Sampled: 06/05/2017 Paramus, NJ Received: 06/13/2017 (201) Finalized: 07/27/2017. Anatomic Pathology
|
|
|
- Corey Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Owner: 240 Farrier Road,, Ithaca, NY Ph: Fax: Page 1 of 7 Oradell Animal Hospital Inc - (3382) Dr John Lucy 580 Winters Ave Sampled: 06/05/2017 Paramus, NJ Received: 06/13/2017 (201) Finalized: 07/27/2017 Anatomic Pathology Department of Biomedical Sciences Phone: Fax: Body, Whole Addendum (Pathology) Addendum Consultation Results: Dr. Andrew D. Miller, DVM, DACVP, a veterinary pathologist, was consulted for his opinion on this case. Dr. Miller agrees that the most significant changes are the granulomatous lymphadenitis noted in the mesenteric lymph node, and the pleuritis in the lung sections. The lymphadenitis is consistent with feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), based on the positive immunoreactivity of macrophages to feline coronavirus antigen. The rare positive immunoreactivity noted in the pleura appears to be equivocal, and is not consistent or striking enough to warrant a firm diagnosis of coronavirus within the pleural tissue. However, this does not exclude an FIP-related pleuritis, as coronavirus may be present in other areas not examined on histology. A differential diagnosis of the pleuritis, given its marked fibrinosuppurative component, would be a bacterial pleuritis. Due to the severe tissue artifact related to autolysis and freeze-thaw, determining the source of bacterial infection is not possible. It is possible that systemic immune suppression related to FIP predisposed this animal to secondary bacterial infection. Culture of frozen lung tissue is available if requested. However, culture may not yield a positive result, and if it does, it will only indicate the underlying bacteria involved; it cannot elucidate the source of the infection. The remaining changes are expected findings and are largely incidental. In addition to the lesions described in the original report, an adrenal cortical adenoma, composed of proliferative, well-differentiated adrenal cortical cells surrounded by a thin capsule, was noted. This lesion is incidental, and often seen in aged animals. The renal adenocarcinoma is a potentially significant lesion; however, there is enough remaining renal parenchyma unaffected by the tumor that it likely did not cause renal insufficiency, and there is no observed metastasis in any of the other examined tissues. The chronic interstitial nephritis may have caused clinical renal signs, but this is an expected lesion in aged cats, the etiology of which is uncertain. Finally, rare, well demarcated, lightly basophilic, homogenous, round deposits (Lafora bodies) are noted in multiple sections of brain. These are age-related changes with no pathologic significance. Dr. Teresa Southard, DVM, PhD, DACVP, a veterinary pathologist, was also consulted and concurs with these findings.
2 Page 2 of 7 Addendum Comments: A Masson's trichrome histochemical stain for collagen confirms mild pancreatic fibrosis. A panel of histochemical stains does not reveal bacterial or fungal organisms in areas of pleuritis. Histochemical Stain Results:Histochemical staining of sections of lung (slide 4) reveals the following: Gram for detection of bacteria: No bacterial organisms are observed in the examined sections. Gomori's methenamine silver (GMS) for detection of fungi: No fungal organisms are observed in the examined sections. Modified Steiner silver for detection of argyrophilic bacteria: No argyrophilic organisms are observed in the examined sections. A Masson's trichrome histochemical stain of a section of pancreas (slide 6) reveals focally coalescing tracts of mature deeply basophilic collagen coursing between multiple lobules. Necropsy, Final Final Report Final Diagnosis: Feline infectious peritonitis Thyroid adenomatous hyperplasia Hepatic biliary cystadenoma Hepatic lipidosis Renal adenocarcinoma Final Comment: Histologic changes and immunohistochemical staining confirm the clinical diagnosis of feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) in this cat and likely account for the demise of this cat. Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) is a fatal, progressive disease resulting from mutations of feline enteric coronavirus leading to systemic viral infection of macrophages. In this case FIP viral antigen is demonstrated within macrophages primarily in the mesenteric lymph node, but also in the pleural exudate, and likely account for the pleural effusion seen on gross examination. Histochemical stains to rule out the presence of bacterial and fungal agents in areas of pleuritis are pending and results will follow in an addendum to this report. Histological evidence of thyroid gland adenomatous hyperplasia, one of the most common proliferative diseases resulting in
3 Page 3 of 7 hyperthyroidism in cats, confirms the clinical diagnosis of hyperthyroidism leading to thyrotoxic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy seen on gross examination. The large liver mass seen on gross examination has histologic features consistent with a biliary cystadenoma, a common, benign neoplasm of cats. Additionally, hepatic lipidosis, a common sequela to prolonged anorexia is confirmed. The renal mass is a primary renal adenocarcinoma rather than a lymphoma as previously suggested from the gross examination. This renal adenocarcinoma is relatively small and unlikely to have clinical significance. The chronic lymphoplasmacytic interstitial nephritis with glomerulosclerosis is considered an incidental age-related finding, while the multifocal renal cortical infacts might be secondary to thromboembolism. A mild focus of fibrosis within the pancreas likely represents scarring from a previous pancreatitis; however, there is no evidence of acute pancreatitis in the sections of tissue examined. A histochemical stain to assess the degree of collagen deposition within the pancreas is pending and results will follow in an addendum to this report. Histologic Findings: Lungs: Moderate, generalized, acute fibrinous pleuritis Mesenteric lymph node: Severe, generalized granulomatous lymphadenitis with lymphoid depletion and fibrosis Right thyroid gland: Generalized adenomatous hyperplasia Left thyroid gland: Focal adenomatous hyperplasia Pancreas: Mild, focal pancreatic fibrosis Kidney: 1. Moderate, generalized, chronic lymphoplasmacytic interstitial nephritis with glomerulosclerosis 2. Renal adenocarcinoma 3. Multifocal, chronic renal cortical infarcts Liver: 1. Biliary cystadenoma 2. Moderate, multifocal, centrilobular hepatic lipidosis Histologic Description: The following tissues are examined: Slide 1: Liver, gallbladder
4 Page 4 of 7 Slide 2: Kidney, urinary bladder Slide 3: Spleen, adrenal gland, right thyroid gland, bone marrow Slide 4: Lung, left thyroid gland Slide 5: Heart Slide 6: Stomach, duodenum, pancreas, jejunum Slide 7: Cecum, colon, mesenteric lymph node Slide 8: Brain Slide 9: Brain Slide 10: Brain Slide 11: Eye Histopathologic changes are detected in these tissues: Liver (Slide 1, 3 sections): In two sections, the parenchyma is expanded and replaced by a well-demarcated, unencapsulated, non-infiltrating mass composed of low cuboidal and flattened polygonal cells arranged in tubules, acini, and cystic spaces on a robust, fibrous stroma. These cells have moderate to scant eosinophilic cytoplasm and central, round, basophilic nuclei with finely stippled chromatin. Anisokaryosis and anisocytosis are mild. Hepatocytes of the remaining hepatic parenchyma are expanded by large, round, well-demarcated, cytoplasmic clear vacuoles (lipidosis). Centrilobular hepatocytes are most frequently affected by lipidosis. Kidney (Slide 2, 3 section): In one section, the cortex is expanded by a large, well-demarcated, unencapsulated, non-infiltrating, moderately cellular nodule that comprises 50% of the section. This mass is composed of low cuboidal, polygonal cells arranged in loose trabeculae and rudimentary tubules on a robust fibrous matrix. Occasional tubules, mostly at the periphery, are dilated and filled with necrotic debris. The polygonal have central, dark nuclei with coarse chromatin and moderate, eosinophilic cytoplasm. Anisokaryosis and anisocytosis are mild. The adjacent cortical tissue is severely displaced and compressed by this mass. In other sections, scattered glomeruli are shrunken and irregular, with distinct loss of capillary loops (sclerosis). The Bowman s capsule of many glomeruli is mildly thickened. Throughout all sections, low to moderate numbers of lymphocytes and plasma cells infiltrate and expand the interstitium, forming loose cords and tight clusters. The interstitial fibrous connective tissue is generally thickened and expanded. In multiple sections, small, sharply demarcated regions of the cortex are shrunken, with tubular loss and close apposition of glomeruli and increased fibrous connective tissue (infarct). Right thyroid gland (Slide 3, 1 section): The entire section is composed of irregular tubules and acini that are variably dilated and filled with colloid, forming variably sized, dilated and folded follicles. In some areas, these tubules are markedly dilated, forming cystic follicles. These tubules and acini are lined by low cuboidal polygonal cells with moderate amounts of eosinophilic cytoplasm and central, dark, round nuclei with coarse chromatin. Adrenal gland (Slide 3, 1 section): The medulla is obscured by an expansile, well-demarcated, densely cellular nodule composed of large polygonal cells with abundant, variably sized, clear cytoplasmic vacuoles arranged in irregular islands and tight packets. These cells have small, dark nuclei with coarse chromatin. Anisokaryosis and anisocytosis are minimal.
5 Page 5 of 7 Bone marrow (Slide 3, 1 section): All lineages are represented. The myeloid:erythroid ratio is approximately 3:1 (myeloid hyperplasia). There are adequate megakaryocytes. Lungs (Slide 4, 4 sections): The pleural surfaces of all sections are generally expanded by a thick layer composed of fibrin and degenerate neutrophils. In some areas, this infiltrate extends into the underlying parenchyma. An immunohistochemical stain for feline enteric coronavirus antigen (feline infectious peritonitis virus) reveals cytoplasmic immunostainning of rare, small aggregates of macrophages within the pleural exudate. Left thyroid gland (Slide 4, 1 section): Approximately 70% of the examined section is slightly shrunken, with small follicles and mild depletion of colloid. In one area, comprising the remaining 30% of the parenchyma, the follicular cells are expanded and numeorus, forming loose tubules and variably sized, often folded follicles similar to those in the right thyroid. Pancreas (Slide 6, 1 section): A poorly demarcated region of the pancreas is expanded by large, thick tracts of coarse collagen, admixed with shrunken, irregular ducts. The exocrine acini are effaced and replaced in this area by the fibrosis. Mesenteric lymph node (Slide 8, 2 sections): The cortex is hypocellular with depleted follicles and replaced by abundant, hyalinized, fibrillar, eosinophilic material. The cortex and medulla are generally dissected by large, anastomosing tracts of fibrosis, obscuring the cortico-medullary junction and effacing normal sinus architecture. Immunohistochemical stain for feline enteric coronavirus antigen (feline infectious peritonitis virus) reveals cytoplasmic immunoreactivity of frequent, scattered, large aggregates of macrophages. Necropsy, Gross Gross Report Preliminary Diagnosis: Thyroid gland adenoma and contralateral atrophy Thyrotoxic cardiomyopathy Biliary cystadenoma Renal lymphoma Pleural effusion Preliminary Comment: The most significant gross finding is a severely enlarged left thyroid gland with concurrent atrophy of the right thyroid. Given the history of hyperthyroidism, this is consistent with a adenomatous hyperplasia or adenoma of the thyroid gland and excessive production of thyroxine. The increased thyroxine production by right thyroid results in a negative feed-back loop on the pituitary which in turn reduces thyroid-stimulating hormone, leading to atrophy of the contralateral gland. Autonomy of thyroid production in thyroid glands is caused by dysregulated proliferation of the follicular cells. In cats, the most common manifestation of this is adenomatous hyperplasia and overt adenomas. There are moderate changes in the heart consistent with pathologic hypertrophy. In cats, thyrotoxic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a common sequela to hyperthyroidism. The pleural effusion might represent an early manifestation of
6 Page 6 of 7 congestive heart failure related to the cardiomyopathy; however, an inflammatory process cannot be ruled out. The mass in the kidney is most consistent with lymphoma, one of the most common neoplasm of cats. While typically a metastatic lesion, primary renal lymphoma can occur in cats. The large liver mass is most consistent with a biliary cystadenoma, which are common, benign neoplasms of cats. Additionally, hepatic lipidosis is a common sequla to prolonged anorexia. The colonic impaction is relatively moderate, and might have cause some discomfort. Accessory spleens is an incidental finding that might be a congenital anomaly or a sequela to healing from previous splenic insult. Freeze-thawing of this cat prior to necropsy might have obscured subtle gross lesions; however, the gross findings in this cat are not consistent with feline infectious peritonitis. The significance of a positive coronavirus PCR assay result from the thoracic effusion is uncertain. Histopathologic examination is pending and results will follow in a final report. Gabor LG, et al (1998). Clinical and anatomical features of lymphosarcoma in 118 cats. Aust Vet J 76(11): Adler R and Wilson DW (1995). Biliary cystadenomas of cats. Vet Pathol 32(4): Gross Findings: Right thyroid gland: Adenoma Left thyroid gland: Moderate atrophy Heart: Moderate thyrotoxic hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Lung, thoracic cavity: Moderate, generalized, sub-acute fibrinous pleural effusion Peritoneum: Moderate sub-acute peritoneal effusion Left kidney: Lymphoma, presumptive Right and left kidneys: Moderate, generalized, chronic interstitial nephritis and fibrosis Liver: 1. Biliary cystadenoma 2. Mild, generalized hepatic lipidosis Colon and rectum: Moderate fecal impaction Spleen: Accessory spleen Gross Description: Examined is the body of frozen and thawed, 4.1 kg, 12-year old, spayed female, brown tabby Domestic shorthair cat, with a
7 Page 7 of 7 body condition score of 5/9 (Purina scale) and moderate postmortem autolysis. Around the nares and left aspect of muzzle is 2 ml of dark red gelatinous material (partially dried blood). Most of the teeth are missing with teeth 103, 104, 404 and 308 remaining (modified Triadan system). Teeth 103 and 104 are loose in the dental alveoli. All teeth are coated by a thick layer of pale tan to white, hard, amorphous material mostly at the base of the crown (calculus). There is a 4 cm circumferential shaved area on left antebrachium. Adhered to this is a piece of 2 cm circumferential white tape. There is a 7 x 8 cm shaved area on the lateral aspect of the right thorax. The ventral abdomen has a 10 x 14 cm shaved area slightly off center extending 6 cm laterally on the left from the umbilicus and 4 cm laterally on the right abdomen. There is an approximately 0.1 x 0.1 cm round skin defect approximately 2 cm cranial dorsal to the caudal mammary papilla (post mortem renal tru-cut biopsy). This defect is surrounded by faint red crust radiating 0.3 cm from the defect in all directions (dried blood). The abdominal cavity contains approximately 25 ml of orange-red, watery, turbid fluid (peritoneal effusion). On the diaphragmatic, cranial surface of the right lateral liver lobe is a 6 x 5 x 3 cm, well-demarcated, raised, locally extensive, soft, mottled tan to pink, slightly umbilicated mass. On cut section, the mass is slightly bulging, pale tan to white, and cystic (biliary cystadenoma). The liver is generally pale, with an enhanced reticular pattern. There are two spleens, a 7.5 x 3.0 cm and a 7.0 x 1.8 cm (accessory spleen). The larger spleen has a 1.0 x 0.3 cm, raised pink-red, friable, stringy, strand adhered to the serosal surface (fibrin). The aborad descending colon and rectum are moderately distended up to 2.8 cm in diameter with firm, dark green material extending 14 cm cranial from the rectum (fecal impaction). Proximal to this impaction, the contents are dark green and pasty, with green staining of the mucosa. The right kidney is moderately, diffusely pale tan-pink with a 1.0 x 0.2 cm focal depression and white-pink thickening of the capsule that does not peel off the cortex (nephritis). The left kidney is similar to the right kidney with a single round, well-demarcated, bulging 4 mm diameter nodule expanding the cortex. On cross-section, the nodule is pale tan to white, and soft to slightly firm. The renal pelvis is mildly irregular and scalloped. Radiating from the pelvis and dissecting the medulla are approximately a dozen thin, pale, firm striations. The cortex is slightly thinned, with an irregular subcapsular contour. The thoracic cavity contains approximately 15 ml of a watery, red, fluid. The visceral pleura of the lungs, the cranial and caudal mediastinum, and parietal pleura have a ground-glass dull surface with moderate, variable thickening and multiple, slightly adhered strands of a stringy, friable, yellow to tan material (fibrinous effusion). The right thyroid gland is 2.5 x 1.2 x 0.5 cm and weighs 2 g. The left thyroid gland is 1.2 x 0.5 x 0.3 cm. The heart weighs 22 g. The left ventricular free wall is 7 mm and the right ventricular free wall is 2 mm. There is a firm pale pink band extending from a left aortic semilunar cusp to the leaflet of the mitral valve (endocardial fibrosis).
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Inflammation Laboratory 1
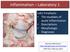 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 2. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: March 2012
 Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Describing and interpreting gross lesions. Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson
 Describing and interpreting gross lesions Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson How to Describe (and Interpret) Lesions Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Look at the specimen: Is it normal or abnormal
Describing and interpreting gross lesions Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson How to Describe (and Interpret) Lesions Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Look at the specimen: Is it normal or abnormal
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: April 2013
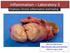 Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Pathology of the Alimentary Tract
 Pathology of the Alimentary Tract Lab 2: Lower alimentary tract SI, LI, cecum, and peritoneum GIST in the cecum of a dog Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 221: November, 2011 3 year
Pathology of the Alimentary Tract Lab 2: Lower alimentary tract SI, LI, cecum, and peritoneum GIST in the cecum of a dog Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 221: November, 2011 3 year
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung. Shannon Martinson,
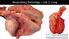 Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 9 month old DSH cat History: Poor doer with stunted growth One month of lethargy one day the
Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 9 month old DSH cat History: Poor doer with stunted growth One month of lethargy one day the
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System. Case studies
 Pathology of the Hematopoietic System Case studies Shannon Martinson, September 2015 Signalment: 9 yr-old MC cat Case Study 1 History: Cat had been anorexic and developed bleeding in the eyes Physical
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System Case studies Shannon Martinson, September 2015 Signalment: 9 yr-old MC cat Case Study 1 History: Cat had been anorexic and developed bleeding in the eyes Physical
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Histopath Laboratory 1 Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Goals: Examine Tissue and Identify the Organ Describe the lesion, grossly and histologically
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System - Lab.
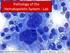 Pathology of the Hematopoietic System - Lab http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Shannon Martinson, September 2015 Case #1 Signalment: 96 kg gilt History: Pig from minimal disease herd. Sudden death Case
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System - Lab http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Shannon Martinson, September 2015 Case #1 Signalment: 96 kg gilt History: Pig from minimal disease herd. Sudden death Case
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Acute pneumonia in a cat
 Acute pneumonia in a cat Elspeth Milne, Anita Schwartz, Alasdair Stuart, Danielle Gunn-Moore, Kerry Simpson and Sionagh Smith, Division of Veterinary Clinical Sciences, University of Edinburgh, United
Acute pneumonia in a cat Elspeth Milne, Anita Schwartz, Alasdair Stuart, Danielle Gunn-Moore, Kerry Simpson and Sionagh Smith, Division of Veterinary Clinical Sciences, University of Edinburgh, United
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Disturbances of Circulation. Histopathology Lab #2 (Web)
 Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury. VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016
 Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION. Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta
 DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
DIABETES MELLITUS: COMPLICATION Benyamin Makes Dept. of Anatomic Pathology FMUI - Jakarta COMPLICATION OF DIABETES Susceptibility to infections including tuberculosis, pneumonia, pyelonephritis, and mucocutaneous
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Courtney S. Wait Signalment: 11 year old FS Labrador Retriever Presenting Complaint/History: The patient presented to the referring DVM for inappetance, vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
What s Your Diagnosis? Courtney S. Wait Signalment: 11 year old FS Labrador Retriever Presenting Complaint/History: The patient presented to the referring DVM for inappetance, vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Liver Lab #2. Bacterial Hepatitis
 Liver Lab #2 Bacterial Hepatitis Case: O12561-04. Adult ewe. Describe the lesion: Multifocal large nodules ranging in size from 1-3.5cm in greatest diameter are present within the liver and are filled
Liver Lab #2 Bacterial Hepatitis Case: O12561-04. Adult ewe. Describe the lesion: Multifocal large nodules ranging in size from 1-3.5cm in greatest diameter are present within the liver and are filled
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021)
 BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021) The thymus is of a pinkish-gray colour, soft, and lobulated
BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021) The thymus is of a pinkish-gray colour, soft, and lobulated
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
Chapter 21 The Lymphatic System Overview of the Lymphatic System The Lymphatic System Protects us against disease Lymphatic system cells respond to: Environmental pathogens Toxins Abnormal body cells,
Portal System & Lymphatic System. When the vein of any organ of the body does not open in the caval vein or heart.
 1. Introduction of portal system 2. Renal portal system 3. Hepatic portal system 4. Hypophysial portal system 5. Introduction of lymphatic system 6. The lymph 7. Lymph vessels 8. Lymph nodes 9. Lymphoid
1. Introduction of portal system 2. Renal portal system 3. Hepatic portal system 4. Hypophysial portal system 5. Introduction of lymphatic system 6. The lymph 7. Lymph vessels 8. Lymph nodes 9. Lymphoid
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, March 2017
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, March 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary injury and responses
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Extracellular degeneration
 Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
Extracellular degeneration By Dr. Hemn Hassan Othman PhD, Pathology Fall 2016 1/17/2017 1 Extracellular Degenerations I / Hyaline Degeneration (Hyalinization): The ward hyaline is derived from the Latin
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB
 Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB Paul Hanna (thanks to Dr s Aburto, Martinson & Fenton) Fall 2014 Slide 1 Spleen from a Beaver Give a morphologic diagnosis and possible etiology &
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB Paul Hanna (thanks to Dr s Aburto, Martinson & Fenton) Fall 2014 Slide 1 Spleen from a Beaver Give a morphologic diagnosis and possible etiology &
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG
 Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Exocrine vs. Endocrine Glands Hypophysis (Pituitary Gland) It lies in a cavity of the sphenoid bone the sella turcica Weighs about 0.5 g, and its normal dimensions in humans are about 10 x 13 x 6 mm.
Endocrine Lab. Heather Fenton VPM 222 November
 Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Almost any suspected tumor can be aspirated easily and safely. Some masses are more risky to aspirate including:
 DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
DOES THIS PATIENT HAVE CANCER? USING IN-HOUSE CYTOLOGY TO HELP YOU MAKE THIS DIAGNOSIS. Joyce Obradovich, DVM, Diplomate, ACVIM (Oncology) Animal Cancer & Imaging Center, Canton, Michigan Almost every
Ordering Physician. Collected REVISED REPORT. Performed. IgG IF, Renal MCR. Lambda IF, Renal MCR. C1q IF, Renal. MCR Albumin IF, Renal MCR
 RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
RenalPath Level IV Wet Ts IgA I Renal IgM I Renal Kappa I Renal Renal Bx Electron Microscopy IgG I Renal Lambda I Renal C1q I Renal C3 I Renal Albumin I Renal ibrinogen I Renal Mayo Clinic Dept. of Lab
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues
 Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
Chapter 1: Cells and Tissues Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life Cells are the building blocks of all living things Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
What s your diagnosis?
 What s your diagnosis? Signalment: 9 year old MC 2.7 kg Papillion Presenting Complaint: Presented for work up of anorexia and vomiting History: He had presented to cardiology for work up of a grad IV/VI
What s your diagnosis? Signalment: 9 year old MC 2.7 kg Papillion Presenting Complaint: Presented for work up of anorexia and vomiting History: He had presented to cardiology for work up of a grad IV/VI
REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION
 Director: Dr. Carole Bolin 4125 Beaumont Road Lansing, MI 48910-8104 Phone: 517-353-1683 Fax: 517-353-5096 www.animalhealth.msu.edu REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Client: White Shepherd Genetics- (295483)
Director: Dr. Carole Bolin 4125 Beaumont Road Lansing, MI 48910-8104 Phone: 517-353-1683 Fax: 517-353-5096 www.animalhealth.msu.edu REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Client: White Shepherd Genetics- (295483)
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #1 Key
 2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #1 Key Test 1, Slide 1. Tissue from a dog. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Prostate gland: Multifocally and extensively infiltrating the prostate gland (1 pt.), and
2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #1 Key Test 1, Slide 1. Tissue from a dog. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Prostate gland: Multifocally and extensively infiltrating the prostate gland (1 pt.), and
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS
 MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES,
MICROSTRUCTURES SMALL INTESTIN LARGE INTESTIN PANCREAS LIVER GALLBLADDER SALIVARY GLANDS ADRENALS THYROID AND PARATHYROID GLANDS HUMAN ANATOMY: MICROSTRUCTURES CLASSIFICATION: LOCATION AND BOUNDARIES,
Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
2/19/2018. Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues. What is Lymph?
 Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues Lymphatic system a transport system for tissue fluids 1. elaborate network of one-way drainage vessels returning lymph to systemic circulation 2. Lymph:
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR
 Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Pathology lab 4 DONE BY : MORAD ABU QAMAR Chronic interstitial inflammation, lung Certain etiologic agents such as viruses are more likely to lead to chronic inflammation, as seen here in the lung of a
Bill, here is the final report on this bear. There really wasn't any evidence that this bear had 'anything wrong with it.'
 From: Ramsay, Edward Charles Date: Wed, Sep 26, 2018 at 7:43 AM Subject: [EXTERNAL] Fw: Lab Results for [28-99-03] BEAR 09/16/18 ~ GREAT SMOKY MTN NTL PA To: Bill Stiver
From: Ramsay, Edward Charles Date: Wed, Sep 26, 2018 at 7:43 AM Subject: [EXTERNAL] Fw: Lab Results for [28-99-03] BEAR 09/16/18 ~ GREAT SMOKY MTN NTL PA To: Bill Stiver
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99 Presenting Complaint: Acute onset of lethargy Vomited twice (partially digested food)
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99 Presenting Complaint: Acute onset of lethargy Vomited twice (partially digested food)
Surgical Pathology Report
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Pathology Shreveport, Louisiana Accession #: Collected: Received: Reported: 6/1/2012 09:18 6/2/2012 09:02 6/2/2012 Patient Name: Med. Rec.
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I. A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin.
 EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
EXPERIMENTAL THERMAL BURNS I A study of the immediate and delayed histopathological changes of the skin. RJ Brennan, M.D. and B. Rovatti M.D. The purpose of this study was to determine the progressive
LADIS Case of the Month
 November 2018 LADIS Case of the Month Drs Valentin Janvier and Brieuc Cossic Hospital for Animals and Animal Health Diagnostic Center Signalment and presenting complaint 13 year old Thoroughbred gelding
November 2018 LADIS Case of the Month Drs Valentin Janvier and Brieuc Cossic Hospital for Animals and Animal Health Diagnostic Center Signalment and presenting complaint 13 year old Thoroughbred gelding
Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology. Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD
 Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD Too many or... Tumour herniation through a torn capsule simulating capsular invasion fibrous capsule with a sharp discontinuity, suggestive
Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD Too many or... Tumour herniation through a torn capsule simulating capsular invasion fibrous capsule with a sharp discontinuity, suggestive
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System
 Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
Lymph I: The Peripheral Lymph System Peripheral = Secondary Primary Immune Organs = bone marrow, thymus Site of maturation of cells of the immune system Secondary Immune Organs = Nodes, MALT, spleen Filter
LYMPHOID ORGANS. Dr. Iram Tassaduq
 LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
LYMPHOID ORGANS Dr. Iram Tassaduq COMPONENTS OF IMMUNE SYSTEM Lymphocytes Diffuse Lymphatic Tissue Lymphatic Nodules Lymph node Spleen Bone marrow Thymus Functions of Immune System Has the ability to distinguish
Cell injury, adaptation and death. Unite one Second Lab.
 Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Compact bone; Many parallel Haversian canals contain: small blood vessels. very small nerve. Interconnected by Volkmann s canals.
 Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Special characteristics of COMPACT BONE (dense bone) Thick; well vascularized Osteocytes and lamellae Concentric rings around blood vessels Most bones: outer compact bone inner spongy bone Marrow cavity
Lymphoma. Types of Lymphoma. Clinical signs
 Lymphoma Lymphoma is a tumour originating from lymphoid tissue, either nodal (lymph ) or extranodal (thymus, spleen, mucosa, conjunctiva, or skin-associated lymphoid tissue). It is one of the most common
Lymphoma Lymphoma is a tumour originating from lymphoid tissue, either nodal (lymph ) or extranodal (thymus, spleen, mucosa, conjunctiva, or skin-associated lymphoid tissue). It is one of the most common
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN. VMB 960 March 25, 2013
 GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN VMB 960 March 25, 2013 REFERENCE Chapters 35-36 Pages 650-678 Chapter 37 Pages 694-701 Chapter 3 Pages 38-49 OBJECTIVES Radiography and Ultrasound
GENERAL ABDOMINAL IMAGING PERITONEAL SPACE, PANCREAS, & SPLEEN VMB 960 March 25, 2013 REFERENCE Chapters 35-36 Pages 650-678 Chapter 37 Pages 694-701 Chapter 3 Pages 38-49 OBJECTIVES Radiography and Ultrasound
Disclosures. Parathyroid Pathology. Objectives. The normal parathyroid 11/10/2012
 Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
The Lymphatic System
 The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
The Lymphatic System The Lymphatic Systems Overview General Functions Organization Components Lymphatic System General Functions Transportation Excess fluid from capillary exchange Fats & fat soluble vitamins
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Thoracic Cavity and Tumors of Lung and Pleura
 Tutorial Module 6 Thoracic Cavity and Tumors of Lung and Pleura Alfonso López Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Sept 28, 2014 Thoracic Cavity There are anatomical differences
Tutorial Module 6 Thoracic Cavity and Tumors of Lung and Pleura Alfonso López Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Sept 28, 2014 Thoracic Cavity There are anatomical differences
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1
 PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Gland Cytology
 Salivary Gland Cytology Diagnostic challenges and potential pitfalls Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic FNA Salivary Gland Lesions Indications Distinguish
Salivary Gland Cytology Diagnostic challenges and potential pitfalls Tarik M. Elsheikh, MD Professor and Medical Director Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic FNA Salivary Gland Lesions Indications Distinguish
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98
 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.
 المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
المرحلة الثالثة م. هالة عباس ناجي Ischaemia It means local anemia, it is characterized by a decrease amount of blood in an organ or region. Causes of Ischemia: *1.External pressure upon an artery e.g:
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract. Shannon Martinson, April 2016
 Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Pathology of the Liver and Biliary Tract 5 Diseases of the Biliary Tract Shannon Martinson, April 2016 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ OUTLINE Normal anatomy & function Hepatobiliary Injury and responses
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
 Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseud
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA
 Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA Jack Yang, MD Department of Pathology, Medical University of South Carolina Objectives Understand the indication of EUS
Pancreatitis: A Potential Pitfall in Endoscopic Ultrasound Guided Pancreatic FNA Jack Yang, MD Department of Pathology, Medical University of South Carolina Objectives Understand the indication of EUS
Urinary System VASTACCESS, INC.
 Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease
 Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
Glomerular pathology in systemic disease Lecture outline Lupus nephritis Diabetic nephropathy Glomerulonephritis Associated with Bacterial Endocarditis and Other Systemic Infections Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
