Human Anatomy and Physiology: 10th Edition Test Bank
|
|
|
- Norman Logan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Human Anatomy and Physiology: 10th Edition Test Bank Human Anatomy and Physiology: 10th Edition Test Bank Sample Chapter 7 The Skeleton 7.1 Matching Questions Figure 7.1 Using Figure 7.1, match the following: 1. A) A 2. B) D 3. C) B 4. D) C 5. E) E 1) Articulates with hip bones of the pelvis.
2 2) Attach to ribs. Learning Outcome: 7.4 Global LO: G7 3) Bares most of the weight. 4) Transvers foramina allow the passage of vertebral arteries. 5) No canals or foramen present.
3 6) Includes the atlas and the axis. 7) Contains a pivot joint that allows you to rotate your head no. Answers: 1) B 2) C 3) D 4) A 5) E6) A 7) A Figure 7.2 Using Figure 7.2, match the following:
4 1. A) B 2. B) E 3. C) D 4. D) A 5. E) C 8) Anchor the pterygoid muscles. 9) Passageway for optic nerve. 10) Encloses pituitary gland.
5 11) Forms parts of the middle cranial fossa, dorsal walls of the orbits, and external walls of the skull. 12) Allow cranial nerves that control eye movements to enter the orbit. Answers: 8) B 9) D 10) E 11) A 12) C Match the following: 1. A) Maxillae 2. B) Temporal bones 3. C) Sphenoid 4. D) Lacrimal bones 13) These very small bones are at the medial wall of each orbit.
6 14) Failure of these anterior bones to fuse causes a condition known as cleft palate. 15) This bone houses the apparatus of the internal and middle ear. 16) This bone is wing-shaped and extends behind the eyes and forms part of the floor of the cranial vault.
7 17) The bones that contain teeth. 18) This bone has a passageway into the nasal cavity. 19) The sella turcica is a portion of this bone.
8 Answers: 13) D 14) D 15) B 16) C 17) A18) D 19) C Match the following: A)Humerus B)Radius 1. C) Phalanges 20) The fingers have three of these bones and the thumb has only two. Section: ) This bone articulates with the glenoid fossa. Section: ) Forearm bone that articulates with most of the carpals. Section: 7.5
9 1 Answers: 20) C 21) A 22) B Match the following: A)Lumbar vertebrae B)Axis 1. C) Atlas 2. D) Coccyx 3. E) Thoracic vertebrae 23) These bones have the thickest body (centrum) with short blunt spinous processes. 24) The fused rudimentary tailbone.
10 25) The bone that articulates with the occipital condyles. 26) These bones have articular facets for the ribs. 27) Allows the head to nod yes.
11 28) Allows the head to shake no. Answers: 23) A 24) D 25) C 26) E 27) C28) B Match the following: 1. A) Connects temporal and parietal bones. 2. B) Connects right and left parietal bones. 3. C) Connects occipital and parietal bones. 4. D) Connects parietal and frontal bones. 5. E) Connects occipital and temporal bones. 29) Lambdoid suture. 30) Sagittal suture.
12 31)Squamosal suture. 32) Coronal suture. Learning Outcome: 7.1 Global LO: G7 33) Occipitomastoid suture.
13 Answers: 29) C 30) B 31) A 32) D 33) E 7.2 True/False Questions 1) The fibula is the major weight-bearing bone of the leg. Answer: FALSE Section: ) All of the bones of the skull, except the mandible, are united by sutures and are therefore immovable. Answer: TRUE, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 3 Application
14 3) The frontal bone articulates with the parietal bone by means of the sagittal suture. Answer: FALSE 4) The mastoid sinuses are located at a position in the skull where they are usually free from infections. Answer: FALSE 5) The vertebral column is held in place primarily by the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments. Answer: TRUE
15 6) Most of the body s weight is carried by the talus and calcaneus. Answer: TRUE Section: ) The most common site of fracture in the humerus is the anatomical neck. Answer: FALSE Section: ) The shallow socket of the shoulder joint restricts the movement of the humerus but does increase the stability of the joint. Answer: FALSE Section: 7.4 Learning Outcome: 7.9
16 9) Costal cartilages join most ribs to the sternum. Answer: TRUE Section: 7.3 Learning Outcome: ) The tubercle of a rib articulates with the transverse process of a vertebra. Answer: TRUE Section: 7.3 Learning Outcome: ) In women of childbearing age, the dimensions of the true pelvis are of utmost importance. Answer: TRUE Section: 7.6 3
17 12) The term vertebrochondralribs refers to the false ribs, that attach to each other before they attach to the sternum. Answer: TRUE Section: 7.3 Learning Outcome: ) In the anatomical position, the lateral forearm bone is the radius. Answer: TRUE Section: ) The vomer along with the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone forms the bony part of the nasal septum. Answer: TRUE
18 15) The temporal bone connects to the zygomatic bone via the temporal process of the temporal bone. Answer: FALSE Learning Outcome: ) The lacrimal bone contains a grove that forms part of lacrimal fossa. Along with the soft tissue of the lacrimal sac, these structures drain tears from the eye into the nasal passage. Answer: TRUE 17) The largest and strongest bone of the face is the maxilla.
19 Answer: FALSE Learning Outcome: ) There are seven cervical, twelve thoracic, and five lumbar vertebrae. Answer: TRUE Learning Outcome: ) Lordosis affects the thoracic vertebrae. Answer: FALSE 20) All vertebrae possess a body, a spine, and transverse foramina. Answer: FALSE
20 Learning Outcome: ) The dens articulates with the occipital bone. Answer: FALSE Learning Outcome: ) The pituitary gland is housed in a saddle-like depression in the temporal bone called the sella turcica. Answer: FALSE
21 23) The ischium articulates with both the ilium and the pubis. Answer: TRUE Section: Multiple Choice Questions 1) The bones in the skull have many different names but what are the boundaries of each bone? Where do they start and stop? 1. A) Bones of the skull are separated by immobile joints called sutures. 2. B) Bones of the skull are continuous but named for their specific markings. 3. C) The boundaries are indistinct and are simply vague generalized regions. 4. D) Boundaries for skull bones are seen only in the infant skull. Answer: A, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 2) Which of the following can be considered a function of the paranasal sinuses? 1. A) The paranasal sinuses are passageways for nerves to pass through.
22 2. B) Sinuses have rough patches that aid in muscle attachment. 3. C) Sinuses are often referred to as vestigial, anatomical features with no know function. 4. D) Sinuses take away a minimal amount of strength from bones while reducing the weight of bones. Answer: D Learning Outcome: 7.3, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 3) Which of the bones of the skull would you most associate with hearing and balance? 1. A) the occipital bone 2. B) the zygomatic bone 3. C) the temporal bone 4. D) the parietal bone Answer: C Bloom s Level: 3 Application 4) Which of the following would be most associated with housing the special sense organs? 1. A) the cranial bones 2. B) hyoid bone
23 3. C) the facial bones 4. D) the bones of the inner ear Answer: C Learning Outcome: 7.2 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 5) Which of the following would be most associated with process of warming and humidifying inhaled air? 1. A) the paranasal sinuses 2. B) the bones comprising the orbits 3. C) the cranial bones 4. D) hyoid bone Answer: A Learning Outcome: 7.3 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 6) Which is the best description for the function of the cranial bones? 1. A) allowing introduction of food into the digestive system 2. B) house the special sense organs 3. C) protection of the brain 4. D) providing passageways for respiratory gases to move into and out of the body
24 Answer: C Learning Outcome: 7.2 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 7) The sphenoid bone is sometimes referred to as a key stone of the skull. This is due to the fact that. 1. A) the sphenoid is wedged in the superior most portion of the skull and supports all of the other bones below (excluding the mandible) 2. B) the intricate shape of the sphenoid makes it critical to the district characteristics of the individual human face 3. C) the sphenoid is in the center of the skull and it articulates (joins) with all of the other bones of the skull (excluding the mandible) 4. D) the sphenoid bone is solid like a stone and provides the strength necessary to support the skull Answer: C, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 8) The sella turcica is part of the bone and houses the gland. 1. A) ethmoid; thymus 2. B) sphenoid; pituitary 3. C) ethmoid; pituitary 4. D) sphenoid; thymuss
25 Answer: B 9) The hypothalamus is a region of the brain controlling many aspects of the endocrine system. It works closely with the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus is directly superior to the pituitary and is therefore. 1. A) the only region of the brain that is outside of the skull 2. B) superior to the crista galli 3. C) inferior to the cribriform plate 4. D) superior to the sella turcica Answer: D Learning Outcome: 7.2, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 10) During concussion (a type of traumatic brain injury) the brain will move within the cranial cavity. Damage is caused to the brain as it crashes into parts of the bony cavity walls. Ironically one of the bone markings that can cause serious damage to the brain is the. This is ironic because one of the functions of this bone marking is to. 1. A) perpendicular plate; separate the left and right halves of the nasal cavity 2. B) pterygoid processes; anchor important chewing muscles 3. C) styloid process; attach to and support the hyoid bone
26 4. D) crista galli; attach to the dura matter holding the brain in place Answer: D Learning Outcome: 7.2, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 6 Evaluation 11) Curvatures of the spine serve the body by. 1. A) applying greater pressure to the intervertebral disks preventing them from slipping 2. B) providing space for soft organs in the various body cavities 3. C) giving additional springiness and flexibility to the spine which absorbs shock 4. D) limiting the flexibility of the spine and preventing hyperextension Answer: C, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 12) When looking at the range of motion of the various sections of the vertebral column the has the most flexibility 1. A) lumbar spine 2. B) thoracic spine 3. C) cervical spine 4. D) sacral spine
27 Answer: C Learning Outcome: 7.6, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 13) The range of motion as well as the direction of motion for the various regions of the spine differs. For example the lumbar spine is capable of flexion and extension but little rotational movement. While the thoracic spine rotates with little flexion or extension. This is due to variation in. 1. A) the orientation of the superior and inferior articular facets 2. B) the composition of the intervertebral disks 3. C) the arrangement of muscular attachment to the spinous processes 4. D) the thickness of the intervertebral disc Answer: A Learning Outcome: 7.6, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 14) The anatomy of the thoracic cage provides ridged support and protection but at the same time is also flexible and mobile. Of the list below, which feature does not aid in the flexibility and movement of the thoracic cage? 1. A) the jugular notch 2. B) the costal spaces occupied by costal muscle 3. C) the sternal angle 4. D) the costal cartilages
28 Answer: A Section: 7.3 Learning Outcome: 7.7, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 15) The glenohumeral joint that articulates the humerus to the pectoral girdle is a highly mobile joint. This mobility comes at a cost because. 1. A) these type of joints are harder to control and coordinate 2. B) muscles that span this mobile joint will only provide a reduced amount of power 3. C) the joint is relatively unstable and can easily dislocate 4. D) the blood vessels that lead to the arm and hand can easily be cut off by the free range of motion Answer: C Section: 7.4 Learning Outcome: 7.9, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 16) Of the list below select the one that gives the least explanation for the relatively high mobility of the arms. 1. A) The relatively open glenoid cavity of the glenohumeral joint. 2. B) The scapula does not articulate to the axial skeleton directly. 3. C) The subscapular notch is a passage way for nerves. 4. D) The clavicle articulates to the axial skeleton at only the sternal end.
29 Answer: C Section: 7.4 Learning Outcome: 7.9, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 17) The proximal end of the ulna illustrates the relationship of form and function. The rounded trochlear notch articulates with the hourglass shape of the trochlea. This forms a joint that allows for. 1. A) the curling of the fingers 2. B) the hyper extension of the forearm 3. C) the rotational motion of the forearm 4. D) the hinge like motion of the forearm Answer: D Section: 7.5 1, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 18) The proximal end of the radius illustrates the relationship of form and function. The cup-like surface of the radial head articulates with the rounded shape of the capitulum. This forms a joint that allows for. 1. A) the rotational motion of the forearm 2. B) the curling of the fingers 3. C) the hinge like motion of the forearm 4. D) the hyper extension of the forearm
30 Answer: A Section: 7.5 1, HAPS2, HAPS7 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 19) The axial skeleton includes. 1. A) the skull, the scapula and the vertebral column 2. B) the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage 3. C) arms, legs, hands, and feet 4. D) the skull, vertebral column, and pelvis Answer: B 20) Which vertebra does not have a body? 1. A) atlas 2. B) last lumbar 3. C) last cervical 4. D) axis Answer: A
31 Learning Outcome: ) The suture that connects the two parietal bones together is the. 1. A) coronal 2. B) squamous 3. C) lambdoid 4. D) sagittal Answer: D 22) The hyoid bone is unique because it. 1. A) is composed of three bones joined together 2. B) is the only bone of the body that does not articulate with any other bone 3. C) is the only irregular bone found in the neck 4. D) is the only bone formed by the fusion of right and left halves Answer: B
32 23) Along with support, the anterior longitudinal ligament of the vertebral column also acts to. 1. A) protect the spinal cord 2. B) hold the discs in place 3. C) prevent hyperextension of the spine 4. D) hold the spine erect Answer: C 24) What are the major functions of the intervertebral discs? 1. A) to hold together the vertebra and support the body 2. B) to remove curvatures of the spine and provide springiness to the spinal column 3. C) to absorb shock and provide flexibility to the spine 4. D) to prevent hyperextension and allow rotation of the spine Answer: C
33 25) Paranasal sinuses are found in which of these facial bones? 1. A) zygomatic bones 2. B) vomer 3. C) nasal conchae 4. D) maxillae Answer: D Learning Outcome: ) Which of the following is an abnormal lateral curvature of the vertebral column often seen in the thoracic region? 1. A) kyphosis 2. B) scoliosis 3. C) swayback 4. D) lordosis Answer: B
34 27) Which part of the vertebral column receives the most stress by bearing most of the weight of the body? 1. A) the cervical region 2. B) the lumbar region 3. C) the sacrum 4. D) the sacral promontory Answer: B Learning Outcome: ) Which bone acts as a moveable base for the tongue? 1. A) zygomatic bone 2. B) palatine 3. C) hyoid bone 4. D) mandible Answer: C 29) Thoracic vertebrae differ from the other vertebrae in that they have. 1. A) no transverse processes
35 2. B) transverse foramina 3. C) costal facets 4. D) no intervertebral discs Answer: C Learning Outcome: ) What is the major function of the axial skeleton? 1. A) provide central support for the body and protect internal organs 2. B) provide a space for the major digestive organs 3. C) provide an attachment point for muscles that allow movement 4. D) give the body resilience Answer: A 31) The antebrachium is composed of which of the following two bones? 1. A) the radius and the ulna 2. B) the scapula and the clavicle 3. C) the humerus and the radius 4. D) the humerus and the clavicle
36 Answer: A Section: ) The true wrist or carpus consists of. 1. A) the phalanges 2. B) the metacarpals 3. C) a group of eight short bones united by ligaments 4. D) the styloid processes of the radius and ulna Answer: C Section: ) Which bone is in direct contact with the first metatarsal? 1. A) lateral cuneiform 2. B) calcaneus 3. C) cuboid 4. D) medial cuneiform Answer: D Section: 7.7
37 4 34) Which bone forms the prominence of the cheek? 1. A) sphenoid bone 2. B) temporal bone 3. C) palatine bone 4. D) zygomatic bone Answer: D Learning Outcome: ) The superior orbital fissure is formed in the sphenoid bone, whereas the inferior orbital fissure is formed between the sphenoid and. 1. A) maxilla 2. B) lacrimal 3. C) palatine 4. D) ethmoid Answer: A
38 36) Which of the following is the abnormal curve often seen in pregnant women as they attempt to preserve their center of gravity toward the end of the pregnancy? 1. A) scoliosis 2. B) kyphosis 3. C) hunchback 4. D) lordosis Answer: D 37) How are thoracic vertebrae 11 and 12 different from the other vertebrae? 12. A) There are two foramina on vertebrae 11 and B) The transverse processes do not have facets that articulate with the tubercles of the ribs. 14. C) The orientation of the articular processes is different from all the other thoracic vertebrae. 15. D) The spinous processes are directed parallel with the centrum. Answer: B Learning Outcome: 7.6
39 38) The superior nasal concha is a part of which bone? 1. A) ethmoid 2. B) maxilla 3. C) vomer 4. D) sphenoid Answer: A Learning Outcome: ) The pelvic girdle does not include the. 1. A) femur 2. B) ilium 3. C) pubis 4. D) ischium Answer: A
40 40) Which of the following bones is not weight bearing? 1. A) femur 2. B) fibula 3. C) tibia 4. D) talus Answer: B Section: ) Which portion of the fibula articulates with the talus? 1. A) calcaneus 2. B) medial malleolus 3. C) head 4. D) lateral malleolus Answer: D Section: ) Which part of the ethmoid bone forms the superior part of the nasal septum? 1. A) perpendicular plate 2. B) orbital plate
41 3. C) cribriform plate 4. D) crista galli Answer: A 43) Which of the following is not a movement that can occur between vertebrae? 1. A) supination 2. B) rotation 3. C) flexion and extension 4. D) lateral flexion Answer: A Learning Outcome: Short Answer Questions 1) The heel bone is called the. Answer: calcaneus
42 Section: ) The lateral condyle of the femur articulates with the lateral condyle of the. Answer: tibia Section: ) The medial condyle of the femur articulates with the medial condyle of the. Answer: tibia Section: ) The largest foramen in the body is the foramen. Answer: obturator
43 Section: ) The smallest short bone in the hand is the. Answer: pisiform Section: ) The styloid process of the points to the thumb. Answer: radius Section: ) Only the vertebrae have transverse foramina. Answer: cervical
44 8) The is the bone confined to the septum of the nose. Answer: vomer 9) Your cheekbone is mostly formed from the bone. Answer: zygomatic Learning Outcome: ) What structure is the missing body of the second cervical vertebrae? Answer: dens
45 Learning Outcome: ) What is the function of the lumbar curvature? Answer: It positions the weight of the trunk over the body s center of gravity, thus providing optimal balance when standing. Learning Outcome: ) What is the purpose of the vertebral curvatures? Answer: Their purpose is to increase the resilience and flexibility of the spine, allowing it to function like a spring rather than a rigid rod., HAPS2 13) Why is the area just distal to the tubercles of the humerus called the surgical neck?
46 Answer: This area is called the surgical neck because it is the most frequently fractured part of the humerus. Section: 7.5 1, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 3 Application 14) Describe the composition of the intervertebral discs. Answer: Intervertebral discs are composed of an inner semifluid nucleus pulposus, which gives the discs elasticity and compressibility, and a covering of fibrocartilage, the annulus fibrosus, which limits expansion and holds successive vertebrae together. Learning Outcome: ) Describe the differences between the bones of the lower and upper limb and briefly state why these differences exist. Answer: The lower limbs carry the weight of the body and are subjected to exceptional forces. These bones are thicker and stronger. The upper limb bones are adapted for flexibility and mobility and are therefore smaller and lighter. Section: 7.7 4, HAPS2
47 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 16) How are the pectoral and pelvic girdles structurally different? How is this difference reflected in their functions? Answer: The pectoral girdle moves freely across the thorax and allows the upper limb a high degree of mobility, while the pelvic girdle is secured to the axial skeleton to provide strength and support. This is why the glenoid cavity of the scapula is relatively shallow and the acetabulum of the pelvis is a deep socket. Section: 7.7 4, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 17) How do the first two cervical vertebrae differ from other cervical vertebrae? What are their functions? Answer: The atlas or C1 vertebra has no body. It articulates with the skull with large curved articular surfaces to allow the skull to rock in a yes motion. The axis or C2 vertebra has a projection called the dens that allows the axis to pivot, giving the head the no motion. The vertebral foramen of the atlas is enlarged so that when the head is pivoted in the no motion, the spinal cord can move. Learning Outcome: 7.5, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 18) Identify the arches of the foot and describe how they are maintained.
48 Answer: There are three arches: the medial and lateral longitudinal arches, and the transverse arch. Together they form a half-cone that distributes the weight of the body. They are maintained by the shape of the foot bones, strong ligaments, and by the pull of some tendons. Section: 7.7 4, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 19) Identify the four major cranial sutures in any order and the bones they connect. Answer: 1. Coronal parietal and frontal 2. Sagittal between the parietal bones 3. Squamous parietal and temporal 4. Lambdoidal parietal and occipital 20) If the hyoid bone is not attached to another bone why is it so important? Answer: The hyoid acts as an attachment point for muscles in the neck region to connect the muscles in the lower jaw region. It allows for the muscles to make a right angle at the junction of the lower jaw and throat. The hyoid serves as a movable base for the tongue and its horns are attachment points for neck muscles that raise and lower the larynx during speech and swallowing.
49 , HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 21) What is the purpose of the articular processes of the vertebrae? Answer: These processes (superior and inferior) allow the vertebral column to flex forward some, but lock the vertebrae if the column is flexed back and limit rotation to avoid injury to the spinal cord and its nerve roots. In a four-legged animal, such as a horse, these processes allow the back to remain in place while you ride it. Learning Outcome: Clinical Questions 1) A skeleton was found in a wooded area. It was brought to a forensic medicine laboratory for identification. The first thing the coroner did was determine the age, sex, and possible size of the person. What was examined in order to get this information? Answer: By examining the shape of the pelvic inlet, the depth of the iliac fossa, the characteristics of the ilium, and the angle inferior to the pubic symphysis, one could determine the sex. Also significant for determining the sex of the skeleton are the position of the acetabulum, the shape of the obturator foramen, and the general design of the ischium. To determine the age of the individual, bone density, the status of growth plates, and markings are important. The markings where muscles were attached will reveal information about the mass and the general shape of the person.
50 Section: 7.6 3, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 2) Jason is a 14-year-old who recently had his nose pierced through the nasal septum. He tells his mother that the area is very tender and warm to the touch. The area is also red. The mother calls the pediatrician s office and the nurse recommends that the mother bring Jason in for evaluation. The nurse explains to the mother that a local infection can spread and cause serious harm. Where do you think the infection could spread and why? Answer: Infection of nasal piercings can spread to the brain and cause serious complications. Infections in the brain may occur because of the direct extension from ear, tooth, mastoid, or sinus infections., HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 3) You are a school nurse in a middle school. You are responsible for screening the children for scoliosis. What is involved in this screening? Answer: Scoliosis literally means twisted disease and is an abnormal rotational curvature causing lateral deviation that occurs most often in the thoracic region. It is quite common during late childhood. The nurse would need to observe the child standing erect, disrobed from the waist up. An older girl may leave her bra on. The child is observed from behind and the nurse would note any asymmetry of the shoulders and hips. With the child bending forward so that the back is parallel to the floor, the nurse may observe from behind, noting tilting of the rib cage.
51 , HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 4) When administering chest compression to someone whose heart has stopped beating, the heel of the hand should be placed on the sternum on a line drawn between the nipples. Why would it be a problem if the hand was placed at a lower part of the sternum? Answer: The compressions could break the xiphoid process of the sternum and drive it into the heart, diaphragm, or liver resulting in possibly deadly complications. Section: 7.3, HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis 5) Sam is an accountant who is especially busy during tax season. By the end of each day he complains of shoulder stiffness and tightness as well as some upper back pain. What might be Sam s problem and how could he prevent the discomfort? Answer: Sam is probably sitting hunched over his desk rather than sitting up properly. This can result in kyphosis and resulting upper back pain and stiffness. Sam needs to practice good posture and/or invest in an ergonomic chair to help him maintain the proper thoracic vertebral curve., HAPS2 Bloom s Level: 4 Analysis
52
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 7.1 Using Figure 7.1, match the following: 1) Articulates with hip bones of the pelvis.
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 7.1 Using Figure 7.1, match the following: 1) Articulates with hip bones of the pelvis.
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7
 TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Chapter 8A. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. Types of Bones. Types of Bones
 Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
Axial skeleton bones and markings
 Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Nervous & Skeletal Systems. Virtual Science University
 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Bio 5/6 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide
 Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton
 The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE:
 SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE: SKELETON: 1. Performs a mechanical function in forming the skeletal support of the body and in forming a leverage system whereby work and movement are possible. 2. Serves as
SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE: SKELETON: 1. Performs a mechanical function in forming the skeletal support of the body and in forming a leverage system whereby work and movement are possible. 2. Serves as
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial Skeleton
 A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
the Skeletal System provided by Academic Web Services Grand Canyon University
 Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
The Axial Skeleton Hyoid Bone. Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14 1 Axial Skeleton Hyoid bone Bones of the orbit Paranasal sinuses Infantile skull Vertebral column
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14 1 Axial Skeleton Hyoid bone Bones of the orbit Paranasal sinuses Infantile skull Vertebral column
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System
 BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
The Skeleton. Bone Markings. The Axial Skeleton
 The Skeleton Consists of bones, cartilage, joints, and ligaments Composed of 206 named bones grouped into two divisions Axial skeleton (80 bones) Appendicular skeleton (126 bones) Bone Markings Bone markings
The Skeleton Consists of bones, cartilage, joints, and ligaments Composed of 206 named bones grouped into two divisions Axial skeleton (80 bones) Appendicular skeleton (126 bones) Bone Markings Bone markings
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5. Subject: The Skeletal System
 Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
bio4165 lab quiz 1 Posterior View Anterior View Lateral View Anterior View bio fall.quarter lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6
 B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
Bones of the wrist and ankle Bones that form within tendons (e.g., patella)
 Skeletal System Review Surface Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Function of Bones Support form the framework that supports the body and cradles soft organs Protection provide a protective case for the brain, spinal
Skeletal System Review Surface Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Function of Bones Support form the framework that supports the body and cradles soft organs Protection provide a protective case for the brain, spinal
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY BARBARA HERLIHY Chapter 8: Skeletal System
 Link download Full : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-thehuman-body-in-health-and-illness-5th-edition-by-barbara-herlihy/ TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY
Link download Full : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-thehuman-body-in-health-and-illness-5th-edition-by-barbara-herlihy/ TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
SD School Anatomy Program 1: Bones QuikNotes. Student Notes
 QuikNotes The transverse plane runs from right to left and divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections. Student Notes The frontal plane lies vertically along the body from head
QuikNotes The transverse plane runs from right to left and divides the body into superior (upper) and inferior (lower) sections. Student Notes The frontal plane lies vertically along the body from head
Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System
 107 Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Adult Skull Bony orbit (FLEZMS) Frontal bone supraorbital foramen frontal sinus Lacrimal bone Ethmoid bone perpendicular plate of ethmoid middle nasal conchae cribriform
107 Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Adult Skull Bony orbit (FLEZMS) Frontal bone supraorbital foramen frontal sinus Lacrimal bone Ethmoid bone perpendicular plate of ethmoid middle nasal conchae cribriform
Skeletal System - Prelab 1
 Skeletal System - Prelab 1 1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that
Skeletal System - Prelab 1 1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES
 Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES Tuberosity Rounded area on bone often roughened for muscle attachment. Tubercle Rounded projection on bone. This is called a tuberosity on the femur. Crest Ridgeline
Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES Tuberosity Rounded area on bone often roughened for muscle attachment. Tubercle Rounded projection on bone. This is called a tuberosity on the femur. Crest Ridgeline
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
The Skeletal System. Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments
 The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Skeletal system overview. Classification of Bones
 Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Labs 9 and 10. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes 1/05/13. Skeletal system overview. Bone are identified by:
 Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System)
 Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Chapter 7 Skeletal System. Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions.
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
 CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton
 Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
Sports Medicine Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX
 Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan 2008 Anatomy of the Upper Body In this section of the
Sports Medicine 25 1.1 Part I : ANATOMY OF THE SPINE, ABDOMEN AND SHOULDER COMPLEX c.w.p. Wagner High School, Sports Medicine, A. Morgan, T. Morgan 2008 Anatomy of the Upper Body In this section of the
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Skeletal System A&P Week 11
 Skeletal System A&P Week 11 Bones 206 bones in the body Smallest are in the middle ear cavity Malleus, incus, stapes Functions of Bone Framework and support Protection Contains/protects red bone marrow
Skeletal System A&P Week 11 Bones 206 bones in the body Smallest are in the middle ear cavity Malleus, incus, stapes Functions of Bone Framework and support Protection Contains/protects red bone marrow
Average # of bones = major subdivisions: Axial skeleton Appendicular Skeleton (appendages) 1. Number and major subdivisions of bones
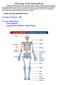 Osteology of the Human Body Without the skeletal system, you would be unable to engage in activities such as walking or grasping objects in your hand. Since the skeleton forms the internal framework of
Osteology of the Human Body Without the skeletal system, you would be unable to engage in activities such as walking or grasping objects in your hand. Since the skeleton forms the internal framework of
Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System
 153 Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Unit 6: Skeletal System: Bone tissue, Bones and Joints (p. 105-152) Ex. 6-1: Histology of Osseous Tissue, p. 113 Model: Osteon Tiss Lamella Osteocyte Lacunae Canaliculi
153 Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Unit 6: Skeletal System: Bone tissue, Bones and Joints (p. 105-152) Ex. 6-1: Histology of Osseous Tissue, p. 113 Model: Osteon Tiss Lamella Osteocyte Lacunae Canaliculi
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round) Bones 2 Parts of a Long Bone epiphysis distal proximal
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round) Bones 2 Parts of a Long Bone epiphysis distal proximal
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Chapter 8. The Appendicular Skeleton. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5: The Skeletal System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. 2. List at least
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5: The Skeletal System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. 2. List at least
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
The Axial Skeleton. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An
C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
