Histopathological Study of Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia in Biopsies Received at Tertiary Care Centre
|
|
|
- Brian Franklin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor ICV: Original Research Article Histopathological Study of Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia in Biopsies Received at Tertiary Care Centre Neetal Desai 1, Ami Shah 2, Hansa Goswami 3 1 3rd Year Resident, B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 2 Associate Professor, Departmentof Pathology, B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India; 3 Professor and Head, Departmentof Pathology, B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. ABSTRACT Introduction: Ocular surface squamous neoplasia(ossn) is an encompassing term for pre-cancerous and cancerous epithelial lesions of the conjunctiva and cornea which includes Dysplasia, Carcinoma in-situ (CIS) and Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma. OSSN is mostly unilateral, occurs in middle aged to older patients. It is associated with factors such as HIV and xeroderma pigmentosum. Aims and Objectives: 1) To evaluate incidence of Dysplasia and Squamous Cell Carcinoma in biopsies received 2) To study the spectrum of histopathological findings in Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia Materials and Method: We examined 52 ocular surface biopsies received in our tertiary care centre during the period of 22 months (August-2015 to May-2017). Slides stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin were examined and dysplasia found in biopsies were categorized into mild, moderate and severe. Invasive squamous cell carcinomas were again categorized according to differentiation into well differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated. In addition to these 52 biopsies, 10 biopsies were excluded from the study which showed normal or only hyperplastic squamous epithelium. Results: Out of 52 biopsies examined, 2 cases showed squamous papilloma,13 cases showed dysplasia-mild being the commonest and 37 cases showed invasive carcinoma, moderate differentiation being the commonest. Conclusion: OSSN is common in middle age and male gender and usually occurs in limbal conjunctiva. Histopathology remains the gold standard for accurate diagnosis and grading of OSSN. Despite increasing awareness, Invasive carcinoma is more prevalent than dysplasia. Prognosis largely depends upon grade and differentiation of tumor and specific microscopic type. Key Words: Dysplasia, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, HIV, Xeroderma Pigmentosum INTRODUCTION Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia(OSSN) is an embracing term for pre-cancerous and cancerous epithelial lesions of the conjunctiva and cornea. It includes the spectrum of Dysplasia, Carcinoma in-situ (CIS) and Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma(SCC) (1 3). OSSN is mostly unilateral and is seen in middle age and older patients. Rarely, it is bilateral especially in immunocompromised patients. Factors causing development of OSSN are exposure to sunlight, HPV type 16 infections and HIV infection (2,5). There is a systemic association of xeroderma pigmentosum with OSSN patients. Other factors associated are old age, heavy cigarette smoking, male sex and light complexion. Clinically, we cannot distinguish CIS from invasive SCC. The presence of feeder vessels, intrinsic vascularity and a nodular lesion should raise suspicion of invasive SCC. This usually presents either as a fleshy, gelatinous lesion or as a sessile, papillomatous lesion mostly in the interpalpebral Corresponding Author: Dr. Neetal Desai, 3rd Year Resident, B.J. Medical College, Ahmedabad; B404, New PG Hostel, Phase 2, Civil Hospital, Asarwa, Ahmedabad ; Mob: ; neetu_khushi13@yahoo.co.in ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online) DOI: /IJCRR Received: Revised: Accepted: Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 9 Issue 20 October
2 region. Unless the lesion is encroaching onto the pupillary area, vision is spared. Presenting clinical features of this entity are swelling, redness, irritation and feeder vessels surrounding the lesion (1,2,5,7,8). Advanced cases can invade the cornea and sclera (9) and on rare occasions the tumor may infiltrate into the orbit causing proptosis. Treatment includes complete surgical excision with 4mm margin clearance without touching the tumor, so called No Touch Technique (1,10,11). Cryotherapy is also useful (8) Reported recurrence rate of OSSN is 15-52%. Lee and Herst reported a 17% recurrence after excision of conjunctival dysplasia, 40% after excision of CIS and 30% for SCC of conjunctiva 2. The recurrence rate can be limited to less than 5% with the above technique. OSSN has a good prognosis. The recurrence rate is about 5% and regional metastasis rate is about 2% With the modern techniques (1,5,12,13). AIMS AND OBJECTIVES 1) To evaluate incidence of Dysplasia and Squamous Cell Carcinoma in biopsies received 2) To study the spectrum of histopathological findings in Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia MATERIALS AND METHOD We examined 52 ocular surface biopsies received in our tertiary care centre during the period of 22 months(august-2015 to May-2017).Slides were stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin. Dysplasia found in biopsies were categorized into mild, moderate and severe (Conjunctival Intraepithelial Neoplasia(CIN)-I,II and III respectively). Slides were carefully examined for foci of invasion. Invasive squamous cell carcinomas were again categorized according to differentiation into well differentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated. In addition to these 52 biopsies, 10 biopsies were excluded from the study which showed normal or only hyperplastic squamous epithelium. RESULTS Out of 52 biopsies examined, results are as shown in (Table:1), with comparison with the study done in 2016 by Kabra RC et al (14).(Table: 2) Two cases of poorly differentiated carcinoma showed histomorphology of spindle cell variant-a known variant of invasive ocular squamous cell carcinoma. One of them was HIV positive patient. In the study by Kabra RC et al, more patients were HIV positive (14). A few cases with moderately and poorly differentiated carcinoma showed extensive stromal necrosis. Maximum(42) cases were found between the age group of years, mean age being 57.5 years. A few cases of moderate dysplasia and well differentiated carcinoma were found in the younger age group(<20 years of age).one male patient was 26 years of age and was a known case of xeroderma pigmentosum, showed histology of well differentiated squamous cell carcinoma on biopsy. Out of 52 cases, 35 were male and 17 were female. Results are compared with the study done by Kabra RC et al (14), in which mean age was 38.2 years and males were more commonly affected (14). Most common location was limbal conjunctiva,30 out of 52 cases.other locations are nasal and temporal conjunctiva. DISCUSSION Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia, within its spectrum, includes Squamous papilloma, Intraepithelial neoplasia or Dysplasia, Intraepithelial Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma. The term CIN(Conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia)-which includes dysplasia and carcinoma in-situ, in vogue today was proposed by Pizarello and Jakobeic, derived from the terminology applied to the intraepithelial cervical malignancies (15). Squamous papilloma of conjunctiva lack malignant potential and when occur in children, they are mostly bilateral and recurrent and associated with HPV infection. When in adults, they are usually solitary and unilateral and confused clinically with squamous cell carcinoma (16).In our study both the cases of squamous papilloma occurred in elder age group with solitary and unilateral lesions. Histopathologically, both cases of papilloma showed papillomatous fronds of squamous epithelium that covered a fibrovascular core. (Figure: 1) It is reported that about 6% of squamous papillomas can present epithelial dysplasia (17). Both cases did not show any changes of dysplasia in our study. Abnormalities in a dysplastic lesion is because of the deranged cellular proliferation that means the abnormal mitotic cells do not fully differentiate as they move upwards in the epithelium (disordered proliferation or altered differentiation). Dysplasia of the conjunctival epithelium is characterized by acanthosis, loss of cellular polarity, and cellular pleomorphism, and it resembles dysplasia of the uterine cervix microscopically. Depending on the extent of the epithelial abnormalities, conjunctival dysplasia can be designated as mild, moderate, or severe (16).(Table: 3). 25 Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 9 Issue 20 October 2017
3 Full thickness epithelial dysplasia without breaching of epithelial basement membrane, is known as carcinoma in situ. As explained by Mittal R et al (18), as the lesion progresses from mild to severe dysplasia, the cells differentiate less and less, losing their squamous features until eventually entire epithelium consists of undifferentiated cells. The dysplastic cells show an increase in the size of nuclei, irregular nuclear membrane, hyperchromatic and fine to coarse nuclear chromatin. Degree of nuclear atypia, irrespective of level of epithelial thickness involved can also cause up gradation or down gradation of severity of dysplasia. Mittal R et al (18) also explained in their study that hyperkeratosis and dyskeratosis that is single cell keratinization with the formation of squamous pearls is not a usual feature of intra epithelial lesions. Increased mitosis with presence of abnormal mitosis can be observed. Mild to moderate chronic inflammatory cell infiltration may be observed and can cause inflammatory destruction of epithelial basement membrane. This should not be confused with invasive squamous cell carcinoma, especially in cases of carcinoma in situ as (18). Nuclear atypia was found in all 9 cases of dysplasia, though more pronounced in moderate and severe dysplasia.(figure: 2 & 3) Some cases of mild dysplasia showed hyperkeratosis but dyskeratosis and pearl formation were not found in any of the cases. Frequent mitosis with atypical mitosis were observed. Lesions associated with HPV show cytopathic effect in cells, resulting in the formation of a halo around the enlarged and wrinkled nucleus with dense chromatin and inconspicuous nucleoli. The halo is surrounded by dense eosinophilic cytoplasm. Such cells are called koilocytes. Koilocytes are pathognomic of HPV infection. As explained by Mittal R et al (18), formation of koilocytes decreases with increasing severity of dysplasia, and they are rarely seen in invasive lesions (18). In our study, none of the cases showed this feature. Invasive squamous cell carcinoma develops from conjunctival intraepithelial neoplasia by breaching the epithelial basement membrane and invading the underlying stromal tissue. As mentioned by Mittal R et al (18), invading tumor can have several patterns like cords, strands and clusters of malignant cells in infiltrative manner, broad pushing fronds with expansive pattern can also be seen. Dense collagenous scleral tissue in cases of conjunctival OSSN and Bowman s membrane in corneal OSSN helps limiting the infiltration. Cytologically cells are large polygonal, but can be small to spindle in shape. Authors also mention that the more the degree of maturation, the dense, eosinophilic is the cytoplasm, the pyknotic is the nucleus. There is single cell keratinization or formation of squamous pearl. Differentiation is in terms of degree of keratinization and accordingly named as welldifferentiated, moderately differentiated and poorly differentiated carcinoma. As observed by Mittal R et al (18) in their study, keratinization is more in well and moderately differentiated tumors with less nuclear pleomorphism cytologically, whereas poorly differentiated tumors have predominance of immature cells with higher nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, more pleomorphic nuclei, increased typical and atypical mitoses and minimal keratinization. (18). Majority (20) cases showed moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with moderate keratinization with polygonal cells with moderate amount of cytoplasm, enlarged nuclei and mild nuclear atypia with frequent mitosis.(figure: 4) One case showed extensive stromal necrosis. Few cases showing well differentiation were difficult to distinguish from carcinoma in-situ especially in cases which showed only occasional foci of microinvasion-termed as microinvasive squamous cell carcinoma. Vascular invasion was also seen in some cases. Out of 17 well differentiated SCC,5 cases showed microinvasion. All 4 cases of poorly differentiated tumors showed features mentioned above.cells showed increased nuclear atypia and mitosis than moderately or well differentiated cases. Invasive squamous cell carcinoma needs to be differentiated from pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia. Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia is a reactive proliferation of the surface epithelium secondary to an inflammatory or infectious process. Histologically it is confused with well differentiated or moderately differentiated carcinoma because it shows irregular invasion, keratin pearl formation and mitotic figures. As mentioned by Mittal R et al (18), disparity between architectural and cytological abnormality with minimal or absent nuclear hyperchromasia, hyperplasia and pleomorphism, helps in differentiating from a true malignancy (18,19). Another differential diagnosis is keratoacanthoma. Microscopically,there are lobules of proliferating squamous epithelium which grows upward and inward and may have increased number of mitotic figures with vesicular nuclei and eosinophilic nucleoli raising the suspicion of SCC.In such cases it should be indicated in the pathology report that SCC cannot be definitively excluded and only the biologic behavior of the lesion will differentiate both the lesions (19). Other ocular surface lesions which can clinically mimic OSSN such as actinic keratosis, pterygium, pinguecula and actinic granuloma can be easily differentiated from OSSN microscopically (18). Pigmented SCC can be confused with melanoma, IHC for keratin establishes the diagnosis (19). Clear cell change/hydropic change of the cytoplasm can be seen in squamous cell carcinoma and one should be cautious while dealing with it because it mimics an aggressive disease such as pagetoid extension in a sebaceous gland carcinoma, Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, or even metastatic renal cell carcinoma, as explained by Mittal R et al (18). Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 9 Issue 20 October
4 There are variants of Invasive Squamous cell carcinoma such as Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, Spindle cell carcinoma, papillary squamous cell carcinoma and Acantholytic/Adenoid squamous cell carcinoma (18). Mucoepidermoid carcinoma is a locally aggressive, mucinproducing variant of squamous cell carcinoma with same clinical presentation as classic squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology is required to make this rare diagnosis. Microscopic features are well documented by Mittal R et al (18) in their study, which include admixture of epidermoid cells, intermediate cells,and mucus producing cells (components can vary within the same tumor), as well as sheets or cords of squamous cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and predominantly mucin-containing cells with pools of mucin surrounded by the neoplastic cells. Mittal R et al (18) also explains that the presence of squamous pearls is the exception rather than the rule. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma has a high rate of recurrence, but local and distant metastases are uncommon. (18,19). Spindle cell carcinoma is another rare and locally more aggressive variant of squamous cell carcinoma of conjunctiva with only few case reports in the literature. Spindle cell carcinoma/sarcomatoid carcinoma microscopically shows biphasic pattern of squamous cell carcinoma with a larger component of malignant spindle cells. The squamous component can be scanty or even not at all apparent on light microscopy (Figure: 5 & 6). In such cases, immunohistochemical stains for cytokeratins, vimentin, p63 and EMA and electron microscopic evidence of squamous differentiation is required for diagnosis as explained by Mittal R et al (18). Spindle cell carcinoma is much more likely to extend through the sclera, cornea and the interior of the globe (18). Two such cases were observed in our study showing poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with spindle cell morphology, one of them was an HIV reactive patient. Papillary squamous cell carcinoma is an exophytic variant of squamous cell carcinoma with a papillary configuration that is tumor cells arranged in papillary fashion surrounding fibrovascular core. They generally have a better prognosis (18). Adenoid squamous cell carcinoma or Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma is another rare, locally aggressive and recurrent variant of SCC. It can even metastasize and should be microscopically differentiated from the less aggressive conventional squamous cell carcinoma. Regular follow up is needed to predict recurrences (18). Management modalities for OSSN include complete surgical excision in well delineated tumors, wide excision in aggressive SCC variants like mucoepidermoid and spindle cell SCC to topical chemotherapy(5-fluorouracil and mitomycin C) and immunotherapy in diffuse unresectable lesions. The overall prognosis in OSSN is good. Mittal R et al (18) mentioned in their study that modern treatment strategies 27 are effective with lower local recurrence rates and regional lymph node metastasis. Aggressive variants like muco-epidermoid and spindle cell carcinoma and OSSN in immunocompromised patients have a worse prognosis (18). CONCLUSION OSSN is common in middle age and male gender and has an association with HPV as well as HIV infections and xeroderma pigmentosum. Histopathology remains the gold standard for accurate diagnosis and grading of OSSN. Despite increasing awareness, Invasive carcinoma is more prevalent than dysplasia. Prognosis largely depends upon grade and differentiation of tumor as well as specific microscopic types.hiv status also predicts prognosis. ACKNOWLEDGEMENT Authors acknowledge the immense help received from the scholars whose articles are cited and included in references of this manuscript. The authors are also grateful to authors/ editors/publishers of all those articles, journals and books from where the literature for this article has been reviewed and discussed. Note: The present study was undertaken at tertiary care centre, Gujarat and all the biopsies considered in the present study were taken at this centre with prior consent of the patients. Ethical committee clearance has not been required as confidentiality of patient s details has not been published. REFERENCES 1. Shields CL, Shields JA. Tumours of the conjunctiva and cornea. Surv Ophthalmol. 2004;49:3 24.[PubMed] 2. Lee GA, Hirst LW. Ocular surface squamous neoplasia. Surv Ophthalmol. 1995;39: [PubMed] 3. Pe er J. Ocular surface squamous neoplasia. Ophthalmol Clin North Am. 2005;18:1 13. vii. [PubMed] 4. Lee GA, Hirst LW. Retrospective study of OSSN. Aust NZJ Ophthalmol. 1997;25:269. [PubMed] 5. Shields JA, Shields CL. Eyelid, Conjunctival and Orbital Tumours. An Atlas and Textbook. 2nd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; pp Shields CL, Demirci H, Karatza E, Shields JA. Clinical survey of 1643 melanocytic and nonmelanocytic conjunctival tumours. Ophthalmology. 2004;111: [PubMed] 7. Farah S, Baum TD, Conton MR. Principles and Practice of Ophthalmology. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; Tumours of cornea and conjunctiva. In: Albert DM, Jakobiec FA, editors; pp Honavar SG, Manjandavida FP. Tumours of the ocular surface: A review. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2015;63: [PMC free article] [PubMed] 9. Nicholson DH, Herschler J. Intraocular extension of squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977;95: [PubMed] Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 9 Issue 20 October 2017
5 10. Mauriello JA, Napolitano J, McLean I. Actinic keratosis and dysplasia of the conjunctiva: A clinicopathological study of 45 cases. Can J Ophthalmol. 1995;30: [PubMed] 11. Shields JA, Shields CL, De Potter P. Surgical management of conjunctival tumours. The 1994 Lynn B. McMahan Lecture. Arch Ophthalmol. 1997;115: [PubMed] 12. Cervantes G, Rodríguez AA, Leal AG. Squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva: Clinicopathological features in 287 cases. Can J Ophthalmol. 2002;37: [PubMed] 13. Shields CL, Fasiuddin AF, Mashayekhi A, Shields JA. Conjunctival nevi: Clinical features and natural course in 410 consecutive patients. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122: [PubMed] 14. Kabra RC, Morawala A, Maheshwari VN. Clinicopathological analysis of 55 cases of ocular surface squamous neoplasia. Ophthal Rev: Int J ophtha & Oto. 2016;1(1): doi: / jooo.2016.i Pizzarello L.D., Jakobiec F.A. Bowen s disease of the conjunctiva: a misomer. In: Jakobiec F.A., editor. Ocular adnexal tumors. Aesculapius; Birmingham, AL: pp Alexandre N. Odashiro, Thomas J. Cummings, Miguel N. Burnier, Jr. Eye and Ocular Adnexa. In: Stacey E. Mills, editor; Joel K. Greenson, Jason L. Hornick, Teri A. Longacre, Victor E. Reuter, Associate editors.sternberg s diagnostic surgical pathology. 6 th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health; p Sjö N, Heegaard S, Prause JU. Conjunctival papilloma.a histopathologically based retrospective study.acta Ophthalmol Scand 2000;78: Mittal R, Rath S, Vemuganti GK. Ocular surface squamous neoplasia Review of etio-pathogenesis and an update on clinico-pathological diagnosis. Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology. 2013;27(3): doi: /j.sjopt Ramon L Font, J Oscar Croxatto, Narsing A Rao.Tumors of the Eye and Ocular Adnexa, AFIP Atlas of Tumor Pathology. Series 4, fascicle 5. The American Registry of Pathology in collaboration with the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology; p Table 1: Number of cases of dysplasia,carcinoma in-situ and invasive carcinoma in different age groups. Age * OSSN-lesion Total Papilloma Intraepithelial neoplasia-dysplasia Mild Moderate Severe Carcinoma In-Situ Invasive Carcinoma Well differentiated Microinvasive carcinoma Moderately differentiated Poorly differentiated TOTAL 52 ( * OSSN- Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia) Table 2: Comparison between current study and study by Kabra RC et al (14). * OSSN-lesion Current Study Study by Kabra RC et al (14) Papilloma 2 - Intraepithelial neoplasia-dysplasia Mild 6 12 Moderate 2 2 Severe 1 9 Carcinoma In-Situ 0 - Invasive Carcinoma Well differentiated 12 9 Microinvasive carcinoma 5 - Moderately differentiated 20 9 Poorly differentiated 4 14 ( * OSSN- Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia) Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 9 Issue 20 October
6 Desai et.al.: Histopathological study of ocular surface squamous neoplasia in biopsies received at tertiary care centre Table 3: Grading of dysplasia Degree of Dysplasia Microscopic Finding Mild ( CIN I) Lower 1/3rd of the epithelium shows dysplasia Moderate (*CIN II) Lower 2/3rd of the epithelium shows dysplasia Severe (*CIN III) >2/3rd of the epithelium shows dysplasia, however surface maturation is preserved. * (*CIN- Conjunctival Intraepithelial Neoplasia) Figure 4: Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Figure 1: Squamous Papilloma. Figure 5: Spindle Cell Variant of SCC, (20x) View. Figure 2: Moderate Dysplasia. Figure 6: Spindle Cell Variant of SCC, High Power(40x) View. Figure 3: Severe Dysplasia. 29 Int J Cur Res Rev Vol 9 Issue 20 October 2017
04/09/2018. Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions. Agenda. Squamous Dysplasia. Squamo-proliferative lesions. Architectural features
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Histopathological Study of Lacrimal Gland Tumors
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pratikkumar B. Desai 1, Ami Shah 2 1 4 th Year Resident, Pathology Department, B.J.Medical College, Civil Hospital, Ahmedabad 2 Associate Professor, M. J. Institute of Ophthalmology, Civil
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pratikkumar B. Desai 1, Ami Shah 2 1 4 th Year Resident, Pathology Department, B.J.Medical College, Civil Hospital, Ahmedabad 2 Associate Professor, M. J. Institute of Ophthalmology, Civil
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Neoplasia 2018 Lecture 2 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. List the differences between benign and malignant tumors. 2. Recognize the histological features of malignancy. 3. Define dysplasia and understand
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN)
 Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (SCCHN) Part 1 Bruce M. Wenig, M.D. Dept. of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Continuum Health Partners New York, NY College of American Pathologists 2004. Materials
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more
 Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
Benign and malignant epithelial lesions: Seborrheic keratosis: A common benign pigmented epidermal tumor occur in middle-aged or older persons more common on the trunk; but extremities, head and neck are
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
A Case Report of Recurrent Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma M Zhao 1, W Lin 2 *, Z Liu 2 ABSTRACT
 A Case Report of Recurrent Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma M Zhao 1, W Lin 2 *, Z Liu 2 ABSTRACT A case of recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva is presented here. A 13-yearsold male
A Case Report of Recurrent Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma M Zhao 1, W Lin 2 *, Z Liu 2 ABSTRACT A case of recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the conjunctiva is presented here. A 13-yearsold male
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Pathology of the skin. 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University
 Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Pathology of the skin 2nd Department of Pathology, Semmelweis University Histology of the skin Epidermis: Stratum corneum Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale Dermis: papillary and reticular
Plaque Radiotherapy in Recurrent or Incomplete- Excised Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Melanoma
 Plaque Radiotherapy in Recurrent or Incomplete- Excised Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Melanoma Masood Naseripour, MD 1 Mohsen Bahmani-Kashkouli, MD 1 Ramin Jaberi, MS 2 Gholam-Hossein Aghaee,
Plaque Radiotherapy in Recurrent or Incomplete- Excised Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Melanoma Masood Naseripour, MD 1 Mohsen Bahmani-Kashkouli, MD 1 Ramin Jaberi, MS 2 Gholam-Hossein Aghaee,
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions
 Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
Squamous Cell Neoplasia and Precursor Lesions Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Arkansas for Medical
HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY
 Bosnian-British School of Pathology November 2012 HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY Slide seminar: Oral Pathology Preferred Diagnoses Dr A Sandison, Slide seminar: Pathology of the Oral Cavity Page 1 of 5 1. Female
Bosnian-British School of Pathology November 2012 HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY Slide seminar: Oral Pathology Preferred Diagnoses Dr A Sandison, Slide seminar: Pathology of the Oral Cavity Page 1 of 5 1. Female
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author N Vivekanand
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(1D):461-465 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2014; 2(1D):461-465 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal
 Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance
 & 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
& 2006 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/06 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate on needle biopsy: histologic features and clinical significance Charles C Guo 1 and
A neoplasm is defined as "an abnormal tissue proliferation, which exceeds that of adjacent normal tissue. This proliferation continues even after
 NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
NEOPLASIA Neoplasia is a very important topic in pathology because neoplasms are both common and serious diseases. A neoplasm literally means a new growth, and this term is used interchangeably with a
Histopathology: skin pathology
 Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: skin pathology These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies
 Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Dysplasia, Mimics and Other Controversies Mary S. Richardson, MD Dept. of Pathology Medical University of South Carolina Charleston, SC Notice of Faculty Disclosure In accordance with ACGME guidelines,
Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update 5/29/2009
 Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Stacey E. Mills, M.D. W.S. Royster Professor of Pathology Director of Surgical and Cytopathology University
Diagnostic Problems in Salivary Gland Pathology An Update Lesions Mimicking Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Stacey E. Mills, M.D. W.S. Royster Professor of Pathology Director of Surgical and Cytopathology University
Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa
 Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa No financial disclosures No discussion of off-label use of medications or unapproved devices 67 year old male referred to Oculoplastics
Nasreen A. Syed, MD F.C. Blodi Eye Pathology Laboratory University of Iowa No financial disclosures No discussion of off-label use of medications or unapproved devices 67 year old male referred to Oculoplastics
Asadi-Amoli et al Adenocarcinoma of RPE Iranian Journal of Ophthalmology - Volume 19, Number 4, 2007
 Adenocarcinoma of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Clinically Diagnosed as Malignant Melanoma; A Case Report with Unsystematic Review of Literature Fahimeh Asadi-Amoli, MD, 1 Hedyeh Moradi, MD 2 Mohammad-Taher
Adenocarcinoma of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Clinically Diagnosed as Malignant Melanoma; A Case Report with Unsystematic Review of Literature Fahimeh Asadi-Amoli, MD, 1 Hedyeh Moradi, MD 2 Mohammad-Taher
University Journal of Pre and Para Clinical Sciences
 ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
ISSN 2455 2879 Volume 2 Issue 1 2016 Metaplastic carcinoma breast a rare case report Abstract : Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast is a rare malignancy with two distinct cell lines described as a breast
Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges
 Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges Michael B. Morgan EPIDEMIOLOGY: Second most common skin cancer, rare in the dark-skinned races. ETIOLOGY: Ultraviolet light, HPV infection. PATHOGENESIS:
Chapter 6 Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Variants and Challenges Michael B. Morgan EPIDEMIOLOGY: Second most common skin cancer, rare in the dark-skinned races. ETIOLOGY: Ultraviolet light, HPV infection. PATHOGENESIS:
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Ocular Neoplasia What s Common? What s New? Richard R Dubielzig
 Ocular Neoplasia What s Common? What s New? Richard R Dubielzig Orbit 288 6% Tumors of the globe make up 3225 out of 6110 total neoplasms = 53%. Tumors of the conjunctiva make up 1192 out of 6110 total
Ocular Neoplasia What s Common? What s New? Richard R Dubielzig Orbit 288 6% Tumors of the globe make up 3225 out of 6110 total neoplasms = 53%. Tumors of the conjunctiva make up 1192 out of 6110 total
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology
 New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS. Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology
 SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology Sebaceous neoplasms Sebaceous adenoma (Benign) Sebaceous carcinoma (Malignant) SEBACEOUS ADENOMA Benign tumours composed of incompletely
SEBACEOUS NEOPLASMS Dr. Prachi Saraogi Clinical Fellow in Dermatology Sebaceous neoplasms Sebaceous adenoma (Benign) Sebaceous carcinoma (Malignant) SEBACEOUS ADENOMA Benign tumours composed of incompletely
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H)
 SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia
 Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box?
 When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
Nasal mucosal melanosis may act as a harbinger of melanoma: A case report
 Nasal mucosal melanosis may act as a harbinger of melanoma: A case report The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Nasal mucosal melanosis may act as a harbinger of melanoma: A case report The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Invasive Papillary Breast Carcinoma
 410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
410 This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial-NoDerivs 3.0 License (www.karger.com/oa-license), applicable to the online version of the
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
number 16 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Zeina Assaf Doctor Maha Shomaf MALIGNANT NEOPLASMS The four fundamental features by which benign and malignant tumors can be distinguished are: 1- differentiation
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA. Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital
 LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
LARYNGEAL DYSPLASIA Tomas Fernandez M; 3 rd year ENT resident, Son Espases University Hospital INTRODUCTION Laryngeal cancer constitutes 1-2% of all malignancies diagnosed worldwide Survival is related
Periocular Malignancies
 Periocular Malignancies Andrew Gurwood, O.D., F.A.A.O., Dipl. Marc Myers, O.D., F.A.A.O. Drs. Myers and Gurwood have no financial interests to disclose. Course Description Discussion of the most common
Periocular Malignancies Andrew Gurwood, O.D., F.A.A.O., Dipl. Marc Myers, O.D., F.A.A.O. Drs. Myers and Gurwood have no financial interests to disclose. Course Description Discussion of the most common
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Objectives. Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System. Role of Salivary Gland FNA 04/26/2018
 Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Salivary Gland FNA: The Milan System Dr. Jennifer Brainard Section Head Cytopathology Cleveland Clinic Objectives Introduce the Milan System for reporting salivary gland cytopathology Define cytologic
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals
 PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals Historical Named after George Papanicolaou, a Greek American Studied cervical epithelium in menstrual cycle of guinea
PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals Historical Named after George Papanicolaou, a Greek American Studied cervical epithelium in menstrual cycle of guinea
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types. Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed
 External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
External Neoplasms in Goats: A Clinicopathological Study on Five Types By Abu-Seida, A.M and Kawkab, A. Ahmed Introduction Introduction Neoplasia is occasionally diagnosed in goats. A survey of 800000
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Epithelial tumors. Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev
 Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Epithelial tumors Dr. F.F. Khuzin, PhD Dr. M.O. Mavlikeev Epithelial tumors Tumors from the epithelium are the most frequent among tumors. There are 2 group features of these tumors: The presence in most
Social History Non- smoker. Past Medical History None; otherwise healthy. Review of Systems Negative other than the ocular issues
 A Very Unusual Case of Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia Erin Boese M4, Gina M. Rogers MD, and Anna S. Kitzmann, MD February 14, 2013 Chief Complaint: Enlarging conjunctival/corneal lesion, left eye History
A Very Unusual Case of Ocular Surface Squamous Neoplasia Erin Boese M4, Gina M. Rogers MD, and Anna S. Kitzmann, MD February 14, 2013 Chief Complaint: Enlarging conjunctival/corneal lesion, left eye History
Diseases of the penis & testis
 Diseases of the penis & testis Done by : Saef B AL-Abbadi Diseases of penis, Condyloma Acuminatum A benign tumor *Tend to recur but only rarely progress into in situ or invasive cancers read this = genital
Diseases of the penis & testis Done by : Saef B AL-Abbadi Diseases of penis, Condyloma Acuminatum A benign tumor *Tend to recur but only rarely progress into in situ or invasive cancers read this = genital
PRIMARY OCULAR CARUNCULAR BASAL CELL CARCINOMA IN A CHINESE PATIENT
 PRIMARY OCULAR CARUNCULAR BASAL CELL CARCINOMA IN A CHINESE PATIENT Chia-Ling Lee, 1 Shiuh-Liang Hsu, 1 and Cheng-Hsien Chang 2,3 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, 2
PRIMARY OCULAR CARUNCULAR BASAL CELL CARCINOMA IN A CHINESE PATIENT Chia-Ling Lee, 1 Shiuh-Liang Hsu, 1 and Cheng-Hsien Chang 2,3 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital, 2
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors
 The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: WHO Update Stuart J. Schnitt, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA Papillary Lesions of the Breast
Penile cancer teams in UK. Common variants. Penile cancer teams. Basaloid squamous carcinoma. The Pathology of Penile Tumours
 The Pathology of Penile Tumours Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Penile cancer teams in UK 12 centres for penile cancer work (10 in England and Wales, 2 in Scotland)
The Pathology of Penile Tumours Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Penile cancer teams in UK 12 centres for penile cancer work (10 in England and Wales, 2 in Scotland)
Disclosure. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None MFMER slide-1
 Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies. Agenda
 Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
Head & Neck Squamous Carcinoma: Artifacts, Challenges, and Controversies Jennifer L. Hunt, MD, MEd Aubrey J. Hough Jr, MD, Endowed Professor of Pathology Chair of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University
FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT
 I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
I: 2047-2051 ISSN: 2277 4998 FORELIMB SWEAT GLAND ADENOCARCINOMA IN A CAT ABEDI G 1, HESARAKI S 2, ASGHARI A 1* 1: Department of Clinical Science, Science and Research branch, Islamic Azad University,
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000
 Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
CLINICAL PEARLS IN OCULAR ONCOLOGY
 CLINICAL PEARLS IN OCULAR ONCOLOGY IRIS NEVUS - Two kinds circumscribed and diffuse - Photodocumentation important to monitor growth - Risk Factors for iris nevus growth to melanoma (ABCDEF) A Age (young),
CLINICAL PEARLS IN OCULAR ONCOLOGY IRIS NEVUS - Two kinds circumscribed and diffuse - Photodocumentation important to monitor growth - Risk Factors for iris nevus growth to melanoma (ABCDEF) A Age (young),
CHAPTER 4 PREDICTIVE VALUE OF EXFOLIATIVE CYTOL- OGY IN PIGMENTED CONJUNCTIVAL LESIONS
 CHAPTER 4 PREDICTIVE VALUE OF EXFOLIATIVE CYTOL- OGY IN PIGMENTED CONJUNCTIVAL LESIONS Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica 26;84:88-9. S. Keijser, C.M. van Luijk, G.S. Missotten, M. Veselic-Charvat, 2 D.
CHAPTER 4 PREDICTIVE VALUE OF EXFOLIATIVE CYTOL- OGY IN PIGMENTED CONJUNCTIVAL LESIONS Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica 26;84:88-9. S. Keijser, C.M. van Luijk, G.S. Missotten, M. Veselic-Charvat, 2 D.
encapsulated thyroid nodule with a follicular architecture and some form of atypia. The problem is when to diagnose
 Histological Spectrum of Papillary Carcinoma of Thyroid A Two Years Study Gomathi Srinivasan 1, M. Vennila 2 1 Associate Professor Pathology, Government Medical College, Omandurar Estate, Chennai 600 002
Histological Spectrum of Papillary Carcinoma of Thyroid A Two Years Study Gomathi Srinivasan 1, M. Vennila 2 1 Associate Professor Pathology, Government Medical College, Omandurar Estate, Chennai 600 002
Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting. factor & may be induced to undergo malignant. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of
 بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
بسم رلاهللا Def. Premalignant lesions may expose to a promoting factor & may be induced to undergo malignant transformation. Carcinoma in situ displays the cytologic features of malignancy without invasion
Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma
 AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
Case year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid
 Case 4 22 year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid gland. No information available relative to a prior fine needle aspiration biopsy. A left lobectomy was performed.
Case 4 22 year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid gland. No information available relative to a prior fine needle aspiration biopsy. A left lobectomy was performed.
Oncocytic-Appearing Salivary Gland Tumors. Oncocytic, Cystic, Mucinous, and High Grade Salivary Gland Tumors SALIVARY GLAND FNA: PART II
 William C. Faquin, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Harvard Medical School Director of Head and Neck Pathology Massachusetts Eye and Ear Massachusetts General Hospital SALIVARY GLAND FNA: PART II Oncocytic,
William C. Faquin, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Harvard Medical School Director of Head and Neck Pathology Massachusetts Eye and Ear Massachusetts General Hospital SALIVARY GLAND FNA: PART II Oncocytic,
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions
 Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions Lin Wai Fung (MSc, MPH, CMIAC) 17/4/2014 Glandular lesions of the uterus Endocervix Endometrium Normal endocervical cells Sheets, strips well-preserved architecture:
Gynecologic Cytopathology: Glandular lesions Lin Wai Fung (MSc, MPH, CMIAC) 17/4/2014 Glandular lesions of the uterus Endocervix Endometrium Normal endocervical cells Sheets, strips well-preserved architecture:
Cytology Report Format
 Squamous Precursor Lesions and Malignancies In Pap Test Dina R. Mody, MD, FCAP Director of Cytology The Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Weill Medical College
Squamous Precursor Lesions and Malignancies In Pap Test Dina R. Mody, MD, FCAP Director of Cytology The Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX Professor of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine Weill Medical College
Case 4 Diagnosis 2/21/2011 TGB
 Case 4 22 year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid gland. No information available relative to a prior fine needle aspiration biopsy. A left lobectomy was performed.
Case 4 22 year old female presented with asymmetric enlargement of the left lobe of the thyroid gland. No information available relative to a prior fine needle aspiration biopsy. A left lobectomy was performed.
ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY. Jonathan I. Epstein.
 1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
1 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SOCIETY COMPANION MEETING: DIFFICULT NEW DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSES IN PROSTATE PATHOLOGY Jonathan I. Epstein Professor Pathology, Urology, Oncology The Reinhard Professor of Urological
TUMOR,NEOPLASM. Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine,
 TUMOR,NEOPLASM Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn The points in this chapter What is a neoplasm (conception) Morphology of neoplasm Macroscopy of Neoplasm
TUMOR,NEOPLASM Pathology Department, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 马丽琴,maliqin198@zju.edu.cn The points in this chapter What is a neoplasm (conception) Morphology of neoplasm Macroscopy of Neoplasm
Pathology of bladder cancer in Egypt; a current study.
 Pathology of bladder cancer in Egypt; a current study. Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of Master degree in urology By Mohamed Atef Mohamed Ahmed M.B.B.CH Supervised by Prof.Dr.: Omar Mohamed Abdel-
Pathology of bladder cancer in Egypt; a current study. Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of Master degree in urology By Mohamed Atef Mohamed Ahmed M.B.B.CH Supervised by Prof.Dr.: Omar Mohamed Abdel-
Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 8 Number 2 Oncocytic carcinoma: A rare malignancy of the parotid gland K Mardi, J Sharma Citation K Mardi, J Sharma.. The Internet Journal of Pathology.
Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed on cytology
 Malaysian J Pathol 2003; 25(2) : CERVICAL 139 143 VILLOGLANDULAR ADENOCARCINOMA CYTOLOGY CASE REPORT Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed
Malaysian J Pathol 2003; 25(2) : CERVICAL 139 143 VILLOGLANDULAR ADENOCARCINOMA CYTOLOGY CASE REPORT Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience
 Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford. Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust
 Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
Dr Sanjiv Manek Oxford Oxford Pathology Course 2010 for FRCPath Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford Radcliffe NHS Trust Ovarian Endometrial Vulvo-vaginal Cervical Illustration-Cellular Pathology. Oxford
64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour
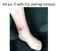 64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour Case History Excision with split-skin grafting Histology moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with large areas of necrosis and brisk mitotic activity.
64 y.o. F with CLL and leg tumour Case History Excision with split-skin grafting Histology moderately differentiated squamous cell carcinoma with large areas of necrosis and brisk mitotic activity.
Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 49, No. 2, pp. 45-49, 2003 Central Poorly Differentiated Adenocarcinoma of the Maxilla: Report of a Case MASAHIRO UMEDA 1), SATOSHI YOKOO 1), YASUYUKI SHIBUYA 1), TAKAHIDE KOMORI
Dermatopathology: The tumor is composed of keratinocytes which show atypia, increase mitoses and abnormal mitoses.
 Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): A common malignant tumor of keratinocytes arising in the epidermis, usually from a precancerous condition: 1- UV induced actinic keratosis, usually of low grade malignancy.
Breast Pathology. Breast Development
 Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1878 A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre Rachana L Y, S.S. Hiremath*, Prabhu M H, S.S
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1878 A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre Rachana L Y, S.S. Hiremath*, Prabhu M H, S.S
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A. Pathological Case Report
 Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A Abstract Dr. Madhuri S.Kate 1, Dr. Preeti Jain 2, Dr. Shailesh S. Patne 3 Introduction: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a locally invasive
Basal cell carcinoma diagnosed on Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology A Abstract Dr. Madhuri S.Kate 1, Dr. Preeti Jain 2, Dr. Shailesh S. Patne 3 Introduction: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is a locally invasive
Los Angeles Society Of Pathologists Dr. Shobha Castelino Prabhu
 Los Angeles Society Of Pathologists Dr. Shobha Castelino Prabhu Loma Linda University Medical Center June 12, 2007 CASE 1 76 year-old gentleman Status post right parotidectomy 1 year ago for a rare tumor
Los Angeles Society Of Pathologists Dr. Shobha Castelino Prabhu Loma Linda University Medical Center June 12, 2007 CASE 1 76 year-old gentleman Status post right parotidectomy 1 year ago for a rare tumor
ONCOLOGY. Csaba Bödör. Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research november 19., ÁOK, III.
 ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
ONCOLOGY Csaba Bödör Department of Pathology and Experimental Cancer Research 2018. november 19., ÁOK, III. bodor.csaba1@med.semmelweis-univ.hu ONCOLOGY Characteristics of Benign and Malignant Neoplasms
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY
 Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
Carcinoma of Unknown Primary site (CUP) in HEAD & NECK SURGERY SEARCHING FOR THE PRIMARY? P r o f J P P r e t o r i u s H e a d : C l i n i c a l U n i t C r i t i c a l C a r e U n i v e r s i t y O f
