CT of Diffuse Tracheal Diseases
|
|
|
- Adelia Robbins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
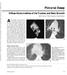
1 Residents Section Structured Review rticle hung et al. T of the Trachea and entral irways Residents Section Structured Review rticle Downloaded from by on 02/15/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Residents inradiology Jonathan H. hung 1 Jeffrey P. Kanne 2 Matthew D. Gilman 1 hung JH, Kanne JP, Gilman MD Keywords: Mounier-Kuhn syndrome, saber-sheath trachea, trachea, tracheal stenosis, tracheomalacia, Wegener granulomatosis DOI: /JR Received December 23, 2009; accepted after revision February 14, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, 55 Fruit St., FND-202, oston, M ddress correspondence to M. D. Gilman (mgilman@partners.org). ME This article is available for ME credit. See for more information. WE This is a Web exclusive article. JR 2011; 196:W240 W X/11/1963 W240 merican Roentgen Ray Society T of Diffuse Tracheal Diseases R adiologists can be instrumental in the diagnosis of tracheal abnormalities. Patients are often initially misdiagnosed with asthma or other obstructive lung disease because there is considerable overlap among the clinical presentation of these ailments and diffuse tracheal diseases. lthough the trachea can be imaged with chest radiography or fluoroscopy, T is the imaging test of choice to evaluate the trachea and central airways. MDT provides high-resolution images that can be used to generate multiplanar reformations, minimum intensity projections, 3D volume-rendered images, and virtual bronchoscopic images. In this article, we will illustrate T findings of diffuse nonmalignant tracheal diseases, emphasizing key differences that aid in diagnosis (Table 1). Key Points 1. T is currently the primary noninvasive examination to evaluate the trachea because it offers multiplanar capabilities, evaluates the morphology of the tracheal wall and lumen, and can be acquired in seconds. 2. The trachea is supported by -shaped cartilaginous rings anteriorly; the posterior trachea is primarily supported by the thin trachealis muscle. 3. The lunate-shaped trachea on inspiration is highly suggestive of tracheomalacia. 4. Traditionally, collapse of greater than 50% of the trachea during expiration was defined as tracheomalacia; however, recent evidence suggests that greater than 50% dynamic expiratory collapse can be seen in healthy patients. 5. In saber-sheath trachea, only the coronal diameter of the intrathoracic trachea is narrowed; primarily men with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease are affected. 6. The posterior wall of the trachea and the central bronchi are classically spared in both relapsing polychondritis and tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica. However, the presence of focal coarse calcification and ossification is highly suggestive of tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica rather than relapsing polychondritis. 7. Nodular calcification of the trachea is common in tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica and amyloidosis. However, amyloidosis tends to involve the airway concentrically, as opposed to tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica which spares the posterior wall. 8. Wegener granulomatosis most often affects the subglottic trachea but can be diffuse or multifocal. 9. Mounier-Kuhn syndrome is unique among the diffuse tracheal diseases in that it results in diffuse airway dilatation. Diverticula project between the cartilaginous rings giving the trachea and proximal bronchi a corrugated appearance. Normal natomy The trachea is composed of approximately shaped anterior cartilaginous rings that support the trachea during expiration. n inner mucosal layer, a submucosal layer, cartilage and muscle, and an adventitial layer comprise the tracheal wall. The posterior wall is formed primarily by the thin trachealis muscle, which lacks cartilaginous support (Fig. 1). The coronal diameter of the normal trachea ranges from 13 to 25 mm in men and from 10 to 21 mm in women, and the sagittal diameter of the normal trachea ranges from 13 to 27 mm in men and from 10 to 23 mm in women [1]. t end expiration, the trachea normally decreases in cross-sectional area, primarily from anterior movement of the posterior wall; there is wide variation in the degree of tracheal expiratory collapse [2, 3]. The arterial supply W240 JR:196, March 2011
2 T of the Trachea and entral irways Downloaded from by on 02/15/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved TLE 1: Imaging Findings of Various Diffuse Tracheal Diseases Tracheal Disease Tracheomalacia Saber-sheath trachea Relapsing polychondritis Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica myloidosis Wegener granulomatosis Mounier-Kuhn syndrome Sarcoidosis T ppearance Severe expiratory collapse of the tracheal lumen; lunate-shaped trachea Decreased coronal diameter with concomitant increase in sagittal diameter Thickening of the cartilaginous trachea with sparing of the posterior membrane alcified or ossified nodules in the cartilaginous trachea with sparing of the posterior membrane alcified or ossified nodular or concentric tracheal wall thickening ircumferential tracheal wall thickening or cartilage defects; subglottic region most often involved Tracheal diameter > 3 cm; main bronchial diameter > 2.4 cm; scalloping of tracheal wall and diverticula Secondary tracheal narrowing from lymphadenopathy or primary tracheal narrowing from tracheal noncaseating granulomas of the trachea is derived from a number of sources including the inferior thyroid artery, the bronchial arteries, and the intercostal arteries. Nonpathologic senescent tracheal calcification is more common in women and tends to be diffuse; calcification occurs along the normal contour of the trachea. Nodular focal calcification suggests underlying disease. Tracheomalacia Tracheomalacia arises from weakness of the tracheobronchial walls and hypotonia in the myoelastic elements. In patients with tracheomalacia, collapse of the intrathoracic trachea secondary to increased intrathoracic pressure during expiration is characteristic and is accentuated during forced expiration [1]. auses of tracheomalacia include long-term intubation or other trauma, congenital abnormalities, chronic extrinsic compression (vascular ring or sling), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic inflammation, and infection [1]. Traditionally, collapse of greater than 50% of the trachea on T during expiration was defined as tracheomalacia [1] (Fig. 2). Tracheal Narrowing Wall Thickened Wall alcification haracteristically, the posterior membranous trachea bows anteriorly, producing an upside down U-shaped air column on transverse T termed the frown sign [4] (Fig. 2). However, recent evidence suggests that tracheal collapse of greater than 50% during dynamic expiration can be seen in up to 78% of healthy patients [3]. In a minority of patients, the trachea may have a lunate configuration during inspiration that is, the trachea is characterized by a coronal diameter that is greater than the sagittal diameter. This finding is highly suggestive of tracheomalacia and can be corroborated with dynamic expiratory T [4] (Fig. 3). In cases not resulting from another diffuse tracheal disease such as relapsing polychondritis or Wegener granulomatosis, the tracheal wall usually has a normal thickness, thereby helping differentiate tracheomalacia from other diffuse tracheal diseases [1]. Saber-Sheath Trachea Saber-sheath trachea is a common tracheal abnormality occurring almost exclusively Useful Differentiators Yes No No Tracheal collapse; history of predisposing condition or trauma Yes No No haracteristic bullet-shaped trachea on axial T; history or imaging findings suggesting chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Yes Yes Sometimes Sparing of the posterior trachea; cartilaginous abnormalities of the ears or nose Yes Yes lways Nodular calcified or nodular ossified tracheal wall thickening sparing the posterior tracheal membrane and superior trachea Yes Yes Often present oncentric calcified or ossified nodular or concentric wall thickening without posterior sparing; may involve the larynx and upper trachea Yes Yes No Subglottic narrowing when focal; history of sinus or renal disease, pulmonary cavitary nodules, or pulmonary hemorrhage No No No Only diffuse tracheal abnormality resulting in both anteroposterior and lateral tracheal dilatation Yes Yes Yes Hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy; perilymphatic pulmonary nodules Inflammatory bowel disease Diffuse or focal tracheal narrowing Yes Yes No History of inflammatory bowel disease or chronic abdominal pain in men with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [1]. The extrathoracic trachea has a normal shape. However, the intrathoracic trachea shows a marked decrease in coronal diameter and an associated increase in sagittal diameter without tracheal wall thickening (Fig. 4). This deformity of the trachea is believed to result from repeated injury to the intrathoracic trachea from chronic coughing. Initially, changes are noted at only the thoracic inlet but can involve the entire intrathoracic trachea over time. Other smoking-related conditions may be present such as emphysema, respiratory bronchiolitis, and lung cancer. Relapsing Polychondritis Relapsing polychondritis (RP) is an autoimmune disease that affects cartilaginous structures such as the nose, ear, and laryngotracheobronchial tree. irway involvement occurs in up to half of patients, with pneumonia being the most common cause of death [5]. On T, RP is characterized by increased attenuation and thickening of the anterior and JR:196, March 2011 W241
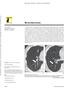
3 hung et al. Downloaded from by on 02/15/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old man with history of wheezing and shortness of breath. and, ontrast-enhanced chest T images show increased ratio of coronal-to-sagittal tracheal diameters (arrows). This finding is characteristic of lunate trachea in this patient with tracheomalacia. Fig. 1 Normal trachea., Diagram of normal trachea in axial plane shows discontinuity of posterior aspect of cartilaginous ring. Posterior wall of trachea is supported by trachealis muscle., xial T image of 55-year-old woman with normal trachea shows typical inverted U-shaped appearance of trachea. Fig year-old man with neck pain after selfinflicted head trauma., Unenhanced T image shows normal tracheal caliber in extrathoracic upper chest., T image shows severe collapse of intrathoracic trachea on expiration; this finding is highly suggestive of tracheomalacia., Difference in caliber of intrathoracic (thick white arrow) and extrathoracic (thin white arrow) trachea is illustrated on sagittal reformation. Incidental note is made of ossification (black arrows) of posterior longitudinal ligament. lateral walls of the large airways and concomitant destruction of the cartilaginous tracheobronchial rings with sparing of the posterior wall [6] (Fig. 5). Tracheomalacia and large airways stenosis may also be present. Tracheobronchopathia Osteochondroplastica Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica is characterized by the development of osseous and cartilaginous nodules in the submucosa of the lower two thirds of the trachea and central bronchi. On T, nodules typically measuring 1 3 mm arise from the cartilaginous rings and protrude into the airway lumen; the location of these nodules is sometimes better depicted with virtual bronchoscopy. Tracheomalacia does not occur, although an association with sabersheath trachea has been described [7]. Similar W242 JR:196, March 2011
4 T of the Trachea and entral irways Downloaded from by on 02/15/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old man with long history of smoking and chronic cough. ontrast-enhanced T image shows increased anteroposterior-to-lateral dimensions of trachea (thick arrow) from smokingrelated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. This finding is characteristic of saber-sheath trachea. Left upper lobe bronchogenic carcinoma (thin arrow) is present. to RP, the posterior walls of the trachea and bronchi are spared. However, the presence of focal coarse calcification and ossification (Fig. 6) is more typical of tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica than RP. myloidosis Tracheobronchial amyloidosis is the most common subtype of thoracic amyloidosis (Fig. 7). T shows diffuse nodular thickening of the trachea and main bronchi, often involving the subglottic trachea. ronchial stenosis or occlusion may result in lobar or segmental atelectasis [8]. Nodular calcified regions within the trachea are common, as in Fig year-old man with history of asthma presents with shortness of breath and cough., ontrast-enhanced T images of chest show smooth thickening (white arrows) of trachea with posterior sparing (black arrows); these findings are most consistent with relapsing polychondritis. tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica. myloidosis typically involves the airway concentrically, whereas tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica and RP characteristically spare the posterior tracheal and bronchial walls. In addition, amyloidosis may affect the larynx, pharynx, and superior trachea in contrast to tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica [9]. Wegener Granulomatosis Wegener granulomatosis is an idiopathic necrotizing granulomatous vasculitis that can affect patients of any age. The upper airways are almost always affected; the lungs and kidneys are involved in most patients (90% and 80%, respectively) [10]. Elevation of cytoplasmic antineutrophil antibodies against protease 3 in cytoplasmic granule titers is common and reflects disease activity. Fig year-old woman with chronic cough., Unenhanced T images show nodular, partially calcified, irregular thickening of trachea and main bronchi (arrows) with posterior sparing; these findings are consistent with tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica. JR:196, March 2011 W243
5 hung et al. Fig year-old woman with history of tracheal amyloidosis. and, xial () and coronal () contrast-enhanced T images of chest show diffuse circumferential thickening (arrows) of trachea. Downloaded from by on 02/15/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old man with chest pain and cough., ontrast-enhanced T image of lower neck shows circumferential soft-tissue thickening and smooth narrowing of subglottic trachea (arrow)., Three-dimensional reconstruction of trachea and proximal airways shows smooth narrowing of subglottic trachea (arrow)., T image obtained using lung window settings shows cavitary lesion in right upper lobe (arrow) in this patient with Wegener granulomatosis. On T, the trachea and main bronchi may be diffusely or focally circumferentially thickened; subglottic stenosis occurs in approximately 25% of patients and bronchial stenosis in about 18% of patients [11] (Fig. 8). Peripheral bronchial narrowing, lobar and segmental atelectasis, or bronchiectasis may also be present. oexistent pulmonary nodules and masses, which are sometimes cavitary; consolidation; and ground-glass opacities may suggest Wegener granulomatosis. Mounier-Kuhn Syndrome Mounier-Kuhn syndrome (tracheobronchomegaly) is unique among the diffuse tracheal diseases in that it is characterized by diffuse airway dilatation. Tracheobronchomegaly arises from either a congenital abnormality or atrophy of the connective tissue of the trachea and central bronchi. tracheal diameter of greater than 3 cm and mainstem bronchi diameters of greater than 2.4 cm are highly suggestive of Mounier-Kuhn syndrome [12, 13]. road diverticula may project between the cartilaginous rings, giving the trachea and proximal bronchi a corrugated appearance (Fig. 9). Mild tracheal dilatation W244 JR:196, March 2011
6 T of the Trachea and entral irways Downloaded from by on 02/15/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved may also occur in the setting of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, although differentiation from Mounier-Kuhn syndrome is usually readily made. Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is an idiopathic systemic disease characterized by the formation of noncaseating hyalinizing granulomas in a variety of tissues including the lungs and airways. Hilar Fig year-old man with history of melanoma., ontrast-enhanced T image of chest shows diffuse dilatation of trachea., oronal reformation shows diffuse central bronchiectasis., Sagittal reformation shows tracheal corrugation (arrows). Overall, findings are consistent with Mounier-Kuhn syndrome. Fig year-old man with shortness of breath and history of sarcoidosis. and, ontrast-enhanced T images of chest show partially calcified, irregular, nodular thickening of trachea (arrows). Tracheal lumen is narrow and abnormal in shape. and mediastinal lymphadenopathy, lung nodules in a perilymphatic distribution, bronchovascular bundle thickening with or without fibrosis, and ground-glass opacities are common T manifestations of sarcoidosis. Large airway involvement, on the other hand, is very uncommon. irway abnormalities may result from extrinsic compression by adjacent diseased lymph nodes or from primary infiltration of the airway walls with noncaseating granulomas [6] (Fig. 10). Upper tracheal and laryngeal involvement is more common than distal central airway involvement [6]. Inflammatory owel Disease Tracheal or bronchial involvement in inflammatory bowel disease is uncommon, often occurring late in the course of disease. Pulmonary manifestations include bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, obliterative JR:196, March 2011 W245
7 hung et al. Downloaded from by on 02/15/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig year-old woman with history of rohn disease. and, Unenhanced T images of chest show circumferential, irregular thickening of trachea (arrows). Mid and lower tracheal lumen is mildly narrowed. bronchiolitis, interstitial fibrosis, and large airway disease [14]. Involvement of the large airways manifests on T as diffuse or focal large airway narrowing. The tracheal wall may be smoothly or irregularly thickened (Fig. 11). This diagnosis should be considered in those presenting with asthma-like symptoms with a history of inflammatory bowel disease or with chronic gastrointestinal complaints. FOR YOUR INFORMTION onclusions Traditionally, the trachea has been an afterthought on noninvasive imaging studies. MDT is the imaging test of choice to evaluate the trachea and central airways because of its high spatial resolution and ability to produce a variety of reformations. Furthermore, T can show abnormalities of the tracheal lumen, tracheal walls, and immediate surrounding tissues. dditionally, tracheal diseases may be misdiagnosed as asthma by the clinician. The radiologist is often the first to suggest the diagnosis of a diffuse tracheal disease and can often suggest a single diagnosis. In cases when the diagnosis is unclear, T can serve as a guide for bronchoscopic evaluation and transbronchial biopsy. This article is available for ME credit. See for more information. References 1. oiselle P. Imaging of the large airways. lin hest Med 2008; 29: Stern E, Graham, Webb W, Gamsu G. Normal trachea during forced expiration: dynamic T measurements. Radiology 1993; 187: oiselle P, O Donnell, ankier, et al. Tracheal collapsibility in healthy volunteers during forced expiration: assessment with multidetector T. Radiology 2009; 252: oiselle P, Ernst. Tracheal morphology in patients with tracheomalacia: prevalence of inspiratory lunate and expiratory frown shapes. J Thorac Imaging 2006; 21: Michet J, McKenna, Luthra H, O Fallon W. Relapsing polychondritis: survival and predictive role of early disease manifestations. nn Intern Med 1986; 104: Kwong JS, Müller NL, Miller RR. Diseases of the trachea and main-stem bronchi: correlation of T with pathologic findings. RadioGraphics 1992; 12: Restrepo S, Pandit M, Villamil M, Rojas I, Perez J, Gascue. Tracheobronchopathia osteochondroplastica: helical T findings in 4 cases. J Thorac Imaging 2004; 19: Prince J, Duhamel D, Levin D, Harrell J, Friedman P. Nonneoplastic lesions of the tracheobronchial wall: radiologic findings with bronchoscopic correlation. RadioGraphics 2002; 22[Spec No]: S215 S Gilad R, Milillo P, Som P. Severe diffuse systemic amyloidosis with involvement of the pharynx, larynx, and trachea: T and MR findings. JNR 2007; 28: nanthakrishnan L, Sharma N, Kanne J. Wegener s granulomatosis in the chest: high-resolution T findings. JR 2009; 192: Lohrmann, Uhl M, Kotter E, urger D, Ghanem N, Langer M. Pulmonary manifestations of Wegener granulomatosis: T findings in 57 patients and a review of the literature. Eur J Radiol 2005; 53: Webb EM, Elicker M, Webb WR. Using T to diagnose nonneoplastic tracheal abnormalities: appearance of the tracheal wall. JR 2000; 174: Marom E, Goodman P, Mcdams H. Diffuse abnormalities of the trachea and main bronchi. JR 2001; 176: Spira, Grossman R, alter M. Large airway disease associated with inflammatory bowel disease. hest 1998; 113: W246 JR:196, March 2011
Pictorial Essay. Diffuse Abnormalities of the Trachea and Main Bronchi. Edith M. Marom 1, Philip C. Goodman, H. Page McAdams
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.196.13 on 12/09/17 from IP address 37.44.196.13. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Diffuse bnormalities of the Trachea and Main ronchi
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.196.13 on 12/09/17 from IP address 37.44.196.13. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Diffuse bnormalities of the Trachea and Main ronchi
Tracheobronchial Involvement in Relapsing Polychondritis Diagnosed on Endobronchial Ultrasound
 CASE REPORT Tracheobronchial Involvement in Relapsing Polychondritis Diagnosed on Endobronchial Ultrasound Dararat Eksombatchai 1, Viboon Boonsarngsuk 1, Naparat Amornputtisathaporn 1, Thitiporn Suwatanapongched
CASE REPORT Tracheobronchial Involvement in Relapsing Polychondritis Diagnosed on Endobronchial Ultrasound Dararat Eksombatchai 1, Viboon Boonsarngsuk 1, Naparat Amornputtisathaporn 1, Thitiporn Suwatanapongched
Pictorial Review of Diffuse Central Airway Diseases: Focus on CT Findings
 DOI: 10.4046/trd.2011.70.1.10 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2011;70:10-20 CopyrightC2011. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights reserved.
DOI: 10.4046/trd.2011.70.1.10 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2011;70:10-20 CopyrightC2011. The Korean Academy of Tuberculosis and Respiratory Diseases. All rights reserved.
Imaging of the trachea
 Keynote Lecture Series Imaging of the trachea Jo-nne O. Shepard, Efren J. Flores, Gerald F. bbott Division of Thoracic Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical
Keynote Lecture Series Imaging of the trachea Jo-nne O. Shepard, Efren J. Flores, Gerald F. bbott Division of Thoracic Imaging, Department of Radiology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical
Residents Section Pattern of the Month
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Cantin et al. ronchiectasis Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Luce Cantin 1 lexander. ankier Ronald L. Eisenberg Cantin L, ankier, Eisenberg
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Cantin et al. ronchiectasis Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Luce Cantin 1 lexander. ankier Ronald L. Eisenberg Cantin L, ankier, Eisenberg
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
Saber-Sheath Trachea: Relation to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
 Saber-Sheath Trachea: Relation to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REGINALD GREENE Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 6..9.9 on //7 from IP address 6..9.9. Copyright ARRS. For personal use only;
Saber-Sheath Trachea: Relation to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease REGINALD GREENE Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 6..9.9 on //7 from IP address 6..9.9. Copyright ARRS. For personal use only;
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Two Cases of Tracheal Disease Misdiagnosed as Difficult-to-Treat Asthma
 Two Cases of Tracheal Disease Misdiagnosed as Difficult-to-Treat Asthma Running-Head: Are you sure about the diagnosis of asthma? Ibrahim Onur Alici 1, Ozlem Kar Kurt 2, Adile Berna Dursun 3, Aydin Yilmaz
Two Cases of Tracheal Disease Misdiagnosed as Difficult-to-Treat Asthma Running-Head: Are you sure about the diagnosis of asthma? Ibrahim Onur Alici 1, Ozlem Kar Kurt 2, Adile Berna Dursun 3, Aydin Yilmaz
Discussing feline tracheal disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
The Role of Multislice CT in Imaging of Different Tracheal Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 8, No., December: 949-958, 203 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Role of Multislice CT in Imaging of Different Tracheal Lesions YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.; MARIAN F. FARID,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 8, No., December: 949-958, 203 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Role of Multislice CT in Imaging of Different Tracheal Lesions YOUSSRIAH Y. SABRI, M.D.; MARIAN F. FARID,
Subject Index. Bacterial infection, see Suppurative lung disease, Tuberculosis
 Subject Index Abscess, virtual 107 Adenoidal hypertrophy, features 123 Airway bleeding, technique 49, 50 Airway stenosis, see Stenosis, airway Anaesthesia biopsy 47 complications 27, 28 flexible 23 26
Subject Index Abscess, virtual 107 Adenoidal hypertrophy, features 123 Airway bleeding, technique 49, 50 Airway stenosis, see Stenosis, airway Anaesthesia biopsy 47 complications 27, 28 flexible 23 26
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Tracheobronchomalacia: morfologic evaluation in 64-MDTC.
 Tracheobronchomalacia: morfologic evaluation in 64-MDTC. Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. A. P. Fontes, A. A. S. M. Santos, A. L. Ferreira Neto, E. Marchiori,
Tracheobronchomalacia: morfologic evaluation in 64-MDTC. Poster No.: C-1779 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. A. P. Fontes, A. A. S. M. Santos, A. L. Ferreira Neto, E. Marchiori,
Thoracic Manifestations of
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay etancourt et al. Inflammatory owel Disease Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.206.177 on 02/06/18 from IP address
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay etancourt et al. Inflammatory owel Disease Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.206.177 on 02/06/18 from IP address
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children. Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital
 FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
FOREIGN BODY ASPIRATION in children Dr. Xayyavong Bouathongthip, M.D Emergency department, children s hospital How common is choking? About 3,000 people die/year from choking Figure remained unchanged
New Horizons in the Imaging of the Lung
 New Horizons in the Imaging of the Lung Postprocessing. How to do it and when do we need it? Peter M.A. van Ooijen, MSc, PhD Principal Investigator, Radiology, UMCG Discipline Leader Medical Imaging Informatics
New Horizons in the Imaging of the Lung Postprocessing. How to do it and when do we need it? Peter M.A. van Ooijen, MSc, PhD Principal Investigator, Radiology, UMCG Discipline Leader Medical Imaging Informatics
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach
 Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
When to suspect Wegener Granulomatosis: A radiologic review
 When to suspect Wegener Granulomatosis: A radiologic review Poster No.: P-0038 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Tilve Gómez, R. Díez Bandera, P. Rodríguez Fernández, M. Garcia Vazquez-Noguerol,
When to suspect Wegener Granulomatosis: A radiologic review Poster No.: P-0038 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Tilve Gómez, R. Díez Bandera, P. Rodríguez Fernández, M. Garcia Vazquez-Noguerol,
Common Blind Spots on Chest CT: Where Are They All Hiding? Part 1 Airways, Lungs, and Pleura
 Residents Section Structured Review Wu et al. Common lind Spots on Chest CT Residents Section Structured Review Carol C. Wu 1 Leila Khorashadi 2 Gerald F. bbott 1 Matthew D. Gilman 1 Wu CC, Khorashadi
Residents Section Structured Review Wu et al. Common lind Spots on Chest CT Residents Section Structured Review Carol C. Wu 1 Leila Khorashadi 2 Gerald F. bbott 1 Matthew D. Gilman 1 Wu CC, Khorashadi
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D.
 Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Original Report. Fibrosis of the Upper Lobes: A Newly Identified Late-Onset Complication After Lung Transplantation?
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 05/04/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Eli Konen 1,2 Gordon L. Weisbrod 1 Smita Pakhale
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 05/04/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Eli Konen 1,2 Gordon L. Weisbrod 1 Smita Pakhale
The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis
 www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
CT Diagnosis of Pulmonary Wegener s Granulomatosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature
 CASE REPORT JIACM 2008; 9(4): 321-5 CT Diagnosis of Pulmonary Wegener s Granulomatosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature Shibani Mehra*, Shailendra Aggarwal Abstract The diagnosis of Wegener s granulomatosis
CASE REPORT JIACM 2008; 9(4): 321-5 CT Diagnosis of Pulmonary Wegener s Granulomatosis: A Case Report and Review of Literature Shibani Mehra*, Shailendra Aggarwal Abstract The diagnosis of Wegener s granulomatosis
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
The Surgical Treatment of Tracheobronchial Tuberculosis. The Thoracic Department of Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University
 The Surgical Treatment of Tracheobronchial Tuberculosis ) The Thoracic Department of Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University Named also: endobronchial tuberculosis,ebtb defined as tuberculous
The Surgical Treatment of Tracheobronchial Tuberculosis ) The Thoracic Department of Beijing Chest Hospital, Capital Medical University Named also: endobronchial tuberculosis,ebtb defined as tuberculous
Downloaded from by on 01/23/18 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.194.46 on 01/23/18 from IP address 46.3.194.46. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved sthma is an inflammatory disease of the lungs characterized
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.194.46 on 01/23/18 from IP address 46.3.194.46. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved sthma is an inflammatory disease of the lungs characterized
Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT
 Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT Alan S. Brody, MD Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Chief, Thoracic Imaging Cincinnati Children s s Hospital Cincinnati, Ohio, USA Pediatric High-Resolution CT Short
Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT Alan S. Brody, MD Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Chief, Thoracic Imaging Cincinnati Children s s Hospital Cincinnati, Ohio, USA Pediatric High-Resolution CT Short
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 7. LUNGS Q1. Fill in the blanks: the lung has lobes and fissures. A. Right, three, two. B. Right, two, one. C. Left, three, two. D. Left, two, three. Q2. The base of the lung
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 7. LUNGS Q1. Fill in the blanks: the lung has lobes and fissures. A. Right, three, two. B. Right, two, one. C. Left, three, two. D. Left, two, three. Q2. The base of the lung
Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014
 Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014 Large number of different types of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Most are very rare Most patients present with one of a smaller number of commoner diseases
Manish Powari Regional Training Day 10/12/2014 Large number of different types of Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD). Most are very rare Most patients present with one of a smaller number of commoner diseases
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
COUGH Dr. A m A it i e t sh A g A garwa w l Le L ctu t rer Departm t ent t o f f M e M dic i in i e
 COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
Case of the Day Chest
 Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Case of the Day Chest Darin White MDCM FRCPC Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic 76 th Annual Scientific Meeting Canadian Association of Radiologists Montreal, QC April 26, 2013 2013 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures
Tracheobronchial lesions - A pictorial review
 Tracheobronchial lesions - A pictorial review Poster No.: E-0002 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Massey, L. Chandratreya; Bristol/UK Keywords: Thorax, CT, MR, Education, Neoplasia,
Tracheobronchial lesions - A pictorial review Poster No.: E-0002 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Massey, L. Chandratreya; Bristol/UK Keywords: Thorax, CT, MR, Education, Neoplasia,
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT
 Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!!
 The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener s)
 August 2011 Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener s) Andrew Noll, Harvard Medical School, Year III Agenda Patient presentation Overview of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener s), abbreviated
August 2011 Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (Wegener s) Andrew Noll, Harvard Medical School, Year III Agenda Patient presentation Overview of granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener s), abbreviated
CT Depiction of Regional Nodal Stations for Lung Cancer Staging
 ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.204.189 on 11/24/17 from IP address 37.44.204.189. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved T epiction of Regional Nodal Stations for Lung ancer
ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.204.189 on 11/24/17 from IP address 37.44.204.189. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved T epiction of Regional Nodal Stations for Lung ancer
Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging
 July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
July 2003 Atopic Pulmonary Disease: Findings on Thoracic Imaging Rebecca G. Breslow Harvard Medical School Year IV Churg-Strauss Syndrome Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis Asthma Atopic Pulmonary Disease Allergic
Pulmonary fibrosis on the lateral chest radiograph: Kerley D lines revisited
 Insights Imaging (2017) 8:483 489 DOI 10.1007/s13244-017-0565-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW Pulmonary fibrosis on the lateral chest radiograph: Kerley D lines revisited Daniel B. Green 1 & Alan C. Legasto 1 & Ian
Insights Imaging (2017) 8:483 489 DOI 10.1007/s13244-017-0565-2 PICTORIAL REVIEW Pulmonary fibrosis on the lateral chest radiograph: Kerley D lines revisited Daniel B. Green 1 & Alan C. Legasto 1 & Ian
Lung Allograft Dysfunction
 Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Acute and Chronic Pulmonary Emboli: Angiography CT Correlation
 ngiography and T of Pulmonary Emboli ardiac Imaging Pictorial Essay D E M N E U T R Y L I M I G O F I N G onrad Wittram 1 Mannudeep K. Kalra Michael M. Maher lan Greenfield Theresa. McLoud Jo-nne O. Shepard
ngiography and T of Pulmonary Emboli ardiac Imaging Pictorial Essay D E M N E U T R Y L I M I G O F I N G onrad Wittram 1 Mannudeep K. Kalra Michael M. Maher lan Greenfield Theresa. McLoud Jo-nne O. Shepard
Introduction to Chest Radiography
 Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Chapter 124: Congenital Disorders of the Trachea. Bruce Benjamin
 Chapter 124: Congenital Disorders of the Trachea Bruce Benjamin Investigation of the larynx and pharynx may be incomplete in infants and children with congenital abnormalities without investigation of
Chapter 124: Congenital Disorders of the Trachea Bruce Benjamin Investigation of the larynx and pharynx may be incomplete in infants and children with congenital abnormalities without investigation of
Wheeze. Dr Jo Harrison
 Wheeze Dr Jo Harrison 9.9.14 Wheeze - Physiology a continuous musical sound that lasts longer than 250 msec. can be high-pitched or low-pitched, consist of single or multiple notes, and occur during inspiration
Wheeze Dr Jo Harrison 9.9.14 Wheeze - Physiology a continuous musical sound that lasts longer than 250 msec. can be high-pitched or low-pitched, consist of single or multiple notes, and occur during inspiration
Hypothesis on the Evolution of Cavitary Lesions in Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection: Thin-Section CT and Histopathologic Correlation
 CT of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection Tae Sung Kim 1 Won-Jung Koh 2 Joungho Han 3 Myung Jin Chung 1 Ju Hyun Lee 1 Kyung Soo Lee 1 O Jung Kwon 2 Kim TS, Koh W-J, Han J, et al. Received
CT of Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Pulmonary Infection Tae Sung Kim 1 Won-Jung Koh 2 Joungho Han 3 Myung Jin Chung 1 Ju Hyun Lee 1 Kyung Soo Lee 1 O Jung Kwon 2 Kim TS, Koh W-J, Han J, et al. Received
8/14/2017. Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features
 What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
The Respiratory System
 C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
C h a p t e r 24 The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
Post treatment contribution in semiological analysis of thoracic helical CT
 Post treatment contribution in semiological analysis of thoracic helical CT Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest - Miscellaneous Authors: M. Gaha, N. Mama, N. Arifa,
Post treatment contribution in semiological analysis of thoracic helical CT Poster No.: C-0996 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest - Miscellaneous Authors: M. Gaha, N. Mama, N. Arifa,
Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes
 CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
CHAPTER e40 Atlas of the Vasculitic Syndromes Carol A. Langford Anthony S. Fauci Diagnosis of the vasculitic syndromes is usually based upon characteristic histologic or arteriographic findings in a patient
Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic Left Lung
 Volume 2013, Article ID 620120, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/620120 Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic
Volume 2013, Article ID 620120, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/620120 Case Report A Unique Case of Left Second Supernumerary and Left Third Bifid Intrathoracic Ribs with Block Vertebrae and Hypoplastic
CT Chest. Verification of an opacity seen on the straight chest X ray
 CT Chest Indications: To assess equivocal plain x-ray findings Staging of lung neoplasm Merastatic workup of extra thoraces malignancies Diagnosis of diffuse lung diseases with HRCT Assessment of bronchietasis
CT Chest Indications: To assess equivocal plain x-ray findings Staging of lung neoplasm Merastatic workup of extra thoraces malignancies Diagnosis of diffuse lung diseases with HRCT Assessment of bronchietasis
Overview of airway involvement in tuberculosis
 bs_bs_banner Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 57 (2013) 576 581 RADIOLOGY PICTORIAL ESSAY Overview of airway involvement in tuberculosis Arundeep Arora, Ashu Seith Bhalla, Manisha Jana
bs_bs_banner Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 57 (2013) 576 581 RADIOLOGY PICTORIAL ESSAY Overview of airway involvement in tuberculosis Arundeep Arora, Ashu Seith Bhalla, Manisha Jana
Interesting Cases. Pulmonary
 Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Vascular Lung Diseases
 Vascular Lung Diseases SESSION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES List the major types of vascular lung disease Recognize and describe the pathology of vascular lung disease: Pulmonary embolism, thrombosis, hypertension,
Vascular Lung Diseases SESSION SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES List the major types of vascular lung disease Recognize and describe the pathology of vascular lung disease: Pulmonary embolism, thrombosis, hypertension,
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
d) Always ensure patient comfort. Be considerate and warm the diaphragm of your stethoscope with your hand before auscultation.
 Auscultation Auscultation is perhaps the most important and effective clinical technique you will ever learn for evaluating a patient s respiratory function. Before you begin, there are certain things
Auscultation Auscultation is perhaps the most important and effective clinical technique you will ever learn for evaluating a patient s respiratory function. Before you begin, there are certain things
Thoracic sarcoidosis: Pictoral review of typical and atypical findings
 Thoracic sarcoidosis: Pictoral review of typical and atypical findings Poster No.: C-0804 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: A. Ferreira, J. Calha; Lisbon/PT Keywords: Sarcoidosis,
Thoracic sarcoidosis: Pictoral review of typical and atypical findings Poster No.: C-0804 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Chest Authors: A. Ferreira, J. Calha; Lisbon/PT Keywords: Sarcoidosis,
Case Presentation VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation. Vasculitis
 Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Case Presentation VASCULITIS The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Cystic Lung Disease: a Comparison of Cystic Size, as Seen on Expiratory and Inspiratory HRCT Scans
 Cystic Lung Disease: a Comparison of Cystic Size, as Seen on Expiratory and Inspiratory HRCT Scans Ki-Nam Lee, MD 1 Seong-Kuk Yoon, MD 1 Seok Jin Choi, MD 2 Jin Mo Goo, MD 3 Kyung-Jin Nam, MD 1 Index words:
Cystic Lung Disease: a Comparison of Cystic Size, as Seen on Expiratory and Inspiratory HRCT Scans Ki-Nam Lee, MD 1 Seong-Kuk Yoon, MD 1 Seok Jin Choi, MD 2 Jin Mo Goo, MD 3 Kyung-Jin Nam, MD 1 Index words:
CT of saber-sheath trachea
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 CT of saber-sheath trachea Jean Paul Trigaux, G. Hermes, P. Dubois, B. Van Beers, L.
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0284-1851 (Print) 1600-0455 (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iard20 CT of saber-sheath trachea Jean Paul Trigaux, G. Hermes, P. Dubois, B. Van Beers, L.
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT
 Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Auscultation of the lung
 Auscultation of the lung Auscultation of the lung by the stethoscope. *Compositions of the stethoscope: 1-chest piece 2-Ear piece 3-Rubber tubs *Auscultation area of the lung(triangle of auscultation).
Auscultation of the lung Auscultation of the lung by the stethoscope. *Compositions of the stethoscope: 1-chest piece 2-Ear piece 3-Rubber tubs *Auscultation area of the lung(triangle of auscultation).
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
VASCULITIS. Case Presentation. Case Presentation
 VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
VASCULITIS Case Presentation The patient is a 24 year old woman who presented to the emergency room with left-sided weakness. She was confused and complained of a severe headache. She was noted to have
Semiology of respiratory system in children Simple choice 1. Mark the intrauterine age of lung development onset from the gut: a) 1 week b) 24 days
 Semiology of respiratory system in children Simple choice 1. Mark the intrauterine age of lung development onset from the gut: a) 1 week b) 24 days c) 6 weeks d) 12 weeks e) 35 weeks 2. Stridor is not
Semiology of respiratory system in children Simple choice 1. Mark the intrauterine age of lung development onset from the gut: a) 1 week b) 24 days c) 6 weeks d) 12 weeks e) 35 weeks 2. Stridor is not
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Non-neoplastic Conditions in the Mediastinum
 2017 WCTI Non-neoplastic Conditions in the Mediastinum Mi Young Kim, MD, PhD Hyun Jung Koo, MD Jae Woo Song, MD, PhD Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University
2017 WCTI Non-neoplastic Conditions in the Mediastinum Mi Young Kim, MD, PhD Hyun Jung Koo, MD Jae Woo Song, MD, PhD Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
A Complication of Tracheobronchopathia Osteochondroplastica Presenting as Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure
 ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.892427 Received: 2014.09.08 Accepted: 2014.10.21 Published: 2015.01.28 A Complication of Tracheobronchopathia Osteochondroplastica Presenting as Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory
ISSN 1941-5923 DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.892427 Received: 2014.09.08 Accepted: 2014.10.21 Published: 2015.01.28 A Complication of Tracheobronchopathia Osteochondroplastica Presenting as Acute Hypercapnic Respiratory
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria
 American College of Radiology ACR Criteria Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and Masses Variant 1: Middle-aged patient (35 60 years old) with an incidental 1.5-cm lung nodule. The lesion was smooth.
American College of Radiology ACR Criteria Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and Masses Variant 1: Middle-aged patient (35 60 years old) with an incidental 1.5-cm lung nodule. The lesion was smooth.
CASE REPORTS. Idiopathic Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung
 CASE REPORTS Idiopathic Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung The Swyer-James Syndrome J. Judson McNamara, M.D., Harold C. Urschel, M.D., J. H. Arndt, M.D., Herman Ulevitch, M.D., and W. B. Kingsley, M.D. I diopathic
CASE REPORTS Idiopathic Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung The Swyer-James Syndrome J. Judson McNamara, M.D., Harold C. Urschel, M.D., J. H. Arndt, M.D., Herman Ulevitch, M.D., and W. B. Kingsley, M.D. I diopathic
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Radiological staging of lung cancer. Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh
 Radiological staging of lung cancer Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh Bronchogenic Carcinoma Accounts for 14% of new cancer diagnoses in 2012. Estimated to kill ~150,000
Radiological staging of lung cancer Shukri Loutfi,MD,FRCR Consultant Thoracic Radiologist KAMC-Riyadh Bronchogenic Carcinoma Accounts for 14% of new cancer diagnoses in 2012. Estimated to kill ~150,000
Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology
 Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Russell Tucker, DVM, DACVR Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual
Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Russell Tucker, DVM, DACVR Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual
