Immunoglobulin G4 related Disease in Genitourinary Organs: An Emerging Fibroinflammatory Entity Often Misdiagnosed Preoperatively as Cancer
|
|
|
- Kristopher Dean
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
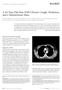
1 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) available at journal homepage: Platinum Opinion Editorial Immunoglobulin G4 related Disease in Genitourinary Organs: An Emerging Fibroinflammatory Entity Often Misdiagnosed Preoperatively as Cancer Rodolfo Montironi a,y, *, Marina Scarpelli a,y, Liang Cheng b, Antonio Lopez-Beltran c, Maurizio Burattini d, Ziya Kirkali e, Francesco Montorsi f a Section of Pathological Anatomy, Polytechnic University of the Marche Region, School of Medicine, United Hospitals, Ancona, Italy; b Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, USA; c Department of Surgery, Cordoba University Medical School, Cordoba, Spain; d Unit of Internal Medicine, Carlo Urbani Hospital, Jesi, Italy; e Departments of Urology, School of Medicine, Dokuz Eylül University, Izmir, Turkey; f Department of Urology, University Vita-Salute, Scientific Institute H San Raffaele, Milan, Italy 1. What is immunoglobulin G4? [(Fig._1)TD$FIG] Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) is the least common of the four subclasses of immunoglobulin G (IgG), namely IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, normally constituting only 3% to 6% of the entire IgG fraction. The major differences among the subclasses lie in the composition and structure of the hinge region that has significant effects on the antigen binding and effector functions of the immunoglobulin molecules, resulting in different functional characteristics of each IgG subclass. For instance, IgG4, in contrast to the other IgG subclasses, does not activate complement and has a low affinity for target antigens. IgG4 is a T-helper 2 (Th2) cell-dependent isotype. Despite uncertainties about its normal function, IgG4 seems to play a significant role in allergic reactions, such as atopic eczema, bronchial asthma, and bullous skin lesions [1]. IgG4 has not attracted the attention of pathologists and clinicians until the recent recognition of the syndrome of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), a fibroinflammatory condition with a marked propensity to present as mass-forming lesions [2]. 2. Pathogenic mechanisms in immunoglobulin G4 related disease Autoimmunity and infectious agents are potential immunologic triggers in IgG4-RD. Interleukins 4, 5, 10, and 13 and Fig. 1 Imaging features (magnetic resonance) of a bladder lesion originally considered to be neoplastic. y These authors contributed equally to this work. * Corresponding author. Pathological Anatomy, Polytechnic University of the Marche Region, School of Medicine, United Hospitals, Via Conca 71, I Torrette, Ancona, Italy. Tel ; Fax: address: r.montironi@univpm.it (R. Montironi) /$ see back matter # 2012 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
2 [(Fig._2)TD$IG] 866 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) Fig. 2 Morphologic and immunohistochemical features of immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related disease: (A) cellular fibrosis with storiform pattern, (B) obliterative phlebitis, (C) dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, and (D) IgG4+ plasma cells. transforming growth factor b are overexpressed through an immune reaction in which Th2 cells predominate, followed by activation of regulatory T cells. These cytokines contribute to the eosinophilia, elevated serum IgG4 and immunoglobulin E concentrations, and fibrosis that are characteristic of IgG4-RD. tion by inflammatory cells results in The inflammatory-cell infiltrate leads progression of Massive infiltraorgan damage. to tumefactive [(Fig._3)TD$IG] Fig. 3 Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis involving (A) the kidney and (B) tubulointerstitial nephritis with an inflammatory infiltrate, fibrosis, and tubular atrophy.
3 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) Table 1 Body sites affected by immunoglobulin G4 related disease Body site Pancreas Bile duct Gall bladder Liver Salivary glands Lacrimal glands and orbit Retroperitoneum and mesentery Cardiovascular/aorta Mediastinum Kidney and ureter Thyroid Breast Lung Central nervous system Prostate Lymph node Clinicopathologic features Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis (type 1 AIP) and idiopathic duct centric chronic pancreatitis (type 2 AIP) Sclerosing cholangitis Acalculous sclerosing cholecystitis Sclerosing cholangitis involving intrahepatic ducts, inflammatory pseudotumor, portal inflammation with or without interface hepatitis, portal sclerosis, large bile duct obstruction, lobular hepatitis, canalicular cholestasis Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis (Küttner tumor), Mikulicz disease Chronic sclerosing dacryoadenitis, inflammatory pseudotumor Retroperitoneal fibrosis, sclerosing mesenteritis Inflammatory abdominal aortic aneurysm Sclerosing mediastinitis Tubulointerstitial nephritis, membranous glomerulopathy, inflammatory pseudotumor Hypothyroidism, Riedel thyroiditis Sclerosing mastitis Inflammatory pseudotumor, interstitial pneumonia Hypophysitis, sclerosing pachymeningitis Prostatitis Lymphadenopathy with Castleman disease-like features, follicular hyperplasia, interfollicular expansion by plasma cells and immunoblasts AIP = autoimmune pancreatitis. [(Fig._4)TD$FIG] Fig. 4 (A) Radical nephrectomy specimen with hydronephrosis and proximal part of the ureter embedded in a mass originally considered to be cancer of the ureter. (B) Histologically, the mass is composed of cellular fibrosis and (C) dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate.
4 868 [(Fig._5)TD$FIG] EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) Fig. 5 (A) Whole-mount section of a bladder specimen involved by immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related disease. (B) Cellular fibrosis with a dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate involves the mucosa extending to (C) the perivesical tissue, and (D) including IgG4+ plasma cells. enlargement of the affected sites and to organ dysfunction. Epithelial damage may result from tissue inflammation and immune-complex deposition. 3. Imaging features and serologic findings The imaging features are generally nonspecific and do not permit reliable distinctions between IgG4-RD and cancer [3] (Fig. 1). Lymph node enlargement, as evidenced by imaging studies, is often associated with IgG4-RD and may be multifocal, with mediastinal, abdominal, and axillary lymph nodes being involved most commonly [4]. The clinical differential diagnosis in such cases with lymphadenopathy includes lymphoma, multicentric Castleman disease, or metastatic malignant tumor. A raised serum IgG4 level is not mandatory for the diagnosis but may be of valuable assistance. Serum IgG4 titer often correlates with disease activity and the number of involved organs. In addition, high serum levels of polyclonal g-globulins often occur [5]. 4. Treatment When vital organs are involved, aggressive treatment is needed because IgG4-RD can lead to organ dysfunction and failure [3]. Glucocorticoids, typically the first line of therapy, appear to be effective (initially, at least) in the majority of patients with IgG4-RD. Although IgG4 concentrations become lower with glucocorticoid treatment in the great majority of patients in whom they are elevated at baseline, they remain above normal values in most patients. The decision to give steroid therapy, however, requires a precise diagnosis, a major determinant of treatment responsiveness being the degree of fibrosis within the affected organs. The possibility of biopsy-based diagnosis relies on the combination of the three major morphologic features described in the next section of this article. Unfortunately, the presence of all these specific features, especially in small fragments, is seen only in a minority of cases. The presence of abundant IgG4+ plasma cells and a high IgG4/IgG ratio are important for tissue diagnosis [6,7]. For patients with recurrent or refractory disease, B-cell depletion with rituximab appears to be a useful approach [8]. Swift clinical responses have been observed. In patients treated with rituximab, IgG4 serum concentrations decline sharply. This decline is associated with clinical improvement within weeks. In view of the high success rate of corticosteroid therapy in IgG4-RD, it can be anticipated that in the future, the only patients who will be treated surgically will be those who are
5 [(Fig._6)TD$FIG] EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) Fig. 6 (A) Enlarged lymph node whose histology is that of type I immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) related lymphadenopathy, that is, (B,C) Castleman s diseaselike morphology, (D) including IgG4+ plasma cells. refractory to steroids or immunoregulatory drugs and/or in whom carcinoma continues to be suspected. 5. The three major morphologic features Cellular fibrosis with storiform pattern is a special type of fibrosis characterized by fibroblast and myofibroblast proliferation with delicate collagen bands forming short fascicles with a storiform pattern or herringbone pattern (Fig. 2A), intermixed with inflammatory cells [6,7]. Obliterative phlebitis, i.e., the lymphoplasmacytic infiltration that involves veins (phlebitis), usually begins at the periphery of venous walls, spreading through the wall as the inflammation progresses (Fig. 2B). The fully developed lesion, the obliterative phlebitis, is characterized by organized obstruction of veins with wall destruction due to dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration [6,7]. Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate is characterized by diffuse but sometimes focal infiltration of small lymphocytes and plasma cells (Fig. 2C). Eosinophils are often observed. The most relevant and important feature is the increased number of IgG4+ plasma cells (Fig. 2D). Analysis of IgG4 immunostaining helps to distinguish IgG4-RD from other conditions. A variety of cut-off points, ranging from >10 to >50 IgG4+ plasma cells per high-power field, has been proposed. The ratio of IgG4-bearing plasma cells to IgG-bearing plasma cells further assists in confirming the diagnosis of IgG4-RD: A ratio >50% is very suggestive of the diagnosis. IgG4-RD is more difficult to diagnose in the late phase of organ involvement, when fewer plasma cells are present and fibrosis may predominate in some tissues. The pattern of fibrosis and the ratio of IgG4 to total IgG provide crucial information in this context [6,7]. 6. Organ involvement IgG4-RD has been described in almost every organ system [3]: the pancreatobiliary tract, liver, salivary glands, nasopharynx, bone marrow, lacrimal gland, extraocular muscles and retrobulbar space, lungs, lymph nodes, meninges, aorta and arteries, skin, breast, thyroid gland, and pericardium, as well as in genitourinary organs (Table 1). Many medical conditions that have long been viewed as conditions confined to single organs are part of the spectrum of IgG4-RD. Mikulicz syndrome, Küttner tumor, and Riedel thyroiditis names embedded in the medical literature for more than a century in some cases may now be replaced by designations that describe a key pathologic feature and perhaps provide more insight into the pathophysiology.
6 870 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) Lymphadenopathy may also develop following an established diagnosis of extranodal IgG4-RD or may be the initial presenting manifestation with subsequent discovery of systemic IgG4-RD. The enlarged lymph nodes may be asymptomatic or may give rise to a mass effect in various body sites. Five histologic patterns of IgG4-related lymphadenopathy have been described [4]. IgG4-RD increases the risk of developing lymphoma. Cases of pulmonary adenocarcinoma, salivary duct carcinoma, urothelial carcinoma in situ, and gastrointestinal clear cell sarcoma in association with IgG4-RD have been reported [6] Immunoglobulin G4 related disease involving genitourinary organs A subset of idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis cases could be classified in the IgG4-related sclerosing disease spectrum. Idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis may extend to involve the kidney (Fig. 3A) and ureter. IgG4-RD may involve the kidneys, leading to disturbances in renal function [9,10]. Radiologic studies may demonstrate the presence of poorly circumscribed nodular masses in the kidneys, often necessitating the exclusion of malignancy. The commonest findings on biopsy or nephrectomy are tubulointerstitial nephritis with an IgG4+, plasma cell-rich inflammatory infiltrate, fibrosis, and tubular atrophy (Fig. 3B). Using electron microscopy, IgG4 electron-dense deposits have been demonstrated in the peritubular basement membrane. The renal glomeruli are usually uninvolved, but few cases with concurrent membranous nephropathy have been recorded. Tubulointerstitial nephritis is steroid responsive, whereas the response of membranous glomerulonephritis can be variable. Very recently, our group had the chance to examine histologically a radical nephrectomy specimen with an 8-cm segment of ureter. The proximal part of the ureter was embedded in a hard and white mass that measured 5 cm at its widest diameter (Fig. 4A 4C). The clinical diagnosis was cancer involving the ureter with hydronephrosis. The lesion showed the typical histologic and immunohistochemical features of IgG4-RD. The process involved the mucosa, the muscularis propria, and the periureteral tissue. Three cases of IgG4-RD involving the ureter have been reported by Kim et al. [11]. A case report with a literature review of IgG4- related ureteritis misdiagnosed as ureteral cancer preoperatively has been published by Joo et al. [12]. IgG4-related chronic sclerosing pyelitis has also been reported. Concerning the bladder, our group has recently examined a partial cystectomy specimen with a whitish and hard mass measuring 6 cm at its widest diameter. The specimen was from a man with a clinical diagnosis of locally advanced bladder cancer. Histologically, the lesion showed the three major features of IgG4-RD, including a discrete number of eosinophils. The lesion involved the whole thickness of the bladder from the mucosa to the perivesical tissue (Fig. 5A 5D). There was an associated regional lymphadenopathy whose histology was that of IgG4-related lymphadenopathy (Type I, Castleman disease-like morphology) (Fig. 6A 6D). The patient also had high serum levels of polyclonal g-globulins (Fig. 7A). Glucocorticoid treatment induced a dramatic improvement compared with the original clinical presentation, including regression of the residual bladder mass, disappearance of the lymphadenopathy, and normal level of serum g-globulins (Fig. 7B). A similar case was observed by Jae Y. Ro (pers. comm.). IgG4-related prostatitis has recently been reported in patients with and without autoimmune pancreatitis [13]. Patients showed lower urinary tract symptoms, and prostate enlargement was evident on digital rectal examination. The symptoms and radiologic findings improved after steroid therapy. Histologically, the prostate showed dense infiltration of IgG4+ plasma cells and lymphocytes, obliterative phlebitis, and gland atrophy with dense fibrosis. IgG4-RD has also been observed in the seminal vesicles. Urethral caruncle is a benign inflammatory and fibrous polypoid urethral mass of unclear etiology. Using immunohistochemical markers, it appears unrelated to the viral infections that result in tumor formation and other mucosal abnormalities of various body sites. Abnormal expression of anaplastic lymphoma kinase protein, as seen in inflammatory myofibroblastic tumors, is absent. Increased numbers of IgG4+ plasma cells in a subset of lesions raise the possibility that some cases may be related to the autoimmune phenomena of IgG4-RD [14,15]. [(Fig._7)TD$FIG] Fig. 7 (A) High serum levels of polyclonal g-globulins (at arrow). (B) Normal level of serum g-globulins following glucocorticoid treatment (at arrow).
7 [(Fig._8)TD$FIG] EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) Fig. 8 (A) Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor. (B) Whole-mount section of the paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor showing the uninvolved testis. (C) The paratesticular lesions exhibiting cellular fibrosis. Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor is a rare, benign condition of unknown etiology characterized by solitary or multiple intrascrotal nodules composed of dense fibrous tissue with a variable, sometimes sparse, inflammatory infiltrate (Fig. 8A 8C). Based on certain similarities to other fibroinflammatory disorders characterized by infiltrates of IgG4-expressing plasma cells, the plasma cell distribution and immunoglobulin isotypes in three cases of paratesticular fibrous and inflammatory pseudotumor were investigated in a recent study. All three cases showed a high number of IgG4+ plasma cells with an IgG4 IgG ratio of 44 48%. This finding indicates that paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor might belong to the growing list of conditions associated with IgG4-RD [16,17]. 7. Conclusions IgG4-RD, a multiorgan system disease that has been recognized in the last 10 yr, is a fibroinflammatory condition with a marked propensity to present as massforming lesions [2,18], characterized by a dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, the presence of abundant IgG4+ plasma cells, frequent elevation of serum IgG4 levels, and a dramatic initial response to glucocorticoid. Correct preoperative identification is crucial to avoid unnecessary major surgical in genitourinary and nongenitourinary organs and initiate corticosteroid therapy. Conflicts of interest: The authors have nothing to disclose.
8 872 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 64 (2013) References [11] Kim SA, Lee SR, Huh J, Shen SS, Ro JY. IgG4-associated inflammatory pseudotumor of ureter: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemi- [1] Tsuboi H, Matsuo N, Iizuka M, et al. Analysis of IgG4 class switchrelated molecules in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res Ther 2012;14:R171. [2] Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK, et al. Consensus statement on the cal study of 3 cases. Hum Pathol 2011;42: [12] Joo M, Chang SH, Kim H, Lee KC, Ro JY. Idiopathic segmental ureteritis, misdiagnosed as ureteral cancer preoperatively: a case report with literature review. Pathol Int 2010;60: pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol 2012;25: [13] Hart PA, Smyrk TC, Chari ST. IgG4-related prostatitis: a rare cause of [3] Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med steroid-responsive obstructive urinary symptoms. Int J Urol 2013; 2012;366: [4] Sato Y, Yoshino T. IgG4-related lymphadenopathy. Int J Rheumatol 2012: [5] Kawa S, Ito T, Watanabe T, et al. The utility of serum IgG4 concentrations as a biomarker. Int J Rheumatol 2012: dx.doi.org/ /2012/ [6] Hirabayashi K, Zamboni G. IgG4-related disease. Pathologica 2012;104: [7] Deshpande V. The pathology of IgG4-related disease: critical issues and challenges. Semin Diagn Pathol 2012;29: : [14] Choi JW, Kim SY, Moon KC, Cho JY, Kim SH. Immunoglobulin g4related sclerosing disease involving the urethra: case report. Korean J Radiol 2012;13: [15] Williamson SR, Scarpelli M, Lopez-Beltran A, Montironi R, Conces MR, Cheng L. Urethral caruncle: a lesion related to IgG4-associated sclerosing disease? J Clin Pathol 2013;66: [16] Bo smu ller H, von Weyhern CH, Adam P, Alibegovic V, Mikuz G, Fend F. Paratesticular fibrous pseudotumor an IgG4-related disorder? Virchows Arch 2011;458: [8] Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, Unizony S, Bloch DB, [17] Hart PA, Moyer AM, Yi ES, Hogan MC, Pearson RK, Chari ST. Stone JH. Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: IgG4-related paratesticular pseudotumor in a patient with autoim- lessons from 10 consecutive patients. Medicine (Baltimore) mune pancreatitis and retroperitoneal fibrosis: an extrapancreatic 2012;91: manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Hum Pathol 2012;43: [9] Cornell LD. IgG4-related kidney disease. Semin Diagn Pathol 2012;29: [18] Clevenger JA, Wang M, Maclennan GT, Montironi R, Lopez-Beltran [10] Alkhasawneh AN, Allan RW. IgG4 inflammatory pseudotumor of A, Cheng L. Evidence for clonal fibroblast proliferation and autoim- the kidney. Case Rep Urol 2012: mune process in idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Hum Pathol 2012/ ;43:
IgG4 Disease. General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman
 IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
IgG4 Disease General Principles of IgG4-related disease. EL Cluvar, AC Bateman Diagnostic Guidelines for IgG4-related disease with a focus on histopathological criteria. V Deshpande, A Khosroshahi Diagnostic
Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease
 Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN While autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) has been recognized since the first description by Sarles et al
Renal manifestations of IgG4-related systemic disease Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic Rochester, MN While autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) has been recognized since the first description by Sarles et al
Overview of the Immunoglobulin G4-related Disease Spectrum
 Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2015;20:124-129 http://dx.doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2015.20.3.124 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 면역글로불린 G4 연관질환의개요 1 한림대학교의과대학한림대학교성심병원내과, 2
Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2015;20:124-129 http://dx.doi.org/10.15279/kpba.2015.20.3.124 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 면역글로불린 G4 연관질환의개요 1 한림대학교의과대학한림대학교성심병원내과, 2
FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY. Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD)
 Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) NHS England FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) First published:
Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) NHS England FOR PUBLIC CONSULTATION ONLY Evidence Review: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4- RD) First published:
Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis of Other Etiology
 94 Jul 2017 Vol 10 No.3 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Original Research Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic
94 Jul 2017 Vol 10 No.3 North American Journal of Medicine and Science Original Research Value of Serum IgG4 in the Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis and in Distinguishing it from Acute and Chronic
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08. Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
 CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
CASE 01 LA Path Slide Seminar 13 March, 08 Deepti Dhall, MD Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Clinical History 60 year old male presented with obstructive jaundice
How 5 Diseases Became One. Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University
 How 5 Diseases Became One Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University Conflicts of Interest None! Mr. M. ID: 65 M PMH Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Awaiting biopsy Skin rash Dyslipidemia Hypertension
How 5 Diseases Became One Moez Tajdin R3 McGill University Conflicts of Interest None! Mr. M. ID: 65 M PMH Benign prostatic hyperplasia Prostate cancer Awaiting biopsy Skin rash Dyslipidemia Hypertension
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci
 CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
CASE REPORT Immunoglobulin G4-Related Disease with Several Inflammatory Foci Akira Sakamaki 1, Kenya Kamimura 1, Kazuhiko Shioji 1, Junko Sakurada 2, Takeshi Nakatsue 3, Yoko Wada 3, Michitaka Imai 1,
ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation
 ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara/Turkey Ozant Helvaci, M.D. Patient T.K., 59 years old, male, married with one child, unemployed, place of birth/
ESIM Winter School 2014 Case Presentation Hacettepe University School of Medicine Ankara/Turkey Ozant Helvaci, M.D. Patient T.K., 59 years old, male, married with one child, unemployed, place of birth/
Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 139409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/139409 Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor Arezou Khosroshahi,
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 139409, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/139409 Clinical Study IgG4-Related Disease Is Not Associated with Antibody to the Phospholipase A2 Receptor Arezou Khosroshahi,
IgG4-related sclerosing disease
 IgG4-related sclerosing disease TERUMI KAMISAWA, KENSUKE TAKUMA, NAOTO EGAWA Department of Internal Medicine Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital 3-18-22 Honkomagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8677, Japan JAPAN
IgG4-related sclerosing disease TERUMI KAMISAWA, KENSUKE TAKUMA, NAOTO EGAWA Department of Internal Medicine Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital 3-18-22 Honkomagome, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8677, Japan JAPAN
Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator
 Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Autoimmune Pancreatitis: A Great Imitator Dushyant V Sahani MD dsahani@partners.org Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Learning Objectives Clinical manifestations
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related Disease
 Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 4716245, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4716245 Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related
Hindawi Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2017, Article ID 4716245, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4716245 Case Report Thoracic Paravertebral Mass as an Infrequent Manifestation of IgG4-Related
Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin G4-related Lymphadenopathy Mimicking Sjögren s Syndrome
 Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 6, December, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.395 Case Report Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases Vol. 22, No. 6, December, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2015.22.6.395 Case Report Mikulicz s Disease with Progressively Transformed Germinal Centers-type Immunoglobulin
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma
 Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 118-22 Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis - Report of 2 Cases - Ji Eun Kwon Sang Kyum Kim Sang-Ryul Lee 1 Woo-Ick Yang Haeryoung Kim 2 Department of Pathology and
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2008; 42: 118-22 Chronic Sclerosing Dacryoadenitis - Report of 2 Cases - Ji Eun Kwon Sang Kyum Kim Sang-Ryul Lee 1 Woo-Ick Yang Haeryoung Kim 2 Department of Pathology and
Key words: diagnosis, immunoglobulin G4, immunoglobulin G4-related diseases, immunohistochemistry, pseudolymphoma. CASE HISTORY
 doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12301 Journal of Dermatology 2013; 40: 998 1003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Case of immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease: Possible immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease cases in cutaneous
doi: 10.1111/1346-8138.12301 Journal of Dermatology 2013; 40: 998 1003 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Case of immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease: Possible immunoglobulin G4-related skin disease cases in cutaneous
Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker
 International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 198314, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/198314 Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker Shigeyuki Kawa, 1 Tetsuya Ito, 2 Takayuki
International Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 198314, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/198314 Review Article The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker Shigeyuki Kawa, 1 Tetsuya Ito, 2 Takayuki
IgG4-related Disease of the Genitourinary Tract
 J Interdiscipl Histopathol 2014; 2(1): 3-18 ISSN: 2146-8362 Review Article IgG4-related Disease of the Genitourinary Tract Mukul K. Divatia, Jae Y. Ro Department of Pathology and Genomic Medicine, Houston
J Interdiscipl Histopathol 2014; 2(1): 3-18 ISSN: 2146-8362 Review Article IgG4-related Disease of the Genitourinary Tract Mukul K. Divatia, Jae Y. Ro Department of Pathology and Genomic Medicine, Houston
Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease
 Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016; 50: 300-305 CASE STUDY Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease Seokhwi
Journal of Pathology and Translational Medicine 2016; 50: 300-305 CASE STUDY Isolated Mass-Forming IgG4-Related Cholangitis as an Initial Clinical Presentation of Systemic IgG4-Related Disease Seokhwi
Renal Pathology Case Conference. Case 2
 Renal Pathology Case Conference Case 2 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN cornell.lynn@mayo.edu March 2, 2008 Clinical presentation 68 year old woman, initially with normal renal function
Renal Pathology Case Conference Case 2 Lynn D. Cornell, M.D. Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN cornell.lynn@mayo.edu March 2, 2008 Clinical presentation 68 year old woman, initially with normal renal function
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition:
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) Reference: NHS England A13X07/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Rituximab for immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) Reference: NHS England A13X07/01 Information Reader Box (IRB) to be inserted on inside front cover for
Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:220-226 Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor Hong Ki Min
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2019;34:220-226 Clinical outcomes and pathological characteristics of immunoglobulin G4-related ophthalmic disease versus orbital inflammatory pseudotumor Hong Ki Min
IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal
 CASE REPORT IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal Miho Otani 1, Masahiro Morinaga 1, Yoshihiko Nakajima 1, Hiromi Tomioka 2, Michiko Nishii
CASE REPORT IgG4-related Kidney Disease in Which the Urinalysis, Kidney Function and Imaging Findings Were Normal Miho Otani 1, Masahiro Morinaga 1, Yoshihiko Nakajima 1, Hiromi Tomioka 2, Michiko Nishii
A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy
 Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 43 (6): 1185-1189, November - December, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0520 A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy Ryuta Watanabe 1, Akira
Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 43 (6): 1185-1189, November - December, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0520 A case of retroperitoneal fibrosis responding to steroid therapy Ryuta Watanabe 1, Akira
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017
 Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis in Korea
 Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2014;19(1):7-12 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 한국에서자가면역췌장염의진단전략 성균관대학교의과대학삼성서울병원내과학교실 이종균 Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Review Article The Korean Journal of Pancreas and Biliary Tract 2014;19(1):7-12 pissn 1976-3573 eissn 2288-0941 한국에서자가면역췌장염의진단전략 성균관대학교의과대학삼성서울병원내과학교실 이종균 Diagnostic Algorithm for Autoimmune Pancreatitis
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) was described more than a
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1229 1234 The Use of Immunoglobulin G4 Immunostaining in Diagnosing Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Involvement in Autoimmune Pancreatitis MAESHA G. DEHERAGODA,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:1229 1234 The Use of Immunoglobulin G4 Immunostaining in Diagnosing Pancreatic and Extrapancreatic Involvement in Autoimmune Pancreatitis MAESHA G. DEHERAGODA,*
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma with systemic disease
 Asian Journal of Surgery (2013) 36, 93e97 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma
Asian Journal of Surgery (2013) 36, 93e97 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-asianjournalsurgery.com CASE REPORT IgG4-related hypophysitis presenting as a pituitary adenoma
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA
 FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
FOLLICULARITY in LYMPHOMA Reactive Follicular Hyperplasia Follicular Hyperplasia irregular follicles Follicular Hyperplasia dark and light zones Light Zone Dark Zone Follicular hyperplasia MIB1 Follicular
6/5/2010. Renal vein invasion & Capsule Penetration (T3a) Adrenal Gland involvement (T4 vs. M1) Beyond Gerota s Fascia? (?T4).
 GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease: Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Extrapancreatic
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. GASTROINTESTINAL
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. GASTROINTESTINAL
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues
 A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
A215- Urinary bladder cancer tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 45 Tissue type: Urinary bladder cancer tissues No. of spots: 2 spots from each cancer case (90
Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Reports in Otolaryngology Volume 2015, Article ID 749890, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/749890 Case Report IgG4-Related Nasal Pseudotumor L. K. Døsen, 1 P. Jebsen, 2 B. Dingsør, 3 and R.
Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
 Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2011, Article ID 236079, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/236079 Case Report An IgG4-Related Salivary Gland Disorder: A Case Series Presenting with a Different Clinical Setting
Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis
 Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Thomas C. Smyrk, MD Associate Professor of Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN 55902 smyrk.thomas@mayo.edu Summary Retroperitoneal fibrosis complicated
Autoimmune Pancreatitis and Retroperitoneal Fibrosis Thomas C. Smyrk, MD Associate Professor of Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester MN 55902 smyrk.thomas@mayo.edu Summary Retroperitoneal fibrosis complicated
Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Involving the Urethra: Case Report
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.803 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(6):803-807 Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Involving the Urethra: Case Report
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.803 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(6):803-807 Immunoglobulin G4-Related Sclerosing Disease Involving the Urethra: Case Report
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules
 Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Take Home Quiz 1 Please complete the quiz below prior to the session. Use the Multiple Primary and Histology Rules Case 1 72 year old white female presents with a nodular thyroid. This was biopsied in
Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4-
 Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4- related disease: a case report and literature review Authors: María Isabel Ortuño Moreno,
Title: An ulcerated gastric ulcer and pseudotumour with pancreatic affectation associated with immunoglobulin G4- related disease: a case report and literature review Authors: María Isabel Ortuño Moreno,
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Plan. Sarcoidosis 21/07/2017. Sarcoidosis Liver involvement. Sarcoidosis GI involvement. Sarcoidosis Diagnosis
 Belfast Pathology 2017 Gastrointestinal tract involvement by systemic disease 21.6.17 Dr Adrian C. Bateman University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, UK Plan Dermatological conditions Chronic
Belfast Pathology 2017 Gastrointestinal tract involvement by systemic disease 21.6.17 Dr Adrian C. Bateman University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust, UK Plan Dermatological conditions Chronic
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Evening specialty conference: Liver
 Evening specialty conference: Liver Joseph Misdraji, M.D. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee)
Evening specialty conference: Liver Joseph Misdraji, M.D. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee)
Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular Glands and Extraocular Muscles
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(3):216-221 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.216 Case Report Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2012;26(3):216-221 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2012.26.3.216 Case Report Unusual Involvement of IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease in Lacrimal and Submandibular
ACCME/Disclosures ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS. Tumor types with ALK rearrangements. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. Jason L.
 Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore
 IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore W. Fong 1,2,3, I. Liew 1, D. Tan 2,3,4, K.H. Lim 5, A. Low 6, Y.Y. Leung 1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology and
IgG4-related disease: features and treatment response in a multi-ethnic cohort in Singapore W. Fong 1,2,3, I. Liew 1, D. Tan 2,3,4, K.H. Lim 5, A. Low 6, Y.Y. Leung 1,2 1 Department of Rheumatology and
Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) can be defined as a
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1010 1016 Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: The Mayo Clinic Experience SURESH T. CHARI,* THOMAS C. SMYRK, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* MARK D. TOPAZIAN,* NAOKI
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1010 1016 Diagnosis of Autoimmune Pancreatitis: The Mayo Clinic Experience SURESH T. CHARI,* THOMAS C. SMYRK, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* MARK D. TOPAZIAN,* NAOKI
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
IgG4-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients
 IgG-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients Dai Inoue, MD, PhD, Kotaro Yoshida, MD, PhD, Norihide Yoneda, MD, PhD, Kumi Ozaki, MD, PhD, Takashi Matsubara, MD, PhD, Keiichi Nagai, MD, PhD,
IgG-Related Disease: Dataset of 235 Consecutive Patients Dai Inoue, MD, PhD, Kotaro Yoshida, MD, PhD, Norihide Yoneda, MD, PhD, Kumi Ozaki, MD, PhD, Takashi Matsubara, MD, PhD, Keiichi Nagai, MD, PhD,
Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis
 J Hematopathol (2011) 4:207 214 DOI 10.1007/s12308-011-0117-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis Imran
J Hematopathol (2011) 4:207 214 DOI 10.1007/s12308-011-0117-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Perifollicular granulomatous inflammation in reactive lymph nodes: a possible morphologic marker for IgG4 plasmacytosis Imran
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology
 Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Glomerulonephritis and other renal pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Dr Ian Roberts Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Present the basic diagnostic features of the commonest conditions causing proteinuria & haematuria Highlight diagnostic pitfalls Nephrotic
Anatomy of the biliary tract
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Anatomy of the biliary tract Figure removed due to copyright reasons. Biliary
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
 2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
2nd Pannonia Congress of pathology Hepato-biliary pathology Autoimmune Liver Diseases Vera Ferlan Marolt Institute of pathology, Medical faculty, University of Ljubljana Slovenia Siofok, Hungary, May 2012
Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis
 Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis Poster No.: C-2005 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Takeda, T. Ueda,
Characteristic feautures of cholangitis with serum IgG4 elevation compared with primary sclerosing cholangitis Poster No.: C-2005 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Takeda, T. Ueda,
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this talk.
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco I have nothing to disclose regarding the information to be reported in this
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass
 [ Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Pearls ] A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass Dimitrios Theofilos, MD ; Christina Triantafillidou, MD, PhD ; Athanasios Zetos, MD
[ Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Pearls ] A 44-Year-Old Man With Chronic Cough, Weakness, and a Mediastinum Mass Dimitrios Theofilos, MD ; Christina Triantafillidou, MD, PhD ; Athanasios Zetos, MD
155.2 Malignant neoplasm of liver not specified as primary or secondary. C22.9 Malignant neoplasm of liver, not specified as primary or secondary
 ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT
 J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 129-133 IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT Han-Jui Lee 1 Yi-Chen Yeh 2,3 Chun-Ku Chen 1,3 Rheun-Chuan Lee 1,3
J Radiol Sci 2013; 38: 129-133 IgG4-related Sclerosing Disease of the Lung without Pancreas Involvement: Presentation on 18F-FDG PET/CT Han-Jui Lee 1 Yi-Chen Yeh 2,3 Chun-Ku Chen 1,3 Rheun-Chuan Lee 1,3
'I GO FOR' (IG4) Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and extrapancreatic imaging features.
 'I GO FOR' (IG4) Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and extrapancreatic imaging features. Poster No.: C-2649 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. P. Patel, T. M. Chandler, S. Barrett, J.
'I GO FOR' (IG4) Autoimmune pancreatitis (AIP) and extrapancreatic imaging features. Poster No.: C-2649 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. P. Patel, T. M. Chandler, S. Barrett, J.
Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome)
 Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome) Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome) Synonyms Crow-Fukase syndrome Multicentric Castleman disease Takatsuki syndrome Acronym coined by Bardwick POEMS Scheinker,
Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome) Osteosclerotic Myeloma (POEMS Syndrome) Synonyms Crow-Fukase syndrome Multicentric Castleman disease Takatsuki syndrome Acronym coined by Bardwick POEMS Scheinker,
Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Bladder:
 Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Bladder: Report of Two Cases 1 Hanna Kim, M.D., Soon Nam Oh, M.D., Sung Eun Rha, M.D., Seung Eun Jung, M.D., Young Joon Lee, M.D., Jae Young Byun, M.D., Chan-Kwon
Inflammatory Myofibroblastic Tumor of the Bladder: Report of Two Cases 1 Hanna Kim, M.D., Soon Nam Oh, M.D., Sung Eun Rha, M.D., Seung Eun Jung, M.D., Young Joon Lee, M.D., Jae Young Byun, M.D., Chan-Kwon
Retroperitoneal fibrosis from bedside to bench
 Retroperitoneal fibrosis from bedside to bench Augusto Vaglio, MD PhD UO Nefrologia, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma augusto.vaglio@virgilio.it THE CONCEPT OF FIBRO-INFLAMMATORY DISEASES Tumour-like,
Retroperitoneal fibrosis from bedside to bench Augusto Vaglio, MD PhD UO Nefrologia, Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria di Parma augusto.vaglio@virgilio.it THE CONCEPT OF FIBRO-INFLAMMATORY DISEASES Tumour-like,
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion and Thrombophlebitis
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.76.4.179 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;76:179-183 A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4046/trd.2014.76.4.179 ISSN: 1738-3536(Print)/2005-6184(Online) Tuberc Respir Dis 2014;76:179-183 A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion
Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc. Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz
 Title Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc Omotehara, Satomi; Nishida, Mutsumi; Satoh, Megumi; Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz CitationJournal of medical
Title Sonographic findings of immunoglobulin G4-related sc Omotehara, Satomi; Nishida, Mutsumi; Satoh, Megumi; Author(s) Akihiro; Nakamaru, Yuji; Hatanaka, Kanako C.; Shimiz CitationJournal of medical
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
CHRONIC PANCREATITIS OR DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA? N. Volkan Adsay, \ MD
 CHRONIC PANCREATITIS OR DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA? N. Volkan Adsay, \ MD Case for discussion 67 y/o male Back pain and weight loss CT: 4.5 cm ill-defined, solid lesion in the head FNA/Core bx: Inconclusive
CHRONIC PANCREATITIS OR DUCTAL ADENOCARCINOMA? N. Volkan Adsay, \ MD Case for discussion 67 y/o male Back pain and weight loss CT: 4.5 cm ill-defined, solid lesion in the head FNA/Core bx: Inconclusive
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3): /ISSN: /IJCEP Sun Young Choi 1, Sanghui Park 2
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):4033-4037 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0020891 Case Report Is the presence of IgG4+ cells within urothelial carcinomas of the renal pelvis that contain rhabdoid and
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(3):4033-4037 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0020891 Case Report Is the presence of IgG4+ cells within urothelial carcinomas of the renal pelvis that contain rhabdoid and
Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis
 Hindawi Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 4876587, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4876587 Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis Eran Berkowitz,
Hindawi Case Reports in Ophthalmological Medicine Volume 2017, Article ID 4876587, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4876587 Case Report IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Isolated Scleritis Eran Berkowitz,
IgG4 cholangitis Case Report: Joanne Verheij, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Academic Medical Center Amsterdam.
 IgG4 cholangitis New Perspectives on Biliary Tract Disease Case Report: male, 64 yrs, truck driver and car industry worker Joanne Verheij, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Academic Medical Center Amsterdam
IgG4 cholangitis New Perspectives on Biliary Tract Disease Case Report: male, 64 yrs, truck driver and car industry worker Joanne Verheij, MD, PhD Department of Pathology Academic Medical Center Amsterdam
Hematologic Malignancies of the Liver : Spectrum of Disease. Zhou Jian
 Hematologic Malignancies of the Liver : Spectrum of Disease Zhou Jian 2015-7-8 Hematologic malignancies include a wide spectrum of lymphoproliferative and myeloproliferative disorders with nodal and extranodal
Hematologic Malignancies of the Liver : Spectrum of Disease Zhou Jian 2015-7-8 Hematologic malignancies include a wide spectrum of lymphoproliferative and myeloproliferative disorders with nodal and extranodal
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1
 Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Plasmacytoid Variant Urothelial Carcinoma: Diagnostic and Grossing Challenges. Kailyn Gibson MS, PA-ASCP, Congli Wang, MD
 1 Plasmacytoid Variant Urothelial Carcinoma: Diagnostic and Grossing Challenges Kailyn Gibson MS, PA-ASCP, Congli Wang, MD Johns Hopkins Hospital Department of Surgical Pathology 2 Plasmacytoid Variant
1 Plasmacytoid Variant Urothelial Carcinoma: Diagnostic and Grossing Challenges Kailyn Gibson MS, PA-ASCP, Congli Wang, MD Johns Hopkins Hospital Department of Surgical Pathology 2 Plasmacytoid Variant
Case: The patient is a 73 year old woman with vague complaints of dyspepsia and abdominal pain. Upper endoscopy showed features of gastritis and a
 Case: The patient is a 73 year old woman with vague complaints of dyspepsia and abdominal pain. Upper endoscopy showed features of gastritis and a nodular lesion in the body of the stomach. The patient
Case: The patient is a 73 year old woman with vague complaints of dyspepsia and abdominal pain. Upper endoscopy showed features of gastritis and a nodular lesion in the body of the stomach. The patient
IgG4-Related Disease
 IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic autoimmune fibroinflammatory disease that produces sclerotic, tumefactive masses containing dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in immunoglobulin (Ig)
IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a systemic autoimmune fibroinflammatory disease that produces sclerotic, tumefactive masses containing dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in immunoglobulin (Ig)
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017
 Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
Prostate cancer ~ diagnosis and impact of pathology on prognosis ESMO 2017 Dr Puay Hoon Tan Division of Pathology Singapore General Hospital Prostate cancer (acinar adenocarcinoma) Invasive carcinoma composed
IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis?
 CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
CASE REPORT IgG4-Negative Autoimmune Pancreatitis with Sclerosing Cholangitis and Colitis: Possible Association with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis? Keita Saeki 1, Shigenari Hozawa 1, Naoteru Miyata 1,
The most common presentation of autoimmune pancreatitis. A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1097 1103 A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer SURESH T. CHARI,* NAOKI TAKAHASHI, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* THOMAS
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:1097 1103 A Diagnostic Strategy to Distinguish Autoimmune Pancreatitis From Pancreatic Cancer SURESH T. CHARI,* NAOKI TAKAHASHI, MICHAEL J. LEVY,* THOMAS
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
The newly recognized fibroinflammatory condition. An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases
 case report J Neurosurg Spine 25:790 794, 2016 An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases Bishan D. Radotra, MD, 1 Ashish Aggarwal, DNB, MCh, 2 Ankur Kapoor, MS, MCh, 2 Navneet
case report J Neurosurg Spine 25:790 794, 2016 An orphan disease: IgG4-related spinal pachymeningitis: report of 2 cases Bishan D. Radotra, MD, 1 Ashish Aggarwal, DNB, MCh, 2 Ankur Kapoor, MS, MCh, 2 Navneet
CME/SAM. Increased Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 Positive Plasma Cell Density and IgG4/IgG Ratio Are Not Specific for IgG4- Related Disease in the Skin
 Increased Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 Positive Plasma Cell Density and IgG4/IgG Ratio Are Not Specific for IgG4- Related Disease in the Skin Julia S. Lehman, MD, 1,2 Thomas C. Smyrk, MD, 1 and Mark R. Pittelkow,
Increased Immunoglobulin (Ig) G4 Positive Plasma Cell Density and IgG4/IgG Ratio Are Not Specific for IgG4- Related Disease in the Skin Julia S. Lehman, MD, 1,2 Thomas C. Smyrk, MD, 1 and Mark R. Pittelkow,
Pancreatic Cancer Masquerading as Pancreatitis
 Pancreatic Cancer Masquerading as Pancreatitis Poster No.: C-2553 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Cahalane, Y. M. Purcell, L. Lavelle, E. R. Ryan, S. Skehan ; 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 Dublin,
Pancreatic Cancer Masquerading as Pancreatitis Poster No.: C-2553 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Cahalane, Y. M. Purcell, L. Lavelle, E. R. Ryan, S. Skehan ; 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 Dublin,
TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL
 TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL Dr Augusto Vaglio, Dr Federica Maritati Unit of Nephrology, University Hospital of Parma, Via Gramsci 14, 43126 Parma
TOCILIZUMAB FOR DIFFICULT TO TREAT IDIOPATHIC RETROPERITONEAL FIBROSIS. A PILOT TRIAL Dr Augusto Vaglio, Dr Federica Maritati Unit of Nephrology, University Hospital of Parma, Via Gramsci 14, 43126 Parma
Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1991, 36
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD
 Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
Case Presentation Turki Al-Hussain, MD Director, Renal Pathology Chapter Saudi Society of Nephrology & Transplantation Consultant Nephropathologist & Urological Pathologist Department of Pathology & Laboratory
Case Presentation. Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD. Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan
 Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies. Mixed follicular and paracortical hyperplasia. Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia
 Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Mimics of Lymphoma in Routine Biopsies Patrick Treseler, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology University of California San Francisco Types of Lymphoid Hyperplasia Follicular hyperplasia (B-cells) Paracortical
Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis
 International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
International Scholarly Research Network Volume 2012, Article ID 412896, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/412896 Review Article Orbital IgG4-Related Disease: Clinical Features and Diagnosis Toshinobu Kubota 1
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus
 Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
Diagnostic And Therapeutic Challenges in IgG4-Related disease in the Sphenoid Sinus Omar Abu Suliman, MBBS, SB-ORL Senior Registrar, otolaryngology Head & neck surgery King Abdullah Medical City, Makkah,
