Mononuclear Phagocytes - Origins, Fates & Functions - Dr. Steffen Jung
|
|
|
- Vernon Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Department of Immunology The Weizmann Institute of Science Rehovot, Israel The mononuclear phagocyte system Van Furth and Cohn (1968) Ilya (Eli) Metchnikoff ( ) Nobel prize 1908 Macrophages Ralph Steinman ( ) Nobel prize 2011 Dendritic cells 2 Role in immunity Homeostasis (physiological inflammation) Unrivalled migratory Naïve T cell stimulators The mononuclear phagocyte system (2) Van Furth and Cohn (1968) Macrophages Dendritic cells 3 Outline of presentation: Mononuclear phagocyte development Mononuclear phagocyte functions in the intestine 1
2 The hematopoetic system Myeloid lineage Common Myeloid Precursor GRANULOCYTES (PMN) MONOCYTES MONONUCLEAR PHAGOCYTES MACROPHAGES Hematopoetic Stem Cell Common Lymphoid Precursor DENDRITIC CELLS, DC T CELLS 4 Lymphoid lineage LYMPHOCYTES B CELLS NK CELLS Mononuclear phagocyte origins CX 3CR1 CX 3CR HSC CMP MP MΦ DC Progenitor 5 CLP MEP Granulocytes Lin - CD34 + ckit + CD16 + CX 3CR1 + Varol et al., 2007 Monocyte subsets Mouse CD115 Ly6C/G CX 3CR1/ CX 3CR1/ blood CX 3CR1 6 Geissmann, Jung & Littman,
3 Monocyte subsets (2) CD115+ blood cells Human monocyte subsets Ziegler-Heitbrock et al., 1996 Human Mouse CD14 ++ CD16 +/- CD14 dim CD Cros et al., 2010 Monocyte subsets (3) CCR2 + Inflammatory monocytes Patrolling monocytes blood 8 Geissmann, Jung & Littman, 2003 Auffray et al., 2009 Monocyte origins Which pathway dominates in steady state? MΦ DC Precursor? CCR2 + CCR2 + 2 Ly6C alternative + but not routes to Ly6C monocytes - Sunderkotter et al., 2007 express CCR2 Yrlid et al., 2006 Varol et al., 2007 CCR2 is required for exit of monocytes from BM Serbina et al., 2006; Shi et al Bone marrow Blood 9 Fogg et al., 2006 Varol et al., 2007 Geissmann, Jung & Littman,
4 Monocyte origins (2) Mixed BM chimeras Blood Lymphocytes equally represented CCR2 -/- (CD45.2) BM from both genotypes WT () BM B cells CD115 Gr1 BM B CD45.2 Monocyte precursors (s) equally represented from genotypes 10 CD135 FSC CD117 CD115 % of Max CD45.2 Ki-Wook Kim Yochai Wolf Mixed BM chimeras CCR2 -/- (CD45.2) BM WT () BM Monocyte origins (3) Ly6C CX3CR CD CD Both monocyte subsets equally affected by CCR2 deficiency Wt / CCR2 -/- ratio MP Ly6C+ BM blood spleen monocytes Conclusion I Mononuclear phagocyte origins Steady state monocytes form a developmental series MΦ DC Precursor 12 Bone marrow Blood 4
5 Monocyte fates Blood 13 Conditional mononuclear phagocyte ablation -DTR mice DTx Receptor (DTR) Diphtheria Toxin (DTx) Mice are naturally DTx resistant because they lack high affinity DTx receptor (hbegfr) Primate DTR transgene confers DTx sensitivity Saito et al., Nat. Biotech Jung et al., Immunity 2002 DTA Promoter DTR + DTx 14 Ablation of : expressing cells All high cdcs Defined macrophage populations Mononuclear phagocyte origins -DTR mice Intestine without graft CX 3CR1 monocytes + DTx Intestine with graft reconstitute macrophages in vivo differentiation 15 Varol et al., JExMed
6 Mononuclear phagocyte origins (2) -DTR mice Donor * gated on + cells DC-depleted mouse + DTx hi cdcs recipient Monocyte recipient s, but not monocytes yield classical splenic cdcs in vivo differentiation 16 Varol et al., JExMed 2007 Mononuclear phagocyte origins (3) are absent from circulation Identification of circulating dedicated cdc precursors, pre-cdc Liu et al., Science 2009 Adoptive transfers 17 Pre cdc B220 CD11b % Donor-derived cells mono Pre-cDC cdc Conclusion II: Mononuclear phagocyte origins YOLK SAC Primitive macrophages E Self renewal HSC BM Through Adulthood FETAL LIVER Prenatal MP Granulocytes monocytes CDP Pre-DC PDC Self renewal Macrophages monocyte-derived Macrophages CD4 + DN CD8α + CD MoDCs FLT3-dependent classical DCs 6
7 Gastrointestinal tract Bioreactor for food breakdown (>10 13 bacteria) Large surface & thin border (single cell epithelial layer) Challenge to the immune system Tolerance > Commensals Defense > Pathogenic enterobacteria Colon CFU/ml Breakdown of balance Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) 19 Intestinal macrophages CX 3CR1 CX 3CR1 20 The CX 3 CR1/L1 reporter animals CX 3CR1 CX 3CL1 Fractalkine CX 3CR1 45 kb CX 3CR1CX 3CR1 :CX 3CL1 cherry Targeted replacement of chemokine receptor with reporter prominent expression in mononuclear phagocytes BAC transgene encoding reporter under CX 3 CL1 promoter control ATG CX 3C mucin stalk T M 21 CX 3 CR1 : CX 3 CL1 Cherry mice Jung et al., MCB 2000 Kim et al., BLOOD,
8 CX 3CR1 :CX 3CL1 cherry Macrophages Epithelial/ Goblet cells 22 Ki-Wook Kim Blood 2011 Intestinal lamina propria mononuclear phagocyte compartment Analysis of colon of CX 3 CR1 gfp mouse Gated on living CD45 + cells 87 % R1 + CD11b - R1 R2 MHC II (I-A b ) R3 2.5 % R2 + CD11b + FSC CD11b + CD103 + CD11b - CD103 + CD11b + DCs 82 % R3 - CD11b - 23 CX 3 CR1 + CD11b + CX 3 CR1 - CD11b + MΦ s CD103 CX 3CR1 / 82 % Zigmond Intestinal lamina propria mononuclear phagocyte compartment (2) CX 33 CR1 + + Macrophages macrophages monocyte-derived CD103 + Dendritic cells predc-derived Varol, C., et al. Bogunovic, M. et al., Immunity Varol, Zigmond & Jung, Nature Reviews Immunology
9 Task division between migratory DCs and resident MFs LAMINA PROPRIA CD103 + dendritic cells CCR7 Th2 CX 3 CR1 + macrophages Th2 Th17 Th1 Treg Treg CCR9, a4b7 Effector site (Maintenance selective expansion) NHC gd LTi Innate lymphoid cells steady state MsnLN 25 naïve CD4 T cell priming site Th1 Th17 Scheme compiled from data of Pabst, Agace, Kelsall, Mowat, Powrie and Pulendran groups Steady state Resident MFs Inflammation Exposure to dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) in drinking water for 7 days Lesions in epithel CD11b Cx3cr1/ 26 Inflammation recruits a novel CX 3 CR1 int cell subset Steady state Inflammation Resident MFs day 4 day 7 CD11b 27 Cx3cr1/ See also: Weber et al., EJI 2010, Platt et al., JI 2010 Rivollier et al., JExMed 2012 % out of CD45 + living cells CD11b Cx3cr1/ CX3CR1 high F4/80 high CX3CR1 dim F4/80 low Neutrophils 9
10 CX 3 CR1 int infiltrate is monocyte-derived w/o graft DSS 2% in drinking water day Monocyte transfer Analysis Ly6C hi monocytes seed tissue, give rise to Ly6C lo cells Monocyte recipient Ly6C day 1 CX 3CR1/ F4/80 MHC II 28 CX 3CR1/ Ly6C F4/80 MHC II day 3 Cells gain CCR7 expression CX 3 CR1 int infiltrate is monocyte-derived, requires CCR2 DSS 2% in drinking water day Mixed monocyte graft CCR2 KO WT Monocyte transfer Analysis Mixed monocyte recipient CX 3CR1/ 29 Only WT cells but not CCR2 deficient cells seed inflamed tissue CX 3 CR1 int monocyte-derived infiltrate promotes inflammation DSS 1% in drinking water day Anti-CCR2 ab Monocyte depletion DSS only DSS + MC21 30 CD11b Ly6C 10
11 Expression analysis of monocyte progeny during steady state and inflammation monocytes Steady state CX 3 CR1 hi resident macrophages CX 3 CR1 int infiltrating macrophages DSS Colitis Resident MFs Infiltrating MFs Steady state DSS Colitis 31 CX 3 CR1 hi resident MFs express IL-10 (Pabst, Kelsall, Pulendran) CX 3 CR1 int MFs express pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL6, IL23) fold change CX3CR1 int over CX3CR1 hi IL6 IL23 QRT-PCR IL10 TNFa CX 3 CR1 int MFs respond to bacterial products Expression of recruited CX 3 CR1 int cells over resident CX 3 CR1 hi cells TLR2 & NOD-like receptor signaling pathway PDG TLR-2 ie- DAP NOD1 RIP2 CARD9 IKKa IKKg IKKb IkB NFkB IL-6 NOD2 32 CX 3 CR1 int MFs respond to bacterial products (2) Infiltrating MFs, but not resident MFs secrete IL-6 in response to TLR2 / NOD2 ligands Pam3 in vitro assay Muramyldi-peptide 33 11
12 Conclusion CD103 + DCs CX 3 CR1 + MF s give rise Education to CX 3 CR1 + macrophages Homeostasis in lamina propria Are in steady state educated by environment Under inflammation monocyte infiltrate fails LN to be tamed respond to bacterial product and exacerbate disease 34 IL10 IL10 IL6 IL6 Inflammation LN CCR 7 Dan Littman Frederic Geissmann Skirball Institute King s College, London NYU Medical Center Simon Yona Ki-wook Kim Diana Rashkovan Yochai Wolf Tegest Aychek Alexander Mildner Rita Krautgammer Chen Varol Tel Aviv-Sourasky Medical Center
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow
 White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Copyright 2014 The Authors. Deposited on: 19 June 2014
 Bain, Calum C., and Mowat, Allan McI. (2014) Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammation. Immunological Reviews, 260 (1). pp. 102-117. ISSN 0105-2896 Copyright 2014 The Authors http://eprints.gla.ac.uk/93404/
Bain, Calum C., and Mowat, Allan McI. (2014) Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammation. Immunological Reviews, 260 (1). pp. 102-117. ISSN 0105-2896 Copyright 2014 The Authors http://eprints.gla.ac.uk/93404/
JPEMS Nantes, Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization
 JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr
JPEMS Nantes, 2014- Basic Immunology Introduction to the immune system Definitions Structure and General Organization Teacher: Pr. Régis Josien, Laboratoire Immunologie and INSERM U1064, CHU Nantes Regis.Josien@univ-nantes.fr
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012
 17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
17 th International Conference of the Inflammation Research Association: Wednesday AM (Day 4) September 9-13, 2012 The Sagamore Resort, Bolton Landing, NY, USA The following report includes highlights
Supplemental Information. Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection. Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15
 Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection Arya Khosravi, Alberto Yáñez, Jeremy G. Price, Andrew Chow, Miriam Merad, Helen
Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 15 Supplemental Information Gut Microbiota Promotes Hematopoiesis to Control Bacterial Infection Arya Khosravi, Alberto Yáñez, Jeremy G. Price, Andrew Chow, Miriam Merad, Helen
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY. CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells. Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation
 IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
IMMUNOLOGICAL MEMORY CD4 T Follicular Helper Cells Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation CD4 T Cell Differentiation Bcl-6 T-bet GATA-3 ROR t Foxp3 CD4 T follicular helper (Tfh) cells FUNCTION Provide essential
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Long-term innate immune memory via effects on bone marrow progenitors
 Long-term innate immune memory via effects on bone marrow progenitors Helen S Goodridge, PhD helen.goodridge@csmc.edu Regenerative Medicine Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, USA Fondation
Long-term innate immune memory via effects on bone marrow progenitors Helen S Goodridge, PhD helen.goodridge@csmc.edu Regenerative Medicine Institute, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, USA Fondation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10134 Supplementary Figure 1. Anti-inflammatory activity of sfc. a, Autoantibody immune complexes crosslink activating Fc receptors, promoting activation of macrophages, and WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, and Applications to Human Disease Dr. Michael A. Caligiuri
 Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
Natural Killer Cells: Development, Diversity, November 26, 2008 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center The James Cancer Hospital and Solove Research Institute Columbus, Ohio, USA 1 Human
M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology
 Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
Code : AS-2246 M.Sc. III Semester Biotechnology End Semester Examination, 2013 Model Answer LBTM: 302 Advanced Immunology A. Select one correct option for each of the following questions:- 2X10=10 1. (b)
General Overview of Immunology. Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center
 General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
General Overview of Immunology Kimberly S. Schluns, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Immunology UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Objectives Describe differences between innate and adaptive immune responses
Felix Yarovinsky. Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii
 Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
CLINICAL USE OF CELLULAR SUBPOPULATION ANALYSIS IN BM
 CLINICAL USE OF CELLULAR SUBPOPULATION ANALYSIS IN BM CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, UNIVERSITY AND UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL OF SALAMANCA (SPAIN)( Sao Paulo, 18th of April, 2009 IDENTIFICATION OF HPC (I) 1.- In vivo
CLINICAL USE OF CELLULAR SUBPOPULATION ANALYSIS IN BM CANCER RESEARCH CENTRE, UNIVERSITY AND UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL OF SALAMANCA (SPAIN)( Sao Paulo, 18th of April, 2009 IDENTIFICATION OF HPC (I) 1.- In vivo
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3412
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary Figure 1 Gata1 expression in heamatopoietic stem and progenitor populations. (a) Unsupervised clustering according to 100 top variable genes across single pre-gm cells. The two main cell
Supplementary Information. Paired immunoglobulin-like receptor A is an intrinsic, self-limiting
 Supplementary Information Paired immunoglobulin-like receptor A is an intrinsic, self-limiting suppressor of IL-5-induced eosinophil development Netali Ben Baruch-Morgenstern 1,4, Dana Shik 1,4, Itay Moshkovits
Supplementary Information Paired immunoglobulin-like receptor A is an intrinsic, self-limiting suppressor of IL-5-induced eosinophil development Netali Ben Baruch-Morgenstern 1,4, Dana Shik 1,4, Itay Moshkovits
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells. Part II: Cells (aka the Sentinels)
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies. Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018
 Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018 Macrophages: Professional phagocytes of the myeloid lineage APC,
Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018 Macrophages: Professional phagocytes of the myeloid lineage APC,
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System
 Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
Manipulating the Tumor Environment
 Manipulating the Tumor Environment Vincenzo Bronte Verona University Hospital vincenzo.bronte@univr.it Escape from immune control can be viewed as one of the «Hallmarks of Cancer» D. Hanahan and R. A.
Manipulating the Tumor Environment Vincenzo Bronte Verona University Hospital vincenzo.bronte@univr.it Escape from immune control can be viewed as one of the «Hallmarks of Cancer» D. Hanahan and R. A.
PBS Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs , 27-30
 PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
PBS 803 - Class #2 Introduction to the Immune System part II Suggested reading: Abbas, pgs. 15-25, 27-30 Learning Objectives Compare and contrast the maturation of B and T lymphocytes Compare and contrast
Copyright 2013 Society for Mucosal Immunology. Deposited on: 21 May 2013
 Bain, C.C., Scott, C.L., Uronen-Hansson, H., Gudjonsson, S., Jansson, O., Grip, O., Guilliams, M., Malissen, B., Agace, W.W., and Mowat, A.M. (23) Resident and pro-inflammatory macrophages in the colon
Bain, C.C., Scott, C.L., Uronen-Hansson, H., Gudjonsson, S., Jansson, O., Grip, O., Guilliams, M., Malissen, B., Agace, W.W., and Mowat, A.M. (23) Resident and pro-inflammatory macrophages in the colon
Supplementary Figure 1 Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression during muscle regeneration (a) Analysis of CR3CR1 mrna expression by real time-pcr
 Supplementary Figure 1 Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression during muscle regeneration (a) Analysis of CR3CR1 mrna expression by real time-pcr at day 0, 1, 4, 10 and 21 post- muscle injury. (b)
Supplementary Figure 1 Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression during muscle regeneration (a) Analysis of CR3CR1 mrna expression by real time-pcr at day 0, 1, 4, 10 and 21 post- muscle injury. (b)
Genetics. Environment. You Are Only 10% Human. Pathogenesis of IBD. Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function IBD
 Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Advances in the Pathogenesis of IBD: Genetics Leads to Function Pathogenesis of IBD Environmental Factors Microbes Scott Plevy, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, Microbiology & Immunology UNC School
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Intestinal dendritic cells in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3761 World J Gastroenterol 2011 September 7; 17(33): 3761-3775 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online)
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327office wjg@wjgnet.com doi:10.3748/wjg.v17.i33.3761 World J Gastroenterol 2011 September 7; 17(33): 3761-3775 ISSN 1007-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-2840 (online)
Part III Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction
 Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells: General Introduction Iván López-Expósito As an organ specialized in food digestion and nutrient absorption, the intestinal mucosa presents a huge surface area (almost
A crucial role for HVEM and BTLA in preventing intestinal inflammation
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2008 A crucial role for HVEM and BTLA in preventing intestinal inflammation Marcos W. Steinberg La Jolla Institute
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2008 A crucial role for HVEM and BTLA in preventing intestinal inflammation Marcos W. Steinberg La Jolla Institute
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes
 Joint Lab Meeting 03/03/2015 Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes Caroline Raffin Bluestone Lab ILCs: Definition - Common lymphoid progenitor
Joint Lab Meeting 03/03/2015 Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes Caroline Raffin Bluestone Lab ILCs: Definition - Common lymphoid progenitor
This is the author s final accepted version.
 Joeris, T., Müller-Luda, K., Agace, W.W. and Mowat, A. M. (2017) Diversity and functions of intestinal mononuclear phagocytes.mucosal Immunology, 10(4), pp. 845-864. (doi:10.1038/mi.2017.22) This is the
Joeris, T., Müller-Luda, K., Agace, W.W. and Mowat, A. M. (2017) Diversity and functions of intestinal mononuclear phagocytes.mucosal Immunology, 10(4), pp. 845-864. (doi:10.1038/mi.2017.22) This is the
T Cell Development. Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD. November 3, 2015
 T Cell Development Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD November 3, 2015 Thymocytes in the cortex of the thymus Early thymocytes development Positive and negative selection Lineage commitment Exit from the thymus and
T Cell Development Xuefang Cao, MD, PhD November 3, 2015 Thymocytes in the cortex of the thymus Early thymocytes development Positive and negative selection Lineage commitment Exit from the thymus and
Liver-Resident Macrophage Necroptosis Orchestrates Type 1 Microbicidal Inflammation and Type-2- Mediated Tissue Repair during Bacterial Infection
 Liver-Resident Macrophage Necroptosis Orchestrates Type 1 Microbicidal Inflammation and Type-2- Mediated Tissue Repair during Bacterial Infection Camille Blériot, Théo Dupuis, Grégory Jouvion, Gérard Eberl,
Liver-Resident Macrophage Necroptosis Orchestrates Type 1 Microbicidal Inflammation and Type-2- Mediated Tissue Repair during Bacterial Infection Camille Blériot, Théo Dupuis, Grégory Jouvion, Gérard Eberl,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice. (a, b) Gating strategies for differentiated cells including PMN (CD11b + Ly6G hi and CD11b + Ly6G
Supplementary Figure 1 Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice. (a, b) Gating strategies for differentiated cells including PMN (CD11b + Ly6G hi and CD11b + Ly6G
Immunology Lecture 4. Clinical Relevance of the Immune System
 Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
Immunology Lecture 4 The Well Patient: How innate and adaptive immune responses maintain health - 13, pg 169-181, 191-195. Immune Deficiency - 15 Autoimmunity - 16 Transplantation - 17, pg 260-270 Tumor
MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW
 MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW YVON LEBRANCHU Service Néphrologie et Immunologie Clinique CHU TOURS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL CD4 + T CELL CYTOKINE PRODUCTION CLONAL
MECHANISMS OF CELLULAR REJECTION IN ORGAN TRANSPLANTATION AN OVERVIEW YVON LEBRANCHU Service Néphrologie et Immunologie Clinique CHU TOURS ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELL CD4 + T CELL CYTOKINE PRODUCTION CLONAL
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Fig. S1. Gpa33 -/- mice do not express Gpa33 mrna or GPA33 protein. (A) The Gpa33 null allele contains a premature translational stop codon (STOP) in exon 2, and almost all of the
Supplementary Material Fig. S1. Gpa33 -/- mice do not express Gpa33 mrna or GPA33 protein. (A) The Gpa33 null allele contains a premature translational stop codon (STOP) in exon 2, and almost all of the
Supplemental Information. Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and. Monocyte-Dendritic Cell Progenitors Independently
 Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and Monocyte-endritic ell Progenitors Independently Produce Functionally istinct Monocytes lberto Yáñez, Simon G. oetzee, ndre
Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Granulocyte-Monocyte Progenitors and Monocyte-endritic ell Progenitors Independently Produce Functionally istinct Monocytes lberto Yáñez, Simon G. oetzee, ndre
Dendritic cells and their role in immunity
 PART I Dendritic cells and their role in immunity CHAPTER 1 Subpopulations and differentiation of mouse dendritic cells Carlos Ardavín Universidad Autónoma 1.1 DENDRITIC CELL SUBPOPULATIONS Dendritic cells
PART I Dendritic cells and their role in immunity CHAPTER 1 Subpopulations and differentiation of mouse dendritic cells Carlos Ardavín Universidad Autónoma 1.1 DENDRITIC CELL SUBPOPULATIONS Dendritic cells
Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author)
 Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The manuscript by Zhuang and colleagues characterizes in depth the phenotype, origin and role of mononuclear phagocytes infiltrating murine cardiac
Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The manuscript by Zhuang and colleagues characterizes in depth the phenotype, origin and role of mononuclear phagocytes infiltrating murine cardiac
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), comprised of Crohn s disease
 BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW ARTICLE Immunoregulatory Role of Myeloid-derived Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Marcelo Cerf Leal, MD*, and Jan Däbritz, MD*,, Abstract: As the frontiers of immunological research
BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW ARTICLE Immunoregulatory Role of Myeloid-derived Cells in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Marcelo Cerf Leal, MD*, and Jan Däbritz, MD*,, Abstract: As the frontiers of immunological research
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
NOD2 Activation promotes anti-inflammatory activity of human Umbilical cord blood MSCs against Inflammatory bowel disease
 NOD2 Activation promotes anti-inflammatory activity of human Umbilical cord blood MSCs against Inflammatory bowel disease Prof. Kyung-Sun Kang, DVM, PhD. Adult Stem Cell Research Center Seoul National
NOD2 Activation promotes anti-inflammatory activity of human Umbilical cord blood MSCs against Inflammatory bowel disease Prof. Kyung-Sun Kang, DVM, PhD. Adult Stem Cell Research Center Seoul National
Monocyte subsets in health and disease. Marion Frankenberger
 Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Prof. Dr. David Voehringer
 Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Department of Infection Biology Institute of Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene Outline of the presentation The concept of type 2 immunity Basophil
Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Department of Infection Biology Institute of Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene Outline of the presentation The concept of type 2 immunity Basophil
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Examples of staining for each antibody used for the mass cytometry analysis.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Examples of staining for each antibody used for the mass cytometry analysis. To illustrate the functionality of each antibody probe, representative plots illustrating the expected
Supplementary Figure 1 Examples of staining for each antibody used for the mass cytometry analysis. To illustrate the functionality of each antibody probe, representative plots illustrating the expected
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
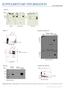 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19814 Figure 3e - - - Beads: Hep SA Sup Hep SA Sup Hep - SA - Sup 150 102 76 102 76 Blot: NP-1 Blot: MECA-32 Blot: VEGF Figure 3f Rbt IgG ctrl IP VEGF IP Extended
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19814 Figure 3e - - - Beads: Hep SA Sup Hep SA Sup Hep - SA - Sup 150 102 76 102 76 Blot: NP-1 Blot: MECA-32 Blot: VEGF Figure 3f Rbt IgG ctrl IP VEGF IP Extended
Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School
 CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
CTLs, Natural Killers and NKTs 1 Shiv Pillai Ragon Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School CTL inducing tumor apoptosis 3 Lecture outline CD8 + Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) Activation/differentiation
Components of the innate immune system
 Components of the innate immune system Before our discussion about innate immunity Differences between innate and adaptive systems: Innate immune system = natural = native -Germline: prepared before exposure
Components of the innate immune system Before our discussion about innate immunity Differences between innate and adaptive systems: Innate immune system = natural = native -Germline: prepared before exposure
Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD. Fiona Powrie
 Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD Fiona Powrie Translational Gastroenterology Unit Experimental Medicine Division Nuffield Dept of Clinical Medicine University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk
Intestinal homeostasis and its breakdown in IBD Fiona Powrie Translational Gastroenterology Unit Experimental Medicine Division Nuffield Dept of Clinical Medicine University of Oxford fiona.powrie@path.ox.ac.uk
Introduction to Immune System
 Introduction to Immune System Learning outcome You will be able to understand, at a fundamental level, the STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS of cell surface and soluble molecules involved in recognition of foreign
Introduction to Immune System Learning outcome You will be able to understand, at a fundamental level, the STRUCTURES and FUNCTIONS of cell surface and soluble molecules involved in recognition of foreign
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Intestinal CD103 þ CD11b dendritic cells restrain colitis via IFN-g-induced anti-inflammatory response in epithelial cells
 nature publishing group OPEN Intestinal CD103 þ CD11b dendritic cells restrain colitis via IFN-g-induced anti-inflammatory response in epithelial cells ARBM Muzaki 1,3, P Tetlak 1,3, J Sheng 1, SC Loh
nature publishing group OPEN Intestinal CD103 þ CD11b dendritic cells restrain colitis via IFN-g-induced anti-inflammatory response in epithelial cells ARBM Muzaki 1,3, P Tetlak 1,3, J Sheng 1, SC Loh
Probing In-Vivo Dendritic Cell functions in Lymphoid Organs
 Thesis for the degree Doctor of Philosophy Submitted to the Scientific Council of the Weizmann Institute of Science Rehovot, Israel עבודת גמר (תזה) לתואר דוקטור לפילוסופיה מוגשת למועצה המדעית של מכון ויצמן
Thesis for the degree Doctor of Philosophy Submitted to the Scientific Council of the Weizmann Institute of Science Rehovot, Israel עבודת גמר (תזה) לתואר דוקטור לפילוסופיה מוגשת למועצה המדעית של מכון ויצמן
IL-12 family members in experimental colitis. Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany
 IL-12 family members in experimental colitis Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany IBD - Pathogenesis Genetic Predisposition Bacterial Antigens Activation of
IL-12 family members in experimental colitis Markus F. Neurath I. Medical Clinic Johannes Gutenberg-University Mainz, Germany IBD - Pathogenesis Genetic Predisposition Bacterial Antigens Activation of
The Skinny of the Immune System
 The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
The Skinny of the Immune System Robert Hostoffer, DO, FACOP, FAAP Associate Professor of Pediatrics Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio Overview 1. Immune system of the skin 2. Immune Players
1. Specificity: specific activity for each type of pathogens. Immunity is directed against a particular pathogen or foreign substance.
 L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and. Specific. (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell
 There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BIOLOGY. Advanced Topics in Immunology
 Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 3 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Desk Number: Title of Exam: Advanced Topics in Immunology Time allowed: 2 hours Total marks
Examination Candidate Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 3 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Desk Number: Title of Exam: Advanced Topics in Immunology Time allowed: 2 hours Total marks
IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia
 Supplementary Figures IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia Yaming Wang, Kristy J. Szretter, William Vermi, Susan Gilfillan, Cristina
Supplementary Figures IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia Yaming Wang, Kristy J. Szretter, William Vermi, Susan Gilfillan, Cristina
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE
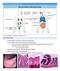 LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
LECTURE 12: MUCOSAL IMMUNITY GUT STRUCTURE - Small intestine in humans is around 3-4 metres long - Internal surface of the small intestines are lined by villi o Villi are composed of absorptive cells (epithelial/enterocytes)
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases. Abul K. Abbas UCSF
 Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Tolerance, autoimmunity and the pathogenesis of immunemediated inflammatory diseases Abul K. Abbas UCSF Balancing lymphocyte activation and control Activation Effector T cells Tolerance Regulatory T cells
Eosinophils are required. for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow
 Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow Van Trung Chu, Anja Fröhlich, Gudrun Steinhauser, Tobias Scheel, Toralf Roch, Simon Fillatreau, James J. Lee, Max Löhning
Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow Van Trung Chu, Anja Fröhlich, Gudrun Steinhauser, Tobias Scheel, Toralf Roch, Simon Fillatreau, James J. Lee, Max Löhning
TEPZZ A_T EP A1 (19) (11) EP A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION. (51) Int Cl.: C07K 16/28 ( ) A61K 39/395 (2006.
 (19) TEPZZ 7 7944A_T (11) EP 2 727 944 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/19 (51) Int Cl.: C07K 16/28 (2006.01) A61K 39/395 (2006.01) (21) Application
(19) TEPZZ 7 7944A_T (11) EP 2 727 944 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: 07.05.2014 Bulletin 2014/19 (51) Int Cl.: C07K 16/28 (2006.01) A61K 39/395 (2006.01) (21) Application
RORγt and IL-17 Responses`
 Falk Workshop Mechanisms of Intestinal Inflammation October 10, 2007 and IL-17 Responses` Dan Littman HHMI, Skirball Institute New York University School of Medicine New paradigm for T Helper Cell Differentiation
Falk Workshop Mechanisms of Intestinal Inflammation October 10, 2007 and IL-17 Responses` Dan Littman HHMI, Skirball Institute New York University School of Medicine New paradigm for T Helper Cell Differentiation
Putting it Together. Stephen Canfield Secondary Lymphoid System. Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s
 Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Putting it Together Stephen Canfield smc12@columbia.edu Secondary Lymphoid System Tonsil Anterior Cervical LN s Axillary LN s Mediastinal/Retroperitoneal LN s Thoracic Duct Appendix Spleen Inguinal LN
Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells Timo Heidt *, Hendrik B. Sager *, Gabriel Courties, Partha Dutta, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Alex Zaltsman, Constantin von zur
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Chronic variable stress activates hematopoietic stem cells Timo Heidt *, Hendrik B. Sager *, Gabriel Courties, Partha Dutta, Yoshiko Iwamoto, Alex Zaltsman, Constantin von zur
CX3CR1 regulates intestinal macrophage homeostasis, bacterial translocation, and colitogenic Th17 responses in mice
 Research article CX3CR1 regulates intestinal macrophage homeostasis, bacterial translocation, and colitogenic Th17 responses in mice Oscar Medina-Contreras, 1 Duke Geem, 1 Oskar Laur, 2 Ifor R. Williams,
Research article CX3CR1 regulates intestinal macrophage homeostasis, bacterial translocation, and colitogenic Th17 responses in mice Oscar Medina-Contreras, 1 Duke Geem, 1 Oskar Laur, 2 Ifor R. Williams,
Normal & Leukaemic haematopoiesis. Dr. Liu Te Chih Dept of Haematology / Oncology National University Health Services Singapore
 Normal & Leukaemic haematopoiesis 2010 Dr. Liu Te Chih Dept of Haematology / Oncology National University Health Services Singapore Use of Immunophenotyping today Lineage assignment Differentiation of
Normal & Leukaemic haematopoiesis 2010 Dr. Liu Te Chih Dept of Haematology / Oncology National University Health Services Singapore Use of Immunophenotyping today Lineage assignment Differentiation of
Concise Review: Dendritic Cell Development in the Context of the Spleen Microenvironment
 THE STEM CELL NICHE Concise Review: Dendritic Cell Development in the Context of the Spleen Microenvironment JONATHAN K. H. TAN, HELEN C. O NEILL School of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, The Australian
THE STEM CELL NICHE Concise Review: Dendritic Cell Development in the Context of the Spleen Microenvironment JONATHAN K. H. TAN, HELEN C. O NEILL School of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, The Australian
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Sarkis K Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology
 Sarkis K Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology The human microbiota The human gut harbors 10 11-10 12 bacteria per gram colonic content (>10 14 total bacteria) Total bacteria outnumber human cells
Sarkis K Mazmanian, California Institute of Technology The human microbiota The human gut harbors 10 11-10 12 bacteria per gram colonic content (>10 14 total bacteria) Total bacteria outnumber human cells
Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany
 How T cells recognize antigen Christian Kurts Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany When do T cells recognize antigen? Antigen uptake Activation phase 1st recognition Effector
How T cells recognize antigen Christian Kurts Institute t of Experimental Immunology University of Bonn, Germany When do T cells recognize antigen? Antigen uptake Activation phase 1st recognition Effector
Chapter 1. Chapter 1 Concepts. MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally!
 MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
MCMP422 Immunology and Biologics Immunology is important personally and professionally! Learn the language - use the glossary and index RNR - Reading, Note taking, Reviewing All materials in Chapters 1-3
Author Manuscript Trends Immunol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 October 1. Monocyte trafficking in acute and chronic inflammation
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Monocyte trafficking in acute and chronic inflammation Molly A. Ingersoll 1, Andrew M. Platt 1, Stephane Potteaux 1,2, and Gwendalyn J. Randolph 1 1 Department Gene
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Monocyte trafficking in acute and chronic inflammation Molly A. Ingersoll 1, Andrew M. Platt 1, Stephane Potteaux 1,2, and Gwendalyn J. Randolph 1 1 Department Gene
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection. Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science
 Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
Memory NK cells during mousepox infection Min Fang, Ph.D, Professor Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Science Infectious Diseases are a Major Cause of Death Worldwide May 14 th 1796 Prevalence
The Immune Response in Time and Space
 The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
The Immune Response in Time and Space Chapters 14 & 4 Sharon S. Evans, Ph.D. Department of Immunology 845-3421 sharon.evans@roswellpark.org September 18 & 23, 2014 Inflammation Inflammation Complex response
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
IFNg. IFNg IL-5 IL-13 IL-17 IL-22. LTi NCR+ ILC3. IL-17 IL-22 IFNg
 Group 1 ILC T-Bet Eomes Nkp46 NK1.1 NK cells IFNg T-Bet ILC1 IFNg low RORgt Group 2 ILC RORa CD127 ILC2 IL-5 IL-13 Group 3 ILC RORc CD127 AhR T-Bet AhR LTi c-kit; CD4+/- NCR+ ILC3 c-kit; Nkp46 IL-17 IL-22
Group 1 ILC T-Bet Eomes Nkp46 NK1.1 NK cells IFNg T-Bet ILC1 IFNg low RORgt Group 2 ILC RORa CD127 ILC2 IL-5 IL-13 Group 3 ILC RORc CD127 AhR T-Bet AhR LTi c-kit; CD4+/- NCR+ ILC3 c-kit; Nkp46 IL-17 IL-22
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep
 The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body Defenses Outline PART 1: INNATE DEFENSES 21.1 Surface barriers act as the first line of defense to keep invaders out of the body (pp. 772 773; Fig. 21.1; Table
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CCR6 + and CCR6 - CD4 + IL-17A +/ex and Treg cells. Quantitative PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcript abundance
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CCR6 + and CCR6 - CD4 + IL-17A +/ex and Treg cells. Quantitative PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcript abundance
1. The scavenger receptor, CD36, functions as a coreceptor for which TLR? a. TLR ½ b. TLR 3 c. TLR 4 d. TLR 2/6
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Cellular and Molecular Immunology, 8th Edition By Abul K. Abbas, MBBS, Andrew H. H. Lichtman, MD, PhD and Shiv Pillai, MBBS, PhD. Chapter 4 (pages 62-74): Innate Immunity
B and T cell Memory. Bengt Lindbom Adap6ve Immunity BMC D14
 B and T cell Memory Bengt Lindbom Adap6ve Immunity BMC D14 Immunity: a historical perspec6ve 430 B.C. Thucydides describes the ongoing plague of Athens:.the same man was never attacked twice 15th century:
B and T cell Memory Bengt Lindbom Adap6ve Immunity BMC D14 Immunity: a historical perspec6ve 430 B.C. Thucydides describes the ongoing plague of Athens:.the same man was never attacked twice 15th century:
Haematopoietic stem cells
 Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
FcγRIIIA (CD16)-expressing monocytes mediate the depletion of tumor-infiltrating Tregs via ipilimumab-dependent ADCC in melanoma patients
 FcγRIIIA (CD16)-expressing monocytes mediate the depletion of tumor-infiltrating Tregs via ipilimumab-dependent ADCC in melanoma patients Emanuela Romano Department of Oncology University of Lausanne and
FcγRIIIA (CD16)-expressing monocytes mediate the depletion of tumor-infiltrating Tregs via ipilimumab-dependent ADCC in melanoma patients Emanuela Romano Department of Oncology University of Lausanne and
The ontogeny and function of intestinal dendritic cells
 The ontogeny and function of intestinal dendritic cells Persson, Emma Published: 2014-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Persson, E. (2014). The ontogeny and function of intestinal
The ontogeny and function of intestinal dendritic cells Persson, Emma Published: 2014-01-01 Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Persson, E. (2014). The ontogeny and function of intestinal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: /nature12026
 doi:1.138/nature1226 a 4 35 3 MCSF level (pg/ml) 25 2 15 1 5 1h3 3h 5h 7h 15h 24h b MPP (CD135 KSL) HSC (CD34 CD15 KSLF) c % 4 ** LPS 3 GFP pos cells 2 PU.1 GFP LPS 1 FSCA Ctl NI 24h LPS Sup.Fig.1 Effect
doi:1.138/nature1226 a 4 35 3 MCSF level (pg/ml) 25 2 15 1 5 1h3 3h 5h 7h 15h 24h b MPP (CD135 KSL) HSC (CD34 CD15 KSLF) c % 4 ** LPS 3 GFP pos cells 2 PU.1 GFP LPS 1 FSCA Ctl NI 24h LPS Sup.Fig.1 Effect
