Traction. Process of drawing or pulling apart. May involve distraction and gliding. Pulling 2 articulating surfaces away from each other
|
|
|
- Noah Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Traction Process of drawing or pulling apart May involve distraction and gliding Pulling 2 articulating surfaces away from each other
2 Axis Traction in line with the long axis of a part Types of Traction
3 Head traction Traction applied to the head for injuries to the cervical vertebrae, intervertebral discs, nerves or muscles Types of Traction
4 Types of Traction Weight Traction application through the use of: Weights Pulleys Ropes
5 Immobilization Fractures that cannot be immobilized in a cast utilize traction for immobilization
6 Immobilization The muscles of the limb act as an internal splint to protect the fracture And provide mechanoreceptive input for pain relief
7 Skin traction Applied with something that encircles the extremity Used when not more than 5-6 pounds of pull is required Used for longitudinal pull on the LE Used for femoral shaft fractures in pediatrics Immobilization
8 Skeletal traction Drilling a small hole transversely into the bone and inserting a small diameter wire (1/8 inch) through the bone Makes it possible for increased tolerances of weight for traction Femoral shaft on an adult would require 20-30# of pull Immobilization
9 Immobilization Skeletal Traction Can be applied to distal areas Comfortable for patients
10 Immobilization Skeletal Traction For femoral fractures it is most commonly applied through the proximal tibia just distal to the tibial tubercle Procedure increases the possibility for infection Aseptic techniques are important
11 Crutchfield Tongs Skeletal Traction for fractures of dislocations of the cervical spine Applied through the outer layer of the skull Allows for 30-40# in against gravity position (with a halo attachment)
12 Spinal Traction Effects Separation of vertebral bodies Distraction/gliding of facet joints Increased tension of spinal ligamentous structures
13 Spinal Traction Effects Increasing the intervertebral foramenal spacing Straightening out the spinal curves Stretching of the spinal musculature
14 Types of Spinal Traction Continuous Applied for up to several hours at a time Long duration requires that only small amounts of weight be used Traction & LBP
15 Types of Spinal Traction Continuous Believed ineffective in actually separating the spinal structures since the patient is not receiving pull sufficient to separate vertebrae
16 Sustained or Static Steady amounts of traction applied for 5-30 minutes Heavy poundage (shorter duration) Most effective with a split table (H friction) Traction tables, mechanical devices Types of Spinal Traction
17 Intermittent Traction Traction force alternately applied and withdrawn every few seconds Pull time is at least 7 seconds, rest ½ the pull time Stretching only occurs after 7-30 seconds of pull Types of Spinal Traction
18 Manual Traction Applied through the hands of the clinician May be more difficult for the patient to relax Difficult to reproduce the force with precision Difficult to maintain the necessary force to produce a separation Types of Spinal Traction
19 Types of Spinal Traction Positional Traction Placing the patient in various positions using pillows, blocks or sandbags to effect the longitudinal pull on the spinal structures
20 Types of Spinal Traction Positional Traction Usually applied in side lying/lateral bending To affect structures on one side
21 Types of Spinal Traction Auto Traction Performed with a specific piece of equipment A traction table in 2 segments that Can be individually angled and rotated The patient s body weight and gravity make up the traction force when the patient is suspended from the trunk in a vertical position.
22 Gravity Lumbar Traction Boots are applied to the ankles, The patient is literally inverted on a table or bar The patient s body weight acts as traction Adding weights to the patients hands increases the traction force Upper body, arms & Head = 50% of body weight Types of Spinal Traction
23 Disc herniation with protrusion Disc protrusion can be reduced Spinal nerve root compression can be reduced Flattening of the protrusion Material drained from the epidural space into the disc space via a suction force Indications for Spinal Traction
24 Indications for Spinal Traction Joint dysfunction Traction applied to a series of spinal segments Each segment in the series receives an equal amount of traction Passive motion for the joints
25 Degenerative Disc Disease Temporary separation of vertebrae If there is a sudden onset of pain, Traction will provide relief of symptoms Indications for Spinal Traction
26 Structural disease secondary to tumor or infection Patients with vascular compromise Conditions where joint movement is contraindicated Contraindications for Traction
27 Contraindications for Traction Acute sprains, strains and inflammation Spinal instability Pregnancy Osteoporosis Hiatal hernia Claustrophobia
28 Patients MUST be able to relax! Split tables virtually eliminate friction Techniques for Lumbar Traction
29 Techniques for Lumbar Traction At least ¼ to ½ of the patient s body weight will be necessary to move the body horizontally
30 Poundage minimums 22-33# for muscle relaxation # to reduce disc pressure by 25% Visible separation of bodies 120# for 15 minutes Cyriax Damage to vertebral structures at 400# Cadaver studies Techniques for Lumbar Traction
31 Friction The resistance to movement Attractive force between and object and the surface that it is resting upon Techniques for Lumbar Traction
32 Coefficient of Friction Human body on a mattress = 0.5 A force of ½ of the patient s body weight will be necessary to move the patient s body horizontally Hmmm does this look like it would be ½ of her body weight? Techniques for Lumbar Traction
33 Disc Herniation with protrusion Sustained traction Longer hold times 60 seconds hold, 20 seconds rest Techniques for Lumbar Traction
34 Techniques for Lumbar Traction Treatment times 10 minutes intermittent 8 minutes sustained To maintain the effect of suction on the disc pressure
35 Postural Traction Most often for unilateral separation Pt. is sidelying over a rolled pillow or a blanket that is 6-8 inches in diameter placed at the level where the separation is to occur Learn more about traction and alternative treatment techniques.
36 Cervical Traction Techniques Positioning Sitting versus supine
37 Cervical Traction Techniques Head Halters Pull needs to be more from the occiput than the mandible Potential problems for patients diagnosed with TMJ disorders
38 Cervical Traction Techniques 9-10# for simple relaxation of cervical musculature 25-40# stepped progression necessary to produce measurable changes in the posterior CS
39 Pull time = twice the relax time 7-30 seconds pull time 120# will RUPTURE a disc Cervical Traction Techniques
40 Cervical Traction Techniques Relaxation decreases muscle guarding Shorter treatment times are tolerated better than longer treatment times
41 Manual Cervical Traction Applied through the hands of an experienced clinician Difficult to reproduce the force Difficult for the patient to relax
42 Spinal Traction Indications Disc herniation with protrusion Nerve root compression
43 Contraindications Structural disease Vascular compromise When movement is contraindicated Acute sprains & strains Inflammation Pregnancy Claustrophobia Spinal Traction
44 Halo Traction for Cervical Fracture Stabilization
45 Cervical Traction for Fracture Stabilization without the Halo attachment
46 Stabilization through external support
47 Stabilization through External Support
48 Traction & Distraction/Glide
Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Head, Neck, and Cervical Spine Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS Pre- Chapter Case Study
 Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS (20 minutes CEU Time) Subjective A 43-year-old male, reported a sudden onset of left-sided neck and upper extremity
Regional Review of Musculoskeletal System: Presented by Michael L. Fink, PT, DSc, SCS, OCS (20 minutes CEU Time) Subjective A 43-year-old male, reported a sudden onset of left-sided neck and upper extremity
It consist of two components: the outer, laminar fibrous container (or annulus), and the inner, semifluid mass (the nucleus pulposus).
 Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
Lumbar Spine The lumbar vertebrae are the last five vertebrae of the vertebral column. They are particularly large and heavy when compared with the vertebrae of the cervical or thoracicc spine. Their bodies
2. The vertebral arch is composed of pedicles (projecting from the body) and laminae (uniting arch posteriorly).
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
VERTEBRAL COLUMN 2018zillmusom I. VERTEBRAL COLUMN - functions to support weight of body and protect spinal cord while permitting movements of trunk and providing for muscle attachments. A. Typical vertebra
10/8/2015. FACTORS IN BACK PAIN introduction 27% Framing the Discussion from a Clinical and Anatomical Perspective
 FACTORS IN BACK PAIN Framing the Discussion from a Clinical and Anatomical Perspective A B M P B a ck Pa i n S u m m i t With Clint Chandler FACTORS IN BACK PAIN introduction Back pain affects 8 out of
FACTORS IN BACK PAIN Framing the Discussion from a Clinical and Anatomical Perspective A B M P B a ck Pa i n S u m m i t With Clint Chandler FACTORS IN BACK PAIN introduction Back pain affects 8 out of
Manual Muscle Testing. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Manual Muscle Testing Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Manual Muscle Testing Evaluation of the function and strength of individual muscles and muscles
Manual Muscle Testing Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Manual Muscle Testing Evaluation of the function and strength of individual muscles and muscles
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles. Striated Skeletal. Smooth
 1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK)
 THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
THE LUMBAR SPINE (BACK) At a glance Chronic back pain, especially in the area of the lumbar spine (lower back), is a widespread condition. It can be assumed that 75 % of all people have it sometimes or
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
Wake me when this makes sense. Today s Objectives. Quote from Maitland. Quote from Maitland 8/4/2012
 Wake me when this makes sense Today s Objectives Selection of techniques Order of efficacy of techniques Ground the theory in reality Application of techniques How do you do what you should do Quote from
Wake me when this makes sense Today s Objectives Selection of techniques Order of efficacy of techniques Ground the theory in reality Application of techniques How do you do what you should do Quote from
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back
 the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
the back book Your Guide to a Healthy Back anatomy Your spine s job is to: Support your upper body and neck Increase flexibility of your spine Protect your spinal cord There are 6 primary components of
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
SPINAL IMMOBILIZATION
 Spinal Immobilization Decision Assessment Recent studies have shown an increase in mortality for patients with isolated penetrating trauma who are spinally immobilized. Therefore spinal immobilization
Spinal Immobilization Decision Assessment Recent studies have shown an increase in mortality for patients with isolated penetrating trauma who are spinally immobilized. Therefore spinal immobilization
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management.
 River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
River North Pain Management Consultants, S.C., Axel Vargas, M.D., Regional Anesthesiology and Interventional Pain Management. Chicago, Illinois, 60611 Phone: (888) 951-6471 Fax: (888) 961-6471 Clinical
 The spine is made of a column of bones. Each bone, or vertebra, is formed by a round block of bone, called a vertebral body. A bony ring attaches to the back of the vertebral body. When the vertebra bones
The spine is made of a column of bones. Each bone, or vertebra, is formed by a round block of bone, called a vertebral body. A bony ring attaches to the back of the vertebral body. When the vertebra bones
NECK AND BACK PAIN AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NECK AND BACK PAIN This booklet provides general information on neck and back pain. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician
AN INTRODUCTION TO NECK AND BACK PAIN This booklet provides general information on neck and back pain. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics. Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003
 Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner
 Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
Cervical Spine Exercise and Manual Therapy for the Autonomous Practitioner Eric Chaconas PT, PhD, DPT, FAAOMPT Assistant Professor and Assistant Program Director Doctor of Physical Therapy Program Eric
SpineFAQs. Lumbar Spondylolisthesis
 SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
SpineFAQs Lumbar Spondylolisthesis Normally, the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) stand neatly stacked on top of one another. The ligaments and joints support the spine. Spondylolisthesis alters the
Patient Information MIS LLIF. Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques
 Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Patient Information MIS LLIF Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques Table of Contents Anatomy of Spine....2 General Conditions of the Spine....4 What is Spondylolisthesis....5
Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers
 Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers Bones Anatomy of the Spine Ligaments & Discs Muscles Quadratus Lumborum (QL) Muscle Strain or Trigger Point The QL originates from the posterior iliac crest and inserts
Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers Bones Anatomy of the Spine Ligaments & Discs Muscles Quadratus Lumborum (QL) Muscle Strain or Trigger Point The QL originates from the posterior iliac crest and inserts
BACK SPASM. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs
 Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs Chapter Five: Movement Examination of the Lumbar Spine Time) (45 minutes
Evidence- Based Examination of the Lumbar Spine Presented by Chad Cook, PT, PhD, MBA, FAAOMPT Practice Sessions/Skill Check- offs Chapter Five: Movement Examination of the Lumbar Spine Time) (45 minutes
PARADIGM SPINE. Patient Information. Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal
 PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
PARADIGM SPINE Patient Information Treatment of a Narrow Lumbar Spinal Canal Dear Patient, This brochure is intended to inform you of a possible treatment option for narrowing of the spinal canal, often
CERVICAL SPINE EVALUATION MARK FIGUEROA PHYSICAL THERAPIST
 CERVICAL SPINE EVALUATION MARK FIGUEROA PHYSICAL THERAPIST OVERVIEW OF CLINICAL REASONING Stage of disorder Pathoanatomical diagnosis Signs and symptoms Consideration of the evidence gathered Common sense
CERVICAL SPINE EVALUATION MARK FIGUEROA PHYSICAL THERAPIST OVERVIEW OF CLINICAL REASONING Stage of disorder Pathoanatomical diagnosis Signs and symptoms Consideration of the evidence gathered Common sense
SpineFAQs. Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment
 SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
Ligaments of the vertebral column:
 In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
In the last lecture we started talking about the joints in the vertebral column, and we said that there are two types of joints between adjacent vertebrae: 1. Between the bodies of the vertebrae; which
Contraindicated and High-Risk Exercises
 Contraindicated and High-Risk Exercises Young sub Kwon, Ph.D. ACSM RCEP, NSCA CSCS,*D Exercise Physiology Laboratory The University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA Introduction Any activity selected
Contraindicated and High-Risk Exercises Young sub Kwon, Ph.D. ACSM RCEP, NSCA CSCS,*D Exercise Physiology Laboratory The University of New Mexico Albuquerque, NM, USA Introduction Any activity selected
The main causes of cervical radiculopathy include degeneration, disc herniation, and spinal instability.
 SpineFAQs Cervical Radiculopathy Neck pain has many causes. Mechanical neck pain comes from injury or inflammation in the soft tissues of the neck. This is much different and less concerning than symptoms
SpineFAQs Cervical Radiculopathy Neck pain has many causes. Mechanical neck pain comes from injury or inflammation in the soft tissues of the neck. This is much different and less concerning than symptoms
Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology
 Physical Therapy Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology Scott Behjani, DPT, OCS Introduction Prevalence 1-year incidence of first-episode LBP ranges from
Physical Therapy Diagnostic and Treatment Approach to the Active Patient with Complex Spine Pathology Scott Behjani, DPT, OCS Introduction Prevalence 1-year incidence of first-episode LBP ranges from
MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES
 WHAT ARE THEY They are injuries to muscles, nerves, tendons ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs. WHAT KIND OF INJURIES ARE MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 1. Fractures- -Open -Closed 2. Dislocations
WHAT ARE THEY They are injuries to muscles, nerves, tendons ligaments, joints, cartilage and spinal discs. WHAT KIND OF INJURIES ARE MUSCULOSKELETAL INJURIES 1. Fractures- -Open -Closed 2. Dislocations
Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar
 BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
BIOMECHANICS OF SPINE Dr Ajit Singh Moderator Dr P S Chandra Dr Rajender Kumar What is biomechanics? Biomechanics is the study of the consequences of application of external force on the spine Primary
Chapter 20: The Spine The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 20: The Spine Anatomy of the Spine Prevention of Injuries to the Spine Cervical Spine Muscle Strengthening Muscles of the neck resist hyperflexion, hyperextension and rotational forces Prior
Chapter 20: The Spine Anatomy of the Spine Prevention of Injuries to the Spine Cervical Spine Muscle Strengthening Muscles of the neck resist hyperflexion, hyperextension and rotational forces Prior
Medical Yogatherapy at Anand Yoga Institute
 Medical Yogatherapy at Anand Yoga Institute Mr. Shankar Khedkar (Yoga Therapist) Contact No: 09960555185. Medical Yogatherapy for Degenerative Musculoskeletal Disorders Aims Skeletal Muscles 1) Adequate
Medical Yogatherapy at Anand Yoga Institute Mr. Shankar Khedkar (Yoga Therapist) Contact No: 09960555185. Medical Yogatherapy for Degenerative Musculoskeletal Disorders Aims Skeletal Muscles 1) Adequate
The Effective Interaction of Traction and Massage Traction Control Unit Cervical Traction
 Relax your patients with the controlled, deep-kneading massage of the Anatomotor. For over 65 years, the Hill Anatomotor has provided a proven method of soft-tissue massage and spinal mobilization which
Relax your patients with the controlled, deep-kneading massage of the Anatomotor. For over 65 years, the Hill Anatomotor has provided a proven method of soft-tissue massage and spinal mobilization which
Y: Orthopedic Specialty
 Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back. Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist
 SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist Back Injury 60 % of all adults experience back pain Most frequent cause of activity limitation in individuals under 45 years
SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist Back Injury 60 % of all adults experience back pain Most frequent cause of activity limitation in individuals under 45 years
Soteria Strains. Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide
 Soteria Strains Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide Section 4 Special Considerations Section 4.3 - Orthopedics V1.0 edited July 28, 2015 A provincial strategy for healthcare workplace musculoskeletal
Soteria Strains Safe Patient Handling and Mobility Program Guide Section 4 Special Considerations Section 4.3 - Orthopedics V1.0 edited July 28, 2015 A provincial strategy for healthcare workplace musculoskeletal
The Biomechanics of the Human Spine. Basic Biomechanics, 6 th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D.
 Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
Chapter 9 The Biomechanics of the Human Spine Structure of the Spine The spine is a curved stack of 33 vertebrae structurally divided into five regions: cervical region - 7 vertebrae thoracic region -
The Spine.
 The Spine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Characteristics of Vertebrae Cervical Spine 1 and 2 Sacrum and Coccyx Curves Lordotic in the Spine Kyphotic Lordotic Ligamentous Support Muscles of the Spine Spinal
The Spine www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Characteristics of Vertebrae Cervical Spine 1 and 2 Sacrum and Coccyx Curves Lordotic in the Spine Kyphotic Lordotic Ligamentous Support Muscles of the Spine Spinal
CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens
 CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
VERTEBRAL COLUMN FUNCTIONS: 1) Support weight - transmits weight to pelvis and lower limbs 2) Houses and protects spinal cord - spinal nerves leave cord between vertebrae 3) Permits movements - *clinical
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE
 VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
VERTEBRAL COLUMN ANATOMY IN CNS COURSE Vertebral body Sections of the spine Atlas (C1) Axis (C2) What type of joint is formed between atlas and axis? Pivot joint What name is given to a fracture of both
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Anatomy of the Spine. Figure 1. (left) The spine has three natural curves that form an S-shape; strong muscles keep our spine in alignment.
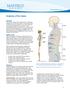 1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
1 2 Anatomy of the Spine Overview The spine is made of 33 individual bony vertebrae stacked one on top of the other. This spinal column provides the main support for your body, allowing you to stand upright,
The Future of Exercise
 The Future of Exercise (1997 and Beyond) ArthurJonesExercise.com 11 Strong Is a Relative Term The first person ever accurately tested for the isolated strength of the muscles that extend the lumbar spine
The Future of Exercise (1997 and Beyond) ArthurJonesExercise.com 11 Strong Is a Relative Term The first person ever accurately tested for the isolated strength of the muscles that extend the lumbar spine
REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY
 The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
The Athlete s Guide to REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY THE ATHLETE S GUIDE TO REACHING PEAK SPORTS PERFORMANCE AND PREVENTING INJURY Table of Contents Introduction...3 Common Sports
Spinal Column. Anatomy Of The Spine
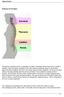 Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
Anatomy Of The Spine The spine is a flexible column, composed of a stack of individual bones. Each bone is called a vertebra. There are seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae) twelve in the thoracic
HERNIATED DISCS AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO HERNIATED S This booklet provides general information on herniated discs. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
AN INTRODUCTION TO HERNIATED S This booklet provides general information on herniated discs. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
Bone Injuries and Treatment. Fractures and Dislocations
 Bone Injuries and Treatment Fractures and Dislocations Bellwork Research the small bones in the foot and wrist. Draw them in your notes. State Standards 16) Understand principles of and successfully perform
Bone Injuries and Treatment Fractures and Dislocations Bellwork Research the small bones in the foot and wrist. Draw them in your notes. State Standards 16) Understand principles of and successfully perform
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion. Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD. Date Created: March 27 th, Last Updated:
 Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
Module: #15 Lumbar Spine Fusion Author(s): Jenni Buckley, PhD Date Created: March 27 th, 2011 Last Updated: Summary: Students will perform a single level lumbar spine fusion to treat lumbar spinal stenosis.
THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE
 THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE Postural Tips To Improve Movement Efficiency and Functional Independence BY DR. AARON LEBAUER, PT, DPT 2 P a g e Disclaimer The information in this book is not a replacement
THE SECRETS TO GOOD POSTURE Postural Tips To Improve Movement Efficiency and Functional Independence BY DR. AARON LEBAUER, PT, DPT 2 P a g e Disclaimer The information in this book is not a replacement
Physical Therapy for patients after spinal surgery with internal fixation devices.
 Physical Therapy for patients after spinal surgery with internal fixation devices www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz After spinal surgery, patients want to know when they are allowed to sit, to walk without a
Physical Therapy for patients after spinal surgery with internal fixation devices www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz After spinal surgery, patients want to know when they are allowed to sit, to walk without a
Back Safety Healthcare #09-066
 Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Back Safety Healthcare Version #09-066 I. Introduction A. Scope of training This training program applies to healthcare employees whose job requires them to lift patients or other heavy objects. Lifting
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
Posture. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Posture Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 10 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Posture = body alignment = the relative arrangement of parts of the body Changes with the positions and movements of the body throughout the day
Musculoskeletal Trauma. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma
 Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Musculoskeletal Trauma Lesson Goal Recognize and manage patients with musculoskeletal trauma Lesson Objectives Describe function of muscular system Describe composition of muscular system Describe, compare,
Using Biomechanical Principles in the Management of Complex Postural Deviations in Sitting
 Using Biomechanical Principles in the Management of Complex Postural Deviations in Sitting ISS 2016 / Part 1 - Basic Principles KELLY WAUGH, PT, MAPT, ATP S E N I O R I N S T R U C TO R / C L I N I C C
Using Biomechanical Principles in the Management of Complex Postural Deviations in Sitting ISS 2016 / Part 1 - Basic Principles KELLY WAUGH, PT, MAPT, ATP S E N I O R I N S T R U C TO R / C L I N I C C
EXERCISE PRESCRIPTION PART 1
 EXERCISE PRESCRIPTION PART 1 Michael McMurray, PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 What is MET? An active rehabilitation system based in the biopsychosocial
EXERCISE PRESCRIPTION PART 1 Michael McMurray, PT, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 What is MET? An active rehabilitation system based in the biopsychosocial
Postural Correction, by Jane Johnson book excerpt
 Postural Correction, by Jane Johnson book excerpt Human Kinetics has kindly provided a free excerpt from Jane Johnson s new book, Postural Correction, exclusively for FHT Members. The excerpt, from chapter
Postural Correction, by Jane Johnson book excerpt Human Kinetics has kindly provided a free excerpt from Jane Johnson s new book, Postural Correction, exclusively for FHT Members. The excerpt, from chapter
Back Health and Safety
 Back Health and Safety Your back is at work every minute of every day, whether you are awake or asleep, active or quiet. Over time the effects of poor posture, bad body mechanics, physical deconditioning
Back Health and Safety Your back is at work every minute of every day, whether you are awake or asleep, active or quiet. Over time the effects of poor posture, bad body mechanics, physical deconditioning
Main Menu. Trunk and Spinal Column click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
1 The Trunk and Spinal Column click here Main Menu K.9 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k9/k9entry.htm[3/27/18, 2:00:55 PM] The Trunk and Spinal Column Vertebral column complex 24 intricate
Low Res SAMPLE SPINAL CURVES THE SPINE
 THE SPINE The normal healthy spine has a naturally curved shape. Like a coiled spring, these curves help to absorb some of the forces that are placed on your spine while standing erect. When looking at
THE SPINE The normal healthy spine has a naturally curved shape. Like a coiled spring, these curves help to absorb some of the forces that are placed on your spine while standing erect. When looking at
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates
 Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates C A S S I T E R P E N I N G P T, D P T, C S C S, C P I C H R I S R I E G E R P T U P S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L J U N E 1 9, 2 0 1 7 Content
Stand Tall with Osteoporosis thru Pilates C A S S I T E R P E N I N G P T, D P T, C S C S, C P I C H R I S R I E G E R P T U P S T A T E U N I V E R S I T Y H O S P I T A L J U N E 1 9, 2 0 1 7 Content
Chiropractic Glossary
 Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Chiropractic Glossary Anatomy Articulation: A joint formed where two or more bones in the body meet. Your foot bone, for example, forms an articulation with your leg bone. You call that articulation an
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton
 Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
erhem Thoracal spine section Elastic shoulder brace with support bracing Application:
 ERH 53/1 Elastic shoulder brace with support bracing Augmentation of proper upright posture Stable fractures of the clavicle Scheuermann s kyphosis Funnel chest Osteoporotic lesions The shoulder brace
ERH 53/1 Elastic shoulder brace with support bracing Augmentation of proper upright posture Stable fractures of the clavicle Scheuermann s kyphosis Funnel chest Osteoporotic lesions The shoulder brace
Current Spine Procedures
 SPINE BOOT CAMP: WHAT YOU DON T KNOW MAY COST YOU! David Abraham, M.D. The Reading Neck and Spine Center Reading, PA Current Spine Procedures Epidural/Transforaminal Injections Lumbar Procedures Laminectomy
SPINE BOOT CAMP: WHAT YOU DON T KNOW MAY COST YOU! David Abraham, M.D. The Reading Neck and Spine Center Reading, PA Current Spine Procedures Epidural/Transforaminal Injections Lumbar Procedures Laminectomy
2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage
 CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
CHAPTER 7-SKELTON FILL-IN NOTES 2 skull, vertebral column, thoracic cage 3 Fig. 7.1 pg. 199 4 I. Skull: A. : Encloses and the brain - 8 bones B. : 14 bones Cranium A. Forehead (brain) Anterior part of
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr Hesarikia BUMS
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Dr. Hesarikia BUMS Subaxial Cervical Spine From C3-C7 ROM Majority of cervical flexion Lateral bending Approximately 50% rotation Ligamentous Anatomy Anterior ALL, PLL, intervertebral
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR PATHOLOGY OF THE INTERVETEBRAL DISK
 PILATES CONDITIONING FOR PATHOLOGY OF THE INTERVETEBRAL DISK Ashlee Tinken August 12, 2017 Comprehensive Apparatus Program Pilates Denver June 2015 ABSTRACT The pathology of the intervertebral disk is
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR PATHOLOGY OF THE INTERVETEBRAL DISK Ashlee Tinken August 12, 2017 Comprehensive Apparatus Program Pilates Denver June 2015 ABSTRACT The pathology of the intervertebral disk is
Most Dangerous Man! FACTS ON STREGNTH. Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
 FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
Sprains. Initially the ankle is swollen, painful, and may turn eccyhmotic (bruised). The bruising, and the initial swelling, is due to ruptured
 Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
Sprains Introduction An ankle sprain is a common injury and usually results when the ankle is twisted, or inverted. The term sprain signifies injury to the soft tissues, usually the ligaments, of the ankle.
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM
 AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
AXIAL SKELETON FORM THE VERTICAL AXIS OF THE BODY CONSISTS OF 80 BONES INCLUDES BONES OF HEAD, VERTEBRAL COLUMN, RIBS,STERNUM APPENDICULAR SKELETON BONES OF THE FREE APPENDAGES & THEIR POINTS OF ATTACHMENTS
Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN
 Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN 37232-8774 615-343-9430 This information is intended for education of the reader about medical conditions
Contact us! Vanderbilt Orthopaedic Institute Medical Center East, South Tower, Suite 4200 Nashville, TN 37232-8774 615-343-9430 This information is intended for education of the reader about medical conditions
VIRGINIA ORTHOPEDIC MANUAL PHYSICAL THERAPY INSTITUTE TECHNIQUE MANUAL
 VIRGINIA ORTHOPEDIC MANUAL PHYSICAL THERAPY INSTITUTE TECHNIQUE MANUAL Lumbar and Thoracic Spine Lumbar AROM Assessment -Patient Positioning: Standing, appropriately undressed so that the lumbar and thoracic
VIRGINIA ORTHOPEDIC MANUAL PHYSICAL THERAPY INSTITUTE TECHNIQUE MANUAL Lumbar and Thoracic Spine Lumbar AROM Assessment -Patient Positioning: Standing, appropriately undressed so that the lumbar and thoracic
5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival. 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back
 Low Back Pain 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn by the start of class, we'll have you out of
Low Back Pain 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: Back Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn by the start of class, we'll have you out of
Lumbar Spine Applied Anatomy. Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education
 Lumbar Spine Applied Anatomy Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Objectives Discuss concepts relevant to pathophysiology and differential diagnosis for lumbar radiculopathy
Lumbar Spine Applied Anatomy Jason Zafereo, PT, OCS, FAAOMPT Clinical Orthopedic Rehabilitation Education Objectives Discuss concepts relevant to pathophysiology and differential diagnosis for lumbar radiculopathy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R. Joints: Part A. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
LEARN * DREAM * AWAKEN* DISCOVER * ENLIGHTEN * INVESTIGATE * QUESTION * EXPLORE
 S C I E N C E H U M A N Spine & Vertebrate The Spine & Vertebrate in Focus This Enrichment4You e-guide provides a brief overview of the spine and vertebrate. In this e-guide you will: Human Body Spine/Vertebrate
S C I E N C E H U M A N Spine & Vertebrate The Spine & Vertebrate in Focus This Enrichment4You e-guide provides a brief overview of the spine and vertebrate. In this e-guide you will: Human Body Spine/Vertebrate
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
POSTURE ANALYSIS. What is good posture?
 POSTURE ANALYSIS What is good posture? Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing or sitting. Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit
POSTURE ANALYSIS What is good posture? Posture is the position in which you hold your body upright against gravity while standing or sitting. Good posture involves training your body to stand, walk, sit
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
The Back. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
The Back Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 9 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The spine has to meet 2 functions Strength Mobility Stability of the vertebral column is provided by: Deep intrinsic muscles of the back Ligaments
Comprehension of the common spine disorder.
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder. Disc degeneration/hernia. Spinal stenosis. Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis). Osteoporotic fracture. Anatomy Anatomy Anatomy
Cervical and Thoracic Spinal Conditions Chapter 11
 Cervical and Thoracic Spinal Conditions Chapter 11 Anatomy Spinal column Vertebrae Cervical (7) convex anteriorly Thoracic (12) concave anteriorly Lumbar (5) convex anteriorly Sacral (5 fused) concave
Cervical and Thoracic Spinal Conditions Chapter 11 Anatomy Spinal column Vertebrae Cervical (7) convex anteriorly Thoracic (12) concave anteriorly Lumbar (5) convex anteriorly Sacral (5 fused) concave
Patient Information ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
 Patient Information ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Table of Contents Anatomy of the Spine...2-3 General Conditions of the Cervical Spine...4 5 What is an ACDF?...6 How is an ACDF performed?...7
Patient Information ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Table of Contents Anatomy of the Spine...2-3 General Conditions of the Cervical Spine...4 5 What is an ACDF?...6 How is an ACDF performed?...7
Skeletal System. Axial Division
 Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Skeletal System Axial Division The Axial Skeleton You will see that each bone has special features (overviewed in section I below) that provide Sites of Attachment (for muscles, ligaments, tendons, etc.)
Cervical Plating BACK PAIN
 BACK PAIN Back Pain Back pain is frequent complaint. It is the commonest cause of work-related absence in the world. Although back pain may be painful and uncomfortable, it is not usually serious. Even
BACK PAIN Back Pain Back pain is frequent complaint. It is the commonest cause of work-related absence in the world. Although back pain may be painful and uncomfortable, it is not usually serious. Even
Bony framework of the vertebral column Structure of the vertebral column
 5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
5.1: Vertebral column & back. Overview. Bones o vertebral column. o typical vertebra. o vertebral canal. o spinal nerves. Joints o Intervertebral disc. o Zygapophyseal (facet) joint. Muscles o 2 compartments:
