Expression of P2X 6 receptors in the enteric nervous system of the rat gastrointestinal tract
|
|
|
- Marianna Cunningham
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: DOI /s ORIGINAL PAPER Expression of P2X 6 receptors in the enteric nervous system of the rat gastrointestinal tract Qiang Yu Zhengqing Zhao Jihu Sun Wei Guo Jiqiang Fu GeoVrey Burnstock Cheng He Zhenghua Xiang Accepted: 23 October 2009 / Published online: 28 November 2009 Springer-Verlag 2009 Abstract Expression of P2X 4 and P2X 6 receptor subunits in the gastrointestinal tract of the rat was studied with double-labeling Xuorescence immunohistochemistry. The results showed that P2X 6 receptors were expressed widely in the submucosal and myenteric plexuses. In the myenteric plexus, P2X 6 receptors were expressed mainly in large size neurons which resembled Dogiel type II neurons. These P2X 6 receptor-immunoreactive (ir) neurons also expressed calbindin 28K, calretinin and neuronal nuclei (NeuN), proteins that are markers of intrinsic sensory neurons. In the submucosal plexus, all the calbindin 28K, calretinin and NeuN-ir cells were immunoreactive for P2X 6 receptors. P2X 6 receptors do not form homomultimers, but rather heteromultimers with either P2X 2 or P2X 4 receptors. P2X 4 Q. Yu and Z. Zhao contributed equally to this work. Q. Yu W. Guo J. Fu C. He Z. Xiang (&) Department of Neurobiology, Institute of Neuroscience, Neuroscience Research Centre of Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, People s Republic of China zhxiang@hotmail.com Z. Zhao Department of Neurology, Neuroscience Research Centre of Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, People s Republic of China J. Sun Department of Physiology, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai, People s Republic of China G. Burnstock Autonomic Neuroscience Centre, Royal Free and University College Medical School, Rowland Hill Street, London NW3 2PF, UK receptors were not expressed in neurons, but were expressed in macrophages of the rat gastrointestinal tract. These data indicate that P2X 6 receptors are mainly expressed on intrinsic sensory neurons and that ATP, via P2X 6 receptors probably in heteromeric combination with P2X 2 receptors, may be involved in regulating the physiological functions of these neurons. Keywords P2X 6 receptor Enteric neuron Gastrointestinal tract Rat Introduction ATP is a primitive signaling molecule that has been retained as a co-transmitter in every nerve type in both the peripheral and central nervous systems, although the relative role of ATP varies considerably in diverent species and pathological conditions (Burnstock 2007a). ATP acts on two types of P2 purinoceptors on evector tissues. P2X and P2Y purinoceptors are ligand-gated cation channels and G- protein-linked receptors, respectively (Ralevic and Burnstock 1998). ATP acting at P2X receptors may function as an excitatory neurotransmitter in central and sympathetic neurons and enteric ganglia (Dunn et al. 2001; Burnstock 2007a). Seven P2X receptor subunits have been cloned and each subunit has unique pharmacological and electrophysiological properties and it is established that three subunits form the cation channel either as homo- or hetero-multimers. The P2X 6 receptor does not form a homomultimer, but only a heteromultimer receptor with either P2X 2 or P2X 4 receptor subunits (North 2002). Morphological and functional data show that ATP, via P2X receptors, regulates the functions of the gastrointestinal tract (see Burnstock 2008). Pharmacological studies have shown that 90% of
2 178 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: cultured myenteric neurons of the guinea-pig small intestine respond to ATP via P2X purinoceptors, the properties of which are similar to those of cloned P2X 1, P2X 2, P2X 4, P2X 5 and P2X 6 receptors (Zhou and Galligan 1996; Barajas-Lopez et al. 1996). Immunohistochemical studies have shown that P2X 2 (mouse, rat and guinea-pig), P2X 3 (mouse, rat and guinea-pig) and P2X 5 (mouse) receptors are expressed in neurons of the submucosal and myenteric ganglia in the gastrointestinal tract (Castelucci et al. 2002, 2003; Van Nassauw et al. 2002; Poole et al. 2002; Xiang and Burnstock 2004a, b; Ruan and Burnstock 2005). In a report from Van Crombruggen et al. (2007), P2X 4 receptor staining was found only in macrophages in the rat distal colon and P2X 6 receptor staining only in enteric glial cells. P2X 2, P2X 4, P2X 5 and P2X 6 receptors are expressed widely in the central nervous system (Burnstock 2007a; Guo et al. 2008). Thus, it is possible that P2X 4 and P2X 6 receptors may be expressed in neurons of the submucosal and myenteric ganglia of the gastrointestinal tract. In this study, we used immunostaining methods to systematically study the expression patterns of P2X 4 and P2X 6 receptors on neurons of the rat gastrointestinal tract. Here, we report that the P2X 6 receptor is widely expressed in the submucosal and myenteric ganglia of the enteric nervous system of the rat, where it may form a heteromultimer receptor with P2X 2 receptors, rather than P2X 4 receptors, which are expressed on macrophages. Materials and methods All experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Second Military Medical University. Six adult rats ( g) were used. The rats were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbitone and perfused through the aorta with 0.9% NaCl solution and 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 mol/l phosphate buver ph 7.4. The digestive tracts were removed and washed with phosphate buvered saline (PBS). One end of the segment was knotted with a silk thread and Wxative was injected into the lumen to Wll it and the open end was also knotted with a silk thread. The Wxative-Wlled segment was then immersed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 mol/l phosphate buver, ph 7.4, for 4 6 h. The mucosa was discarded and the submucosal and myenteric plexuses of the gastric corpus, jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon of the rats were used as whole-mount preparations. Immunohistochemistry The development and speciwcity of the P2X 4 and P2X 6 receptor polyclonal antisera have been previously reported (Xiang et al. 1998; Oglesby et al. 1999). The following protocol was used for double immunostaining of P2X 6 receptors with calbindin D-28K, NeuN (neuronal nuclei marker), calretinin, GFAP (enteric glial cell marker) and PGP9.5 (neuronal maker), and P2X 4 with ED1 (a marker of activated macrophages). The preparations were washed 3 5 min in PBS, and then preincubated in antiserum solution 1(10% normal bovine serum, 0.2% Triton X-100, 0.4% sodium azide in 0.01 mol/l PBS ph 7.2) for 30 min, followed by incubation with diverent combinations of P2X 6 antibody diluted 1:800, P2X 4 antibody diluted 1:400, calbindin antibody (mouse anti-rat; SWANT) diluted 1:500, calretinin antibody (mouse anti-rat; SWANT) diluted 1:500, NeuN antibody (mouse anti-rat; Chemicon) diluted 1:400, ED1(mouse anti-rat; chemicon) antibody diluted 1:400, GFAP antibody (mouse anti-rat; Biomeda) diluted 1:400, PGP9.5 antibody (mouse anti-rat; Neuromics) diluted 1:200 in antiserum solution 2 (1% normal bovine serum, 0.2% Triton X-100, 0.4% sodium azide in 0.01 mol/l PBS ph 7.2), at room temperature. Subsequently, the preparations were incubated with Cy3-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG diluted 1:400 for P2X 6 and P2X 4 antibodies and FITC-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG diluted 1:200 for calbindin, calretinin, NeuN, GFAP, PGP9.5 and ED1 antibodies in antiserum solution 2 for 2 h at room temperature. Both Cy3-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit IgG and FITC-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgG are specialized for multiple immunostaining from Jackson Immunoresearch Lab. All the incubations and reactions were separated by 3 10 min washes in PBS. Control experiments were carried out with P2X 4 or P2X 6 antibody preabsorbed with P2X 4 or P2X 6 peptides. No staining was observed in those preparations incubated with antiserum solutions preabsorbed with P2X 4 or P2X 6 peptides. A further negative control of omitting the primary antibody was also carried out. No staining was also observed in those preparations. In order to further conwrm the speciwcity of the P2X 4 and P2X 6 receptor antibodies, western blot analysis was carried out. Rats were deeply anesthetized by sodium pentobarbital (60 mg/kg) and killed by decapitation. The proximal colon was rapidly removed, washed with ice-cold PBS and lysed with 20 mm Tris HCl buver, ph 8.0, containing 1% NP-40, 150 mm NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 10% glycerol, 0.1% mercaptoethanol, 0.5 mm dithiothreitol, and a mixture of proteinase and phosphatase inhibitors (Sigma). Protein concentration was determined by the bovine serum albumin (BCA) protein assay method using BCA as standard (BCA protein assay kit from Beyotime). Protein samples (100 μg) from the colon were loaded per lane, separated by SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide gels) and then were electrotransferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were blocked with 10% nonfat dry milk in Tris-buVered saline for 1 h and incubated overnight
3 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: at 4 C with P2X 4 or P2X 6 antibody (Roche Palo Alto, CA, USA) diluted 1:1,000 in 2% BSA in PBS. The membranes were then incubated with alkaline phosphatase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Sigma) diluted 1:5,000 in 2% BSA in PBS for 1 h at room temperature. The color development was performed with 400 μg/ml nitro-blue tetrazolium, 200 μg/ml 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate and 100 mg/ml levamisole in TSM2 (0.1 mol/l Tris HCl2 buver, ph 9.5, 0.1 mol/l NaCl and 0.05 mol/l MgCl 2 ) in the dark. Bands were scanned using a densitometer (GS-700; Bio-Rad Laboratories). Western blotting, performed on tissue extracts derived from the rat proximal colon (Fig. 1), assessed the speciwcity of the polyclonal P2X 4 and P2X 6 receptor antibody. An immunoreactive band was detected at about kda that corresponded to the molecular weight of the P2X 4 and P2X 6 receptor (Fig. 1, lanes 1 and 3). Preadsorption of the antiserum with the peptide antigen resulted in the absence of the band (Fig. 1, lanes 2 and 4), indicating that the antibodies detected the appropriate antigen sequence. Quantitative analysis Some of the preparations were counterstained with NeuN antiserum or PGP9.5 in order to assess the number of neurons in the ganglia (Figs. 4, 7, 9). For Xuorescence immunocytochemistry, whole-mount preparations were used to perform a quantitative analysis as previously described (Van Nassauw et al. 2002). BrieXy, positively stained neuron bodies in the submucosal and myenteric ganglia were counted per visual Weld (area of 0.62 mm 2 ). Ten randomly chosen Welds in each whole-mount preparation and three preparations of each rat were analyzed. At least four rats were used for each marker. The percentage of neurons immunoreactive for a particular marker that were also positive for a diverent marker was calculated and expressed as mean standard error of the mean. Fig. 1 Western blotting from colon extracts. M molecular weight marker. Lanes 1 and 3 P2X 4 and P2X 6 receptor immunoreactive bands are located at about 43 kda, respectively. Lanes 2 and 4, preabsorption of the P2X 4 and P2X6 receptor antisera with its peptide antigen, respectively, which resulted in the absence of the band Photomicroscopy Images were taken with the Nikon digital camera DXM1200 (Nikon, Japan) attached to a Nikon Eclipse E600 microscope (Nikon). Images were imported into a graphics package (Adobe Photoshop). Results P2X 6 receptor immunoreactivity occurred in nerve cell bodies in all regions that were examined in the myenteric plexus of the stomach, ileum, proximal and distal colon, and in the submucosal plexus of the jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon. Immunoreactivity occurred in the perikarya of the nerve cells, but not in the processes in either the submucosal or myenteric plexuses. In the myenteric plexus, the majority of positive cells were large (42 6 μm long diameter), although a few small positive cells (18 5 μm in diameter) were also found in some ganglia. The large positive cells had negative eccentric nuclei. In the gastric corpus myenteric plexus, about 10% of ganglion cells were immunostained with the P2X 6 receptor antiserum and most of the positive ganglion neurons were moderately immunostained (Figs. 2a, 3a, 4a). In the small intestine myenteric plexus of whole-mount preparations, P2X 6 receptor-immunoreactive (ir) neurons were found in all ganglia and about 23 and 27% of ganglion cells were positively immunostained for the P2X 6 receptor in the jejunum and ileum, respectively. Both large and small positive ganglion neurons were present, but the majority of them were large size cells (Figs. 2d, g, 3d, g, 4d, g). In the myenteric plexus of the distal colon, about 25% of ganglion neurons were positively stained by the P2X 6 receptor antiserum. Large and small positive ganglion neurons were also present in the myenteric plexus of the colon (Figs. 2j, m, 3j, m, 4j, m). Double-labeling studies were conducted to identify the major classes of neurons with P2X 6 receptor immunoreactivity in the myenteric plexus of the gastric corpus, jejunum, ileum proximal and distal colon, and the submucosal plexus of the jejunum, ileum, and proximal and distal colon. In the myenteric plexus of all segments we examined, almost all the P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons were also immunoreactive for calbindin 28K and calretinin, although occasionally a few P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons, usually with small diameter cell bodies, were not found to be immunoreactive for calbindin 28K or calretinin (Figs. 2, 3). There are two diverent types of neurons in the myenteric plexus of all segments of the gastrointestinal tract. In the NeuN NC neurons, NeuN localizes in both the nucleus and cytoplasm, and in the NeuN N neurons, NeuN localizes only in the nucleus (Fig. 4). Almost all of the P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons
4 180 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Fig. 2 Colocalization of P2X 6 receptor-ir and calbindin-ir in the myenteric plexus of the rat gastrointestinal tract. a, d, g, j and m P2X 6 receptor-ir cells (red) in the myenteric plexus of gastric corpus, jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon, respectively. b, e, h, k and n Calbindin 28K-ir cells (green) in the myenteric plexus of gastric corpus, jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon from the same Welds as a, d, g, j and m, respectively. c, f, i, l and o The merged images from a and b, d and e, g and h, j and k, m and o, respectively. Note that all the large size cells express both P2X 6 receptor-ir and calbindin 28K-ir (scale bars 60 μm) overlapped with the NeuN NC neurons expressing NeuN (Fig. 4). In the submucosal plexus of the jejunum, ileum and distal colon, about 52 60% of P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons were immunoreactive for calbindin 28K (Fig. 5), about 78 85% of P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons for calretinin (Fig. 6), and almost all the P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons were labeled with NeuN (Fig. 7). Table 1 summarizes the percentages of P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons that were immunoreactive for calbindin 28K, calretinin and NeuN in the submucosal plexus of the jejunum, ileum and distal colon. P2X 4 receptor immunoreactivity did not occur in nerve cells in any regions that were examined in the myenteric plexus and submucosal plexus preparations of the rat gastrointestinal tract, but did occur in macrophage-like cells (Fig. 8a). Double immunostaining showed that these P2X 4 receptor-ir cells were also immunoreactive for ED1 (a marker of activated macrophage) (Fig. 8b, c). In order to further conwrm the type of cells expressing P2X 6 receptors in the enteric plexuses, a GFAP antibody was used. Double immunostaining clearly demonstrated that P2X 6 receptor-ir cells did not express GFAP-ir, which is a marker of the enteric glial cell (Fig. 9). As the cells with P2X 6 receptor-ir also expressed NeuN and PGP9.5, but did not express GFAP, all of these cells can be identiwed as neurons.
5 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Fig. 3 Colocalization of P2X 6 receptor-ir and calretinin-ir in the myenteric plexus of the rat gastrointestinal tract. a, d, g, j and m P2X 6 receptor-ir cells (red) in the myenteric plexus of gastric corpus, jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon, respectively. b, e, h, k and n Calretinin-ir cells (green) in the myenteric plexus of gastric corpus, jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon from the same Welds as a, d, g, j and m, respectively. c, f, i, l and o The merged images from a and b, d and e, g and h, j and k, m and o, respectively. Note that all the large size cells express both P2X 6 receptor-ir and calretinin-ir (scale bars 60 μm) Discussion In the present study, the distribution patterns and morphological characteristics of P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons have been studied systematically in all the major regions of the rat gastrointestinal tract. The results show that P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons are distributed widely in the myenteric plexus of stomach, jejunum, ileum and colon, and the submucosal plexus of jejunum, ileum and colon. Several previous studies have shown that there are intrinsic sensory neurons in the intestine (Langley and Magnus 1905; Crema et al. 1970; Furness et al. 1995). They have been identiwed in the small intestine of the guinea-pig as Dogiel type II neurons (Kirchgessner et al. 1992; Kunze et al. 1995; Bertrand et al. 1997). Dogiel type II neurons with similar electrophysiological properties, projections and chemistries have been found in the large intestine of the guinea-pig and in the rat small intestine, which suggests that these neurons are also intrinsic sensory neurons in other regions and species (Mann et al. 1997; Lomax et al. 1999; Neunlist et al. 1999). Calbindin 28K is believed to be expressed in intrinsic sensory neurons of submucosal and myenteric plexuses of the guinea-pig (Furness 2000). Intrinsic sensory neurons, with Dogiel type II morphology, in the myenteric plexus of the rat ileum were also reported to express calbindin and calretinin.
6 182 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Fig. 4 Colocalization of P2X 6 receptor-ir and NeuN-ir in the myenteric plexus of the rat gastrointestinal tract. a, d, g, j and m P2X 6 receptor-ir cells (red) in the myenteric plexus of gastric corpus, jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon, respectively. b, e, h, k and n NeuN-ir cells (green) in the myenteric plexus of gastric corpus, jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon from the same Welds as a, d, g, j and m, respectively. c, f, i, l and o The merged images from a and b, d and e, g and h, j and k, m and o, respectively. Note that all the large size cells express both P2X 6 receptor-ir and NeuN-ir (scale bars 60 μm) Thus, calbindin and calretinin are also markers of intrinsic sensory neurons in the myenteric plexus of the rat ileum (Mann et al. 1999). In this study, we show that in the myenteric plexus the majority of P2X 6 receptor-positive cells were of the Dogiel II neuron shape, i.e., large size, and long diameter of about 42 6 μm. The double immunostaining study showed that almost all the P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons were found to coexist with calbindin 28K and calretinin, although occasionally a few small P2X 6 receptor-ir neurons were not found to be immunoreactive for calbindin 28K and calretinin in some myenteric ganglia. It could be deduced that P2X 6 receptors in the myenteric plexus of the rat are expressed in intrinsic sensory neurons. In the submucosal plexus, 52 60% of neurons expressing P2X 6 receptors were also immunoreactive for calbindin, and 78 85% of these neurons for calretinin. Thus, a group of neurons expressing P2X 6 receptors also express both calbindin and calretinin. In the myenteric plexus and submucosal plexus of the guinea-pig, calbindin is exclusively expressed on intrinsic sensory neurons and calretinin is exclusively expressed on cholinergic secretomotor and vasodilator neurons, but not on intrinsic sensory neurons (Furness 2000). In contrast, both calbindin and calretinin appear to be markers for intrinsic sensory neurons in mouse gastrointestinal tract (Sang and Young 1996, 1998), showing that there is a
7 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Fig. 5 Colocalization of P2X 6 receptor-ir and calbindin 28K-ir in the submucosal plexus of the rat gastrointestinal tract. a, d, g and j P2X 6 receptor-ir cells (red) in the submucosal plexus of jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon, respectively. b, e, h and k Calbindin-28K-ir cells (green) in the submucosal plexus of jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon from the same Welds as a, d, g, j and m, respectively. c, f, i and l The merged images from a and b, d and e, g and h, j and k, respectively. Note that all the calbindin 28K-ir cells are also immunoreactive for P2X 6 receptors (scale bars 60 μm) species diverence in the expression patterns of these two calcium binding proteins in enteric neurons. The neuronal nuclei (NeuN) antibody was initially described as a result of attempts to identify novel proteins involved in the regulation of neuronal phenotype. The appearance of NeuN is coincident with neuronal diverentiation and the neuron s exit from the cell cycle (Mullen et al. 1992). It has been recently shown that nerve cell bodies with the shape of Dogiel type II neurons in both myenteric and submucous ganglia in the guinea-pig ileum express NeuN immunoreactivity. It was suggested that NeuN is a selective marker for intrinsic sensory neurons (Costa et al. 2001; Poole et al. 2002). It is reported that NeuN labels the nuclei of almost all the enteric neurons (Chiocchetti et al. 2003), but that cytoplasmic expression of NeuN appears to be restricted to Dogiel type II neurons (Chiocchetti et al. 2003; Van Nassauw et al. 2005). In the present study, two types of neurons expressing NeuN immunoreactivity are identiwed. The NeuN NC neurons expressing NeuN immunoreactivity in both the cytoplasm and nuclei were also immunoreactive for P2X 6 receptors in all segments of the rat gastrointestinal tract. To our knowledge, there are no reports about NeuN immunoreactivity in intrinsic sensory neurons of rat myenteric neurons. Thus, this study has demonstrated for the Wrst time intrinsic sensory neurons of rat myenteric neurons that express NeuN. We have also shown that the pattern of expression of calbindin and calretinin appears to be comparable to that seen in the mouse, rather than the guinea-pig, both being markers for intrinsic sensory neurons. Furthermore, our study demonstrates that P2X 6 receptors are selectively expressed on intrinsic sensory neurons of the rat myenteric plexus. In the submucosal plexus, almost all the neurons expressing P2X 6 receptors are also immunoreactive for NeuN and vice versa. Only the NeuN NC -ir neurons remain to be identiwed in the submucosal plexus of the rat intestinal tract. Further experiments need to be carried out in order to determine whether all the NeuN NC neurons in
8 184 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Fig. 6 Colocalization of P2X 6 receptor-ir and calretinin-ir in the submucosal plexus of the rat gastrointestinal tract. a, d, g and j P2X 6 receptor-ir cells (red) in the submucosal plexus of jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon, respectively. b, e, h and k Calretinin-ir cells (green) in the submucosal plexus of jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon from the same Welds as a, d, g, j and m, respectively. c, f, i and l The merged images from a and b, d and e, g and h, j and k, respectively. Note that all the calretinin-ir cells are also immunoreactive for P2X 6 receptors the submucsoal plexus of the rat intestinal tract are intrinsic sensory neurons. Seven P2X receptor subunits have been cloned (Burnstock 2007b). There has been some ambiguity in the interpretation of electrophysiological results regarding which P2X receptor subunit(s) are present in myenteric ganglion neurons. Zhou and Galligan (1996) suggested that the electrophysiological properties of myenteric neurons in the small intestine indicated that 10% of them expressed P2X 1 or P2X 3 receptors and that most of them expressed P2X 2 or P2X 5 receptors. The report of Lepard et al. (1997) showed that the P2X 2 receptor was the main purinoceptor subunit, but Barajas-Lopez et al. (1996) suggested that P2X 4 and P2X 6, perhaps as heteromultimers, were dominantly expressed on myenteric neurons. Molecular cloning of P2X receptor subunits indicates that a subunit is composed of a 379- to 472-amino acid protein, in which the N and C terminals are in the cytoplasm connected by two-transmembrane-spanning segments and a large extracellular loop (Ralevic and Burnstock 1998; North 2002). It is speculated that a receptor is assembled with multiple subunits (Ralevic and Burnstock 1998; Khakh et al. 2001). P2X receptor subunits are able to form homo- and heteromeric multimers as the functional receptor channels. Homomeric P2X 1, P2X 2, P2X 3, P2X 4, P2X 5 and P2X 7 channels and heteromeric P2X 1/2, P2X 1/5, P2X 1/4, P2X 2/3, P2X 2/6, P2X 4/6 and P2X 4/7 receptor channels have been characterized following heterologous expression (Khakh et al. 2001; Burnstock 2007b; Guo et al. 2007). Our previous morphological data showed that P2X 2 and P2X 3 receptors were widely expressed in neurons of the submucosal and myenteric ganglia in the rat gastrointestinal tract (Xiang and Burnstock 2004a, b). Some P2X 2 receptor-ir neurons in the rat myenteric ganglia are of the Dogiel type II shape, with large cell bodies, that were immunoreactive for both calbindin and calretinin (Xiang and Burnstock 2004b). Thus, P2X 2 and P2X 6 receptor subunits expressed on P2X receptor-containing neurons could assemble into homomeric P2X 2 channels or heteromeric
9 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Fig. 7 Colocalization of P2X 6 receptor-ir and NeuN-ir in the submucosal plexus of the rat gastrointestinal tract. a, d, g and j P2X 6 receptor-ir cells (red) in the submucosal plexus of jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon, respectively. b, e, h and k NeuN-ir cells (green) in the submucosal plexus of jejunum, ileum, proximal and distal colon from the same Welds as a, d, g and j, respectively. c, f, i and l The merged images from a and b, d and e, g and h, j and k, respectively. Note that almost all the NeuN-ir cells are also immunoreactive for P2X 6 receptors and vice versa (scale bars 60 μm) Table 1 Quantitative analysis of double-labeling studies between P2X 6 receptors and calbindin (CB), P2X 6 receptors and calretinin (CR) and P2X 6 receptors and NeuN in the submucosal plexus of rat jejunum, ileum and distal colon Region P2X 6 -ir+ P2X 6 -ir+ P2Y 6 -ir+ P2Y 6 -ir+ P2Y 6 -ir+ P2Y 6 -ir+ CB-ir+ CB-ir CR-ir+ CR-ir NeuN+ NeuN- Jejunum % 48 8% 42 6% 58 5% 95 9% 5 2% Ileum % 46 6% 81 9% 19 6% 97 9% 3 1% Distal colon % 40 7% 85 5% 15 3% 96 8% 4 1% The Wrst column shows the mean number of P2X 6 -ir neurons also labeled with CB SEM, expressed as a percentage underneath. The second column shows the mean number of P2X 6 -ir neurons that were not immunopositive for CB SEM, expressed as a percentage underneath. The third column shows the mean number of P2X 6 receptors-ir neurons also immunopositive for CR SEM, expressed as a percentage underneath. The fourth column shows the mean number of P2X 6 receptors-ir neurons that were not immunopositive for CR SEM, expressed as a percentage underneath. The Wfth column shows the mean number of P2X 6 receptors-ir neurons also immunopositive for NeuN SEM, expressed as a percentage underneath. The sixth column shows the mean number of P2X 6 receptors-ir neurons that were not immunopositive for NeuN SEM, expressed as a percentage underneath
10 186 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Fig. 8 P2X 4 receptor immunoreactivity in the myenteric plexus of rat ileum and co-localization with ED1 (a marker of activated macrophages). a P2X 4 receptor-ir cells (red). b ED1-ir cells (green) from the same Weld as a. c Merged image from a and b, note that all the P2X 4 receptor-ir cells are also immunoreactive for ED1. No neuron-like cells were found to be immunoreactive for P2X 4 receptors (scale bar a, b 60 μm, c 30 μm) P2X 2/6 in enteric neurons of the rat gastrointestinal tract. Further studies using speciwc antagonists are required for unequivocal support of these possible functional combinations of P2X receptor multimers. In this report we found that P2X 4 receptor subunits were expressed only in macrophages, which is consistent with previous reports, and that P2X 6 receptor subunits were expressed only in neurons of the enteric plexus, which divers from a previous report (Van Crombruggen et al. 2007). The speciwcity of the P2X 6 receptor antibody used in this study had been conwrmed by previous reports (Oglesby et al. 1999; Loesch and Burnstock 2001; Glass et al. 2002), and further by preabsorption controls and Western blot experiments reported in this study. In the previous report by Van Crombruggen et al. (2007), the antibodies were obtained from diverent commercial suppliers and this may account for the diverences in the expression patterns found between their study and ours. In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that P2X 6 receptor subunits are distributed widely in the rat gastrointestinal tract. In the myenteric plexus the P2X 6 receptor localizes mainly in the intrinsic primary averent neurons, as these P2X 6 receptor-ir cells are also immunoreactive for calbindin 28K, calretinin and NeuN, and their morphology resembles that of Dogiel type II neurons. In the submucosal plexus, all the calbindin 28K, calretinin and NeuN-ir cells are immunoreactive for P2X 6 receptors, although some of the P2X 6 receptor-ir cells are not immunoreactive for calbindin 28K and calretinin. The P2X 4 receptor was not expressed by neurons of the rat gastrointestinal tract, but was expressed by macrophages. These data indicate that P2X 6 receptors are mainly expressed on intrinsic sensory
11 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Fig. 9 Double immunostaining of P2X 6 receptors with GFAP or PGP9.5. a P2X 6 receptor-ir cells in the myenteric plexus of rat ileum. b GFAP-ir cells in the same Weld as a. c The merged image from a and b; note that no GFAP-ir and P2X 6 receptor-ir was found to coexist in the same cells. d PGP9.5-ir cells in the myenteric plexus of the proximal colon. e P2X 6 receptor-ir cells in the myenteric plexus of the proximal colon from the same Weld as d. f The merged image from d and e, note that all the P2X 6 receptor-ir cells also express PGP9.5-ir (scale bars a f 60 μm) neurons and that ATP, via P2X 6 receptors probably in heteromeric combination with P2X 2 receptors, may be involved in regulating the physiological functions of these neurons. Acknowledgments The authors thank Dr. Gillian E. Knight for her excellent editorial assistance. We also thank Roche Bioscience, Palo Alto, CA for kindly supplying P2X antisera and peptides. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of P. R. China ( to Z. Xiang). References Barajas-Lopez C, Huizinga JD, Collins SM, Gerzanich V, Espinosa- Luna R, Peres AL (1996) P2x-purinoceptors of myenteric neurones from the guinea-pig ileum and their unusual pharmacological properties. Br J Pharmacol 119: Bertrand PP, Kunze WA, Bornstein JC, Furness JB, Smith ML (1997) Analysis of the responses of myenteric neurons in the small intestine to chemical stimulation of the mucosa. Am J Physiol 273:G422 G435 Burnstock G (2007a) Physiology and pathophysiology of purinergic neurotransmission. Physiol Rev 87: Burnstock G (2007b) Purine and pyrimidine receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 64: Burnstock G (2008) The journey to establish purinergic signalling in the gut. Neurogastroenterol Motil 20(Suppl 1):8 19 Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Poole DP, Furness JB (2002) The distribution of purine P2X(2) receptors in the guinea-pig enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol 117: Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Furness JB (2003) P2X(2) purine receptor immunoreactivity of intraganglionic laminar endings in the mouse gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 312: Chiocchetti R, Poole DP, Kimura H, Aimi Y, Robbins HL, Castelucci P, Furness JB (2003) Evidence that two forms of choline acetyltransferase are diverentially expressed in subclasses of enteric neurons. Cell Tissue Res 311:11 22 Costa M, Brody K, Brookes SJH (2001) A new marker for enteric primary averent neurones. Neurogastroenterol Mot 13:383 Crema A, Frigo GM, Lecchini S (1970) A pharmacological analysis of the peristaltic rexex in the isolated colon of the guinea-pig or cat. Br J Pharmacol 39: Dunn PM, Zhong Y, Burnstock G (2001) P2X receptors in peripheral neurons. Prog Neurobiol 65: Furness JB (2000) Types of neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Auton Nerv Syst 81:87 96 Furness JB, Johnson PJ, Pompolo S, Bornstein JC (1995) Evidence that enteric motility rexexes can be initiated through entirely intrinsic mechanisms in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil 7:89 96 Glass R, Loesch A, Bodin P, Burnstock G (2002) P2X4 and P2X6 receptors associate with VE-cadherin in human endothelial cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 59(5): Guo C, Masin M, Qureshi OS, Murrell-Lagnado RD (2007) Evidence for functional P2X4/P2X7 heteromeric receptors. Mol Pharmacol 72: Guo W, Xu X, Gao X, Burnstock G, He C, Xiang Z (2008) Expression of P2X5 receptors in the mouse CNS. Neuroscience 156: Khakh BS, Burnstock G, Kennedy C, King BF, North RA, Seguela P, Voigt M, Humphrey PP (2001) International union of pharmacology. XXIV. Current status of the nomenclature and properties of P2X receptors and their subunits. Pharmacol Rev 53: Kirchgessner AL, Tamir H, Gershon MD (1992) IdentiWcation and stimulation by serotonin of intrinsic sensory neurons of the submucosal plexus of the guinea pig gut: activity-induced expression of Fos immunoreactivity. J Neurosci 12:
12 188 Histochem Cell Biol (2010) 133: Kunze WA, Bornstein JC, Furness JB (1995) IdentiWcation of sensory nerve cells in a peripheral organ (the intestine) of a mammal. Neuroscience 66:1 4 Langley JN, Magnus R (1905) Some observations of the movements of the intestine before and after degenerative section of the mesenteric nerves. J Physiol 33:34 51 LePard KJ, Messori E, Galligan JJ (1997) Purinergic fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials in myenteric neurons of guinea pig: distribution and pharmacology. Gastroenterology 113: Loesch A, Burnstock G (2001) Immunoreactivity to P2X(6) receptors in the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system: an ultrastructural study with extravidin and colloidal gold-silver labelling. Neuroscience 106: Lomax AE, Sharkey KA, Bertrand PP, Low AM, Bornstein JC, Furness JB (1999) Correlation of morphology, electrophysiology and chemistry of neurons in the myenteric plexus of the guineapig distal colon. J Auton Nerv Syst 76:45 61 Mann PT, Southwell BR, Ding YQ, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N, Furness JB (1997) Localisation of neurokinin 3 (NK3) receptor immunoreactivity in the rat gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 289:1 9 Mann PT, Furness JB, Southwell BR (1999) Choline acetyltransferase immunoreactivity of putative intrinsic primary averent neurons in the rat ileum. Cell Tissue Res 297: Mullen RJ, Buck CR, Smith AM (1992) NeuN, a neuronal speciwc nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development 116: Neunlist M, Reiche D, Michel K, Pfannkuche H, Hoppe S, Schemann M (1999) The enteric nervous system: region and target speciwc projections and neurochemical codes. Eur J Morphol 37: North RA (2002) Molecular physiology of P2X receptors. Physiol Rev 82: Oglesby IB, Lachnit WG, Burnstock G, Ford APDW (1999) Subunit speciwcity of polyconal antisera to the carboxy terminal regions of P2X receptors P2X1 through P2X7. Drug Dev Res 47: Poole DP, Castelucci P, Robbins HL, Chiocchetti R, Furness JB (2002) The distribution of P2X3 purine receptor subunits in the guinea pig enteric nervous system. Auton Neurosci 101:39 47 Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50: Ruan HZ, Burnstock G (2005) The distribution of P2X5 purinergic receptors in the enteric nervous system of mouse. Cell Tissue Res 319: Sang Q, Young HM (1996) Chemical coding of neurons in the myenteric plexus and external muscle of the small and large intestine of the mouse. Cell Tissue Res 284:39 53 Sang Q, Young HM (1998) The identiwcation and chemical coding of cholinergic neurons in the small and large intestine of the mouse. Anat Rec 251: Van Crombruggen K, Van Nassauw L, Timmermans JP, Lefebvre RA (2007) Inhibitory purinergic P2 receptor characterisation in rat distal colon. Neuropharmacol 53(2): Van Nassauw L, Brouns I, Adriaensen D, Burnstock G, Timmermans JP (2002) Neurochemical identiwcation of enteric neurons expressing P2X(3) receptors in the guinea-pig ileum. Histochem Cell Biol 118: Van Nassauw L, Wu M, De Jonge F, Adriaensen D, Timmermans JP (2005) Cytoplasmic, but not nuclear, expression of the neuronal nuclei (NeuN) antibody is an exclusive feature of Dogiel type II neurons in the guinea-pig gastrointestinal tract. Histochem Cell Biol 124: Xiang Z, Burnstock G (2004a) Development of nerves expressing P2X3 receptors in the myenteric plexus of rat stomach. Histochem Cell Biol 122: Xiang Z, Burnstock G (2004b) P2X2 and P2X3 purinoceptors in the rat enteric nervous system. Histochem Cell Biol 121: Xiang Z, Bo X, Burnstock G (1998) Localization of ATP-gated P2X receptor immunoreactivity in rat sensory and sympathetic ganglia. Neurosci Lett 256: Zhou X, Galligan JJ (1996) P2X purinoceptors in cultured myenteric neurons of guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol 496(Pt 3):
Introduction ORIGINAL PAPER. Zhenghua Xiang Æ Geoffrey Burnstock
 Histochem Cell Biol (2006) 125: 327 336 DOI 10.1007/s00418-005-0071-3 ORIGINAL PAPER Zhenghua Xiang Æ Geoffrey Burnstock Distribution of P2Y 6 and P2Y 12 receptor: their colocalization with calbindin,
Histochem Cell Biol (2006) 125: 327 336 DOI 10.1007/s00418-005-0071-3 ORIGINAL PAPER Zhenghua Xiang Æ Geoffrey Burnstock Distribution of P2Y 6 and P2Y 12 receptor: their colocalization with calbindin,
Immunohistochemical localization of calcium binding proteins and some neurotransmitters in myenteric plexus of goat stomach
 J. Vet. Sci. (2006),G7(4), 315 319 J O U R N A L O F Veterinar y Science Immunohistochemical localization of calcium binding proteins and some neurotransmitters in myenteric plexus of goat stomach Heungshik
J. Vet. Sci. (2006),G7(4), 315 319 J O U R N A L O F Veterinar y Science Immunohistochemical localization of calcium binding proteins and some neurotransmitters in myenteric plexus of goat stomach Heungshik
T he enteric nervous system controls the function of the
 70 INTESTINAL MOTILITY Cholinergic and nitrergic inter in the myenteric plexus of the human colon A J Porter, D A Wattchow, SJHBrookes, M Costa... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
70 INTESTINAL MOTILITY Cholinergic and nitrergic inter in the myenteric plexus of the human colon A J Porter, D A Wattchow, SJHBrookes, M Costa... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence
Wei Guo Æ Jihu Sun Æ Xiaohui Xu Æ Geoffrey Bunstock Æ Cheng He Æ Zhenghua Xiang
 Histochem Cell Biol (2009) 131:29 41 DOI 10.1007/s00418-008-0493-9 ORIGINAL PAPER P2X receptors are differentially expressed on vasopressinand oxytocin-containing neurons in the supraoptic and paraventricular
Histochem Cell Biol (2009) 131:29 41 DOI 10.1007/s00418-008-0493-9 ORIGINAL PAPER P2X receptors are differentially expressed on vasopressinand oxytocin-containing neurons in the supraoptic and paraventricular
Purinergic Neuron-to-Glia Signaling in the Enteric Nervous System Dr. Brian D. Gulbransen
 1 Assistant Professor Neuroscience Program and Department of Physiology Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan USA The requirement to nourish and sustain an organism, as well as to defend it
1 Assistant Professor Neuroscience Program and Department of Physiology Michigan State University East Lansing, Michigan USA The requirement to nourish and sustain an organism, as well as to defend it
Eliades, Erlandson, Ruiz UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XVII (2014)
 Effects of Hibernation on the Enteric Nervous System of the Thirteenlined Ground Squirrels. Lauren Eliades, Martin Erlandson, Amelia Ruiz Faculty Sponsors: Dr. Sumei Liu and Dr. Scott Cooper, Department
Effects of Hibernation on the Enteric Nervous System of the Thirteenlined Ground Squirrels. Lauren Eliades, Martin Erlandson, Amelia Ruiz Faculty Sponsors: Dr. Sumei Liu and Dr. Scott Cooper, Department
Purinergic receptors and synaptic transmission in enteric neurons
 Purinergic Signalling (2008) 4:255 266 DOI 10.1007/s11302-007-9088-5 REVIEW Purinergic receptors and synaptic transmission in enteric neurons Jianhua Ren & Paul P. Bertrand Received: 25 May 2007 / Accepted:
Purinergic Signalling (2008) 4:255 266 DOI 10.1007/s11302-007-9088-5 REVIEW Purinergic receptors and synaptic transmission in enteric neurons Jianhua Ren & Paul P. Bertrand Received: 25 May 2007 / Accepted:
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
*,1 James J. Galligan
 British Journal of Pharmacology (2004) 141, 1294 1302 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp REVIEW Enteric P2X receptors as potential targets for drug
British Journal of Pharmacology (2004) 141, 1294 1302 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0007 1188/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/bjp REVIEW Enteric P2X receptors as potential targets for drug
20 2 Stomach Fig. 2.1 An illustration showing different patterns of the myenteric plexus peculiar to the regions in the guinea-pig stomach stained wit
 Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
2.4 Autonomic Nervous System
 2.4 Autonomic Nervous System The ANS regulates visceral activities normally outside the realm of consciousness and voluntary control: Circulation. Digestion. Sweating. Pupillary size. The ANS consists
2.4 Autonomic Nervous System The ANS regulates visceral activities normally outside the realm of consciousness and voluntary control: Circulation. Digestion. Sweating. Pupillary size. The ANS consists
The Identification and Chemical Coding of Cholinergic Neurons in the Small and Large Intestine of the Mouse
 THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 251:185 199 (1998) The Identification and Chemical Coding of Cholinergic Neurons in the Small and Large Intestine of the Mouse Q. SANG* AND H.M. YOUNG Department of Anatomy and Cell
THE ANATOMICAL RECORD 251:185 199 (1998) The Identification and Chemical Coding of Cholinergic Neurons in the Small and Large Intestine of the Mouse Q. SANG* AND H.M. YOUNG Department of Anatomy and Cell
Morphometry of Myenteric Neurons in Stomach
 Morphometry of Myenteric Neurons in Stomach Narbada Saini and Madhur Gupta Department of Anatomy, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh 160012 India Corresponding author:
Morphometry of Myenteric Neurons in Stomach Narbada Saini and Madhur Gupta Department of Anatomy, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh 160012 India Corresponding author:
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
H irschsprung s disease (HD) is a congenital disorder
 712 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The loss of calretinin expression indicates aganglionosis in Hirschsprung s disease I Barshack, E Fridman, I Goldberg, Y Chowers, J Kopolovic... See end of article for authors affiliations...
712 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The loss of calretinin expression indicates aganglionosis in Hirschsprung s disease I Barshack, E Fridman, I Goldberg, Y Chowers, J Kopolovic... See end of article for authors affiliations...
LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER
 ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 21, No. 2, 1988 LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER SHASHI WADHWA AND VEENA BIJLANI Department of Anatomy, All-India Institute
ACTA HISTOCHEM. CYTOCHEM. Vol. 21, No. 2, 1988 LOCALIZATION OF SUBSTANCE P-IMMUNOREACTIVITY IN THE DEVELOPING HUMAN URINARY BLADDER SHASHI WADHWA AND VEENA BIJLANI Department of Anatomy, All-India Institute
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology e-mail: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Morphological changes in the enteric nervous system caused by carcinoma of the human large intestine
 FOLIA HISTOCHEMICA ET CYTOBIOLOGICA Vol. 48, No. 1, 2010 pp. 157-162 Morphological changes in the enteric nervous system caused by carcinoma of the human large intestine Janusz Godlewski Department of
FOLIA HISTOCHEMICA ET CYTOBIOLOGICA Vol. 48, No. 1, 2010 pp. 157-162 Morphological changes in the enteric nervous system caused by carcinoma of the human large intestine Janusz Godlewski Department of
GANGLIONIC AND NON-GANGLIONIC NEURONS
 Papers on Anthropology XXVI/2, 2017, pp. 9 16 GANGLIONIC AND NON-GANGLIONIC NEURONS D. Batulevičius, G. Skripkienė, G. Graužinytė, A. Grigaitė, V. Skripka GANGLIONIC AND NON-GANGLIONIC NEURONS IN FROG
Papers on Anthropology XXVI/2, 2017, pp. 9 16 GANGLIONIC AND NON-GANGLIONIC NEURONS D. Batulevičius, G. Skripkienė, G. Graužinytė, A. Grigaitė, V. Skripka GANGLIONIC AND NON-GANGLIONIC NEURONS IN FROG
Human Obestatin ELISA
 K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine
 Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
Physiological processes in the GI tract:
 Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
Gastrointestinal physiology for medical students General principal of gastrointestinal function Motility, nervous control and blood circulation Physiological processes in the GI tract: Motility Secretion
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Overview of digestion or, gut reactions - to food
 1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
1 Key concepts in Digestion. Indigestion module Overview of digestion or, gut reactions to food Prof. Barry Campbell Gastroenterology Cellular & Molecular Physiology email: bjcampbl@liv.ac.uk http://pcwww.liv.ac.uk/~bjcampbl
Enterprise Interest None
 Enterprise Interest None EUROPEAN SOCIETY of PATHOLOGY AMSTERDAM 29th CONGRESS Parkinson s disease: myenteric gliosis in an experimental rat model Lina Carvalho 1, Ana Lúcia Silva 2, Sofia Viana 2,3, Inês
Enterprise Interest None EUROPEAN SOCIETY of PATHOLOGY AMSTERDAM 29th CONGRESS Parkinson s disease: myenteric gliosis in an experimental rat model Lina Carvalho 1, Ana Lúcia Silva 2, Sofia Viana 2,3, Inês
Mechanosensitive Enteric Neurons in the Myenteric Plexus of the Mouse Intestine
 in the Myenteric Plexus of the Mouse Intestine Gemma Mazzuoli*, Michael Schemann Human Biology, Technische Universität München, Freising, Germany Abstract Background: Within the gut the autonomous enteric
in the Myenteric Plexus of the Mouse Intestine Gemma Mazzuoli*, Michael Schemann Human Biology, Technische Universität München, Freising, Germany Abstract Background: Within the gut the autonomous enteric
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range
 Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Prevertebral ganglia and intestinofugal afferent neurones
 i6 VISCERAL PERCEPTION Prevertebral ganglia and intestinofugal afferent neurones J H Szurszewski, L G Ermilov, S M Miller... Intestinofugal afferent neurones (s) are a unique subset of myenteric ganglion
i6 VISCERAL PERCEPTION Prevertebral ganglia and intestinofugal afferent neurones J H Szurszewski, L G Ermilov, S M Miller... Intestinofugal afferent neurones (s) are a unique subset of myenteric ganglion
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
The Autonomic Nervous
 Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Di erent receptors mediating the inhibitory action of exogenous ATP and endogenously released purines on guinea-pig intestinal peristalsis
 British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 128, 313 ± 320 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Di erent receptors mediating the inhibitory action
British Journal of Pharmacology (1999) 128, 313 ± 320 ã 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0007 ± 1188/99 $15.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/bjp Di erent receptors mediating the inhibitory action
Two-color lateral flow assay for multiplex detection of causative agents behind acute febrile illnesses
 Supplementary Information Two-color lateral flow assay for multiplex detection of causative agents behind acute febrile illnesses Seoho Lee 1,2, Saurabh Mehta 2,3*, David Erickson 1,2* 1 Sibley School
Supplementary Information Two-color lateral flow assay for multiplex detection of causative agents behind acute febrile illnesses Seoho Lee 1,2, Saurabh Mehta 2,3*, David Erickson 1,2* 1 Sibley School
A. Positions and Honors
 PART II (Form Pages 7 to 9) Continued Name of Applicant (Last, first, middle): 31. BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Provide the following information for the sponsor (co-sponsor). DO NOT EXCEED FOUR PAGES. NAME OF
PART II (Form Pages 7 to 9) Continued Name of Applicant (Last, first, middle): 31. BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH Provide the following information for the sponsor (co-sponsor). DO NOT EXCEED FOUR PAGES. NAME OF
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University
 1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
1. Materials and Methods 1.1 Animals experiments process The experiments were approved by the Institution Animal Ethics Committee of Jilin University (Reference NO. 2015-003). 96 Kunming (KM) mice (8 weeks;
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table S1. Primers and fluorescent probes used for qrt-pcr analysis of relative expression levels of PPP family phosphatases. gene name forward primer, 5-3 probe, 5-3 reverse primer,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Table S1. Primers and fluorescent probes used for qrt-pcr analysis of relative expression levels of PPP family phosphatases. gene name forward primer, 5-3 probe, 5-3 reverse primer,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Original Article Expression of the P2Y2 receptor in the terminal rectum of fetal rats with anorectal malformation
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(2):1669-1676 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003704 Original Article Expression of the P2Y2 receptor in the terminal rectum of fetal rats with anorectal malformation Yuan-Mei
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(2):1669-1676 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0003704 Original Article Expression of the P2Y2 receptor in the terminal rectum of fetal rats with anorectal malformation Yuan-Mei
Postnatal development of P2 receptors in the murine gastrointestinal tract
 Neuropharmacology xx (6) 1e15 www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropharm Postnatal development of P2 receptors in the murine gastrointestinal tract Cristina Giaroni a, Gillian E. Knight b, Elena Zanetti a, Anna
Neuropharmacology xx (6) 1e15 www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropharm Postnatal development of P2 receptors in the murine gastrointestinal tract Cristina Giaroni a, Gillian E. Knight b, Elena Zanetti a, Anna
Plasticity of myenteric neurons
 Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2008; 10(2): 75-80 Plasticity of myenteric neurons N Saini and M Gupta Department of Anatomy, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India-
Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2008; 10(2): 75-80 Plasticity of myenteric neurons N Saini and M Gupta Department of Anatomy, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India-
Intestinal smooth muscles display rhythmic electrical. Identification of Neurons That Express Stem Cell Factor in the Mouse Small Intestine
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1998;115:898 908 Identification of Neurons That Express Stem Cell Factor in the Mouse Small Intestine HEATHER M. YOUNG,* SHIGEKO TORIHASHI, DANIELA CIAMPOLI,* and KENTON M. SANDERS *Department
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1998;115:898 908 Identification of Neurons That Express Stem Cell Factor in the Mouse Small Intestine HEATHER M. YOUNG,* SHIGEKO TORIHASHI, DANIELA CIAMPOLI,* and KENTON M. SANDERS *Department
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Essential Medium, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Huvec were cultured in
 Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
ab E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit
 ab139469 E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For testing ubiquitin E3 ligase activity through assessment of their ability to undergo auto-ubiquitinylation This product is for
ab139469 E3 Ligase Auto- Ubiquitilylation Assay Kit Instructions for Use For testing ubiquitin E3 ligase activity through assessment of their ability to undergo auto-ubiquitinylation This product is for
INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS
 1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
1 INTRODUCTION TO GASTROINTESTINAL FUNCTIONS 2 Learning outcomes List two main components that make up the digestive system Describe the 6 essential functions of the GIT List factors (neurological, hormonal
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN LA CROSSE. Graduate Studies EFFECTS OF HIBERNATION ON GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT AND
 UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN LA CROSSE Graduate Studies EFFECTS OF HIBERNATION ON GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT AND NEUROCHEMICAL CODING IN THE ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM OF THIRTEEN-LINED GROUND SQUIRREL (Ictidomys
UNIVERSITY OF WISCONSIN LA CROSSE Graduate Studies EFFECTS OF HIBERNATION ON GASTROINTESTINAL TRANSIT AND NEUROCHEMICAL CODING IN THE ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM OF THIRTEEN-LINED GROUND SQUIRREL (Ictidomys
Protocol for Western Blo
 Protocol for Western Blo ng SDS-PAGE separa on 1. Make appropriate percentage of separa on gel according to the MW of target proteins. Related recommenda ons and rou ne recipes of separa on/stacking gels
Protocol for Western Blo ng SDS-PAGE separa on 1. Make appropriate percentage of separa on gel according to the MW of target proteins. Related recommenda ons and rou ne recipes of separa on/stacking gels
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
TRACP & ALP double-stain Kit
 Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Angiotensin receptors and actions in guinea pig enteric nervous system
 Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289: G614 G626, 2005; doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00119.2005. Angiotensin receptors and actions in guinea pig enteric nervous system Guo-Du Wang, Xi-Yu Wang, Hong-Zhen Hu,
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 289: G614 G626, 2005; doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00119.2005. Angiotensin receptors and actions in guinea pig enteric nervous system Guo-Du Wang, Xi-Yu Wang, Hong-Zhen Hu,
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
GLUCOSE TRANSPORTERS IN THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER
 Papers on Anthropology XXI, 2012, pp. 50 55 GLUCOSE TRANSPORTERS IN THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER PIRET HUSSAR 1, INDREK BENNO 2, ÜLO HUSSAR 1 1 Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tartu,
Papers on Anthropology XXI, 2012, pp. 50 55 GLUCOSE TRANSPORTERS IN THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER PIRET HUSSAR 1, INDREK BENNO 2, ÜLO HUSSAR 1 1 Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, University of Tartu,
T. K. Smith,, J. C. Bornstein,21b and J. B. Furnesslvb
 The Journal of Neuroscience, April 1992, U(4): 1502-l 510 Convergence of Reflex Pathways Excited by Distension and Mechanical Stimulation of the Mucosa onto the Same Myenteric Neurons of the Guinea Pig
The Journal of Neuroscience, April 1992, U(4): 1502-l 510 Convergence of Reflex Pathways Excited by Distension and Mechanical Stimulation of the Mucosa onto the Same Myenteric Neurons of the Guinea Pig
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR NEUROSCIENCE BMP-218 November 4, 2014 DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM The nervous system is composed of two primary divisions: 1. CNS - Central Nervous System (Brain + Spinal Cord)
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice. 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n):
 Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Section: Chapter 5: Multiple Choice 1. The structure of synapses is best viewed with a(n): p.155 electron microscope. light microscope. confocal microscope. nissle-stained microscopic procedure. 2. Electron
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody
 Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line
 B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Cell Line Cell Culture Conditions B SYS GmbH B SYS GmbH nachr α 4 β 2 CHO Page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 BACKGROUND...3 1.1 Human Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors...3 1.2 B SYS
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Regul Pept. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 April 10.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Regul Pept. 2008 April 10; 147(1-3): 1 3. Do enteric neurons make hypocretin? Christian R. Baumann a,c,*, Erika L. Clark a, Nigel
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Regul Pept. 2008 April 10; 147(1-3): 1 3. Do enteric neurons make hypocretin? Christian R. Baumann a,c,*, Erika L. Clark a, Nigel
Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells. in the nasal mucosa. Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD,
 Radulovic 1 1 2 3 Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells in the nasal mucosa 4 5 6 7 Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD, Stephen R Durham MD, Kayhan T Nouri-Aria
Radulovic 1 1 2 3 Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells in the nasal mucosa 4 5 6 7 Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD, Stephen R Durham MD, Kayhan T Nouri-Aria
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Effects of Tegaserod on Ileal Peristalsis of Guinea Pig In Vitro
 J Pharmacol Sci 94, 144 152 (2004) Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2004 The Japanese Pharmacological Society Full Paper Effects of Tegaserod on Ileal Peristalsis of Guinea Pig In Vitro Sang Won Ji
J Pharmacol Sci 94, 144 152 (2004) Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2004 The Japanese Pharmacological Society Full Paper Effects of Tegaserod on Ileal Peristalsis of Guinea Pig In Vitro Sang Won Ji
Differential role of tachykinin NK 3 receptors on cholinergic excitatory neurotransmission in the mouse stomach and small intestine
 British Journal of Pharmacology (8) 155, 1195 13 & 8 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 7 1188/8 $32. www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Differential role of tachykinin NK 3 receptors on
British Journal of Pharmacology (8) 155, 1195 13 & 8 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 7 1188/8 $32. www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPER Differential role of tachykinin NK 3 receptors on
Architecture of enteric neural circuits involved in intestinal motility
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2008; 12(Suppl 1): 3-19 Architecture of enteric neural circuits involved in intestinal motility M. COSTA, S.H. BROOKES Department of Physiology
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2008; 12(Suppl 1): 3-19 Architecture of enteric neural circuits involved in intestinal motility M. COSTA, S.H. BROOKES Department of Physiology
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis. Keith Sharkey
 Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis Keith Sharkey Department of Physiology & Pharmacology University of Calgary Dr. Keith Sharkey Financial Interest
Getting into the weed: the endocannabinoid system of the gut-brain axis in energy homeostasis Keith Sharkey Department of Physiology & Pharmacology University of Calgary Dr. Keith Sharkey Financial Interest
Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary. y Antigens A. antibodies
 Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(1), 115-119 NOTE Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary y Antigens A ntibodies SHIGEKI YABE, MASAMI MURAKAMI*, KAYOKO MARUYAMA, HIDEKO MIWA,
Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(1), 115-119 NOTE Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary y Antigens A ntibodies SHIGEKI YABE, MASAMI MURAKAMI*, KAYOKO MARUYAMA, HIDEKO MIWA,
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
DISTRIBUTION AND DIMENSIONS OF NADPH- DIAPHORASE POSITIVE GANGLIONATED PLEXUSES IN PORCINE COMMON HEPATIC DUCT WALL
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 4, 254 259 DISTRIBUTION AND DIMENSIONS OF NADPH- DIAPHORASE POSITIVE GANGLIONATED PLEXUSES IN PORCINE COMMON HEPATIC DUCT WALL Summary I. S. STEFANOV
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2012), 15, No 4, 254 259 DISTRIBUTION AND DIMENSIONS OF NADPH- DIAPHORASE POSITIVE GANGLIONATED PLEXUSES IN PORCINE COMMON HEPATIC DUCT WALL Summary I. S. STEFANOV
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Gastrointestinal Physiology
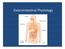 Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
Gastrointestinal Physiology Digestion and Absorption Definition Digestion: i Food dis dissolved d and broken down. Physical digestion: Propulsion and mixing of food by muscle in the alimentary tract. Chemical
Introduction to Autonomic
 Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
Part 2 Autonomic Pharmacology 3 Introduction to Autonomic Pharmacology FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM The autonomic nervous system (Figure 3 1) is composed of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
5-Hydroxytryptamine 4 Receptor Agonists Initiate the Peristaltic Reflex in Human, Rat, and Guinea Pig Intestine
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1998;115:370 380 5-Hydroxytryptamine 4 Receptor Agonists Initiate the Peristaltic Reflex in Human, Rat, and Guinea Pig Intestine JOHN R. GRIDER, AMY E. FOXX ORENSTEIN, and JI GUANG JIN
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1998;115:370 380 5-Hydroxytryptamine 4 Receptor Agonists Initiate the Peristaltic Reflex in Human, Rat, and Guinea Pig Intestine JOHN R. GRIDER, AMY E. FOXX ORENSTEIN, and JI GUANG JIN
Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria Xi Liu a,b,
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supporting Information Protein-Mediated Anti-Adhesion Surface against Oral Bacteria Xi Liu a,b,
Introduction to Gastrointestinal Physiology and GI Hormones Jack Grider, Ph.D
 Introduction to Gastrointestinal Physiology and GI Hormones Jack Grider, Ph.D OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the general organization of the gut. 2. Identify the levels of neural control and describe the interaction
Introduction to Gastrointestinal Physiology and GI Hormones Jack Grider, Ph.D OBJECTIVES: 1. Describe the general organization of the gut. 2. Identify the levels of neural control and describe the interaction
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Electrical Properties of Neurons. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Electrical Properties of Neurons Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Neuronal Communication Neurons communicate with other cells, often over long distances. The electrical
Electrical Properties of Neurons Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Neuronal Communication Neurons communicate with other cells, often over long distances. The electrical
APPENDIX Heparin 2 mg heparin was dissolved in 0.9 % NaCl (10 ml). 200 µl of heparin was added to each 1 ml of blood to prevent coagulation.
 APPENDIX 1 Preparation of reagents 1.1. Preparation of dosing solution Nonylphenol 15 mg of Nonylphenol was dissolved in olive oil (10 ml) and used as stock solution. The stock solution was serially diluted
APPENDIX 1 Preparation of reagents 1.1. Preparation of dosing solution Nonylphenol 15 mg of Nonylphenol was dissolved in olive oil (10 ml) and used as stock solution. The stock solution was serially diluted
Department of Physiology, Okayama University Medical School
 The Japanese Journal of Physiology 15, pp.243-252, 1965 Department of Physiology, Okayama University Medical School BAYLISS and STARLING 1) and others 6, 7, 9, 12, 14, 15) have reported that the stimulation
The Japanese Journal of Physiology 15, pp.243-252, 1965 Department of Physiology, Okayama University Medical School BAYLISS and STARLING 1) and others 6, 7, 9, 12, 14, 15) have reported that the stimulation
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author: John Williams, M.D., Ph.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Enteric nervous system development in cavitary viscera allocated to the celiac plexus
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2008, 49(1):63 67 ORIGINAL PAPER Enteric nervous system development in cavitary viscera allocated to the celiac plexus ALINA MARIA ŞIŞU 1), CODRUŢA ILEANA
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2008, 49(1):63 67 ORIGINAL PAPER Enteric nervous system development in cavitary viscera allocated to the celiac plexus ALINA MARIA ŞIŞU 1), CODRUŢA ILEANA
Enteric Dopaminergic Neurons: Definition, Developmental Lineage, and Effects of Extrinsic Denervation
 1330 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 11, 2004 24(6):1330 1339 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Enteric Dopaminergic Neurons: Definition, Developmental Lineage, and Effects of Extrinsic Denervation Z.
1330 The Journal of Neuroscience, February 11, 2004 24(6):1330 1339 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Enteric Dopaminergic Neurons: Definition, Developmental Lineage, and Effects of Extrinsic Denervation Z.
Tachykinin-Dependent and -Independent Components of Peristalsis in the Guinea Pig Isolated Distal Colon
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2001;120:938 945 Tachykinin-Dependent and -Independent Components of Peristalsis in the Guinea Pig Isolated Distal Colon MARCELLO TONINI,* VALERIA SPELTA,* FABRIZIO DE PONTI, ROBERTO DE
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2001;120:938 945 Tachykinin-Dependent and -Independent Components of Peristalsis in the Guinea Pig Isolated Distal Colon MARCELLO TONINI,* VALERIA SPELTA,* FABRIZIO DE PONTI, ROBERTO DE
Intestinal inflammation and activation of sensory nerve pathways: a functional and morphological study in the nematode infected rat
 822 Gut 2001;49:822 827 Department of Internal Medicine, University of Bologna, Italy R De Giorgio G Barbara V Stanghellini R Corinaldesi Intestinal Diseases Research Program and Division of Gastroenterology,
822 Gut 2001;49:822 827 Department of Internal Medicine, University of Bologna, Italy R De Giorgio G Barbara V Stanghellini R Corinaldesi Intestinal Diseases Research Program and Division of Gastroenterology,
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Neurotransmitter Systems I Identification and Distribution Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
Differential expression of P2X receptors on neurons from different parasympathetic ganglia
 Neuropharmacology 48 (2005) 766e777 www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropharm Differential expression of P2X receptors on neurons from different parasympathetic ganglia Bei Ma, Huai-Zhen Ruan, Geoffrey Burnstock,
Neuropharmacology 48 (2005) 766e777 www.elsevier.com/locate/neuropharm Differential expression of P2X receptors on neurons from different parasympathetic ganglia Bei Ma, Huai-Zhen Ruan, Geoffrey Burnstock,
Chapter 13. Honeybee Venom Detected by Enzyme Immunoassay
 Chapter 13 Honeybee Venom Detected by Enzyme Immunoassay Mary K. Janis Department of Biological Sciences University of Alaska Anchorage Anchorage, Alaska 99508 (907) 786-1952, afmkj@acad2.alaska.edu Mary
Chapter 13 Honeybee Venom Detected by Enzyme Immunoassay Mary K. Janis Department of Biological Sciences University of Alaska Anchorage Anchorage, Alaska 99508 (907) 786-1952, afmkj@acad2.alaska.edu Mary
