Head & Neck Contouring
|
|
|
- Abel McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN September 12, 2014
2 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD Greg Robinson, RT(T), CMD 9/8/2014 2
3 Special Dedication Kian Ang, MD, PhD Gilbert H. Fletcher Memorial Distinguished Chair Professor of Radiation Oncology at the University of Texas M. D. Anderson Cancer Center Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Mentor and friend 9/8/2014 3
4 Objectives: Review contouring guidelines of the brachial plexus. Review contouring of various normal structures. Review lymph node stations. Review sample dose constraints. Review LN at risk for harboring metastatic disease based on the primary site. 9/8/2014 4
5 References: Hall et al., Development and validation of a standardized method for contouring the brachial plexus: preliminary dosimetric analysis among patients treated with IMRT for head-and-neck cancer, Int. J. Radiation Biol. Phys., vol 72, No 5, pp , /8/2014 5
6 Brachial plexus image references Netter, Frank H. Atlas of Human Anatomy, 5 th Edition. 2011; plate 418. Harnsberger, Osborn, Macdonald, Ross. Diagnostic and Surgical Imaging Anatomy: Brain, Head & Neck, Spine. 2006; page /8/2014 6
7 (2)
8 Brachial Plexus 9/8/2014 8
9 Method Contour C5, T1, and T2 Contour anterior and middle scalene muscles Using a 5 mm contouring tool, contour from the neural foramina to in between the ant & mid scalene m. For the levels where there is no neural foramina, contour only the small space between the scalene muscles. Stop 1-2 slice below clavicle head. 9/8/2014 9
10 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
11 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
12 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
13 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
14 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
15 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
16 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
17 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
18 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
19 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
20 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
21 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
22 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
23 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
24 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
25 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
26 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
27 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
28 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
29 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
30 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
31 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
32 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
33 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
34 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
35 Brachial Plexus 9/8/
36 Brachial Plexus A typical dose constraint is to not let the brachial plexus exceed Gy. MRI can visualize the brachial plexus much better than CT, but most radiotherapy patients are planned from CT. The contouring guidelines only approximate the brachial plexus. 9/8/
37 Normal Structures Parotid Gland: yellow Submandibular Gland: light green Internal Carotid Artery: red Internal Jugular Vein: blue Hyoid Bone: magenta Sternocleidomastoid Muscle: cyano 9/8/
38 Parotid 9/8/
39 Parotid 9/8/
40 Parotid 9/8/
41 Internal carotid artery: red 9/8/
42 Internal jugular vein: blue 9/8/
43 Parotid gland: yellow 9/8/
44 Sternocleidomastoid m.: cyano 9/8/
45 Internal carotid artery: red 9/8/
46 Internal jugular vein: blue 9/8/
47 Sternocleidomastoid m.: cyano 9/8/
48 Parotid gland: yellow 9/8/
49 Internal carotid artery: red 9/8/
50 Internal jugular vein: blue 9/8/
51 Sternocleidomastoid m.: cyano 9/8/
52 Parotid: yellow 9/8/
53 Internal carotid artery: red 9/8/
54 Internal jugular vein: blue 9/8/
55 Sternocleidomastoid m.: cyano 9/8/
56 Normal structures 9/8/
57 Normal structures 9/8/
58 Normal structures 9/8/
59 Normal structures 9/8/
60 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
61 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
62 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
63 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
64 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
65 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
66 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
67 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
68 Submandibular gland: light green 9/8/
69 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
70 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
71 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
72 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
73 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
74 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
75 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
76 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
77 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
78 Hyoid bone: magenta 9/8/
79 Sternocleidomastoid m.: cyano 9/8/
80 Internal carotid artery: red 9/8/
81 Internal jugular vein: blue 9/8/
82 Normal structures 9/8/
83 Normal structures 9/8/
84 Normal structures 9/8/
85 Normal structures 9/8/
86 Normal structures 9/8/
87 Normal structures 9/8/
88 Normal structures 9/8/
89 Normal structures 9/8/
90 Normal structures 9/8/
91 Normal structures 9/8/
92 Normal structures 9/8/
93 Normal structures 9/8/
94 Normal structures 9/8/
95 Normal structures 9/8/
96 Normal structures 9/8/
97 Normal structures 9/8/
98 Normal structures 9/8/
99 Normal structures 9/8/
100 Normal structures 9/8/
101 Normal structures 9/8/
102 Normal structures 9/8/
103 Normal structures 9/8/
104 Normal structures 9/8/
105 Normal structures 9/8/
106 Normal structures 9/8/
107 Normal structures 9/8/
108 Oblique view 9/8/
109 Oblique view 9/8/
110 Contouring the Lymph Nodes Reference: Vincent Grégoire, Kian Ang, et al, Delineation of the neck node levels for head and neck tumors: a 2013 update. DAHANCA, EORTC, HKNPCSG, NCIC, CTG, NCRI, RTOG, TROG consensus guidelines, Radiotherapy and Oncology 110 (2014) Clifford Chao, Practical Essentials of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy, second edition, 2005, chapter 7, pp /8/
111 Level Ia Submental group: midline region between the anterior belly of the right & left digastric m. Drains the skin of the chin, mid-lower lip, tip of the tongue, anterior mandibular alveolar ridge, and the floor of the mouth. 9/8/
112 Level Ib Submandibular group: space between the inner side of the mandible laterally and the digastric muscle medially; from the symphysis menti anteriorly to the submandibular gland posteriorly. Drain the submental nodes, lower nasal cavity, the hard and soft palate, the maxillary and mandibular alveolar ridges, the cheek, both lips, and most of the anterior tongue. 9/8/
113 Simplified version Stroking a cat. The midline space is the region of level Ia The space next to the jaw is the region of level Ib. 9/8/
114 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
115 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
116 Key point: The submandibular gland forms the posterior border of the Level Ib nodal group. 9/8/
117 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
118 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
119 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
120 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
121 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
122 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
123 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
124 Level Ia: blue; & Level Ib: brown 9/8/
125 Level Ib: brown 9/8/
126 Level Ib: brown 9/8/
127 Level Ib: brown 9/8/
128 Level Ib: brown 9/8/
129 Level Ib: brown 9/8/
130 Level II Upper jugular group: lie in the space between the deep (medial) surface of the sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM) laterally, and the medial edge of the internal carotid artery and the scalenius muscle medially; this space extends from the posterior edge of the submandibular gland anteriorly to the posterior edge of the SCM posteriorly, and from the lateral process of the first cranial vertebra to the caudal edge of the hyoid bone. 9/8/
131 Level II Receives from the face, parotid gland, submandibular, submental, & retropharyngeal nodes. Drains from nasal cavity, oral cavity, nasopharynx, oropharynx, larynx, major salivary glands. Involvement is more common from oropharynx and nasopharynx than oral cavity, larynx, or hypopharynx. 9/8/
132 Level II 9/8/
133 Level II 9/8/
134 Level II 9/8/
135 Level II 9/8/
136 Level II 9/8/
137 Level II 9/8/
138 Level II 9/8/
139 Level II 9/8/
140 Level II 9/8/
141 Level II 9/8/
142 Level II 9/8/
143 Level II 9/8/
144 Level II 9/8/
145 Level II 9/8/
146 Key points: Sternocleidomastoid muscle establishes the lateral and posterior borders of level II Medial border of the internal carotid artery establishes the medial border of level II. Posterior edge of the submandibular gland establishes the anterior border of level II. 9/8/
147 Level II 9/8/
148 Level II 9/8/
149 9/8/
150 Level II 9/8/
151 Level II 9/8/
152 Level II 9/8/
153 Level II 9/8/
154 Level II 9/8/
155 Level II 9/8/
156 Level II 9/8/
157 Level II 9/8/
158 Level II 9/8/
159 Key point The bottom of the hyoid bone marks the border between level II and level III. 9/8/
160 Level II 9/8/
161 Level II 9/8/
162 Level III Middle jugular lymph nodes: extends from the caudal edge of the body of the hyoid to the caudal edge of cricoid cartilage. Anterior limit: the anterior edge of the SCM or the posterior third of the thyro-hyoid muscle. Posterior limit: the posterior edge of SCM. Lateral limit: deep surface of SCM. Medial: medial edge of common carotid artery & scalene muscles 9/8/
163 Level III Receives lymph from Level II & V, retropharyngeal, pretracheal, & recurrent laryngeal nodes. At risk: oral cavity, nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx, and larynx. 9/8/
164 Level III 9/8/
165 Level III 9/8/
166 Level III 9/8/
167 Level III 9/8/
168 Level III 9/8/
169 Level III 9/8/
170 Level III 9/8/
171 Level III 9/8/
172 Level III 9/8/
173 Level III 9/8/
174 Level III 9/8/
175 Level IV: Caudal jugular LN Can be divided into IVa (lower jugular LN) and Ivb (medial supraclavicular LN) At risk: IVa: hypopharynx, larynx, thyroid, and cervical esophagus. At risk IVb: hypopharynx, sub-glottic larynx, trachea, thyroid, and cervical esophagus. 9/8/
176 Level IV Cranial: lower margin of cricoid cartilage Caudal: 2 cm cranial to sternoclavicular joint (N0) or sternoclavicular joint (N+). Anterior: posterolateral edge of SCM muscle Posterior: anterior edge of paraspinal muscle Lateral: lateral border of SCM Medial: medial border of vessel bundle, lateral border of thyroid. 9/8/
177 Level V: Posterior triangle group Dorsal cervical LN along the spinal accessory nerve. Va: upper posterior triangle nodes Vb: lower posterior triangle nodes Vc: lateral supraclavicular nodes 9/8/
178 Level V Cranial: base of skull Caudal: transverse cervical vessels, cranial border of clavicle (noncontrast CT) Anterior: posterior edge of SCM muscle Posterior: anterior edge of trapezius muscle Lateral: platysma muscle, skin Medial: paraspinal muscle 9/8/
179 Level V At risk: primary cancers of the nasopharynx, oropharynx, thyroid gland, skin of the posterior scalp. 9/8/
180 Levels IV & V 9/8/
181 Levels IV & V 9/8/
182 Levels IV & V 9/8/
183 Levels IV & V 9/8/
184 Levels IV & V 9/8/
185 Levels IV & V 9/8/
186 Levels IV & V 9/8/
187 Levels IV & V 9/8/
188 Levels IV & V 9/8/
189 Levels IV & V 9/8/
190 Levels IV & V 9/8/
191 Levels IV & V 9/8/
192 Levels IV & V 9/8/
193 Levels IV & V 9/8/
194 Levels IV & V 9/8/
195 Levels IV & V 9/8/
196 Levels IV & V 9/8/
197 Levels IV & V 9/8/
198 Levels IV & V 9/8/
199 Levels IV & V 9/8/
200 Levels IV & V 9/8/
201 Levels IV & V 9/8/
202 Levels IV & V 9/8/
203 Levels IV & V 9/8/
204 Levels IV & V 9/8/
205 Levels IV & V 9/8/
206 Levels IV & V 9/8/
207 Levels IV & V 9/8/
208 Levels IV & V 9/8/
209 Levels IV & V 9/8/
210 Levels IV & V 9/8/
211 Levels IV & V 9/8/
212 Levels IV & V 9/8/
213 Dose constraints Spinal cord: 45 Gy is common, but some protocols allow Gy. Brainstem: 50 Gy Lips: 25 Gy (non-oral cavity primary) Lips: 45 Gy (oral cavity primary) Oral cavity: 30 Gy (for non-oral cavity primary) Parotid gland: 26 Gy (mean dose) 9/8/
214 LN at risk: clinical N0 Nasopharynx: Maxillary sinus (T1-2): Maxillary sinus (T3-4): Oral tongue (T3-4): Floor of mouth: Buccal, RMT (T1-2): (Ib-V, RPLN) none Ipsilat (I, II, RPLN) Bilat (I-V) Bilat (I-V) Ipsi (I-III) 9/8/
215 LN at risk: clinical N0 Tonsil (T1-2): Tonsil (T3-4): Base of tongue: Ipsi (Ib-V) Bilat (Ib-V, RPLN) Bilat (Ib-V, RPLN) 9/8/
216 LN at risk: clinical N0 TVC (T1-2): TVC (T3-4): Supraglottic Hypopharynx none Bilat (II-V) Bilat (II-V) Bilat (II-V, RPLN) 9/8/
217 Questions 9/8/
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
Practice teaching course on head and neck cancer management
 28-29 October 2016 - Saint-Priest en Jarez, France Practice teaching course on head and neck cancer management IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL MEDICAL EDUCATION EDUCATION www.excemed.org
28-29 October 2016 - Saint-Priest en Jarez, France Practice teaching course on head and neck cancer management IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL MEDICAL EDUCATION EDUCATION www.excemed.org
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide
 The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide Alba L. Reyes Ortiz, MD Elena Capilla, MD. Lina Cruz Hernández,
The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide Alba L. Reyes Ortiz, MD Elena Capilla, MD. Lina Cruz Hernández,
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY-
 TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
Volumi di trattamento del cavo orale
 SIMPOSIO: Neoplasie del cavo orale Volumi di trattamento del cavo orale F. Miccichè ! DICHIARAZIONE Relatore: Francesco Miccichè Come da nuova regolamentazione della Commissione Nazionale per la Formazione
SIMPOSIO: Neoplasie del cavo orale Volumi di trattamento del cavo orale F. Miccichè ! DICHIARAZIONE Relatore: Francesco Miccichè Come da nuova regolamentazione della Commissione Nazionale per la Formazione
The following images were all acquired using a CTI Biograph
 Positron Emission Tomography/ Computed Tomography Imaging of Head and Neck Tumors: An Atlas Michael M. Graham, MD, PhD, and Yusuf Menda, MD Department of Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA. Address
Positron Emission Tomography/ Computed Tomography Imaging of Head and Neck Tumors: An Atlas Michael M. Graham, MD, PhD, and Yusuf Menda, MD Department of Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA. Address
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Since the first description of the radical neck dissection by George Crile almost a century
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neck Dissection Classification Update Revisions Proposed by the American Head and Neck Society and the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery K. Thomas Robbins, MD; Garry
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Neck Dissection Classification Update Revisions Proposed by the American Head and Neck Society and the American Academy of Otolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery K. Thomas Robbins, MD; Garry
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition. Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx
 AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx AJCC 7 th edition Lip and Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx KEY CHANGES Skin of head and neck (Vermilion of the lip)
AJCC Cancer Staging 8 th edition Lip and Oral Cavity Oropharynx (p16 -) and Hypopharynx Larynx AJCC 7 th edition Lip and Oral cavity Pharynx Larynx KEY CHANGES Skin of head and neck (Vermilion of the lip)
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
Josh Howard CMD Upendra Parvathaneni MBBS, FRANZCR
 Anatomic and Dosimetric Correlation in the Treatment of Advanced Larynx Cancer- When is the Brachial Plexus at Risk? Josh Howard CMD Upendra Parvathaneni MBBS, FRANZCR AAMD 39th Annual Meeting - Seattle
Anatomic and Dosimetric Correlation in the Treatment of Advanced Larynx Cancer- When is the Brachial Plexus at Risk? Josh Howard CMD Upendra Parvathaneni MBBS, FRANZCR AAMD 39th Annual Meeting - Seattle
Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer
 106 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Indication of definitive radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy (1) Resectable, but medically unfit, or high
106 年 12 月修訂 Protocol of Radiotherapy for Head and Neck Cancer Indication of radiotherapy Indication of definitive radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy (1) Resectable, but medically unfit, or high
Thyroid INTRODUCTION ANATOMY SUMMARY OF CHANGES
 AJC 7/14/06 1:19 PM Page 67 Thyroid C73.9 Thyroid gland SUMMARY OF CHANGES Tumor staging (T) has been revised and the categories redefined. T4 is now divided into T4a and T4b. Nodal staging (N) has been
AJC 7/14/06 1:19 PM Page 67 Thyroid C73.9 Thyroid gland SUMMARY OF CHANGES Tumor staging (T) has been revised and the categories redefined. T4 is now divided into T4a and T4b. Nodal staging (N) has been
A Pathologist s Guide to Neck Dissection. Neck Dissections. Lymphatics of head and neck. Neck Dissections
 A Pathologist s Guide to Neck Dissection North American Society for Head and Neck Pathology Companion Meeting 2006 Sigrid Wayne, M.D. Department of Pathology University of Iowa The presence of cervical
A Pathologist s Guide to Neck Dissection North American Society for Head and Neck Pathology Companion Meeting 2006 Sigrid Wayne, M.D. Department of Pathology University of Iowa The presence of cervical
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group. Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer. Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i & 11-1C-106i
 Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Management of unknown primary with neck node metastasis: Current evidence
 Management of unknown primary with neck node metastasis: Current evidence Dr. Pooja Nandwani Patel Associate Professor Dept. of Radiation Oncology GCRI, Ahmedabad Introduction- Approach to Topic What is
Management of unknown primary with neck node metastasis: Current evidence Dr. Pooja Nandwani Patel Associate Professor Dept. of Radiation Oncology GCRI, Ahmedabad Introduction- Approach to Topic What is
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA
 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
AIRWAY MANAGEMENT SUZANNE BROWN, CRNA OBJECTIVE OF LECTURE Non Anesthesia Sedation Providers Review for CRNA s Informal Questions encouraged 2 AIRWAY MANAGEMENT AWARENESS BASICS OF ANATOMY EQUIPMENT 3
Q&A. Fabulous Prizes. Collecting Cancer Data: Pharynx 12/6/12. NAACCR Webinar Series Collecting Cancer Data Pharynx
 Collecting Cancer Data Pharynx NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
Collecting Cancer Data Pharynx NAACCR 2012 2013 Webinar Series Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide
 The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide Poster No.: C-0483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit
The importance of knowing the lymphatic spread patterns of head and neck cancer for accurate nodal staging on CT: A practical schematic guide Poster No.: C-0483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles. Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer
 Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer Email:diptendrasarkar@yahoo.co.in HNC : common inclusives Challenges Anatomical preservation R0 Surgical
Surgery in Head and neck cancers.principles Dr Diptendra K Sarkar MS,DNB,FRCS Consultant surgeon,ipgmer Email:diptendrasarkar@yahoo.co.in HNC : common inclusives Challenges Anatomical preservation R0 Surgical
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Anatomy of Head of Neck Cancer
 Anatomy of Head of Neck Cancer J. Robert Newman, MD The ENT Center of Central GA H&N Cancer Overview Most categories of cancer are represented in the H&N Squamous cell carcinoma most common mucosal cancer
Anatomy of Head of Neck Cancer J. Robert Newman, MD The ENT Center of Central GA H&N Cancer Overview Most categories of cancer are represented in the H&N Squamous cell carcinoma most common mucosal cancer
Case Scenario 1. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
Case Scenario 1 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of
Suprahyoid and Infrahyoid Neck Overview
 10 Imaging Approaches & Indications Neither CT nor MR is a perfect modality for imaging the extracranial H&N. MR is most useful in the suprahyoid neck (SHN) because it is less affected by oral cavity dental
10 Imaging Approaches & Indications Neither CT nor MR is a perfect modality for imaging the extracranial H&N. MR is most useful in the suprahyoid neck (SHN) because it is less affected by oral cavity dental
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
"The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck
 "The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck Poster No.: C-2457 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. K.
"The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck Poster No.: C-2457 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. K.
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI
 Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
Anatomy of Oral Cavity DR. MAAN AL-ABBASI By the end of this lecture you should be able to: 1. Differentiate different parts of the oral cavity 2. Describe the blood and nerve supply of mucosa and muscles
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy. Raleigh E. Lingeman
 Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Advanced Anatomy of the Neck
 AACE 2018 Advanced Anatomy of the Neck Alex Tessnow, MD, MBA, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Dallas, TX Content contributed by: H. Jack Baskin, Daniel Duick, Diana Dean, Robert A. Levine,
AACE 2018 Advanced Anatomy of the Neck Alex Tessnow, MD, MBA, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Dallas, TX Content contributed by: H. Jack Baskin, Daniel Duick, Diana Dean, Robert A. Levine,
Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck. Raymond P. Wood II:
 Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck Raymond P. Wood II: In approaching the problem of a mass in the neck, one immediately encounters the fact that there are normally palpable masses in the neck (eg, almost all
Chapter 13: Mass in the Neck Raymond P. Wood II: In approaching the problem of a mass in the neck, one immediately encounters the fact that there are normally palpable masses in the neck (eg, almost all
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
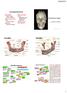 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Case Scenario. 7/13/12 Anterior floor of mouth biopsy: Infiltrating squamous cell carcinoma, not completely excised.
 Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
Case Scenario 7/5/12 History A 51 year old white female presents with a sore area on the floor of her mouth. She claims the area has been sore for several months. She is a current smoker and user of alcohol.
HEAD & NECK ANATOMY - MCQ HEAD & NECK ANATOMY
 . ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
. ' HEAD & NECK ANATOMY I. Deep investing layer of cervical fascia splits to enclose: A. Sternocleidomastoid B. Trapezius C. Parotid gland D. Omohyoid 2. Regarding the prevertebral fascia, the following
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Over the past 18 years, numerous classifications have been proposed to distinguish
 ORGNAL ARTCLE An maging-based Classification for the Cervical Nodes Designed as an Adjunct to Recent Clinically Based Nodal Classifications Peter M. Som, MD; Hugh D. Curtin, MD; Anthony A. Mancuso, MD
ORGNAL ARTCLE An maging-based Classification for the Cervical Nodes Designed as an Adjunct to Recent Clinically Based Nodal Classifications Peter M. Som, MD; Hugh D. Curtin, MD; Anthony A. Mancuso, MD
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Head and Neck Tumours
 Head and Neck Tumours Introductory Notes The following sites are included: Lip, oral cavity Pharynx: oropharynx, nasopharynx, hypopharynx Larynx: supraglottis, glottis, subglottis Nasal cavity and paranasal
Head and Neck Tumours Introductory Notes The following sites are included: Lip, oral cavity Pharynx: oropharynx, nasopharynx, hypopharynx Larynx: supraglottis, glottis, subglottis Nasal cavity and paranasal
FACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 Neck Dissection Pornchai O-charoenrat MD, PhD Division of Head, Neck and Breast Surgery Department of Surgery FACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Introduction Status of the cervical lymph nodes is the
Neck Dissection Pornchai O-charoenrat MD, PhD Division of Head, Neck and Breast Surgery Department of Surgery FACULTY OF MEDICINE SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Introduction Status of the cervical lymph nodes is the
Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學
 Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學 陳家媛 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 cychen@wanfang.gov.tw Normal Suprahyoid neck: the old way Nasopharynx Oropharynx Oral cavity Staging of SCC Spaces of Suprahyoid Neck: a New Way Deep
Head and Neck Image 頭頸部放射影像學 陳家媛 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 cychen@wanfang.gov.tw Normal Suprahyoid neck: the old way Nasopharynx Oropharynx Oral cavity Staging of SCC Spaces of Suprahyoid Neck: a New Way Deep
Cervical Lymph Nodes
 Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
General Anatomic Layout
 General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
General Anatomic Layout 2 Core Messages At the start of the dissection exercise, we must take a panoramic look for orientation. We then establish the limits of the area of operation and the main landmarks.
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Treatment Planning for Breast Cancer: Contouring Targets. Julia White MD Professor
 Treatment Planning for Breast Cancer: Contouring Targets Julia White MD Professor Outline 1. RTOG Breast Cancer Atlas 2. Target development on Clinical Trials Whole Breast Irradiation 2-D Radiotherapy
Treatment Planning for Breast Cancer: Contouring Targets Julia White MD Professor Outline 1. RTOG Breast Cancer Atlas 2. Target development on Clinical Trials Whole Breast Irradiation 2-D Radiotherapy
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
2. Guidelines for Reporting Head and Neck Tumours
 39 40 2. Guidelines for Reporting Head and Neck Tumours Compilation and editing of this volume: Dr. Modini Jayawickrama (Consultant Histopathologist) List of contributors Consultant Histopathologists Dr.
39 40 2. Guidelines for Reporting Head and Neck Tumours Compilation and editing of this volume: Dr. Modini Jayawickrama (Consultant Histopathologist) List of contributors Consultant Histopathologists Dr.
Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer
 1 Charles Poole April Case Study April 30, 2012 Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer Abstract: Introduction: This study
1 Charles Poole April Case Study April 30, 2012 Evaluation of Whole-Field and Split-Field Intensity Modulation Radiation Therapy (IMRT) Techniques in Head and Neck Cancer Abstract: Introduction: This study
Thyroid gland. importance. relations and connections. external laryngeal nerves. malformations.
 Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Anatomy of the Airway
 Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy of the Airway Nagelhout, 5 th edition, Chapter 26 Morgan & Mikhail, 5 th edition, Chapter 23 Mary Karlet, CRNA, PhD Airway Anatomy The airway consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, and
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
6. Cervical Lymph Nodes and Unknown Primary Tumors of the Head and Neck
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical sciences Structure and Nerve Supply of The Larynx This presentation was originally prepared by: Dr. Kumar Notes were added by:
Lecture 01. The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018
 Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a review
 J Radiat Oncol (2012) 1:129 146 DOI 10.1007/s13566-012-0020-4 REVIEW Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a review Tony J. C. Wang & Nadeem Riaz & Simon K. Cheng & Jiade
J Radiat Oncol (2012) 1:129 146 DOI 10.1007/s13566-012-0020-4 REVIEW Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a review Tony J. C. Wang & Nadeem Riaz & Simon K. Cheng & Jiade
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
An Introduction to Head & Neck Radiotherapy.
 An Introduction to Head & Neck Radiotherapy. Vincent GREGOIRE, M.D., Ph.D. Head and Neck Oncology Program, Radiation Oncology Dept. & Center for Molecular Imaging and Experimental Radiotherapy, Université
An Introduction to Head & Neck Radiotherapy. Vincent GREGOIRE, M.D., Ph.D. Head and Neck Oncology Program, Radiation Oncology Dept. & Center for Molecular Imaging and Experimental Radiotherapy, Université
Anatomical cervical CT atlas for radiotherapy: A teaching model of lymph node levels for head and neck cancer treatment
 Anatomical cervical CT atlas for radiotherapy: A teaching model of lymph node levels for head and neck cancer treatment Poster No.: C-1690 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Head and Neck
Anatomical cervical CT atlas for radiotherapy: A teaching model of lymph node levels for head and neck cancer treatment Poster No.: C-1690 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Head and Neck
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Ultrasonographic identification of the anatomical landmarks that define cervical lymph nodes spaces
 Review Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 1, 29-34 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.151.lml1uia2 Ultrasonographic identification of the anatomical landmarks that define cervical lymph nodes spaces Lavinia Manuela
Review Med Ultrason 2013, Vol. 15, no. 1, 29-34 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.151.lml1uia2 Ultrasonographic identification of the anatomical landmarks that define cervical lymph nodes spaces Lavinia Manuela
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
SURGERY. This article is one of a. of the Head and Neck
 SURGERY of the Head and Neck Mary Sutton, CST, CFA This article is one of a series that will discuss head and neck surgeries from an otolaryngology perspective. Most of these surgeries involve cancer,
SURGERY of the Head and Neck Mary Sutton, CST, CFA This article is one of a series that will discuss head and neck surgeries from an otolaryngology perspective. Most of these surgeries involve cancer,
14. Mucosal Melanoma of the Head and Neck
 1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
1 Terms of Use The cancer staging form is a specific document in the patient record; it is not a substitute for documentation of history, physical examination, and staging evaluation, or for documenting
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
doi: /j.ijrobp
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.03.004 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 72, No. 5, pp. 1362 1367, 2008 Copyright Ó 2008 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/08/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.03.004 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 72, No. 5, pp. 1362 1367, 2008 Copyright Ó 2008 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/08/$ see front
HEAD & NECK. FACE Muscles, nerve supply - sensory and motor, blood supply, Danger area Level 2: Applied anatomy
 HEAD & COURSE CONTENT COMPETENCIES The first year medical student should be able to understand and describe the gross anatomy of muscles, fascia, vessels, nerves, bones, joints and viscera of the head
HEAD & COURSE CONTENT COMPETENCIES The first year medical student should be able to understand and describe the gross anatomy of muscles, fascia, vessels, nerves, bones, joints and viscera of the head
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Head and Neck Examination
 Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
Head and Neck Examination Statement of Goals Understand and perform an examination of the head and neck. Learning Objectives Head Ears Nose Sinus A. Describe the anatomy of the head, including regions
