The DRAI (Donors >12 yrs old) versus Requirements
|
|
|
- Rafe Goodwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Q# or Pg # Pg 1 Question or section as it appears on the DRAI questionnaire (Donors >12 yrs old) Donor Name, Person Interviewed (name, relationship), Contact Information (phone, address, city, state, zip), The interview was conducted by (telephone or in person), Person conducting interview and completing the form (print name, signature, date/time) FDA Final Guidance, HCT/P Donor Eligibility (8-8-07) (relevant parts only) DE Final Rule not used here since Final Guidance covers expectations in more detail. C. What sources of information do I review? 1. The donor medical history interview ( (n)) is a documented dialogue concerning the donor's medical history and relevant social behavior: a. With a living donor; or b. If the donor is not living or is unable to participate in the interview, then with one or more individuals who can provide the information sought. These individuals might be: The donor s next of kin; The nearest available relative; A member of the donor s household; An individual with an affinity relationship with the donor (e.g., caretaker, friend, partner); or The donor s primary treating physician. The medical history interview may take place in person or by telephone. Specific AATB Standards, 13 th edition, 2012 or EBAA Medical Standards, October 2011 (relevant parts only) D4.220 Donor Risk Assessment An inquiry shall be conducted with the donor (if living) or the deceased donor s next of kin, the nearest available relative, a member of the donor s household, other individual with an affinity relationship (caretaker, friend, significant life partner) and/or the primary treating physician), using a standardized questionnaire. Questions shall be formulated using these Standards, current federal regulations and guidance. The inquiry record shall document the donor s name, and the relationship between the donor and the interviewee(s) and shall indicate the name(s) of the interviewer(s) and interviewee(s). The questionnaire shall be maintained as part of the donor s record. A2.000 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS UNOS/OPTN Policy (includes the 1994 PHS Guidelines) 2.0 MINIMUM PROCUREMENT STANDARDS FOR AN ORGAN PROCUREMENT ORGANIZATION (OPO) Obtaining the donor s medical/ behavioral history. The Host OPO will attempt to obtain a history on each potential donor to screen for medical conditions that may affect the donated organ function and for the presence of transmissible diseases and/or malignancies, treated and untreated, or any other known condition that may be transmitted by the donor organ that may reasonably impact the candidate or recipient. This history should also be used to identify whether the potential donor has factors associated with increased risk for disease transmission, including blood borne pathogens HIV, Hepatitis B, and Hepatitis C. If the donor meets the criteria set forth in the current US Public Health Service (PHS) guidance, the Host OPO must communicate this information regarding donor history to all transplant programs Other Page 1 of 51
2 Since a donor medical history interview is a documented dialog ( (n)), if a donor medical history questionnaire is self-administered, the interviewer should review and verify the answers with the individual who has filled out the questionnaire form. DONOR RISK ASSESSMENT INTERVIEW A documented dialogue in person or by telephone with an individual or individuals who would be knowledgeable of the donor s relevant medical history and social behavior. Before tissue is made available for distribution, the Donor Eligibility Determination must be made by a responsible person. Reference Appendix II for requirements related to the donor eligibility process. Prior to making an eligibility determination, the donor must be screened according to D Medical and social histories are important aspects of donor evaluation. Adequate donor evaluation includes: 4. Donor history evaluation: this must include the donor s name, social history and donor information obtained from at least one of the following: d) Donor risk assessment interview f) Treating physician interview D1.300 Documentation of Donor Information Donor screening forms and/or copies of relevant medical records reviewed must be receiving organs from the donor. Page 2 of 51
3 completed and retained on all donated eye tissue as part of the donor record. See Section L A unique donor identifying number, i.e, medical examiner or coroner case number, hospital medical record number, social security or driver s license number, shall be obtained and recorded in the donor record. Glossary Definition of Terms Donor Risk Assessment Interview. A documented dialogue in person or by telephone with an individual or individuals who would be knowledgeable of the donor s relevant medical history and social behavior. For example this may be: the donor, if living; the next of kin; the nearest available relative; a member of the donor s household; other individual with an affinity relationship (e.g., caretaker, friend, significant life partner); and/or the primary treating physician. Alternatively, a living donor may complete a written questionnaire. Relevant social history is elicited by questions regarding certain activities or behaviors that are considered to place such a potential donor Page 3 of 51
4 at increased risk for a relevant communicable disease agent or disease. Pg 1 I want to advise you of the sensitive and personal nature of some of these questions. They are similar to those asked when someone donates blood. We ask these questions for the health of those who may receive her/his* gift. I will read each question and you will need to answer to the best of your knowledge with a Yes or No. 1. Where was she/he* born? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 27. Persons or their sexual partners who were born or lived in certain countries in Africa (Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Niger, or Nigeria) after 1977 (Refs. 66 and 76) (risk factor for HIV group O). (vcjd risk could apply if the 25) Persons who, since 1977, were born in or have lived in any area of central or west Africa (includes Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Niger, and Nigeria) and persons known to have had sexual contact with any such person 3 ; 3 Tissue Banks using an HIV test that has been approved by FDA to include a donor screening claim for detection of HIV Group O antibodies are not required to screen for this risk history. It is common practice by OPO, Tissue Bank, and Eye Bank professionals to include this type of preamble to prepare the interviewee. Page 4 of 51
5 donor was born during the target time periods) F1.100 Donor Suitability Review In the case of pediatric donors who have been breastfed within the past 12 months and/or are 18 months of age or less, the birth mother s risk for transmissible disease shall be evaluated for HIV, HBV, HCV and other infectious agents when indicated. See Appendix II. (vcjd risk could apply if the donor was born in a risk country during the target time periods) Reference Appendix II for requirements related to the donor eligibility process. D1.120 Screening for FDA Defined Relevant Communicable Disease Agents and Diseases The FDA defines communicable disease agents and diseases considered relevant (Ref. Appendix I). Tissue from persons exhibiting risk factors for, clinical evidence of, or physical evidence of relevant communicable disease and high risk behavior associated with relevant communicable disease Page 5 of 51
6 2. What was her/his* occupation? 3. Did she/he* have any health problems due to exposure to toxic substances such as pesticides, lead, mercury, gold, asbestos, agent orange, etc.? 3a. Describe toxic substance and treatment. 4. Did she/he* have a family physician, a specialist, or visit a medical facility, which can include, for example, a clinic or urgent care center? C. What sources of information do I review? 2. The donor medical history must not be used for transplant purposes (Ref. Appendix II). D4.320 Miscellaneous Adverse Conditions Tissue from donors with any of the following conditions shall be evaluated by the Medical Director for suitability for transplantation in accordance with the tissue bank s SOPM: 2) Ingestion of, or exposure to, toxic substances. Before tissue is made available for distribution, the Donor Eligibility Determination must be made by a responsible Standard question to open interview and it relates to risk assessment at Q3. Title 10 of New York Codes, Rules and Regulations, Section , Selection and testing requirements for tissue donors. (a) tissue for clinical use shall not be released from donors with any of the following conditions: (9) except for donors of eye tissue, significant exposure to a substance that may be transferred in toxic doses, such as lead, mercury and gold; Page 6 of 51
7 4a. When? 4b. Why? 4c. Provide any contact information (e.g., name, group, facility, phone number, etc.): interview ( (n)) is a documented dialogue concerning the donor's medical history and relevant social behavior: a. With a living donor; or b. If the donor is not living or is unable to participate in the interview, then with one or more individuals who can provide the information sought. These individuals might be:. The donor s primary treating physician. person. Reference Appendix II for requirements related to the donor eligibility process. Prior to making an eligibility determination, the donor must be screened according to D Medical and social histories are important aspects of donor evaluation. Adequate donor evaluation includes: 4. Donor history evaluation: this must include the donor s name, social history and donor information obtained from at least one of the following: f) Treating physician interview 5. Did she/he* take any medication recently or on a regular basis such as those prescribed, non-prescribed, dietary supplements, etc.? 5a. What was it and/or what was it used for? If a steroid, such as prednisone, ask: 5a(i) How long? 5a(ii) What was the dose? III. THE DONOR- ELIGIBILITY DETERMINATION ( ) D. What communicable disease agents or diseases, not listed in (r)(1), have been determined to be relevant? Sepsis Availability of Appropriate Screening and/or Testing Measures: Appropriate screening measures have been developed for detection of sepsis, such as the medical history interview, and clinical and physical evidence. (Screening measures for sepsis are discussed in sections IV.E., IV.F. and IV.G. of this D4.310 Infections The Medical Director or licensed physician designee shall not release allogeneic tissue for transplantation from donors who exhibit any of the following findings: 1) Evidence, detected by review of Relevant Medical Records of significant active infection at the time of donation for Relevant Communicable Disease Agents or Diseases (RCDADs). These include, but are not limited to: septicemia, viral disease. A2.000 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS RELEVANT MEDICAL Essential Information for Kidney Offers. (xiv) Current medication and transfusion history; Page 7 of 51
8 document.) RECORDS a collection of documents including a current donor risk assessment interview, a physical assessment/physical examination of the donor, laboratory test results (in addition to results of testing for required relevant communicable disease agents), relevant donor records, existing coroner and autopsy reports, as well as information obtained from any source or records which may pertain to donor suitability regarding high risk behaviors, and clinical signs and symptoms for any relevant communicable disease agent or disease (RCDAD), and/or treatments related to medical conditions suggestive of such risk. 24) Persons who have known or suspected sepsis at the time of death, or at the time of donation in the case of a Living Donor. (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) D1.120 Screening for FDA Defined Relevant Communicable Disease Agents Page 8 of 51
9 6. Did she/he* recently have any symptoms such as: 6a. a fever? 6b. cough? 6c. diarrhea? 6d. swollen lymph nodes? 6e. weight loss? 6f. a rash? 6g. sores in the mouth or on the skin? 6h. night sweats? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 12. Persons who are deceased and have a documented medical diagnosis of sepsis or have documented clinical evidence consistent with a diagnosis of sepsis that is not explained by other clinical conditions at the time of death. For example, if a statement such as rule-out sepsis is noted in the medical records, and subsequent notations indicate a diagnosis other than sepsis, a potential donor might and Diseases D1.110 EBAA Contraindications to Transplant Tissue from persons with the following are potentially health threatening for the recipient(s) or pose a risk to the success of the surgery and shall not be offered for surgical purposes: A. All Ocular Donors 5. active bacterial or viral meningitis; 6. active bacterial or fungal endocarditis; (same as immediately above) Guidelines for Preventing Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Through Transplantation of Human Tissue and Organs - May 20, 1994 / Vol. 43 / No. RR-8 (relevant part only) Laboratory and Other Medical 3. Persons whose history, physical examination, medical records, or autopsy reports reveal other evidence of HIV infection or highrisk behavior, such as a diagnosis of AIDS, unexplained weight loss, night sweats, blue or purple spots on the skin or mucous membranes typical of Kaposi s sarcoma, unexplained lymphadenopathy lasting >1 month, unexplained temperature >100.5 F (38.6 C) for >10 days, unexplained persistent cough and shortness of breath, opportunistic infections, OPTN/UNOS DTAC requested addition of neurological symptoms to this list to cover recent encephalopathy. Page 9 of 51
10 6i. severe headache? 6j. rapid decline in mental ability? 6k. seizures? 6l. tremors? 6m. difficulty walking? If any answer in question 6. is yes, ask when this occurred and describe (symptom) and reasons, if known. still be eligible. (although section F of the guidance usually doesn t apply to the medical history interview, it s listed here as a reference due to list of symptoms provided) F. What clinical evidence do I look for when screening a donor? You must review relevant medical records for clinical evidence of relevant communicable disease agents and diseases (. You should look for the following examples of clinical evidence of relevant communicable disease. Except as noted in this section and in accordance with (d), you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following examples of clinical evidence of relevant communicable disease. 1. HIV infection:. Unexplained weight loss; Unexplained night sweats; Blue or purple spots on or under the skin or mucous membranes typical of Kaposi s sarcoma; unexplained persistent diarrhea, male-to-male sexual contact, sexually transmitted diseases, or needle tracks or other signs of parenteral drug abuse. Page 10 of 51
11 Disseminated lymphadenopathy (swollen lymph nodes) for longer than one month; Unexplained temperature of > 100.5F (38.06C) for more than 10 days; Unexplained persistent cough or shortness of breath; Opportunistic infections; Unexplained persistent diarrhea; and/or Unexplained persistent white spots or unusual blemishes in the mouth (Ref. 79). 2. Hepatitis infection: Unexplained jaundice; Unexplained hepatomegaly; and/or 5. WNV infection (Refs. 5, 6, and 7). Because signs and symptoms of WNV can be nonspecific, you should consider the following clinical evidence in light of other information obtained about the donor in making a donor eligibility determination. Mild symptoms might include fever, headache, body aches, or eye pain; - mild symptoms might also occasionally be accompanied by a skin rash on the trunk of the body; or Page 11 of 51
12 - swollen lymph glands. 7. Did she/he* know anyone who had a smallpox vaccination? 7a. Did she/he* have contact with this person which includes touching the vaccination site, handling bandages that cover it, or handling bedding, clothing, or any other material that came in contact with the vaccination site? 7a(i). When did this contact occur? If in the past 8 weeks, 7a(ii). Did she/he* experience any symptoms or complications such as a rash, fever, muscle aches, headaches, nausea, or eye involvement? 7a(ii)a. Explain: E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 14. Persons who acquired a clinically recognizable vaccinia virus infection by contact with someone who received the smallpox vaccine (i.e., touching the vaccination area or the scab, including the covering bandages, or touching clothing, towels, or bedding that might have come into contact with an unbandaged vaccination area or scab) (Ref. 12). For living donors who developed skin lesions as a result of contact with someone who received the smallpox vaccine, you should question the donor regarding the loss of the scab, and you should examine the skin. For cadaveric donors, you should examine the skin. If no scab is present, we do not recommend deferral of: o a cadaveric donor; o a living donor if the scab 26) Persons who have had a recent smallpox vaccination (vaccinia virus) and persons who acquired a clinically recognizable vaccinia virus infection by close contact 8 with someone who received the smallpox vaccine; and, 8 CLOSE CONTACT: SMALLPOX Physical contact with the vaccination site, touching the bandages or covering of the vaccination site, or handling bedding or clothing that had been in contact with an unbandaged vaccination site. (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) Page 12 of 51
13 spontaneously separated; or o after three months from the date of vaccination of the vaccine recipient, a living donor whose scab was otherwise removed. If a scab is present, you should consider: o a cadaveric donor to be ineligible; or o a living donor to be deferred until the scab spontaneously separates. You should defer persons who developed other complications of vaccinia infection acquired through contact with a vaccine recipient until 14 days after all vaccinia complications have completely resolved. Note: We do not recommend deferral of a cadaveric donor who previously had complications of vaccinia acquired through contact with a vaccine recipient, but has no visible signs of vaccine complications, if the date of resolution of the vaccinia complications is unknown. We do not recommend deferral of contacts who never developed skin lesions or other complications of vaccinia infection. 8. In the past 12 months was she/he* in lockup, jail, prison, Guidelines for Preventing Transmission of Human Page 13 of 51
14 or any juvenile correctional facility? 8a. How long? 8b. Where? 8c. Why? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 8. Persons who have been in juvenile detention, lock up, jail or prison for more than 72 consecutive hours in the preceding 12 months (Refs. 29, 67, and 68) (risk factor for HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C). 8) Persons who have been in a juvenile correctional facility, lockup, jail or prison for more than 72 consecutive hours in the preceding 12 months; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) Immunodeficiency Virus Through Transplantation of Human Tissue and Organs - May 20, 1994 / Vol. 43 / No. RR-8 (relevant part only) Donor Exclusion Criteria Regardless of their HIV antibody test results, persons who meet any of the criteria listed below should be excluded from donation of organs or tissues unless the risk to the recipient of not performing the transplant is deemed to be greater than the risk of HIV transmission and disease (e.g., emergent, lifethreatening illness requiring transplantation when no other organs/tissues are available and no other lifesaving therapies exist). In such a case, informed consent regarding the possibility of HIV transmission should be obtained from the recipient. 7. Inmates of correctional systems. (This exclusion is to address issues such as difficulties with informed consent and increased prevalence of HIV in this population.) 9. In the past 12 months was she/he* bitten or scratched by any animal? 9a. What kind of animal; such 23) Persons who, within the past six months, were bitten by an animal suspected to be Title 10 of New York Codes, Rules and Regulations, Section , Selection and testing Page 14 of 51
15 as a pet, stray, or wild animal? 9b. When? 9c. Did she/he* receive any medical treatment? 9c(i). By whom? 9d. Was the animal suspected of having rabies? 9e. Was the animal quarantined or tested? 9e(i). Which one? If yes to tested, 9e(ii). What was the result? infected with rabies. Individuals with suspected rabies shall not be accepted as donors under any circumstances. (see Title 10 of New York Codes, Rules and Regulations, Section ); D1.110 EBAA Contraindications to Transplant Tissue from persons with the following are potentially health threatening for the recipient(s) or pose a risk to the success of the surgery and shall not be offered for surgical purposes: A. All Ocular Donors 7. suspected rabies and persons who, within the past six months, were bitten by an animal suspected to be infected with rabies; requirements for tissue donors. (a) allogeneic tissue for clinical use shall not be released from donors with any of the following conditions: (11) within the preceding six months, receipt of a bite from an animal suspect of rabies; (b) Individuals with suspected rabies or evidence of HIV infection shall not be accepted as donors under any circumstances. 10. In the past 12 months was she/he* told by a healthcare professional that they had a West Nile virus infection? 10a. When was she/he* diagnosed? If this occurred within the past 4 months ask: 10a(i). What was the name of E. What risk factors do I look for when screening a donor? 15. Persons who have had a medical diagnosis or suspicion of WNV infection (based on symptoms and/or laboratory results, or confirmed WNV viremia) you should defer for 120 days following diagnosis or D4.310 Infections The Medical Director or licensed physician designee shall not release allogeneic tissue for transplantation from donors who exhibit any of the following findings: 1) Evidence, detected by review of Relevant Medical Records of significant active infection at the time of donation for Relevant Communicable Page 15 of 51
16 the doctor/clinic? 11. In the past 12 months did she/he* have any shots or immunizations, such as MMR, yellow fever, hepatitis B, flu, etc.? 11a. When? 11b. What kind was it? onset of illness, whichever is later (Refs. 5, 6, and 7) 16. Persons who have tested positive or reactive for WNV infection using an FDA-licensed or investigational WNV NAT donor screening test in the preceding 120 days (Refs. 5 and 7). II. THE DONOR- ELIGIBILITY DETERMINATION, C. What is a relevant communicable disease agent or disease? FDA believes that the following communicable disease agents and diseases meet these standards for identification of relevant communicable disease agent or disease not specifically identified in the regulations: West Nile Virus (WNV). E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 13. Persons who have had smallpox vaccination (vaccinia virus) in the preceding 8 Disease Agents or Diseases (RCDADs). These include, but are not limited to: WNV 20) Persons who, within the previous 120 days, have been told by a healthcare professional that they were suspected or known to have had a West Nile Virus (WNV) infection based on symptoms, and/or those who are known to have tested positive for WNV by a NAT assay within this time frame. (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) 26) Persons who have had a recent smallpox vaccination (vaccinia virus) and persons who acquired a clinically recognizable vaccinia virus infection by close contact 8 with someone who received the smallpox vaccine Page 16 of 51
17 If smallpox/vaccinia is named, ask these questions: 11b(i).Did she/he* experience any symptoms or complications such as a rash, fever, muscle aches, headaches, nausea, or eye involvement? 11b(i)a. When did these symptoms resolve? 11b(ii).Did the scab fall off or was it picked off? 11b(ii)a. When? weeks (Ref. 12) should be evaluated as follows: a. For persons who had no vaccinia complications (see Appendix 4 for definition of vaccinia complication): You should defer the donor until after the vaccination scab has separated spontaneously, or for 21 days post-vaccination, whichever is the later date, and until the physical examination or physical assessment includes a confirmation that there is no scab at the vaccination site. In cases where a scab was removed before separating spontaneously, you should defer the donor for two months after vaccination. Note: We do not recommend deferral of a cadaveric donor who was vaccinated at least 21 days ago and who has no visible scab, if you are unable to obtain a history of how the scab separated. b. For persons who have experienced vaccinia complications (see Appendix 4), you should defer the donor until 14 days after all vaccinia complications have completely resolved. Note: We do not recommend deferral of a cadaveric donor who previously had vaccinia complications but who currently Page 17 of 51
18 has no visible signs of vaccinia complications, if you are unable to obtain a history of the exact date of resolution of the vaccinia complications. 12. In the past 12 months did she/he* get a tattoo, touch up of an old tattoo, or permanent makeup? 12a. Were shared or nonsterile instruments, needles or ink used? 12b. Was the procedure performed outside of the United States or Canada? 12b(i). Where? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 10. Persons who have undergone tattooing, ear piercing or body piercing in the preceding 12 months, in which sterile procedures were not used, e.g., contaminated instruments and/or ink were used, or shared instruments that had not been sterilized between uses were used (Ref. 69). 12) Persons who within 12 months prior to donation have undergone tattooing, acupuncture, ear or body piercing in which shared instruments are known to have been used; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) 13. In the past 12 months did she/he* have acupuncture, ear or body piercing? 13a. Were shared or nonsterile instruments or needles used? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or 12) Persons who within 12 months prior to donation have undergone tattooing, acupuncture, ear or body piercing in which shared instruments are known to have Page 18 of 51
19 13b. Was the procedure performed outside of the United States or Canada? 13b(i). Where? behaviors. 10. Persons who have undergone tattooing, ear piercing or body piercing in the preceding 12 months, in which sterile procedures were not used, e.g., contaminated instruments and/or ink were used, or shared instruments that had not been sterilized between uses were used (Ref. 69). been used; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) 14. In the past 12 months did she/he* live with a person who has hepatitis? 14a. What type of hepatitis did that person have? 14b. Was that person sick from the virus during that time, such as having abdominal pain, joint pain, exhaustion, fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or yellowing of the eyes or skin? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 9. Persons who have lived with (resided in the same dwelling) another person who has hepatitis B or clinically active (symptomatic) hepatitis C infection in the preceding 12 months (Ref. 69). 9) Persons who have lived with (resided in the same dwelling) another person having viral hepatitis, except for asymptomatic hepatitis C, within 12 months preceding donation; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) 15. In the past 12 months did she/he* come into contact with someone else s blood? 15a. Describe what happened and when: E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the 6. Persons who have been exposed within the preceding 12 months to known or suspected HIV, HBV, and/or HCV infected blood through Guidelines for Preventing Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Through Transplantation of Human Tissue and Organs - May 20, 1994 / Vol. 43 / No. RR-8 (relevant part only) Donor Exclusion Criteria Regardless of their HIV antibody Page 19 of 51
20 15b. Was the other person involved known to have had, or suspected of having, HIV or hepatitis? following conditions or behaviors. 6. Persons who have been exposed in the preceding 12 months to known or suspected HIV, HBV, and/or HCV-infected blood through percutaneous inoculation (e.g., needle stick) or through contact with an open wound, non-intact skin, or mucous membrane (Refs. 18 and 64). percutaneous inoculation (e.g., needlestick) or through contact with an open wound, non-intact skin, or mucous membrane; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) test results, persons who meet any of the criteria listed below should be excluded from donation of organs or tissues unless the risk to the recipient of not performing the transplant is deemed to be greater than the risk of HIV transmission and disease (e.g., emergent, lifethreatening illness requiring transplantation when no other organs/tissues are available and no other lifesaving therapies exist). In such a case, informed consent regarding the possibility of HIV transmission should be obtained from the recipient. 6. Persons who have been exposed in the preceding 12 months to known or suspected HIV-infected blood through percutaneous inoculation or through contact with an open wound, nonintact skin, or mucous membrane. 16. In the past 12 months did she/he* have an accidental needle-stick? 16a. Describe what happened and when: 16b. Was the needle E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 6. Persons who have been exposed within the preceding 12 months to known or suspected HIV, HBV, and/or HCV infected blood through percutaneous inoculation (e.g., needlestick) or through contact Guidelines for Preventing Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Through Transplantation of Human Tissue and Organs - May 20, 1994 / Vol. 43 / No. RR-8 (relevant part only) Donor Exclusion Criteria Regardless of their HIV antibody test results, persons who meet any of the criteria listed below Page 20 of 51
21 contaminated with blood from someone known to have had, or suspected of having, HIV or hepatitis? 6. Persons who have been exposed in the preceding 12 months to known or suspected HIV, HBV, and/or HCV-infected blood through percutaneous inoculation (e.g., needle stick) or through contact with an open wound, non-intact skin, or mucous membrane (Refs. 18 and 64). with an open wound, non-intact skin, or mucous membrane; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) should be excluded from donation of organs or tissues unless the risk to the recipient of not performing the transplant is deemed to be greater than the risk of HIV transmission and disease (e.g., emergent, lifethreatening illness requiring transplantation when no other organs/tissues are available and no other lifesaving therapies exist). In such a case, informed consent regarding the possibility of HIV transmission should be obtained from the recipient. 7. Persons who have been exposed in the preceding 12 months to known or suspected HIV-infected blood through percutaneous inoculation or through contact with an open wound, nonintact skin, or mucous membrane. Pg 7 As I described before, I want to remind you of the sensitive and personal nature of some of these questions. We are required to ask these questions about all potential donors. Next, I will ask you about her/his* sexual history. 17. In the past 12 months did she/he* have a sexually transmitted infection such as syphilis, gonorrhea, genital E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for 11) Persons who had or have Guidelines for Preventing Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Through Transplantation of Human Tissue Preamble to prepare interviewee for risk questions related to sexual behavior Page 21 of 51
22 herpes, or genital warts? 17a. What was it? when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 17. Persons who have been treated for or had syphilis within the preceding 12 months. We do not recommend deferral of donors if evidence is presented that the treatment occurred more than 12 months ago and was successful. been treated for syphilis or gonorrhea during the preceding 12 months. Donors may be acceptable if evidence is presented that the treatment occurred more than 12 months ago and was successful; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) and Organs - May 20, 1994 / Vol. 43 / No. RR-8 (relevant part only) Laboratory and Other Medical 3. Persons whose history, physical examination, medical records, or autopsy reports reveal other evidence of HIV infection or highrisk behavior, such as.. sexually transmited diseases,.. Pg 7 For the next part, sexual activity and sex refer to any method of sexual contact including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. 18. In the past 5 years was she/he* sexually active, even once? complete the following questions (18a. to 18g.) 18a. Did she/he* have sex in exchange for money or drugs? 18a(i) When? 18b. MALE DONOR only: Did he have sex with another E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 1. Men who have had sex with another man in the preceding 5 years (Refs. 17 through 46) (risk factor for HIV and 1) Men who have had sex with another man within the preceding five years; 2) Persons who have injected drugs for a non-medical reason in the preceding five years, including intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous injections; 3) Persons with hemophilia or Guidelines for Preventing Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Through Transplantation of Human Tissue and Organs - May 20, 1994 / Vol. 43 / No. RR-8 (relevant part only) Donor Exclusion Criteria Regardless of their HIV antibody test results, persons who meet any of the criteria listed below should be excluded from donation of organs or tissues unless the risk to the recipient of not performing the transplant is Educating the historian in regard to meaning of sexual activity and sex is required when using this form and the capture question format. Page 22 of 51
23 male? (N/A) Donor is Female 18b(i). When? 18c. Did she/he* have sex with a person who has had sex in exchange for money or drugs? 18c(i). When? 18d. FEMALE DONOR only: Did she have sex with a male who had sex with another male? (N/A) Donor is Male 18d(i). When? 18e. Did she/he* have sex with a person who used a needle to inject drugs that were not prescribed by their own doctor? 18e(i). When? 18f. Did she/he* have sex with a person who has received clotting factors for a bleeding problem? 18f(i). What was it and when was it used? Hepatitis B). 2. Persons who have injected drugs for a non-medical reason in the preceding 5 years, including intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous injections (Refs. 18, 21, 22, 25, 27, 29, 33, 34, 36, 38, 42, and 45 through 59) (risk factor HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C). 3. Persons with hemophilia or other related clotting disorders who have received humanderived clotting factor concentrates in the preceding 5 years (Refs. 18 and 60) (risk factor for HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C). A donor who received clotting factors once to treat an acute bleeding event more than 12 months ago may be eligible to donate. 4. Persons who have engaged in sex in exchange for money or drugs in the preceding 5 years (Refs. 18, 21, 22, 24, 25, 27, 29, 33, 34, 38, 40, 44, 45, 46, 61, 62, and 63) (risk factor for HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C). 5. Persons who have had sex in the preceding 12 months with any person described in criteria 1 through 4 of this section or related clotting disorders who have received human-derived clotting factor concentrates in the preceding five years; 4) Persons who have had sex in exchange for money or drugs in the preceding five years; 5) Persons who have had sex in the preceding 12 months with any person described in the 4 items above or with any person who has HIV infection, including a positive test for HIV, hepatitis B infection, or clinically active (symptomatic) hepatitis C 2 infection; 2 CLINICALLY ACTIVE HEPATITIS C - infection with hepatitis C virus when it is symptomatic. This means that: the person demonstrates related symptoms such as jaundice, icterus, fatigue, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, low grade fever, headache, joint pain, and/or flu-like symptoms AND, HCV infection is suspected or has been diagnosed or anti-hcv (EIA) testing is positive. Also, knowledge of a recent/current positive test for HCV NAT would qualify as a clinically active HCV infection. deemed to be greater than the risk of HIV transmission and disease (e.g., emergent, lifethreatening illness requiring transplantation when no other organs/tissues are available and no other lifesaving therapies exist). In such a case, informed consent regarding the possibility of HIV transmission should be obtained from the recipient. 1. Men who have had sex with another man in the preceding 5 years. 2. Persons who report nonmedical intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous injection of drugs in the preceding 5 years. 3. Persons with hemophilia or related clotting disorders who have received human-derived clotting factor concentrates 4. Men and women who have engaged in sex in exchange for money or drugs in the preceding 5 years. 5. Persons who have had sex in the preceding 12 months with any person described in items 1-4 above or with a person known or suspected to have HIV infection. Page 23 of 51
24 18g. Did she/he* have sex with a person who had a positive test for, or was suspected of having, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, or HIV? 18g(i). Which virus and when? 18g(ii). Was that person sick from the virus during that time, such as having abdominal pain, joint pain, exhaustion, fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or yellowing of the eyes or skin? with any person who has HIV infection, including a positive or reactive test for HIV virus (Refs. 17 and 18), hepatitis B infection (Ref. 64), or clinically active (symptomatic) hepatitis C infection (Refs. 65 and 66). (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) 19. In the past 5 years did she/he* receive clotting factors for a bleeding problem? 19a. When? 19b. What was the reason? 19c. Was it human derived? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 3. Persons with hemophilia or other related clotting disorders who have received humanderived clotting factor concentrates in the preceding 5 years (Refs. 18 and 60) (risk factor for HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C). A donor who received clotting factors once to treat an acute bleeding event more than 12 months ago may be eligible to donate. 3) Persons with hemophilia or related clotting disorders who have received human-derived clotting factor concentrates in the preceding five years; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) Guidelines for Preventing Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Through Transplantation of Human Tissue and Organs - May 20, 1994 / Vol. 43 / No. RR-8 (relevant part only) Donor Exclusion Criteria Regardless of their HIV antibody test results, persons who meet any of the criteria listed below should be excluded from donation of organs or tissues unless the risk to the recipient of not performing the transplant is deemed to be greater than the risk of HIV transmission and disease (e.g., emergent, lifethreatening illness requiring transplantation when no other organs/tissues are available and no other lifesaving therapies exist). In such a case, informed Page 24 of 51
25 20. Did she/he* EVER use or take drugs, such as steroids, cocaine, amphetamines, or anything NOT prescribed by her/his* doctor? 20a. What was it? 20b. How often and how long was it used? 20c. When was it last used? 20d. Were needles used? If no, 20d(i). How was it taken? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 2. Persons who have injected drugs for a non-medical reason in the preceding 5 years, including intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous injections (Refs. 18, 21, 22, 25, 27, 29, 33, 34, 36, 38, 42, and 45 through 59) (risk factor HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C). 2) Persons who have injected drugs for a non-medical reason in the preceding five years, including intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous injections; (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) consent regarding the possibility of HIV transmission should be obtained from the recipient. 3. Persons with hemophilia or related clotting disorders who have received human-derived clotting factor concentrates 3.6 ALLOCATION OF LIVERS Minimum Information for Liver Offers Essential Information Category. (vii) Social and drug activity histories; 3.7 ALLOCATION OF THORACIC ORGANS Minimum Information for Thoracic Organ Offers Essential Information. (iv) and drug activity histories; Desirable Information for Heart Offers. (f) Two or more of the following: vii. History of cocaine or amphetamine use Guidelines for Preventing Transmission of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Through Transplantation of Human Tissue and Organs - May 20, 1994 / Vol. 43 / No. RR-8 (relevant part only) Donor Exclusion Criteria Regardless of their HIV antibody Page 25 of 51
26 test results, persons who meet any of the criteria listed below should be excluded from donation of organs or tissues unless the risk to the recipient of not performing the transplant is deemed to be greater than the risk of HIV transmission and disease (e.g., emergent, lifethreatening illness requiring transplantation when no other organs/tissues are available and no other lifesaving therapies exist). In such a case, informed consent regarding the possibility of HIV transmission should be obtained from the recipient. 9. Persons who report nonmedical intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous injection of drugs in the preceding 5 years. Also: 21. Did she/he* EVER have a transplant or medical procedure that involved being E. What risk factors or Laboratory and Other Medical 3. Persons whose history, physical examination, medical records, or autopsy reports reveal other evidence of HIV infection or highrisk behavior, such as., or needle tracks or other signs of parenteral drug abuse. Page 26 of 51
27 exposed to live cells, tissues or organs from an animal? 21b.Did she/he* live with, or have sex with, a person who had? conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or behaviors. 29. Persons who are xenotransplantation product recipients or intimate contacts of a xenotransplantation product recipient (Ref. 77). For the purpose of this document, we define the following terms: Xenotransplantation is any procedure that involves the transplantation, implantation, or infusion into a human recipient of either: (1) live cells, tissues, or organs from a nonhuman animal source; or (2) human body fluids, cells, tissues, or organs that have had ex vivo contact with live nonhuman animal cells, tissues, or organs. Xenotransplantation products include live cells, tissues, or organs used in xenotransplantation. Biological products, drugs, or medical devices sourced from nonliving cells, tissues or organs from nonhuman animals, including but not limited to porcine 21) Persons who are known to have risks associated with xenotransplantation 5 (i.e. receipt of a xenotransplantation product 6 or who has had intimate contact 7 with a Recipient of a xenotransplantation product); (superscript references 5,6,7 above match the FDA definitions) (reference Appendix II for FDA donor criteria) Page 27 of 51
28 insulin and porcine heart valves, are not considered xenotransplantation products. Xenotransplantation product recipient means a person who undergoes xenotransplantation. 22. Was she/he* EVER told by a physician that she/he* had a disease of the brain or a neurological disease such as Alzheimer s, Parkinson s, multiple sclerosis, or epilepsy? Intimate contact of a xenotransplantation product recipient means a person who has engaged in activities that could result in intimate exchange of body fluids, including blood or saliva, with a xenotransplantation product recipient. Examples of intimate contacts include sexual partners, household members who share razors or toothbrushes, and health care workers or laboratory personnel with repeated percutaneous, mucosal, or other direct exposures. We do not consider sharing of housing or casual contact, such as hugging or kissing without the exchange of saliva, to be intimate contact. E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or 14) Persons with a diagnosis of dementia or any degenerative or demyelinating disease of the central nervous system (CNS) or other neurological disease of unknown etiology. Note: Page 28 of 51
29 22a. What was she/he* told by a physician? behaviors. 20. Persons who have been diagnosed with dementia or any degenerative or demyelinating disease of the central nervous system or other neurological disease of unknown etiology (Refs. 3 and 75). Potential donors who have a diagnosis of delirium (e.g., delirium caused by toxic/metabolic diseases or recent head trauma) would not necessarily be considered to have a diagnosis of dementia and should be evaluated by the Medical Director. (HCT/Ps from donors with dementia confirmed by gross and microscopic examination of the brain to be caused by cerebrovascular accident or brain tumor and who are confirmed not to have evidence of TSE on microscopic examination of the brain may be acceptable based on an evaluation by the Medical Director). Tissues from donors with dementia, confirmed by gross and microscopic examination of the brain to be caused by cerebrovascular accident, brain tumor, head trauma, or toxic/metabolic dementia and who are confirmed not to have evidence of TSE on microscopic examination of the brain, may be acceptable based on an evaluation of this information by the Medical Director.); Possibly related but this will fit better where a query regarding recent neuro symptoms will be added: 17) Persons with encephalitis or meningitis of viral or unknown etiology that is active; D1.110 EBAA Contraindications to Transplant Tissue from persons with the following are potentially health threatening for the recipient(s) or pose a risk to the success of the surgery and shall not be offered for surgical purposes: A. All Ocular Donors 4. Active viral encephalitis of unknown origin or progressive encephalopathy (e.g., subacute sclerosing panencephalitis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, etc.); Page 29 of 51
30 5. active bacterial or viral meningitis; 23. Was she/he* EVER refused as a blood donor or told not to donate? 23a. What was the reason? 22) Persons who have been permanently deferred as a blood donor for unknown reasons or who have a history of positive infectious disease test results for HIV, HBV, or HCV; 24. Was she/he* EVER a U.S. military member, a civilian military employee, or a dependent of either? 24a. Did she/he* ever live or work on a U.S. military base outside the United States? E. What risk factors or conditions do I look for when screening a donor?..you should determine to be ineligible any potential donor who exhibits one or more of the following conditions or Also: 9) Persons with a generic history of hepatitis of an unspecified etiology or a current or past diagnosis of clinical, symptomatic viral hepatitis unless evidence from the time of illness documents that the hepatitis was diagnosed as either hepatitis A or due to cytomegalovirus or Epstein-Barr virus hepatitis. (Note: A verbal history of viral hepatitis occurring before the age of 11 years is acceptable); 19) Persons determined to be at risk for variant CJD (vcjd) because they are known to meet any of the following criteria: c. Is a current or former U.S. Page 30 of 51
Donor Risk Assessment Interview (Donor >12 yrs old)
 Your logo Donor Risk Assessment Interview (Donor >12 yrs old) Your address Donor Name: First Middle Last Person Interviewed: Name Relationship Contact Information: ( ) Phone Address City State Zip The
Your logo Donor Risk Assessment Interview (Donor >12 yrs old) Your address Donor Name: First Middle Last Person Interviewed: Name Relationship Contact Information: ( ) Phone Address City State Zip The
Uniform DRAI - Donor >12 yrs old Requirements Crosswalk
 Q# or Pg # Pg 1 Question or section as it appears on the Uniform DRAI - Donor >12 yrs old 9-10-14 Donor Name, Person Interviewed (name, relationship), Contact Information (phone, address, city, state,
Q# or Pg # Pg 1 Question or section as it appears on the Uniform DRAI - Donor >12 yrs old 9-10-14 Donor Name, Person Interviewed (name, relationship), Contact Information (phone, address, city, state,
Hot Topics in Tissue Safety
 Hot Topics in Tissue Safety 37 th Annual AATB Meeting National Harbor, Maryland 03 October 2013 Scott A. Brubaker, CTBS Chief Policy Officer PHS Guideline for Reducing Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Hepatitis
Hot Topics in Tissue Safety 37 th Annual AATB Meeting National Harbor, Maryland 03 October 2013 Scott A. Brubaker, CTBS Chief Policy Officer PHS Guideline for Reducing Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Hepatitis
Uniform Donor Risk Assessment Interview (Donor >12 yrs old)
 Your logo Uniform Donor Risk Assessment Interview (Donor >12 yrs old) Your address Donor Name: First Middle Last Person Interviewed: Name Relationship Contact Information: ( ) Phone Address City State
Your logo Uniform Donor Risk Assessment Interview (Donor >12 yrs old) Your address Donor Name: First Middle Last Person Interviewed: Name Relationship Contact Information: ( ) Phone Address City State
ABO: Tissue#:
 Donor Name: Place of Interview: - Date-Time Interviewed: --/--/ --:-- Person Conducting Interview and Completing Form: - Person Interviewed: - Relationship to Potential Donor: - Address: - Phone: - Phone
Donor Name: Place of Interview: - Date-Time Interviewed: --/--/ --:-- Person Conducting Interview and Completing Form: - Person Interviewed: - Relationship to Potential Donor: - Address: - Phone: - Phone
FORM TITLE: Risk Behavior Assessment. 1. Are you a male who has had sex with another male in the preceding five years?
 RELESE DTE: 12/07/2012 EFFECTIVE DTE: 12/13/2012 1. re you a male who has had sex with another male in the preceding five years? 2. Have you injected drugs for non-medical reason in the preceding five
RELESE DTE: 12/07/2012 EFFECTIVE DTE: 12/13/2012 1. re you a male who has had sex with another male in the preceding five years? 2. Have you injected drugs for non-medical reason in the preceding five
Directed Semen Donor Eligibility Requirements
 Directed Semen Donor Eligibility Requirements Directed (known) reproductive donors using the University Andrology Sperm Banking Program must follow FDA requirements to prevent the transmission of relevant
Directed Semen Donor Eligibility Requirements Directed (known) reproductive donors using the University Andrology Sperm Banking Program must follow FDA requirements to prevent the transmission of relevant
DHQ Flowcharts v2.0 eff. February 2016
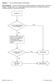 Question: 1. Are you feeling healthy and well today? Donor Eligibility: A person should be free of infectious diseases, including colds, on the day of donation. A person who is not in good health should
Question: 1. Are you feeling healthy and well today? Donor Eligibility: A person should be free of infectious diseases, including colds, on the day of donation. A person who is not in good health should
Current Infectious Disease Screening for the Live Organ Donor
 2013 Public Health and Safety Guidelines for reducing HIV, HBV and HCV Transmission Though Organ Transplantation: Implications for Counseling and Disclosure Dianne LaPointe Rudow DNP, ANP-BC, CCTC Director
2013 Public Health and Safety Guidelines for reducing HIV, HBV and HCV Transmission Though Organ Transplantation: Implications for Counseling and Disclosure Dianne LaPointe Rudow DNP, ANP-BC, CCTC Director
Question: 1. Are you currently taking an antibiotic?
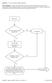 Question: 1. Are you currently taking an antibiotic? Donor Eligibility: A donor with an infection that could cause bacteremia/sepsis or other relevant communicable disease should not donate. The reason
Question: 1. Are you currently taking an antibiotic? Donor Eligibility: A donor with an infection that could cause bacteremia/sepsis or other relevant communicable disease should not donate. The reason
TRANSMISSIBLE SPONGIFORM ENCEPHALOPATHIES ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING October2010. Issue Summary
 TRANSMISSIBLE SPONGIFORM ENCEPHALOPATHIES ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING 28-29October2010 Issue Summary Informational Topic: FDA s Geographic Donor Deferral Policy to Reduce the Possible Risk of Transmission
TRANSMISSIBLE SPONGIFORM ENCEPHALOPATHIES ADVISORY COMMITTEE MEETING 28-29October2010 Issue Summary Informational Topic: FDA s Geographic Donor Deferral Policy to Reduce the Possible Risk of Transmission
Question: 1. Are you currently taking an antibiotic?
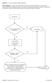 Question: 1. Are you currently taking an antibiotic? Donor Eligibility: A donor with an infection that could cause bacteremia/sepsis or other relevant communicable disease should not donate. The reason
Question: 1. Are you currently taking an antibiotic? Donor Eligibility: A donor with an infection that could cause bacteremia/sepsis or other relevant communicable disease should not donate. The reason
DHQ v2.0, February 2016 Table Detailing Changes from v1.3 v1.3 Revised language in v2.0 Rationale Question 1: Are you
 DHQ v2.0, February 2016 Table Detailing s from v1.3 v1.3 Revised language in v2.0 Rationale Question 1: Are you Q 1, No Feeling healthy and well today? Question 2: Are you Q 2, No change Currently taking
DHQ v2.0, February 2016 Table Detailing s from v1.3 v1.3 Revised language in v2.0 Rationale Question 1: Are you Q 1, No Feeling healthy and well today? Question 2: Are you Q 2, No change Currently taking
HEALTH SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE. Work-up. Donor ID EdgeCell #:
 HEALTH SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE Héma-Québec Registre des Donneurs de Cellules Souches 4045 Côte-vertu, St-Laurent, QC, Canada, H4R 2W7 Tél : + 514-832-1031 Fax : + 514-832-0266 www.hema-quebec.qc.ca CT
HEALTH SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE Héma-Québec Registre des Donneurs de Cellules Souches 4045 Côte-vertu, St-Laurent, QC, Canada, H4R 2W7 Tél : + 514-832-1031 Fax : + 514-832-0266 www.hema-quebec.qc.ca CT
UNOS # NA. Person(s) Interviewed (First and last name) Relationship(s) to him/her. Print Name Title Signature
 UNOS # Form-0005 - Medical History and Behavioral Donor Name (First and last name) Date/Time of Interview Person(s) Interviewed (First and last name) Relationship(s) to him/her Person Conducting Interview
UNOS # Form-0005 - Medical History and Behavioral Donor Name (First and last name) Date/Time of Interview Person(s) Interviewed (First and last name) Relationship(s) to him/her Person Conducting Interview
User Instructions Allogeneic HPC, Apheresis and HPC, Marrow Donor History Questionnaire. Table of Contents
 User Instructions Allogeneic HPC, Apheresis and HPC, Marrow Donor History Questionnaire Table of Contents Purpose Introduction Capture Questions Methods of Administration DHQ Materials - Structure and
User Instructions Allogeneic HPC, Apheresis and HPC, Marrow Donor History Questionnaire Table of Contents Purpose Introduction Capture Questions Methods of Administration DHQ Materials - Structure and
HEALTH SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE CT Work-up. Donor ID EdgeCell #:
 HEALTH SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE CT Work-up Héma-Québec Registre des Donneurs de Cellules Souches 4045 Côte-vertu, St-Laurent, QC, Canada, H4R 2W7 Tél : + 514-832-1031 Fax : + 514-832-0266 www.hema-quebec.qc.ca
HEALTH SCREENING QUESTIONNAIRE CT Work-up Héma-Québec Registre des Donneurs de Cellules Souches 4045 Côte-vertu, St-Laurent, QC, Canada, H4R 2W7 Tél : + 514-832-1031 Fax : + 514-832-0266 www.hema-quebec.qc.ca
Safety Tips from the WorkSafe People
 Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C
 Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
Commonly Asked Questions About Chronic Hepatitis C From the American College of Gastroenterology 1. How common is the hepatitis C virus? The hepatitis C virus is the most common cause of chronic viral
USER INSTRUCTIONS HPC, Cord Blood Donor History Questionnaire. Table of Contents
 Page 1 of 9 USER INSTRUCTIONS HPC, Cord Blood Donor History Questionnaire Table of Contents Purpose Introduction Capture Questions Methods of Administration DHQ Materials Structure and Content Reformatting
Page 1 of 9 USER INSTRUCTIONS HPC, Cord Blood Donor History Questionnaire Table of Contents Purpose Introduction Capture Questions Methods of Administration DHQ Materials Structure and Content Reformatting
Patient Name: MRN: DOB: Treatment Location:
 Page 1 of 5 I. TO (Required) This Section is required to be completed by all patients who undergo kidney transplant surgery. I hereby consent to and authorize Dr. and his/her assistant(s), including supervised
Page 1 of 5 I. TO (Required) This Section is required to be completed by all patients who undergo kidney transplant surgery. I hereby consent to and authorize Dr. and his/her assistant(s), including supervised
Increased Risk Donors for Organ Transplantation
 A Tool Kit to Assist Transplant Programs in the Use of Increased Risk Donors for Organ Transplantation February 2016 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 1.0 Increased Risk Donor Tool Kit... 3 1.1
A Tool Kit to Assist Transplant Programs in the Use of Increased Risk Donors for Organ Transplantation February 2016 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 1.0 Increased Risk Donor Tool Kit... 3 1.1
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
User Instructions Allogeneic HPC, Apheresis and HPC, Marrow Donor History Questionnaire. Table of Contents
 User Instructions Allogeneic HPC, Apheresis and HPC, Marrow Donor History Questionnaire Table of Contents Purpose Introduction Methods of Administration DHQ Materials - Structure and Content Reformatting
User Instructions Allogeneic HPC, Apheresis and HPC, Marrow Donor History Questionnaire Table of Contents Purpose Introduction Methods of Administration DHQ Materials - Structure and Content Reformatting
Case 1. FDA, Legal, and EBAA Medical Standards Panel. Case 1. Case 1 6/25/2012. Samuel B. Barone, M.D. Office of Cellular, Tissue, and Gene Therapies
 Case 1 FDA, Legal, and EBAA Medical Standards Panel Samuel B. Barone, M.D. Office of Cellular, Tissue, and Gene Therapies Medical Directors Symposium Eye Bank Association of America Annual Meeting 47 y/o
Case 1 FDA, Legal, and EBAA Medical Standards Panel Samuel B. Barone, M.D. Office of Cellular, Tissue, and Gene Therapies Medical Directors Symposium Eye Bank Association of America Annual Meeting 47 y/o
Hepatitis Case Investigation
 * indicates required fields Does patient also have: Hepatitis Case Investigation West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology
* indicates required fields Does patient also have: Hepatitis Case Investigation West Virginia Electronic Disease Surveillance System Division of Surveillance and Disease Control Infectious Disease Epidemiology
Name of Recipient: Recipient s DOB (if known) Relationship to Recipient: (Example: mother, father, sister, brother, friend, etc)
 The Christ Hospital Health Network DONOR REGISTRATION INFORMATION Phone: 513-585-2493 Fax: 513-585-0433 (Please be advised donor information is needed ONLY to register donor in the Christ Hospital system.
The Christ Hospital Health Network DONOR REGISTRATION INFORMATION Phone: 513-585-2493 Fax: 513-585-0433 (Please be advised donor information is needed ONLY to register donor in the Christ Hospital system.
RISK OF DISEASE TRANSMISSION FROM ORGAN DONORS PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE
 Receiving an organ transplant carries many risks, including the risk of getting a disease from the June 2017 donor. This is true for every organ we transplant. BC Transplant makes every effort to minimize
Receiving an organ transplant carries many risks, including the risk of getting a disease from the June 2017 donor. This is true for every organ we transplant. BC Transplant makes every effort to minimize
STI s. (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
 STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
STI s (Sexually Transmitted Infections) Build Awareness In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise. One of the primary defenses in the fight
HEPATITIS C, ACUTE CRUDE DATA. Number of Cases 5 Annual Incidence a LA County 0.05 California b 0.10 United States b 0.68 Age at Diagnosis Mean 38
 2016 Annual Morbidity Report HEPATITIS C, ACUTE a Rates calculated based on less than 19 cases or events are considered unreliable b Calculated from: CDC. Notice to Readers: Final 2016 Reports of Nationally
2016 Annual Morbidity Report HEPATITIS C, ACUTE a Rates calculated based on less than 19 cases or events are considered unreliable b Calculated from: CDC. Notice to Readers: Final 2016 Reports of Nationally
Hepatitis B. What Is Hepatitis? What Are The Two Stages Of Hepatitis? Published on: 5 Oct 2010
 Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Published on: 5 Oct 2010 Hepatitis B What Is Hepatitis? Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver. Inflammation causes soreness and swelling. Hepatitis can be caused by many things. Hepatitis is most commonly
Hepatitis B is a virus that attacks the liver. It is highly infectious. Hepatitis B is transmitted primarily
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training.
 You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
You will now begin the Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training. The following program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and your Client must take to reduce your risks of exposure.
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
[Type here] Version Approval Dates Announcement Date Effective Standards Committee: Jan 2019
![[Type here] Version Approval Dates Announcement Date Effective Standards Committee: Jan 2019 [Type here] Version Approval Dates Announcement Date Effective Standards Committee: Jan 2019](/thumbs/95/123651537.jpg) SECTION D AUTHORIZATION, INFORMED CONSENT, DONOR SCREENING, AND TISSUE RECOVERY, COLLECTION, AND ACQUISITION D1.000 GENERAL POLICIES In addition to the requirements at the series of standards at B1.500,
SECTION D AUTHORIZATION, INFORMED CONSENT, DONOR SCREENING, AND TISSUE RECOVERY, COLLECTION, AND ACQUISITION D1.000 GENERAL POLICIES In addition to the requirements at the series of standards at B1.500,
What is hepatitis? What is hepatitis A? How is it spread? What are the symptoms? How soon do symptoms appear? How is hepatitis A diagnosed?
 Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees
 BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS Online Training for Buncombe County Public School Employees Buncombe County Public Schools require employees to receive annual training for Bloodborne Pathogens. This online training
The 2008 Guidelines for Gamete and Embryo Donation
 2008 Guidelines for gamete and embryo donation: a Practice Committee report Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, and the Practice Committee of the Society for Assisted
2008 Guidelines for gamete and embryo donation: a Practice Committee report Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine, and the Practice Committee of the Society for Assisted
Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments
 Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments LHDs are responsible for investigating and reporting all physician reported cases of acute hepatitis C (HCV). For clients known to have
Hepatitis C Best Practice Guidelines For Local Health Departments LHDs are responsible for investigating and reporting all physician reported cases of acute hepatitis C (HCV). For clients known to have
Blood Borne Pathogens. Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N.
 Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
MEDICAL ADVISORY. July 18, 2017
 MEDICAL ADVISORY July 18, 2017 The following changes were made at the June 16, 2017 meeting of the Medical Advisory Board, and will become effective immediately. B1.100 Eye Bank Inspection The Accreditation
MEDICAL ADVISORY July 18, 2017 The following changes were made at the June 16, 2017 meeting of the Medical Advisory Board, and will become effective immediately. B1.100 Eye Bank Inspection The Accreditation
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
 Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: Bacterial (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Syphilis) Viral (Hepatitis B,
Allogeneic donor selection and blood collection. by Mohammed Abu-basha
 Allogeneic donor selection and blood collection 1 An allogeneic (also called homologous) donation (allo- from the Greek meaning "other") is when a donor gives blood for storage at a blood bank for transfusion
Allogeneic donor selection and blood collection 1 An allogeneic (also called homologous) donation (allo- from the Greek meaning "other") is when a donor gives blood for storage at a blood bank for transfusion
Welcome to Your Reading Assignment
 Welcome to Your Reading Assignment This workbook contains four reading assignments. It is filled with easy-to-read articles you can use to help keep yourself and those you care about safe. After each reading
Welcome to Your Reading Assignment This workbook contains four reading assignments. It is filled with easy-to-read articles you can use to help keep yourself and those you care about safe. After each reading
Greater Glasgow and Clyde. Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts
 Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
MONTEFIORE MEDICAL CENTER TRANSPLANT PROGRAM LIVING DONOR EVALUATION FORM History Questionnaire
 MONTEFIORE MEDICAL CENTER TRANSPLANT PROGRAM LIVING DONOR EVALUATION FORM History Questionnaire Donor s Name: Today s Date: Social Security #: Date of Birth Age Sex Address: Telephone #: (home) (work)
MONTEFIORE MEDICAL CENTER TRANSPLANT PROGRAM LIVING DONOR EVALUATION FORM History Questionnaire Donor s Name: Today s Date: Social Security #: Date of Birth Age Sex Address: Telephone #: (home) (work)
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Cord Blood Medical History/ Health Assessment Questionnaire
 OTT BRM EDM VAN Date: YYYY / MM / DD Phone Interview (if applicable) Informed Consent on file * Mandatory fields GENERAL INFORMATION *Last Name As per government ID *First Name As per government ID *DOB
OTT BRM EDM VAN Date: YYYY / MM / DD Phone Interview (if applicable) Informed Consent on file * Mandatory fields GENERAL INFORMATION *Last Name As per government ID *First Name As per government ID *DOB
X-Plain Hepatitis B Reference Summary
 X-Plain Hepatitis B Reference Summary Introduction Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks the liver. The virus is transmitted through
X-Plain Hepatitis B Reference Summary Introduction Hepatitis B is the most common serious liver infection. It is caused by the hepatitis B virus that attacks the liver. The virus is transmitted through
"Hepatitis" means inflammation of the liver and also refers to a group of viral infections that
 Understanding Viral Hepatitis in African Americans Health Note Viral Hepatitis "Hepatitis" means inflammation of the liver and also refers to a group of viral infections that Viral hepatitis is the leading
Understanding Viral Hepatitis in African Americans Health Note Viral Hepatitis "Hepatitis" means inflammation of the liver and also refers to a group of viral infections that Viral hepatitis is the leading
General HIV/AIDS Information
 General HIV/AIDS Information The History of HIV In the summer of 1981, physicians in San Francisco observed that young, previously healthy homosexual men were developing an unusual type of pneumonia which
General HIV/AIDS Information The History of HIV In the summer of 1981, physicians in San Francisco observed that young, previously healthy homosexual men were developing an unusual type of pneumonia which
HIV, STI AND OTHER BLOOD- BORNE DISEASES. Kolářová M., EPI Autumn 2015
 HIV, STI AND OTHER BLOOD- BORNE DISEASES Kolářová M., EPI Autumn 2015 Chlamydia infection Genital warts Gonorrhoea Hepatitis B Hepatitis C HIV infection and AIDS Human papillomavirus infection Sexually
HIV, STI AND OTHER BLOOD- BORNE DISEASES Kolářová M., EPI Autumn 2015 Chlamydia infection Genital warts Gonorrhoea Hepatitis B Hepatitis C HIV infection and AIDS Human papillomavirus infection Sexually
Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1
 Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1 The Risk of STIs 1) What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? Referred to as a sexually transmitted infection (STI) infectious diseases spread from person to person through
Chapter 25 Notes Lesson 1 The Risk of STIs 1) What is a sexually transmitted disease (STD)? Referred to as a sexually transmitted infection (STI) infectious diseases spread from person to person through
BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens]
![BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens] BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS. CAP Safety Meetings. Revision: CAP Safety Meetings [Bloodborne Pathogens]](/thumbs/73/68341667.jpg) BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS CAP Safety Meetings Revision: 10-2011 2011 Copyright - PEC/Premier Safety Management, Inc. All Rights Reserved Revision: [10-2011] 1 THEBLOODBORNEPATHOGENSSTANDARD The Bloodborne Pathogens
BLOODBORNEPATHOGENS CAP Safety Meetings Revision: 10-2011 2011 Copyright - PEC/Premier Safety Management, Inc. All Rights Reserved Revision: [10-2011] 1 THEBLOODBORNEPATHOGENSSTANDARD The Bloodborne Pathogens
Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea What is it: A bacterial infection of the genitals, anus, or throat. How common: The CDC estimates 820,000 people in the United States get Gonorrhea
Quick Study: Sexually Transmitted Infections Gonorrhea What is it: A bacterial infection of the genitals, anus, or throat. How common: The CDC estimates 820,000 people in the United States get Gonorrhea
HIV/AIDS. Communication and Prevention. Davison Community Schools Grade Six June 2018
 HIV/AIDS Communication and Prevention Davison Community Schools Grade Six June 2018 Discussing Sensitive Matters with Your Parents Parents: A child s first and most important teacher Parent s role is to
HIV/AIDS Communication and Prevention Davison Community Schools Grade Six June 2018 Discussing Sensitive Matters with Your Parents Parents: A child s first and most important teacher Parent s role is to
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel
 Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Bloodborne Pathogens Training For School Personnel OSHA Defined: Occupational Safety and Health Administration Published a standard to reduce or eliminate health risk, resulting in: Annual training of
Making Your Blood Donation Safe
 BLOOD DONOR EDUCATIONAL MATERIALS Making Your Blood Donation Safe Pete Lawson Burned in a wildfire, LifeStream blood donations saved his life. WWW.LSTREAM.ORG NEW! Important Information on Iron! Recent
BLOOD DONOR EDUCATIONAL MATERIALS Making Your Blood Donation Safe Pete Lawson Burned in a wildfire, LifeStream blood donations saved his life. WWW.LSTREAM.ORG NEW! Important Information on Iron! Recent
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS
 F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS page 1 Viral Hepatitis Pain in the stomach Skin and whites of the eyes turning yellow, also called jaundice Q: What are the types of viral hepatitis? A: Hepatitis A Q: What
F REQUENTLY A SKED Q UESTIONS page 1 Viral Hepatitis Pain in the stomach Skin and whites of the eyes turning yellow, also called jaundice Q: What are the types of viral hepatitis? A: Hepatitis A Q: What
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview
 Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Chapter 2 Hepatitis B Overview 23 24 This page intentionally left blank. HEPATITIS B OVERVIEW Hepatitis B Virus The hepatitis B virus (HBV) belongs to the Hepadnaviridae family and is known to cause both
Living with #HIV. What you need to know. What is HIV? Platinum Health offers unlimited HIV tests, treatment, counselling and support.
 Living with #HIV What you need to know What is HIV? HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. Your health is our Number 1 Priority Platinum Health offers unlimited HIV tests, treatment, counselling and support.
Living with #HIV What you need to know What is HIV? HIV is the virus that causes AIDS. Your health is our Number 1 Priority Platinum Health offers unlimited HIV tests, treatment, counselling and support.
STD Notes. Myths about STDs
 STD Notes Sexually transmitted diseases (STD's) or sexually transmitted infections (STI's) are infectious diseases that spread from person to person through intimate contact. STD's can affect males and
STD Notes Sexually transmitted diseases (STD's) or sexually transmitted infections (STI's) are infectious diseases that spread from person to person through intimate contact. STD's can affect males and
ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING
 ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING OBJECTIVE Define Blood borne pathogens Instruct how to recognize exposure to BBP Prevent or reduce risk of BBP exposure Identify high risk groups Review ACS exposure protocol
ACS BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN TRAINING OBJECTIVE Define Blood borne pathogens Instruct how to recognize exposure to BBP Prevent or reduce risk of BBP exposure Identify high risk groups Review ACS exposure protocol
MEDICAL HISTORY FORM ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS
 ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS CONFIRM THE STUDY BAR CODE ON PAGES 1 THROUGH 6 OF THIS FORM DO NOT PLACE A STUDY BAR CODE LABEL ON THIS INSTRUCTION PAGE. Interview Instructions The interview should be conducted
ADMINISTRATION INSTRUCTIONS CONFIRM THE STUDY BAR CODE ON PAGES 1 THROUGH 6 OF THIS FORM DO NOT PLACE A STUDY BAR CODE LABEL ON THIS INSTRUCTION PAGE. Interview Instructions The interview should be conducted
Hepatitis STARS Program. Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003
 Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
Hepatitis 2003 STARS Program Geri Brown, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine October 4, 2003 Outline n Hepatitis A Epidemiology and screening Transmission n Hepatitis B Epidemiology
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (INFECTIONS)
 SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (INFECTIONS) HIV/AIDS - TRANSMISSION Sexual intercourse Anal, oral, & vaginal Multiple partners Sharing needles Mother to infant Born or breast milk Blood transfusions Open
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES (INFECTIONS) HIV/AIDS - TRANSMISSION Sexual intercourse Anal, oral, & vaginal Multiple partners Sharing needles Mother to infant Born or breast milk Blood transfusions Open
Confirmed (Laboratory Tests) Serum positive for IgM anti-hbc or, hepatitis B surface antigen (HbsAg).
 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B is a liver disease that results from infection with the Hepatitis B virus. It can range in severity from a mild illness lasting a few weeks to a serious, lifelong illness. Hepatitis
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of Transmission for School Staff
 CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
For Residence Hall Students Only
 Immunization Record 2016-2017 Please print all information. PLEASE MAIL OR FAX COMPLETED FORMS (TWO PAGES) TO: Mount St. Joseph University, Wellness Center, 5701 Delhi Road, Cincinnati, OH 45233-1670 ATTN:
Immunization Record 2016-2017 Please print all information. PLEASE MAIL OR FAX COMPLETED FORMS (TWO PAGES) TO: Mount St. Joseph University, Wellness Center, 5701 Delhi Road, Cincinnati, OH 45233-1670 ATTN:
BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B. Acute HBV Questionnaire
 BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B Informed Consent: Please read to individual and answer any questions There are about 60,000 people with hepatitis B in BC. We want to find
BC Enhanced Hepatitis Strain Surveillance Project Hepatitis B Informed Consent: Please read to individual and answer any questions There are about 60,000 people with hepatitis B in BC. We want to find
Hepatitis C. Kim Dawson October 2010
 Hepatitis C Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn: More about Hepatitis C. The importance of the liver. Risk factors and prevention. Signs and symptoms. Hepatitis C Virus: Is a virus that
Hepatitis C Kim Dawson October 2010 Objectives: You will learn: More about Hepatitis C. The importance of the liver. Risk factors and prevention. Signs and symptoms. Hepatitis C Virus: Is a virus that
WOMENCARE. Herpes. Source: PDR.net Page 1 of 8. A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407)
 WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Herpes Basics: Herpes is a common viral disease characterized by painful blisters of the mouth or genitals. The herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes
WOMENCARE A Healthy Woman is a Powerful Woman (407) 898-1500 Herpes Basics: Herpes is a common viral disease characterized by painful blisters of the mouth or genitals. The herpes simplex virus (HSV) causes
Universal Precautions
 Universal Precautions James Madison University Brought to you by Office of Health Promotion, JMU Health Center (2007) Purpose of this Training Teach the principles behind the prevention of disease transmission.
Universal Precautions James Madison University Brought to you by Office of Health Promotion, JMU Health Center (2007) Purpose of this Training Teach the principles behind the prevention of disease transmission.
Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another?
 Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another? HIV transmission can occur when blood, semen (including pre-seminal fluid or "pre-cum"),
Frequently Asked Questions about HIV/AIDS: Transmission and Prevention How is HIV passed from one person to another? HIV transmission can occur when blood, semen (including pre-seminal fluid or "pre-cum"),
Sexually Transmitted Infections
 Sexually Transmitted Infections STI Director/ Centers for Disease Control Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: -Bacterial (Chlamydia, LGV,
Sexually Transmitted Infections STI Director/ Centers for Disease Control Overview Definition of STIs: What are they? Transmission: How are they spread? Types of infection: -Bacterial (Chlamydia, LGV,
Vaccination Policy. Background: Meningococcal Disease on Campus
 Vaccination Policy EDMC institutions shall recognize all state and federal vaccination and immunization requirements. Institutions, with the support of EDMC regulatory affairs and compliance and legal
Vaccination Policy EDMC institutions shall recognize all state and federal vaccination and immunization requirements. Institutions, with the support of EDMC regulatory affairs and compliance and legal
School Nursing and Health. Standard Precautions. (aka Universal Precautions)
 School Nursing and Health Standard Precautions (aka Universal Precautions) August 2016 1 Standard Precautions Occupational Safety and Health Administration Federal Law 29 CFR bloodborne Pathogens 1910.1030(g)(2)(i)
School Nursing and Health Standard Precautions (aka Universal Precautions) August 2016 1 Standard Precautions Occupational Safety and Health Administration Federal Law 29 CFR bloodborne Pathogens 1910.1030(g)(2)(i)
Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May Contains information for:
 APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
Biology 3201 Unit 2 Reproduction: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STD s/sti s)
 Biology 3201 Unit 2 Reproduction: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STD s/sti s) STI s once called venereal diseases More than 20 STIs have now been identified most prevalent among teenagers and young adults.
Biology 3201 Unit 2 Reproduction: Sexually Transmitted Infections (STD s/sti s) STI s once called venereal diseases More than 20 STIs have now been identified most prevalent among teenagers and young adults.
July 14, Division of Dockets Management (HFA 305) Food and Drug Administration 5630 Fishers Lane, Rm Rockville, MD 20852
 July 14, 2015 Division of Dockets Management (HFA 305) Food and Drug Administration 5630 Fishers Lane, Rm. 1061 Rockville, MD 20852 Submitted via http://www.regulations.gov Re: Docket No. FDA-2015-D-1211
July 14, 2015 Division of Dockets Management (HFA 305) Food and Drug Administration 5630 Fishers Lane, Rm. 1061 Rockville, MD 20852 Submitted via http://www.regulations.gov Re: Docket No. FDA-2015-D-1211
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
How is it transferred?
 STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
STI s What is a STI? It is a contagious infection that is transferred from one person to another through sexual intercourse or other sexually- related behaviors. How is it transferred? The organisms live
You WILL survive Blood Borne Pathogens. Joanne Hathorn RN IL/NCSN Sheri Boress RN IL/NCSN Health Services WPS 60
 You WILL survive Blood Borne Pathogens Joanne Hathorn RN IL/NCSN Sheri Boress RN IL/NCSN Health Services WPS 60 At first you may be afraid of children getting sick, bleeding knees and bloody noses in your
You WILL survive Blood Borne Pathogens Joanne Hathorn RN IL/NCSN Sheri Boress RN IL/NCSN Health Services WPS 60 At first you may be afraid of children getting sick, bleeding knees and bloody noses in your
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Blood Borne Viruses (BBV) & What You Need To Know
 Blood Borne Viruses (BBV) & What You Need To Know P R E S E N T E D B Y Dee Smith WHAT YOU LL LEARN What are the 3 BBVs? S&S of each of the BBVs Transmission of BBVs What infection prevention & control
Blood Borne Viruses (BBV) & What You Need To Know P R E S E N T E D B Y Dee Smith WHAT YOU LL LEARN What are the 3 BBVs? S&S of each of the BBVs Transmission of BBVs What infection prevention & control
*IMPORTANT* PLEASE FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS TO COMPLY WITH FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY S IMMUNIZATION POLICY
 *IMPORTANT* PLEASE FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS TO COMPLY WITH FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY S IMMUNIZATION POLICY The FIU Immunization Documentation Form must be processed prior to registering for your
*IMPORTANT* PLEASE FOLLOW THESE INSTRUCTIONS TO COMPLY WITH FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY S IMMUNIZATION POLICY The FIU Immunization Documentation Form must be processed prior to registering for your
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training
 Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Bloodborne Pathogen Refresher Training This program will review your occupational risks and the steps that you and the County must take to reduce your risks of exposure. Employees must report any occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens. Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety
 Bloodborne Pathogens Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety Diseases of Concern Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Hepatitis C (non-a non-b Hepatitis) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus aka the
Bloodborne Pathogens Penn State University Environmental Health & Safety Diseases of Concern Hepatitis B (Serum Hepatitis) Hepatitis C (non-a non-b Hepatitis) HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus aka the
Hepatitis B. What is hepatitis B? How is HBV spread?
 2015 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is a liver condition caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). HBV can be chronic, in which case it can lead to liver failure, liver cancer, or
2015 Hepatitis B Hepatitis B What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is a liver condition caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). HBV can be chronic, in which case it can lead to liver failure, liver cancer, or
Life Threatening Vocational Hazards Diseases and Toxins
 Life Threatening Vocational Hazards Diseases and Toxins INTRODUCTION What is the blood-borne pathogens standard? 29CFR 1910.1030 Who needs blood-borne pathogens (BBP) training? What content needs to be
Life Threatening Vocational Hazards Diseases and Toxins INTRODUCTION What is the blood-borne pathogens standard? 29CFR 1910.1030 Who needs blood-borne pathogens (BBP) training? What content needs to be
How does HBV affect the liver?
 Hepatitis B Why is the liver important? Your liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions. It s the largest solid organ in the body and is located under your rib cage on the upper right
Hepatitis B Why is the liver important? Your liver is a vital organ that performs many essential functions. It s the largest solid organ in the body and is located under your rib cage on the upper right
Confronting Ebola. Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy
 Confronting Ebola Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy All materials provided by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. October 16, 2014 What You Need to Know about Ebola The
Confronting Ebola Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy All materials provided by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. October 16, 2014 What You Need to Know about Ebola The
In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise.
 Adapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007 In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise.
Adapted From: Sexually Transmitted Infections Pamphlet. Public Health Agency of Canada, 2007 In Canada and around the world, the trend is clear: sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are on the rise.
BLOOD DONOR INTERVIEW AND PHYSICAL
 EXERCISE : BLOOD DONOR INTERVIEW AND PHYSICAL Skills: 20 points Objectives:. Determine if an individual is eligible to donate blood by proper performance of the donor interview. 2. Identify the conditions
EXERCISE : BLOOD DONOR INTERVIEW AND PHYSICAL Skills: 20 points Objectives:. Determine if an individual is eligible to donate blood by proper performance of the donor interview. 2. Identify the conditions
Communicable Diseases
 Chapter 23 Communicable Diseases Disease that s spread from one living organism to another or through the environment Infection occurs when pathogens in the body multiply and damage body cells Main Pathogens
Chapter 23 Communicable Diseases Disease that s spread from one living organism to another or through the environment Infection occurs when pathogens in the body multiply and damage body cells Main Pathogens
Increased Risk Donors. November 1, 2018 BC Kidney Days. Jagbir Gill MD MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UBC
 Increased Risk Donors November 1, 2018 BC Kidney Days Jagbir Gill MD MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UBC Median dialysis exposure prior to DDKT Case scenarios Which donors should we accept kidneys
Increased Risk Donors November 1, 2018 BC Kidney Days Jagbir Gill MD MPH Associate Professor of Medicine UBC Median dialysis exposure prior to DDKT Case scenarios Which donors should we accept kidneys
Awareness Support Information Prevention
 #CThis #CureThis Awareness Support Information Prevention For more information visit: www.hepinfo.ie What is Hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver, causing it to become inflamed
#CThis #CureThis Awareness Support Information Prevention For more information visit: www.hepinfo.ie What is Hepatitis C? Hepatitis C is a viral infection that affects the liver, causing it to become inflamed
HIV/AIDS. The Essential Facts
 HIV/AIDS The Essential Facts Educating the Church About HIV/AIDS Over the past decade, limited attention has been paid to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) epidemic in the United States. New England
HIV/AIDS The Essential Facts Educating the Church About HIV/AIDS Over the past decade, limited attention has been paid to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) epidemic in the United States. New England
Breastfeeding Center Milk Connection Questionnaire and Release for Donor
 Breastfeeding Center Milk Connection Questionnaire and Release for Donor All of us at The Breastfeeding Center are deeply grateful to you for your important gift to infants in our community. Your donated
Breastfeeding Center Milk Connection Questionnaire and Release for Donor All of us at The Breastfeeding Center are deeply grateful to you for your important gift to infants in our community. Your donated
OVERVIEW SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS REPORTS STI BASICS WATCH OUT! HOW TO PREVENT STIs. Sexually Transmitted Infections Reports
 UNIT NINE: UNDERSTANDING & PREVENTING SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS OVERVIEW SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS REPORTS STI BASICS WATCH OUT! HOW TO PREVENT STIs Overview When compared to the other industrialized
UNIT NINE: UNDERSTANDING & PREVENTING SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS OVERVIEW SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS REPORTS STI BASICS WATCH OUT! HOW TO PREVENT STIs Overview When compared to the other industrialized
