SEVERE IMPAIRMENT OF SOLUTE-FREE WATER CLEARANCE IN PATIENTS WITH HIV
|
|
|
- Garry Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 SEVERE IMPAIRMENT OF SOLUTE-FREE WATER CLEARANCE IN PATIENTS WITH HIV INFECTION Running head: HIV-associated damage at the loop of Henle Waldo H. BELLOSO 1, Carlos G. MUSSO 2, Mariana de PAZ SIERRA 1, Matilde NAVARRO 2, Marisa L. SANCHEZ 1, Ariel G. PERELSZTEIN 1, Juliana REYNALDI 2 1.Infectious Diseases Section, Internal Medicine Service 2.Renal Physiology Section, Nephrology Service Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires, Buenos Aires, Argentina Corresponding author: Waldo H. Belloso, MD. Infectious Diseases Section, Internal Medicine Service, Hospital Italiano de Buenos Aires. Peron 4190 (1181 ACH), Buenos Aires, Argentina waldo.belloso@hospitalitaliano.org.ar Word count: 1780
2 2 Abstract Renal disease is a well recognized complication among individuals with HIV infection. Either viral infection itself and the use of some antiretroviral drugs contribute to this major cause of serious non AIDS-defining condition that may affect both the glomeruli and the renal tubules. The thick ascending loop of Henle constitutes the main location for free-water clearance determining kidney s ability to concentrate and dilute urine in a direct and indirect fashion, respectively. We compared this renal capacity in patients with HIV infection (with or without tenofovir-based antiretroviral therapy) with matched seronegative controls by means of an acute overload of hypotonic sodium chloride solution (Chaimovitz test). Regardless of the presence of antiretroviral treatment, HIV-infected individuals showed a markedly impaired renal capacity to handle water excess under challenge conditions. This finding may have clinical significance in patients at risk for decreases in serum osmolality such as the elderly, neurocognitive impaired and those with hyponatremia due to concomitant medications. (Abstract word count: 155) Key words: HIV infection, renal disease, tubular damage, free-water clearance, osmolality, hyponatremia
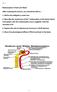
3 3 Introduction Renal disease is increasingly recognized as a cause of morbidity and mortality among patients with HIV infection. Among the several conditions contributing with this fact are the longer survival of patients on antiretroviral treatment, specific effects of some antiretroviral drugs and viral-related factors [1,2]. Traditional risk factors for renal disease such as hypertension, diabetes and hyperlipidemia are more prevalent in seropositive patients and are also associated with the advancing age of the HIV-positive population [3]. In addition, these variables can be associated with exposure to combination antiretroviral therapy (cart) which may produce direct toxic effects on the nephron. Although the underlying mechanism is still unclear, tenofovir may produce proximal tubule damage characterized by proteinuria, normoglycemic glycosuria, hypokalemic renal tubular acidosis and phosphaturia [4]. These relatively infrequent findings may appear in the context of preserved renal function, although in some studies a decrease in the estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (egfr) has been reported [5,6,7]. Both decreased egrf and proximal tubule damage through diminished activation of Vitamin D- may contribute with overall cardiovascular risk in patients with HIV infection [8,9]. Atazanavir has also been reported as associated with an increased risk of reduction in egfr or Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) when used in combination with tenofovir [3, 10]. Proteinuria is an important finding in patients with HIV infection. Its prevalence in patients under cart ranges between 10 and 30%, and constitutes an independent risk factor for progression of CKD and all-cause mortality [11, 12, 13]. Urine protein-creatinin ratio (UPCR) or urine albumin-creatinin ratio (UACR) are commonly accepted measures of quantitative daily proteinuria [14].
4 4 Albuminuria indicates glomerular damage, while proteinuria includes albumin as well as other proteins that may reflect either renal tubular or glomerular damage. UACR or UPCR are less susceptible to the variability that may result from fluctuations in intravascular volume [15, 16]. An increased UACR is suggestive of glomerular injury, while a high UPCR with low UACR may identify patients with renal tubular disorders [17]. Usually renal compromise assessment have restricted to egfr, but not tubular compromise. While egfr could be ultimately affected by tubular disease, usual evaluations performed in patients with HIV infection including proteinuria- are oriented towards glomerular health. Nevertheless, both drugs and HIV per se may produce tubular damage [18, 19, 20]. Among the main function of the renal tubules is to produce reabsorption of substances and to determine the amount of solute-compromised and solute-free water that will be excreted in urine. The evaluation of tubular function is somewhat more complex since requires the analysis of fractional excretion of solutes and/or determination of specific proteins that are normally reabsorbed at the proximal tubule such as retinol-binding protein (RBP) or Beta-2-microglobulin [21, 22 ]. The objective of the present study was to analyze the overall tubular function, and in particular that from the proximal tubule and the thick ascending loop of Henle (TALH) in patients with HIV infection receiving or not tenofovir-containing antiretroviral treatment in comparison with seronegative controls, by applying an hyposaline fluid acute overload (Chaimovitz` test)
5 5 Materials and Methods Patients with confirmed HIV infection were selected in accordance with pre-specified criteria. Inclusion criteria were as follows: adult patients with confirmed HIV-1 infection who agreed to provide written informed consent. Patients under antiretroviral treatment must had a stable regimen for over six months and undetectable (<50 copies/ml) viral load for at least three months. Exclusion criteria included patients with HIV primary infection, personal history of nephropathy, history or current evidence of acute or chronic renal failure, plasma creatinin >1.3 mg/dl, creatinin clearance <60ml/min, presence of glucosuria/proteinuria, prior heart failure, concurrent opportunistic infection, current use of tenofovir plus didanosine, chronic active hepatitis B or C, and use of potentially nephrotoxic agents in the prior week before the test (e.g diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme antagonists, AT1 angiotensin II receptor antagonists or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents). A group of seronegative patients were also selected for comparisons Chaimovitz test The functional evaluation of the proximal tubule and the TALH can be carried out using the Chaimovitz' test, which is based on the exploration of the tubular response to an acute fluid overload [23, 24, 25]. This salt and water overload -twenty cc/kg of mineralized water PO and two liters of IV hypotonic solution (0.45%) intravenously infused in two hours- suppresses the activity of anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone and thus defunctionalizes the distal tubule. Sodium is the major solute reabsorpted at the proximal tubule, and thus the function of this segment can be analyzed through its local sodium clearance. In addition, the analysis of the fractional excretion (FE) of phosphorus and uric acid -mainly reabsorpted at the same segmentmay constitute an alternative way of assessing proximal tubule functioning. In contrast, water
6 6 handling may account for the evaluation of the TALH, since this segment is responsible for the generation of free water clearance or local sodium reabsorption which in turn contribute to medullar hypertonicity that determine consequent water reabsorption. As previously shown that the presence of renal incompetence for sodium reabsorption can be detected by the Chaimovitz' test [26]. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board and all participants provided written informed consent prior to the performance of all the study evaluations. Comparisons between two groups were performed with Mann-Whitney Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test and between three groups with Kruskal-Wallis Test. Comparisons within groups pre and post dilution were performed with Wilcoxon Signed Rank test, with p<0.05 as the level of significance
7 7 Results A total of 31 patients were included in the analysis. Among patients with HIV infection, ten individuals (1 female) were currently receiving stable antiretroviral treatment regimen including tenofovir (Tenofovir Group), while eleven patients (1 female) were not receiving tenofovir (Nontenofovir Group) - in fact three patients were not receiving antiretroviral treatment-. Median CD4+ T-cell count was 464 cells/mm 3 (r ) and 475 cells/mm 3 (r ) in the Tenofovir and Non-tenofovir groups, respectively. Ten seronegative patients (2 females) were selected as control. Median age was 48 and 51 years in both HIV positive groups, and 24,5 years in the control group. All baseline values in both HIV+ groups were within physiological range, except for urinary osmolarity (UOsm) that was lower than expected for a fasting state. Baseline serum values and fractional excretion of solutes were similar between HIV+ groups with the exception of plasma magnesium that was lower in the Tenofovir Group (data not shown). Serum sodium and plasma osmolarity were significantly lower and urine osmolarity was significantly higher than normally expected values in both HIV+ groups either at baseline and at maximal dilution status. At dilutional status, most serum and fractional excretion values were similar between HIV+ groups, with the exception of plasma magnesium that was higher and fractional excretion of potassium and calcium that were lower in the tenofovir group. Serum urea, calcium, magnesium were lower and FE of calcium was higher in the dilutional status in both HIV+ groups in comparison with basal values (Table 1). Free water clearance (sodium reabsorption at TALH) was significantly lower, while urine osmolarity was higher in the dilutional state in HIV+ patients than in seronegative controls (Table 2).
8 8 Discussion Chronic kidney disease associated with HIV-1 infection can affect not only the glomerular portion of the nephron but also the different portions of the renal tubules. CKD may persist clinically silent for many years, supporting the current recommendation to include laboratory determinations in addition to clinical evaluation in the follow up of patients with HIV infection [27].. The restriction of routine analysis to a periodical determination of BUN and serum creatinine may result insufficient to detect early tubular damage. While HIV-related kidney disease has been usually regarded as glomerular damage, tubular dysfunction -mainly associated with drug toxicity- is an important and frequently overlooked component of renal pathology. Different approaches have been previously published aiming to detect tubular damage in patients with HIV [21]. Tenofovir-related tubular damage has been associated with subclinical mitochondrial damage in patients switching to tenofovir-based regimens from thymidine analogs [28] In our study, most basal (fasting) serum and fractional excretion values of electrolytes were similar between HIV+ groups, and -as expected- were within normal range (Table 1). However natremia and serum osmolarity values were lower and urine osmolarity values were somewhat higher than expected. This findings suggest the presence of an impairment in urine concentration in both HIV+ groups. Analyzing the values obtained with acute volume overload there were no significant differences in serum or in FE values between both HIV+ groups, except for magnesemia -which was lower in the Non-tenofovir group, and FE of potassium and calcium which were significantly higher in the Non-tenofovir group (Table 1). While volume expansion usually increases electrolyte excretion, the differences found in both HIV+ groups may warrant further confirmation.
9 9 Urine osmolarity, plasma sodium clearance and free water clearance showed no significant difference between HIV+ groups, but were significantly different from seronegative controls (Table 2). Urine osmolarity difference suggests that kidney`s dilutional effort was insufficient to protect plasma sodium and plasma osmolality in HIV-positive patients under these conditions. Although Chaimovitz test has been reported as an approach to evaluate tubular function in the young and elderly population, to our knowledge this is the first report of the use of this test in patients with HIV-1 infection. Although this test may not be feasible for routine screening of seropositive patients under follow up, an approach towards evaluating concentration/dilution capacity may be warranted at least in some selected groups, such as the elderly, patients with neurocognitive impairment, prior kidney disease or those with concomitant use of potentially interacting medication In this selected group of patients with no evidence of baseline renal compromise, we found no significant abnormalities in proximal sodium handling nor in the FE of solutes transported mainly by the proximal tubule, such as phosphate and uric acid. However free-water clearance was significantly lower in patients with HIV infection than in seronegative controls, which may reflect an attempt of the kidney to preserve sodium that is being lost at the TALH in these patients. Although extremely uniform in our study, this finding may require further confirmation given the reduced number of patients evaluated. We consistently found a significant functional reduction in the free-water clearance in all HIV+ individuals evaluated regardless of the presence of tenofovir. These findings suggest that kidney`s ability to either concentrate and dilute urine is severely impaired in patients with HIV infection, with the potential risk to develop osmolality abnormalities under contraction or water overload scenarios.
10 10 In the clinical setting, these findings indicate an increased risk for dehydration or hyponatremia in HIV-infected patients undergoing water deprivation or water overload respectively, as well as in the context of receiving drugs that could cause hyponatremia such as diuretics or psychoactive drugs.
11 11 References 1. Phair J, Pallela F. Renal disease in HIV-infected individuals. Curr Opin HIV AIDS 2011; 6: Estrella MM, Fine DM, Atta MG. Recent developments in HIV-related kidney disease. HIV Ther 2010 September 4(5): Mocroft A, Kirk O, Reiss P et al. Estimated glomerular filtration rate, chronic kidney disease and antiretroviral drug use in HIV-positive patients. AIDS 2010; 24(11): Mathew G, Knaus SJ. Acquired Fanconi s syndrome associated with tenofovir therapy. J Gen Intern Med 2006; 21(11):C3-C5. 5. Fernandez-Fernandez B, Montoya-Ferrer A, Sanz AB, Sánchez-Niño MD, Izquierdo MC, Poveda J, Sainz-Prestel V, Ortiz-Martin N, Parra-Rodriguez A, Selgas R, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A. Tenofovir nephrotoxicity: 2011 Update. AIDS Res Treat 2011; Rodriguez-Novoa S, Alvarez E, Labarga P, Soriano V. Renal toxicity associated with tenofovir use. Exp Opin Drug Safety 2010; 9(4); Cooper RD, Wiebe N, Smith N, Keiser P, Naicker S, Tonelli M. Systematic review and meta-analysis: renal safety of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate in HIV-infected patients. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 51(%): Go AS, Chertow GM, Fan D, McCulloch CE, Hsu CY. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events and hospitalization. N Engl J Med 2004; 351(13): Choi AI, Li Y, Deeks SG, Grunfeld C, Volberding PA, Schlipak MG. Association between kidney function and albuminuria with cardiovascular events in HIV-infected persons. Circulation 2010; 121: Dazo C, Fahey P, Puls RL, Winston A, Boesecke C, Avhingsanon A, Amin J, Rooney JF, Belloso WH, Cooper DA, Emery S for the Altair Study Group. Small and significant and non-progressive decline in glomerular filtration rate is observed in therapy-naive
12 12 HIV-positive subjects commencing ritonavir-boosted atazanavir compared to either efavirenz or zidovudine/abacavir, all with tenofovir/emtricitabine after 48 weeks, a randomized controlled study. Presented at the 18th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic infections (CROI 2011), Boston, MA, March Wyatt CM, Hoover DR, Shi Q, Seaberg E, Wei C, Tien PC, Karim R, Lazar J, Young MA, Cohen MH, Klotman PE, Anastos K. Microalbuminuria is associated with all-cause and AIDS mortality in women with HIV infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Sep 1;55(1): Gardner LI, Holmberg SD, Williamson JM, Szczech LA, Carpenter CC, Rompalo AM, Schuman P, Klein RS. Development of proteinuria or elevated serum creatinine and mortality in HIV-infected women. HIV Epidemiology Research Study Group.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Feb 1;32(2): Choi AI, Scherzer R, Bacchetti P, Tien PC, Saag MS, Gibert CL, Szczech LA, Grunfeld C, Shlipak MG.. Cystatin C, albuminuria, and 5-year all-cause mortality in HIV-infected persons. Source University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA. Am J Kidney Dis. 010 Nov;56(5): Epub 2010 Aug 14. Gupta SK, Smurzynski M, Franceschini N, Bosch RJ, Szczech LA, Kalayjian RC; AIDS Clinical Trials Group Longitudinal Linked Randomized Trials Study Team The effects of HIV type-1 viral suppression and non-viral factors on quantitative proteinuria in the highly active antiretroviral therapy era. Antivir Ther. 2009;14(4): Kalayjian R, Renal Issues in HIV infection, Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 2011; 8: Kalayjian R, Kidney disease in HIV-infected persons. Curr Infect Dis Rep 2012; 14: Samarawickrama A, Nambiar K, Gilleece Y, Fisher M, Host S. Value of Urine Protein/Creatinine and Albumin/Creatinine Ratios in Assessing Renal Disease in HIV
13 13 infection. 17th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, San Francisco, CA. Abstract Vashistha H, Husain M, Kumar D, Singhal PC. Tubular cell HIV-1 gp120 expression induces caspase 8 activation and apoptosis. Ren Fail. 2009;31(4): Szczech L. Renal dysfunction and tenofovir toxicity in HIV-infected patients. Topics HIV Med 2008; 16(4):122-6, 20. Vrouenraets SM, Fux CA, Wit FW, Garcia EF, Furrer H, Brinkman K, Hoek FJ, Abeling NG, Krediet RT, Reiss P, Prepare Study Group. Persistent decline in estimated but not measured glomerular filtration rate on tenofovir may reflect tubular rather than glomerular toxicity. AIDS 2011; 25(17): Hall AM, Edwards SG, Lapsley M, Connolly JO, Chetty K, O Farrell S, Unwin RJ, Williams IG. Subclinical tubular injury in HIV-infected individuals on antiretroviral therapy: a cross-sectional analysis. Am J Kidney Dis 2009; 54(6): Labarga P, Barreiro P, Martin-Carbonero L, Rodriguez-Novoa S, Solera C, Medrano J, Rivas P, Albalater M, Blanco F, Moreno V, Vispo E, Soriano V. Kidney tubular abnormalities in the absence of impaired glomerular function in HIV patients treated with tenofovir. AIDS 2009; 10(6): Chaimovitz C, Levi J, Better O, Oslander L, Benderli A. Studies on the site of renal salt loss in a patient with Bartter s syndrome. Pediatr Res 1973;7; Macías-Nuñez JF, García Iglesias C, Bondía Roman A, Rodriguez Commes L, Corbacho Becerra L, Tabernero Romo JM, De Castro del Pozo S. Renal handling of sodium in old people: a functional study. Age and ageing 1978; 7: Musso CG, Fainstein I, Kaplan R, Macías Nuñez JF. Función tubular renal en el muy anciano. Rev Esp Geriatr Gerontol 2004; 39(5):314-9.
14 Musso CG, Macías-Nuñez JF. Dysfunction of the thick loop of Henle and senescence: from molecular biology to clinical geriatrics. Int Urol Nephrol Mar;43(1): Epub 2010 Nov Gupta SK, Eustace JA, Winston JA, Boydstun II, Ahuja TS, Rodriguez RA, Tashima KT, Roland M, Franceschini N, Palella FJ, Lennox JL, Klotman PE, Nachman SA, Hall SD, Szczech LA. Guidelines for the management of chronic kidney disease in HIV-infected patients: recommendations of the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: Maggi P, Montinaro V, Bellacosa C, Pietanza S, Volpe A, Graziano G, Strippoli GF, Angarano G. Early markers of tubular dysfunction in antiretroviral-experienced HIVinfected patients treated with tenofovir versus abacavir. AIDS Patient Care STDS Jan;26(1):5-11. Epub 2011 Dec 2.
15 15 Tables Table 1. Comparison between HIV+ Tenofovir Group and HIV+ Non-tenofovir group at baseline and at maximum dilution (Chaimovitz Test). Median (range) values HIV+Tenofovir Group p- HIV+ Non- Group p- Between value tenofovir value groups Baseline Dilution Baseline Dilution p value Serum Urea (mg/dl) (14-53) (14-44) (15-57) (12-50) Serum creatinin (mg/dl) 0.82 ( ) ( (0.52- ( ) 1.07) 1.0) Serum glucose (mg/dl) ( (60- (68-99) 145) (69-105) 220) Serum uric acid (mg/dl) ( (2.8- (3.9-7) 5.8) ( ) 6.6) Serum calcium (mg/dl) ( ( ( (8.1-10) 8.8) 10.4) 8.7) Serum sodium (mmol/l) ( ( ( ( ) 137) 143) 140) Serum potassium ( ( (mmol/l) ( ) 5.0) ( ) 4.3) Serum phosphate ( ( (mmol/l) ( ) 3.9) ( ) 3.2)
16 16 Serum magnesium ( ( (mmol/l) ( ) 2.2) ( ) 2.0) Serum chloride ( ( (99- (mmol/l) (96-107) 108) 107) 107) Est.GFR (MDRD) (65-125) ( (79.4- (ml/min/1.73m 2 ) 134) ( ) 141) FE sodium 0.59 ( ) ( (%) ( ) ( ) 1.56) FE potassium (%) ( ( ( ) 19) (0.8-13) 18) FE chloride (%) 0.68 ( ) 1.4 ( ( ( ) 5.7) 5.0) FE phosphate (%) (0.6- (6-20) ( ) (3-23) 19) FE calcium (%) 0.68 ( ) 1.4 ( ( ( ) 1.3) 2.8) FE magnesium (%) ( ( ( (0.8-3) 7.48) 4.9) 5.0) FE urea (%) 0.47 ( ) ( (0.44- ( ) 4.6) 1.1) FE uric acid (%) ( ( (2.0-29) ( ) 10.0) 8.7) Plasma osmolality ( ( ( (mosm/l) 292) ( ) 298) 289)
17 17 Urine osmolality ( ( ( ( (mosm/l) 759) 594) 854) 323)
18 18 Table 2. Chaimovitz test specific results. Comparison between HIV+ groups and seronegative controls. HIV+ Tenofovir Group HIV+ Nontenofovir Group Seronegative controls p- value Urine osmolality (mosm/l) (38-594) 92 (37-323) 40 (30-59) Free-water clearance (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) Proximal sodium clearance (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) Distal sodium reabsorption (Henle) (%) Osmolar clearance (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) *p<0.05 between HIV+ groups 3.07 ( ) 5.5 ( ) 15.2 ( ) < ( ) 1.4 ( ) 17.8 ( ) (18-93) 91 (61-98)* 86 (81-92) 2.17 ( ) 2.6 ( )* 3.15 ( ) 0.005
Clinical Study Impaired Urine Dilution Capability in HIV Stable Patients
 International Nephrology, Article ID 381985, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/381985 Clinical Study Impaired Urine Dilution Capability in HIV Stable Patients Waldo H. Belloso, 1 Mariana de Paz Sierra,
International Nephrology, Article ID 381985, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/381985 Clinical Study Impaired Urine Dilution Capability in HIV Stable Patients Waldo H. Belloso, 1 Mariana de Paz Sierra,
This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source:
 This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source: Kelly, Mark D., Gibson, Abby, Bartlett, Harry, Rowling, Diane, & Patten, John (2013) Tenofovir-associated
This is the author s version of a work that was submitted/accepted for publication in the following source: Kelly, Mark D., Gibson, Abby, Bartlett, Harry, Rowling, Diane, & Patten, John (2013) Tenofovir-associated
TDF Renal Dysfunction
 TDF Renal Dysfunction Sarala Naicker MBChB, FRCP, PhD Division of Nephrology Dept of Internal Medicine University of the Witwatersrand Johannesburg South Africa SA HIV Clinician Society Conference Cape
TDF Renal Dysfunction Sarala Naicker MBChB, FRCP, PhD Division of Nephrology Dept of Internal Medicine University of the Witwatersrand Johannesburg South Africa SA HIV Clinician Society Conference Cape
COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE
 BHIVA AUTUMN CONFERENCE 2012 Including CHIVA Parallel Sessions Dr Ian Williams University College London Medical School COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE > 1,000: Speaker Name Statement Ian Williams
BHIVA AUTUMN CONFERENCE 2012 Including CHIVA Parallel Sessions Dr Ian Williams University College London Medical School COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE > 1,000: Speaker Name Statement Ian Williams
Renal safety of tenofovir in HIV-infected patients who switch from stavudine or zidovudine to tenofovir
 Original Article Vol. 29 No. 3 Renal safety of tenofovir:- Wiwattanathum P & Sungkanuparph S. 113 Renal safety of tenofovir in HIV-infected patients who switch from stavudine or zidovudine to tenofovir
Original Article Vol. 29 No. 3 Renal safety of tenofovir:- Wiwattanathum P & Sungkanuparph S. 113 Renal safety of tenofovir in HIV-infected patients who switch from stavudine or zidovudine to tenofovir
short communication pre-existing albuminuria predicts AIDS and non-aids mortality in women initiating antiretroviral therapy
 Antiviral Therapy 2011; 16:591 596 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1766) short communication pre-existing albuminuria predicts AIDS and non-aids mortality in women initiating antiretroviral therapy Christina M Wyatt
Antiviral Therapy 2011; 16:591 596 (doi: 10.3851/IMP1766) short communication pre-existing albuminuria predicts AIDS and non-aids mortality in women initiating antiretroviral therapy Christina M Wyatt
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB
 COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
COMPLETE INHIBITION OF RENAL RESERVE IN CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE BY A COMBINATION OF ACEI AND ARB CG Musso ¹, J Reynaldi¹, N Imperiali ¹, L Algranati ¹, DG Oreopoulos ² Nephrology Department Hospital Italiano
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001
 Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Renal Quiz - June 22, 21001 1. The molecular weight of calcium is 40 and chloride is 36. How many milligrams of CaCl 2 is required to give 2 meq of calcium? a) 40 b) 72 c) 112 d) 224 2. The extracellular
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
AGING KIDNEY IN HIV DISEASE
 AGING KIDNEY IN HIV DISEASE Michael G. Shlipak, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Chief, General Internal Medicine, San Francisco VA Medical Center Kidney, Aging and HIV
AGING KIDNEY IN HIV DISEASE Michael G. Shlipak, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine, Epidemiology and Biostatistics, UCSF Chief, General Internal Medicine, San Francisco VA Medical Center Kidney, Aging and HIV
KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin
![KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin KD02 [Mar96] [Feb12] Which has the greatest renal clearance? A. PAH B. Glucose C. Urea D. Water E. Inulin](/thumbs/87/96174332.jpg) Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
Renal Physiology MCQ KD01 [Mar96] [Apr01] Renal blood flow is dependent on: A. Juxtaglomerular apparatus B. [Na+] at macula densa C. Afferent vasodilatation D. Arterial pressure (poorly worded/recalled
NATURAL HISTORY AND SURVIVAL OF PATIENTS WITH ASCITES. PATIENTS WHO DO NOT DEVELOP COMPLICATIONS HAVE MARKEDLY BETTER SURVIVAL THAN THOSE WHO DEVELOP
 PROGNOSIS Mortality rates as high as 18-30% are reported for hyponatremic patients. High mortality rates reflect the severity of underlying conditions and are not influenced by treatment of hyponatremia
PROGNOSIS Mortality rates as high as 18-30% are reported for hyponatremic patients. High mortality rates reflect the severity of underlying conditions and are not influenced by treatment of hyponatremia
Renal-Related Questions
 Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Renal-Related Questions 1) List the major segments of the nephron and for each segment describe in a single sentence what happens to sodium there. (10 points). 2) a) Describe the handling by the nephron
Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities
 Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities Renal Disease/ Hypertension/ Diabetes in African-Americans M. Keith Rawlings, MD Medical Director Peabody Health Center AIDS Arms, Inc Dallas, TX Chair, Internal Medicine
Special Challenges and Co-Morbidities Renal Disease/ Hypertension/ Diabetes in African-Americans M. Keith Rawlings, MD Medical Director Peabody Health Center AIDS Arms, Inc Dallas, TX Chair, Internal Medicine
(KFTs) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD
 Kidney Function Tests (KFTs) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran Composition and Properties
Kidney Function Tests (KFTs) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran Composition and Properties
1. remove: waste products: urea, creatinine, and uric acid foreign chemicals: drugs, water soluble vitamins, and food additives, etc.
 Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
Making Water! OR is it really Just Water Just Ask the Nephron!! Author: Patricia L. Ostlund ostlundp@faytechcc.edu (910) 678-9892 Fayetteville Technical Community College Fayetteville, NC 28303 Its just
The principal functions of the kidneys
 Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
Renal physiology The principal functions of the kidneys Formation and excretion of urine Excretion of waste products, drugs, and toxins Regulation of body water and mineral content of the body Maintenance
HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY
 Journal of Aging Research & Clinical Practice Volume 6, 2017 J Aging Res Clin Practice 2017;inpress Published online in press HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE
Journal of Aging Research & Clinical Practice Volume 6, 2017 J Aging Res Clin Practice 2017;inpress Published online in press HUGE EQUATION ACCURACY FOR SCREENING CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE: A PROSPECTIVE
Functions of Proximal Convoluted Tubules
 1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
1. Proximal tubule Solute reabsorption in the proximal tubule is isosmotic (water follows solute osmotically and tubular fluid osmolality remains similar to that of plasma) 60-70% of water and solute reabsorption
Slide #1 Case Presentation: Kidney Disease
 Slide #1 Case Presentation: Kidney Disease Christina Wyatt, MD Mount Sinai, New York Slide #2 Disclosures Investigator-initiated research support Gilead Sciences Honoraria for internal education Bristol
Slide #1 Case Presentation: Kidney Disease Christina Wyatt, MD Mount Sinai, New York Slide #2 Disclosures Investigator-initiated research support Gilead Sciences Honoraria for internal education Bristol
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D.
 RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
RENAL SYSTEM 2 TRANSPORT PROPERTIES OF NEPHRON SEGMENTS Emma Jakoi, Ph.D. Learning Objectives 1. Identify the region of the renal tubule in which reabsorption and secretion occur. 2. Describe the cellular
Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF)
 Frontier AIDS Education and Training Center Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF) Brian R. Wood, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Washington Medical Director, Frontier AETC ECHO January 28, 2016
Frontier AIDS Education and Training Center Tenofovir Alafenamide (TAF) Brian R. Wood, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of Washington Medical Director, Frontier AETC ECHO January 28, 2016
Renal safety of tenofovir containing antiretroviral regimen in a Singapore cohort
 Chua et al. AIDS Research and Therapy 2012, 9:19 SHORT REPORT Open Access Renal safety of tenofovir containing antiretroviral regimen in a Singapore cohort Arlene C Chua 1*, Ryan M Llorin 1, Kelvin Lai
Chua et al. AIDS Research and Therapy 2012, 9:19 SHORT REPORT Open Access Renal safety of tenofovir containing antiretroviral regimen in a Singapore cohort Arlene C Chua 1*, Ryan M Llorin 1, Kelvin Lai
Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders. Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November
 Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November Renal Failure Up to 25% of acute renal failure is drug induced
Renal Transporters- pathophysiology of drug - induced renal disorders Lisa Harris, Pharmacist, John Hunter Hospital, Newcastle, 2015 November Renal Failure Up to 25% of acute renal failure is drug induced
5/10/2014. Observation, control of blood pressure. Observation, control of blood pressure and risk factors.
 Overview The Kidneys Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department City Hospital Renal physiology Renal pathophysiology Acute kidney injury Chronic kidney disease Assessing renal function GFR Proteinuria
Overview The Kidneys Nicola Barlow Clinical Biochemistry Department City Hospital Renal physiology Renal pathophysiology Acute kidney injury Chronic kidney disease Assessing renal function GFR Proteinuria
** TMP mean page 340 in 12 th edition. Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2:
 QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions
 Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
Renal Physiology II Tubular functions LO. 42, 43 Dr. Kékesi Gabriella Basic points of renal physiology 1. Glomerular filtration (GF) a) Ultrafiltration 2. Tubular functions active and passive a) Reabsorption
Composition: Each Tablet contains. Pharmacokinetic properties:
 Composition: Each Tablet contains Torsemide 5/10/20/40/100mg Pharmacokinetic properties: Torsemide is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak serum concentrations are achieved within 1 hour
Composition: Each Tablet contains Torsemide 5/10/20/40/100mg Pharmacokinetic properties: Torsemide is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Peak serum concentrations are achieved within 1 hour
Chapter 23. Composition and Properties of Urine
 Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
Chapter 23 Composition and Properties of Urine Composition and Properties of Urine (1 of 2) urinalysis the examination of the physical and chemical properties of urine appearance - clear, almost colorless
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Update on HIV-Related Kidney Diseases. Agenda
 Update on HIV-Related Kidney Diseases ANDY CHOI THE MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF HIV/AIDS DECEMBER 15, 2006 Agenda 1. EPIDEMIOLOGY: A) END STAGE RENAL DISEASE (ESRD) B) CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD) 2. HIV-ASSOCIATED
Update on HIV-Related Kidney Diseases ANDY CHOI THE MEDICAL MANAGEMENT OF HIV/AIDS DECEMBER 15, 2006 Agenda 1. EPIDEMIOLOGY: A) END STAGE RENAL DISEASE (ESRD) B) CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE (CKD) 2. HIV-ASSOCIATED
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Na + Transport 1 and 2 Linda Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES: After studying this lecture, the student should understand: 1. The terminology applied to single nephron function, including the meaning of TF/P
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University
 Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
Renal System Dr. Naim Kittana Department of Biomedical Sciences Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences An-Najah National University Declaration The content and the figures of this seminar were directly
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting. Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA
 Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Management of New-Onset Proteinuria in the Ambulatory Care Setting Akinlolu Ojo, MD, PhD, MBA Urine dipstick results Negative Trace between 15 and 30 mg/dl 1+ between 30 and 100 mg/dl 2+ between 100 and
Safety Profile of Viread and Truvada. Ian McGowan, MD PhD FRCP Cape Town MTN Regional Meeting September, 2008
 Safety Profile of Viread and Truvada Ian McGowan, MD PhD FRCP Cape Town MTN Regional Meeting September, 2008 Overview Safety assessment in drug development Physiology 101 Renal Bone Liver Safety profile
Safety Profile of Viread and Truvada Ian McGowan, MD PhD FRCP Cape Town MTN Regional Meeting September, 2008 Overview Safety assessment in drug development Physiology 101 Renal Bone Liver Safety profile
mid ihsan (Physiology ) GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B **
 (Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
(Physiology ) mid ihsan GFR is increased when A -Renal blood flow is increased B -Sym. Ganglion activity is reduced C-A and B ** Colloid pressure in the efferent arteriole is: A- More than that leaving
Renal Pharmacology. Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics BIMM118
 Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Diuretics: Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors Thiazides Loop Diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics Renal Pharmacology Kidneys: Represent 0.5% of total body weight, but receive ~25% of the total arterial blood
Chapter 21. Diuretic Agents. Mosby items and derived items 2008, 2002 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Chapter 21 Diuretic Agents Renal Structure and Function Kidneys at level of umbilicus Each weighs 160 to 175 g and is 10 to 12 cm long Most blood flow per gram of weight in body 22% of cardiac output (CO)
Nephrology - the study of the kidney. Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system
 Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Urinary System Nephrology - the study of the kidney Urology - branch of medicine dealing with the male and female urinary systems and the male reproductive system Functions of the Urinary System 1. Regulation
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance
 Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
Functional morphology of kidneys Clearance Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important
Short communication Impact of tenofovir dose adjustment on both estimated glomerular filtration rate and tenofovir trough concentration
 Antiviral Therapy 2017; 22:529 533 (doi: 10.3851/IMP3137) Short communication Impact of tenofovir dose adjustment on both estimated glomerular filtration rate and tenofovir trough concentration Sylvie
Antiviral Therapy 2017; 22:529 533 (doi: 10.3851/IMP3137) Short communication Impact of tenofovir dose adjustment on both estimated glomerular filtration rate and tenofovir trough concentration Sylvie
Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions
 Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most
Counter-Current System Regulation of Renal Functions Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most
Kidney Physiology. Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed
 Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control.
 Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control. Chapter 26 Yanal A Shafagoj. MD. PhD Lecture-1 Introduction 31/3/2015 1 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine
Urine Formation by the Kidneys: I. Glomerular Filtration, Renal Blood Flow and Their Control. Chapter 26 Yanal A Shafagoj. MD. PhD Lecture-1 Introduction 31/3/2015 1 University of Jordan Faculty of Medicine
Real Life Experience of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine Dual Therapy As a Switching Regimen in HIVTR Cohort
 Real Life Experience of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine Dual Therapy As a Switching Regimen in HIVTR Cohort Yagci-Caglayik D 1, Gokengin D 2, Inan A 3, Ozkan-Ozdemir H 4, Inan D 5, Akbulut A 6, Korten V 1,
Real Life Experience of Dolutegravir and Lamivudine Dual Therapy As a Switching Regimen in HIVTR Cohort Yagci-Caglayik D 1, Gokengin D 2, Inan A 3, Ozkan-Ozdemir H 4, Inan D 5, Akbulut A 6, Korten V 1,
Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production
 Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production Urinalysis can provide insight into hydration status, renal function or dysfunction, systemic disease, and toxic insults. Accurate interpretation of urinalysis
Functional Renal Physiology and Urine Production Urinalysis can provide insight into hydration status, renal function or dysfunction, systemic disease, and toxic insults. Accurate interpretation of urinalysis
Excretion Chapter 29. The Mammalian Excretory System consists of. The Kidney. The Nephron: the basic unit of the kidney.
 Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
Excretion Chapter 29 The Mammalian Excretory System consists of The Kidney 1. Vertebrate kidneys perform A. Ion balance B. Osmotic balance C. Blood pressure D. ph balance E. Excretion F. Hormone production
After studying this lecture, you should be able to...
 Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
Reabsorption of Salt and Water After studying this lecture, you should be able to... 1. Define the obligatory water loss. 2. Describe the mechanism of Na ++ reabsorption in the distal tubule and explain
Proteinuria, Creatinine Clearance, and Immune Activation in Antiretroviral- Naive HIV-Infected Subjects
 BRIEF REPORT Proteinuria, Creatinine Clearance, and Immune Activation in Antiretroviral- Naive HIV-Infected Subjects Samir K. Gupta, 1 Lauren Komarow, 2 Roy M. Gulick, 4 Richard B. Pollard, 5 Gregory K.
BRIEF REPORT Proteinuria, Creatinine Clearance, and Immune Activation in Antiretroviral- Naive HIV-Infected Subjects Samir K. Gupta, 1 Lauren Komarow, 2 Roy M. Gulick, 4 Richard B. Pollard, 5 Gregory K.
Antiviral Therapy 13:
 Antiviral Therapy 13:1091 1095 Short communication Cystatin C as a marker of renal function is affected by HIV replication leading to an underestimation of kidney function in HIV patients Stefan Mauss
Antiviral Therapy 13:1091 1095 Short communication Cystatin C as a marker of renal function is affected by HIV replication leading to an underestimation of kidney function in HIV patients Stefan Mauss
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD
 Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
Renal physiology D.HAMMOUDI.MD Functions Regulating blood ionic composition Regulating blood ph Regulating blood volume Regulating blood pressure Produce calcitrol and erythropoietin Regulating blood glucose
Fanconi-like syndrome and rhabdomyolysis in a person with HIV infection. on highly active antiretroviral treatment including tenofovir
 1 Letter to the Editor Fanconi-like syndrome and rhabdomyolysis in a person with HIV infection on highly active antiretroviral treatment including tenofovir The nucleotide analogue, tenofovir disoproxil
1 Letter to the Editor Fanconi-like syndrome and rhabdomyolysis in a person with HIV infection on highly active antiretroviral treatment including tenofovir The nucleotide analogue, tenofovir disoproxil
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
HIHIM 409 7/26/2009. Kidney and Nephron. Fermamdo Vega, M.D. 1
 Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Function of the Kidneys Nephrology Fernando Vega, M.D. Seattle Healing Arts Center Remove Wastes Regulate Blood Pressure Regulate Blood Volume Regulates Electrolytes Converts Vitamin D to active form Produces
Diuretic Use in Neonates
 Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Diuretic Use in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/ Diuretics
Neonatal Nursing Education Brief: Diuretic Use in the Neonate http://www.seattlechildrens.org/healthcareprofessionals/education/continuing-medical-nursing-education/neonatalnursing-education-briefs/ Diuretics
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 07 Page July 2016
 earliest reports of kidney disease in HIV infection were published in the 1980s; retrospectively, these subsequently became recognized as HIVwww.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus
earliest reports of kidney disease in HIV infection were published in the 1980s; retrospectively, these subsequently became recognized as HIVwww.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
HIV Related Kidney Disease in Jamaican Children
 HIV Related Kidney Disease in Jamaican Children Professor Russell Pierre Faculty of Medical Sciences The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica 3rd Jamaican Paediatric Nephrology Conference 2018
HIV Related Kidney Disease in Jamaican Children Professor Russell Pierre Faculty of Medical Sciences The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica 3rd Jamaican Paediatric Nephrology Conference 2018
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion
 Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
Renal Reabsorption & Secretion Topics for today: Nephron processing of filtrate Control of glomerular filtration Reabsorption and secretion Examples of solute clearance rates Hormones affecting kidney
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Table S2. Antiretroviral Therapies Taken with Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir
 Supplementary Data Statistical Analysis Due to the limited number of patients with acute kidney injury and concern for model overfitting, covariates included in multivariable logistic regression analyses
Supplementary Data Statistical Analysis Due to the limited number of patients with acute kidney injury and concern for model overfitting, covariates included in multivariable logistic regression analyses
THE PROGNOSIS OF PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND DIABETES MELLITUS
 214 ILEX PUBLISHING HOUSE, Bucharest, Roumania http://www.jrdiabet.ro Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 21(3):23-212 doi: 1.2478/rjdnmd-214-25 THE PROGNOSIS OF PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND DIABETES
214 ILEX PUBLISHING HOUSE, Bucharest, Roumania http://www.jrdiabet.ro Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis. 21(3):23-212 doi: 1.2478/rjdnmd-214-25 THE PROGNOSIS OF PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE AND DIABETES
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018. Rahmeh Alsukkar
 Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Physiology (6) 2/4/2018 Rahmeh Alsukkar **unfortunately the sheet does not involve the slides. ** the doctor repeat a lot of things from the previous lecture so this sheet will begin from slide 139 to
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Use the following diagram to answer the next question. 1. In the diagram above, pressure filtration occurs in a. W b. X c. Y d. Z
 Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Part A: Multiple Choice Questions Value: 32 Marks Suggested time: 40 minutes Instructions: For each question select the best answer and record your choice on the Scantron card provided. Using an HB pencil,
Emtricitabine / Tenofovir disoproxil Stada 200 mg/245 mg film-coated tablets , Version 1.3 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
 Emtricitabine / Tenofovir disoproxil Stada 200 mg/245 mg film-coated tablets 30.5.2016, Version 1.3 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.2 Elements for a public summary Emtricitabine / Tenofovir
Emtricitabine / Tenofovir disoproxil Stada 200 mg/245 mg film-coated tablets 30.5.2016, Version 1.3 PUBLIC SUMMARY OF THE RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN VI.2 Elements for a public summary Emtricitabine / Tenofovir
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yongjian Wang, Hanyu Lou, Lizhen Shan, Yiming Zhao
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5):5263-5268 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067528 Case Report Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia with pathological fractures during tenofovir therapy in a chronic hepatitis
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(5):5263-5268 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0067528 Case Report Hypophosphatemic osteomalacia with pathological fractures during tenofovir therapy in a chronic hepatitis
Relationships Between Renal Parameters and Serum and Urine Markers of Inflammation in Those With and Without HIV Infection.
 AID-2014-0234-ver9-Shinha_1P.3d 02/16/15 4:12pm Page 1 AIDS RESEARCH AND HUMAN RETROVIRUSES Volume 31, Number 00, 2015 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/aid.2014.0234 AID-2014-0234-ver9-Shinha_ 1 P Type:
AID-2014-0234-ver9-Shinha_1P.3d 02/16/15 4:12pm Page 1 AIDS RESEARCH AND HUMAN RETROVIRUSES Volume 31, Number 00, 2015 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/aid.2014.0234 AID-2014-0234-ver9-Shinha_ 1 P Type:
Renal System Physiology
 M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
M58_MARI0000_00_SE_EX09.qxd 7/18/11 2:37 PM Page 399 E X E R C I S E 9 Renal System Physiology Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Prior to the lab, suggest to the students that they become familiar with the
Differences in Calculated Glomerular Filtration Rates (GFR) in Efavirenz (EFV) or Tenofovir (TDF)-treated Adults in ESS40006
 13th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections Denver, CO, USA. February 5-9, 2006 Poster Number 777 Differences in Calculated Glomerular Filtration Rates (GFR) in Efavirenz (EFV) or Tenofovir
13th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections Denver, CO, USA. February 5-9, 2006 Poster Number 777 Differences in Calculated Glomerular Filtration Rates (GFR) in Efavirenz (EFV) or Tenofovir
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
Recent developments in HIV and the kidney Frank A. Post a and Stephen G. Holt b
 Recent developments in HIV and the kidney Frank A. Post a and Stephen G. Holt b a Department of HIV/GU Medicine, King s College London, London and b Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust,
Recent developments in HIV and the kidney Frank A. Post a and Stephen G. Holt b a Department of HIV/GU Medicine, King s College London, London and b Brighton and Sussex University Hospitals NHS Trust,
1950 CID 2009:49 (15 December) HIV/AIDS. Received 17 April 2009; accepted 31 July 2009; electronically published 13 November 2009.
 HIV/AIDS BRIEF REPORT Long-Term Evolution and Determinants of Renal Function in HIV-Infected Patients Who Began Receiving Combination Antiretroviral Therapy in 1997 1999, ANRS CO8 APROCO-COPILOTE Catherine
HIV/AIDS BRIEF REPORT Long-Term Evolution and Determinants of Renal Function in HIV-Infected Patients Who Began Receiving Combination Antiretroviral Therapy in 1997 1999, ANRS CO8 APROCO-COPILOTE Catherine
EU-Risk Management Plan for Emtricitabine/Tenofovir (NL/H/3635/001/DC and NL/H/3636/001/DC) V1.3
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary 200 mg/245 mg film-coated tablets VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology HIV-1 infection In this decade, the global prevalence of HIV-1 infection stabilized
VI.2 Elements for a public summary 200 mg/245 mg film-coated tablets VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology HIV-1 infection In this decade, the global prevalence of HIV-1 infection stabilized
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
URINE CONCENTRATION AND REGULATION OF ECF OSMOLARITY
 URINE CONCENTRATION AND REGULATION OF ECF OSMOLARITY Dilute and concentrated urine 1-Dilute urine : Nephron function continuous reabsorption. Solutes while failing to reabsorbe water in distal tubule and
URINE CONCENTRATION AND REGULATION OF ECF OSMOLARITY Dilute and concentrated urine 1-Dilute urine : Nephron function continuous reabsorption. Solutes while failing to reabsorbe water in distal tubule and
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
CLINICAL PEARLS OF NEW HIV MEDICATIONS PHARMACIST OBJECTIVES TECHNICIAN OBJECTIVES. At the end of this presentation pharmacists will be able to:
 CLINICAL PEARLS OF NEW HIV MEDICATIONS Cindy Lou Zoellner, PharmD, BCPS Added Qualifications in Infectious Diseases Senior Clinical Pharmacy Specialist in HIV Parkland Health & Hospital System Volunteer
CLINICAL PEARLS OF NEW HIV MEDICATIONS Cindy Lou Zoellner, PharmD, BCPS Added Qualifications in Infectious Diseases Senior Clinical Pharmacy Specialist in HIV Parkland Health & Hospital System Volunteer
Diagram of the inner portions of the kidney
 Excretory and Endocrine functions of the kidney The kidneys are the main excretory organs which eliminate in the urine, most metabolites primarily those containing nitrogen such as ammonia, urea and creatinine.
Excretory and Endocrine functions of the kidney The kidneys are the main excretory organs which eliminate in the urine, most metabolites primarily those containing nitrogen such as ammonia, urea and creatinine.
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
URINARY NET CHARGE IN HYPERCHLOREMIC METABOLIC ACIDOSIS. Seema Kumar, Meera Vaswani*, R.N. Srivastava and Arvind Bagga
 INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-JANUARY 1998 Original Articles URINARY NET CHARGE IN HYPERCHLOREMIC METABOLIC ACIDOSIS Seema Kumar, Meera Vaswani*, R.N. Srivastava and Arvind Bagga From the Departments of
INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-JANUARY 1998 Original Articles URINARY NET CHARGE IN HYPERCHLOREMIC METABOLIC ACIDOSIS Seema Kumar, Meera Vaswani*, R.N. Srivastava and Arvind Bagga From the Departments of
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE STUDY POPULATION
 COMPARISON OF TREATING METABOLIC ACIDOSIS IN CKD STAGE 4 HYPERTENSIVE KIDNEY DISEASE WITH FRUITS & VEGETABLES OR SODIUM BICARBONATE This was a 1-year, single-center, prospective, randomized, interventional
COMPARISON OF TREATING METABOLIC ACIDOSIS IN CKD STAGE 4 HYPERTENSIVE KIDNEY DISEASE WITH FRUITS & VEGETABLES OR SODIUM BICARBONATE This was a 1-year, single-center, prospective, randomized, interventional
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE. Jules B. Puschett, M.D.
 DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE Jules B. Puschett, M.D. Diuretic Resistance A clinical circumstance in which patients do not respond to a combination of salt restriction and even large
DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT OF DIURETIC RESISTANCE Jules B. Puschett, M.D. Diuretic Resistance A clinical circumstance in which patients do not respond to a combination of salt restriction and even large
Mannitol-induced Metabolic Alkalosis
 Electrolyte & Blood Pressure :, 00 ) Mannitolinduced Metabolic Alkalosis Kyung Pyo Kang, M.D., Sik Lee, M.D., Kyung Hoon Lee, M.D., and Sung Kyew Kang, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute
Electrolyte & Blood Pressure :, 00 ) Mannitolinduced Metabolic Alkalosis Kyung Pyo Kang, M.D., Sik Lee, M.D., Kyung Hoon Lee, M.D., and Sung Kyew Kang, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute
Excretory System 1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- X- Y- Z- b) Which of the following is not a function of the organ shown? A. to produce
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Objectives. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Objectives
 The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (2) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 TUBULAR FUNCTIONS (Learning objectives 54-57) 1 Tubular Transport About 99% of filtrated water and more than 90% of the filtrated
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY, HOMEOSTASIS OF FLUID COMPARTMENTS (2) Dr. Attila Nagy 2017 TUBULAR FUNCTIONS (Learning objectives 54-57) 1 Tubular Transport About 99% of filtrated water and more than 90% of the filtrated
