This is a free sample of content from Parkinson's Disease. Click here for more information or to buy the book.
|
|
|
- Elijah Tate
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A AADC. See Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase AAV. See Adeno-associated virus Acetylcholine (ACh), functional imaging, ACh. See Acetylcholine Adaptive immune system central nervous system, cross-regulation with innate immunity in central nervous system, misfolded proteins in immune activation, Parkinson s disease dysfunction, prospects for study, 391 therapeutic targeting, Adeno-associated virus (AAV) gene therapy vectors, 129 mouse models of Parkinson s disease, 265 Aging DNA polymerase-g studies in mutant mice, 218 macroautophagy in protein quality control effects, 336 mitochondria aging hypothesis, , Akinesia, motor control, a-methyl-p-tyrosine, animal models of Parkinson s disease, 24 a-synuclein (SNCA) aggregation potential, autophagy autophagy response, , 337 chaperone-mediated autophagy degradation, 316 inhibition by mutant forms, , mitophagy role, 318 autosomal dominant Parkinson s disease clinical features, 24, biomarkers, function, gain-of-function and accumulation, gene dosage in Parkinson s disease, 66 knockdown therapy, Lewy body. See Dementia with Lewy bodies; Lewy body lipid interactions, loci. See PARK1; PARK4 misfolded proteins in immune activation, pathogenic effects cytoskeleton, endoplasmic reticulum/golgi apparatus, 76 lysosome, 75 mitochondria, 75 nucleus, 76 proteasome, 75 secretion and uptake, 77 synapse, 74 posttranslational modifications, protein protein interactions, 71 structure, synucleopathy models, 69 therapeutic targeting, transgenic mouse, ubiquitin proteasome system effects of mutation, AMPA receptor, neuronal phenotype of Parkinson s disease, 204 Amphetamines, animal models of Parkinson s disease, Animal models. See a-methyl-p-tyrosine; Amphetamines; Drosophila; 6-Hydroxydopamine; Isoquinoline; Lipopolysaccharide; 1-Methyl-4-phenyl- 1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; Mouse models; Paraquat; Reserpine; Rotenone Apoptosis. See Programmed cell death Aromatic amino acid decarboxylase (AADC), gene therapy, ATP13A2, mutation Parkinson s disease, ubiquitin proteasome system dysfunction, Autophagy a-synuclein autophagy response, , 337 chaperone-mediated autophagy degradation, 316 inhibition by mutant forms, , mitophagy role, 318 cytoplasmic cell death overview, 355 paranatos, necroptosis, 356 DJ-1 role, 322 functions, leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 role, macroautophagy in protein quality control 399
2 Autophagy (Continued) aging effects, 336 impairment in Parkinson s disease, 336 overview, oxidative stress effects, mitophagy parkin-dependent mitophagy, 320 Parkinson s disease, molecular mechanisms, 315 organelle specificity, PINK1 function isoforms, 321 overview, protective function, 321 programmed cell death defects in Parkinson s disease, mitophagy, overview, prospects for study in Parkinson s disease, 322, types, , Autosomal dominant Parkinson s disease clinical features, gene mutations, 24 25, mouse models, 263 pedigrees, 50, Autosomal recessive Parkinson s disease clinical features, gene mutations, 25 26, mouse models, 264 pedigrees, 50, B Basal ganglia function and motor symptoms, functional imaging at rest, 168 functional organization classic model, corticostriatal connections, 155 corticosubthalamic connections, domains, subcortical connections, 156 gross anatomy, nuclei globus pallidus external segment, 150 substantia nigra pars compacta, subthalamic nucleus, pathophysiology dyskinesia, 157 parkinsonism, striatum compartments, output nuclei globus pallidus internal segment, 149 substantia nigra pars reticulata, projections afferents, efferents, 149 neurons and interneurons, Bcl-2 proteins, apoptosis mediation, b-glucocerebrosidase (GBA) a-synuclein accumulation effects, 75 mutation and Parkinson s disease risk, Bioinformatics biomarker discovery, overview, Braak staging, Parkinson s disease, 41 Bradykinesia motor control, Parkinson s disease, 18 speed selection abnormalities, 186 C Calcium flux L-type calcium channels dopaminergic neuron susceptibility role in Parkinson s disease, therapeutic targeting, metabolic burden on neurons, mitochondria in homeostasis, , 294, neuronal pacemaking and ionic homeostasis challenge, neuron vulnerability in Parkinson s disease dopaminergic neurons, nondopaminergic neurons, 220 Caspase, activation in apoptosis, 348, 350 CBD. See Corticobasal degeneration CDK5. See Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 Charcot, Jean-Martin, 2, 4 5, 7 10, 12, 17 Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), overview, 43 Clarke, Robert Henry, Clinical presentation, Parkinson s disease autosomal dominant Parkinson s disease, autosomal recessive Parkinson s disease, exclusion criteria, 38 historical perspective, 1 7 motor symptoms animal models assessment, MPTP monkey model, bradykinesia, 18 overview, postural and gait impairment, 19 rest tremor, rigidity, 19 nonmotor symptoms, Corticobasal degeneration (CBD), overview, 43 CTE. See Chronic traumatic encephalopathy 400
3 Cyclin-dependent kinase-5 (CDK5), dysfunction in Parkinson s disease, D Dardarin. See Leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 Default mode network (DMN), functional imaging, Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) differential diagnosis, 23 parkinsonism etiology, 25 Diagnosis, Parkinson s disease clinical examination, 21 criteria, 22 differential diagnosis dementia with Lewy bodies, 23 drug-induced parkinsonism, essential tremor, 23 fragile X-tremor ataxia syndrome, 24 multiple system atrophy, 23, progressive supranuclear palsy, 23 24, vascular parkinsonism, 22 historical perspective, 1 7 imaging, incorrect diagnosis features, 21 medical history, 20 DIP. See Drug-induced parkinsonism DJ-1 apoptosis protection, autophagy role, 322 features, 26, 57, 100 modulation, 285 evolution, function, knockout mouse, locus. See PARK7 mutation studies of parkinsonism development, prospects for study, 106 DLB. See Dementia with Lewy bodies DMN. See Default mode network DNA polymerase-g (POLG) aging studies in mutant mice, 218 mutation effects, 298 L-Dopa. See Levodopa Dopamine functional imaging, , history of Parkinson s disease treatment, striatum dopamine quantification in animal models of Parkinson s disease, 252 Drosophila advantages as Parkinson s disease model system, gene identification in Parkinson s disease, genetic and compound screening, 279 knockdown studies, 279 mutagenesis and loss-of-function studies, 278 overexpression studies, prospects for Parkinson s disease studies, PTEN-induced putative kinase-1/parkin pathway studies links with other PARK loci, mitochondrial fission promotion and fusion inhibition, mitochondrial integrity, mitochondrial transport, mitophagy promotion, site-specific transgenesis, 279 Drug-induced parkinsonism (DIP) differential diagnosis, drug types, 25 Dyskinesia. See specific dyskinesias E Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) a-synuclein mutant effects, 76 apoptosis response, 351 protein quality control. See Autophagy; Ubiquitin proteasome system Epidemiology, Parkinson s disease, ER. See Endoplasmic reticulum Essential tremor (ET), differential diagnosis, 23 ET. See Essential tremor F FDDNP, protein aggregation imaging, FDOPA. See Positron emission tomography fmri. See Functional magnetic resonance imaging Fragile X-tremor ataxia syndrome (FXTAS), differential diagnosis, 24 Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) default mode network, principles, 165 FXTAS. See Fragile X-tremor ataxia syndrome G GAD. See Glutamic acid decarboxylase Gaucher s disease, parkinsonism risks, GBA. See b-glucocerebrosidase GCH-1. See GTP cyclohydrolase-1 GDNF. See Glial-derived neurotrophic factor Gene therapy enzyme replacement aromatic amino acid decarboxylase, glutamic acid decarboxylase, GTP cyclohydrolase-1, 130, 132 tyrosine hydroxylase, 130,
4 Gene therapy (Continued) glial-derived neurotrophic factor, principles, viral vectors adeno-associated virus, 129 lentivirus, 128 Genetics, Parkinson s disease classification by loci, identification of new genes and risk factors, linkage analysis, loci. See specific loci monogenetic Parkinson s disease, pedigrees, 50, risk gene mutations in Parkinson s disease, Genomics, Parkinson s disease aberrant network activity identification, bioinformatics biomarker discovery, overview, historical perspective, Mendelian versus complex disease, therapeutic application, Glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) a-synuclein knockdown therapy, direct injection studies, functional overview, 133 gene therapy, parkin, prospects, Globus pallidus external segment, 150 internal segment, 149 Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD), gene therapy, Gowers, William, 2, 7, 10 GTP cyclohydrolase-1 (GCH-1), gene therapy, 130, 132 H Historical perspective, Parkinson s disease clinical descriptions, 1 3 differential diagnosis, 2, 4 7 genomics, treatment, 7 13 Horsley, Victor, 12 HtrA2. See Omi/HtrA2 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) animal models of Parkinson s disease, 244 brain physiology, structure, 242 toxicity mechanisms, 246 Hypokinesia, motor control, I Inflammation adaptive immune response. See Adaptive immune system innate immune response. See Innate immune system Innate immune system cross-regulation with adaptive immunity in central nervous system, inflammation in Parkinson s disease animal Parkinson s disease model studies lipopolysaccharide, 376 overview, 374 toxin models, transgenic mouse studies, epidemiological studies, 374 microglia activation in Parkinson s disease, activators, 376 characteristics and functions in brain, prospects for study, 377 systemic inflammation impact on innate immune cells, 372 T cell activation, 374 misfolded proteins in immune activation, Isoquinoline, animal models of Parkinson s disease, J Jellinger staging, multiple system atrophy, 42 K Knockout mouse. See Mouse models L Lentivirus, gene therapy vectors, 128 Leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 (LRRK2) autophagy role, autosomal dominant Parkinson s disease clinical features, 25, 55 56, discovery, functions cytoskeleton, membrane trafficking, Parkinson s disease protein pathway overlap, 95 locus. See PARK8 mutation frequency, functional effects, 94 sites, 92 protein protein interactions,
5 structure, 92 transgenic mouse, 267 Levodopa, history of Parkinson s disease treatment, Levodopa-induced dyskinesia (LID) functional imaging, MPTP monkey model, 235 Lewy body. See also a-synuclein; Dementia with Lewy bodies characteristics, detection in animal models of Parkinson s disease, immunohistochemistry multiple system atrophy, Parkinson s disease, 35 36, 67 multiple system atrophy glial cytoplasmic inclusions, 40, 66 Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) animal models of Parkinson s disease, 250 innate inflammation studies in Parkinson s disease models, 376 LPS. See Lipopolysaccharide LRRK2. See Leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 L-type calcium channel. See Calcium flux M Macrophage. See Microglia Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Parkinson s disease diagnosis, 22 Methamphetamine, animal models of Parkinson s disease, N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), neuronal phenotype of Parkinson s disease, Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mitochondria effects, 296 monkey models of Parkinson s disease anatomo-pathology, , 245 behavioral assessment, 235 cognitive impairment, 234 dyskinesia, 235 Lewy body lack, 233 limitations, motor symptoms, sleep disturbances, species, 232 mouse models of Parkinson s disease, species response in modeling Parkinson s disease, 231, 245 structure, 242 toxicity mechanisms, 245 ubiquitin proteasome system effects, 332 Microglia activation in Parkinson s disease, , 387 activators in Parkinson s disease, 376 characteristics and functions in brain, Mitochondria aging hypothesis, , a-synuclein function, 75, calcium homeostasis role, , 294, compartments, links with other PARK loci, mitochondrial fission promotion and fusion inhibition, mitochondrial integrity, mitochondrial transport, mitophagy promotion, dynamics fusion/fission, motility and regional distribution, turnover, 301 genetics, mitophagy. See Autophagy neuronal function, oxidative phosphorylation system complex I blockade consequences, 296 overview, 295 oxidative stress, Parkinson s disease dysfunction overview, , Parkin targets, 320 programmed cell death fragmentation, pathways, , 349 Monkey models. See 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine Motor control akinesia, animal model assessment, bradykinesia, hypokinesia, levels of description, motor symptom to motor control, overview, 188 rigidity, Mouse models, Parkinson s disease autosomal dominant Parkinson s disease, 263 autosomal recessive Parkinson s disease, 264 characterization, 266 knockout mouse models DJ-1, overview, parkin, PTEN-induced putative kinase-1, 268 MPTP, overview, 262 prospects, transgenic mouse models 403
6 Mouse models, Parkinson s disease (Continued) a-synuclein, constructs, 262 innate inflammation studies, leucine-rich repeat kinase-2, 267 test-off conditional models, 262, 264 virus-induced models, MPTP. See 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine MRI. See Magnetic resonance imaging MSA. See Multiple system atrophy Multiple system atrophy (MSA) brain morphology, 34, 39 clinical features, 38 differential diagnosis, 23, glial cytoplasmic inclusions, 40 Jellinger staging, 42 Lewy body immunohistochemistry, pathology comparison with Parkinson s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy, substantia nigra degeneration, N Necroptosis, dysfunction in Parkinson s disease, 356 Neuronal phenotype, Parkinson s disease calcium channel, L-type targeting, metabolic burden spiking, synaptic transmission, 209 mitochondria aging hypothesis, oxidative stress, overview, pacemaking and ionic homeostasis challenge, reconciliation with other pathogenesis models, vulnerable neurons dopaminergic neurons, non-dopaminergic neurons, 220 Niemann-Pick disease, parkinsonism risks, NMDAR. See N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor 6-OHDA. See 6-Hydroxydopamine O Omi/HtrA2 modulation, function, 284 Oxidative stress a-synuclein role, macroautophagy effects, mitochondria MPTP effects, 296 role, P p53, expression in Parkinson s disease, 352 p62, parkin-dependent mitophagy, 320 Paranatos, dysfunction in Parkinson s disease, Paraquat animal models of Parkinson s disease, structure, 242 PARK, autosomal dominant Parkinson s disease clinical features, 24 PARK1. See also a-synuclein autosomal-dominant Parkinson s disease clinical features, 24 PARK2. See also Parkin features, 25, mutation and Parkinson s disease susceptibility, 53 PARK4. See also a-synuclein autosomal-dominant Parkinson s disease clinical features, 24 PARK5. See also Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase-1 autosomal-dominant Parkinson s disease clinical features, PARK6. See also PTEN-induced putative kinase-1 features, 26, 57 mutation and Parkinson s disease susceptibility, 53 PARK7. See also DJ-1 features, 26, 57 PARK8. See also Leucine-rich repeat kinase-2 autosomal dominant Parkinson s disease clinical features, 25, 55 56, PARK9. See ATP13A2 PARK13. See Omi/HtrA2 Parkin apoptosis protection, 348 features, 25, 56 57, 100 links with other PARK loci, mitochondrial fission promotion and fusion inhibition, mitochondrial integrity, mitochondrial transport, mitophagy promotion, evolution, 101 function, gene therapy, knockout mouse, locus. See PARK2 mitochondrial targets, 320 mitophagy role, 320,
7 mutation studies of parkinsonism development, prospects for study, 106 ubiquitin proteasome system effects of mutation, Parkinson, James, 1 3, 17 Parkinson-dementia complex (PDC), overview, Parkinson s disease-related cognitive pattern (PDCP), functional imaging, Parkinson s disease-related pattern (PDRP), positron emission tomography, Parkinson s disease tremor-related pattern (PDTP), positron emission tomography, 168 PCD. See Programmed cell death PDC. See Parkinson-dementia complex PDCP. See Parkinson s disease-related cognitive pattern PDRP. See Parkinson s disease-related pattern PDTP. See Parkinson s disease tremor-related pattern PET. See Positron emission tomography PIB. See Pittsburgh Compound B PINK1. See PTEN-induced putative kinase-1 Pittsburgh Compound B (PIB), protein aggregation imaging, Placebo therapy, historical perspective, POLG. See DNA polymerase-g Positron emission tomography (PET) default mode network, 171 functional imaging dopaminergic dysfunction and motor symptoms, metabolic networks, levodopa-induced dyskinesia, neurotransmitter imaging, Parkinson s disease diagnosis, 21 principles, protein aggregation imaging, resting metabolism studies, Programmed cell death (PCD) apoptosis animal models of Parkinson s disease, assays, Bcl-2 proteins, caspase activation, 348, 350 cyclin-dependent kinase-5 dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum response, 351 p53 expression, 352 pathways, autophagy defects in Parkinson s disease, mitophagy, overview, mitochondria fragmentation, pathways, , 349 overview, Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) brain morphology, 34, 39 clinical features, differential diagnosis, 23 24, pathology comparison with Parkinson s disease and multiple system atrophy, staging, substantia nigra degeneration, tau immunohistochemistry, 35, 37 pathology, 40 Proteasome. See Ubiquitin proteasome system Protein quality control. See Autophagy; Ubiquitin proteasome system PSP. See Progressive supranuclear palsy PTEN-induced putative kinase-1 (PINK1) apoptosis protection, 348 autophagy function isoforms, 321 overview, , 354 protective function, 321 features, 26, 57, 100 links with other PARK loci, mitochondrial fission promotion and fusion inhibition, mitochondrial integrity, mitochondrial transport, mitophagy promotion, evolution, 101 function, knockout mouse, 268 locus. See PARK6 mutation studies of parkinsonism development, prospects for study, 106 R Reserpine, animal models of Parkinson s disease, 248 Rest tremor, Parkinson s disease, Rigidity motor control, Parkinson s disease, 19 Rotenone, animal models of Parkinson s disease, 247 S Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) Parkinson s disease diagnosis, 21 principles, protein aggregation imaging,
8 Sleep disorders, Parkinson s disease MPTP monkey model, overview, 20 SNc. See Substantia nigra pars compacta SNCA. See a-synuclein SPECT. See Single-photon emission computed tomography STN. See Subthalamic nucleus Striatum basal ganglia projections afferents, corticostriatal connections, 155 efferents, 149 neurons and interneurons, output nuclei globus pallidus internal segment, 149 substantia nigra pars reticulata, compartments, dopamine quantification in animal models of Parkinson s disease, 252 dopaminergic terminal quantification in animal models of Parkinson s disease, 252 Substantia nigra, degeneration in parkinsonian disorders, Substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) dopaminergic neuron quantification in animal models of Parkinson s disease, neuron vulnerability in Parkinson s disease, Substantia nigra pars reticulata, Subthalamic nucleus (STN) corticosubthalamic connections, overview, Surgical therapy, historical perspective, T Tau, progressive supranuclear palsy immunohistochemistry, 35, 37 pathology, 40 T cell activation in Parkinson s disease, 374, central nervous system, 382 cross-regulation with innate immunity in central nervous system, regulatory T cell therapeutic targeting, TDP-43-related parkinsonism, overview, 44 TH. See Tyrosine hydroxylase Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), gene therapy, 130, 132 U Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase-1 (UCHL1) locus. See PARK5 Parkinson s disease susceptibility gene, 58 Ubiquitin proteasome system (UPS) ATP13A2 mutation and dysfunction, MPTP effects, 332 overview, parkin mutation effects, protein misfolding versus clearance in Parkinson s disease, a-synuclein mutation effects, UCHL1. See Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase-1 V Vascular parkinsonism, differential diagnosis, 22 Ventral tegmental area (VTA), dopaminergic neuron susceptibility in Parkinson s disease, 214, 216 Vibratory therapy, historical perspective, 9 VTA. See Ventral tegmental area 406
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview
 Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
Movement Disorders: A Brief Overview Albert Hung, MD, PhD Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School August 17, 2006 Cardinal Features of Parkinsonism Tremor Rigidity Bradykinesia Postural imbalance
2/14/2013. The Pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease. February, inherited forms of PD. Autosomal Recessive Parkinson s Disease
 inherited forms of PD The Pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease February, 2013 PARK1 dominant α-synuclein presynaptic protein PARK2 recessive parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase PARK3 dominant 2p13? PARK4 dominant
inherited forms of PD The Pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease February, 2013 PARK1 dominant α-synuclein presynaptic protein PARK2 recessive parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase PARK3 dominant 2p13? PARK4 dominant
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817.
 Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
Parkinsonism or Parkinson s Disease I. Symptoms: Main disorder of movement. Named after, an English physician who described the then known, in 1817. Four (4) hallmark clinical signs: 1) Tremor: (Note -
A Parkinson s Disease and related disorders
 A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
A 3.5.2 Parkinson s Disease and related disorders 10 November 2016 Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Basal ganglia: components and localization (inter)connections and functions
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease. SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease
 Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Making Every Little Bit Count: Parkinson s Disease SHP Neurobiology of Development and Disease Parkinson s Disease Initially described symptomatically by Dr. James Parkinson in 1817 in An Essay on the
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II. Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy
 Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Cheyenne 11/28 Neurological Disorders II Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy -E.g Bovine4 Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE= mad cow disease), Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, scrapie (animal only) -Sporadic:
Novel Targets of disease modifying therapy for Parkinson disease. David G. Standaert, MD, PhD John N. Whitaker Professor and Chair of Neurology
 Novel Targets of disease modifying therapy for Parkinson disease David G. Standaert, MD, PhD John N. Whitaker Professor and Chair of Neurology Disclosures Dr. Standaert has served as a paid consultant
Novel Targets of disease modifying therapy for Parkinson disease David G. Standaert, MD, PhD John N. Whitaker Professor and Chair of Neurology Disclosures Dr. Standaert has served as a paid consultant
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Pathogenesis of Degenerative Diseases and Dementias D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) Dementias Defined: as the development of memory impairment and other cognitive deficits
Damage on one side.. (Notes) Just remember: Unilateral damage to basal ganglia causes contralateral symptoms.
 Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Lecture 20 - Basal Ganglia Basal Ganglia (Nolte 5 th Ed pp 464) Damage to the basal ganglia produces involuntary movements. Although the basal ganglia do not influence LMN directly (to cause this involuntary
Malattia di Parkinson: patogenesi molecolare e nuove strategie terapeutiche
 LA NEUROSONOLOGIA NELLE PATOLOGIE DEGENERATIVE E VASCOLARI CEREBRALI San Benedetto del Tronto 6-8 novembre 2017 Malattia di Parkinson: patogenesi molecolare e nuove strategie terapeutiche Giuseppe De Michele
LA NEUROSONOLOGIA NELLE PATOLOGIE DEGENERATIVE E VASCOLARI CEREBRALI San Benedetto del Tronto 6-8 novembre 2017 Malattia di Parkinson: patogenesi molecolare e nuove strategie terapeutiche Giuseppe De Michele
Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective. Dr John Coyle
 Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective Dr John Coyle Overview Introduction Epidemiology and aetiology Pathogenesis Diagnosis and clinical features Treatment Psychological issues/ non
Parkinson s Disease in the Elderly A Physicians perspective Dr John Coyle Overview Introduction Epidemiology and aetiology Pathogenesis Diagnosis and clinical features Treatment Psychological issues/ non
Modeling Parkinson s disease: systems to test gene-environment interactions
 Modeling Parkinson s disease: systems to test gene-environment interactions Jason Cannon, Ph.D. Pittsburgh Institute of Neurodegenerative Diseases University of Pittsburgh Outline Parkinson s disease (PD)
Modeling Parkinson s disease: systems to test gene-environment interactions Jason Cannon, Ph.D. Pittsburgh Institute of Neurodegenerative Diseases University of Pittsburgh Outline Parkinson s disease (PD)
Gene Therapy (2003) 10, & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved /03 $
 (2003) 10, 1721 1727 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0969-7128/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/gt REVIEW Gene therapy progress and prospects: Parkinson s disease EA Burton 1, JC Glorioso 2
(2003) 10, 1721 1727 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0969-7128/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/gt REVIEW Gene therapy progress and prospects: Parkinson s disease EA Burton 1, JC Glorioso 2
Chapter 8. Parkinsonism. M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University.
 Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
Chapter 8 Parkinsonism M.G.Rajanandh, Dept. of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. Definition of Parkinson s Disease Parkinson's disease is a progressive, neurodegenerative disease
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
The motor regulator. 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus
 The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
The motor regulator 1) Basal ganglia/nucleus Neural structures involved in the control of movement Basal Ganglia - Components of the basal ganglia - Function of the basal ganglia - Connection and circuits
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease
 Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Visualization and simulated animations of pathology and symptoms of Parkinson s disease Prof. Yifan HAN Email: bctycan@ust.hk 1. Introduction 2. Biochemistry of Parkinson s disease 3. Course Design 4.
Recent Advances in the cause and treatment of Parkinson disease. Anthony Schapira Head of Dept. Clinical Neurosciences UCL Institute of Neurology UCL
 Recent Advances in the cause and treatment of Parkinson disease Anthony Schapira Head of Dept. Clinical Neurosciences UCL Institute of Neurology UCL SOME BACKGROUND incidence rate (per 100.000 person years)
Recent Advances in the cause and treatment of Parkinson disease Anthony Schapira Head of Dept. Clinical Neurosciences UCL Institute of Neurology UCL SOME BACKGROUND incidence rate (per 100.000 person years)
Parkinson s Disease. Prevalence. Mark S. Baron, M.D. Cardinal Features. Clinical Characteristics. Not Just a Movement Disorder
 Prevalence Parkinson s Disease Mark S. Baron, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Movement Disorders Section VCU School of Medicine Common disorder Approaching 1% by 65 yrs of age, 2% by 80 yrs of age
Prevalence Parkinson s Disease Mark S. Baron, M.D. Associate Professor of Neurology Movement Disorders Section VCU School of Medicine Common disorder Approaching 1% by 65 yrs of age, 2% by 80 yrs of age
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
USING PRECISION MEDICINE TO HELP PATIENTS WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE. The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson s Research
 USING PRECISION MEDICINE TO HELP PATIENTS WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson s Research MJFF IS THE WORLD S LARGEST NONPROFIT FUNDER OF PD RESEARCH Our Mission We are
USING PRECISION MEDICINE TO HELP PATIENTS WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson s Research MJFF IS THE WORLD S LARGEST NONPROFIT FUNDER OF PD RESEARCH Our Mission We are
FOUNDATION OF UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S DISEASE
 FOUNDATION OF UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S DISEASE DEE SILVER M.D MOVEMENT DISORDER SPECIALIST MEDICAL DIRECTOR -- PARKINSON ASSOCIATION OF SAN DIEGO 1980 TO PRESENT SCRIPPS MEMORIAL HOSPITAL, LA JOLLA CA.
FOUNDATION OF UNDERSTANDING PARKINSON S DISEASE DEE SILVER M.D MOVEMENT DISORDER SPECIALIST MEDICAL DIRECTOR -- PARKINSON ASSOCIATION OF SAN DIEGO 1980 TO PRESENT SCRIPPS MEMORIAL HOSPITAL, LA JOLLA CA.
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
Connections of basal ganglia
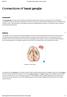 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Supplementary data Multiple hit hypotheses for dopamine neuron loss in Parkinson s disease
 Supplementary data Multiple hit hypotheses for dopamine neuron loss in Parkinson s disease David Sulzer Departments of Neurology, Psychiatry and Pharmacology, Black 309, 650 West, 168th Street, Columbia
Supplementary data Multiple hit hypotheses for dopamine neuron loss in Parkinson s disease David Sulzer Departments of Neurology, Psychiatry and Pharmacology, Black 309, 650 West, 168th Street, Columbia
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
The Biology of Parkinson s Disease and its treatments
 The Biology of Parkinson s Disease and its treatments Paola Sacchetti, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Director MS Neuroscience Department of Biology University of Hartford, CT psacchett@hartford.edu (860)768-5926
The Biology of Parkinson s Disease and its treatments Paola Sacchetti, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Director MS Neuroscience Department of Biology University of Hartford, CT psacchett@hartford.edu (860)768-5926
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms
 III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
III./3.1. Movement disorders with akinetic rigid symptoms III./3.1.1. Parkinson s disease Parkinson s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder worldwide after Alzheimer s disease.
Parkinson's Disease Glossary
 Parkinson's Disease Glossary A guide to the scientific language of Parkinson s disease for the non-scientist Acetylcholine: One of the chemical neurotransmitters in the brain and other areas of the central
Parkinson's Disease Glossary A guide to the scientific language of Parkinson s disease for the non-scientist Acetylcholine: One of the chemical neurotransmitters in the brain and other areas of the central
Genetic Parkinson s studying the few to treat the many
 Edinburgh Talk 01.12.12 Genetic Parkinson s studying the few to treat the many Miratul Muqit, Wellcome Trust Intermediate Fellow, Honorary Consultant Neurologist, MRC Protein Phosphorylation Unit, University
Edinburgh Talk 01.12.12 Genetic Parkinson s studying the few to treat the many Miratul Muqit, Wellcome Trust Intermediate Fellow, Honorary Consultant Neurologist, MRC Protein Phosphorylation Unit, University
TUESDAY, MARCH 28, 2017 WEDNESDAY, MARCH 29, 2017 WELCOME RECEPTION (VIENNA CITY HALL)
 KEY: PRE CONFERENCE SYMPOSIUM SPONSORED SYMPOSIUM SYMPOSIUM PLENARY LECTURE FORUM OTHER EVENT *PRE-REGISTRATION IS REQUIRED FOR THE INFORMAL NETWORKING WITH PROFESSOR LUNCH SESSION TUESDAY, MARCH 28, 2017
KEY: PRE CONFERENCE SYMPOSIUM SPONSORED SYMPOSIUM SYMPOSIUM PLENARY LECTURE FORUM OTHER EVENT *PRE-REGISTRATION IS REQUIRED FOR THE INFORMAL NETWORKING WITH PROFESSOR LUNCH SESSION TUESDAY, MARCH 28, 2017
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Abstracts and affiliations
 Dopamine Discovery Day August 30, 2012 Rikshospitalet Store auditorium, Oslo, Norway Organized by Linda H. Bergersen & Vidar Gundersen Institute of Basic Medical Sciences & Centre for Molecular Biology
Dopamine Discovery Day August 30, 2012 Rikshospitalet Store auditorium, Oslo, Norway Organized by Linda H. Bergersen & Vidar Gundersen Institute of Basic Medical Sciences & Centre for Molecular Biology
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM. Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine
 DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
DISORDERS OF THE MOTOR SYSTEM Jeanette J. Norden, Ph.D. Professor Emerita Vanderbilt University School of Medicine THE MOTOR SYSTEM To understand disorders of the motor system, we need to review how a
Overview. Overview. Parkinson s disease. Secondary Parkinsonism. Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits
 Overview Overview Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits The differential diagnosis of Parkinson s disease Primary vs. Secondary Parkinsonism Proteinopathies:
Overview Overview Parkinsonism: Motor symptoms associated with impairment in basal ganglia circuits The differential diagnosis of Parkinson s disease Primary vs. Secondary Parkinsonism Proteinopathies:
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
ARTICLE The scientific and clinical basis for the treatment of Parkinson disease (2009)
 ARTICLE The scientific and clinical basis for the treatment of Parkinson disease (2009) C. Warren Olanow, MD, FRCPC Matthew B. Stern, MD Kapil Sethi, MD Address correspondence to Dr. C. Warren Olanow,
ARTICLE The scientific and clinical basis for the treatment of Parkinson disease (2009) C. Warren Olanow, MD, FRCPC Matthew B. Stern, MD Kapil Sethi, MD Address correspondence to Dr. C. Warren Olanow,
Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease
 Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease FABIO G. TEIXEIRA,MIGUEL M.CARVALHO KRISHNA M. PANCHALINGAM ANA J.RODRIGUES
Impact of the Secretome of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Brain Structure and Animal Behavior in a Rat Model of Parkinson s Disease FABIO G. TEIXEIRA,MIGUEL M.CARVALHO KRISHNA M. PANCHALINGAM ANA J.RODRIGUES
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease
 Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Clinical Features and Treatment of Parkinson s Disease Richard Camicioli, MD, FRCPC Cognitive and Movement Disorders Department of Medicine University of Alberta 1 Objectives To review the diagnosis and
Parkinson's Disease Glossary
 Parkinson's Disease Glossary A guide to the scientific language of Parkinson s disease Acetylcholine: One of the chemical neurotransmitters in the brain and other areas of the central and peripheral nervous
Parkinson's Disease Glossary A guide to the scientific language of Parkinson s disease Acetylcholine: One of the chemical neurotransmitters in the brain and other areas of the central and peripheral nervous
Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson s disease
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Presented by Meagan Koepnick, Josh McDonald, Abby Narayan, Jared Szabo Mentored by Dr. Doorn
 Presented by Meagan Koepnick, Josh McDonald, Abby Narayan, Jared Szabo Mentored by Dr. Doorn Objectives What agents do we currently have available and what do we ideally need? What biomarkers exist for
Presented by Meagan Koepnick, Josh McDonald, Abby Narayan, Jared Szabo Mentored by Dr. Doorn Objectives What agents do we currently have available and what do we ideally need? What biomarkers exist for
05-Nov-15. Impact of Parkinson s Disease in Australia. The Nature of Parkinson s disease 21st Century
 Peter Silburn Professor Clinical Neuroscience University of Queensland Queensland Brain Institute Neurosciences Queensland Impact of in Australia Second most common neurodegenerative disorder Up to 64,000
Peter Silburn Professor Clinical Neuroscience University of Queensland Queensland Brain Institute Neurosciences Queensland Impact of in Australia Second most common neurodegenerative disorder Up to 64,000
The Parkinson s You Can t See
 The Parkinson s You Can t See We principally see the motor phenomena of Parkinson's disease, but is there an early stage without visible features? Might this provide a window for disease-modifying therapy?
The Parkinson s You Can t See We principally see the motor phenomena of Parkinson's disease, but is there an early stage without visible features? Might this provide a window for disease-modifying therapy?
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE. Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer
 DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
DRUG TREATMENT OF PARKINSON S DISEASE Mr. D.Raju, M.pharm, Lecturer PARKINSON S DISEASE (parkinsonism) is a neurodegenerative disorder which affects t h e b a s a l g a n g l i a - and is associated with
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
Strick Lecture 4 March 29, 2006 Page 1 Basal Ganglia OUTLINE- I. Structures included in the basal ganglia II. III. IV. Skeleton diagram of Basal Ganglia Loops with cortex Similarity with Cerebellar Loops
TUESDAY, MARCH 26, 2019 WEDNESDAY, MARCH 27, 2019
 KEY: PRE CONFERENCE SYMPOSIUM SPONSORED SYMPOSIUM SYMPOSIUM PLENARY LECTURE FORUM OTHER EVENT *PRE-REGISTRATION IS REQUIRED FOR THE INFORMAL NETWORKING WITH PROFESSOR LUNCH SESSION TUESDAY, MARCH 26, 2019
KEY: PRE CONFERENCE SYMPOSIUM SPONSORED SYMPOSIUM SYMPOSIUM PLENARY LECTURE FORUM OTHER EVENT *PRE-REGISTRATION IS REQUIRED FOR THE INFORMAL NETWORKING WITH PROFESSOR LUNCH SESSION TUESDAY, MARCH 26, 2019
NEUROPLASTICITY IN THE NIGROSTRIATAL SYSTEM OF MPTP-TREATED MICE AT THE PRESYMPTOMATIC AND EARLY SYMPTOMATIC STAGES OF PARKINSONISM
 NEUROPLASTICITY IN E NIGROSTRIATAL SYSTEM OF MPTP-TREATED MICE AT E PRESYMPTOMATIC AND EARLY SYMPTOMATIC STAGES OF PARKINSONISM Michael V. Ugrumov Institute of Developmental Biology RAS, Moscow, Russia
NEUROPLASTICITY IN E NIGROSTRIATAL SYSTEM OF MPTP-TREATED MICE AT E PRESYMPTOMATIC AND EARLY SYMPTOMATIC STAGES OF PARKINSONISM Michael V. Ugrumov Institute of Developmental Biology RAS, Moscow, Russia
TUESDAY, MARCH 26, 2019 WEDNESDAY, MARCH 27, 2019
 KEY: PRE CONFERENCE SYMPOSIUM SPONSORED SYMPOSIUM SYMPOSIUM PLENARY LECTURE FORUM OTHER EVENT *PRE-REGISTRATION IS REQUIRED FOR THE INFORMAL NETWORKING WITH PROFESSOR LUNCH SESSION TUESDAY, MARCH 26, 2019
KEY: PRE CONFERENCE SYMPOSIUM SPONSORED SYMPOSIUM SYMPOSIUM PLENARY LECTURE FORUM OTHER EVENT *PRE-REGISTRATION IS REQUIRED FOR THE INFORMAL NETWORKING WITH PROFESSOR LUNCH SESSION TUESDAY, MARCH 26, 2019
Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE
 Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE LEARNING OBJECTIVES The Course Participant will: 1. Be familiar with the pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease (PD) 2. Understand clinical
Scott J Sherman MD, PhD The University of Arizona PARKINSON DISEASE LEARNING OBJECTIVES The Course Participant will: 1. Be familiar with the pathogenesis of Parkinson s Disease (PD) 2. Understand clinical
Multiple choice questions: ANSWERS
 Multiple choice questions: ANSWERS Chapter 1. Redefining Parkinson s disease 1. Common non-motor features that precede the motor findings in Parkinson s disease (PD) include all of the following except?
Multiple choice questions: ANSWERS Chapter 1. Redefining Parkinson s disease 1. Common non-motor features that precede the motor findings in Parkinson s disease (PD) include all of the following except?
FDG-PET e parkinsonismi
 Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
Parkinsonismi FDG-PET e parkinsonismi Valentina Berti Dipartimento di Scienze Biomediche, Sperimentali e Cliniche Sez. Medicina Nucleare Università degli Studi di Firenze History 140 PubMed: FDG AND parkinsonism
First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy"
 Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
Parkinson's Disease First described by James Parkinson in his classic 1817 monograph, "An Essay on the Shaking Palsy" Parkinson s disease (PD) is a neurological disorder characterized by a progressive
USING LUHMES CELLS AS A MODEL SYSTEM TO STUDY DOPAMINERGIC NEURON CELL BIOLOGY. Tigwa H. Davis, Ph.D. Senior Scientist October 16, 2014
 USING LUHMES CELLS AS A MODEL SYSTEM TO STUDY DOPAMINERGIC NEURON CELL BIOLOGY Tigwa H. Davis, Ph.D. Senior Scientist October 16, 2014 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit organization with
USING LUHMES CELLS AS A MODEL SYSTEM TO STUDY DOPAMINERGIC NEURON CELL BIOLOGY Tigwa H. Davis, Ph.D. Senior Scientist October 16, 2014 About ATCC Founded in 1925, ATCC is a non-profit organization with
212 Index C-SB-13,
 Index A Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, treatment, 15 Age-associated memory impairment (AAMI), 5 Alzheimer s disease (AD), 40, 95 96 apolipoprotein E genotype and risk for, 58 cellular neurodegeneration
Index A Acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, treatment, 15 Age-associated memory impairment (AAMI), 5 Alzheimer s disease (AD), 40, 95 96 apolipoprotein E genotype and risk for, 58 cellular neurodegeneration
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Motor Systems: Basal Ganglia Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Two major descending s Pyramidal vs. extrapyramidal Motor cortex Pyramidal system Pathway for voluntary movement Most fibers originate
! slow, progressive, permanent loss of neurologic function.
 UBC ! slow, progressive, permanent loss of neurologic function.! cause unknown.! sporadic, familial or inherited.! degeneration of specific brain region! clinical syndrome.! pathology: abnormal accumulation
UBC ! slow, progressive, permanent loss of neurologic function.! cause unknown.! sporadic, familial or inherited.! degeneration of specific brain region! clinical syndrome.! pathology: abnormal accumulation
Learnings from Parkinson s disease: Critical role of Biomarkers in successful drug development
 Learnings from Parkinson s disease: Critical role of Biomarkers in successful drug development Ken Marek Coalition Against Major Diseases and FDA 2014 Annual Scientific Workshop Oct 2014 Disclosure Co-founder
Learnings from Parkinson s disease: Critical role of Biomarkers in successful drug development Ken Marek Coalition Against Major Diseases and FDA 2014 Annual Scientific Workshop Oct 2014 Disclosure Co-founder
Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity. Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS
 Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS singhs@buffalo.edu 716-829-2453 1 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS
Treatment of Parkinson s Disease and of Spasticity Satpal Singh Pharmacology and Toxicology 3223 JSMBS singhs@buffalo.edu 716-829-2453 1 Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS
Parkinson's Disease. Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology
 Parkinson's Disease Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology 18 February 2002 Parkinson Disease Neurological disease affecting over four million patients
Parkinson's Disease Robert L. Copeland, Ph.D. Howard University College of Medicine Department of Pharmacology 18 February 2002 Parkinson Disease Neurological disease affecting over four million patients
Parkinson Disease. Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC. Presented by: Ontario s Geriatric Steering Committee
 Parkinson Disease Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC Key Learnings Parkinson Disease (L. Kalia) Key Learnings Parkinson disease is the most common but not the only cause of parkinsonism Parkinson disease is
Parkinson Disease Lorraine Kalia, MD, PhD, FRCPC Key Learnings Parkinson Disease (L. Kalia) Key Learnings Parkinson disease is the most common but not the only cause of parkinsonism Parkinson disease is
Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers
 Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers 2018 Movement Disorders Half Day Symposium Elise Anderson MD Medical Co-Director, PBSI Movement Disorders 6/28/2018 1 Disclosures GE Speaker,
Evaluation of Parkinson s Patients and Primary Care Providers 2018 Movement Disorders Half Day Symposium Elise Anderson MD Medical Co-Director, PBSI Movement Disorders 6/28/2018 1 Disclosures GE Speaker,
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
outlined a path to the clinic for a stem cell-based therapy for PD. A consensus emerged among participants
 MEETING REPORTS Meeting Reports Proceedings: Cell Therapies for Parkinson s Disease From Discovery to Clinic ROSA CANET-AVILES, GEOFFREY P. LOMAX,ELLEN G. FEIGAL, CATHERINE PRIEST CIRM was established
MEETING REPORTS Meeting Reports Proceedings: Cell Therapies for Parkinson s Disease From Discovery to Clinic ROSA CANET-AVILES, GEOFFREY P. LOMAX,ELLEN G. FEIGAL, CATHERINE PRIEST CIRM was established
EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE
 EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE Katerina Markopoulou, MD, PhD Director Neurodegenerative Diseases Program Department of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem Clinical Assistant Professor
EMERGING TREATMENTS FOR PARKINSON S DISEASE Katerina Markopoulou, MD, PhD Director Neurodegenerative Diseases Program Department of Neurology NorthShore University HealthSystem Clinical Assistant Professor
Basal Ganglia. Today s lecture is about Basal Ganglia and it covers:
 Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Basal Ganglia Motor system is complex interaction between Lower motor neurons (spinal cord and brainstem circuits) and Upper motor neurons (pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts) plus two main regulators
Parkinson s Disease Update
 Parkinson s Disease Update Elise Anderson MD Providence Center for Parkinson s Disease October 26, 2017 11/6/2017 1 Disclosures GE Speaker, DaTSCAN 11/6/2017 2 Outline PD diagnosis Motor and nonmotor symptoms
Parkinson s Disease Update Elise Anderson MD Providence Center for Parkinson s Disease October 26, 2017 11/6/2017 1 Disclosures GE Speaker, DaTSCAN 11/6/2017 2 Outline PD diagnosis Motor and nonmotor symptoms
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
Mendelian forms of Parkinson s disease
 Mendelian forms of Parkinson s disease Thomas Gasser To cite this version: Thomas Gasser. Mendelian forms of Parkinson s disease. BBA - Molecular Basis of Disease, Elsevier, 2009, 1792 (7), pp.587. .
Mendelian forms of Parkinson s disease Thomas Gasser To cite this version: Thomas Gasser. Mendelian forms of Parkinson s disease. BBA - Molecular Basis of Disease, Elsevier, 2009, 1792 (7), pp.587. .
Seminar. Parkinson s disease
 Parkinson s disease Lorraine V Kalia, Anthony E Lang Lancet 2015; 386: 896 912 Published Online April 20, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/ S0140-6736(14)61393-3 Morton and Gloria Shulman Movement Disorders
Parkinson s disease Lorraine V Kalia, Anthony E Lang Lancet 2015; 386: 896 912 Published Online April 20, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/ S0140-6736(14)61393-3 Morton and Gloria Shulman Movement Disorders
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN
 Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
Parkinson s Academy Registrar Masterclass Sheffield DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS SARAH MARRINAN 17 th September 2014 Objectives Importance of age in diagnosis Diagnostic challenges Brain Bank criteria Differential
THIS IS NOT YOUR GRANDMOTHER S DISEASE: WHAT DOES BEING DIAGNOSED WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE MEAN TODAY?
 THIS IS NOT YOUR GRANDMOTHER S DISEASE: WHAT DOES BEING DIAGNOSED WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE MEAN TODAY? THURSDAY MARCH 14, 2019 REBECCA GILBERT, MD, PHD VICE PRESIDENT, CHIEF SCIENTIFIC OFFICER, APDA AMERICAN
THIS IS NOT YOUR GRANDMOTHER S DISEASE: WHAT DOES BEING DIAGNOSED WITH PARKINSON S DISEASE MEAN TODAY? THURSDAY MARCH 14, 2019 REBECCA GILBERT, MD, PHD VICE PRESIDENT, CHIEF SCIENTIFIC OFFICER, APDA AMERICAN
LUP. Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Biochimica et biophysica acta. This paper has been peerreviewed but
LUP Lund University Publications Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in Biochimica et biophysica acta. This paper has been peerreviewed but
Targeting the Progression of Parkinson s Disease
 Targeting the Progression of Parkinson s Disease Current Neuropharmacology, 2009, 7, 9-36 9 J.L. George 1, S. Mok 1, D. Moses 2, S. Wilkins 1, A.I. Bush 1, R.A. Cherny 1 and D.I. Finkelstein 1,* 1 The
Targeting the Progression of Parkinson s Disease Current Neuropharmacology, 2009, 7, 9-36 9 J.L. George 1, S. Mok 1, D. Moses 2, S. Wilkins 1, A.I. Bush 1, R.A. Cherny 1 and D.I. Finkelstein 1,* 1 The
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Genotypic and phenotypic overlaps in Parkinson s disease and parkinsonisms
 Genotypic and phenotypic overlaps in Parkinson s disease and parkinsonisms Enza Maria Valente CSS-Mendel Institute, Rome University of Salerno The «shaking palsy»: clinica features Involuntary tremulous
Genotypic and phenotypic overlaps in Parkinson s disease and parkinsonisms Enza Maria Valente CSS-Mendel Institute, Rome University of Salerno The «shaking palsy»: clinica features Involuntary tremulous
Neuroimaging and Neurostimulation: Going inside the black box
 Neuroimaging and Neurostimulation: Going inside the black box Benzi M. Kluger M.D., M.S. Director, Movement Disorders Center Associate Professor of Neurology & Psychiatry University of Colorado OUTLINE
Neuroimaging and Neurostimulation: Going inside the black box Benzi M. Kluger M.D., M.S. Director, Movement Disorders Center Associate Professor of Neurology & Psychiatry University of Colorado OUTLINE
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001
 BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
BIOL 4374/BCHS 4313 Cell Biology Exam #1 February 13, 2001 SS# Name This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. Good luck! 1. (2) The
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Dopamine Transporter Imaging with Single Photon Emission File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: dopamine_transporter_imaging_with_single_photon_emission_computed_tomography
Corporate Medical Policy Dopamine Transporter Imaging with Single Photon Emission File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: dopamine_transporter_imaging_with_single_photon_emission_computed_tomography
Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease
 What is Alzheimer s disease Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease, AD, is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys a person s memory and ability to learn, reason, make judgements,
What is Alzheimer s disease Fact Sheet Alzheimer s disease Alzheimer s disease, AD, is a progressive brain disorder that gradually destroys a person s memory and ability to learn, reason, make judgements,
Parkinson s UK Brain Bank
 Parkinson s UK Brain Bank From Brain to Breakthrough Dr George Gveric Manager 19 October 2018 Coordinated approach Donors Relatives Information Reporting Researchers Tissue supply Quality assurance Expertise
Parkinson s UK Brain Bank From Brain to Breakthrough Dr George Gveric Manager 19 October 2018 Coordinated approach Donors Relatives Information Reporting Researchers Tissue supply Quality assurance Expertise
Movement Disorders. Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology. Background. Myasthenia Gravis. Many Types
 Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Background Movement Disorders Psychology 372 Physiological Psychology Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. Listen to the audio lecture while viewing these slides Early Studies Found some patients with progressive weakness
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Brain Diseases I!
 Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases I - Parkinsonism! Bio 3411! Wednesday!! Lecture XIII. Brain Diseases - I.! 1! Brain Diseases I! NEUROSCIENCE 5 th ed! Page!!Figure!!Feature! 408 18.9 A!!Substantia Nigra in
Is Deep Brain Stimulation a Viable Treatment for Parkinson s Disease?
 Is Deep Brain Stimulation a Viable Treatment for Parkinson s Disease? Brocha Gold Brocha Gold Is majoring in Biology Abstract Treatment options for those suffering from Parkinson s Disease are as diverse
Is Deep Brain Stimulation a Viable Treatment for Parkinson s Disease? Brocha Gold Brocha Gold Is majoring in Biology Abstract Treatment options for those suffering from Parkinson s Disease are as diverse
Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease
 Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease Abstract The basal ganglia is a key control centre involved with the regulation of movement. It is therefore a primary interest
Down regulation of the HCN2 channel in rat models of Parkinson s disease Abstract The basal ganglia is a key control centre involved with the regulation of movement. It is therefore a primary interest
Drug Therapy of Parkinsonism. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Drug Therapy of Parkinsonism Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Parkinsonism is a progressive neurological disorder of muscle movement, usually
Drug Therapy of Parkinsonism Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Parkinsonism is a progressive neurological disorder of muscle movement, usually
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
 Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery for Parkinson s Disease Demystifying Medicine 24 January 2012 Kareem A. Zaghloul, MD, PhD Staff Physician, Surgical Neurology Branch NINDS Surgery for Parkinson s Disease
HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN. Nafisa Jadavji, PhD
 HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN Nafisa Jadavji, PhD NafisaJadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Introduction Brain Nutrition Peer Review Questions BREAK Dementia and Alzheimer's disease Parkinson s
HOW NUTRITION CHANGES THE AGING BRAIN Nafisa Jadavji, PhD NafisaJadavji@carleton.ca Lecture Outline Introduction Brain Nutrition Peer Review Questions BREAK Dementia and Alzheimer's disease Parkinson s
Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies. Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai
 Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai 1 Scope Modality of treatment Pathophysiology of PD and dopamine metabolism Drugs Are there
Parkinson s disease Therapeutic strategies Surat Tanprawate, MD Division of Neurology University of Chiang Mai 1 Scope Modality of treatment Pathophysiology of PD and dopamine metabolism Drugs Are there
Pushing the plasticity: The role of exercise in the management of neurological illness
 Pushing the plasticity: The role of exercise in the management of neurological illness Michael Gaetz Ph.D. Associate Professor, Kinesiology Department Faculty of Health Sciences University of the Fraser
Pushing the plasticity: The role of exercise in the management of neurological illness Michael Gaetz Ph.D. Associate Professor, Kinesiology Department Faculty of Health Sciences University of the Fraser
Clinical Cell Biology Organelles in Health and Disease
 Department of Ophthalmology University of Kiel, University Medical Center Director: Prof. Dr. Johann Roider Clinical Cell Biology Organelles in Health and Disease Prof. Dr. Alexa Klettner Clinical cell
Department of Ophthalmology University of Kiel, University Medical Center Director: Prof. Dr. Johann Roider Clinical Cell Biology Organelles in Health and Disease Prof. Dr. Alexa Klettner Clinical cell
