DRY EYE DISEASE (DED) OR
|
|
|
- Deirdre Bryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LABORATORY SCIENCES Modulation of Integrin 4 1 (VLA-4) in Dry Eye Disease Tatiana Ecoiffier, MS, MEng; Jaafar El Annan, MD; Saadia Rashid, MD; Debra Schaumberg, ScD, OD, MPH; Reza Dana, MD, MSc, MPH Objective: To study the effect of topical application of very late antigen 4 (VLA-4) small-molecule antagonist (anti VLA-4 sm) in a mouse model of dry eye disease. Methods: (or control vehicle) was applied topically to mice placed in a controlledenvironment chamber. Corneal fluorescein staining and conjunctival T-cell enumeration were performed in the different treatment groups. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to quantify expression of inflammatory cytokines in the cornea and conjunctiva. Results: Dry eye syndrome induced increased corneal fluorescein staining, corneal and conjunctival tumor necrosis factor messenger RNA expression, and T-cell infiltration into the conjunctiva. Very late antigen 4 blockade significantly decreased corneal fluorescein staining compared with the untreated dry eye disease and control vehicle treated groups (P.1 and P=.2, respectively). In addition, VLA-4 blockade was associated with a significant decrease in conjunctival T-cell numbers (P.1 vs control vehicle treated group) and tumor necrosis factor- transcript levels in the cornea (P=.4 vs control vehicle treated group) and conjunctiva (P=.48 vs control vehicle treated group). Conclusion: Application of topical anti VLA-4 sm led to a significant decrease in dry eye signs and suppression of inflammatory changes at the cellular and molecular levels. Clinical Relevance: Topical blockade of VLA-4 may be a novel therapeutic approach to treat the clinical signs and inflammatory changes accompanying dry eye disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 28;126(12): Author Affiliations: Schepens Eye Research Institute and Department of Ophthalmology, Harvard Medical School (Ms Ecoiffier and Drs El Annan, Rashid, Schaumberg, and Dana), Division of Ophthalmic Epidemiology, Brigham and Women s Hospital (Dr Schaumberg), and Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary (Dr Dana), Boston. DRY EYE DISEASE (DED) OR keratoconjunctivitis sicca is a common ocular surface disease affecting tens of millions of people worldwide. 1 It is one of the leading reasons for patients seeking eye care for treatment of symptoms of ocular discomfort and visual disturbance and commonly leads to problems with activities that require sustained visual attention such as reading and driving. 2 To date, the pathogenesis of DED is not fully understood, but recent studies 3-5 have demonstrated that DED is associated with ocular surface inflammation, which contributes to the disease process and the symptoms. 6 Therefore, targeting molecules involved in mediating inflammation could be a promising approach for the treatment of DED. Inflammation is a complex response to local injury or trauma involving various immunocytes and numerous mediators. The assembly of the inflammatory response would be impossible without the controlled migration of leukocytes, of which cell adhesion molecules such as integrins are key components for migration and activation of these cells. Integrins are heterodimeric molecules and cell surface transmembrane glycoproteins that mediate cell-cell and cellmatrix interactions. Very late antigen 4 (VLA-4 [integrin 4 1 ]) exerts its functions through interaction with its ligands fibronectin, vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1), and mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule 1. It has been demonstrated that VLA-4 can serve as a target for treatment of inflammatory disorders. For example, blocking of VLA-4 with monoclonal antibody has been shown to reduce relapses of multiple sclerosis. 7 The use of anti- 4 monoclonal antibody has also been demonstrated to be effective in suppressing endotoxin-induced uveitis 8 and in inhibiting eosinophil infiltration in a guinea pig model of allergic conjunctivitis. 9 Recently, VLA-4 blockade with a peptide inhibitor has also led to inhibition of the development of experimental autoimmune uveitis. 1 Although inflammation has been shown to be related to the pathogenesis of dry eye disease, topical blockade of VLA-4 or other integrins has not been investigated in DED, to our knowledge. Therefore, we examined the therapeutic effects of VLA-4 small-molecule antagonist (anti VLA-4 sm) on dry eye using the controlledenvironment chamber (CEC) model, which reliably induces signs of DED in mice
2 METHODS MOUSE MODEL OF DED The protocol was approved by the institutional animal care and use committee, and all animals were treated according to the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology atement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research. Sixto eight-week-old female C57Bl/6 mice (Taconic Farms, Germantown, New York) were used in these experiments. Dry eye disease was induced by exposure of mice to a CEC 11 for 1 days during which mice also received administration of scopolamine hydrobromide to maximize ocular dryness. Briefly, scopolamine hydrobromide (.5 mg/.2 ml; Sigma-Aldrich Inc, Louis, Missouri) was injected subcutaneously in the dorsal skin of mice 4 times daily. The mice placed in the CEC were continuously exposed to a relative humidity below 3%, an airflow of 15 L/min, and a constant temperature (21 C-23 C) as previously described. 11 Age-matched mice that were kept in a normal nondesiccating environment (relative humidity 7%, no additional airflow, temperature 21 C-23 C, and no scopolamine administration) were used as normal controls. ANTI VLA-4 SM FORMULATION AND TREATMENT REGIMEN BIO-889 (anti VLA-4 sm) and a control compound (BIO- 9257) were commercially obtained (Biogen Idec, Inc, Cambridge, Massachusetts). BIO-889 is the pegylated, more stable version of 2(S)-{[1-(3,5-dichloro-benzenesulfonyl)-pyrrolidine- 2(S)-carbonyl]-amino}-4-[4-methyl-2(S)-(methyl-{2-[4-(3-o- tolyl-ureido)-phenyl]-acetyl}-amino)-pentanoylamino]- butyric acid, which has been identified as a highly selective and potent (K D =9 pm [picomolars]) small-molecule antagonist to integrin 4 1 (VLA-4). 12 BIO-889 was in a Tris-lactose buffer (15 mg/ml [ph 7.5]). To control for the exposure of the eyes to this pegylated compound, was used as a control consisting of the pegylated conjugate of (2S,4R)-4-[6-(3- hydroxypropanamido)hexanamido]-1-(phenylsulfonyl) pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid, which is an inactive compound with physicochemical properties similar to those of BIO-889 in a Tris-lactose buffer (ph 7.5). Forty-eight hours after dry eye induction, mice were randomized to receive anti VLA-4 sm BIO-889 or control vehicle on both eyes. An eyedrop (5 µl) was topically applied to the eyes of the unanesthetized mice twice a day from day 2 to day 1. The untreated dry eye group received no eyedrops. Ocular signs of dry eye disease were measured at day 2, day 5, day 7, and day 1. Mice were then euthanized at day 1 for cellular and molecular studies. MEASUREMENT OF CORNEAL FLUORESCEIN STAINING Corneal fluorescein staining was performed at baseline (day ) and then at day 2 (before administration of the first eyedrop dose), day 5, day 7, and day 1. Fluorescein (5% [1 µl]) was applied to the lateral conjunctival sac of the mice as previously described. 13 Eyes were examined for fluorescein staining after 3 minutes using a slitlamp biomicroscope under cobalt blue light. Punctate staining was recorded in a masked fashion using the standard National Eye Institute grading system, 14 giving a score from to 3 for each of 5 areas of the cornea. IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STAINING The following antibodies were used for immunohistochemical staining: purified hamster antimouse CD3e monoclonal antibody (T-cell marker, catalog No ; and isotype control purified hamster IgG1, catalog No D), secondary antibody Cy-3 goat anti-armenian hamster antibody (catalog No ), and fluorescein isothiocyanate conjugated (FITC) rat antimouse CD4 (catalog No ; and isotype FITC rat IgG2a, catalog No ). All primary antibodies and isotype-matched controls were purchased from BD Pharmingen, San Diego, California; secondary antibody was purchased from Jackson Laboratories, Bar Harbor, Maine. For cross-sectional staining of the conjunctiva, whole eyeballs were excised. They were frozen in OCT, cut into 7-µm frozen sections, and fixed in acetone for 15 minutes at room temperature. All antibodies were diluted in 2% bovine serum albumin. To block nonspecific staining, cross sections were blocked with anti-fcr monoclonal antibody CD16/CD32 (catalog No , BD Pharmingen) for 3 minutes. Next, the tissues were immunostained with primary antibodies or isotype-matched control antibodies overnight at 4 C. After 3 thorough washings with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 1 minutes each, cross sections were incubated with the secondary antibody for 1 hour at room temperature. The cross sections were then washed in PBS again 3 times and were mounted using mounting medium (Vector Shield; Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, California). Three eyeballs from 3 mice per group were used for T-cell enumeration in the bulbar and tarsal conjunctivae. Serial cross sections per slide were studied under an epifluorescence microscope (model E8; Nikon, Melville, New York) with a 4 objective lens. The mean number of cells was obtained by averaging the cell numbers per cross sections studied. RNA ISOLATION, REVERSE TRANSCRIPTION POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION, AND REAL-TIME POLYMERASE CHAIN REACTION Total RNA from whole-mount corneas was isolated using a microkit (RNeasy; Qiagen, udio City, California) and was stored at 8 C until future use. The first strand of complementary DNA (cdna) was synthesized with random hexamers using a transcriptase (SuperScriptIII Reverse Transcriptase; Invitrogen, San Diego, California) according to the manufacturer s protocol. Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed with FAM-MGB dye-labeled predesigned primers (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, California) for tumor necrosis factor (TNF)- (assay ID.Mm _m1), glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (assay ID. Mm _g1), CD4 (assay ID. Mm441891_m1), interferon (IFN- ) inducible protein 1 (or CXCL1 [IP-1]) (assay ID. Mm445235_m1), and VCAM-1 (assay ID. Mm449197_m1) according to the manufacturer s recommendations. One microliter of cdna was loaded in each well, and assays were performed in duplicates. A nontemplate control was included in all experiments to evaluate DNA contamination. The results of quantitative real-time PCR were analyzed using the comparative threshold cycle method and were normalized to GAPDH as an internal control. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS We compared the changes in corneal fluorescein staining scores between treatment groups over time using repeatedmeasures analysis of variance. For the outcomes of total conjunctival T cells, TNF messenger RNA (mrna) levels, and transcript levels of IP-1, CD4, and VCAM-1, comparisons between pairs of treatment groups were performed using Mann-Whitney test (Inat3 software; Graphpad Software, Inc, La Jolla, California). 1696
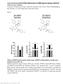
3 RESULTS CORNEAL FLUORESCEIN STAINING IN DRY EYES TREATED WITH TOPICAL BLOCKADE OF VLA-4 Minimal or no corneal punctate staining was observed at day. At day 2, all mice showed increased corneal fluorescein staining, corresponding to dry eye induction in the CEC model. Topical treatment was started at day 2, followed by evaluation of the differences in corneal fluorescein staining scores between the groups at day 5 vs day 2, day 7 vs day 2, and day 1 vs day 2 (Figure 1). The control compound () treated group (n=16) and the anti VLA-4 sm treated group (n=16) had staining scores that decreased with time compared with the untreated dry eye group (n=11). However, the anti VLA-4 sm treated group significantly differed in the magnitude of the staining decrease compared with the untreated dry eye group (P.1 for trend) and the control treated group (P=.2 for trend). ENUMERATION OF CD3 T CELLS IN THE CONJUNCTIVA Conjunctival infiltration by T cells is a hallmark of clinically significant DED. 3-6 Accordingly, CD3 T cells were enumerated in the conjunctiva of dry eye mice, and the changes based on therapy were assessed (Figure 2). The total number of CD3 T cells was significantly increased in the untreated dry eye group compared with the normal group (P.1). This trend was observed for CD4 (P=.1) and CD4 (P=.4) T cells. Application of topical anti VLA-4 sm led to a significant decrease in the total number of conjunctival T cells compared with that in the untreated dry eye group and the control treated group (14-21 cross sections per group [P.1 for both]). The effect of VLA-4 blockade on T-cell infiltration was evident for CD4 T cells (P.1 vs untreated DED group and vs treated group) and for CD4 T cells (P.1 vs untreated DED group; P=.1 vs treated group). In contrast, the effect of topical application of on T-cell infiltration was evident for CD4 T cells (P=.2 vs untreated DED group) but not for CD4 T cells (P=.49 vs untreated DED group) or total CD3 T cells (P=.15 vs untreated DED group). EXPRESSION OF TNF- IN THE CORNEA AND CONJUNCTIVA Real-time PCR was used as a quantitative technique to evaluate the levels of RNA transcripts encoding TNF- and IFN- in the cornea. No significant changes among the groups were observed in IFN- mrna levels (data not shown). However, induction of DED led to a 1.7- fold increase in TNF- expression in the cornea by day 1 (Figure 3). Application of topical anti VLA-4 sm (n=1) significantly decreased TNF- expression compared with that in the untreated DED group (n=9) (P =.8) and the treated group (n=1) (P=.4), with a final value for TNF- mrna at day 1 Relative CFS Compared With Day Day 5 vs Day 2 Day 7 vs Day 2 Day 1 vs Day 2 Figure 1. Evolution of corneal fluorescein score (CFS) over time compared with day 2 (start of treatment). A negative value denotes a staining score decreasing with time and represents an amelioration of the corneal epithelial barrier function. Topical application of very late antigen 4 small-molecule (VLA-4 sm) antagonist significantly decreased the CFS. P.1 for trend for anti VLA-4 sm treated group vs untreated dry eye disease group. P=.2 for trend for anti VLA-4 sm treated group vs control treated group. P values were obtained by repeated-measures analysis of variance. Data represent mean (SEM). in the anti VLA-4 sm treated group close to that seen in normal control eyes. The same trend was observed in the conjunctiva, with a significant decrease in TNF- transcripts in the anti VLA-4 sm treated group (n=1) vs the treated group (n=19) (P=.48). EXPRESSION OF CONJUNCTIVAL IP-1, CD4, AND VCAM-1 mrna Real-time PCR was performed to quantify the level of RNA transcripts encoding IP-1, CD4, and VCAM-1 in the conjunctiva of mice in the different groups (Figure 4). The mrna levels of IP-1 were increased 8.2 fold; CD4, 2.4 fold; and VCAM-1, 1.6 fold in the untreated DED group (n=5) compared with those in normal mice (n=5). The expression levels of these 3 markers decreased in the BIO treated (n=7) and BIO-889 treated (n=11) groups. However, the most noticeable suppression in the transcript levels was seen in the anti VLA-4 sm treated group. COMMENT The past decade of research has shed light on the importance of inflammation as a component of DED in rodent models 3,4 and in humans. 5 Lymphocytic infiltration of the lacrimal gland by T cells has been described in Sjögren syndrome 15 and in non-sjögren DED. 16,17 Most important, studies 18,19 have shown that ocular surface inflammation, including conjunctival infiltration by T cells and overexpression of mediators of inflammation, is also present in most patients with keratoconjunctivitis sicca. This suggests that inflammation, as a cause or as a consequence of DED, is an important facet of the disease process. Given the relevance of VLA-4 in T-cell recruitment and activation, we tested the effect of topical VLA-4 blockade in a murine model of DED. The data presented herein, derived from a masked controlled trial of anti VLA-4 sm, suggest a significant beneficial effect of VLA-4 blockade in treating the ocular signs and revers- 1697
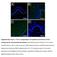
4 A No. of Cells per Cross Section Total CD3 + CD3 + CD4 CD3 + CD4 Normal B Ep Ep Figure 2. Enumeration of CD3 T cells in the conjunctiva. A, Blockade of very late antigen 4 small molecule (VLA-4 sm) significantly decreased the numbers of total conjunctival T cells (*P.1 vs untreated dry eye disease group; P.1 vs control BIO-925 treated group), CD4 T cells, and CD4 T cells ( P=.1 vs control treated group). also had an effect on CD4 T cells ( P=.2 vs untreated dry eye disease group). Data represent mean (SEM). B, Representative CD3 (red) and nuclear (blue) immunostaining of conjunctival cross section showing decreased T-cell infiltration (arrows) in the anti VLA-4 sm treated group vs the treated group. Ep indicates epithelial layer;, stromal layer. TNF-α mrna Relative Fold of Expression Cornea Conjunctiva mrna Relative Fold of Expression IP-1 CD4 VCAM-1 Figure 3. Real-time polymerase chain reaction results showing that very late antigen 4 small-molecule (VLA-4 sm) blockade significantly decreased tumor necrosis factor (TNF- ) messenger RNA (mrna) levels compared with those in the treated control group in the cornea (*P=.4) and in the conjunctiva ( P=.48). Data represent mean (SEM). Figure 4. Real-time polymerase chain reaction showing transcript levels of interferon (IFN- ) inducible protein 1 (IP-1), CD4, and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) in the conjunctivae of the different groups. Data represent mean (SEM). mrna indicates messenger RNA; VLA-4 sm, very late antigen 4 small molecule. ing the inflammatory changes of DED at the cellular and molecular levels. (BIO-889) treated eyes demonstrated significant reversal in corneal epithelial damage as manifested by decreased fluorescein staining scores compared with those in the untreated DED and control vehicle treated groups. The improvement in corneal fluorescein staining, T-cell number, and TNF- levels seen with the control agent () is likely due to the lubricating effect of this treatment in the mice with DED. ill, this amelioration is significantly enhanced in the anti VLA-4 sm treated group, suggesting that the efficacy observed could not be simply because of the lubricating effect of a topical application. Indeed, VLA-4 has been reported to be expressed in several types of immune and inflammatory cells, including T cells, 2 and the interaction between VLA-4 and its ligand VCAM-1 is important for the migration and infiltration of immune cells 1698
5 into inflammatory sites. 21 This is in accord with our data suggesting that the therapeutic effect of VLA-4 topical blockade is due, at least in part, to the inhibition of T-cell infiltration into the ocular surface. Indeed, double staining for CD3 and CD4 showed a 3-fold increase in CD4 T cells but only a 5% increase in CD4 T cells, suggesting a role for the CD4 subset of T cells in the pathogenesis of DED, consistent with previous findings in humans and in animal models of DED VLA-4 blockade was able to suppress T-cell infiltration to levels approaching those seen in normal eyes. Results have demonstrated the immunotherapeutic potential of VLA-4 antagonist in other inflammatory diseases, which has been attributed to the relevance of VLA-4 VCAM-1 interaction in the homing of activated T cells in inflamed tissues, 25 consistent with the results of our present study. Proinflammatory cytokines (such as TNF- ) secreted by T cells or macrophages at sites of inflammation can activate VCAM-1, facilitating adhesion and transendothelial migration of immunocytes from the intravascular compartment to tissue matrices. The precise delineation of the regulation and function of the cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion factors overexpressed in the dry eye state requires further investigation. Notwithstanding this, it is still intriguing that IP-1 is profoundly overexpressed in DED. IP-1 is a CXC chemokine that has a critical role in the recruitment of helper T-cell types 1 and It has been demonstrated recently that the interleukin 17F signaling pathway is involved in induction of IP-1 expression in bronchial epithelial cells, 27 and the longer and shorter forms of the interleukin 17F gene are expressed in activated CD4 Tcells ThesuppressionofIP-1geneexpressionbytopical VLA-4 blockade may be a critical mechanism by which VLA-4 antagonism suppresses T-cell infiltration in DED. Taken together, our data strengthen the concept of an immune-based pathogenesis in DES. In addition, we show for the first time that topical blockade of VLA-4 leads to a significant decrease in the clinical signs of DED and inflammatory changes at the cellular and molecular levels. It is anticipated that ongoing investigations of novel biologic strategies that specifically target pathogenic molecules and pathways involved in DES will lead to more effective therapies for this highly prevalent ocular condition. Submitted for Publication: March 4, 28; final revision received May 14, 28; accepted June 4, 28. Correspondence: Reza Dana, MD, MSc, MPH, Schepens Eye Research Institute, Harvard Medical School, 2 aniford, Boston, MA 2114 (reza.dana@schepens.harvard.edu). Financial Disclosure: None reported. Funding/Support: This study was supported by a research grant from Biogen Idec, Inc, to Dr Dana. Role of the Sponsor: Biogen Idec, Inc, had no role in the design and conduct of the study; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of the data; or in the preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript. REFERENCES 1. Schaumberg DA, Sullivan DA, Buring JA, Dana MR. Prevalence of dry eye syndrome among US women. Am J Ophthalmol. 23;136(2): Miljanović BM, Dana R, Sullivan DA, Schaumberg DA. Impact of dry eye syndrome on vision-related quality of life. Am J Ophthalmol. 27;143(3): Luo L, Li DQ, Doshi A, Farley W, Corrales RM, Pflugfelder SC. Experimental dry eye stimulates production of inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9 and activates MAPK signaling pathways on the ocular surface. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 24; 45(12): Pflugfelder SC, Farley W, Luo L, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 knockout confers resistance to corneal epithelial barrier disruption in experimental dry eye. Am J Pathol. 25;166(1): Gulati A, Sacchetti M, Bonini S, Dana R. Chemokine receptor CCR5 expression in conjunctival epithelium of patients with dry eye syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 26;124(5): ern ME, Pflugfelder SC. Inflammation in dry eye. Ocul Surf. 24;2(2): einman L. Blocking adhesion molecules as therapy for multiple sclerosis: natalizumab. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 25;4(6): Hafezi-Moghadam A, Noda K, Almulki L, et al. VLA-4 blockade suppresses endotoxin-induced uveitis: in vivo evidence for functional integrin up-regulation. FASEB J. 27;21(2): Ebihara N, Yokoyama T, Kimura T, et al. Anti VLA-4 monoclonal antibody inhibits eosinophil infiltration in allergic conjunctivitis model of guinea pig. Curr Eye Res. 1999;19(1): Martín AP, de Moraes LV, Tadokoro CE, et al. Administration of a peptide inhibitor of 4-integrin inhibits the development of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 25;46(6): Barabino S, Shen L, Chen L, Rashid S, Rolando M, Dana MR. The controlledenvironment chamber: a new mouse model of dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 25;46(8): Pepinsky RB, Lee WC, Cornebise M, et al. Design, synthesis, and analysis of a polyethelene glycol modified (PEGylated) small molecule inhibitor of integrin 4 1 with improved pharmaceutical properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 25;312 (2): Barabino S, Chen W, Dana MR. Tear film and ocular surface tests in animal models of dry eye: uses and limitations. Exp Eye Res. 24;79(5): Lemp MA. Report of the National Eye Institute/Industry workshop on Clinical Trials in Dry Eyes. CLAO J. 1995;21(4): Matsumoto I, Tsubota K, Satake Y, et al. Common T cell receptor clonotype in lacrimal glands and labial salivary glands from patients with Sjögren s syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1996;97(8): Damato BE, Allan D, Murray SB, Lee WR. Senile atrophy of the human lacrimal gland: the contribution of chronic inflammatory disease. Br J Ophthalmol. 1984; 68(9): Williamson J, Gibson AA, Wilson T, Forrester JV, Whaley K, Dick WC. Histology of the lacrimal gland in keratoconjunctivitis sicca. Br J Ophthalmol. 1973;57 (11): Pflugfelder SC, Huang AJ, Feuer W, Chuchovski PT, Pereira IC, Tseng SC. Conjunctival cytologic features of primary Sjögren s syndrome. Ophthalmology. 199; 97(8): Baudouin C, Haouat N, Brignole F, Bayle J, Gastaud P. Immunopathological findings in conjunctival cells using immunofluorescence staining of impression cytology specimens. Br J Ophthalmol. 1992;76(9): Elices MJ, Osborn L, Takada Y, et al. VCAM-1 on activated endothelium interacts with the leukocyte integrin VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/ fibronectin binding site. Cell. 199;6(4): Postigo AA, Teixidó J,Sánchez-Madrid F. The 4 1/VCAM-1 adhesion pathway in physiology and disease. Res Immunol. 1993;144(9): ern ME, Gao J, Schwalb TA, et al. Conjunctival T-cell subpopulations in Sjögren s and non-sjögren s patients with dry eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 22;43 (8): Niederkorn JY, ern ME, Pflugfelder SC, et al. Desiccating stress induces T cell mediated Sjögren s syndrome like lacrimal keratoconjunctivitis. J Immunol. 26; 176(7): De Paiva CS, Villareal AL, Corrales RM, et al. Dry eye induced conjunctival epithelial squamous metaplasia is modulated by interferon-. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 27;48(6): McMurray RW. Adhesion molecules in autoimmune disease. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1996;25(4): einman L. A brief history of T H 17, the first major revision in the T H 1/T H 2 hypothesis of T cell mediated tissue damage [published correction appears in Nat Med. 27;13(3):385]. Nat Med. 27;13(2): Kawaguchi M, Kokubu F, Huang SK, et al. The IL-17F signaling pathway is involved in the induction of IFN- inducible protein 1 in bronchial epithelial cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 27;119(6): Kawaguchi M, Adachi M, Oda N, Kokubu F, Huang SK. IL-17 cytokine family. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 24;114(6): Yao Z, Painter SL, Fanslow WC, et al. Human IL-17: a novel cytokine derived from T cells. J Immunol. 1995;155(12): Fossiez F, Djossou O, Chomarat P, et al. T cell interleukin-17 induces stromal cells to produce proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines. J Exp Med. 1996; 183(6):
Role of Th17 cells in the immunopathogenesis of dry eye disease
 Role of Th17 cells in the immunopathogenesis of dry eye disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Chauhan,
Role of Th17 cells in the immunopathogenesis of dry eye disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters Citation Chauhan,
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease. Sunali Goyal MD
 Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal MD Mentor: Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Claes Dohlman Chair in Ophthalmology Director, Cornea & Refractive Surgery Massachusetts
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic VEGF-C suppresses Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal MD Mentor: Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Claes Dohlman Chair in Ophthalmology Director, Cornea & Refractive Surgery Massachusetts
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Dry Eye Disease.
 Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Dry Eye Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Dry Eye Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Therapeutic Efficacy of Topical Epigallocatechin Gallate in Murine Dry Eye
 Therapeutic Efficacy of Topical Epigallocatechin Gallate in Murine Dry Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Therapeutic Efficacy of Topical Epigallocatechin Gallate in Murine Dry Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
Chronic Dry Eye Disease is Principally Mediated by Effector Memory Th17 Cells
 Chronic Dry Eye Disease is Principally Mediated by Effector Memory Th17 Cells The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Chronic Dry Eye Disease is Principally Mediated by Effector Memory Th17 Cells The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
LABORATORY SCIENCES. Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C in Dry Eye Disease
 ONLINE FIRST LABORATORY SIENES Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal, MD; Sunil K. hauhan, DVM, PhD; Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Objective: To determine
ONLINE FIRST LABORATORY SIENES Blockade of Prolymphangiogenic Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Dry Eye Disease Sunali Goyal, MD; Sunil K. hauhan, DVM, PhD; Reza Dana, MD, MPH, MSc Objective: To determine
Chronic dry eye disease is principally mediated by effector memory Th17 cells
 nature publishing group Chronic dry eye disease is principally mediated by effector memory Th17 cells Y Chen 1, SK Chauhan 1, H Soo Lee 1, DR Saban 1 and R Dana 1 Recent experimental and clinical data
nature publishing group Chronic dry eye disease is principally mediated by effector memory Th17 cells Y Chen 1, SK Chauhan 1, H Soo Lee 1, DR Saban 1 and R Dana 1 Recent experimental and clinical data
Topical Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids for Treatment of Dry Eye
 Topical Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids for Treatment of Dry Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published
Topical Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids for Treatment of Dry Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Financial Disclosures
 March 19, 2015 Financial Disclosures Consultant: Alcon Allergan Bausch & Lomb Modernizing Medicine Ophthalmologyweb.co m Investor: Novabay Ophthotech Ocular Surface Disease Ocular surface disease is often
March 19, 2015 Financial Disclosures Consultant: Alcon Allergan Bausch & Lomb Modernizing Medicine Ophthalmologyweb.co m Investor: Novabay Ophthotech Ocular Surface Disease Ocular surface disease is often
The Controlled-Environment Chamber: A New Mouse Model of Dry Eye
 The Controlled-Environment Chamber: A New Mouse Model of Dry Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published
The Controlled-Environment Chamber: A New Mouse Model of Dry Eye The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published
The CCR6/CCL20 Axis Mediates Th17 Cell Migration to the Ocular Surface in Dry Eye Disease
 The CCR6/CCL20 Axis Mediates Th17 Cell Migration to the Ocular Surface in Dry Eye Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
The CCR6/CCL20 Axis Mediates Th17 Cell Migration to the Ocular Surface in Dry Eye Disease The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
LABORATORY SCIENCES. Chemokine Receptor CCR5 Expression in Conjunctival Epithelium of Patients With Dry Eye Syndrome
 LABORATORY SCIENCES Chemokine Receptor CCR5 Expression in Conjunctival Epithelium of Patients With Dry Eye Syndrome Abha Gulati, MD; Marta Sacchetti, MD; Stefano Bonini, MD; Reza Dana, MD, MPH Objective:
LABORATORY SCIENCES Chemokine Receptor CCR5 Expression in Conjunctival Epithelium of Patients With Dry Eye Syndrome Abha Gulati, MD; Marta Sacchetti, MD; Stefano Bonini, MD; Reza Dana, MD, MPH Objective:
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Evidence of Corneal Lymphangiogenesis in Dry Eye Disease
 INIA SIENES Evidence of orneal ymphangiogenesis in Dry Eye Disease A Potential ink to Adaptive Immunity? Sunali Goyal, MD; Sunil K. hauhan, PhD; Jaafar El Annan, MD; Nambi Nallasamy, AB; Qiang Zhang, MD;
INIA SIENES Evidence of orneal ymphangiogenesis in Dry Eye Disease A Potential ink to Adaptive Immunity? Sunali Goyal, MD; Sunil K. hauhan, PhD; Jaafar El Annan, MD; Nambi Nallasamy, AB; Qiang Zhang, MD;
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Overview & pathophysiology of Dry Eye and the use of cyclosporine eye drops in dry eye...
 Overview & pathophysiology of Dry Eye and the use of cyclosporine eye drops in dry eye... This Allergan sponsored session was held on July 24, 2005, Hotel Satya Ashoka, Jabalpur. The session was followed
Overview & pathophysiology of Dry Eye and the use of cyclosporine eye drops in dry eye... This Allergan sponsored session was held on July 24, 2005, Hotel Satya Ashoka, Jabalpur. The session was followed
Current Practice Pattern for Dry Eye Patients in South Korea: A Multicenter Study
 pissn: 11-8942 eissn: 92-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 14;28(2):115-121 http://dx.doi.org/.3341/kjo.14.28.2.115 Original Article Current Practice Pattern for Dry Eye Patients in South Korea: A Multicenter Study
pissn: 11-8942 eissn: 92-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 14;28(2):115-121 http://dx.doi.org/.3341/kjo.14.28.2.115 Original Article Current Practice Pattern for Dry Eye Patients in South Korea: A Multicenter Study
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, psoriasis
 IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
REAL-WORLD UTILIZATION PATTERNS OF CYCLOSPORINE OPHTHALMIC EMULSION 0.05% WITHIN MANAGED CARE
 REAL-WORLD UTILIZATION PATTERNS OF CYCLOSPORINE OPHTHALMIC EMULSION 0.05% WITHIN MANAGED CARE Tina H Chiang 1, John G Walt 1, John P McMahon, Jr. 2, James E Mansfield, Jr. 2, Susan Simonyi 3 1 Allergan
REAL-WORLD UTILIZATION PATTERNS OF CYCLOSPORINE OPHTHALMIC EMULSION 0.05% WITHIN MANAGED CARE Tina H Chiang 1, John G Walt 1, John P McMahon, Jr. 2, James E Mansfield, Jr. 2, Susan Simonyi 3 1 Allergan
Immunology of Asthma. Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph. Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline! Consensus characteristics! Allergens:role in asthma! Immune/inflammatory basis! Genetic basis!
Inflammatory Cytokine and Osmolarity Changes in the Tears of Dry Eye Patients Treated with Topical 1% Methylprednisolone
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.203 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 55(1):203-208, 2014 Inflammatory Cytokine and Osmolarity Changes in the Tears of Dry Eye Patients
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.1.203 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 55(1):203-208, 2014 Inflammatory Cytokine and Osmolarity Changes in the Tears of Dry Eye Patients
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Dr.Sushil Kumar Tripathi
 Rabamipide:360 Benefits in Dry eye syndrome Dr.Sushil Kumar Tripathi Prevalence of Dry Eye Syndrome: vone in four patients attending ophthalmic clinics report symptoms of dry eye. vprevalence of dry eye
Rabamipide:360 Benefits in Dry eye syndrome Dr.Sushil Kumar Tripathi Prevalence of Dry Eye Syndrome: vone in four patients attending ophthalmic clinics report symptoms of dry eye. vprevalence of dry eye
IL-17 in health and disease. March 2014 PSO13-C051n
 IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
BREAKING THE VICIOUS CIRCLE OF DRY EYE DISEASE
 BREAKING THE VICIOUS CIRCLE OF DRY EYE DISEASE In this article, Christian Roesky, PhD, Chief Executive Officer, Novaliq, discusses the underserved condition of dry eye disease, and presents two products
BREAKING THE VICIOUS CIRCLE OF DRY EYE DISEASE In this article, Christian Roesky, PhD, Chief Executive Officer, Novaliq, discusses the underserved condition of dry eye disease, and presents two products
The first comprehensive definition of DED was published in
 Special Issue Definition and Diagnostic Criteria of Dry Eye Disease: Historical Overview and Future Directions Jun Shimazaki Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Dental College, Ichikawa General Hospital,
Special Issue Definition and Diagnostic Criteria of Dry Eye Disease: Historical Overview and Future Directions Jun Shimazaki Department of Ophthalmology, Tokyo Dental College, Ichikawa General Hospital,
Downloaded From: https://iovs.arvojournals.org/pdfaccess.ashx?url=/data/journals/iovs/933423/ on 07/23/2018
 Report Flow Cytometry in Impression Cytology Specimens A New Method for Evaluation of Conjunctival Inflammation Christophe Baudouin* Frangoise Brignole,\ Franck Becquet* Pierre-Jean Pisella* and Alain
Report Flow Cytometry in Impression Cytology Specimens A New Method for Evaluation of Conjunctival Inflammation Christophe Baudouin* Frangoise Brignole,\ Franck Becquet* Pierre-Jean Pisella* and Alain
DRY EYE IS ONE OF THE MOST
 EPIDEMIOLOGY SECTION EDITOR: LESLIE HYMAN, PhD Prevalence of Dry Eye Disease Among US Men Estimates From the Physicians Health Studies Debra A. Schaumberg, ScD, OD, MPH; Reza Dana, MD, MPH; Julie E. Buring,
EPIDEMIOLOGY SECTION EDITOR: LESLIE HYMAN, PhD Prevalence of Dry Eye Disease Among US Men Estimates From the Physicians Health Studies Debra A. Schaumberg, ScD, OD, MPH; Reza Dana, MD, MPH; Julie E. Buring,
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 04 Page April 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.19 Original Research Article Use of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.19 Original Research Article Use of Plasma Rich in Growth Factors
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Ophthalmic Immunomodulators Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary
 Ophthalmic Immunomodulators Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,4 Agent Indication Dosage and Administration Restasis (cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion)
Ophthalmic Immunomodulators Prior Authorization with Quantity Limit Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,4 Agent Indication Dosage and Administration Restasis (cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion)
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Efficacy of the Mineral Oil and Hyaluronic Acid Mixture Eye Drops in Murine Dry Eye
 pissn: -894 eissn: 9-98 Korean J Ophthalmol 5;9():-7 http://dx.doi.org/.4/kjo.5.9.. Original Article Efficacy of the Mineral Oil and Hyaluronic Acid Mixture Eye Drops in Murine Dry Eye Jung Han Choi, Jung
pissn: -894 eissn: 9-98 Korean J Ophthalmol 5;9():-7 http://dx.doi.org/.4/kjo.5.9.. Original Article Efficacy of the Mineral Oil and Hyaluronic Acid Mixture Eye Drops in Murine Dry Eye Jung Han Choi, Jung
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
1998 DESCRIPTION Evaluation of Subjective and Objective tests for diagnosing tear-film disorders known to cause ocular irritation.
 DEWS DRY EYE: DIAGNOSTIC TEST TEMPLATE RAPPORTEUR A.J.Bron 18 th Oct 2004 TEST Mixed tests TO Ocular Irritation / Dry Eye REFERENCES DIAGNOSE VERSION of TEST Multiple tests DESCRIPTION Evaluation of Subjective
DEWS DRY EYE: DIAGNOSTIC TEST TEMPLATE RAPPORTEUR A.J.Bron 18 th Oct 2004 TEST Mixed tests TO Ocular Irritation / Dry Eye REFERENCES DIAGNOSE VERSION of TEST Multiple tests DESCRIPTION Evaluation of Subjective
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Uchino Y, Uchino M, Yokoi N, et al. Alteration of tear mucin 5AC in office workers using visual display terminals: the Osaka Study. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online June 5,
Supplementary Online Content Uchino Y, Uchino M, Yokoi N, et al. Alteration of tear mucin 5AC in office workers using visual display terminals: the Osaka Study. JAMA Ophthalmol. Published online June 5,
High-frequency Topical Cyclosporine 0.05% in the Treatment of Severe Dry Eye Refractory to Twice-daily Regimen
 High-frequency Topical Cyclosporine 0.05% in the Treatment of Severe Dry Eye Refractory to Twice-daily Regimen The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
High-frequency Topical Cyclosporine 0.05% in the Treatment of Severe Dry Eye Refractory to Twice-daily Regimen The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access
CLINICAL TRIALS. Topical Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist for Treatment of Dry Eye Disease
 ONLINE FIRST CLINICAL TRIALS Topical Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist for Treatment of Dry Eye Disease A Randomized Clinical Trial Francisco Amparo, MD, MSc; Mohammad H. Dastjerdi, MD; Andre Okanobo,
ONLINE FIRST CLINICAL TRIALS Topical Interleukin 1 Receptor Antagonist for Treatment of Dry Eye Disease A Randomized Clinical Trial Francisco Amparo, MD, MSc; Mohammad H. Dastjerdi, MD; Andre Okanobo,
Does in-office manual expression for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) work?
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282816021 Does in-office manual expression for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) work? Conference
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/282816021 Does in-office manual expression for Meibomian Gland Dysfunction (MGD) work? Conference
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Analysis of Topical Cyclosporine Treatment of Patients With Dry Eye Syndrome
 Analysis of Topical Cyclosporine Treatment of Patients With Dry Eye Syndrome Effect on Conjunctival Lymphocytes CLINICAL SCIENCES Kathleen S. Kunert, MD; Ann S. Tisdale, MS; Michael E. Stern, PhD; J. A.
Analysis of Topical Cyclosporine Treatment of Patients With Dry Eye Syndrome Effect on Conjunctival Lymphocytes CLINICAL SCIENCES Kathleen S. Kunert, MD; Ann S. Tisdale, MS; Michael E. Stern, PhD; J. A.
Comparison of tear osmolarity and ocular comfort between daily disposable contact lenses: hilafilcon B hydrogel versus narafilcon A silicone hydrogel
 Int Ophthalmol (2012) 32:229 233 DOI 10.1007/s10792-012-9556-y ORIGINAL PAPER Comparison of tear osmolarity and ocular comfort between daily disposable contact lenses: hilafilcon B hydrogel versus narafilcon
Int Ophthalmol (2012) 32:229 233 DOI 10.1007/s10792-012-9556-y ORIGINAL PAPER Comparison of tear osmolarity and ocular comfort between daily disposable contact lenses: hilafilcon B hydrogel versus narafilcon
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and
 Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Effect of tear deficiency on the course of endotoxin-induced keratitis
 UDC 617.713-002.-092.9:617.764.1-008.811.4 Effect of tear deficiency on the course of endotoxin-induced keratitis T.B. Gaydamaka, 1 S.Ya. Rafalyuk 2 1 Filatov Eye Disease and Tissue Therapy Institute 2
UDC 617.713-002.-092.9:617.764.1-008.811.4 Effect of tear deficiency on the course of endotoxin-induced keratitis T.B. Gaydamaka, 1 S.Ya. Rafalyuk 2 1 Filatov Eye Disease and Tissue Therapy Institute 2
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Immunology and Pathophysiology of Dry Eye
 Immunology and Pathophysiology of Dry Eye Associate Prof. Banu Bozkurt, MD, FEBO MSc in Immunology Selcuk University Medical Faculty, Konya, Turkey 47th PanHellenic Ophthalmology Congress 28-31 May 2014,
Immunology and Pathophysiology of Dry Eye Associate Prof. Banu Bozkurt, MD, FEBO MSc in Immunology Selcuk University Medical Faculty, Konya, Turkey 47th PanHellenic Ophthalmology Congress 28-31 May 2014,
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Therapeutic Effects of 0.1% Tacrolimus Eye Drops for Refractory Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 3 Ver. VI (Mar. 2016), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org Therapeutic Effects of 0.1% Tacrolimus
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 3 Ver. VI (Mar. 2016), PP 44-48 www.iosrjournals.org Therapeutic Effects of 0.1% Tacrolimus
QUALITATIVE INTERPRETATION OF VISUAL ACUITY IN DRY EYE PATIENTS
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Special Issue Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 10 (59) No. 2-2017 QUALITATIVE INTERPRETATION OF VISUAL ACUITY IN DRY EYE PATIENTS C. TRIHENEA 1 A. STANILA
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Special Issue Series VI: Medical Sciences Vol. 10 (59) No. 2-2017 QUALITATIVE INTERPRETATION OF VISUAL ACUITY IN DRY EYE PATIENTS C. TRIHENEA 1 A. STANILA
Dry eye syndrome in diabetic children
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 6, 2007 / pp. 873-878 Dry eye syndrome in diabetic children A. AKINCI 1, E. CETINKAYA 2, Z. AYCAN 2 1 Department of Pediatric Ophthalmology 2 Department
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 6, 2007 / pp. 873-878 Dry eye syndrome in diabetic children A. AKINCI 1, E. CETINKAYA 2, Z. AYCAN 2 1 Department of Pediatric Ophthalmology 2 Department
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity
 Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Treatment of dry eye by autologous serum application in Sjögren s syndrome
 390 Br J Ophthalmol 1999;83:390 395 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Clinical science Ophthalmology, Tokyo Dental College, Chiba, Japan K Tsubota E Goto H Fujita M Ono H Inoue S Shimmura Ophthalmology, Keio University
390 Br J Ophthalmol 1999;83:390 395 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Clinical science Ophthalmology, Tokyo Dental College, Chiba, Japan K Tsubota E Goto H Fujita M Ono H Inoue S Shimmura Ophthalmology, Keio University
Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in H5N1 viral pathogenesis and the potential use of its inhibitors
 Title Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in HN viral pathogenesis and the potential use of its inhibitors Author(s) Lee, MY; Cheung, CY; Peiris, JSM Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2, v. 9 n. Suppl. 4, p. 29-
Title Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in HN viral pathogenesis and the potential use of its inhibitors Author(s) Lee, MY; Cheung, CY; Peiris, JSM Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2, v. 9 n. Suppl. 4, p. 29-
Dry Eye Assessment and Management Study ELIGIBILITY OCULAR EVALUATION FORM
 Page 1 of 13 BEFORE COMPLETING THE OCULAR EXAMINATION, YOU MUST BE ABLE TO ANSWER YES TO THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS: Have you done MMP9? (SVonly) The Following are done at Baseline: Have you done Tear Osmolarity?
Page 1 of 13 BEFORE COMPLETING THE OCULAR EXAMINATION, YOU MUST BE ABLE TO ANSWER YES TO THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS: Have you done MMP9? (SVonly) The Following are done at Baseline: Have you done Tear Osmolarity?
Dry eye disease (DED) is a common multifactorial
 Immunology and Microbiology MyD88 Deficiency Protects Against Dry Eye Induced Damage Rose Y. Reins, Carolina Lema, Justin Courson, Carolina M. E. Kunnen, and Rachel L. Redfern University of Houston, College
Immunology and Microbiology MyD88 Deficiency Protects Against Dry Eye Induced Damage Rose Y. Reins, Carolina Lema, Justin Courson, Carolina M. E. Kunnen, and Rachel L. Redfern University of Houston, College
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity. Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China
 Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China Multiple functions of B cells in immunity LeBien and Tedder, Blood (2008) B cell functions in autoimmune pathogenesis The Immunopathogensis
Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China Multiple functions of B cells in immunity LeBien and Tedder, Blood (2008) B cell functions in autoimmune pathogenesis The Immunopathogensis
Breaking the Cycle. Yijie (Brittany) Lin, MD, MBA, Reena Garg, MD New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai
 Lin, Garg Ophthalmology Times 1 Breaking the Cycle Yijie (Brittany) Lin, MD, MBA, Reena Garg, MD New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai Abstract A 32 year-old female with a history of LASIK surgery
Lin, Garg Ophthalmology Times 1 Breaking the Cycle Yijie (Brittany) Lin, MD, MBA, Reena Garg, MD New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai Abstract A 32 year-old female with a history of LASIK surgery
Efficacy and Safety of Diquafosol Ophthalmic Solution in Patients with Dry Eye Syndrome: A Japanese Phase 2 Clinical Trial
 Efficacy and Safety of Ophthalmic Solution in Patients with Dry Eye Syndrome: A Japanese Phase 2 Clinical Trial Yukihiro Matsumoto, MD, 1 Yuichi Ohashi, MD, 2 Hitoshi Watanabe, MD, 3 Kazuo Tsubota, MD,
Efficacy and Safety of Ophthalmic Solution in Patients with Dry Eye Syndrome: A Japanese Phase 2 Clinical Trial Yukihiro Matsumoto, MD, 1 Yuichi Ohashi, MD, 2 Hitoshi Watanabe, MD, 3 Kazuo Tsubota, MD,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
1. Supplementary Figures and Legends Supplementary Fig. 1. S1P-mediated transcriptional regulation of integrins expressed in OP/monocytoid cells. Real-time quantitative PCR analyses of mrna for two integrins,
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Assessment of leukocyte adhesion in flow chambers
 Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Evaluation of directed and random motility in microslides Motility experiments in IBIDI microslides, image acquisition and processing were performed as described. PMN, which ended up in an angle < 180
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
High incidence of corneal epithelium antibodies in
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1988, 72, 921-925 High incidence of corneal epithelium antibodies in Fuchs' heterochromic cyclitis E LA HEY, G S BAARSMA, A ROTHOVA, L BROERSMA, R VAN DER GAAG, AND A
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1988, 72, 921-925 High incidence of corneal epithelium antibodies in Fuchs' heterochromic cyclitis E LA HEY, G S BAARSMA, A ROTHOVA, L BROERSMA, R VAN DER GAAG, AND A
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
 MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 02 Page February 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i2.155 Prevalence of Dry Eye Diseases in the
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i2.155 Prevalence of Dry Eye Diseases in the
Immunological impression cytology of the conjunctival epithelium in patients with thyroid orbitopathy-related dry eye
 Immunological impression cytology of the conjunctival epithelium in patients with thyroid orbitopathy-related dry eye S.L. Hsu 1, P.Y. Lee 1, C.H. Chang 1 and C.H. Chen 2,3 1 Department of Ophthalmology,
Immunological impression cytology of the conjunctival epithelium in patients with thyroid orbitopathy-related dry eye S.L. Hsu 1, P.Y. Lee 1, C.H. Chang 1 and C.H. Chen 2,3 1 Department of Ophthalmology,
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Female Pro-ins2 -/- mice at 5-6 weeks of age were either inoculated i.p. with a single dose of CVB4 (1x10 5 PFU/mouse) or PBS and treated with αgalcer or control vehicle. On day
Supplementary Figure 1. Female Pro-ins2 -/- mice at 5-6 weeks of age were either inoculated i.p. with a single dose of CVB4 (1x10 5 PFU/mouse) or PBS and treated with αgalcer or control vehicle. On day
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Supplementary Figure 1 Production of cytokines and chemokines after vaginal HSV-2 infection. C57BL/6 mice were (a) treated intravaginally with 20 µl of PBS or infected with 6.7x10 4 pfu of HSV-2 in the
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis
 Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts
 Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Very Late Antigen 1 Blockade Markedly Promotes Survival of Corneal Allografts The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Ophthalmology Times Case Study Yasmin Mali, MD. Case Study
 Ophthalmology Times Case Study Yasmin Mali, MD Case Study A 57 year old female with presented with ocular irritation and discomfort in both eyes for several months. Patient was previously started on a
Ophthalmology Times Case Study Yasmin Mali, MD Case Study A 57 year old female with presented with ocular irritation and discomfort in both eyes for several months. Patient was previously started on a
The Pathogenesis of Chlamydia pneumoniae in Multiple Sclerosis: Current Thoughts and Future Directions
 The Pathogenesis of Chlamydia pneumoniae in Multiple Sclerosis: Current Thoughts and Future Directions Seminars in Pathology March 9, 2010 Charles W. Stratton, M.D. Features of C. pneumoniae Infection
The Pathogenesis of Chlamydia pneumoniae in Multiple Sclerosis: Current Thoughts and Future Directions Seminars in Pathology March 9, 2010 Charles W. Stratton, M.D. Features of C. pneumoniae Infection
Comparison of Cryopreserved Amniotic Membrane and Umbilical Cord Tissues for use in Foot and Ankle Reconstructive Procedures
 Comparison of Cryopreserved Amniotic Membrane and Umbilical Cord Tissues for use in Foot and Ankle Reconstructive Procedures Howard M. Kimmel 1, Ek Kia Tan 2, Hua He 2, Julie O Connell 3 1 Buckeye Foot
Comparison of Cryopreserved Amniotic Membrane and Umbilical Cord Tissues for use in Foot and Ankle Reconstructive Procedures Howard M. Kimmel 1, Ek Kia Tan 2, Hua He 2, Julie O Connell 3 1 Buckeye Foot
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
TGF- 2, Tenascin, and Integrin 1 Expression in Superior Limbic Keratoconjunctivitis
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS TGF- 2, Tenascin, and Integrin 1 Expression in Superior Limbic Keratoconjunctivitis Akira Matsuda, Yoshitsugu Tagawa and Hidehiko Matsuda Department of Ophthalmology, Hokkaido
LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS TGF- 2, Tenascin, and Integrin 1 Expression in Superior Limbic Keratoconjunctivitis Akira Matsuda, Yoshitsugu Tagawa and Hidehiko Matsuda Department of Ophthalmology, Hokkaido
Efficacy of Tear Eosinophil Cationic Protein Level Measurement Using Filter Paper for Diagnosing Allergic Conjunctival Disorders
 Efficacy of Tear Eosinophil Cationic Protein Level Measurement Using Filter Paper for Diagnosing Allergic Conjunctival Disorders Jun Shoji*, Minoru Kitazawa*, Noriko Inada*, Mitsuru Sawa*, Tetsuya Ono,
Efficacy of Tear Eosinophil Cationic Protein Level Measurement Using Filter Paper for Diagnosing Allergic Conjunctival Disorders Jun Shoji*, Minoru Kitazawa*, Noriko Inada*, Mitsuru Sawa*, Tetsuya Ono,
Division of Ophthalmology, Department of Visual Sciences, Nihon University School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan
 Ophthalmology Volume 2016, Article ID 3573142, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3573142 Clinical Study Clinical Usefulness of Monitoring Expression Levels of CCL24 (Eotaxin-2) mrna on the Ocular
Ophthalmology Volume 2016, Article ID 3573142, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3573142 Clinical Study Clinical Usefulness of Monitoring Expression Levels of CCL24 (Eotaxin-2) mrna on the Ocular
Title: Keeping Step with DEWS2: Clinical Applications Lecturer: Scott G. Hauswirth, OD
 Title: Keeping Step with DEWS2: Clinical Applications Lecturer: Scott G. Hauswirth, OD Course Description: The Dry Eye Workshop 2 was an assemblage of experts in dry eye disease from around the world,
Title: Keeping Step with DEWS2: Clinical Applications Lecturer: Scott G. Hauswirth, OD Course Description: The Dry Eye Workshop 2 was an assemblage of experts in dry eye disease from around the world,
Evidence for Technology in the Treatment of Advanced Dry Eye
 Evidence for Technology in the Treatment of Advanced Dry Eye COPE 44435-AS Chris Lievens, OD, MS, FAAO Evidence for Technology in the Treatment of Advanced Dry Eye COPE: 44435-AS Chris Lievens, OD MS FAAO
Evidence for Technology in the Treatment of Advanced Dry Eye COPE 44435-AS Chris Lievens, OD, MS, FAAO Evidence for Technology in the Treatment of Advanced Dry Eye COPE: 44435-AS Chris Lievens, OD MS FAAO
Chapter 3, Part A (Pages 37-45): Leukocyte Migration into Tissues
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 3, Part A (pages 37-45) of Cellular and Molecular Immunology (Seventh Edition), by Abul K. Abbas, Andrew H. Lichtman and Shiv Pillai. Chapter 3, Part A (Pages
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
Among the benign intraepithelial melanocytic proliferations, Inflamed Conjunctival Nevi. Histopathological Criteria. Resident Short Reviews
 Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Resident Short Reviews Inflamed conjunctival nevi (ICN) may suggest malignancy because of their rapid growth and atypical histology. The objective of this study was to characterize the diagnostic features
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Pathologic Stage. Lymph node Stage
 ASC ASC a c Patient ID BMI Age Gleason score Non-obese PBMC 1 22.1 81 6 (3+3) PBMC 2 21.9 6 6 (3+3) PBMC 3 22 84 8 (4+4) PBMC 4 24.6 68 7 (3+4) PBMC 24. 6 (3+3) PBMC 6 24.7 73 7 (3+4) PBMC 7 23. 67 7 (3+4)
ASC ASC a c Patient ID BMI Age Gleason score Non-obese PBMC 1 22.1 81 6 (3+3) PBMC 2 21.9 6 6 (3+3) PBMC 3 22 84 8 (4+4) PBMC 4 24.6 68 7 (3+4) PBMC 24. 6 (3+3) PBMC 6 24.7 73 7 (3+4) PBMC 7 23. 67 7 (3+4)
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
