Downloaded from by on 02/06/18 from IP address Copyright ARRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved
|
|
|
- Agnes Mathews
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Downloaded from by on 02/06/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Imaging of Parapharyngeal Space Lesions: Focus on the Prestyloid ompartment T he parapharyngeal space is a deep potential neck space shaped as an inverted pyramid extending from the base of the skull to the hyoid bone. The differentiation of a prestyloid lesion from a poststyloid lesion is critical for guiding the surgeon in both the differential diagnosis as well as the potential surgical approach. Normal natomy The parapharyngeal space may be divided into two compartments on the basis of its relationship to the styloid process or, more precisely, to the tensor-vascular-styloid fascia (Fig. 1). The importance of the parapharyngeal space also lies in its relationship with the other spaces of the neck [1]. The masticator and parotid spaces are located laterally, the pharyngeal mucosal space is located medially, and the retropharyngeal space is located posteromedially (Fig. 1). The contents of the prestyloid compartment include the minor or ectopic salivary gland, branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve, internal maxillary artery, ascending pharyngeal artery, and pharyngeal venous plexus, whereas those of the poststyloid compartment include the internal carotid artery, internal jugular vein, cranial nerves IX XII, cervical sympathetic chain, and glomus bodies. Ji Hoon Shin 1, Ho Kyu Lee 1, Sang Yoon Kim 2, hoong Gon hoi 1, Dae hul Suh 1 ongenital or Developmental Lesions ranchial left yst The parapharyngeal space is a rare location for a branchial cleft cyst. The pharyngeal attachment and lack of deformity of the derivatives of the first branchial apparatus support the view that parapharyngeal space cysts originate in the second branchial apparatus. rapidly growing, infected branchial cleft cyst can present with lower cranial nerve palsies [2] (Fig. 2). ystic Lymphangioma (ystic Hygroma) Lymphangiomas form from errors in the development of the lymphatic system and can have variable vascularity [3]. Most lymphangiomas occur during early childhood because the greatest lymphatic development occurs between birth and 2 years. MR imaging usually shows the signal intensity of a multiloculated cystic lesion that does not displace adjacent soft-tissue structures because of the lesion s compressibility (Fig. 3). Neoplastic Lesions Tumors of the parapharyngeal space account for less than 0.5% of head and neck neoplasms [4]. However, various neoplastic lesions can involve the prestyloid parapharyngeal space. Intrinsic tumors are minor or Pictorial Essay ectopic salivary gland tumors and neurogenic tumors arising from the branches of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve. On the other hand, extrinsic tumors are most commonly parotid tumors of deep lobe origin, neurogenic tumors arising from the vagus nerve, or various tumors originating from the other surrounding spaces. Minor or Ectopic Salivary Gland Tumors Pleomorphic adenomas comprise the majority of minor or ectopic salivary gland tumors and are the most common neoplasms to originate in the prestyloid parapharyngeal space [5]. Malignant tumors, such as mucoepidermoid carcinoma or adenoid cystic carcinoma, are uncommon. Furthermore, several rare tumors, including basal cell adenoma, can originate from the minor salivary gland (Fig. 4). Preservation of the fat plane between the mass and the parotid gland strongly suggests an extraparotid origin. Neurogenic Tumors Neurogenic tumors are the second most common neoplasms originating from the prestyloid parapharyngeal space and are the most common poststyloid parapharyngeal space tumors. Most neurogenic tumors arise from the trigeminal nerve in the prestyloid parapharyngeal space and arise from the va- Received February 5, 2001; accepted after revision May 31, Department of Radiology, University of Ulsan ollege of Medicine, san Medical enter, Poongnap-Dong, Songpa-Ku, Seoul , South Korea. ddress correspondence to H. K. Lee. 2 Department of Otolaryngology, University of Ulsan ollege of Medicine, san Medical enter, Songpa-Ku, Seoul , South Korea. JR 2001;177: X/01/ merican Roentgen Ray Society JR:177, December
2 Shin et al. Downloaded from by on 02/06/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved gus nerve in the poststyloid parapharyngeal space. In tumors arising from the poststyloid parapharyngeal space, anteromedial displacement of the carotid sheath structures is frequent because the vagus nerve and sympathetic chain are posterior to the internal carotid artery, whereas posterolateral displacement of the carotid sheath structures is frequent in tumors arising from the prestyloid parapharyngeal space [5]. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors are rare, highly aggressive tumors capable of arising de novo or from preexisting benign neurofibromas or schwannomas; 25 75% of this type of tumor are associated with neurofibromatosis [6] (Fig. 5). D Tumors from the Other Surrounding Spaces Tumors of the skull base or tumors of the vertebrae, such as chordomas or meningiomas, can extend into the parapharyngeal space. Pharyngeal mucosal space lesions, such as nasopharynx carcinoma, may have extensive submucosal and parapharyngeal space extension. The most common extrinsic tumors involving the prestyloid parapharyngeal space are parotid tumors arising from the deep lobe of the parotid gland [5]. Pleomorphic adenomas are the most commonly encountered parotid gland tumors. Occasionally, a dumbbell shape is seen with the waist formation by the narrow stylomandibular tunnel in the deep Fig. 1. Normal anatomy of parapharyngeal space. S = buccal space, I = internal carotid artery, IJV = internal jugular vein, MS = masticator space, PMS = pharyngeal mucosal space, PPS = parapharyngeal space, PS = parotid space, PVS = prevertebral space, RPS = retropharyngeal space, SMS = submandibular space, T = torus tubarius., xial unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image obtained at nasopharynx level shows fat-filled prestyloid parapharyngeal space (asterisks) located between masticator space and pharyngeal mucosal space. Torus tubarius represents pharyngeal mucosal space at nasopharynx level. Poststyloid parapharyngeal space containing major neurovascular bundle of internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein is located posteriorly., xial unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image obtained at oropharynx level shows that parotid space containing parotid gland forms posterolateral boundary of parapharyngeal space (asterisks), and retropharyngeal space and prevertebral space form posteromedial boundary of parapharyngeal space (asterisks)., oronal unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows continuity of prestyloid parapharyngeal space (asterisks) with submandibular space. Pharyngeal mucosal space is located medially. D, xial schematic at nasopharynx level shows that parapharyngeal space is divided into prestyloid and poststyloid compartments by tensor-vascular-styloid fascia connecting tensor veli palatini muscle with styloid process. lobe parotid tumors. The loss of the fat line between the mass and the parotid gland suggests a deep lobe parotid origin (Fig. 6). Schwannomas and paragangliomas may arise in the poststyloid parapharyngeal space and extend into the prestyloid parapharyngeal space (Fig. 7). Infiltrative masses involving the parapharyngeal space are soft-tissue sarcomas of fatty, muscular, or fibrous origin, arising mainly from the adjacent spaces (Fig. 8). Usually, associated bone destruction is also present (Fig. 8). Rarely, astleman s disease, arising from the lymph nodes in the adjacent spaces, can involve the prestyloid parapharyngeal space [7] (Fig. 9) JR:177, December 2001
3 Imaging of Parapharyngeal Space Lesions Downloaded from by on 02/06/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Infectious or Inflammatory Lesions Most commonly, infections of the masticator space involve the parapharyngeal space and accompany medial displacement of the parapharyngeal space fat. Obliteration of the parapharyngeal space fat plane is also frequently associated with infections of the masticator space. Odontogenic infection is most commonly the source of an inflammatory mass in the masticator space and is frequently associated with facial swelling, pain, and trismus [5]. Fig. 2. Second branchial cleft cyst in 35-year-old woman with multiple lower cranial palsies that subsided after removal of lesion., xial enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows well-marginated, nonenhancing mass that is slightly hyperintense to cerebrospinal fluid in right prestyloid parapharyngeal space, displacing internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein to its posterolateral side (arrow)., T2-weighted spin-echo MR image shows mass is slightly hypointense to cerebrospinal fluid. Displacement of internal carotid artery and internal jugular vein to its posterolateral side (arrow) can also be seen., Unenhanced coronal T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows mass (arrowheads) occupying right parapharyngeal space from below skull base to upper level of submandibular gland. On aspiration, contents contained pus. Fig. 3. ystic lymphangioma in 2-year-old boy with left parotid area swelling., xial enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows multiloculated, nonenhancing cystic mass (arrows) in left prestyloid parapharyngeal space and in left parotid space., xial T2-weighted spin-echo MR image shows hyperintense mass (arrows)., oronal short tau inversion recovery MR image clearly shows bilateral multiloculated cystic lesions (arrows). The pharyngeal tonsil and submandibular gland can be another source of infection involving the parapharyngeal space. ellulitis or abscess may form as a complication of acute tonsillitis or sialoadenitis (Fig. 10). On the contrary, infections may readily spread from the parapharyngeal space into other areas of the neck or extend via the retropharyngeal space into the upper mediastinum because of the parapharyngeal space s close attachment and free communication with the other neck spaces [8]. onclusion The majority of lesions, mostly tumors, involving the prestyloid parapharyngeal space are either neurogenic tumors or salivary gland tumors from the deep lobe of the parotid gland or from the minor salivary gland. y observing the direction of displacement or infiltration of the parapharyngeal space, internal carotid artery displacement, and presence or absence of the medial fat plane, it is possible to localize a lesion to one of several spaces in the neck [1, 5]. JR:177, December
4 Shin et al. Downloaded from by on 02/06/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 4. asal cell adenoma in 61-year-old woman with bulging mass on left oral cavity., xial unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows round, solid and cystic (peripheral high-signal-intensity) (asterisk) mass in left prestyloid parapharyngeal space. ystic contents were hemorrhagic on aspiration. Linear fat line between tumor and parotid gland (arrow) suggests extraparotid origin of tumor., xial T2-weighted spin-echo MR image shows signal intensity of mass is slightly increased. Linear fat line between tumor and parotid gland (arrow) can also be seen., oronal enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows moderate enhancement of solid portion. D Fig. 5. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor arising from trigeminal nerve in 35-year-old man with right tinnitus and hearing disturbance., xial unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows ovoid isointense mass (short arrows) in right prestyloid parapharyngeal space. Laterally displaced parapharyngeal space fat suggests its origin in prestyloid parapharyngeal space (long arrow)., xial T2-weighted spin-echo MR image shows tumor (arrows) is slightly hyperintense to muscle., xial T2-weighted spin-echo MR image shows tumor (arrows) extends into eustachian tube (arrowheads). D, oronal enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows strong enhancement of mass (arrows). Foramen ovale is widened by tumor (arrowhead), suggesting its perineural extension JR:177, December 2001
5 Imaging of Parapharyngeal Space Lesions Downloaded from by on 02/06/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 6. Mucoepidermoid carcinoma of deep lobe parotid gland in 40-year-old man with left soft palate area swelling., ontrast-enhanced T scan shows inhomogeneously enhancing mass (asterisk) in left prestyloid parapharyngeal space. Stylomandibular tunnel (arrows) is widened by tumor, suggesting deep lobe parotid tumor. Medial fat line (arrowhead) between mass and pharyngeal mucosa is displaced but preserved., xial unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows low-signal-intensity mass (asterisk). Medial fat line (arrowhead) between mass and pharyngeal mucosa is displaced but preserved, whereas lateral fat line between mass and parotid gland is not seen, indicating parotid origin., xial enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows inhomogeneously enhancing mass (asterisk). Preservation of medial fat line (arrowhead) between mass and pharyngeal mucosa can also be seen. Fig. 7. Paraganglioma in 61-year-old woman with left submandibular area swelling., xial unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows slightly inhomogeneous low-signal-intensity mass in left parapharyngeal space. nteromedial displacement of internal carotid artery (arrow) indicates poststyloid parapharyngeal space origin of tumor., xial T2-weighted spin-echo MR image shows slightly inhomogeneously hyperintense mass. nteromedial displacement of internal carotid artery (arrow) can also be seen., oronal enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows location of tumor on carotid bifurcation with clear splaying of internal and external carotid arteries (arrowheads). These findings are highly specific for carotid body tumor. Fig. 8. Rhabdomyosarcoma in 10-year-old boy with left infraauricular area swelling., xial unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows lobulated, bulky low-signal-intensity mass involving left masticator, parotid, prevertebral, and parapharyngeal spaces. Medial margin of mandible (arrow) was partially destroyed by tumor., xial enhanced T1-weighted MR image shows inhomogeneous dense enhancement. Partial destruction of medial margin of mandible (arrow) is also seen. JR:177, December
6 Shin et al. Downloaded from by on 02/06/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 9. astleman s disease arising from retropharyngeal space in 34-year-old woman with painless swelling on right side of oropharynx., xial unenhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows well-marginated, isointense mass in right parapharyngeal space. Parapharyngeal space fat is displaced anteriorly (short arrow), and posterolateral displacement and separation of internal and external carotid arteries are seen (long arrows)., xial T2-weighted spin-echo MR image also clearly shows posterolateral displacement and separation of internal and external carotid arteries (arrows). Linear hypointense signal is seen in mass (arrowheads), which was revealed to be perivascular lamellar fibrosis on pathologic correlation., oronal enhanced T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows moderate enhancement of mass. References 1. hong VF, Fan YF. Radiology of the parapharyngeal space. ustralas Radiol 1998;42: Shin JH, Lee HK, Kim SY, et al. Parapharyngeal second branchial cleft cyst manifesting as cranial nerve palsies: MR findings. JNR 2001; 22: Mra Z, Emami J, Simpson GT II. Parapharyngeal lymphangioma mimicking a peritonsillar abscess. Ear Nose Throat J 1996;75: atsakis JG, Sneige N. Parapharyngeal and retropharyngeal space diseases. nn Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1989;98: Tom M, Rao VM, Guglielmo F. Imaging of the parapharyngeal space: anatomy and pathology. rit Rev Diagn Imaging 1991;31: Lee JH, Lee HK, hoi G, Suh D, Lee KS, Khang SK. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath Fig. 10. bscess associated with sialoadenitis of submandibular gland in 33-year-old woman with painful swelling of left submandibular area., ontrast-enhanced T scan shows abscess formation with air in left parapharyngeal space (arrows)., ontrast-enhanced T scan obtained from lower level clearly shows left submandibular gland enlargement (arrowheads) with surrounding fluid collection. tumor in the parapharyngeal space: tumor spread through the eustachian tube. JNR 2001; 22: Shin JH, Lee HK, Kim SY, et al. astleman s disease in the retropharyngeal space: T and MR imaging findings. JNR 2000;21: ass RM. pproaches to the diagnosis and treatment of tumors of the parapharyngeal space. Head Neck Surg 1982;4: JR:177, December 2001
Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學
 Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學 陳家媛 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 cychen@wanfang.gov.tw Normal Suprahyoid neck: the old way Nasopharynx Oropharynx Oral cavity Staging of SCC Spaces of Suprahyoid Neck: a New Way Deep
Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學 陳家媛 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 cychen@wanfang.gov.tw Normal Suprahyoid neck: the old way Nasopharynx Oropharynx Oral cavity Staging of SCC Spaces of Suprahyoid Neck: a New Way Deep
Clinical evaluation. Imaging Surgical treatment
 Parapharyngeal Space Khalid adhussain AL-Qahtani a MD,MSc,FRCS(c) Assistant Professor Consultant of Otolaryngology Advance Head & Neck Oncology, Thyroid & Parathyroid,Microvascular Reconstruction, ti and
Parapharyngeal Space Khalid adhussain AL-Qahtani a MD,MSc,FRCS(c) Assistant Professor Consultant of Otolaryngology Advance Head & Neck Oncology, Thyroid & Parathyroid,Microvascular Reconstruction, ti and
Head&Neck Imaging. ssregypt.com. Parapharyngeal Spaces. Mamdouh mahfouz MD
 Head&Neck Imaging Parapharyngeal Spaces ssregypt.com Mamdouh mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com Definitio n Fat filled triangular space lateral the pharynx Extends from the skull base to the oropharynx Parapharyngeal
Head&Neck Imaging Parapharyngeal Spaces ssregypt.com Mamdouh mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com Definitio n Fat filled triangular space lateral the pharynx Extends from the skull base to the oropharynx Parapharyngeal
"The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck
 "The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck Poster No.: C-2457 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. K.
"The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck Poster No.: C-2457 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. K.
The parapharyngeal space: Review of the anatomy and pathologic conditions.
 The parapharyngeal space: Review of the anatomy and pathologic conditions. Poster No.: C-2264 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Contreras Chacon, D. B. García Figueredo, M. Cuadrado,
The parapharyngeal space: Review of the anatomy and pathologic conditions. Poster No.: C-2264 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Contreras Chacon, D. B. García Figueredo, M. Cuadrado,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Parapharyngeal Space Schwannomas. Preoperative Imaging Determination of the Nerve of Origin
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Parapharyngeal Space Schwannomas Preoperative Imaging Determination of the Nerve of Origin David M. Saito, MD; Christine M. Glastonbury, MD; Ivan H. El-Sayed, MD; David W. Eisele, MD Objectives:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Parapharyngeal Space Schwannomas Preoperative Imaging Determination of the Nerve of Origin David M. Saito, MD; Christine M. Glastonbury, MD; Ivan H. El-Sayed, MD; David W. Eisele, MD Objectives:
Case Report Pleomorphic Adenomas of the Parapharyngeal Space
 Case Reports in Otolaryngology, Article ID 168401, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/168401 Case Report Pleomorphic Adenomas of the Parapharyngeal Space Estemihan AkJn, 1 TuLba Karagöz, 2 Murad Mutlu,
Case Reports in Otolaryngology, Article ID 168401, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/168401 Case Report Pleomorphic Adenomas of the Parapharyngeal Space Estemihan AkJn, 1 TuLba Karagöz, 2 Murad Mutlu,
C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital
 C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital Objectives Review basics of head and neck imaging Discuss our spatial approach
C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital Objectives Review basics of head and neck imaging Discuss our spatial approach
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Suprahyoid and Infrahyoid Neck Overview
 10 Imaging Approaches & Indications Neither CT nor MR is a perfect modality for imaging the extracranial H&N. MR is most useful in the suprahyoid neck (SHN) because it is less affected by oral cavity dental
10 Imaging Approaches & Indications Neither CT nor MR is a perfect modality for imaging the extracranial H&N. MR is most useful in the suprahyoid neck (SHN) because it is less affected by oral cavity dental
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Tumours of Parapharyngeal space
 Tumours of Parapharyngeal space The parapharyngeal spaces (PPS), as the name implies, lie laterally on either side of the pharynx. They are potential spaces, filled with fat and areolar tissue containing
Tumours of Parapharyngeal space The parapharyngeal spaces (PPS), as the name implies, lie laterally on either side of the pharynx. They are potential spaces, filled with fat and areolar tissue containing
Parapharyngeal Space Tumors: Our Experience In A Tertiary Hospital In Andhra Pradesh, India
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 28 Number 2 Parapharyngeal Space Tumors: Our Experience In A Tertiary Hospital In Andhra Pradesh, India S Tati, G Gole, S Chinnababu, V Satyanarayana, S
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 28 Number 2 Parapharyngeal Space Tumors: Our Experience In A Tertiary Hospital In Andhra Pradesh, India S Tati, G Gole, S Chinnababu, V Satyanarayana, S
Imaging of Parapharyngeal Space and Infratemporal Fossa
 10.5005/jp-journals-10003-1096 INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE Imaging of Parapharyngeal Space and Infratemporal Fossa Sanjay Jain, Aman Kumar, Harshal Dhongade, Ravi Varma ABSTRACT Cross-sectional imaging is an
10.5005/jp-journals-10003-1096 INVITED REVIEW ARTICLE Imaging of Parapharyngeal Space and Infratemporal Fossa Sanjay Jain, Aman Kumar, Harshal Dhongade, Ravi Varma ABSTRACT Cross-sectional imaging is an
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
CT Evaluation Of Parapharyngeal Masses: Pictorial Essay
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 10 Number 2 K Rajagopal, A Ramesh, S Sreepathi, C Shetty Citation K Rajagopal, A Ramesh, S Sreepathi, C Shetty.. The Internet Journal of Radiology. 2008
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 10 Number 2 K Rajagopal, A Ramesh, S Sreepathi, C Shetty Citation K Rajagopal, A Ramesh, S Sreepathi, C Shetty.. The Internet Journal of Radiology. 2008
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Neoplasms that present as a swelling in the neck may be either
 Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
Salivary ultrasound. Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK
 Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
04 Development of the Face and Neck. Development of the Face Development of the neck
 04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
1/13/2009. Classification:
 SUPPURATIONS OF SPACES RELATED TO THE PHARYNX Assistant Professor, Department of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University Classification: I. Intratonsillar abscess.
SUPPURATIONS OF SPACES RELATED TO THE PHARYNX Assistant Professor, Department of Otolaryngology Head & Neck Surgery Faculty of Medicine, Alexandria University Classification: I. Intratonsillar abscess.
Management of Parapharyngeal Space Tumors at the National Cancer Institute, Egypt
 Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 6, No., March: 3-, 00 Management of Parapharyngeal Space Tumors at the National Cancer Institute, Egypt AMR ATTIA, M.D.*; MAJED EL-SHAFIEY, M.D.*; SALAH
Journal of the Egyptian Nat. Cancer Inst., Vol. 6, No., March: 3-, 00 Management of Parapharyngeal Space Tumors at the National Cancer Institute, Egypt AMR ATTIA, M.D.*; MAJED EL-SHAFIEY, M.D.*; SALAH
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Infection of the Pharyngeal Spaces
 Lecture (4) pharynx د.سنمار Infection of the Pharyngeal Spaces Parapharyngeal Abscess Definition: Collection of pus in the parapharyngeal space which is a connective tissue space lies on the lateral side
Lecture (4) pharynx د.سنمار Infection of the Pharyngeal Spaces Parapharyngeal Abscess Definition: Collection of pus in the parapharyngeal space which is a connective tissue space lies on the lateral side
Parapharyngeal Space Tumors
 10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1059 REVIEW ARTICLE Pratima S Khandawala Senior Registrar, Department of ENT, Holy Family Hospital, Bandra, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India Correspondence: Pratima S Khandawala, Senior
10.5005/jp-journals-10001-1059 REVIEW ARTICLE Pratima S Khandawala Senior Registrar, Department of ENT, Holy Family Hospital, Bandra, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India Correspondence: Pratima S Khandawala, Senior
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Neckmasses in infancy and childhood: Clinical and radiological classification and imaging approaches M. Mearadji
 Neckmasses in infancy and childhood: Clinical and radiological classification and imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Neck masses are a frequent
Neckmasses in infancy and childhood: Clinical and radiological classification and imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Neck masses are a frequent
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
Case Studies in the Skull Base
 Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Cervical Sympathetic Chain Schwannoma
 CASE REPORT Cervical Sympathetic Chain Schwannoma Chang-Chun Lin, Chen-Chi Wang,* Shi-An Liu, Ching-Ping Wang, Wen-Hsien Chen Schwannomas are benign, slow-growing tumors that arise from Schwann cells of
CASE REPORT Cervical Sympathetic Chain Schwannoma Chang-Chun Lin, Chen-Chi Wang,* Shi-An Liu, Ching-Ping Wang, Wen-Hsien Chen Schwannomas are benign, slow-growing tumors that arise from Schwann cells of
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
fossa of the mandibular condyle
 The Road Map For Diagnosis And Management Of Parapharyngeal Tumors Professor: Hossam Thabet, MD. Otolaryngolgy-Head & Neck Suegery Alexandria University, Egypt Fakhry & Al Rajhi Hospital, Saudi Arabia
The Road Map For Diagnosis And Management Of Parapharyngeal Tumors Professor: Hossam Thabet, MD. Otolaryngolgy-Head & Neck Suegery Alexandria University, Egypt Fakhry & Al Rajhi Hospital, Saudi Arabia
Primary Jugular Foramen Meningioma: Imaging Appearance and Differentiating Features
 ndré J. Macdonald 1 Karen L. Salzman 1 H. Ric Harnsberger 1 Erik Gilbert 2 lough Shelton 2 Received May 16, 2003; accepted after revision ugust 12, 2003. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University
ndré J. Macdonald 1 Karen L. Salzman 1 H. Ric Harnsberger 1 Erik Gilbert 2 lough Shelton 2 Received May 16, 2003; accepted after revision ugust 12, 2003. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University
Perineural Tumor Spread. In Head & Neck Cancer
 Head and Neck Imaging Conference University of Perineural Tumor Spread In Head & Neck Cancer Philip Chapman MD University of Alabama, Birmingham OBJECTIVES: 1. Define (PNTS) 2. Distinguish from pathologic
Head and Neck Imaging Conference University of Perineural Tumor Spread In Head & Neck Cancer Philip Chapman MD University of Alabama, Birmingham OBJECTIVES: 1. Define (PNTS) 2. Distinguish from pathologic
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology
 Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology Kevin T. Brumund, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Surgery Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Diego Health Sciences VA Medical
Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology Kevin T. Brumund, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Surgery Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Diego Health Sciences VA Medical
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity.
 A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity. Poster No.: C-2266 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Lavelle, J. F. Gerstenmaier,
A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity. Poster No.: C-2266 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Lavelle, J. F. Gerstenmaier,
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV
 DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Shadow because the air
 Thyroid Ultrasound Thyroid US examination needs: 1. high frequency transducer 2. extended patient's neck 3. check all the neck area because the swelling could be in areas other than the thyroid such as
Thyroid Ultrasound Thyroid US examination needs: 1. high frequency transducer 2. extended patient's neck 3. check all the neck area because the swelling could be in areas other than the thyroid such as
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
CT of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Significance of Widening of the Preoccipital Soft Tissue on Axial Scans
 839 CT of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Significance of Widening of the Preoccipital Soft Tissue on Axial Scans John Hoe 1 Axial CT scans of 60 patients with biopsy-proved nasopharyngeal carcinoma were reviewed
839 CT of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Significance of Widening of the Preoccipital Soft Tissue on Axial Scans John Hoe 1 Axial CT scans of 60 patients with biopsy-proved nasopharyngeal carcinoma were reviewed
Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 :
 Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 : 2015-2-28 General Data Name:OOO Chart Number:OOOOOOO Date of Admission:2014 年 08 月 04 日 Age: 33 y/o Sex:female Occupation : 會計 Chief Complaint Palpable soft tissue mass
Case Presentation 主治醫師 : 宋文鑫日期 : 2015-2-28 General Data Name:OOO Chart Number:OOOOOOO Date of Admission:2014 年 08 月 04 日 Age: 33 y/o Sex:female Occupation : 會計 Chief Complaint Palpable soft tissue mass
Parapharyngeal Space Lesions
 Hong Kong J Radiol. 2018;21:136-42 DOI: 10.12809/hkjr1816425 PICTORIAL ESSAY Parapharyngeal Space Lesions DCW Tang, AYH Wan, GKY Lee, JHM Cheng, WK Kan, JLS Khoo Department of Radiology, Pamela Youde Nethersole
Hong Kong J Radiol. 2018;21:136-42 DOI: 10.12809/hkjr1816425 PICTORIAL ESSAY Parapharyngeal Space Lesions DCW Tang, AYH Wan, GKY Lee, JHM Cheng, WK Kan, JLS Khoo Department of Radiology, Pamela Youde Nethersole
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Dr. Faghih
 Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Basic Anatomy and Physiology of the Lips and Oral Cavity Dr. Faghih It is divided into seven specific subsites : 1. Lips 2. dentoalveolar ridges 3. oral tongue 4. retromolar trigone 5. floor of mouth 6.
Giant Parapharyngeal Pleomorphic Adenoma with Intracranial Extension: a case report
 J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 95-99 Giant Parapharyngeal Pleomorphic Adenoma with Intracranial Extension: a case report Yen-Ling Lin 1 Sheung-Fat Ko 1 Cheng-Hong Toh 1 Kar-Wai Lui 1 Shih-Ming Jung 2 Shu-Hang
J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 95-99 Giant Parapharyngeal Pleomorphic Adenoma with Intracranial Extension: a case report Yen-Ling Lin 1 Sheung-Fat Ko 1 Cheng-Hong Toh 1 Kar-Wai Lui 1 Shih-Ming Jung 2 Shu-Hang
Salivary Gland Imaging. Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016
 Salivary Gland Imaging Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016 Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal anatomy Discuss work up, management and differential diagnosis of commonly referred clinical scenarios
Salivary Gland Imaging Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016 Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal anatomy Discuss work up, management and differential diagnosis of commonly referred clinical scenarios
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
1. What is the embryologic origin of the major salivary glands, and when do they develop? 2. What is the embryologic origin of minor salivary glands?
 Salivary Gland Chapters 37, 38, 39, 40 Shapiro 1. What is the embryologic origin of the major salivary glands, and when do they develop? Outpouchings of oral ectoderm in the 6th 8 th week 2. What is the
Salivary Gland Chapters 37, 38, 39, 40 Shapiro 1. What is the embryologic origin of the major salivary glands, and when do they develop? Outpouchings of oral ectoderm in the 6th 8 th week 2. What is the
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY-
 TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
Tumours of the parapharyngeal space pose a. Surgical Approach to Parapharyngeal Tumours - Our Experience. Our Experience
 Our Experience Surgical Approach to Parapharyngeal Tumours - Our Experience Devjani Ghosh Shrestha, 1 Kinjal Shankar Majumdar, 1 Nirmalya Samanta, 1 Utpal Jana 2 ABSTRACT Introduction The complex anatomy
Our Experience Surgical Approach to Parapharyngeal Tumours - Our Experience Devjani Ghosh Shrestha, 1 Kinjal Shankar Majumdar, 1 Nirmalya Samanta, 1 Utpal Jana 2 ABSTRACT Introduction The complex anatomy
Oropharynx and Oral Cavity
 455 17 Oropharynx and Oral Cavity Th. Vogl 17.1 Anatomy, Imaging Techniques and Imaging Findings 456 17.1.1 Normal Anatomy 456 17.1.2 Imaging Techniques 456 17.1.3 Imaging Findings 456 17.2 Congenital
455 17 Oropharynx and Oral Cavity Th. Vogl 17.1 Anatomy, Imaging Techniques and Imaging Findings 456 17.1.1 Normal Anatomy 456 17.1.2 Imaging Techniques 456 17.1.3 Imaging Findings 456 17.2 Congenital
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland
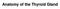 Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
Multiplanar CT and MRI of Collections in the Retropharyngeal Space: Is It an Abscess?
 Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Pictorial Essay Hoang et al. Multiplanar Imaging of Retropharyngeal Space Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by
Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Pictorial Essay Hoang et al. Multiplanar Imaging of Retropharyngeal Space Neuroradiology/Head and Neck Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by
Cervical Sympathetic Chain Schwannomas Masquerading as Carotid Body Tumors
 Cervical Sympathetic Chain Schwannomas Masquerading as Carotid Body Tumors Jean M. Panneton, MD, and Barry W. Rusnak, MD, Rochester, Minnesota, and Winnipeg, Canada Cervical sympathetic chain (CSC) schwannoma
Cervical Sympathetic Chain Schwannomas Masquerading as Carotid Body Tumors Jean M. Panneton, MD, and Barry W. Rusnak, MD, Rochester, Minnesota, and Winnipeg, Canada Cervical sympathetic chain (CSC) schwannoma
Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands
 Head & Neck Surgery Course Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Thyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco
Head & Neck Surgery Course Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Thyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
Oropharyngeal cancer
 Cancer Imaging (2005) 5, S52 S57 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2005.0030 CI MULTIDISCIPLINARY SYMPOSIUM: HEAD & NECK CANCER Monday 3 October 2005, 14:00 16:00 Oropharyngeal cancer Robert Hermans Department of
Cancer Imaging (2005) 5, S52 S57 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2005.0030 CI MULTIDISCIPLINARY SYMPOSIUM: HEAD & NECK CANCER Monday 3 October 2005, 14:00 16:00 Oropharyngeal cancer Robert Hermans Department of
Sonography of the Cervical Vagus Nerve: Normal Appearance and Abnormal Findings
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.112 on 01/20/18 from IP address 37.44.192.112. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Francesco Giovagnorio 1 arlo Martinoli 2 Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.112 on 01/20/18 from IP address 37.44.192.112. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Francesco Giovagnorio 1 arlo Martinoli 2 Received
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies. Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology
 The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology www.ifhnos.net The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology www.ifhnos.net The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS. Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3
 PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3 MK CASE PRESENTATION 28 yo Female presented to the ENT Clinic in October 2016, with the complaint of chronic
PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3 MK CASE PRESENTATION 28 yo Female presented to the ENT Clinic in October 2016, with the complaint of chronic
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies. No Disclosures or Conflicts of Interest. Anatomy 10/4/2013
 Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
A study on structural variations of the parotid glands
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Jayamma C et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3790-3794 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151444
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Jayamma C et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3790-3794 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151444
Prevertebral Abscess with Anterior Pharyngeal Shift and Epidural Involvement
 January 28, 2013 Prevertebral Abscess with Anterior Pharyngeal Shift and Epidural Involvement Daniel Killeen, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Brief introduction to our patient Review anatomy and
January 28, 2013 Prevertebral Abscess with Anterior Pharyngeal Shift and Epidural Involvement Daniel Killeen, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda Brief introduction to our patient Review anatomy and
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 4/30/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 18 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 4/30/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 18 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
ARTICLE. Imaging the cranial nerves in cancer
 Cancer Imaging (2004) 4, S1 S5 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2004.0006 CI ARTICLE Vincent Chong Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Outram Road, Singapore 169608, Singapore Corresponding
Cancer Imaging (2004) 4, S1 S5 DOI: 10.1102/1470-7330.2004.0006 CI ARTICLE Vincent Chong Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Singapore General Hospital, Outram Road, Singapore 169608, Singapore Corresponding
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Imaging Of Cystic Paravertebral Masses:
 Imaging Of Cystic Paravertebral Masses: Differential Diagnosis and Key Discriminators John P. Lichtenberger III, MD, Maj, USAF, MC Brent McCarragher, MD, CPT, USA John R. Dryden, MD, LT, USN P. Gabriel
Imaging Of Cystic Paravertebral Masses: Differential Diagnosis and Key Discriminators John P. Lichtenberger III, MD, Maj, USAF, MC Brent McCarragher, MD, CPT, USA John R. Dryden, MD, LT, USN P. Gabriel
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
