' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' ' s p s U M OSTEOPOROSIS: PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND BONE REMODELLING
|
|
|
- Toby Skinner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ' s p s U M ' OSTEOPOROSIS: PATHOPHYSIOLOGY AND BONE REMODELLING Louis~Georges Ste~Marie, MD, CSPQ, Associate Professor of Medicine, Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universite de Montreal, Director, Laboratory of Metabolic Bone Diseases, Centre de Recherche Clinique Andre Viallet, Hopi tal Saint~Luc, Montreal, Quebec ABSTRACT RESUME Osteoporosis is a skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and deterioration of bone micro-architecture resulting in bone fragility. Normal bone remodelling in the adult follows a precise sequence of cellular events: activation, bone resorption, reversal phase and then, bone formation. This sequence of cellular activities occurring at a given site on trabecular bone surfaces or in cortical bone is called the bone remodelling unit (BRU). Bone mass results from the sum of focal bone balance at each BRU. After the age of 35, there is a physiological bone loss due to focal imbalance between the resorption and the formation phases at the BRU level. In Type I osteoporosis, observed in postmenopausal women, there is a predominant trabecular bone loss due to an increased number of new BRUs and a more pronounced unbalanced coupling between resorption and formation. This results in thinning of trabeculae but also in irreversible trabecular perforations with subsequent deterioration of the trabecular bone micro-architecture. In Type II osteoporosis, observed in older people, cortical bone loss is mainly due to secondary hyperparathyroidism due to vitamin D and/or calcium deficiency. L' osteoporose est une maladie du squelette caracterisee par une faible masse osseme et une deterioration de Ia micro-architecture des os qui conduit a leur fragilisation. Le remplacement des tissus osseux chez l'adulte s'effectue sewn une sequence precise d'evenements au niveau cellulaire : activation, resorption, phase de reversion et formation. Cette sequence d' activites cellulaires qui s' observe en des lieux precis de Ia surface osseuse trabeculaire ou dans l' os cortical porte le nom d' «unite de remade/age osseux" (bone remodelling unit ou BRU). La masse osseme depend de Ia somme des bilans osseux focaux a chaque BRU. Apres l' age de 35 ans, on observe une perte physiowgique de tissm osseux due a un desequilibre focal entre les phases de resorption et de formation au niveau des BRU. Dans l'osteoporose de type I, observee chez les femmes menopausees, on observe surtout une perte d'os trabeculaire due a une augmentation du nombre de nouveaux BRU eta un desequilibre plm prononce entre les phenomenes de resorption et de formation. Ceci entraine un amincissement de Ia surface osseme trabeculaire ainsi que des perforations irreversibles de l' os trabeculaire conduisant a une deterioration de Ia micro-architecture osseuse. Dans l' osteoporose de type II, observee chez les personnes plus iigees, Ia perte d' os cortical est principalement due a l'hyperparathyroidisme secondaire came par une carence en vitamine D ou en calcium. KEY WORDS Osteoporosis, pathophysiowgy, bone remodeling, histomorphometry. J SOGC 1995;17: JOURNAL SOGC 1205 DECEMBER 1995
2 INTRODUCING NIDAGEL FOR BAGTERIAL VAGINOSIS. Bacterial vaginosis' is the most common vaginal infection: Now there's a product with fewer side effects than oral metronidazole: Cure rates with new NidaGel vaginal gel (78-91 %)" 8 have been shown to be similar to those seen with oral metronidazole (71-88%)? 913 As a low dose local therapy, NidaGel has a much lower incidence of cramps, pain, nausea and metallic taste commonly associated with oral metronidazole? The most common adverse effect seen with NidaGel is symptomatic vaginal candidiasis.' With no reported alcohol interaction~ a short 5 day therapy and a greaseless, colourless, non-staining gel, NidaGellets your patients be a little less worried about their vaginosis, and a little more about their weekend. Sanford Guide to Antimicrobial Therapy recommends NidaGel as a first line therapy for bacterial vaginosis.14 TFormerly called: Non-specific vaginitis, Garnerella vaginalis, Haemophilus vaginitis or anaerobic vaginosis. -~ ~ ~No LOCAL THERAPY FOR A LOCAL PROBLEM. IFEARING I Ferring Inc. 515 Consumers Road, Suite 304, Toronto, ON M2J 4Z2
3 DEFINITION The currently accepted definition of osteoporosis is: "A systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, with a consequent increase in bone fragility and susceptibility to fracture risk." 1 A major component of the bone fragility in osteoporosis is the low bone mass which results from either: 1 ) a small peak bone mass achieved at young adulthood, 2) an increased bone loss occurring at menopause or at later ages or 3) a combination of both mechanisms. Many factors will influence the achievement of peak bone mass and subsequent bone loss including physical activity, genetic factors (mainly for peak bone mass), nutritional, and hormonal factors. A classification of osteoporosis has been proposed distinguishing the disease into Type I and Type II on the basis of age of onset, type of fractures, and hormonal changes. 2 It is hypothesized that their underlying pathophysiology is different. Type I osteoporosis (or postmenopausal osteoporosis) occurs mainly in women after menopause and will result in vertebral crush fractures due to the fact that the bone loss induced by estrogen deficiency affects predominantly trabecular bone. Type II osteoporosis (or senile osteoporosis) is observed in both sexes after the age of 70. It causes mainly hip fractures resulting from a predominant loss of cortical bone, possibly due to secondary hyperparathyroidism which is frequently observed in the elderly. NORMAL BONE REMODELLING Throughout adult life, bone is continuously being turned over. This leads to the renewal of bone tissue, maintaining the biomechanical properties of the skeleton. The major bone cells involved in bone remodelling are the osteoclasts which are responsible for bone resorption and the osteoblasts which synthesize bone matrix and lead to its mineralization. The process of bone remodelling is a precise sequence of cellular activities occurring at a given site on trabecular bone surfaces or in cortical bone.' First, there is a phase of activation leading to the retraction of lining cells from the bone surface. In the bone marrow, osteoclast precursors proliferate and differentiate themselves into mature osteoclasts. These active osteoclasts are attracted to this specific locus of bone surface. The second step is the phase of bone resorption by the team of osteoclasts which will excavate an erosion cavity (Howship's lacuna). This lasts for seven to 20 days and then the osteoclasts disappear. The reversal phase follows, during which mononuclear cells prepare the bony lacuna for the next step. It is at this stage that the factors involved in the coupling of bone formation to bone resorption (possibly insulin growth factor II, transforming growth factor B, collagen fragments... ) play their roles. They stimulate the proliferation and the differentiation of the osteoblasts. During the phase of bone formation, the osteoblasts synthesize layers of osteoid matrix which are mineralized subsequently. The result of this bone forming activity is the bone structural unit (BSU) which is delineated on one side by the bottom of the "ex"-lacuna and on the other by the trabecular border. The thickness of the BSU can be measured by histomorphometry and it is globally a good parameter of bone formation. This temporal and spatial sequence of cellular activities is called the bone remodelling unit (BRU). This constitutes an intermediary level of organization between the cellular level and the organ level. Therefore, bone mass will be affected by the focal bone balance (resulting from the difference between the bone resorption and the bone formation) at each BRU and by the number of BRUs. AGE DEPENDENT BONE LOSS After the age of 35, bone mass decreases with age. This bone loss results from a focal imbalance between the resorption and the formation phases at the BRU level, the quantity of deposited bone being smaller than that resorbed. 4 The bone loss is, thus, the sum of the focal bone deficits of all of the BRUs. This imbalance is mainly due to a decrease in the formation period which results in thinner BSUs. Consequently, the bony trabeculae become thinner. Although bone resorption does not seem to be increased (the depth of the resorption cavities is not increased), i osteoclasts can perforate these thin trabeculae. When trabecular perforations do occur, bone loss then becomes irreversible.' In addition, the perforations will lead to a loss of trabecular elements resulting in discontinuity of the trabecular network. This deterioration of the trabecular bone micro-architecture will contribute, independently of the low bone mass, to the decreased mechanical resistance of bone.' JOURNAL SOGC 1207 DECEMBER 1995
4 PosT-MENOPAUSAL BoNE Loss AND TYPE I OSTEOPOROSIS At the time of the menopause, the negative balance between bone formation and bone resorption is more pronounced. The decrease of estrogen secretion leads to the activation of bone remodelling with an increased number of new BRUs. In addition, there is possibly a stimulation of bone resorption either due to more active osteoclasts or a greater number of osteoclasts at each resorption site.' Adding to the age dependent decrease in bone formation, these two mechanisms will cause the accelerated bone loss observed in the first years after menopause." Moreover, the trabecular perforation phenomenon is more marked due to increased resorption activity on thinned trabeculae. This increased bone remodelling at menopause translates into rises in serum and urinary concentrations of biochemical markers of bone formation (total and bone isoenzyme of serum alkaline phosphatase, serum osteocalcin) and of bone resorption (urinary excretion of calcium, hydroxyproline and pyridinolines).10 TYPE II OSTEOPOROSIS With advancing age, the cortical thickness decreases whereas the cortical porosity increases. The bone remodelling is accelerated in cortical bone and at the cortico-endosteal envelope leading to an expansion of the medullary cavity at the expense of the cortex. 11 Histomorphometric analyses of bone biopsies taken from subjects with recent femoral neck fractures showed that the trabecular bone volume was normal but the cortical thickness was decreased with increased parameters of bone resorption. 1 ' Secondary hyperparathyroidism due to vitamin D and/or calcium deficiency is not rare in the elderly population.11 This hyperparathyroidism might play an important role in the increased fragility of the femoral neck by increasing cortical bone remodelling. In addition, it was shown recently that there was a significant increase in the serum level of undercarboxylated osteocalcin (ucoc) in an elderly institutionalized population.h This increased ucoc was found to be a marker of the risk of hip fracture. The mechanism by which ucoc is linked to bone fragility is yet unclear. SECONDARY OSTEOPOROSIS Osteoporosis can be induced by various diseases, drugs, and immobilization. In these cases, the bone disease is called "secondary osteoporosis." The mechanism(s) underlying the bone loss in secondary osteoporosis will vary according to the cause. In hyperthyroidism, there is an increase in bone remodelling with an increased birthrate ofbrus which will lead to an increased number of focal bone deficits. The sum of the latter will result in an accelerated bone loss. Excess of glucocorticoids (iatrogenic or endogenous Cushing's syndrome) is mainly due to a marked depression of the osteoblastic activity resulting in reduced thickness of the BSU. When glucocorticoids are administered at high doses, secondary hyperparathyroidism might develop as a result. This will increase the birthrate of the BRUs and thus, bone loss will be more marked. Osteoporosis due to immobilization is usually also quite severe because there is the same combination of increased birthrate of the BRUs with decreased bone formation. In conclusion, the underlying mechanisms of osteoporosis are multiple. Recent advances in bone histomorphometry and biochemical markers of bone remodelling have increased our understanding of the pathophysiology of the disease. This knowledge is important for the proper use of currently available preventive measures and treatments. However, the precise mechanisms of the control of bone remodelling are not well known. Their elucidation will help in designing new therapeutic approaches. REFERENCES 1. Anonymous. Consensus development conference: diagnosis, prophylaxis and treatment of osteoporosis. Am J Med 1993;94: Riggs BL, Melton Ill U. Evidence for two distinct syndromes of involutional osteoporosis. Am J Med 1983;75: Eriksen EF. Normal and pathological remodelling of human trabecular bone: three-dimensional reconstruction of the remodelling sequence in normals and in metabolic bone disease. Endocrine Rev 1986;7: Lips P, Courpron P, Meunier PJ. Mean wall thickness of trabecular bone packets in the human iliac crest biopsies. Bone Miner 1989;6: JOURNAL SOGC 1208 DECEMBER 1995
5 5. Cohen-Solal ME, Shih MS, Lundy MW, Parfitt AM. A new method for measuring cancellous bone erosion depth: application to the cellular mechanisms of bone loss in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 1991;6: Parfitt AM, Matthews CHE, Villanueva AR, Kleerekoper M, Frame B, Rao DS. Relationships between surface volume and thickness of iliac trabecular bone in aging and in osteoporosis. Implications for the microanatomic and cellular mechanisms of bone loss. J Clin Invest 1983; 72: Steiniche T, Christiansen P, Vesterby A et al. Marked changes in iliac crest bone structure in postmenopausal osteoporotic patients without any signs of disturbed bone remodelling or balance. Bone 1994;15: Eriksen EF, Hodgson SF, Eastell R, Cedel SL, O'Fallon WM, Riggs BL. Cancellous bone remodeling in type I (postmenopausal) osteoporosis: quantitative assessment of rates of formation, resorption, and bone loss at tissue and cellular levels. J Bone Miner Res 1990;5: Dempster DW, Lindsay R. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis. Lancet 1993;341: Delmas PD. Biochemical markers of bone turnover. J Bone Miner Res 1993:8(suppl 2):S549-S Reeve J. Osteoporosis. In: Cohen RD, Lewis B, Alberti KGMM, Denman AM (Eds). The metabolic and molecular basis of acquired diseases. London, Balliere Tindall 1990: Lips P, Netelenbos JC, Jongen HKM et al. Histomorphometric profile and vitamin D status in patients with femoral neck fracture. Metab Bone Dis Rei Res 1982; 4: Compston JE, Silver AC, Croucher PI, Brown RC, Woodhead JS. Elevated serum intact parathyroid hormone levels in elderly patients with hip fracture. Clin Endocrinol 1989;31 : Szulc P, Chapuy MC, Meunier PJ, Delmas PD. Serum undercarboxylated osteocalcin is a marker of the risk of hip fracture in elderly women. J Clin Invest 1993; 91: JOURNAL SOGC 1209 DECEMBER 1995
Bone Cell Biology. David W. Dempster, PhD. Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University. Bone Remodeling
 Bone Cell Biology David W. Dempster, PhD Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University Bone Remodeling The skeleton, out of site and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about
Bone Cell Biology David W. Dempster, PhD Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University Bone Remodeling The skeleton, out of site and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about
Bone Cell Biology. The Remodeling Cycle. Bone Remodeling. Remodeling Maintains Mechanical Strength. David W. Dempster, PhD
 Bone Remodeling Bone Cell Biology David W. Dempster, PhD Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University The skeleton, out of site and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about
Bone Remodeling Bone Cell Biology David W. Dempster, PhD Professor of Clinical Pathology Columbia University The skeleton, out of site and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about
The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It!
 The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It! April 7, 2001 Joseph E. Zerwekh, Ph.D. Interrelationship of Intestinal, Skeletal, and Renal Systems to the Overall Maintenance of Normal Calcium
The Skeletal Response to Aging: There s No Bones About It! April 7, 2001 Joseph E. Zerwekh, Ph.D. Interrelationship of Intestinal, Skeletal, and Renal Systems to the Overall Maintenance of Normal Calcium
BIOLOGY and BIOMECHANICS OF NORMAL & OSTEOPOROTIC BONE
 BIOLOGY and BIOMECHANICS OF NORMAL & OSTEOPOROTIC BONE Andreas Panagopoulos, MD, PhD Assistant Professor in Orthopaedics University Hospital of Patras, Orthopaedic Clinic Objectives Bone structure and
BIOLOGY and BIOMECHANICS OF NORMAL & OSTEOPOROTIC BONE Andreas Panagopoulos, MD, PhD Assistant Professor in Orthopaedics University Hospital of Patras, Orthopaedic Clinic Objectives Bone structure and
Osteoporosis. Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease
 Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
Osteoporosis Treatment of a Silently Developing Disease Marc K. Drezner, MD Senior Associate Dean Emeritus Professor of Medicine Emeritus University of Wisconsin-Madison Auditorium The Forest at Duke October
BONE REMODELLING. Tim Arnett. University College London. Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology
 BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
BONE REMODELLING Tim Arnett Department of Anatomy and Developmental Biology University College London The skeleton, out of sight and often out of mind, is a formidable mass of tissue occupying about 9%
Pathophysiology of Postmenopausal & Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis. March 15, 2016 Bone ECHO Kate T Queen, MD
 Pathophysiology of Postmenopausal & Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis March 15, 2016 Bone ECHO Kate T Queen, MD Review: normal bone formation Bone Modeling Remodeling Peak Bone Mass Maximum bone mass
Pathophysiology of Postmenopausal & Glucocorticoid Induced Osteoporosis March 15, 2016 Bone ECHO Kate T Queen, MD Review: normal bone formation Bone Modeling Remodeling Peak Bone Mass Maximum bone mass
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
BONE HISTOLOGY SLIDE PRESENTATION
 BONE HISTOLOGY SLIDE PRESENTATION PRESENTED BY: SKELETECH, INC. Clients and Friends: SkeleTech invites you to use these complimentary images for your own presentations or as teaching slides for bone biology.
BONE HISTOLOGY SLIDE PRESENTATION PRESENTED BY: SKELETECH, INC. Clients and Friends: SkeleTech invites you to use these complimentary images for your own presentations or as teaching slides for bone biology.
Influence of remodeling on the mineralization of bone tissue
 Influence of remodeling on the mineralization of bone tissue G. Boivin, D. Farlay, Y. Bala, A. Doublier, P.J. Meunier, P.D. Delmas INSERM Unité 831, Université de Lyon, Lyon, France. Short Title : Bone
Influence of remodeling on the mineralization of bone tissue G. Boivin, D. Farlay, Y. Bala, A. Doublier, P.J. Meunier, P.D. Delmas INSERM Unité 831, Université de Lyon, Lyon, France. Short Title : Bone
CIC EDIZIONI INTERNAZIONALI. Bone fragility: current reviews and clinical features. Mini review
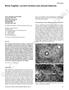 Mini review Paolo Tranquilli Leali, MD, FBSE Carlo Doria, MD, PhD Alexandros Zachos, MD Adriano Ruggiu, MD Fabio Milia, MD Francesca Barca, MD Orthopaedic Department, University of Sassari, Sassari, Italy
Mini review Paolo Tranquilli Leali, MD, FBSE Carlo Doria, MD, PhD Alexandros Zachos, MD Adriano Ruggiu, MD Fabio Milia, MD Francesca Barca, MD Orthopaedic Department, University of Sassari, Sassari, Italy
Skeletal Manifestations
 Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
Skeletal Manifestations of Metabolic Bone Disease Mishaela R. Rubin, MD February 21, 2008 The Three Ages of Women Gustav Klimt 1905 1 Lecture Outline Osteoporosis epidemiology diagnosis secondary causes
What is Osteoporosis?
 What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
What is Osteoporosis? 2000 NIH Definition A skeletal disorder characterized by compromised bone strength predisposing a person to an increased risk of fracture. Bone strength reflects the integration of
Fragile Bones and how to recognise them. Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey
 Fragile Bones and how to recognise them Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by compromised bone
Fragile Bones and how to recognise them Rod Hughes Consultant physician and rheumatologist St Peter s hospital Chertsey Osteoporosis Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder characterised by compromised bone
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Calcif Tissue Int. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 January 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Calcif Tissue Int. 2010 January ; 86(1): 67 71. doi:10.1007/s00223-009-9315-x. Morphological Assessment of Basic Multicellular Unit
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Calcif Tissue Int. 2010 January ; 86(1): 67 71. doi:10.1007/s00223-009-9315-x. Morphological Assessment of Basic Multicellular Unit
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Osteoporosis. Current Trend in Osteoporosis Management for Elderly in HK- Medical Perspective. Old Definition of Osteoporosis
 Current Trend in Osteoporosis Management for Elderly in HK- Medical Perspective Dr Dicky T.K. Choy Physician Jockey Club Centre for Osteoporosis Care and Control, CUHK Osteoporosis Global public health
Current Trend in Osteoporosis Management for Elderly in HK- Medical Perspective Dr Dicky T.K. Choy Physician Jockey Club Centre for Osteoporosis Care and Control, CUHK Osteoporosis Global public health
CIC Edizioni Internazionali. Bone quality and bone strength: benefits of the bone-forming approach. Mini-review
 Bone quality and bone strength: benefits of the bone-forming approach Giovanni Iolascon Laura Frizzi Gioconda Di Pietro Annarita Capaldo Fabrizio Luciano Francesca Gimigliano Department of Medical and
Bone quality and bone strength: benefits of the bone-forming approach Giovanni Iolascon Laura Frizzi Gioconda Di Pietro Annarita Capaldo Fabrizio Luciano Francesca Gimigliano Department of Medical and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SERUM OSTEOCALCIN, SHALL WE CONSIDER IT AS A BIOCHEMICAL MARKER FOR OSTEOPOROSIS IN POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN
 SERUM OSTEOCALCIN, SHALL WE CONSIDER IT AS A BIOCHEMICAL MARKER FOR OSTEOPOROSIS IN POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN V. S. Kalai Selvi 1, K. Prabhu 2, Monika Gupta 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: V. S. Kalai Selvi, K.
SERUM OSTEOCALCIN, SHALL WE CONSIDER IT AS A BIOCHEMICAL MARKER FOR OSTEOPOROSIS IN POSTMENOPAUSAL WOMEN V. S. Kalai Selvi 1, K. Prabhu 2, Monika Gupta 3. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: V. S. Kalai Selvi, K.
Osteoporosis. Open Access. John A. Kanis. Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK
 Journal of Medical Sciences (2010); 3(3): 00-00 Review Article Osteoporosis Open Access John A. Kanis WHO Collaborating Centre for Metabolic Bone Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK incorporated into
Journal of Medical Sciences (2010); 3(3): 00-00 Review Article Osteoporosis Open Access John A. Kanis WHO Collaborating Centre for Metabolic Bone Diseases, University of Sheffield, UK incorporated into
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis
 Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
Chapter 39: Exercise prescription in those with osteoporosis American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York:
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals. Massimo Marenzana
 CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
CT Imaging of skeleton in small animals Massimo Marenzana Introduction Osteoporosis is a disease in which bones become fragile and more likely to break. It can be defined as a systemic skeletal disease
Overview. Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases. People Centred Positive Compassion Excellence
 Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
Overview Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease Dr Chandini Rao Consultant Rheumatologist Bone Biology Osteoporosis Osteomalacia Paget s Disease Cases Bone Biology Osteoporosis Increased bone remodelling
BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie. Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis
 BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis Food for thought... How old would you be if you didn t know how old you were? DEFINITION: Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (OP) is a disease
BONE HEALTH Dr. Tia Lillie Exercise, Physical Activity and Osteoporosis Food for thought... How old would you be if you didn t know how old you were? DEFINITION: Osteoporosis Osteoporosis (OP) is a disease
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
Author(s): University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Cell and Developmental Biology License: Unless otherwise noted, the content of this course material is licensed under a Creative Commons
The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease
 The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease Howard Morris PhD, FAACB, FFSc(RCPA) President, IFCC Professor of Medical Sciences, University of South Australia, Clinical Scientist, SA Pathology
The Role of the Laboratory in Metabolic Bone Disease Howard Morris PhD, FAACB, FFSc(RCPA) President, IFCC Professor of Medical Sciences, University of South Australia, Clinical Scientist, SA Pathology
Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method
 190.19 - Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method Collagen crosslinks, part of the matrix of bone upon which bone mineral is deposited, are biochemical markers the excretion of which provides a quantitative measurement
190.19 - Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method Collagen crosslinks, part of the matrix of bone upon which bone mineral is deposited, are biochemical markers the excretion of which provides a quantitative measurement
Reduced bone formation in non-steroid treated
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1989; 48: 483-487 Reduced bone formation in non-steroid treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis J E COMPSTON,' S VEDI,1 R W E MELLISH,' P CROUCHER,' AND M M O'SULLIVAN2
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1989; 48: 483-487 Reduced bone formation in non-steroid treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis J E COMPSTON,' S VEDI,1 R W E MELLISH,' P CROUCHER,' AND M M O'SULLIVAN2
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues
 An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
An Introduction to the Skeletal System Skeletal system includes Bones of the skeleton Cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues Functions of the Skeletal System Support Storage of minerals (calcium)
The Bare Bones of Osteoporosis. Wendy Rosenthal, PharmD
 The Bare Bones of Osteoporosis Wendy Rosenthal, PharmD Definition A systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, with a consequent increase
The Bare Bones of Osteoporosis Wendy Rosenthal, PharmD Definition A systemic skeletal disease characterized by low bone mass and microarchitectural deterioration of bone tissue, with a consequent increase
Osteoporosis. When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of.
 Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Osteoporosis When we talk about osteoporosis, we have to be familiar with the constituents of bone and what it is formed of. Osteoblasts by definition are those cells present in the bone and are involved
Because the low bone mass and deterioration
 OSTEOPOROSIS A look at recent expert guidelines and key studies in bone health, the findings of which affect your patients young and old Steven R. Goldstein, MD Dr. Goldstein is Professor of Obstetrics
OSTEOPOROSIS A look at recent expert guidelines and key studies in bone health, the findings of which affect your patients young and old Steven R. Goldstein, MD Dr. Goldstein is Professor of Obstetrics
Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary
 Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 FDA Indication 1 : Forteo (teriparatide) is indicated for: the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis
Forteo (teriparatide) Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1 FDA Indication 1 : Forteo (teriparatide) is indicated for: the treatment of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis
SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over 3 Weeks. A SEPARATE WORKSHEET WILL BE PROVIDED.
 BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
BIO 211; Anatomy and Physiology I REFERENCE: CHAPTER 07 1 Dr. Lawrence Altman Naugatuck Valley Community College LECTURE TOPICS OUTLINE SKELETAL SYSTEM I NOTE: LAB ASSIGNMENTS for this topic will run over
Elecsys bone marker panel. Optimal patient management starts in the laboratory
 bone marker panel Optimal patient management starts in the laboratory Complete solution for osteoporosis The most complete bone metabolism panel on a single platform bone marker assays are important diagnostic
bone marker panel Optimal patient management starts in the laboratory Complete solution for osteoporosis The most complete bone metabolism panel on a single platform bone marker assays are important diagnostic
Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist
 VOLUME 8, ISSUE 3, YEAR 2009 Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist Peter R. McNally, DO, FACP, FACG University Colorado at Denver, School of Medicine, Center for Human Simulation Series Introduction:
VOLUME 8, ISSUE 3, YEAR 2009 Metabolic Bone Disease and the Gastroenterologist Peter R. McNally, DO, FACP, FACG University Colorado at Denver, School of Medicine, Center for Human Simulation Series Introduction:
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS
 TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS Summary Prevention is the key issue in the management of osteoporosis. HRT is the agent of choice for prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates and Calcitonin
TREATMENT OF OSTEOPOROSIS Summary Prevention is the key issue in the management of osteoporosis. HRT is the agent of choice for prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bisphosphonates and Calcitonin
Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength
 Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength Consultant / advisor: Amgen, Eli Lilly, Merck Disclosures Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA mbouxsei@bidmc.harvard.edu
Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength Consultant / advisor: Amgen, Eli Lilly, Merck Disclosures Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA mbouxsei@bidmc.harvard.edu
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis
 Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
Clinician s Guide to Prevention and Treatment of Osteoporosis Published: 15 August 2014 committee of the National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF) Tipawan khiemsontia,md outline Basic pathophysiology screening
Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
C h a p t e r 6 Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin
Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method
 190.19 - Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method Collagen crosslinks, part of the matrix of bone upon which bone mineral is deposited, are biochemical markers the excretion of which provides a quantitative measurement
190.19 - Collagen Crosslinks, Any Method Collagen crosslinks, part of the matrix of bone upon which bone mineral is deposited, are biochemical markers the excretion of which provides a quantitative measurement
THE ORIGINS AND PREVENTION OF OSTEOPOROSIS IN WOMEN
 Proc. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 1998; 29:425-431 THE ORIGINS AND PREVENTION OF OSTEOPOROSIS IN WOMEN D.W. Purdie, * Centre for Metabolic Bone Disease, Hull Royal Infirmary, The University of Hull and
Proc. R. Coll. Physicians Edinb. 1998; 29:425-431 THE ORIGINS AND PREVENTION OF OSTEOPOROSIS IN WOMEN D.W. Purdie, * Centre for Metabolic Bone Disease, Hull Royal Infirmary, The University of Hull and
Osteoporosis, Osteomalasia & rickets. Bone disorders
 Osteoporosis, Osteomalasia & rickets Bone disorders Thank You for Your comments Voice--- Ok Lecture too long--- this is in schedule??? More interaction--- I can do that inshalla Slides are crowded--- but
Osteoporosis, Osteomalasia & rickets Bone disorders Thank You for Your comments Voice--- Ok Lecture too long--- this is in schedule??? More interaction--- I can do that inshalla Slides are crowded--- but
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY. Osteoporosis. A Thesis Submitted to the. University Honors Program. In Partial Fulfillment of the
 NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Osteoporosis A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements of the Baccalaureate Degree With University Honors Department of
NORTHERN ILLINOIS UNIVERSITY Osteoporosis A Thesis Submitted to the University Honors Program In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements of the Baccalaureate Degree With University Honors Department of
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases. Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary
 Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Fig Articular cartilage. Epiphysis. Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line. Marrow cavity. Yellow bone marrow. Periosteum. Nutrient foramen Diaphysis
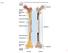 Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Fig. 7.1 Articular cartilage Epiphysis Red bone marrow Epiphyseal line Marrow cavity Yellow bone marrow Nutrient foramen Diaphysis Site of endosteum Compact bone Spongy bone Epiphyseal line Epiphysis Articular
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health. Noah S. Schenkman, MD
 Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Calcium Nephrolithiasis and Bone Health Noah S. Schenkman, MD Associate Professor of Urology and Residency Program Director, University of Virginia Health System; Charlottesville, Virginia Objectives:
Osteoporosis Update. Greg Summers Consultant Rheumatologist
 Osteoporosis Update Greg Summers Consultant Rheumatologist DEFINITION OSTEOPOROSIS is LOW BONE MASS (& micro-architectural deterioration) causing AN INCREASED RISK OF FRACTURE 23 years 82 years 23 y/o
Osteoporosis Update Greg Summers Consultant Rheumatologist DEFINITION OSTEOPOROSIS is LOW BONE MASS (& micro-architectural deterioration) causing AN INCREASED RISK OF FRACTURE 23 years 82 years 23 y/o
European Journal of Endocrinology (1997) ISSN
 European Journal of Endocrinology (1997) 137 167 171 ISSN 0804-4643 Change in C-terminal cross-linking domain of type I collagen in urine, a new marker of bone resorption, during and after gonadotropin-releasing
European Journal of Endocrinology (1997) 137 167 171 ISSN 0804-4643 Change in C-terminal cross-linking domain of type I collagen in urine, a new marker of bone resorption, during and after gonadotropin-releasing
The Bone Formation Defect in Idiopathic Juvenile Osteoporosis Is Surface-specific
 The Bone Formation Defect in Idiopathic Juvenile Osteoporosis Is Surface-specific F. RAUCH, 1 R. TRAVERS, 1 M. E. NORMAN, 2 A. TAYLOR, 2 A. M. PARFITT, 3 and F. H. GLORIEUX 1 1 Genetics Unit, Shriners
The Bone Formation Defect in Idiopathic Juvenile Osteoporosis Is Surface-specific F. RAUCH, 1 R. TRAVERS, 1 M. E. NORMAN, 2 A. TAYLOR, 2 A. M. PARFITT, 3 and F. H. GLORIEUX 1 1 Genetics Unit, Shriners
WHAT KEEPS OUR BONES STRONG?
 WHAT KEEPS OUR BONES STRONG? The role of diet and lifestyle in osteoporosis prevention Thomas Walczyk PhD, Associate Professor Food Science and Technology Programme Department of Chemistry, Faculty of
WHAT KEEPS OUR BONES STRONG? The role of diet and lifestyle in osteoporosis prevention Thomas Walczyk PhD, Associate Professor Food Science and Technology Programme Department of Chemistry, Faculty of
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue
 Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Chapter 6 Part B Bones and Skeletal Tissue 6.5 Bone Development Ossification (osteogenesis) is the process of bone tissue formation Formation of bony skeleton begins in month 2 of development Postnatal
Understanding Osteoporosis
 Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Understanding Osteoporosis Professor Juliet E. Compston Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT NOTICE This book is intended not as
Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism
 Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C516, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: wanghuiping@zju.edu.cn
Endocrine Regulation of Calcium and Phosphate Metabolism Huiping Wang ( 王会平 ), PhD Department of Physiology Rm C516, Block C, Research Building, School of Medicine Tel: 88208252 Email: wanghuiping@zju.edu.cn
OSTEOPOROSIS OSTEOPOROSIS. page 1 / 5
 page 1 / 5 page 2 / 5 osteoporosis pdf CONTENTS Overview 1 Background 1 Risk factors 4 Model synthesis 4 Possibilities for the future 5 Summary, conclusions and recommendations for research 7 Consequences
page 1 / 5 page 2 / 5 osteoporosis pdf CONTENTS Overview 1 Background 1 Risk factors 4 Model synthesis 4 Possibilities for the future 5 Summary, conclusions and recommendations for research 7 Consequences
Postmenopausal osteoporosis is a systemic
 OSTEOPOROSIS: HARD FACTS ABOUT BONES Steven T. Harris, MD, FACP* ABSTRACT As a consequence of the aging process, osteoporosis affects all men and women. Agerelated loss of bone mass leads to skeletal fragility
OSTEOPOROSIS: HARD FACTS ABOUT BONES Steven T. Harris, MD, FACP* ABSTRACT As a consequence of the aging process, osteoporosis affects all men and women. Agerelated loss of bone mass leads to skeletal fragility
Peggers Super Summaries Basic Sciences Bone
 Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio
 Osteoporosis 1 Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio 1) Objectives: a) To understand bone growth and development
Osteoporosis 1 Nutritional Aspects of Osteoporosis Care and Treatment Cynthia Smith, FNP-BC, RN, MSN, CCD Pars Osteoporosis Clinic, Belpre, Ohio 1) Objectives: a) To understand bone growth and development
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
Objectives. Discuss bone health and the consequences of osteoporosis on patients medical and disability status.
 Objectives Discuss bone health and the consequences of osteoporosis on patients medical and disability status. Discuss the pathophysiology of osteoporosis and major risk factors. Assess the major diagnostic
Objectives Discuss bone health and the consequences of osteoporosis on patients medical and disability status. Discuss the pathophysiology of osteoporosis and major risk factors. Assess the major diagnostic
Osteoporosis update. Dr. Claire Vandevelde Consultant Rheumatologist, LTHT
 Osteoporosis update Dr. Claire Vandevelde Consultant Rheumatologist, LTHT Outline Background BMD Tools for assessing fracture risk Case study Denosumab Treatment breaks BMD BMD predicts fracture risk but
Osteoporosis update Dr. Claire Vandevelde Consultant Rheumatologist, LTHT Outline Background BMD Tools for assessing fracture risk Case study Denosumab Treatment breaks BMD BMD predicts fracture risk but
Outline. Estrogens and SERMS The forgotten few! How Does Estrogen Work in Bone? Its Complex!!! 6/14/2013
 Outline Estrogens and SERMS The forgotten few! Clifford J Rosen MD rosenc@mmc.org Physiology of Estrogen and estrogen receptors Actions of estrogen on bone BMD, fracture, other off target effects Cohort
Outline Estrogens and SERMS The forgotten few! Clifford J Rosen MD rosenc@mmc.org Physiology of Estrogen and estrogen receptors Actions of estrogen on bone BMD, fracture, other off target effects Cohort
BMD: A Continuum of Risk WHO Bone Density Criteria
 Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis AGING MENOPAUSE OTHER RISK FACTORS RESORPTION > FORMATION Bone Loss LOW PEAK BONE MASS Steven T Harris
Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis Osteoporosis Diagnosis: BMD, FRAX and Assessment of Secondary Osteoporosis AGING MENOPAUSE OTHER RISK FACTORS RESORPTION > FORMATION Bone Loss LOW PEAK BONE MASS Steven T Harris
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies
 Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone Remodeling & Repair Pathologies Skeletal system remodels itself to maintain homeostasis Remodeling Maintainence replaces mineral reserves (osteocytes) of the matrix Remodelling recycles (osteoclasts)
Bone quality: the material and structural basis of bone strength
 J Bone Miner Metab (28) 2:1 8 Springer 28 DOI 1.17/s774-7-793-5 REVIEW ARTICLE Ego Seeman Bone quality: the material and structural basis of bone strength Received: August 1, 27 / Accepted: August 13,
J Bone Miner Metab (28) 2:1 8 Springer 28 DOI 1.17/s774-7-793-5 REVIEW ARTICLE Ego Seeman Bone quality: the material and structural basis of bone strength Received: August 1, 27 / Accepted: August 13,
JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL ACADEMIC RESEARCH FOR MULTIDISCIPLINARY Impact Factor 1.393, ISSN: , Volume 2, Issue 7, August 2014
 HYPOVITAMINOSIS D IN INDIAN FEMALES WITH POSTMENOPAUSAL OSTEOPOROSIS DR. SHAH WALIULLAH 1 DR. VINEET SHARMA 2 DR. R N SRIVASTAVA 3 DR. YASHODHARA PRADEEP 4 DR. A A MAHDI 5 DR. SANTOSH KUMAR 6 1 Research
HYPOVITAMINOSIS D IN INDIAN FEMALES WITH POSTMENOPAUSAL OSTEOPOROSIS DR. SHAH WALIULLAH 1 DR. VINEET SHARMA 2 DR. R N SRIVASTAVA 3 DR. YASHODHARA PRADEEP 4 DR. A A MAHDI 5 DR. SANTOSH KUMAR 6 1 Research
Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on
 Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on Strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by The Society for Endocrinology
Submission to the National Institute for Clinical Excellence on Strontium ranelate for the prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis by The Society for Endocrinology
Skeletal Tissues. Skeletal tissues. Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs.
 Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
Skeletal Tissues Functions 1) support 2) protection 3) movement Skeletal tissues Frame; muscles, organs and CT attach. Brain, spinal cord, thoracic organs; heart and lungs. Aids muscle contraction; generate
COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION OF NEW MEDICINAL PRODUCTS IN THE TREATMENT OF PRIMARY OSTEOPOROSIS
 European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 14 December 2005 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/552/95 Rev. 2 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) DRAFT GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION
European Medicines Agency Evaluation of Medicines for Human Use London, 14 December 2005 Doc. Ref. CPMP/EWP/552/95 Rev. 2 COMMITTEE FOR MEDICINAL PRODUCTS FOR HUMAN USE (CHMP) DRAFT GUIDELINE ON THE EVALUATION
Product: Denosumab (AMG 162) Clinical Study Report: month Primary Analysis Date: 21 November 2016 Page 1
 Date: 21 November 2016 Page 1 2. SYNOPSIS Name of Sponsor: Amgen Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA, USA Name of Finished Product: Prolia Name of Active Ingredient: denosumab Title of Study: Randomized, Double-blind,
Date: 21 November 2016 Page 1 2. SYNOPSIS Name of Sponsor: Amgen Inc., Thousand Oaks, CA, USA Name of Finished Product: Prolia Name of Active Ingredient: denosumab Title of Study: Randomized, Double-blind,
Osteoporosis. Overview
 v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
v2 Osteoporosis Overview Osteoporosis is defined as compromised bone strength that increases risk of fracture (NIH Consensus Conference, 2000). Bone strength is characterized by bone mineral density (BMD)
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis
 Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
Anabolic Therapy With Teriparatide Indications Beyond Osteoporosis Andreas Panagopoulos MD, PhD Upper Limb & Sports Medicine Orthopaedic Surgeon Assistant Professor, University of Patras Outline Teriparatide
OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE. Nothing to Disclose. Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco
 OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco Nothing to Disclose 1 Case History 59 YO WM referred for evaluation of diffuse
OSTEOMALACIA UPDATE Daniel D Bikle, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of California and VA Medical Center San Francisco Nothing to Disclose 1 Case History 59 YO WM referred for evaluation of diffuse
Parathyroid Hormone and Teriparatide for the Treatment of Osteoporosis: A Review of the Evidence and Suggested Guidelines for Its Use
 0163-769X/05/$20.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 26(5):688 703 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2005 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/er.2004-0006 Parathyroid Hormone and Teriparatide for the Treatment of Osteoporosis:
0163-769X/05/$20.00/0 Endocrine Reviews 26(5):688 703 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2005 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/er.2004-0006 Parathyroid Hormone and Teriparatide for the Treatment of Osteoporosis:
Drugs Affecting Bone. Rosa McCarty PhD. Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics
 Drugs Affecting Bone Rosa McCarty PhD Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics rmccarty@unimelb.edu.au Objectives At the end of this lecture you should have gained: An understanding of bone metabolism
Drugs Affecting Bone Rosa McCarty PhD Department of Pharmacology & Therapeutics rmccarty@unimelb.edu.au Objectives At the end of this lecture you should have gained: An understanding of bone metabolism
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of
 Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Bone What is bone? Specialized form of connective tissue: mineralized collagen matrix, therefore very rigid and strong while still retaining some degree of flexibility Other types of connective tissue:
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure I. An Introduction to the Skeletal System, p. 180 Objective: Describe the functions of the skeletal system The skeletal system includes: - bones of the skeleton
ANATOMY C027A: MINERALIZED TISSUE BIOLOGY: SKELETAL TISSUES. Please answer THREE Questions. All questions carry equal marks.
 Module Code: C27A UNIVERSITY OF LONDON (University College London) BSc DEGREE 2001 ANATOMY C027A: MINERALIZED TISSUE BIOLOGY: SKELETAL TISSUES 16 May 2001, 10.00am 1) Discuss the roles of ph, po2, phosphate
Module Code: C27A UNIVERSITY OF LONDON (University College London) BSc DEGREE 2001 ANATOMY C027A: MINERALIZED TISSUE BIOLOGY: SKELETAL TISSUES 16 May 2001, 10.00am 1) Discuss the roles of ph, po2, phosphate
Rama Nada. - Mousa Al-Abbadi. 1 P a g e
 - 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
- 1 - Rama Nada - - Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 P a g e Bones, Joints and Soft tissue tumors Before we start: the first 8 minutes was recalling to Dr.Mousa s duties, go over them in the slides. Wherever you see
Upcoming Agents for Osteoporosis
 Upcoming Agents for Osteoporosis May 5, 2017 Michael R. McClung, MD, FACP Director, Oregon Osteoporosis Center Portland, Oregon, USA Professorial Fellow, Institute of Health and Ageing Australian Catholic
Upcoming Agents for Osteoporosis May 5, 2017 Michael R. McClung, MD, FACP Director, Oregon Osteoporosis Center Portland, Oregon, USA Professorial Fellow, Institute of Health and Ageing Australian Catholic
Modélisation par éléments finis des effets des médicaments sur le remodelage osseux : Approche mécanobiologique
 Modélisation par éléments finis des effets des médicaments sur le remodelage osseux : Approche mécanobiologique Ridha Hambli Prisme Institute 8, Rue Léonard de Vinci, 45072 Orléans cedex 2, France Phone
Modélisation par éléments finis des effets des médicaments sur le remodelage osseux : Approche mécanobiologique Ridha Hambli Prisme Institute 8, Rue Léonard de Vinci, 45072 Orléans cedex 2, France Phone
Monitoring hormone replacement therapy by biochemical markers of bone metabolism in menopausal women
 727 REVIEW Monitoring hormone replacement therapy by biochemical markers of bone metabolism in menopausal women E Dogan, C Posaci... Biochemical markers of bone metabolism are divided into two groups:
727 REVIEW Monitoring hormone replacement therapy by biochemical markers of bone metabolism in menopausal women E Dogan, C Posaci... Biochemical markers of bone metabolism are divided into two groups:
Regulation of the skeletal mass through the life span
 Regulation of the skeletal mass through the life span Functions of the skeletal system Mechanical protection skull Movement leverage for muscles Mineral metabolism calcium store Erythropoiesis red blood
Regulation of the skeletal mass through the life span Functions of the skeletal system Mechanical protection skull Movement leverage for muscles Mineral metabolism calcium store Erythropoiesis red blood
ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION
 Parathyroid Hormone for Treatment of Osteoporosis Carolyn Crandall, MD ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Background: Osteoporosis is a common condition associated with multiple deleterious consequences. No therapy
Parathyroid Hormone for Treatment of Osteoporosis Carolyn Crandall, MD ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Background: Osteoporosis is a common condition associated with multiple deleterious consequences. No therapy
Prevention and Treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS 骨質疏鬆的預防與治療
 Prevention and Treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS 骨質疏鬆的預防與治療 Gwo Jaw Wang, M.D. 王國照教授 University of Virginia (U.S.A.) & National Cheng Kung University (Taiwan) Learning Objectives Pathophysiology of osteoporosis
Prevention and Treatment of OSTEOPOROSIS 骨質疏鬆的預防與治療 Gwo Jaw Wang, M.D. 王國照教授 University of Virginia (U.S.A.) & National Cheng Kung University (Taiwan) Learning Objectives Pathophysiology of osteoporosis
Histomorphometric classification of
 I Clin Pathol 1995;48:229-235 University Department of Medicine, Hope Hospital, Salford M T A Rehman Department of Osteoarticular Pathology, Medical School, University of Manchester, Manchester J A Hoyland
I Clin Pathol 1995;48:229-235 University Department of Medicine, Hope Hospital, Salford M T A Rehman Department of Osteoarticular Pathology, Medical School, University of Manchester, Manchester J A Hoyland
Bone Turnover Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis and Diseases Associated with High Bone Turnover. Original Policy Date
 MP 2.04.10 Bone Turnover Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis and Diseases Associated with High Bone Turnover Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013
MP 2.04.10 Bone Turnover Markers for the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis and Diseases Associated with High Bone Turnover Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1
 Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
Bone Tissue- Chapter 5 5-1 Bone Functions Support Protection Assistance in movement Mineral storage and release Blood cell production Triglyceride storage 5-2 Bone Chemistry Water (25%) Organic Constituent
OSTEOPOROSIS MANAGEMENT AND INVESTIGATION. David A. Hanley, MD, FRCPC
 OSTEOPOROSIS MANAGEMENT AND INVESTIGATION David A. Hanley, MD, FRCPC There is a huge care gap in the management of osteoporosis in this country. As yet unpublished findings from the Canadian Multicentre
OSTEOPOROSIS MANAGEMENT AND INVESTIGATION David A. Hanley, MD, FRCPC There is a huge care gap in the management of osteoporosis in this country. As yet unpublished findings from the Canadian Multicentre
A Case of Cushing Syndrome Diagnosed by Recurrent Pathologic Fractures in a Young Woman
 A Case of Cushing Syndrome Diagnosed by Recurrent Pathologic Fractures in a Young Woman JY Han, et al CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2012.19.2.153 Vol. 19, No. 2, 2012 A Case of Cushing Syndrome
A Case of Cushing Syndrome Diagnosed by Recurrent Pathologic Fractures in a Young Woman JY Han, et al CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.11005/jbm.2012.19.2.153 Vol. 19, No. 2, 2012 A Case of Cushing Syndrome
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH. 8 - BONE AND CARTILAGE.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: BONE CLASSIFICATIONS There are four classifications of bones based on their 1. Long bones are greater in length than in width - Found in the upper and lower limbs (ex: arm,
Awaisheh. Mousa Al-Abbadi. Abdullah Alaraj. 1 Page
 f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
f #3 Awaisheh Abdullah Alaraj Mousa Al-Abbadi 1 Page *This sheet was written from Section 1 s lecture, in the first 10 mins the Dr. repeated all the previous material relating to osteoporosis from the
Effects of Anti RANK ligand Denosumab on Beta Thalassemia induced osteoporosis
 Effects of Anti RANK ligand Denosumab on Beta Thalassemia induced osteoporosis Mohamed Yassin 1 Ashraf T. Soliman2, Mohamed O. Abdelrahman3, Vincenzo De Sanctis 4 Departments of, 1 Hematology 2Pediatric
Effects of Anti RANK ligand Denosumab on Beta Thalassemia induced osteoporosis Mohamed Yassin 1 Ashraf T. Soliman2, Mohamed O. Abdelrahman3, Vincenzo De Sanctis 4 Departments of, 1 Hematology 2Pediatric
Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength
 Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength Consultant / advisor: Amgen, Eli Lilly, Merck Disclosures Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA mbouxsei@bidmc.harvard.edu
Beyond BMD: Bone Quality and Bone Strength Consultant / advisor: Amgen, Eli Lilly, Merck Disclosures Mary L. Bouxsein, PhD Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA mbouxsei@bidmc.harvard.edu
