George F. Martin, PhD Collection Spec Martin 1 linear foot,
|
|
|
- Jason Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 George F. Martin, PhD Collection Spec Martin 1 linear foot, Medical Heritage Center Prior Health Sciences Library The Ohio State University 376 W. 10th Ave. Columbus, OH INTRODUCTION Access The collection is open to the public and is available for viewing in the Medical Heritage Center. Materials do not circulate and must be used in the supervised reading room. Restrictions, including copyright, may exist and some materials may be too fragile to photocopy or digitize. The MHC charges for duplication services, which must be performed by staff. Citation [Identification of item], George F. Martin, PhD Collection, Spec Martin, Medical Heritage Center, John A. Prior Health Sciences Library, The Ohio State University. Processing Notes This collection was processed July 12 18, 2011 by Kristin Rodgers. The collection is arranged alphabetically. The reprints are arranged by year and then alphabetically within that year. Property Rights The Ohio State University Medical Heritage Center owns the property rights to this collection. Provenance This collection was donated to the Medical Heritage Center by George F. Martin on August 23, HISTORICAL SKETCH George F. Martin was born February 20, 1937 in Englewood, New Jersey. He married Muriel Joy Brandkamp on August 13, 1960 and they have two children, George and Laurie. He earned his B.S. in biology from Bob Jones University in Greenville, South Carolina and from the University of Alabama his M.S. in 1963 and his Ph.D. in Martin served as a professor and researcher in the Department of Anatomy at the Ohio State University from 1965 until He directed over a dozen courses in the dental and medical school throughout his career, but his major teaching was in neuroscience and neuroanatomy. His received numerous grants from the National Science Foundation and the National Institutes of Health (NIH). He also received a Javits Award from the NIH ( ). The Senator Jacob Javits Awards in the Neurosciences is a conditional, seven-year research 1
2 grant given to scientists for their superior competence and outstanding productivity. Javits Awards provide long-term support to investigators with a history of exceptional talent, imagination, and preeminent scientific achievement. Martin s research largely in opossums, has involved comparative neurology and developmental neurobiology, with interest in the development of the spinal cord and in spinal cord injury. Martin has authored 154 publications and 107 abstracts. Martin served on many Ohio State committees as well as many national ones. Some of his national work included serving on the Executive Committee of the American Association of Anatomists and as Chair of its Nomenclature Committee. He also served as a member of the NIH site visit teams, scientific review sessions, and the chair of special study sessions for the National Institutes of Health. Martin was the recipient of the first Ohio State University Distinguished Teaching Award in the basic sciences, and essentially every year since received a Distinguished Teaching Award from the medical class. He received a Distinguished Scholar Award from Ohio State in He was Pre-Clincal Professor of the Year from the medical school class of 1992, and Professor of the Year in He was named a Presidential Professor (renamed Distinguished Professor in 1995) by Ohio State in He was inducted into the Alpha Omega Alpha Medical Honor Society, although he was not a physician, as a symbol of the esteem with which he is held by the students in that honorary society. The OSU Health Sciences post-doctoral fellowship association established an annual lecture in his name. SCOPE AND CONTENT NOTE The George F. Martin, PhD Collection (1 linear foot) contains article reprints, photographs, and a CV of Martin. CONTAINER LISTING Box File Description Date(s) 1 1 Curriculum Vitae Photographs n.d. 1 3 Reprint: Rubrobulbar Projections of the Opossum 1970 (Didelphis virginiana) 1 4 Reprint: The projections of the Deep Cerebellar Nuclei 1973 of the Opossum, Didelphis marsupialis virginiana 1 5 Reprint: The Organization of Projection Neurons in the 1974 Opossum Red Nucleus 1 6 Reprint: The Direct Spinal Area of the Inferior Olivary 1975 Nucleus: An Electron Microscopic Study 1 7 Reprint: Functional Localization and Cortical 1975 Architecture in the Nine-banded Armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus mexicanus) 1 8 Reprint: The Inferior Olivary Nucleus of the Opossum 1975 (Didelphis marsupialis virginiana), Its Organization and Connections 1 9 Reprint: A Neuroanatomical Analysis of Spinal Cord
3 Injury in the Rhesus Monkey 1 10 Reprint: The Vestibular Complex of the American 1977 Opossum Didelphis 1 11 Reprint: Evidence for Direct Bulbospinal Projections to 1979 Laminae IX, X and the Intermediolateral Cell Column. Studies using Axonal Transport Techniques in the North 1 12 Reprint: The Precise Origin of the Tectospinal Pathway 1979 in Three Common Laboratory Animals: A Study Using the Horseradish Peroxidase Method 1 13 Reprint: Afferent Connections of the Inferior Olivary 1980 Nucleus with Preliminary Notes of Their Development: Studies Using the North 1 14 Reprint: The Development of Major Projections to the 1980 Inferior Olivary Nucleus 1 15 Reprint: The Early Development of Corticobulbar and 1980 Corticospinal Systems 1 16 Reprint: The Pontocerebellar System in the Opossum, 1980 Didelphis 1 17 Reprint: Projections from the Brain Stem Reticular 1980 Formation to Laminae I and II of the Spinal Cord. Studies using Light and Electron Microscopic Techniques in the North 1 18 Reprint: Evidence for Collateral Innervation of the 1981 Cervical and Lumbar Enlargements of the Spinal Cord by Single Reticular and Raphe Neurons. Studies using Fluorescent Markers in Double-Labeling Experiments on the North 1 19 Reprint: Organization of Projections from the Gracile, 1981 Medical Cuneate and Lateral Cuneate Nuclei in the North 1 20 Reprint: Spinal Projections from the Medullary Reticular 1981 Formation of the North : Evidence for Connectional Heterogeneity 1 21 Reprint: The Brainstem Origin of Monoaminergic 1982 Projections to the Spinal Cord of the North American Opossum: A Study Using Fluorescent Tracers and Fluorescence Histochemistry 1 22 Reprint: Development of Raphe-Spinal Connections in 1982 the North 1 23 Reprint: The Origin of Brain Stem-Spinal Projections at 1982 Different Stages of Development in the North American Opossum 1 24 Reprint: Raphespinal Projections in the North American 1982 Opossum: Evidence for Connectional Heterogeneity 1 25 Reprint: Anatomical Demonstration of the Location and
4 Collateralization of Rubral Neurons Which Project to the Spinal Cord, Lateral Brainstem and Inferior Olive in the North 1 26 Reprint: The Auditory Brainstem Nuclei and Some of 1983 their Projections to the Inferior Colliculus in the North 1 27 Reprint: Brainstem Projections to the Facial Nucleus of 1983 the Opossum. A Study Using Axonal Transport Techniques 1 28 Reprint: Observations on the Early Development of 1983 Ascending Spinal Pathways 1 29 Reprint: Collateral Innervation of the Inferior Colliculus 1984 in the North : A Study Using Fluorescent Markers in a Double Labeling Paradigm 1 30 Reprint: The Neuronal Types and the Distribution of Hydroxytryptamine and Enkephalin-like Immunoreactive Fibers in the Dorsal Cochlear Nucleus of the North 1 31 Reprint: A Study of Overlap and Collateralization of 1984 Bulbar Reticular and Raphe Neurons which Project to the Spinal Cord and Diencephalon of the North 1 32 Reprint: The Development of Commissural Connections 1985 of Somatic Motor-Sensory Areas of Neocortex in the North 1 33 Reprint: Major Projections of the Reticular Formation Reprint: An Autoradiographic Analysis of Ascending 1986 Projections from the Medullary Reticular Formation in the Rat 1 35 Reprint: Observations on the Development of Descending Spinal Pathways in the North American Opossum Reprint: Development of the Basilar Pons in the North 1987 : Dendrogenesis and Maturation of Afferent and Efferent Connections 2 2 Reprint: Development of Brainstem and Cerebellar 1987 Projections to the Diencephalon with Notes on Thalamocortical Projections: Studies in the North 2 3 Reprint: Organization of Forebrain Projections from the 1987 Medullary Reticular Formation in the North American Opossum. Evidence for Connectional Heterogeneity 2 4 Reprint: The Timing of Granule Cell Differentiation and 1987 Mossy Fiber Morphogenesis in the Opossum 2 5 Reprint: Catecholaminergic Innervation of the Spinal
5 Cord in the North, Didelphis 2 6 Reprint: The Development of Selected Rubral 1988 Connections in the North 2 7 Reprint: Evidence for Developmental Plasticity of the 1988 Rubrospinal Tract. Studies Using the North American Opossum 2 8 Reprint: The Origin of Projections from the Medullary 1988 Reticular Formation to the Spinal Cord, the Diencephalon and the Cerebellum at Different Stages of Development in the North : Studies Using Single and Double Labeling Techniques 2 9 Reprint: The Brainstem Origin of Enkephalin- and 1989 Substance P Like Immunoreactive Axons in the Spinal Cord of the North 2 10 Reprint: Developmental Plasticity of the Rubrospinal 1989 Tract in the North 2 11 Reprint: The Early Development of Major Projections to 1989 the Dorsal Striatum in the North 2 12 Reprint: Development of Catecholaminergic Projections 1990 to the Spinal Cord in the North, Didelphis 2 13 Reprint: Origins and Terminations of Bulbospinal Axons 1990 That Contain Serotonin and Either Enkephalin or Substance-P in the North 2 14 Reprint: The Response of Rubrospinal Neurons to 1990 Axotomy in the Adult Opossum, Didelphis 2 15 Reprint: Cerebellorubral Degeneration after Resection 1991 of Cerebellar Dentate Nucleus Neoplasms: Evaluation with MR Imaging 2 16 Reprint: The Development of Descending Spinal 1991 Pathways in the North 2 17 Reprint: Evidence for New Growth and Regeneration of 1991 Cut Axons in Developmental Plasticity of the Rubrospinal Tract in the North 2 18 Reprint: Ipsilaterally Projecting Rubrospinal Neurons in 1991 Adult and Developing Opossums 2 19 Reprint: Organization of Midbrain Catecholamine 1991 Containing Nuclei and Their Projections to the Striatum in the North, Didelphis 2 20 Reprint: The Origin of Serotoninergic Projections to the 1991 Lumbosacral Spinal Cord at Different Stages of Development in the North 2 21 Reprint: The Origins of Supraspinal Projections to Lumbosacral and Cervical Levels of the Spinal Cord in the Gray Short-Tailed Brazilian Opossum, Monodelphis
6 domestica 2 22 Reprint: The Origins of Supraspinal Projections to the 1992 Cervical and Lumbar Spinal Cord at Different Stages of Development in the Gray Short-Tailed Brazilian Opossum, Monodelphis Domestica 2 23 Reprint: The Response of Rubrospinal Neurons to 1992 Axotomy at Different Stages of Development in the North 2 24 Reprint: Development of an Astrocytic Response to 1993 Lesions of the Spinal Cord in the North American Opossum: An Immunohistochemical Study Using Anti- Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein 2 25 Reprint: The Development of Myelin in the Spinal Cord 1993 of the North and its Possible Role in Loss of Rubrospinal Plasticity. A Study Using Myelin Basic Protein and Galactocerebroside Immuno- Histochemistry 2 26 Reprint: Development of Radial Glia and Astrocytes in 1993 the Spinal Cord of the North (Didelphis ): An Immunohistochemical Study Using Anti-Vimentin and Anti-Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein 2 27 Reprint: The Early Development of Major Projections 1993 from Caudal Levels of the Spinal Cord to the Brainstem and Cerebellum in the Gray Short-Tailed Brazilian Opossum, Monodelphis Domestica 2 28 Reprint: Models of Spinal Cord Regeneration Reprint: The Distribution of GAP-43 Immunoreactivity in 1995 the Central Nervous System of Adult Opossums (Didelphis ) with Notes on their Development 2 30 Reprint: Plasticity of Descending Spinal Pathways in 1995 Developing Mammals 2 31 Reprint: Early Development and Developmental 1996 Plasticity of the Fasciculus Gracilis in the North (Didelphis ) 2 32 Reprint: Evidence for GAP-43 within Descending Spinal 1996 Axons in the North, Didelphis 2 33 Reprint: Evidence for Growth of Supraspinal Axons 1996 Through the Lesion After Transection of the Thoracic Spinal Cord in the Developing Opossum Didelphis 2 34 Reprint: Growth of Dorsal Spinocerebellar Axons through a Lesion of their Spinal Pathway during Early Development in the North, Didelphis
7 2 35 Reprint: Development and Developmental Plasticity of 1997 Descending Spinal Pathways in the North American Opossum, Didelphis 2 36 Reprint: Developmental Plasticity of Selected 1997 Spinocerebellar Axons. Studies Using the North, Didelphis 2 37 Reprint: Adult Opossums (Didelphis ) 1998 Demonstrate Near Normal Locomotion after Spinal Cord Transection as Neonates 2 38 Reprint: Origin, Course, and laterality of Spinocerebellar 1998 Axons in the North, Didelphis 2 39 Reprint: Regeneration of Supraspinal Axons After 1998 Transection of the Thoracic Spinal Cord in the Developing Opossum, Didelphis 2 40 Reprint: Developmental Plasticity of Ascending Spinal Axons Studies Using the North, Didelphis
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Spinal Cord Organization. January 12, 2011
 Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Dwight Palmer Collection Spec Palmer 4 linear feet, no date
 Medical Heritage Center Health Sciences Library The Ohio State University 376 W. 10th Ave. Columbus, OH 43210 Dwight Palmer Collection Spec.200103.Palmer 4 linear feet, no date INTRODUCTION Access The
Medical Heritage Center Health Sciences Library The Ohio State University 376 W. 10th Ave. Columbus, OH 43210 Dwight Palmer Collection Spec.200103.Palmer 4 linear feet, no date INTRODUCTION Access The
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Dwight Palmer Collection Spec Palmer 4 linear feet, no date
 Medical Heritage Center Prior Health Sciences Library The Ohio State University 376 W. 10th Ave. Columbus, OH 43210 Dwight Palmer Collection Spec.200103.Palmer 4 linear feet, no date INTRODUCTION Access
Medical Heritage Center Prior Health Sciences Library The Ohio State University 376 W. 10th Ave. Columbus, OH 43210 Dwight Palmer Collection Spec.200103.Palmer 4 linear feet, no date INTRODUCTION Access
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Non-cranial nerve nuclei
 Brainstem Non-cranial nerve nuclei Nucleus Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Infeiro olivary nucleus Pontine nucleus inferior colliculus superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Pretectal area Site
Brainstem Non-cranial nerve nuclei Nucleus Gracile nucleus Cuneate nucleus Infeiro olivary nucleus Pontine nucleus inferior colliculus superior colliculus Red nucleus Substantia nigra Pretectal area Site
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu
 Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu The gross anatomy of the spinal cord Spinal cord segments Spinal nerves Spinal cord gray and white
Table of Contents: Chapter 1 The organization of the spinal cord Charles Watson and Gulgun Kayalioglu The gross anatomy of the spinal cord Spinal cord segments Spinal nerves Spinal cord gray and white
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons
 Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons 1. Overview of the brainstem subdivisions 2. Embryonic development of the brainstem 3. Medulla oblongata external features 4. Internal structure of the medulla oblongata
Brainstem: Medulla oblongata and pons 1. Overview of the brainstem subdivisions 2. Embryonic development of the brainstem 3. Medulla oblongata external features 4. Internal structure of the medulla oblongata
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Brainstem. Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences
 Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
Brainstem Amadi O. Ihunwo, PhD School of Anatomical Sciences Lecture Outline Constituents Basic general internal features of brainstem External and Internal features of Midbrain Pons Medulla Constituents
THE BACK. Dr. Ali Mohsin. Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D.
 Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
Cerebellum 1/20/2016. Outcomes you need to be able to demonstrate. MHD Neuroanatomy Module
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Brainstem. Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem
 Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi
 Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Spinal cord. We have extension of the pia mater below L1-L2 called filum terminale
 Spinal cord Part of the CNS extend from foramen magnum to the level of L1-L2 (it is shorter than the vertebral column) it is covered by spinal meninges. It is cylindrical in shape. It s lower end become
Spinal cord Part of the CNS extend from foramen magnum to the level of L1-L2 (it is shorter than the vertebral column) it is covered by spinal meninges. It is cylindrical in shape. It s lower end become
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve)
 Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Medial View of Cerebellum
 Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Page 1 L 58. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems /2013 RETICULAR FORMATION
 Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems 1 2012/2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver
Page 1 L 58 Douglas L. Oliver, Ph.D. The University of Connecticut Schools of Medicine and Dental Medicine Humans Systems: Organ Systems 1 2012/2013 RETICULAR FORMATION Lecture Lecture: Douglas Oliver
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Copy Right Hongqi ZHANG Department of Anatomy Fudan University 1. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Spinal cord. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Spinal cord Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Spinal cord Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem 1-Midbrain
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Spinal cord Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 Spinal cord Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem 1-Midbrain
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Spinal Interneurons. Control of Movement
 Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Conscious and Non-Conscious Proprioception Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Divisions of Somatosensory Systems The pathways that convey sensory modalities from the body to consciousness are
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook and required/recommended
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal.
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne Stensaas, PhD Note: Waxman is very sketchy on today s pathways and nonexistent on the Trigeminal. Resources: Pathway Quiz for HyperBrain Ch. 5 and
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
Doctor Osama Asa ad Khader. Mohammad Alsalem
 6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
Motor systems.... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington
 Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
The Cerebellum. Outline. Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Pain classifications slow and fast
 Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Somatic Nervous System: Motor Output *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m63208 1 Somatic Nervous System: Motor Output * Steven Telleen Based on Motor Responses by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
OpenStax-CNX module: m63208 1 Somatic Nervous System: Motor Output * Steven Telleen Based on Motor Responses by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Duus' Topical Diagnosis in Neurology
 Duus' Topical Diagnosis in Neurology Anatomy - Physiology - Signs - Symptoms Bearbeitet von Michael Frotscher 1. Auflage 2005. Taschenbuch. 532 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 13 612804 6 Format (B x L): 19 x
Duus' Topical Diagnosis in Neurology Anatomy - Physiology - Signs - Symptoms Bearbeitet von Michael Frotscher 1. Auflage 2005. Taschenbuch. 532 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 13 612804 6 Format (B x L): 19 x
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Cerebellum. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
OVERVIEW. Today. Sensory and Motor Neurons. Thursday. Parkinsons Disease. Administra7on. Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online
 OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
Arterial Blood Supply
 Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
IV. THE SPINAL CORD BLOOD SUPPLY
 IV. THE SPINAL CORD Spinal cord is covered by o Pia Mater Spinalis Film Teminale Denticulate Ligament ---------------------- Cordotomy o Arachnoid Membrane Subarachnoid Space ----------------------- Lumbar
IV. THE SPINAL CORD Spinal cord is covered by o Pia Mater Spinalis Film Teminale Denticulate Ligament ---------------------- Cordotomy o Arachnoid Membrane Subarachnoid Space ----------------------- Lumbar
Lecture X. Brain Pathways: Movement!
 Bio 3411 Readings (background only) Bio 3411 Monday Neuroscience 4 th ed Page(s) Feature 423-451Upper motor control of Brain Stem and Spinal Cord The Brain Atlas 3 rd ed Page(s) Feature 198-199 Vestibular
Bio 3411 Readings (background only) Bio 3411 Monday Neuroscience 4 th ed Page(s) Feature 423-451Upper motor control of Brain Stem and Spinal Cord The Brain Atlas 3 rd ed Page(s) Feature 198-199 Vestibular
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Lecture X. Brain Pathways: Movement!
 Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings (background only) Neuroscience 5 th ed Page(s) Feature 353-398Upper motor control of Brain Stem and Spinal Cord Neuroscience 4 th ed Page(s) Feature 423-451Upper motor control
Bio 3411 Monday 1 Readings (background only) Neuroscience 5 th ed Page(s) Feature 353-398Upper motor control of Brain Stem and Spinal Cord Neuroscience 4 th ed Page(s) Feature 423-451Upper motor control
Brainstem: Midbrain. 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain:
 Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement. Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement. Neural control of movement
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord
 Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
Gross Morphology of Spinal Cord Lecture Objectives Describe the gross anatomical features of the spinal cord. Describe the level of the different spinal segments compared to the level of their respective
UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION
 UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION COURSE TITLE: INTRODUCTION TO NEUROSCIENCE COURSE CODE: FISA 8525 CREDIT HOURS: COURSE DURATION: 3 CREDITS (54 HOURS)
UNIVERSITY OF PUERTO RICO SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHYSIOLOGY DEPARTMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION COURSE TITLE: INTRODUCTION TO NEUROSCIENCE COURSE CODE: FISA 8525 CREDIT HOURS: COURSE DURATION: 3 CREDITS (54 HOURS)
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
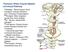
 ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Brain Stem. Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14
 Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
Nervous System (Part A-3) Module 8 -Chapter 14 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/9/13 Cellular structure of the nervous system Neurons Neuroglia Nervous System Divisions Central nervous system Peripheral nervous
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Abdullah AlZibdeh. Dr. Maha ElBeltagy. Maha ElBeltagy
 19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
C14 / CNS / MC3. What two stuctures make up the central nervous system?
 C14 / CNS / MC3 What two stuctures make up the central nervous system? The CNS starts embryonic development as a neural tube. What adult structures develop from the neural tube? What structures are part
C14 / CNS / MC3 What two stuctures make up the central nervous system? The CNS starts embryonic development as a neural tube. What adult structures develop from the neural tube? What structures are part
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0595 TITLE: Enhancing Propriospinal Relays to Improve Functional Recovery after SCI PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George Smith CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University of the Commonwealth
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0595 TITLE: Enhancing Propriospinal Relays to Improve Functional Recovery after SCI PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: George Smith CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Temple University of the Commonwealth
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
The Cerebellum. The Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges References... 3
 Section I Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges... 1 1 Orientation... 3 References... 3 2 Development... 7 Early Morphogenesis... 7 FormationoftheBrainRegions... 9 Histogenesis...
Section I Orientation, Development, Gross Anatomy, Blood Supply and Meninges... 1 1 Orientation... 3 References... 3 2 Development... 7 Early Morphogenesis... 7 FormationoftheBrainRegions... 9 Histogenesis...
Sheet lab 3. Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation:
 Sheet lab 3 Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation: This section is at lower third of medulla and is the most close part to spinal cord and it has some characteristic of spinal cord
Sheet lab 3 Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation: This section is at lower third of medulla and is the most close part to spinal cord and it has some characteristic of spinal cord
