3.4 The Brain and Spinal Cord SW *
|
|
|
- Wesley Garrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OpenStax-CNX module: m The Brain and Spinal Cord SW * Stephen E. Wisecarver Based on The Brain and Spinal Cord by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to: Abstract Explain the functions of the spinal cord Identify the hemispheres and lobes of the brain Describe the types of techniques available to clinicians and researchers to image or scan the brain The brain is a remarkably complex organ comprised of billions of interconnected neurons and glia. It is a bilateral, or two-sided, structure that can be separated into distinct lobes. Each lobe is associated with certain types of functions, but, ultimately, all of the areas of the brain interact with one another to provide the foundation for our thoughts and behaviors. In this section, we discuss the overall organization of the brain and the functions associated with dierent brain areas, beginning with what can be seen as an extension of the brain, the spinal cord. 1 The Spinal Cord It can be said that the spinal cord is what connects the brain to the outside world. Because of it, the brain can act. The spinal cord is like a relay station, but a very smart one. It not only routes messages to and from the brain, but it also has its own system of automatic processes, called reexes. The top of the spinal cord merges with the brain stem, where the basic processes of life are controlled, such as breathing and digestion. In the opposite direction, the spinal cord ends just below the ribscontrary to what we might expect, it does not extend all the way to the base of the spine. The spinal cord is functionally organized in 30 segments, corresponding with the vertebrae. Each segment is connected to a specic part of the body through the peripheral nervous system. Nerves branch out from the spine at each vertebra. Sensory nerves bring messages in; motor nerves send messages out to the muscles and organs. Messages travel to and from the brain through every segment. Some sensory messages are immediately acted on by the spinal cord, without any input from the brain. Withdrawal from heat and knee jerk are two examples. When a sensory message meets certain parameters, the spinal cord initiates an automatic reex. The signal passes from the sensory nerve to a simple processing center, which initiates a motor command. Seconds are saved, because messages don't have to go the brain, be * Version 1.1: Jun 2, :35 am
2 OpenStax-CNX module: m processed, and get sent back. In matters of survival, the spinal reexes allow the body to react extraordinarily fast. The spinal cord is protected by bony vertebrae and cushioned in cerebrospinal uid, but injuries still occur. When the spinal cord is damaged in a particular segment, all lower segments are cut o from the brain, causing paralysis. Therefore, the lower on the spine damage is, the fewer functions an injured individual loses. 2 The Two Hemispheres The surface of the brain, known as the cerebral cortex, is very uneven, characterized by a distinctive pattern of folds or bumps, known as gyri (singular: gyrus), and grooves, known as sulci (singular: sulcus), shown in Figure 1. These gyri and sulci form important landmarks that allow us to separate the brain into functional centers. The most prominent sulcus, known as the longitudinal ssure, is the deep groove that separates the brain into two halves or hemispheres: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere. Figure 1: The surface of the brain is covered with gyri and sulci. A deep sulcus is called a ssure, such as the longitudinal ssure that divides the brain into left and right hemispheres. (credit: modication of work by Bruce Blaus) There is evidence of some specialization of functionreferred to as lateralizationin each hemisphere, mainly regarding dierences in language ability. Beyond that, however, the dierences that have been found
3 OpenStax-CNX module: m have been minor. What we do know is that the left hemisphere controls the right half of the body, and the right hemisphere controls the left half of the body. The two hemispheres are connected by a thick band of neural bers known as the corpus callosum, consisting of about 200 million axons. The corpus callosum allows the two hemispheres to communicate with each other and allows for information being processed on one side of the brain to be shared with the other side. Normally, we are not aware of the dierent roles that our two hemispheres play in day-to-day functions, but there are people who come to know the capabilities and functions of their two hemispheres quite well. In some cases of severe epilepsy, doctors elect to sever the corpus callosum as a means of controlling the spread of seizures (Figure 2). While this is an eective treatment option, it results in individuals who have split brains. After surgery, these split-brain patients show a variety of interesting behaviors. For instance, a split-brain patient is unable to name a picture that is shown in the patient's left visual eld because the information is only available in the largely nonverbal right hemisphere. However, they are able to recreate the picture with their left hand, which is also controlled by the right hemisphere. When the more verbal left hemisphere sees the picture that the hand drew, the patient is able to name it (assuming the left hemisphere can interpret what was drawn by the left hand). Figure 2: (a, b) The corpus callosum connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain. (c) A scientist spreads this dissected sheep brain apart to show the corpus callosum between the hemispheres. (credit c: modication of work by Aaron Bornstein) 3 Forebrain Structures The two hemispheres of the cerebral cortex are part of the forebrain (Figure 3), which is the largest part of the brain. The forebrain contains the cerebral cortex and a number of other structures that lie beneath the cortex (called subcortical structures): thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and the limbic system (collection of structures). The cerebral cortex, which is the outer surface of the brain, is associated with higher level processes such as consciousness, thought, emotion, reasoning, language, and memory. Each cerebral hemisphere can be subdivided into four lobes, each associated with dierent functions.
4 OpenStax-CNX module: m Figure 3: The brain and its parts can be divided into three main categories: the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. 3.1 Lobes of the Brain The four lobes of the brain are the frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (Figure 4). The frontal lobe is located in the forward part of the brain, extending back to a ssure known as the central sulcus. The frontal lobe is involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language. It contains the motor cortex, which is involved in planning and coordinating movement; the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for higher-level cognitive functioning; and Broca's area, which is essential for language production.
5 OpenStax-CNX module: m Figure 4: The lobes of the brain are shown. People who suer damage to Broca's area have great diculty producing language of any form (Figure 4). For example, Padma was an electrical engineer who was socially active and a caring, involved mother. About twenty years ago, she was in a car accident and suered damage to her Broca's area. She completely lost the ability to speak and form any kind of meaningful language. There is nothing wrong with her mouth or her vocal cords, but she is unable to produce words. She can follow directions but can't respond verbally, and she can read but no longer write. She can do routine tasks like running to the market to buy milk, but she could not communicate verbally if a situation called for it. Probably the most famous case of frontal lobe damage is that of a man by the name of Phineas Gage. On September 13, 1848, Gage (age 25) was working as a railroad foreman in Vermont. He and his crew were using an iron rod to tamp explosives down into a blasting hole to remove rock along the railway's path. Unfortunately, the iron rod created a spark and caused the rod to explode out of the blasting hole, into Gage's face, and through his skull (Figure 5). Although lying in a pool of his own blood with brain matter emerging from his head, Gage was conscious and able to get up, walk, and speak. But in the months following his accident, people noticed that his personality had changed. Many of his friends described him as no longer being himself. Before the accident, it was said that Gage was a well-mannered, soft-spoken man, but he began to behave in odd and inappropriate ways after the accident. Such changes in personality would be consistent with loss of impulse controla frontal lobe function.
6 OpenStax-CNX module: m Beyond the damage to the frontal lobe itself, subsequent investigations into the rod's path also identied probable damage to pathways between the frontal lobe and other brain structures, including the limbic system. With connections between the planning functions of the frontal lobe and the emotional processes of the limbic system severed, Gage had diculty controlling his emotional impulses. However, there is some evidence suggesting that the dramatic changes in Gage's personality were exaggerated and embellished. Gage's case occurred in the midst of a 19 th century debate over localizationregarding whether certain areas of the brain are associated with particular functions. On the basis of extremely limited information about Gage, the extent of his injury, and his life before and after the accident, scientists tended to nd support for their own views, on whichever side of the debate they fell (Macmillan, 1999). Figure 5: (a) Phineas Gage holds the iron rod that penetrated his skull in an 1848 railroad construction accident. (b) Gage's prefrontal cortex was severely damaged in the left hemisphere. The rod entered Gage's face on the left side, passed behind his eye, and exited through the top of his skull, before landing about 80 feet away. (credit a: modication of work by Jack and Beverly Wilgus) The temporal lobe is located on the side of the head (temporal means near the temples), and is associated with hearing, memory, emotion, and some aspects of language. The auditory cortex, the main
7 OpenStax-CNX module: m area responsible for processing auditory information, is located within the temporal lobe. Wernicke's area, important for speech comprehension, is also located here. Whereas individuals with damage to Broca's area have diculty producing language, those with damage to Wernicke's area can produce sensible language, but they are unable to understand it (Figure 6). Figure 6: Damage to either Broca's area or Wernicke's area can result in language decits. The types of decits are very dierent, however, depending on which area is aected. The occipital lobe is located at the very back of the brain, and contains the primary visual cortex, which is responsible for interpreting incoming visual information. The occipital cortex is organized retinotopically, which means there is a close relationship between the position of an object in a person's visual eld and the position of that object's representation on the cortex. You will learn much more about how visual information is processed in the occipital lobe when you study sensation and perception. 3.2 Other Areas of the Forebrain Other areas of the forebrain, located beneath the cerebral cortex, include the thalamus and the limbic system. The thalamus is a sensory relay for the brain. All of our senses, with the exception of smell, are routed through the thalamus before being directed to other areas of the brain for processing (Figure 7).
8 OpenStax-CNX module: m Figure 7: processing. The thalamus serves as the relay center of the brain where most senses are routed for The limbic system is involved in processing both emotion and memory. Interestingly, the sense of smell projects directly to the limbic system; therefore, not surprisingly, smell can evoke emotional responses in ways that other sensory modalities cannot. The limbic system is made up of a number of dierent structures, but three of the most important are the hippocampus, the amygdala, and the hypothalamus (Figure 8). The hippocampus is an essential structure for learning and memory. The amygdala is involved in our experience of emotion and in tying emotional meaning to our memories. The hypothalamus regulates a number of homeostatic processes, including the regulation of body temperature, appetite, and blood pressure. The hypothalamus also serves as an interface between the nervous system and the endocrine system and in the regulation of sexual motivation and behavior.
9 OpenStax-CNX module: m Figure 8: The limbic system is involved in mediating emotional response and memory. 4 Midbrain and Hindbrain Structures The midbrain is comprised of structures located deep within the brain, between the forebrain and the hindbrain. The reticular formation is centered in the midbrain, but it actually extends up into the forebrain and down into the hindbrain. The reticular formation is important in regulating the sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alertness, and motor activity. The substantia nigra (Latin for black substance) and the ventral tegmental area (VTA) are also located in the midbrain (Figure 9). Both regions contain cell bodies that produce the neurotransmitter dopamine, and both are critical for movement. Degeneration of the substantia nigra and VTA is involved in Parkinson's disease. In addition, these structures are involved in mood, reward, and addiction (Berridge & Robinson, 1998; Gardner, 2011; George, Le Moal, & Koob, 2012).
10 OpenStax-CNX module: m Figure 9: The substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area (VTA) are located in the midbrain. The hindbrain is located at the back of the head and looks like an extension of the spinal cord. It contains the medulla, pons, and cerebellum (Figure 10). The medulla controls the automatic processes of the autonomic nervous system, such as breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate. The word pons literally means bridge, and as the name suggests, the pons serves to connect the brain and spinal cord. It also is involved in regulating brain activity during sleep. The medulla, pons, and midbrain together are known as the brainstem.
11 OpenStax-CNX module: m Figure 10: The pons, medulla, and cerebellum make up the hindbrain. The cerebellum (Latin for little brain) receives messages from muscles, tendons, joints, and structures in our ear to control balance, coordination, movement, and motor skills. The cerebellum is also thought to be an important area for processing some types of memories. In particular, procedural memory, or memory involved in learning and remembering how to perform tasks, is thought to be associated with the cerebellum. Recall that H. M. was unable to form new explicit memories, but he could learn new tasks. This is likely due to the fact that H. M.'s cerebellum remained intact. 5 Summary The brain consists of two hemispheres, each controlling the opposite side of the body. Each hemisphere can be subdivided into dierent lobes: frontal, parietal, temporal, and occipital. In addition to the lobes of the cerebral cortex, the forebrain includes the thalamus (sensory relay) and limbic system (emotion and memory circuit). The midbrain contains the reticular formation, which is important for sleep and arousal, as well as the substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area. These structures are important for movement,
12 OpenStax-CNX module: m reward, and addictive processes. The hindbrain contains the structures of the brainstem (medulla, pons, and midbrain), which control automatic functions like breathing and blood pressure. The hindbrain also contains the cerebellum, which helps coordinate movement and certain types of memories. Individuals with brain damage have been studied extensively to provide information about the role of dierent areas of the brain, and recent advances in technology allow us to glean similar information by imaging brain structure and function. These techniques include CT, PET, MRI, fmri, and EEG. 6 Review Questions Exercise 1 (Solution on p. 13.) The is a sensory relay station where all sensory information, except for smell, goes before being sent to other areas of the brain for further processing. a. amygdala b. hippocampus c. hypothalamus d. thalamus Exercise 2 (Solution on p. 13.) Damage to the disrupts one's ability to comprehend language, but it leaves one's ability to produce words intact. a. amygdala b. Broca's Area c. Wernicke's Area d. occipital lobe Exercise 3 (Solution on p. 13.) A(n) uses magnetic elds to create pictures of a given tissue. a. EEG b. MRI c. PET scan d. CT scan Exercise 4 (Solution on p. 13.) Which of the following is not a structure of the forebrain? a. thalamus b. hippocampus c. amygdala d. substantia nigra 7 Critical Thinking Questions Exercise 5 (Solution on p. 13.) Before the advent of modern imaging techniques, scientists and clinicians relied on autopsies of people who suered brain injury with resultant change in behavior to determine how dierent areas of the brain were aected. What are some of the limitations associated with this kind of approach? Exercise 6 (Solution on p. 13.) Which of the techniques discussed would be viable options for you to determine how activity in the reticular formation is related to sleep and wakefulness? Why?
13 OpenStax-CNX module: m Solutions to Exercises in this Module Solution to Exercise (p. 12) D Solution to Exercise (p. 12) C Solution to Exercise (p. 12) B Solution to Exercise (p. 12) D Solution to Exercise (p. 12) The same limitations associated with any case study would apply here. In addition, it is possible that the damage caused changes in other areas of the brain, which might contribute to the behavioral decits. Such changes would not necessarily be obvious to someone performing an autopsy, as they may be functional in nature, rather than structural. Solution to Exercise (p. 12) The most viable techniques are fmri and PET because of their ability to provide information about brain activity and structure simultaneously. Glossary Denition 10: amygdala structure in the limbic system involved in our experience of emotion and tying emotional meaning to our memories Denition 10: auditory cortex strip of cortex in the temporal lobe that is responsible for processing auditory information Denition 10: Broca's area region in the left hemisphere that is essential for language production Denition 10: cerebellum hindbrain structure that controls our balance, coordination, movement, and motor skills, and it is thought to be important in processing some types of memory Denition 10: cerebral cortex surface of the brain that is associated with our highest mental capabilities Denition 10: computerized tomography (CT) scan imaging technique in which a computer coordinates and integrates multiple x-rays of a given area Denition 10: corpus callosum thick band of neural bers connecting the brain's two hemispheres Denition 10: electroencephalography (EEG) recording the electrical activity of the brain via electrodes on the scalp Denition 10: forebrain largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex, the thalamus, and the limbic system, among other structures Denition 10: frontal lobe part of the cerebral cortex involved in reasoning, motor control, emotion, and language; contains motor cortex Denition 10: functional magnetic resonance imaging (fmri) MRI that shows changes in metabolic activity over time
14 OpenStax-CNX module: m Denition 10: gyrus (plural: gyri) bump or ridge on the cerebral cortex Denition 10: hemisphere left or right half of the brain Denition 10: hindbrain division of the brain containing the medulla, pons, and cerebellum Denition 10: hippocampus structure in the temporal lobe associated with learning and memory Denition 10: hypothalamus forebrain structure that regulates sexual motivation and behavior and a number of homeostatic processes; serves as an interface between the nervous system and the endocrine system Denition 10: lateralization concept that each hemisphere of the brain is associated with specialized functions Denition 10: limbic system collection of structures involved in processing emotion and memory Denition 10: longitudinal ssure deep groove in the brain's cortex Denition 10: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) magnetic elds used to produce a picture of the tissue being imaged Denition 10: medulla hindbrain structure that controls automated processes like breathing, blood pressure, and heart rate Denition 10: midbrain division of the brain located between the forebrain and the hindbrain; contains the reticular formation Denition 10: motor cortex strip of cortex involved in planning and coordinating movement Denition 10: occipital lobe part of the cerebral cortex associated with visual processing; contains the primary visual cortex Denition 10: parietal lobe part of the cerebral cortex involved in processing various sensory and perceptual information; contains the primary somatosensory cortex Denition 10: pons hindbrain structure that connects the brain and spinal cord; involved in regulating brain activity during sleep Denition 10: positron emission tomography (PET) scan involves injecting individuals with a mildly radioactive substance and monitoring changes in blood ow to dierent regions of the brain Denition 10: prefrontal cortex area in the frontal lobe responsible for higher-level cognitive functioning Denition 10: reticular formation midbrain structure important in regulating the sleep/wake cycle, arousal, alertness, and motor activity Denition 10: somatosensory cortex essential for processing sensory information from across the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain
15 OpenStax-CNX module: m Denition 10: substantia nigra midbrain structure where dopamine is produced; involved in control of movement Denition 10: sulcus (plural: sulci) depressions or grooves in the cerebral cortex Denition 10: temporal lobe part of cerebral cortex associated with hearing, memory, emotion, and some aspects of language; contains primary auditory cortex Denition 10: thalamus sensory relay for the brain Denition 10: ventral tegmental area (VTA) midbrain structure where dopamine is produced: associated with mood, reward, and addiction Denition 10: Wernicke's area important for speech comprehension
The Brain and Spinal Cord *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49006 1 The Brain and Spinal Cord * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m49006 1 The Brain and Spinal Cord * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By the end of this section, you
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER
 BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
BRAIN: CONTROL CENTER ORCHESTRA Scientists now believe the brain functions much like an orchestra, where different instruments each play a different part. Scans show that the brain divides different aspects
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Forebrain Brain Structures Limbic System. Brain Stem Midbrain Basil Ganglia. Cerebellum Reticular Formation Medulla oblongata
 Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
Brain structures (1) Cut out the following cards (2) Identify the three major divisions of the brain (as defined by your book). Initially, try this without any form of aid such as your textbook. (3) Organize
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Brain Structures. Some scientists divide the brain up into three parts. Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain
 The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
The Brain Phineas Gage Play The Frontal Lobes and Behavior: The Story of Phineas Gage (12:03) Module #25 from The Brain: Teaching Modules (2 nd edition). http://www.learner.org/resources/series1 42.html
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
The Central Nervous System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44749 1 The Central Nervous System * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44749 1 The Central Nervous System * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
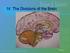 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
CNS Tour (Lecture 12)
 A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1
 Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Biological Bases of the Brain Unit 2, Part 1 Phineas Gage Phineas Gage was a railroad worker who had an iron bar go into his brain He survived but his personality was changed The Brain Lesion tissue destruction
Biological Process 9/7/10. (a) Anatomy: Neurons have three basic parts. 1. The Nervous System: The communication system of your body and brain
 Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Biological Process Overview 1. The Nervous System: s (a) Anatomy, (b) Communication, (c) Networks 2. CNS/PNS 3. The Brain (a) Anatomy, (b) Localization of function 4. Methods to study the brain (Dr. Heidenreich)
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp
Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
10/15/2010. Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: Biology and Behavior. The Nervous System
 Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Biology and Behavior Behavioral neuroscience: 2-1 Biology and Behavior To survive, human beings must be able to perform three interrelated activities: sensing events, or stimuli; processing stimuli; and
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Chapter 2 Test. 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. *a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain e.
 Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system:
 Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
Nervous system, integration: Overview, and peripheral nervous system: Some review & misc. parts [Fig. 28.11B, p. 573]: - white matter --> looks white due to the myelinated sheaths, which are quite fatty.
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain
 General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
General Psychology Biology & Behavior: The Brain These are general notes designed to assist students who are regularly attending class and reading assigned material: they are supplemental rather than exhaustive
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain, a part of which is shown in [link] and spinal cord and is covered with three layers of protective
The Central Nervous System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The central nervous system (CNS) is made up of the brain, a part of which is shown in [link] and spinal cord and is covered with three layers of protective
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Human Nervous System
 Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Human Nervous System A network of interconnected parts that controls behavior & connects us to the world Central Nervous System consists of the brain and spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System consists
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Neurons. Biological Basis of Behavior. Three Types of Neurons. Three Types of Neurons. The Withdrawal Reflex. Transmission of message 10/2/2017
 Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Neurons Basic units of the nervous system Receive, integrate, and transmit information Biological Basis of Behavior Chapter 2 The adult human brain has ~180 BILLION cells ~ 80 billion neurons Three Types
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Unit 3 REVIEW. Name: Date:
 Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
Name: Date: 1. A person whose hand had been amputated actually felt sensations on his nonexistent fingers when his face was stroked. This best illustrates the consequences of A) lateralization. B) hemispherectomy.
LESSON 1.2 WORKBOOK How does brain structure impact its function?
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Central nervous system (CNS) contains the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. For a complete list of defined
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Central nervous system (CNS) contains the brain and spinal cord. Peripheral nervous system (PNS) includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. For a complete list of defined
Test Bank. Multiple Choice
 Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Psychology study guide chapter 2
 Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Psychology study guide chapter 2 Phrenology Developed by Franz Gall in the early 1800 s Study of bumps on the skull and the relationship to mental abilities and character traits Yielded one big idea: different
Chapter 3: Biology and Behavior
 Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Chapter 3: Case Study: The Brain of Phineas Gage Section 1: The Nervous System Section 2: The Brain: Our Control Center Section 3: The Endocrine System Section 4: Heredity: Our Genetic Background Lab:
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini
 Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini Level 1 Only Name: Period: Please highlight the correct answer/response in yellow
Ch. 2: The Biological Perspective Take Home Test on Peripheral Nervous System and the Brain Human Behavior Mr. Minervini Level 1 Only Name: Period: Please highlight the correct answer/response in yellow
The Brain Studying & Structures. Unit 3
 The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Composed of gray matter and arranged in raised ridges (gyri), grooves (sulci), depressions (fissures).
 PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Brain-Behavior Network. Central Nervous System. Cerebral Cortex Gyrus and Sulcus. Nervous System
 Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System
 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System 49a A&P: Nervous System -! Synaptic Transmission and Central Nervous System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
2) All of our thoughts, feelings, and behaviour can be traced to the activity of the a. neurons. b. ganglia. c. genes. d. nerve fibres.
 Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Chapter 2 Biology and Behaviour 1) The specialized cell that transmits signals throughout the nervous system is called the a. neuron. b. glial cell. c. myelin. d. neurotransmitter. Correct: The neuron
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Seventh Edition. The Nervous System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Seventh Edition The Nervous System Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering
8.3 The Central Nervous System. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Anatomy of the Human Brain
 Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
Anatomy of the Human Brain Overview Lobes of the brain (Forebrain) Midbrain/Hindbrain Protection and Blood supply Structure and Function of a neuron Synaptic Transmission Neurotransmitters The brain Most
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13
 Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology
 Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
Chapter 3 Biological Psychology Introduction Reductionism? Scientists in many fields use a strategy called reductionism; they attempt to explain complex phenomena by reducing them to combinations of simpler
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior. Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed)
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
Myers PSYCHOLOGY (7th Ed) Chapter 2 Neuroscience, Genetics and Behavior James A. McCubbin, PhD Clemson University Worth Publishers Neural Biological Psychology branch of psychology concerned with the links
How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system?
 How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system? Lobes of the cerebral cortex? What is the sensory cortex?
How do we study the brain? What are the parts of the hindbrain? What is the reticular formation? Parts of the forebrain? Parts of the limbic system? Lobes of the cerebral cortex? What is the sensory cortex?
3/20/13. :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System
 :: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
:: Slide 1 :: :: Slide 39 :: How Is the Nervous System Organized? Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System and Endocrine System The nervous system is organized into several major branches, each
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Neural Communication. Neural Communication. Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior. Definitions
 Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
Myers PSYCHOLOGY - Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior 1. Neural communication - Neurons - How Neurons Communicate - How Neurotransmitters Influence Us 2. The nervous system 3. The endocrine system 4.
25/09/2012. Capgras Syndrome. Chapter 2. Capgras Syndrome - 2. The Neural Basis of Cognition
 Chapter 2 The Neural Basis of Cognition Capgras Syndrome Alzheimer s patients & others delusion that significant others are robots or impersonators - paranoia Two brain systems for facial recognition -
Chapter 2 The Neural Basis of Cognition Capgras Syndrome Alzheimer s patients & others delusion that significant others are robots or impersonators - paranoia Two brain systems for facial recognition -
Activity Overview. A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity 1A. The Brain: It s All In Your Mind
 A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
Chapter 14, Part 2! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial Nerves! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Week 2 Psychology. The Brain and Behavior
 Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Week 2 Psychology The Brain and Behavior In this lesson, we will focus on the nervous system. We will learn about the Nervous System and its Command Center the Brain Characteristics and Divisions of the
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM STRUCTURAL ORGANIZATION OF THE BRAIN The central nervous system (CNS), consisting of the brain and spinal cord, receives input from sensory neurons and directs
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
