Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (2 ma - 20min) in Patients with Non-Fluent Aphasia Disorder
|
|
|
- Earl Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (2 ma - 20min) in Patients with Non-Fluent Aphasia Disorder M. Saidmanesh, HR.Pouretemad, A. Amini, R. Nilipor, H. Ekhtiari Abstract we aimed to investigate the correlation between stimulation intensity, duration of session of transcranial direct current stimulation (ten 20- min anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (2mA) sessions and lesion location with the aphasia recovery and improvement of naming picture, Aphasia Quotient and working memory in Persian patients with non fluent aphasia disorder. To achieve this goal we evaluate the Efficacy of transcranial direct current stimulation on dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the brain upon non fluent aphasia recovery, included 20 chronic and stroke-induced aphasia patients who each underwent 10 sessions of Anodal - transcranial direct current stimulation (2 mili- Ampere - 20min) and 10 sessions of sham- transcranial direct current stimulation (20-min) combined with a computerized anemia treatment. It was revealed that after ten 20-min anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (2mA), it significantly improves naming scores, working memory, Aphasia Quotient or severity and the Correlation Rate in non fluent aphasia patients as compared to sham- transcranial direct current stimulation. Additionally, our study demonstrated, there are significant differences between the results of our test According to the following variable, lesion location, but not genders variation. Treatment with10 sessions of Anodal - transcranial direct current stimulation (2 ma - 20min) enhance the non fluent aphasia recovery and improvement of naming picture, working memory and Aphasia Quotient or severity and lesion location but not gender factor play a main role in it. Key words Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation, non fluent aphasia, left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (LDPC) INTRODUCTION One of the main impairment of language ability is aphasia or speechlessness disorders. It usually caused by head injury (left hemisphere, or stroke), but it can develop slowly from a brain tumor, dementia, infection and dysnomia (learning disability) [1]-[5]. According to last literatures, the main reason of the aphasia is stroke, approximately, 80,000 cases of adult aphasia is due to stroke, and more than 50 60% of them have chronic impairment[ 6],[7]. The aphasia disorders can be divided into: global, Broca s, trans-cortical motor, mixed transcortical, Wernicke s, trans- cortical sensory, conduction, and anomic types, moreover, the WAB demonstrate severities of aphasia as aphasia quotients (AQ), this kind of classification is according to the assessing profiles of language for repetition, fluency, comprehension, and naming[1]. During the acute phase of stroke, the global type of aphasia are more prevalence form and consist approximately 20-40% of aphasias, whereas the classic aphasia are found only in a 25 percent of patients, and 10-15% of patients are unclassifiable[8]. The ranges of language disorder are different and vary from naming picture, unable in speaking, writing, and reading to deficits in working memory (WM). Here working memory capacity has been identified as a unitary process of a single (resource) pool for attention, linguistic, and other plenary processing. The main reason of those kind disorders, is impairment in left hemisphere (LH) or in left dorsolateral part of prefrontal cortex (DLPFC)[1],[8].The critical function of left dorsolateral part of prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) in verbal working memory (WM) has been approved by Didit Span Test in pathological studies and in the study including effects of Trans Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) on left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. This study showed that local damage and destruction of left DLPFC region, not right DLPFC region, Cause degradation in verbal working memory (WM) [1]. Previous studies also suggested that stimulation by transcranial direct current has a positive effect on the left dorsolateral part of prefrontal cortex, resulted in an improved ability to name pictures, working memory (WM) [9]-[12]. Today s, stimulation by transcranial direct current (tdcs) as a safe and non-invasive brain stimulation techniques and painless form of neuron stimulation methods have become increasingly important for the diagnosis and treatment of neuropsychiatric diseases [1]. These techniques are used to stimulate cortical neuronal assemblies. This methods works by sending the current from an active electrode to a 133
2 reference electrode, a part being diverted through the scalp and the remainder being delivered to tissue of the brain, thereby it leading to increase or decrease of cortical excitability [13].Here the current polarity determined the direction of the tdcs-induced effect. According to this, the stimulation of the brain can be classified as; Cathodal, Anodal and Sham stimulations. Stimulation by anodal is positive and it can increase the excitability of the neuron. In Contrary to this, the stimulation by the cathode decrease the excitability of the neurons in the stimulated area for reach to more constant level of activity Here the sham stimulation is one of the important stimulation, because it plays as a control groups. These types of stimulation help to prove the positive or negative effects of stimulation [1],[14]- [16]. It is important to remind, the ability of tdcs for creating cortical changes even after the end of stimulation is one of the important aspects of it. The stimulating effects and the continuity of this kind of change depend on the length stimulation as well as the intensity of stimulation and the session durations and location of the brain lesion. For example, in the several studies it was revealed that after five 20-min anodal tdcs (1 ma) sessions it has beneficial effect on aphasia recovery [19],[20]. And also, it was reported that stimulation by the same parameters enhanced working memory (WM) in healthy persons, as measured by three-back working memory method [21], and in patients with Parkinson s disease [22]. Review of the literatures shows that more sessions (> 5 sessions), longer sessions (> 20-min), and greater stimulation intensity (> 1 ma) may be able to elicited even greater success [13],[21]. Along to those, many treatments were designed to reveal the role of other stimulation intensity of tdcs and number of sessions in aphasia recovery. Therefore, for increasing the knowledge and helping to them, we decided to investigate the effect of ten 20-min anodal tdcs (2 ma) sessions on naming score and working memory according to the role of lesion location in the aphasia recovery, in the patient with non fluent aphasia disorder. Material and methods: Subjects: Twenty right hand Persian patients with chronicnon fluent aphasia disorders (range years; mean age, ± 2.4 years, at 60 month poststroke) participated in our present study. All of the subjects gave their written informed consent before participation (Table 1). In our study the patients were excluded if had been any speech therapy or had been used medication or psychotropic drugs during the 4 weeks prior to the study. And also, they were informed to avoid alcohol, cigarettes and drink of caffeinated things on the day of the test, and none reported fatigue due to inadequate sleep. The Persian aphasia test: This test includes the tests of continuous speech (content and fluency of speech), auditory perception, and continuous orders, naming and repeating. Each test had 10 scores that were in totally 60 scores. At the end of the test, the obtained number multiplied by 10 and then divided by 6. The obtained number is Aphasia Quotient [23],[24]. The Pictures naming aphasia test: This test consists 50 pictures witch patient should be tell the name of them. This kind of test according to the type and variety of category are classified to three groups, including the Name of animals (12 animals), 11 fruit and 27 categories of Construction. If the patient fails to express the desired word after 10 seconds, He or she was semantic guidance in initially and in the absence of response, he or she was phonetic guidance. Every patient's answer to the pictures recorded on the answer sheets and then the total number of correct answers, correct answers with no guidance, correct answers with semantic guidance, correct answers with phonetic guidance, wrong answers and not response answers were obtained[ 23]. The 2 back test: The 2 -back task has been used to evaluate the working memory ability in neurologically intact individuals as well as multiple clinical populations. It Includes 100 Number (1 to 9), that are randomly repeated. The 2-back needs contributors to process a stream of incoming data and respond when the current stimulus is the same as the stimulus 2 items ago. In this study, the number of correct answers has been considered as a test score [25]. The Computer program naming aphasia test: Program used in this study included 60 Image, Which com in three semantic categories including animals, fruits, and objects (20 images in each semantic category). During treatment with tdcs, Images and their name was presented using the computer. And none of these images wasn t seen in 134
3 the Pictures naming aphasia test [23],[ 24]. Electrodes and stimulation of the brain: In this study Direct current was induced by a pair of electrodes in a 5 5cm saline-soaked synthetic sponge and delivered by a battery steered constant current stimulator using (included of 20 min of 2 ma). According to Knoch et al. the device used, is particularly trustful for studies: a switch can be enabled to interrupt the electrical current while retaining the (ON) display and showing the stimulation parameters throughout the procedure to the participant [26]. In these conditions the interaction between the two hemispheres during task execution is also under control. So in present study for left DLPFC stimulation, the anodal electrode was located over the left DLPFC and the cathodal electrode over the right DLPFC. For the stimulation of sham group, the electrodes were located at the same positions as for stimulation in active manner, but the stimulator was turned on only for 30 s. Thus, these participants felt the primary itching sensation associated with trans direct current stimulating (tdcs), but received no active current for the remainder of the stimulation period [26]. Experimental Design: Twenty participants (8 women; and 12 man) were randomly assigned to receive cathodal electrode over the right predestinated DLPFC area (by using of the 10/20 EEG system) and anodal electrode as a active stimulation over the left predestinated DLPFC area ( n = 20) and sham stimulation or no stimulation group (n = 20) [27]. After selecting the participants, we consisted three ordered phases, separated by at least 3 days [19, 21 and 28]. In the first phase, the written informed consent was given to the participants prior to their inclusion in the study. Then the technique of MMSE test for Dementia and test for identify the type of aphasia was done in the same session [23],[ 24]. In the second phase (3 day after the first session), picture naming, Working Memory and Aphasia Quotient Were evaluated by The Pictures Naming Aphasia test, 2-back test and Persian aphasia test, respectively, and results were recorded in the patient questionnaire as a before tdcs treatment results. In the last phase (including treatment session), for stimulation of the left DLPFC and right DLPFC the anodal electrode and cathodal electrode were located over the left and right DLPFC respectively for 10 days. In this study, for active stimulation, the subjects received a steady current of 2 ma intensity for 20 min. the last studies have indicated that this kind of stimulation intensity is safe and can be more effective than 1 ma stimulation[ 19, 21and 28]. During the stimulation period, Patients Underwent the Computer program naming test for the naming performance. This test helps them to naming and tells pictures. At the end of treatment, picture naming, Working Memory and Aphasia Quotient Were evaluated by The Pictures Naming test, 2- back test and Persian aphasia test, respectively, and results were recorded in the patient questionnaire. For Statistical analysis, data was analyzed by SPSS 19 and Manova test and used Pearson correlation coefficient. It also describes the test score (before and after treatment). Results: All subjects without any complications ended the tree treatment phases. The ratings of Subject s selfreported of attention, perceived pain and fatigue were not statically significant during the treatment sessions, (F (2, 13) <1, p>0. 26). All of our measures completed within 20 minutes of the tdcs cessation. The results of statistical analysis of the naming Persian aphasia test without any guidance, with semantic guidance and with phonetic guidance are shown in the tables below (Table 2 and Fig.1). 135
4 According to the Multivariate analysis of variance (Hotelling,s Trace), the relationship between naming performance, before and following A-tDCS treatment were significant in The Pictures naming Persian aphasia test(fig1a). P و = 0/000 F = 208/551. And also, the relationship between naming performance before and following A-tDCS treatment among patients with different lesion location (anterior and posterior-anterior), were significant (P = 0/003 Fو = 7/873, (see table 3and Fig.1B) But there are no significant relationships between patients with different sex (Variable sex) in the same conditions (see table 4 and Fig. 1C) P = 1/038. = F و 0/406 Here, when the variables, gender and location of the lesion, considered together, no significant (P = Fو = 1/263) relationships were revealed 0/325 between the results of the naming aphasia test among patients before and following A-tDCS treatment (Table 5 and Fig.1D). 136
5 137
6 The 2 Back Test: The results of statistical analysis of the 2 back test are shown in the tables above and below (see Table 2-4 and 6) and Fig 2). In the table 2 and figure 1A it was shown that, the results of statistical analysis the 2 back test before and following A-tDCS treatment was significant (P و = 0/000 F = 164/395), And also, the result of the 2 back test was significant among patients with different lesion location (anterior and posterior-anterior) (Table3, Fig. 2B). P = 0/010, F = 5/539, But not sex (Table 4 and Fig. 2C). P = 0/982, F = 0/056. Here, when the variables, gender and location of the lesion, considered together, no significant (P = Fو = 0/669) relationships were revealed 0/585 between the results of the 2 back test among patients before and following A-tDCS treatment (Table 6 and Fig. 1D). 138
7 139
8 Aphasia Quotient test: The results of statistical analysis of The Aphasia Quotient test are shown in the tables above and below (Table 2-4 and 7) and Fig 3. From the table 2 and figure 3A it was concluded that, there are a significant difference between the results of The Aphasia Quotient test among the patients before and following A-tDCS treatment ( P = 0/000,F = 659/266 And also, the result of Aphasia Quotient test was significant difference among patients with different lesion locations(anterior and posterior-anterior)(table3, Fig3B). P = Fو = 15/312), But there are no significant relationships 0/000 between patients with different sex (Table4, Fig3C). P = 0/806 = 0/327 Fو Like other tests, the variables such as gender and location of the lesion, when considered together, there no significant (P Fو = 1/601 relationships were revealed between the = 0/234 results of Aphasia Quotient test among patients before and following A-tDCS treatment(table 7)and Fig3D. 140
9 The Correlation Rate of two-back test, total naming score and Aphasia Quotient: As shown in Table 8; The Pearson correlation between twoback test and the total naming score is significant. P =. /000,r = 0/763 The correlation between two-back test and Aphasia Quotient is significant. P =. /000,r = 0/801 The correlation between Aphasia Quotient and the total naming score is significant. P =. /000,r = 0/889 treatment of aphasia disorders, however, it seems insufficient. Discussion: One of the main and effective treatments is treatment with The aphasia disorders related to stroke is one of the main tanscranial direct current stimulation (tdcs). Treatment with impairment of language ability. It usually caused by head tanscranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) is a safe, painless injury or by impairment in left hemisphere (LH) or in left and relatively noninvasive method for modulating cortical dorsolateral part of prefrontal cortex. activity. It delivers a weak and brief polarizing electrical Deficits in working memory, unable to naming picture, current to the cortex through a pair of electrodes, and speaking, writing, and reading are the main symptom of it. according to the current flow polarity, the excitability of the Today, there have been proposed various methods for the brain can either be increased via anodal stimulation (A- tdcs) 141
10 or decreased via cathodal stimulation (C -tdcs)[14],[29]. Currently, transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) is used widely as a Clinical therapy for many diseases such as certain psychological disorders, post-stroke motor deficits such as aphasia disorders and fibromyalgia[ 30]. The our present study was designed to evaluate the effect of tdcs upon non fluent Persian aphasia recovery, included 20 patients with chronic, stroke- induced aphasia who each underwent 10 sessions of A-tDCS (2 ma and 20-min) and 10 sessions of Sham-Tdcs (20-min) combined with a computerized anemia treatment and also the role of lesion location in recovery of non fluent aphasia. Our results revealed that ten 20-min anodal tdcs (2 ma) sessions, significantly improves naming scores, Aphasia Quotient or severity, working memory and the Correlation Rate in non fluent aphasia patients as compared to sham-tdcs. Additionally, our study demonstrated, there was a significant difference in the results of our test before and following A- tdcs treatment between patients with different lesion locations (anterior and posterior-anterior),but not different gender (Variable sex). In our present study, the difference in treatment outcome between A-tDCS and S-tDCS wasn t related to the patients blood pressure and heart rate; because they recorded from preto post-tdcs administrations were found to be comparable across both tdcs conditions. Most early studies of tanscranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) performed in humans was on cortical regions of brain. Because monitoring of cortical excitability changes is easier than other parts of the brain. The brain has two hemispheres, right and left hemispheres. Every part of the hemispheres has different functions and damage to them can lead to diseases. Aphasia (non fluent aphasia) is a disease that occurs by lesion to the left hemisphere (LH). The study by Baker and his colleague revealed a positive and linear relationship between severity of activation of the LH, especially the left frontal cortex, and non fluent aphasia recovery. They concluded that, this region (LH) is exceedingly important for aphasia recovery. other studies showed that, tanscranial direct current stimulation over a region of the left cortex of frontal lob implicated in aphasia recovery and improved aphasia( non fluent aphasia)[11],[ 31] So according to important role of left hemisphere especially left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in aphasia, we evaluated the effectiveness of tanscranial direct current stimulation on dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in aphasia disorders patients [14]. Recent studies have suggested that the patient with aphasia often exhibit deficits in working memory and naming picture. [14]. The study by Tino et al and Beeli et al revealed that stimulation of the DLPFC by trans direct current (tdcs) Can affect in the working memory, risk-taking behavior, making of adecision and in response to visual material emotions in healthy people. In addition, stimulation of the frontopolar cortex by tdcs was proven to affect in performance of a 142 probabilistic classification learning task. Therefore, it has been convincingly shown that tdcs can affect in functions of prefrontal cortex (working memory) [14],[33]. In the similar study by others it was revealed that tdcs modulated efficiency of working memory by hanging the brain activity in a polarityspecific way. They observed a growth in working memory performance and amplified oscillatory power in the anodal tdcs treatment not cathodal tdcs treatment as shown in current study. Marco Sandrini and his colleagues (2012) investigated the effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) on working memory load performance, and they concluded that, verbal Working memory (tested by n-back task (2-back) and ANOVA before and after the application of bilateral tdcs over posterior parietal cortex (left anodal-right cathodal, left cathodal-right anodal or sham) was a significant interaction between tdcs and task [34]. These findings are in agreement with our results demonstrating that Anodal-tDCS over the left cortex improves language processing and working memory. In the study by Datte and his colleague, it was revealed that receiving anodal tdcs (1 ma for 20 minutes for about 5 days) by Ten patients with chronic and stroke- induced aphasia, resulted in significantly improvement of the naming accuracy in treated items compared with sham tdcs. Patients who showed the most progress were those with peri-lesional areas closest to the stimulation site [15],[35] and [36]. Alessia Monti and his colleagues measured The naming function before and immediately after tdcs treatment over the damaged left fronto-temporal areas by a computer-controlled task, and they concluded that, Cathodal tdcs over the damaged left fronto-temporal areas in patients with chronic non-fluent aphasia improves naming score[37]. It seems that A-tDCS increases cortical excitability, it presumably improved the patients ability to name pictures by focally stimulating function of the left frontal cortex Similar to the present research. Other studies have implicated the specific cortical location of left hemisphere in aphasia recovery, it is probable that improved speech and language functioning following aphasia treatment relies, at least partly, on spared left hemisphere regions [13],[23],[32]. We concluded that, after ten 20-min anodal tdcs (2 ma) sessions, the working memory and total naming score would be improved in the patient with non fluent aphasia and also the lesion location has a main role in aphasia recovery. Reference: [1] Julie Baker, Ph.D., Chris Rorden, et al.using transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) to treat stroke patients with aphasia Stroke June; 41(6): [2] Crosson B, McGregor K, Gopinath KS, et al. Functional MRI of language in aphasia: A review of
11 the literature and the methodological challenges. Neuropsychol Rev 2007; 17: [3] Postman-Caucheteux WA, Birn RM, Pursley RH, et al. Single-trial fmri shows contralesional activity linked to overt naming errors in chronic aphasic patients. J Cogn Neurosci In Press. [4] Crinion JT, Leff AP. Recovery and treatment of aphasia after stroke: functional imaging studies. Curr Opin Neurol 2007; 20: [5] Fridriksson J, Bonilha L, et al. Activity in preserved left hemisphere regions predicts anomia severity in aphasia. Cereb Cortex In Press. [6] Margaret A2010. Naeser, Ph.D.1, Paula I. et al, Improved Language in a Chronic Nonfluent Aphasia Patient Following Treatment with CPAP and TMS, Cogn Behav Neurol. March ; 23(1): [7] Margaret A et al 2010 and Pedersen PM et al 2004, Vinter K, Olsen TS. Aphasia after stroke: type, severity and prognosis. The Copenhagen aphasia study. Cerebrovasc Dis; 17: [8] Eun Kyoung Kang1, Hae Min Sohn2, et al. Severity of Post-stroke Aphasia According to Aphasia Type and Lesion Location in Koreans, J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: [9] David V. Smith1,2 and John A. ClitheroManipulating executive function with transcranial direct current stimulation,september 2009 ; Volume 3 Article 26 ; 1. [10] Dockery, C. A., Hueckel-Weng, et al. Enhancement of planning ability by transcranial direct current stimulation. J. Neurosci. 2009;.29, [11] Julius Fridriksson, Ph.D. Preservation and modulation of specific left hemisphere regions is vital for treated recovery from anomia in stroke; J Neurosci September 1; 30(35) [12] Beauchamp, M. H., Dagher, A., et al. Dynamic functional changes associated with cognitive skill learning of an adapted version of the Tower of London task. Neuroimage. 2003; 20, [13] Abraham P Arul-Anandam1,et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation - what is the evidence for its efficacy and safety? Reports 27 July 2009, 1:58. [14] Tino Zaehle1,2, Pascale Sandmann et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation of the prefrontal cortex modulates working memory performance: combined behavioural and electrophysiological evidence Neuroscience 2011, 12:2 [15] Patrick Ragert, Yves Vandermeeren, et al. Improvement of spatial tactile acuity by transcranial direct current stimulation, Clin Neurophysiol. 2008April ; 119(4): [16] Wassermann EM, Grafman J. Recharging cognition with DC brain polarization. Trends Cogn Sci 2005; 9: [17] Hollie A. Power1, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation of the primary motor cortex affects cortical drive to human musculature as assessed by intermuscular coherence; J Physiol (2006) pp [18] Gerloff C, Braun C, et al. Coherent corticomuscular oscillations originate from primary motor cortex: evidence from patients with early brain lesions. Human Brain Mapping (2006).27, [19] Fregni F, Boggio PS, et al. Treatment of major depression with transcranial direct current stimulation. Bipolar Disord 2006, 8: [20] Boggio PS, Rigonatti SP, et al. A randomized, double-blind clinical trial on the efficacy of cortical direct current stimulation for the treatment of major depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2008, 11: [21] Fregni F, Boggio PS, Nitsche MA, et al. Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation of prefronta cortex enhances working memory. Exp Brain Res 2005, 166: [22] Boggio PS, Ferrucci R, Rigonatti SP, et al. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on working memory in patients with Parkinson s disease. J Neurol Sci 2006, 249:31-8. [23] Reza Nilipour persian aphasia naming Test. University of social Walfare & rehabilitation(2011). sciences, tehran, Iran. [24] Reza Nilipour).Persian WAB-1. University of social Walfare & rehabilitation sciences, tehran, Iran. (2012). [25] Adrian M. Owen,1 Kathryn M. et al. N-Back Working Memory Paradigm: A Meta-Analysis of Normative Functional Neuroimaging Studies Human Brain Mapping 2005; 25: [26] Daria Knoch, Michael A. Nitsche, Urs et al. Studying the Neurobiology of Social Interaction with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation The Example of Punishing Unfairness. Cerebral Cortex September 2008; 18: [27] DaSilva, A. F., Volz, M. S, et al. Electrode Positioning and Montage in Transcranial Direct 143
12 Current Stimulation. J. Vis. Exp May (51), [28] Felipe Fregni a,, Fernanda Orsati, et al. Transcranial direct current stimulation of the prefrontal cortex modulates the desire for specific foods. Appetite [29] Nitsche MA, Cohen LG, Wassermann EM, et al: Transcranial direct current stimulation: State of the art Brain Stimulation 2008, 1: [30] Angela Valle, Suely Roizenblatt, Sueli Botte,et al. Efficacy of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) for the treatment of fibromyalgia: results of a randomized, shamcontrolled longitudinal clinical trialj Pain Manag ; 2(3): [31] Sarno M, Levita E. Recovery in treated aphasia in the first year post-stroke. Stroke 1979; 10:663. [32] Purpura DP, McMurtry JG: Intracellular activities and evoked potential changes during polarization of the motor cortex. J Neurophysiol 1965, 28: [33] Beeli G, Casutt G, Baumgartner T. Modulating presence and impulsiveness by external stimulation of the brain. Behavioral and Brain Functions 2008, 4:33. [34] Sandrini M, Fertonani A, Cohen LG. Double dissociation of working memory load effects induced by bilateral parietal modulation. Neuropsychologia Feb;50(3): [35] Datta, A., Baker, J.M., Bikson, M. Individualized model predicts brain current flow during transcranial direct current stimulation treatment in responsive stroke patient Brain Stimulation In Press (2011). [36] Nitsche MA, Liebetanz D, Lang N, et al. Safety criteria for transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) in humans. Clin Neurophysiol 2003; 114: [37] A Monti, F Cogiamanian,S Marceglia. Improved naming after transcranial direct current stimulation in aphasia J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2008;79: PO Box: Fax: Hamid Reza Pouretemad is Professor of clinical psychology and is currently working in Institute for Cognitive Science Studies (ICSS) Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. P.O.Box: Abdollah Amini is currently a PhD student in Anatomical Sciences and Biology, in Cell and Molecular Biology Research Center, Medical Faculty, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. D.amini2005@yahoo.com Reza Nilipour works as a teacher in speech therapy Department, University of Medical Sciences, and Tehran, Iran. Hamed Ekhtiari works as a Faculty Member in Institute of Cognitive Sciences, Tehran. Iran BIOGRAPHIES Mohsen saidmanesh has received BSc and MSc degree in speech therapy from the Tehran University, Iran, in 2007 and 2011 respectively. He is currently working as a PhD student in cognitive neuroscience and working in Institute for Cognitive Science Studies (ICSS), Tehran, Iran: d.amini2008@yahoo.com 144
Recovery mechanisms from aphasia
 Recovery mechanisms from aphasia Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 977 Acquired language and reading impairments 1 Research questions Which brain systems can support recovery from aphasia? Which compensatory route
Recovery mechanisms from aphasia Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 977 Acquired language and reading impairments 1 Research questions Which brain systems can support recovery from aphasia? Which compensatory route
fmri scans were compared pre- and post-treatment and perilesional activated volumes on the left hemisphere were compared.
 Methods that modulate cortical excitability have potential as adjuvant treatments for aphasia rehabilitation. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) is a non-invasive method of stimulation with
Methods that modulate cortical excitability have potential as adjuvant treatments for aphasia rehabilitation. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) is a non-invasive method of stimulation with
Using Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation to Treat Stroke Patients With Aphasia
 Using Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation to Treat Stroke Patients With Aphasia Julie M. Baker, PhD; Chris Rorden, PhD; Julius Fridriksson, PhD Background and Purpose Recent research suggests that
Using Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation to Treat Stroke Patients With Aphasia Julie M. Baker, PhD; Chris Rorden, PhD; Julius Fridriksson, PhD Background and Purpose Recent research suggests that
Can brain stimulation help with relearning movement after stroke?
 stroke.org.uk Final report summary Can brain stimulation help with relearning movement after stroke? The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on motor learning after stroke PROJECT CODE: TSA
stroke.org.uk Final report summary Can brain stimulation help with relearning movement after stroke? The effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on motor learning after stroke PROJECT CODE: TSA
tdcs in Clinical Disorders
 HBM Educational course Brain Stimulation: Past, Present and Future Hamburg, June 8th, 2014 tdcs in Clinical Disorders Agnes Flöel NeuroCure Clinical Research Center, Neurology, & Center for Stroke Research
HBM Educational course Brain Stimulation: Past, Present and Future Hamburg, June 8th, 2014 tdcs in Clinical Disorders Agnes Flöel NeuroCure Clinical Research Center, Neurology, & Center for Stroke Research
Title: Measuring and inducing brain plasticity in chronic aphasia
 Title: Measuring and inducing brain plasticity in chronic aphasia Author: Julius Fridriksson PII: S0021-9924(11)00031-1 DOI: doi:10.1016/j.jcomdis.2011.04.009 Reference: JCD 5550 To appear in: JCD Please
Title: Measuring and inducing brain plasticity in chronic aphasia Author: Julius Fridriksson PII: S0021-9924(11)00031-1 DOI: doi:10.1016/j.jcomdis.2011.04.009 Reference: JCD 5550 To appear in: JCD Please
PsychoBrain. 31 st January Dr Christos Pliatsikas. Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading
 PsychoBrain 31 st January 2018 Dr Christos Pliatsikas Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading By the end of today s lecture you will understand Structure and function of
PsychoBrain 31 st January 2018 Dr Christos Pliatsikas Lecturer in Psycholinguistics in Bi-/Multilinguals University of Reading By the end of today s lecture you will understand Structure and function of
Cognitive enhancement. using tdcs. Does tdcs. enhance cognition? Does tdcs enhance cognition? Why combine tdcs with other treatments?
 Cognitive enhancement Does tdcs enhance cognition? using tdcs Why combine tdcs with other treatments? Anna-Katharine Brem, PhD, MASNP Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Oxford Berenson-Allen
Cognitive enhancement Does tdcs enhance cognition? using tdcs Why combine tdcs with other treatments? Anna-Katharine Brem, PhD, MASNP Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Oxford Berenson-Allen
Localizing lesion locations to predict extent of aphasia recovery. Abstract
 Localizing lesion locations to predict extent of aphasia recovery Abstract Extensive research has related specific lesion locations to language impairment in aphasia. However, far less work has focused
Localizing lesion locations to predict extent of aphasia recovery Abstract Extensive research has related specific lesion locations to language impairment in aphasia. However, far less work has focused
Neural basis of conceptual knowledge: insights from noninvasive
 Neural basis of conceptual knowledge: insights from noninvasive brain stimulation JSPS Fellowship 2013 Bridge Fellowship 2015 Gorana Pobric School of Psychological Sciences University of Manchester Neuroscience
Neural basis of conceptual knowledge: insights from noninvasive brain stimulation JSPS Fellowship 2013 Bridge Fellowship 2015 Gorana Pobric School of Psychological Sciences University of Manchester Neuroscience
Magnetic and Electrical Stimulation in the Treatment of Aphasia
 Magnetic and Electrical Stimulation in the Treatment of Aphasia Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) No financial conflicts Roy Hamilton, MD, MS, FAAN,
Magnetic and Electrical Stimulation in the Treatment of Aphasia Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) No financial conflicts Roy Hamilton, MD, MS, FAAN,
Therapeutic Uses of Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Current & Developing
 Therapeutic Uses of Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Current & Developing Alvaro Pascual-Leone, MD, PhD Berenson-Allen Center for Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Harvard Catalyst Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
Therapeutic Uses of Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Current & Developing Alvaro Pascual-Leone, MD, PhD Berenson-Allen Center for Noninvasive Brain Stimulation Harvard Catalyst Beth Israel Deaconess Medical
Higher Cortical Function
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Higher Cortical Function Objectives Describe the association cortical areas processing sensory, motor, executive, language, and emotion/memory information (know general location
Patients with disorders of consciousness: how to treat them?
 Patients with disorders of consciousness: how to treat them? Aurore THIBAUT PhD Student Coma Science Group LUCA meeting February 25 th 2015 Pharmacological treatments Amantadine Giacino (2012) 184 TBI
Patients with disorders of consciousness: how to treat them? Aurore THIBAUT PhD Student Coma Science Group LUCA meeting February 25 th 2015 Pharmacological treatments Amantadine Giacino (2012) 184 TBI
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) and language
 1 Centro Interdipartimentale Mente/Cervello (CIMeC), Centro di Riabilitazione Neurocognitiva (CeRiN), Università degli Studi di Trento, Rovereto, Italy 2 Centro Clinico per la Neurostimolazione, le Neurotecnologie
1 Centro Interdipartimentale Mente/Cervello (CIMeC), Centro di Riabilitazione Neurocognitiva (CeRiN), Università degli Studi di Trento, Rovereto, Italy 2 Centro Clinico per la Neurostimolazione, le Neurotecnologie
funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura Avanzino
 Department of Experimental Medicine, section of Human Physiology Centre for Parkinson s Disease and Movement Disorders - University of Genoa funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura
Department of Experimental Medicine, section of Human Physiology Centre for Parkinson s Disease and Movement Disorders - University of Genoa funzioni motorie e cognitive (nella malattia di Parkinson) Laura
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html n Learning and Memory n Human Communication n Emotion 1 What is memory? n Working Memory:
The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan. Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1
 The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1 Psycholinguistics / Neurolinguistics Happy Hour!!! Tuesdays 7/11, 7/18, 7/25 5:30-6:30 PM @ the Boone Center
The neurolinguistic toolbox Jonathan R. Brennan Introduction to Neurolinguistics, LSA2017 1 Psycholinguistics / Neurolinguistics Happy Hour!!! Tuesdays 7/11, 7/18, 7/25 5:30-6:30 PM @ the Boone Center
shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all of the above.
 Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Section: Chapter 14: Multiple Choice 1. Alex the parrot: pp.529-530 shows syntax in his language. has a large neocortex, which explains his language abilities. shows remarkable cognitive abilities. all
Transcranial direct current stimulation: A spark of hope for neurorehabilitation?
 Transcranial direct current stimulation: A spark of hope for neurorehabilitation? Introduction Neurological diseases and accidents are some of the most traumatic and disabling found in modern medicine.
Transcranial direct current stimulation: A spark of hope for neurorehabilitation? Introduction Neurological diseases and accidents are some of the most traumatic and disabling found in modern medicine.
Critical Review: Amanda Davidson M.Cl.Sc (SLP) Candidate Western University: School of Communication Sciences and Disorders
 Critical Review: Are therapeutic interventions that include non-invasive brain stimulation (tdcs/rtms) with language therapy effective at improving auditory comprehension in patients with aphasia following
Critical Review: Are therapeutic interventions that include non-invasive brain stimulation (tdcs/rtms) with language therapy effective at improving auditory comprehension in patients with aphasia following
Summary of my talk. Cerebellum means little brain but a huge neural resource. Studying the cerebellum in. Chris Miall
 Studying the cerebellum in sensory motor control Chris Miall Behavioural Brain Sciences School of Psychology University of Birmingham Summary of my talk Cerebellum means little brain but a huge neural
Studying the cerebellum in sensory motor control Chris Miall Behavioural Brain Sciences School of Psychology University of Birmingham Summary of my talk Cerebellum means little brain but a huge neural
Clinical Applications of tdcs: past, present and future
 Clinical Applications of tdcs: past, present and future Felipe Fregni, MD, PhD, MPH, MMSc, MEd Spaulding Neuromodulation Center Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard
Clinical Applications of tdcs: past, present and future Felipe Fregni, MD, PhD, MPH, MMSc, MEd Spaulding Neuromodulation Center Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard
Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications.
 Dr. Peter J. Fiester November 14, 2012 Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications. Briefly discuss a few examples
Dr. Peter J. Fiester November 14, 2012 Define functional MRI. Briefly describe fmri image acquisition. Discuss relative functional neuroanatomy. Review clinical applications. Briefly discuss a few examples
Pump up the volume! Can transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) enhance Cognitive Bias Modification in Addiction?
 Pump up the volume! Can transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) enhance Cognitive Bias Modification in Addiction? Reinout W. Wiers Thomas E. Gladwin Tess den Uijl Addiction Development and Psychopathology
Pump up the volume! Can transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) enhance Cognitive Bias Modification in Addiction? Reinout W. Wiers Thomas E. Gladwin Tess den Uijl Addiction Development and Psychopathology
The role of transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) in rehabilitation of stroke patients with aphasia
 ENCEPHALOS 55, 12-16, 2018 The role of transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) in rehabilitation of stroke patients with aphasia PANAGIOTIS D. KARAGOUNIS * Key words: TDCS, neurorehabilitation,
ENCEPHALOS 55, 12-16, 2018 The role of transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) in rehabilitation of stroke patients with aphasia PANAGIOTIS D. KARAGOUNIS * Key words: TDCS, neurorehabilitation,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Department of Neurology, Faculdade de Ciências Médicas da Santa Casa de São Paulo (FCMSCSP), São Paulo (SP), Brazil
 DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2016.0194060617 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Non-invasive brain stimulation and computational models in post-stroke aphasic patients: single session of transcranial magnetic stimulation and
DOI: 10.1590/1516-3180.2016.0194060617 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Non-invasive brain stimulation and computational models in post-stroke aphasic patients: single session of transcranial magnetic stimulation and
Learning Objectives.
 Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
Emilie O Neill, class of 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the types of deficits that occur with lesions in association areas including: prosopagnosia, neglect, aphasias, agnosia, apraxia 2. Discuss
The Effects of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) on Reducing. the Desire for Methadone among Addicts under Treatment in Taleghani
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 [4]:179-185 [http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html] ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2017, 9 [4]:179-185 [http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html] ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Sophie C. Andrews, a Kate E. Hoy, a Peter G. Enticott, a Zafiris J. Daskalakis, b Paul B. Fitzgerald a
 Brain Stimulation (2011) 4, 84 9 www.brainstimjrnl.com Improving working memory: the effect of combining cognitive activity and anodal transcranial direct current stimulation to the left dorsolateral prefrontal
Brain Stimulation (2011) 4, 84 9 www.brainstimjrnl.com Improving working memory: the effect of combining cognitive activity and anodal transcranial direct current stimulation to the left dorsolateral prefrontal
Psy /16 Human Communication. By Joseline
 Psy-302 11/16 Human Communication By Joseline Lateralization Left Hemisphere dominance in speech production in 95% of right handed and 70% of left handed people Left -> Timing, Sequence of events Right
Psy-302 11/16 Human Communication By Joseline Lateralization Left Hemisphere dominance in speech production in 95% of right handed and 70% of left handed people Left -> Timing, Sequence of events Right
Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language
 Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language Based on: Chapter 18 and 19, Breedlove, Watson, Rosenzweig, 6e/7e. Cerebral Cortex Brain s most complex area with billions of neurons and
Cognitive Neuroscience Cortical Hemispheres Attention Language Based on: Chapter 18 and 19, Breedlove, Watson, Rosenzweig, 6e/7e. Cerebral Cortex Brain s most complex area with billions of neurons and
The origins of localization
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions. Michael E. Goldberg, M.D.
 Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Association Cortex, Asymmetries, and Cortical Localization of Affective and Cognitive Functions Michael E. Goldberg, M.D. The origins of localization The concept that different parts of the brain did different
Short duration transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) modulates verbal memory
 Brain Stimulation (2012) 5, 468 74 www.brainstimjrnl.com Short duration transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) modulates verbal memory Amir Homayoun Javadi, a,b Paul Cheng, c Vincent Walsh a,c
Brain Stimulation (2012) 5, 468 74 www.brainstimjrnl.com Short duration transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) modulates verbal memory Amir Homayoun Javadi, a,b Paul Cheng, c Vincent Walsh a,c
Severity of Post-stroke Aphasia According to Aphasia Type and Lesion Location in Koreans
 J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 123-7 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.123 Severity of Post-stroke Aphasia According to Aphasia Type and Lesion Location in Koreans To determine the relations between
J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 123-7 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.1.123 Severity of Post-stroke Aphasia According to Aphasia Type and Lesion Location in Koreans To determine the relations between
After the Diagnosis: Rehabilitation & Support Options for Mild Dementia
 After the Diagnosis: Rehabilitation & Support Options for Mild Dementia Dr. Toni Nicholls, Clinical Neuropsychologist Peronne Village, cottage #20, Worthing, Christ Church 621-2022 Say these aloud Dog
After the Diagnosis: Rehabilitation & Support Options for Mild Dementia Dr. Toni Nicholls, Clinical Neuropsychologist Peronne Village, cottage #20, Worthing, Christ Church 621-2022 Say these aloud Dog
Aging, cognitive-motor function, and tcs. Brad Manor, PhD. October 31, 2017 LEASE DO NOT COPY
 Aging, cognitive-motor function, and tcs Brad Manor, PhD October 31, 2017 Disclosures - NIH / NIA - Michael J. Fox Foundation - U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation - Marcus Applebaum Research Award
Aging, cognitive-motor function, and tcs Brad Manor, PhD October 31, 2017 Disclosures - NIH / NIA - Michael J. Fox Foundation - U.S.-Israel Binational Science Foundation - Marcus Applebaum Research Award
( Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, TMS) TMS, TMS TMS TMS TMS TMS TMS Q189
 102 2004 35 2 3 : 1 2 2 ( 1 DK29220 ; 2 100083) ( Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation TMS) TMS TMS TMS TMS TMS TMS TMS ; ; ; Q189 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation ( TMS) : Physiology Psychology Brain Mapping
102 2004 35 2 3 : 1 2 2 ( 1 DK29220 ; 2 100083) ( Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation TMS) TMS TMS TMS TMS TMS TMS TMS ; ; ; Q189 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation ( TMS) : Physiology Psychology Brain Mapping
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Transcranial Direct-Current Stimulation
 Introduction (tdcs) is a non-invasive form of brain stimulation similar to transcranial magnetic stimulation, but instead of using magnets, it uses a lowintensity, constant current applied through scalp
Introduction (tdcs) is a non-invasive form of brain stimulation similar to transcranial magnetic stimulation, but instead of using magnets, it uses a lowintensity, constant current applied through scalp
Title:Atypical language organization in temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by a passive semantic paradigm
 Author's response to reviews Title:Atypical language organization in temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by a passive semantic paradigm Authors: Julia Miro (juliamirollado@gmail.com) Pablo Ripollès (pablo.ripolles.vidal@gmail.com)
Author's response to reviews Title:Atypical language organization in temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by a passive semantic paradigm Authors: Julia Miro (juliamirollado@gmail.com) Pablo Ripollès (pablo.ripolles.vidal@gmail.com)
Innovative Aphasia Intervention: Optimize Treatment Outcomes through Principles of Neuroplasticity, Caregiver Support, and Telepractice
 Innovative Aphasia Intervention: Optimize Treatment Outcomes through Principles of Neuroplasticity, Caregiver Support, and Telepractice Washington Speech-Language-Hearing Association Annual Convention
Innovative Aphasia Intervention: Optimize Treatment Outcomes through Principles of Neuroplasticity, Caregiver Support, and Telepractice Washington Speech-Language-Hearing Association Annual Convention
Introduction to TMS Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
 Introduction to TMS Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Lisa Koski, PhD, Clin Psy TMS Neurorehabilitation Lab Royal Victoria Hospital 2009-12-14 BIC Seminar, MNI Overview History, basic principles, instrumentation
Introduction to TMS Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Lisa Koski, PhD, Clin Psy TMS Neurorehabilitation Lab Royal Victoria Hospital 2009-12-14 BIC Seminar, MNI Overview History, basic principles, instrumentation
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
REHEARSAL PROCESSES IN WORKING MEMORY AND SYNCHRONIZATION OF BRAIN AREAS
 REHEARSAL PROCESSES IN WORKING MEMORY AND SYNCHRONIZATION OF BRAIN AREAS Franziska Kopp* #, Erich Schröger* and Sigrid Lipka # *University of Leipzig, Institute of General Psychology # University of Leipzig,
REHEARSAL PROCESSES IN WORKING MEMORY AND SYNCHRONIZATION OF BRAIN AREAS Franziska Kopp* #, Erich Schröger* and Sigrid Lipka # *University of Leipzig, Institute of General Psychology # University of Leipzig,
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Session 4 Virtual Lesion Approach I Alexandra Reichenbach MPI for Biological Cybernetics Tübingen, Germany Today s Schedule Virtual Lesion Approach : Study Design Rationale
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Session 4 Virtual Lesion Approach I Alexandra Reichenbach MPI for Biological Cybernetics Tübingen, Germany Today s Schedule Virtual Lesion Approach : Study Design Rationale
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Can group singing help long term aphasia?
 PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation research project.
PRIORITY BRIEFING The purpose of this briefing paper is to aid Stakeholders in prioritising topics to be taken further by PenCLAHRC as the basis for a specific evaluation or implementation research project.
Safety and Tolerability of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) on Children and Adolescents. Sarah Amare. Carleton University
 1 Safety and Tolerability of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) on Children and Adolescents Sarah Amare Carleton University 1 2 Prologue This present study which examines the safety and tolerability
1 Safety and Tolerability of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) on Children and Adolescents Sarah Amare Carleton University 1 2 Prologue This present study which examines the safety and tolerability
Combining tdcs and fmri. OHMB Teaching Course, Hamburg June 8, Andrea Antal
 Andrea Antal Department of Clinical Neurophysiology Georg-August University Goettingen Combining tdcs and fmri OHMB Teaching Course, Hamburg June 8, 2014 Classical Biomarkers for measuring human neuroplasticity
Andrea Antal Department of Clinical Neurophysiology Georg-August University Goettingen Combining tdcs and fmri OHMB Teaching Course, Hamburg June 8, 2014 Classical Biomarkers for measuring human neuroplasticity
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention
 University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Psychology ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2-9-2010 Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention David B.
University of New Mexico UNM Digital Repository Psychology ETDs Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2-9-2010 Transcranial direct current stimulation modulates shifts in global/local attention David B.
Perceptual Learning. Motor Learning. Stimulus-Response Learning. Relational Learning
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Learning and Memory Human Communication Emotion 1 Working Memory: What is memory? Limited
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Review ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu www.cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Learning and Memory Human Communication Emotion 1 Working Memory: What is memory? Limited
LEASE DO NOT COPY. Cognitive Enhancement with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs)
 Cognitive Enhancement with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) David Fischer Berenson-Allen Center for Noninvasive Brain Stimulation, BIDMC Harvard Medical School Neuroenhancement The enhancement
Cognitive Enhancement with Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) David Fischer Berenson-Allen Center for Noninvasive Brain Stimulation, BIDMC Harvard Medical School Neuroenhancement The enhancement
MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience
 MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience School of Psychological Sciences Faculty of Medical & Human Sciences Module Information *Please note that this is a sample guide to modules. The exact
MSc Neuroimaging for Clinical & Cognitive Neuroscience School of Psychological Sciences Faculty of Medical & Human Sciences Module Information *Please note that this is a sample guide to modules. The exact
Maximizing Generalization Effects of Semantic Feature Analysis
 1 Maximizing Generalization Effects of Semantic Feature Analysis Numerous treatments have been developed that have successfully facilitated naming in aphasia (see Laine & Martin, 2006 for a review). However,
1 Maximizing Generalization Effects of Semantic Feature Analysis Numerous treatments have been developed that have successfully facilitated naming in aphasia (see Laine & Martin, 2006 for a review). However,
3/1/18. Overview of the Talk. Important Aspects of Neuroimaging Technology
 3/1/18 Considerations for the Use of Neuroimaging for Predicting Recovery of Speech and Language in Aphasia Linda I. Shuster, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Overview of the Talk Important aspects of neuroimaging technology
3/1/18 Considerations for the Use of Neuroimaging for Predicting Recovery of Speech and Language in Aphasia Linda I. Shuster, Ph.D., CCC-SLP Overview of the Talk Important aspects of neuroimaging technology
How Therapy Changes the Human Brain
 Selected Neural Plasticity References How Therapy Changes the Human Brain Martha S. Burns, Ph.D.,ccc-slp Joint Appointment Professor Northwestern University Bryck & Fisher (2012) Training the Brain: Practical
Selected Neural Plasticity References How Therapy Changes the Human Brain Martha S. Burns, Ph.D.,ccc-slp Joint Appointment Professor Northwestern University Bryck & Fisher (2012) Training the Brain: Practical
The basics of tdcs: Marom Bikson. The City College of New York of CUNY
 The basics of tdcs: Technology and Mechanism Marom Bikson Lucas Parra, Jacek Dmochowski,Asif Rahman, Niranjan Khadka, Mark Jackson, Dennis Truong, Belen Lafon, Gregory Kronberg, Devin Adair, Nigel Gebodh
The basics of tdcs: Technology and Mechanism Marom Bikson Lucas Parra, Jacek Dmochowski,Asif Rahman, Niranjan Khadka, Mark Jackson, Dennis Truong, Belen Lafon, Gregory Kronberg, Devin Adair, Nigel Gebodh
FUNCTIONAL MRI IN EPILEPSY December 6 th 2013
 FUNCTIONAL MRI IN EPILEPSY December 6 th 2013 Matthias J Koepp, MD, PhD UCL Institute of Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure
FUNCTIONAL MRI IN EPILEPSY December 6 th 2013 Matthias J Koepp, MD, PhD UCL Institute of Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg
 Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Lecture 35 Association Cortices and Hemispheric Asymmetries -- M. Goldberg The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite
Chapter 2 Test. 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. *a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain e.
 Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Cognitive Psychology In and Out of the Laboratory 5th Edition Galotti TEST BANK Full clear download (no formatting errors) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/cognitive-psychology-laboratory-5thedition-galotti-test-bank/
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Excellent Network Courses. Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University
 Excellent Network Courses Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University Agnosia Visual Agnosia Lissauer (1890) described 2 types: a) Apperceptive Cannot see objects b) Associative Does
Excellent Network Courses Department of Neurology Affiliated hospital of Jiangsu University Agnosia Visual Agnosia Lissauer (1890) described 2 types: a) Apperceptive Cannot see objects b) Associative Does
The role of non-invasive brain stimulation in neurorehabilitation of poststroke
 Case Report http://www.alliedacademies.org/journal-brain-neurology/ The role of non-invasive brain stimulation in neurorehabilitation of poststroke dysphagia. Meysam Amidfar*, Hadis Jalainejad Fasa University
Case Report http://www.alliedacademies.org/journal-brain-neurology/ The role of non-invasive brain stimulation in neurorehabilitation of poststroke dysphagia. Meysam Amidfar*, Hadis Jalainejad Fasa University
Ronney Jorge S. Raimundo, a,b Carlos E. Uribe, b Joaquim P. Brasil-Neto b ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Comportamento, Brasılia, DF, Brazil
 Brain Stimulation (2012) 5, 196 200 www.brainstimjrnl.com ORIGINAL ARTICLES Lack of clinically detectable acute changes on autonomic or thermoregulatory functions in healthy subjects after transcranial
Brain Stimulation (2012) 5, 196 200 www.brainstimjrnl.com ORIGINAL ARTICLES Lack of clinically detectable acute changes on autonomic or thermoregulatory functions in healthy subjects after transcranial
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Neuroimaging biomarkers and predictors of motor recovery: implications for PTs
 Neuroimaging biomarkers and predictors of motor recovery: implications for PTs 2018 Combined Sections Meeting of the American Physical Therapy Association New Orleans, LA February 21-24, 2018 Presenters:
Neuroimaging biomarkers and predictors of motor recovery: implications for PTs 2018 Combined Sections Meeting of the American Physical Therapy Association New Orleans, LA February 21-24, 2018 Presenters:
Test Bank. Multiple Choice
 Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Chapter 2: The Brain: An Overview of Structure and Function Test Bank Multiple Choice 1. Evolutionary structures within the are the most primitive. a. hindbrain b. thalamus c. forebrain d. midbrain Answer
Chapter 2 Knowledge Production in Cognitive Neuroscience: Tests of Association, Necessity, and Sufficiency
 Chapter 2 Knowledge Production in Cognitive Neuroscience: Tests of Association, Necessity, and Sufficiency While all domains in neuroscience might be relevant for NeuroIS research to some degree, the field
Chapter 2 Knowledge Production in Cognitive Neuroscience: Tests of Association, Necessity, and Sufficiency While all domains in neuroscience might be relevant for NeuroIS research to some degree, the field
TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab
 TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab This report details my summer research project for the REU Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience program as
TMS Disruption of Time Encoding in Human Primary Visual Cortex Molly Bryan Beauchamp Lab This report details my summer research project for the REU Theoretical and Computational Neuroscience program as
Semantic Processing Ability in Persian-Speaking Alzheimer s Patients
 December 2016, Volume 14, Number 4 Semantic Processing Ability in Persian-Speaking Alzheimer s Patients CrossMark Omid Azad 1* 1. Department of Linguistics, Faculty of Persian Literature and Foreign Languages,
December 2016, Volume 14, Number 4 Semantic Processing Ability in Persian-Speaking Alzheimer s Patients CrossMark Omid Azad 1* 1. Department of Linguistics, Faculty of Persian Literature and Foreign Languages,
Announcements. Exam 1. VII. Imaging techniques of the brain. Anatomical/Structural Scans. Structural Scans: CT. Structural Scans: CT 2/17/2014
 Exam 1 None at the moment! Announcements Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1 None at the moment! Announcements Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1. Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6%
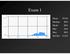 Exam 1 Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% None at the moment! Announcements VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1 Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% None at the moment! Announcements VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
The latest on functional imaging studies of aphasic stroke Cathy J. Price and Jenny Crinion
 The latest on functional imaging studies of aphasic stroke Cathy J. Price and Jenny Crinion Purpose of review Functional neuro-imaging studies of aphasic stroke offer the potential for a better understanding
The latest on functional imaging studies of aphasic stroke Cathy J. Price and Jenny Crinion Purpose of review Functional neuro-imaging studies of aphasic stroke offer the potential for a better understanding
CHAPTER 17: HEALTH PSYCHOLOGY CHAPTER 18: NEUROPSYCHOLOGY
 OUTLINE CHAPTER 17: HEALTH PSYCHOLOGY Role of Health Psychologists Stress & Illness Pain Management CHAPTER 18: NEUROPSYCHOLOGY Brain trauma Disorders of brain atrophy Neuro-assessment Professor Fazakas-DeHoog
OUTLINE CHAPTER 17: HEALTH PSYCHOLOGY Role of Health Psychologists Stress & Illness Pain Management CHAPTER 18: NEUROPSYCHOLOGY Brain trauma Disorders of brain atrophy Neuro-assessment Professor Fazakas-DeHoog
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs)
 Clinical Memorandum Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) August 2018 Authorising Committee/Department: Responsible Committee Responsible Department: Document Code: Board Section of Electroconvulsive
Clinical Memorandum Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) August 2018 Authorising Committee/Department: Responsible Committee Responsible Department: Document Code: Board Section of Electroconvulsive
Neuroimaging methods vs. lesion studies FOCUSING ON LANGUAGE
 Neuroimaging methods vs. lesion studies FOCUSING ON LANGUAGE Pioneers in lesion studies Their postmortem examination provided the basis for the linkage of the left hemisphere with language C. Wernicke
Neuroimaging methods vs. lesion studies FOCUSING ON LANGUAGE Pioneers in lesion studies Their postmortem examination provided the basis for the linkage of the left hemisphere with language C. Wernicke
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) A Promising Treatment for Depression?
 Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) A Promising Treatment for Depression? transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) Alternating current (AC) 1-3 ma, 9V Direct Current (DC) Direct current:
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) A Promising Treatment for Depression? transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tdcs) Alternating current (AC) 1-3 ma, 9V Direct Current (DC) Direct current:
Effects of Long-Term Use of Anodal tdcs on Working Memory
 Oliver Sokol Effects of Long-Term Use of Anodal tdcs on Working Memory Comparing the difference in performance between active and sham anodal tdcs on a dual n-back task over 11 sessions. Master s Thesis
Oliver Sokol Effects of Long-Term Use of Anodal tdcs on Working Memory Comparing the difference in performance between active and sham anodal tdcs on a dual n-back task over 11 sessions. Master s Thesis
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Copyright 2002 American Academy of Neurology. Volume 58(8) 23 April 2002 pp
 Copyright 2002 American Academy of Neurology Volume 58(8) 23 April 2002 pp 1288-1290 Improved executive functioning following repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation [Brief Communications] Moser,
Copyright 2002 American Academy of Neurology Volume 58(8) 23 April 2002 pp 1288-1290 Improved executive functioning following repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation [Brief Communications] Moser,
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
 Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Scientific evidence in major depression and schizophrenia C.W. Slotema Parnassia Bavo Group The Hague, the Netherlands Faraday s law (1831) Electrical current magnetic
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Scientific evidence in major depression and schizophrenia C.W. Slotema Parnassia Bavo Group The Hague, the Netherlands Faraday s law (1831) Electrical current magnetic
Enhancement of non-dominant hand motor function by anodal transcranial direct current stimulation
 Neuroscience Letters 404 (2006) 232 236 Enhancement of non-dominant hand motor function by anodal transcranial direct current stimulation Paulo S. Boggio b,c,, Letícia O. Castro c, Edna A. Savagim c, Renata
Neuroscience Letters 404 (2006) 232 236 Enhancement of non-dominant hand motor function by anodal transcranial direct current stimulation Paulo S. Boggio b,c,, Letícia O. Castro c, Edna A. Savagim c, Renata
FRONTAL TDCS MODULATES ORBITOFRONTAL REALITY FILTERING
 Neuroscience 265 (2014) 21 27 FRONTAL TDCS MODULATES ORBITOFRONTAL REALITY FILTERING A. L. MANUEL, a * A. W. DAVID, b M. BIKSON b AND A. SCHNIDER a,c a Laboratory of Cognitive Neurorehabilitation, Department
Neuroscience 265 (2014) 21 27 FRONTAL TDCS MODULATES ORBITOFRONTAL REALITY FILTERING A. L. MANUEL, a * A. W. DAVID, b M. BIKSON b AND A. SCHNIDER a,c a Laboratory of Cognitive Neurorehabilitation, Department
Biomarkers in Schizophrenia
 Biomarkers in Schizophrenia David A. Lewis, MD Translational Neuroscience Program Department of Psychiatry NIMH Conte Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders University of Pittsburgh Disease Process
Biomarkers in Schizophrenia David A. Lewis, MD Translational Neuroscience Program Department of Psychiatry NIMH Conte Center for the Neuroscience of Mental Disorders University of Pittsburgh Disease Process
What is EEG Neurofeedback?
 What is EEG Neurofeedback? By Elaine Offstein, MA, Board Certified Educational Therapist All systems of our body and brain are designed to constantly work to maintain life-sustaining balance that scientists
What is EEG Neurofeedback? By Elaine Offstein, MA, Board Certified Educational Therapist All systems of our body and brain are designed to constantly work to maintain life-sustaining balance that scientists
Brian A. Coffman, PhD
 Brian A. Coffman, PhD Research Instructor Department of Psychiatry University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital Pittsburgh, PA Dr. Brian Coffman is a Research Instructor
Brian A. Coffman, PhD Research Instructor Department of Psychiatry University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine UPMC Western Psychiatric Hospital Pittsburgh, PA Dr. Brian Coffman is a Research Instructor
Non-therapeutic and investigational uses of non-invasive brain stimulation
 Non-therapeutic and investigational uses of non-invasive brain stimulation Robert Chen, MA, MBBChir, MSc, FRCPC Catherine Manson Chair in Movement Disorders Professor of Medicine (Neurology), University
Non-therapeutic and investigational uses of non-invasive brain stimulation Robert Chen, MA, MBBChir, MSc, FRCPC Catherine Manson Chair in Movement Disorders Professor of Medicine (Neurology), University
Cognitive domain: Knowledge Answer location: Introduction: Knowledge from Cognitive Deficits Question type: MS Ans: C
 1 McBride and Cutting, Cognitive Psychology: Theory, Process, and Methodology Instructor Resources Chapter 2: Cognitive Neuroscience Multiple Choice 1. Neuroscientists have learned a great deal about which
1 McBride and Cutting, Cognitive Psychology: Theory, Process, and Methodology Instructor Resources Chapter 2: Cognitive Neuroscience Multiple Choice 1. Neuroscientists have learned a great deal about which
Research Article Cerebellar Cathodal Transcranial Direct Stimulation and Performance on a Verb Generation Task: A Replication Study
 Hindawi Neural Plasticity Volume 2017, Article ID 1254615, 12 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1254615 Research Article Cerebellar Transcranial Direct Stimulation and Performance on a Generation Task:
Hindawi Neural Plasticity Volume 2017, Article ID 1254615, 12 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/1254615 Research Article Cerebellar Transcranial Direct Stimulation and Performance on a Generation Task:
Statement on Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression. Position statement CERT03/17
 Statement on Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression Position statement CERT03/17 Approved by the Royal College of Psychiatrists, Committee on ECT and Related Treatments: February 2017
Statement on Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for Depression Position statement CERT03/17 Approved by the Royal College of Psychiatrists, Committee on ECT and Related Treatments: February 2017
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13
 Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Brain and Behavior Lecture 13 Technology has improved our ability to know how the brain works. Case Study (Phineas Gage) Gage was a railroad construction foreman. An 1848 explosion forced a steel rod through
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates declarative memory
 Brain Stimulation (2012) 5, 231 41 www.brainstimjrnl.com Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates declarative memory Amir Homayoun Javadi, a,b
Brain Stimulation (2012) 5, 231 41 www.brainstimjrnl.com Transcranial direct current stimulation (tdcs) of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates declarative memory Amir Homayoun Javadi, a,b
Est-ce que l'eeg a toujours sa place en 2019?
 Est-ce que l'eeg a toujours sa place en 2019? Thomas Bast Epilepsy Center Kork, Germany Does EEG still play a role in 2019? What a question 7T-MRI, fmri, DTI, MEG, SISCOM, Of ieeg course! /HFO, Genetics
Est-ce que l'eeg a toujours sa place en 2019? Thomas Bast Epilepsy Center Kork, Germany Does EEG still play a role in 2019? What a question 7T-MRI, fmri, DTI, MEG, SISCOM, Of ieeg course! /HFO, Genetics
Brain Stimulation xxx (2012) 1e11. Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect. Brain Stimulation. journal homepage:
 Brain Stimulation xxx (2012) 1e11 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Brain Stimulation journal homepage: www.brainstimjrnl.com 1 2 3 4 5 6 Q6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
Brain Stimulation xxx (2012) 1e11 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Brain Stimulation journal homepage: www.brainstimjrnl.com 1 2 3 4 5 6 Q6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
