 6-7). Fig.6. Cross-section through the anterior distal intestine of four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (assembly; 100x) (original photo)
5 Lucrări ştiinţifice - vol. 51 seria Zootehnie Mention should be made of the fact that the presence of such lymphocytary infiltrations inside the mucous tunic may be related to the abovementioned immunitary activity, correlated with the type of food, once known that the Aristichthys nobilis consumes mainly zooplankton (cyclopes, copepods, chladoceres, kelicerates) with keratinous cover which, in most cases, cause lesions at the level of the mucous tunic's epithelium. On its whole, the thickness of the mucous tunic is of 1000 µm; in this case, too, the muscular part of the mucous is very well represented, its thickness being of µm. Fig.7. Cross-section through the anterior distal intestine of four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (detail: lymphatic follicle; 200x) (foto original) In one summer-old bighead carp individuals, in the segment of the medium intestine, the mucous tunic is the most evident one, showing either conic or bifurcated folds, with a high epithelium, the calyx-shaped cells of this level being weakly represented; the corione is lax, weakly-impregnated with lymphocytes (Fig. 8). The height of the mucous tunic in this segment of the digestive tractus is of 250 µm, while the muscular tunic is µm thick. Fig.8. Cross-section through the medium intestine of one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (assembly; 200x) (original photo)
6 Universitatea de Ştiinţe Agricole şi Medicină Veterinară Iaşi In four summer-old individuals, the segment of the average intestine evidences a well-developed mucous, with folds of various shapes - some of them cylindrical, others amply trapezoidal - covered by a prismatic epithelium with a striated plateau, very rich in calyx-shaped cells in full activity. Both the corione and the epithelium evidence strong lymphocitary infiltrations, very big lymphatic follicles - some of them of µm in size (Fig. 9) - being visible in the trapezoidal folds. Fig.9. Cross-section through the medium intestine of four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (assembly; 100x) (original photo) At this level of the digestive tube, a strong erosion in the epithelium of the mucous tunic may be noticed, together with lymphocytes migration towards the intestinal lumen (Fig. 10). The thickness of the mucous tunic is, on the whole, of 625 µm, the muscular one being also relatively well-developed - with a thickness value of 375 µm. Fig.10. Cross-section through the medium intestine of four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (detail: mucous erosion and lymphocytes migration towards the intestinal lumen; 200x) (foto original)
7 Lucrări ştiinţifice - vol. 51 seria Zootehnie In one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis individuals, the posterior intestine shows a thin wall, with a less high mucous tunic, of 87.5 µm, with small and dense folds, a hardly visible epithelium and a very lax corione, weakly impregnated with lymphocytes. The muscular tunic is extremely thin, of only 37.5 µm (Fig. 11). Fig.11. Cross-section through the posterior intestine of one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (assembly; 400x) (original photo) The posterior segment of the digestive tractus - in four summer-old bighead carp representatives, with a µm thick mucous tunic, evidences numerous calyx-shaped cells, being intensely folded, most of the folds being cylindroidal in shape, while others are trapezoidal, the latter's corione being intensely infiltrated with lymphocytes; otherwise, the corione appears less infiltrated with lymphocytes. At this intestinal level, the muscular tunic is 250 µm thick (Figs.12-13). Fig.12. Cross-section through the posterior intestine of four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (assembly; 200x) (original photo)
8 Universitatea de Ştiinţe Agricole şi Medicină Veterinară Iaşi Fig.13. Cross-section through the posterior intestine of four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis (detail: epithelium with striated plateau and calyx-shaped cells; 400x) (foto original) As evidenced by the graphical plot, as well (Figs ), both in the stage of fingerlings and at ages of four summers, the thickness of the mucous and muscular tunics generally record decreasing values along the length of the digestive tractus, starting from the post-oesophagian segment of the anterior intestine, up to the level of the posterior intestine, with the only exception of the muscular tunic (Fig. 15) which, in the one summer-old individuals, remains constant in the first two segments under investigation, with a thickness value of µm, after which - at the level of the medium intestine - records a slight increase in thickness (of 25 µm), comparatively with the segment of the distal anterior intestine, attaining a value of µm, which is probably due to the fact that - at the level of the posterior intestine - the muscular tunic is extremely thin (37.5 µm), a compensation being therefore possible as to the advancing activity of the content of the final intestine. Fig.14. Graphical representation of the thickness of mucous tunic in one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis individuals
9 Lucrări ştiinţifice - vol. 51 seria Zootehnie µm ant. post-oesoph. int. ant. distal int. mediu int. posterior int. Fig.15. Graphical representation of the thickness of muscular tunic in one summer-old Aristichthys nobilis individuals µm ant. post-oesoph. int. ant. distal int. mediu int. posterior int. Fig.16. Graphical representation of the thickness of mucous tunic in four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis individuals Fig.17. Graphical representation of the thickness of muscular tunic in four summer-old Aristichthys nobilis individuals
10 Universitatea de Ştiinţe Agricole şi Medicină Veterinară Iaşi CONCLUSIONS One of the main observations made on the microscopic structure of the various segments of the digestive tractus, in Aristichthys nobilis, as well as on their micrometric thickness values, refers to the fact that the aspect of the tunics (the mucous and the muscular one, especially) get modified as a function of age. Variation in the shape of the mucous tunic s folds (simpler in one summer-old individuals and more complex in four summer-old ones) was also observed, alongwith variations in the thickness of the muscular and mucous tunics (lower micrometric values in one summer-old individuals and higher micrometric values in four summer-old ones). For both categories of ages taken into study, the mucous and muscular tunics are more well-developed in the segment of the post-oesophagian anterior intestine than in the rest of the digestive tractus, which entitles one to consider this portion as a stomach, in spite of the typically intestinal aspect of the mucous tunic. REFERENCES 1. ATHIKESAVAN, S., VINCENT, S., AMBROSE, T., VELMURUGAN, B., Nickel induces histopatological changes in the different tissues of freshwater fish, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix (Valenciennes), J. Environ. Biol., 27 (2): BERRY, P. Y., LOW, M. P., Comparative studies on some aspects of the morphology and histology of Ctenopharyngodon idella, Aristichthys nobilis, and their hybrid (Cyprinidae), Copeia, 4: BREMER, H., Histological and histochemical studies on the detection of the esogaster in the agastric cyprinidae Aristichthys nobilis Rich. (Marble carp), Gegenbaurus Morphol. Jahrb., 124 (5): CUI, F. Y., LIN, T., LIU, D. M., ZHANG, L. Q., Excess propagation and biological control of zooplanktonic Cyclops in drinking water sources, Water Sci. Technol., 52 (8): HUMASON, L. G., Animal tissue techniques, W. H. Freeman and Company, USA, 468p. 6. LAZAREVA, L. P., OMAROV, M. O., LEZINA, A. N., Feeding and growth of the bighead carp, Aristichthys nobilis, in the waters of Dagestan, Journal of Ichthyology, 17 (1): MARCIAK, Z., BOGDAN, E., Food requirements of juvenile stages of grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella Val., silver carp, Hypophthalmichthys molitrix Val., and bullhead carp Aristichthys nobilis Rich., EMS Special Publication, 4: MARTOJA, R., MARTOJA, M., Initiation aux techniques de l histologie animale, Éd. Masson et Cie, Paris, 345 p. 9. MUREŞAN, E., GABOREANU, M., BOGDAN, A. T., BABA, A. I., Tehnici de histologie normală şi patologică, Ed. Ceres, Bucureşti, 478 p. 10. TREVISAN, P., Histomorphological and histochemical researches on the digestive tract of the freshwater grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella (cypriniformes), Anat. Anz., 145 (3):
ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACTUS IN HYPOPHTHALMICHTHYS MOLITRIX
 Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Al. I. Cuza Iaşi, s. Biologie animală, Tom LIV, 2008 ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACTUS IN HYPOPHTHALMICHTHYS MOLITRIX Gabriela VASILE, Gianina COMĂNESCU, Elena
Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Al. I. Cuza Iaşi, s. Biologie animală, Tom LIV, 2008 ON THE STRUCTURE OF THE DIGESTIVE TRACTUS IN HYPOPHTHALMICHTHYS MOLITRIX Gabriela VASILE, Gianina COMĂNESCU, Elena
Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Secţiunea Genetică şi Biologie Moleculară, TOM IX, 2008
 Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Secţiunea Genetică şi Biologie Moleculară, TOM IX, 2008 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON THE α-amylase ACTIVITY AND STRUCTURE OF THE MEDIAN SEGMENT OF
Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Secţiunea Genetică şi Biologie Moleculară, TOM IX, 2008 EXPERIMENTAL STUDIES ON THE α-amylase ACTIVITY AND STRUCTURE OF THE MEDIAN SEGMENT OF
STRUCTURAL MODIFICATIONS OF THE SHEEP LIVER PARENCHYMA IN FLUKE INFESTATION
 Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Al.I.Cuza Iaşi, s. Biologie animală, Tom L, 2004 STRUCTURAL MODIFICATIONS OF THE SHEEP LIVER PARENCHYMA IN FLUKE INFESTATION BY DIANA GHEŢEU 1, ANCA NEAGU 1, GIANINA
Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Al.I.Cuza Iaşi, s. Biologie animală, Tom L, 2004 STRUCTURAL MODIFICATIONS OF THE SHEEP LIVER PARENCHYMA IN FLUKE INFESTATION BY DIANA GHEŢEU 1, ANCA NEAGU 1, GIANINA
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
The Alimentary Canal of the Aphid Prociphilus Tesselata Fitch
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 38, Issue 3 (May, 1938) 1938-05 The Alimentary Canal of the Aphid Prociphilus
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 38, Issue 3 (May, 1938) 1938-05 The Alimentary Canal of the Aphid Prociphilus
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
ON THE ACTIVITY OF AMYLASES DACTYLIS GLOMERATA
 Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Secţiunea Genetică şi Biologie Moleculară, TOM VIII, 27 ON THE ACTIVITY OF AMYLASES DACTYLIS GLOMERATA ELENA CIORNEA 1*, GABRIELA VASILE 1 Key
Analele Ştiinţifice ale Universităţii Alexandru Ioan Cuza, Secţiunea Genetică şi Biologie Moleculară, TOM VIII, 27 ON THE ACTIVITY OF AMYLASES DACTYLIS GLOMERATA ELENA CIORNEA 1*, GABRIELA VASILE 1 Key
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Histology Lab. looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira book and you can use BlueHistolgy website
 Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Digestive System. The group of organs which performs the function of digestion constitute digestive system.
 Digestive System Definition:- The active biological process by which food materials impermeable to the cell membrane is converted into permeable to the cell membrane is called digestion. The group of organs
Digestive System Definition:- The active biological process by which food materials impermeable to the cell membrane is converted into permeable to the cell membrane is called digestion. The group of organs
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4
 Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4 CHAPTER 3: Cells and Tissues 1. The smallest unit of living tissue is called a. All living organisms are composed of these basic units where all life processes
Anatomy and Physiology Homework: Chapters 3-4 CHAPTER 3: Cells and Tissues 1. The smallest unit of living tissue is called a. All living organisms are composed of these basic units where all life processes
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
RESULTS CONCERNING THE USE OF THE NERISTIN SYNTHETIC HORMONE IN THE ARTIFICIAL REPRODUCTION OF THE HYPOPHTHALMYCHTYS MOLITRIX (VAL) SPECIES
 Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 42 (2) (2009), Timişoara RESULTS CONCERNING THE USE OF THE NERISTIN SYNTHETIC HORMONE IN THE ARTIFICIAL REPRODUCTION OF THE HYPOPHTHALMYCHTYS MOLITRIX
Lucrări ştiinţifice Zootehnie şi Biotehnologii, vol. 42 (2) (2009), Timişoara RESULTS CONCERNING THE USE OF THE NERISTIN SYNTHETIC HORMONE IN THE ARTIFICIAL REPRODUCTION OF THE HYPOPHTHALMYCHTYS MOLITRIX
STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA)
 STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA) Petruţ T. 1, D. Condur 1, N. Velicu 1, V. Călin 1 1 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Spiru Haret, 9-11 Energeticienilor
STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA) Petruţ T. 1, D. Condur 1, N. Velicu 1, V. Călin 1 1 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Spiru Haret, 9-11 Energeticienilor
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB
 PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB.1 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTRODUCTION Cells are the smallest units of life, and are named according to their function. Cells
PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB.1 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTRODUCTION Cells are the smallest units of life, and are named according to their function. Cells
Tissues and organs PART 1
 Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Digestive system L 2. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Digestive system L 2 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the general structure of digestive tract: a-mucosa. b-submucosa. c-muscularis externa d-adventitia
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Upper Respiratory Histology
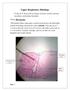 Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Upper Respiratory Histology - Today we ll discuss the histology of larynx, trachea, primary, secondary, and tertiary bronchus. *First: The Larynx: -The picture below represents a section in the larynx,
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHANGES OF THE SMALL INTESTINE MUCOSAE IN PIGLETS WITH ANOXIA AND PARTURITION HYPOXIA
 HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHANGES OF THE SMALL INTESTINE MUCOSAE IN PIGLETS WITH ANOXIA AND PARTURITION HYPOXIA Olga-Alina RADA 1, Liliana VASILE 3, H. SĂRĂNDAN 2, H. CERNESCU 2, Diana BREZOVAN 2, Mihaela OSTAN
HISTOPATHOLOGIC CHANGES OF THE SMALL INTESTINE MUCOSAE IN PIGLETS WITH ANOXIA AND PARTURITION HYPOXIA Olga-Alina RADA 1, Liliana VASILE 3, H. SĂRĂNDAN 2, H. CERNESCU 2, Diana BREZOVAN 2, Mihaela OSTAN
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Histology review. Histology. Slides. Epithelial tissue. Another example - kidney. Simple cuboidal epithelium. What to look for
 Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
Histology review Histology What to look for Histology Practical = 50 pts Some slides set up on scopes (~10) Some Powerpoint pictures on the projector Questions I will ask: What kind of tissue? General
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
MARY TALBOT, University of Omaha. INTRODUCTION.
 THE STRUCTURE OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM IN CREOPHILUS VILLOSIS MARY TALBOT, University of Omaha. INTRODUCTION. The beetles used in this study were procured at the Columbus, Ohio, Packing House, where they
THE STRUCTURE OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM IN CREOPHILUS VILLOSIS MARY TALBOT, University of Omaha. INTRODUCTION. The beetles used in this study were procured at the Columbus, Ohio, Packing House, where they
URINARY SYSTEM. Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3
 URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
(A) Diarrhea. (B) Stomach cramps. (C) Dehydration due to excess fluid loss. (D) A, B, and C are correct. (E) Only answer B is correct.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 21: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 1. A 26-year-old male is treated in the emergency department for severe gastrointestinal disturbance. Which of the following
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
THE ALIMENTARY CANAL OF IIARPALUS PENN- SYLVANICUS DEJ. (CARABIDAE: COLEOPTERA)
 THE ALIMENTARY CANAL OF IIARPALUS PENN- SYLVANICUS DEJ. (CARABIDAE: COLEOPTERA) F. B. WHITTINGTON Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio During the latter part of September, 1932, a species of Carabidae,
THE ALIMENTARY CANAL OF IIARPALUS PENN- SYLVANICUS DEJ. (CARABIDAE: COLEOPTERA) F. B. WHITTINGTON Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio During the latter part of September, 1932, a species of Carabidae,
Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN:
 Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Available online at www.jpsscientificpublications.com Volume 3; Issue - 1; Year 2017; Page: 969 973 Indo Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Research (IAJMR) ISSN: 2454-1370 MORPHOLOGICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES
 Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Lab 1 ANIMAL TISSUES Levels of Organization Animals are multicellular heterotrophs whose cells lack cell walls. Most animals exhibit a hierarchical level of organization: Cells are organized into tissues
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Urinary system. Urinary system
 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Histology of the Eye
 Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
AMELOGENESIS. Prof. Shaleen Chandra
 AMELOGENESIS Epithelial Enamel Organ Outer Enamel Epithelium Stellate Reticulum Stratum Intermedium Inner Enamel Epithelium Cervical Loop Life Cycle of Ameloblasts Morphogenic stage Organizing Stage Formative
AMELOGENESIS Epithelial Enamel Organ Outer Enamel Epithelium Stellate Reticulum Stratum Intermedium Inner Enamel Epithelium Cervical Loop Life Cycle of Ameloblasts Morphogenic stage Organizing Stage Formative
D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module. 1) Connective tissue
 D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module 1) Connective tissue Objectives: 1) identify the components (cells, fibres) present in "ordinary" connective tissue 2) differentiate the three types
D1120 Connective Tissue and Muscle Laboratory Module 1) Connective tissue Objectives: 1) identify the components (cells, fibres) present in "ordinary" connective tissue 2) differentiate the three types
The Respiratory System. Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb
 The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
The Respiratory System Prof. Dr.Mohammed Hisham Al-Muhtaseb Objectives (lecture + practical) 1. Identify the conduction part of the respiratory tract and analyze the function of each segment 2. Identify
GUIDE TO: Diagnosing Coccidiosis & Necrotic Enteritis
 GUIDE TO: Diagnosing Coccidiosis & Necrotic Enteritis Site of Infection Species E. acervulina E. brunetti E. maxima E. mivati E. tenella E. necatrix Oocyst Size 2µ{ 18.3 x 14.6 24.6 x 18.8 30.5 x 20.7
GUIDE TO: Diagnosing Coccidiosis & Necrotic Enteritis Site of Infection Species E. acervulina E. brunetti E. maxima E. mivati E. tenella E. necatrix Oocyst Size 2µ{ 18.3 x 14.6 24.6 x 18.8 30.5 x 20.7
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Prepared By Student. Dania Abed Al-majeed. Rahma Raad Hanna. Balqees Mohammed Aasim. Dania Hisham. Rasha Rafiee
 Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
Prepared By Student Rahma Raad Hanna Balqees Mohammed Aasim Dania Hisham Dania Abed Al-majeed Rasha Rafiee Epithelia Epithelia can be derived from ectoderm, mesoderm or endoderm -ectoderm gives rise to
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
by authors and SVSBT.
 The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy
 Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Collin College BIOL 2401 : Human Anatomy & Physiology Ex. 1 :Language of Anatomy The Anatomical Position Used as a reference point when referring to specific areas of the human body Body erect Head and
Epithelial Tissue. SAC Request. Epithelial Tissue 27/06/12. Linings and? BIOL241
 Epithelial Tissue Linings and? BIOL241 SAC Request From Audrey Rose Cabinet Coordinator Student Administrative Council SAC is looking for dedicated students to apply for the Student Cabinet, Fee Board,
Epithelial Tissue Linings and? BIOL241 SAC Request From Audrey Rose Cabinet Coordinator Student Administrative Council SAC is looking for dedicated students to apply for the Student Cabinet, Fee Board,
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
RESEARCH REGARDING THE HISTOSTRUCTURE OF THE NASAL CONCHA ON BIRDS ANTIGENICALLY STIMULATED
 RESEARCH REGARDING THE HISTOSTRUCTURE OF THE NASAL CONCHA ON BIRDS ANTIGENICALLY STIMULATED Abstract Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LIX () ISSN 065-95, ISSN Online 067-66, ISSN-L
RESEARCH REGARDING THE HISTOSTRUCTURE OF THE NASAL CONCHA ON BIRDS ANTIGENICALLY STIMULATED Abstract Scientific Works. Series C. Veterinary Medicine. Vol. LIX () ISSN 065-95, ISSN Online 067-66, ISSN-L
MAST-CELLS are present in the digestive tract of all classes of vertebrates
 The Distribution of Mast-Cells in the Digestive Tract of Laboratory Animals: Its Bearings on the Problem of the Location of Histamine in Tissues By I. MOTA, A. G. FERRI, AND S. YONEDA 251 (From the Laboratory
The Distribution of Mast-Cells in the Digestive Tract of Laboratory Animals: Its Bearings on the Problem of the Location of Histamine in Tissues By I. MOTA, A. G. FERRI, AND S. YONEDA 251 (From the Laboratory
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR
 SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR M. D. Kulkarni And A. H. Shinde Department of Zoology Yashwantrao Chavan Arts & Science College, Mangrulpir Dist. Washim. (Received
SEASONAL CHANGES IN HISTOLOGYOF THE THYROID GLAND CALOTIS VERSICOLOR M. D. Kulkarni And A. H. Shinde Department of Zoology Yashwantrao Chavan Arts & Science College, Mangrulpir Dist. Washim. (Received
A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development
 Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 47: 433-444, 1971 A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development By Hsi-Kuei Tsai Department of Anatomy, College
Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 47: 433-444, 1971 A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development By Hsi-Kuei Tsai Department of Anatomy, College
January 07, ANIMALS Digestive System Stomach.notebook. The Stomach. (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
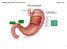 (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
(cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
ANATOMY 261. Introduction to Dynamic Histology
 ANATOMY 261 Introduction to Dynamic Histology INSTRUCTORS: HEAD T.A.s LECTURES: LABORATORY: Dr. Craig Mandato Dr. C. R. Morales Paul Simon (paul.simon@mail.mcgill.ca) Dana Pearl (dana.pearl@mail.mcgill.ca)
ANATOMY 261 Introduction to Dynamic Histology INSTRUCTORS: HEAD T.A.s LECTURES: LABORATORY: Dr. Craig Mandato Dr. C. R. Morales Paul Simon (paul.simon@mail.mcgill.ca) Dana Pearl (dana.pearl@mail.mcgill.ca)
A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove.
 By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
By Dr. Raja Ali A deep groove encircles the body of the circumvallate papilla. Serous (von Ebner s) glands (serous) drain into the base of this groove. The flow of fluid from these glands serves to wash
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Derived copy of Types of Tissues *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m56110 1 Derived copy of Types of Tissues * Stephanie Fretham Based on Types of Tissues by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m56110 1 Derived copy of Types of Tissues * Stephanie Fretham Based on Types of Tissues by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU HISTOLOGY: w Study of the structure and function of tissues and organs at the microscopic levels. w Tissues
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU HISTOLOGY: w Study of the structure and function of tissues and organs at the microscopic levels. w Tissues
Sheet #9. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheet #9 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Elastic fibers The main function of elastic fibers is to provide elasticity. In other words these fibers are able to restore the original
Sheet #9 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Elastic fibers The main function of elastic fibers is to provide elasticity. In other words these fibers are able to restore the original
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Tissue: is a group of cells that serve the same function, they are surrounded by extra cellular matrix. The 4 basic types of tissue: 1. epithelial
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Tissue: is a group of cells that serve the same function, they are surrounded by extra cellular matrix. The 4 basic types of tissue: 1. epithelial
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa!
 A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
A Rough look at the tonsils and adenoids, for Bonny Peppa! tonsils (two oval masses in the back of the throat) Lymphoid organs include: adenoids (two glands located at the back of the nasal passage) appendix
The PHARYNX. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D
 The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
The PHARYNX Dr. Nabil Khouri MD Ph.D PHARYNX Fibromuscular tube lined with mucous membrane extends from base of skull to lower border of cricoid cartilage (C-6). 12-14 cm long At the lower border of cricoid
GI Histology Lab 1. Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji
 GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II. Ventral Lobe Epithelium
 Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
Published Online: 1 June, 1960 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.7.3.511 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on September 28, 2018 The Fine Structure of the Epithelial Cells of the Mouse Prostate* II.
