Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Tractography of Median Nerve: Normative Diffusion Values
|
|
|
- Colin Miller
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tractography of Median Nerve Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Neslihan Kabakci 1 Bengi Gürses 1 Zeynep Firat 1 Ali Bayram 1 Aziz Müfit Uluğ 2,3 Arzu Kovanlıkaya 1 İlhami Kovanlıkaya 1 Kabakci N, Gürses B, Firat Z, et al. Keywords: diffusion tensor imaging, median nerve, MRI DOI: /AJR Received January 29, 2007; accepted after revision May 13, Preliminary data presented at the 2006 Annual Scientific Meeting of the European Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology, Warsaw, Poland. 1 Department of Radiology, Yeditepe University Hospital, Devlet Yolu Ankara Cad , Kozyataği, Istanbul, Turkey. Address correspondence to N. Kabakci (nkabakci@yeditepe.edu.tr). 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Yeditepe University School of Engineering, Istanbul, Turkey. 3 Department of Radiology, Weill Medical College of Cornell University, New York, NY. AJR 2007; 189: X/07/ American Roentgen Ray Society Tensor Imaging and Tractography of Median Nerve: Normative s OBJECTIVE. The purposes of this study were to visualize the human median nerve on diffusion tensor imaging and to determine the normal fractional anisotropy (FA) value and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of the normal median nerve. SUBJECTS AND METHODS. The wrists of 20 healthy volunteers and of two patients with carpel tunnel syndrome were examined with a 3-T MRI system with a standard eight-channel sensitivity-encoding head coil. tensor imaging was performed with a spin-echo echo-planar sequence. A T1-weighted sequence was performed for anatomic reference. After tractography, the FA value and ADC of the whole nerve were calculated automatically. Manual focal measurements also were obtained at the levels of the flexor retinaculum, wrist, and forearm. RESULTS. We visualized the median nerve with MR diffusion tensor tractography and followed the nerve for approximately 77.5 mm. We found the normative diffusion values of the median nerve were an FA of ± (SD) and an ADC of ± mm 2 /s. There was a statistically significant difference between the FA values obtained at the level of the flexor retinaculum and the values obtained from the other parts of the median nerve (p < ). We found a decrease in FA value (p < 0.01) and an increase in ADC (p < 0.05) with advancing age. CONCLUSION. The normative diffusion values of the human median nerve can be used as a reference in evaluation, diagnosis, and follow-up of entrapment, trauma, and regeneration of the median nerve. he median nerve is one of three T main nerves of the forearm. It arises from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus (C6 T1). At the wrist level, it passes under the flexor retinaculum deep in relation to the flexor digitorum superficialis tendons through the carpal tunnel and divides into digital and muscular branches distal in relation to the flexor retinaculum. Several entrapment and compression syndromes affect these nerves of the forearm. Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common peripheral neuropathy of the upper extremity resulting from dysfunction of the median nerve. CTS is characterized by numbness in the first three digits and the radial aspect of the fourth digit and by thenar atrophy. There are several diagnostic methods for CTS, such as the Phalen maneuver, Flick test, and electromyography [1, 2]. Although the sensitivity and specificity of MRI in the diagnosis of CTS are low (sensitivity, 23 96%; specificity, 39 87%), a few signs, such as nerve enlargement, nerve flattening, and increased nerve signal intensity, do occur [1]. With application of the appropriate magnetic field gradients, MRI can be sensitized to the thermally driven random motion (diffusion) of water molecules in the direction of the field gradient. This technique is called diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) [3]. Many materials have intrinsic structural properties that hinder diffusion so that diffusivity is greater in some directions than in others. This property is known as anisotropy. If there is no directional variation in diffusion rate, diffusion is said to be isotropic. Biologic tissues often are anisotropic because structures such as cell membranes and large protein molecules restrict the motion of water molecules. This property is called restricted diffusion. DWI usually shows diffusion information in one direction. In an anisotropic sample, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is required to fully characterize diffusion. In theory, to determine all elements of the diffusion tensor, at least six independent measurements with diffusion gradients applied sequentially along six noncollinear directions are required [4 7]. The direction of maximum diffusivity has been shown to coincide with the fiber tract orientation [6, 7]. In white matter fiber bun- AJR:189, October
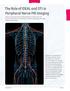
2 Fig year-old healthy subject who underwent tractography. A, Coronal color-coded map shows median nerve (arrows). B, Axial color-coded map obtained with aid of coronal map shows median nerve (arrow). C, Anatomic T1-weighted reference MR image confirms localization of median nerve. dles, water molecules move more along the fibers than in other directions [8]. With special fiber tracking software, it is possible to visualize neural tracts with DTI data [3]. Peripheral nerve imaging can be useful in the diagnosis of nerve compression, inflammation, trauma, and neuropathy and in the postoperative follow-up of nerve repair procedures. MR neurographic methods with fat-saturated heavily T2-weighted sequences or STIR T2- weighted sequences also can be used for peripheral nerve imaging [9]. DTI has been used mostly in imaging of the CNS to visualize white matter tracts. Several studies [10 12] have shown the clinical applications of DTI in neuronal disorders such as stroke, epilepsy, and CNS tumors. In a few studies [8, 12, 13], peripheral nerves have been visualized with DTI. For use of DTI in the diagnosis of pathologic conditions affecting peripheral nerves, the normative values of these nerves must be determined. In this study, our aims were to visualize the human median nerve with DTI and to determine the normal fractional anisotropy (FA) value and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) for use in the diagnosis of CTS, the most common peripheral neuropathy. Subjects and Methods Imaging was performed on the wrists of 21 volunteers (six men, 14 women; mean age, 27.5 years; A range, years) with no history of medication use, surgery, or neurologic disorder related to the median nerve. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects. We also imaged the wrists of two patients with CTS to explore the applicability of the method to pathologic conditions. The examinations were performed on a 3-T MRI system (Intera Achieva, Philips Medical Systems) with a maximum gradient amplitude of 30 mt/m, slew rate of 150 T/m/s, and an eightchannel sensitivity-encoding head coil. During imaging, the coil was positioned in the center of the magnet bore. The subject was in a prone position with the hands over the head within the coil and immobilized with cushions, sandbags, and bandages. This positioning produced little discomfort for the subjects. A single-shot spin-echo echo-planar DTI sequence was used with the following parameters: TR/TE, 4,600/90; flip angle, 90 ; field of view, 140 mm; matrix size, ; number of signals averaged, 3. weighting with a b value of 1,000 s/mm 2 was applied in 32 directions. An image without diffusion gradients also was acquired. Total sequence duration was 7 minutes 49 seconds. The data were obtained from 35 axial slices of 4-mm thickness with no gap. For anatomic reference, a T1-weighted axial sequence was obtained (382/20; flip angle, 90 ; field of view, 140 mm; number of signals averaged, 2). After DTI data were transferred to a PC, manufacturer-supplied software (PRIDE, Philips Medical Systems) was used for fiber tracking. The first step was to use color-coded maps in the coronal plane to B locate the nerve (Fig. 1A). Circular regions of interest (ROIs) were placed in the anatomic location of the median nerve expected on the basis of information from coronal and axial color-coded maps (Fig. 1B). ROI placement was done at two levels: the distal radioulnar joint and one of the most proximal slices. The locations of the coded fibers were confirmed by use of the anatomic location on T1-weighted reference images (Fig. 1C). A circular ROI larger than the nerve was used for this purpose (Fig. 2A). The anisotropy threshold was 0.3. After anatomic confirmation of the median nerve tract, the number of coded fibers, mean fiber length, mean FA value, and mean ADC were calculated with the software. The ADC calculated was one third of the trace of the diffusion tensor. On the color-coded map, three points along the tract of the median nerve in the axial and coronal planes were determined for focal FA measurements. One of the measurements was obtained at the level of flexor retinaculum. The other measurements were obtained at the wrist and forearm levels. At the wrist level, FA was measured from the median nerve at the level of musculotendinous junctions of the flexor digitorum and palmaris longus muscles. At the forearm level, the measurement was obtained approximately 5 cm proximal to the flexor retinaculum in the center of the flexor digitorum muscle bundles. For these measurements, ROIs smaller than the nerve were selected to avoid partial volume effects (Fig. 2B). Statistical analyses were performed with commercially available software (SPSS 11.0, SPSS). C 924 AJR:189, October 2007
3 Tractography of Median Nerve The mean FA values and ADCs obtained from the whole median nerve and focal measurements were compared by Friedman variance analysis and Wilcoxon s signed rank test. The comparison of FA values and ADCs on the basis of age was evaluated with Spearman s rank correlation test. A value of p < 0.05 was considered significant. Results The images of three of the 21 volunteer subjects were initially discarded because of the presence of motion artifacts. We repeated imaging of two of these subjects and included their data in the analysis. As a result, the median nerves of 20 subjects were visualized with DTI and fiber tracking. Figures 3 6 show the tractographic images of the median nerves of selected subjects. A Fig year-old healthy subject who underwent tractography. A, Axial color-coded map shows that for tractography, region of interest is larger than nerve. B, Axial color-coded map shows that for focal fractional anisotropy measurement, region of interest is smaller than nerve. Fig year-old healthy subject. Tractographic Fig year-old healthy subject. Tractographic The number and length of the tracked fibers, mean FA value, and mean ADC are summarized in Table 1. The mean number of tracked fibers was 1,417, and the mean length was 77.5 mm (range, mm). The FA values of the normal median nerve ranged from 0.69 to The mean FA value for all of the subjects was ± (SD). The ADCs of normal median nerves were between 0.74 and mm 2 /s. The mean ADC was ± mm 2 /s. The mean FA value was 0.72 ± 0.05 for the women and 0.69 ± 0.01 for men. The mean ADC for the women was 0.97 ± 0.10 and that for the men was 1.12 ± There was no statistically significant difference between the values for men and those for women. There were, however, significant differences with advancing age: a B Fig year-old healthy subject. Tractographic Fig year-old healthy subject. Tractographic significant increase in ADC (Spearman s rank correlation, p < 0.05; ρ = 0.547) and a significant decrease in FA value (Spearman s rank correlation, p <0.01; ρ =0.726). The mean FA value and ADC of focal measurements of the median nerve at the flexor retinaculum, wrist, and forearm levels are shown in Table 2. At the flexor retinaculum level, the mean FA value was 0.59 ± 0.07 and the mean ADC, 0.97 ± mm 2 /s. At the wrist level, the mean FA value was 0.72 ± 0.07 and the mean ADC, 0.95 ± mm 2 /s. At the forearm level, the mean FA value was 0.71 ± 0.08 and the mean ADC, 0.98 ± mm 2 /s. There was a statistically significant difference between the FA value obtained from the flexor retinaculum level and those obtained from the other parts of the me- AJR:189, October
4 TABLE 1: Number and Length of Tracked Fibers, Mean, and Mean for Median Nerves (n =20) Subject No. Age (y) No. of Fibers Fiber Length (mm) Mean Mean , , , , , , , , , , Mean , ± ± dian nerve (p < ). No statistical difference was observed between ADCs measured at the three anatomic locations. In the two patients with CTS, the mean FA values of the median nerve were 0.41 and These values were both 2 SDs below the normal value. Discussion DTI has been used mostly in visualization of white matter fibers in the CNS [7]. The results of our study show that DTI and fiber tracking at 3 T can be used to visualize the peripheral nerves. In a study with three healthy volunteers, Skorpil et al. [14] used DTI with fiber tracking on a 1.5-T MRI system to image the sciatic nerves in vivo. Hiltunen et al. [8] later used a 3-T MRI system to study the median, ulnar, and radial nerves and the tibial and peroneal nerves of six healthy subjects. Meek et al. [13] were the first to image abnormalities in the peripheral nerve with DTI. In a postoperative evaluation 3 months after fascicular nerve repair, those authors visualized the median nerve, which could be tracked only up to the transection site 1 month after the procedure. That report showed DTI to be capable of depicting living nerve fibers. Further prospective large series are needed, however, to assess the value of DTI in nerve repair surgery. Several indexes can be used for quantitative analysis of DWI and DTI data. We used ADC and FA value. ADC is a scalar value reflecting molecular diffusivity under motion restriction and is independent of magnetic field strength [8, 15, 16]. Like T1- and T2-weighted relaxation, diffusivity is thought to be an intrinsic tissue parameter and has been used primarily in the diagnosis of acute cerebral ischemia [5]. The other parameter, FA value, is one of the most common anisotropy metrics. It ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 is isotropic and 1 is fully anisotropic. The direction of maximum diffusivity is mapped with red, green, and blue color coding in which brightness is modulated by FA. The result is a summary map from which the degree of anisotropy and local fiber direction can be determined [7]. In our study, the normal FA value and ADC of the median nerve were defined. To our knowledge, only one study [9] has shown the FA value and ADC of this nerve. In that study, the FA values of four subjects were between 0.69 and 0.89, and the ADCs ranged from 0.94 to mm 2 /s. In our study, the whole median nerve tract had a mean FA value of ± and a mean ADC of ± mm 2 /s. We believe that these normative values may play an important role in the diagnosis of CTS because, as shown in this study, focal FA measurement of the nerve at the flexor retinaculum level showed a significant difference from values at other levels. Under the flexor retinaculum, the position of the median nerve is constant among the flexor tendons. Therefore, the motion of water molecules through the myelin sheath can be affected, causing FA values to vary. By a similar mechanism, CTS also can cause a change in FA values. FA values can aid in follow-up after nerve repair procedures. We found that although there was a difference in FA values, ADCs did not differ significantly in different parts of the median nerve. This finding shows that diffusion anisotropy indexes may be more sensitive than ADC in the evaluation of nerves for pathologic conditions. In the two patients with CTS in this study, we found the mean FA values of human median nerve were 0.41 and 0.44, both 2 SDs below the normal value. In this study, the age-related change in anisotropy indexes found in the median nerve was similar to previously reported age-related anisotropy changes in the brain [17, 18]. Although the oldest subject in our study was only 35 years old, we observed that with increasing age, FA value in normal human median nerves decreased (p < 0.01) and ADC increased (p > 0.05). A decrease in the number of myelinated fibers in the peripheral nerve with advancing age has been reported [19, 20]. A progressive age-related decrease in conduction velocity of the median nerve after the age of 20 years also has been reported [20, 21]. We believe that the changes in FA value and ADC may be associated with the decrease in fiber number with advancing age. These results indicate that patient age may have to be considered in comparing the anisotropy indexes of healthy subjects with those of persons with peripheral nerve disorders. Age-matched control groups may be necessary in such studies. Imaging of the peripheral nerves with DTI is thought to have difficulties such as differentiating the nerves from surrounding structures such as ligaments and muscles. Because muscle fibers are shorter than nerve fibers and have a relatively low anisotropy index, this difficulty can be overcome with use of fiber length and degree of anisot- 926 AJR:189, October 2007
5 Tractography of Median Nerve TABLE 2: Focal and s for Median Nerve (n = 20) Subject No. Flexor Retinaculum Wrist Forearm Mean 0.59 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.02 ropy [8]. For this purpose, we set the anisotropy threshold at 0.3. The color-coded maps, especially in the coronal plane, combined with anatomic reference views made it easy to localize median nerve tracts. There are several disadvantages to the technique used. The major limitation is a relatively long data acquisition time, which makes the sequence more susceptible to motion artifacts. Especially in postoperative follow-up, image degradation due to motion artifacts can be a serious problem because of the uncomfortable positioning for median nerve visualization. Another limitation is that spatial resolution is low, even with a 3-T MRI system. In our study, the in-plane resolution was mm 2, which can be improved with dedicated wrist coils. In conclusion, we found that in DTI of 20 healthy subjects, the FA value of normal median nerve was ± and the ADC was ± mm 2 /s. Our findings suggest that FA value and ADC can be used in the diagnosis of CTS because focal FA measurement of the nerve at the flexor retinaculum level showed a significant difference from FA values in other parts of the nerve. Age-related changes in anisotropy also should be taken into account in evaluation of the median nerve. References 1. Andreisek G, Crook DW, Burg D, Marincek B, Weishaupt D. Peripheral neuropathies of the median, radial, and ulnar nerves: MR imaging features. RadioGraphics 2006; 26: Sallomi D, Janzen DL, Munk PL, Connell DG, Tirman PF. Muscle denervation patterns in upper limb nerve injuries: MR imaging findings and anatomic basis. AJR 1998; 171: Stieltjes B, Kaufmann WE, van Zijl PC, et al. tensor imaging and axonal tracking in the human brainstem. Neuroimage 2001; 14: Zhang S, Laidlow DH, Kindlmann G. tensor MRI visualization. In: Hansen CD, Johnson CR. The visualization handbook. Oxford, UK: Elsevier, 2005: Bammer R. Basic principles of diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol 2003; 45: Basser P, Pierpaoli C. Microstructural and physiological features of tissues elucidated by quantitative-diffusion-tensor MRI. J Magn Reson B 1996; 111: Jellison BJ, Field AS, Medow J, et al. tensor imaging of cerebral white matter: a pictorial review of physics, fiber tract anatomy, and tumor imaging patterns. Am J Neuroradiol 2004; 25: Hiltunen J, Suortti T, Arvela S, Seppa M, Joensuu R, Hari R. tensor imaging and tractography of distal peripheral nerves at 3T. Clin Neurophysiol 2005; 116: Bendszus M, Stoll G. Technology insight: visualizing peripheral nerve injury using MRI. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2005; 1: Le Bihan D, van Zijl P. From the diffusion coefficient to the diffusion tensor. NMR Biomed 2002; 15: Raybaud C, Shroff M, Rutka JT, Chuang SH. Imaging surgical epilepsy in children. Childs Nerv Syst 2006; 22: Inoue T, Ogasawara K, Beppu T, Ogawa A, Kabasawa H. tensor imaging for preoperative evaluation of tumor grade in gliomas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2005; 107: Meek MF, Stenekes MW, Hoogduin HM, Nicolai JP. In vivo three-dimensional reconstruction of human median nerves by diffusion tensor imaging. Exp Neurol 2006; 198: Skorpil M, Karlsson M, Nordell A. Peripheral nerve diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 2004; 22: Masutani Y, Aoki S, Abe O, Hayashi N, Otomo K. MR diffusion tensor imaging: recent advance and new techniques for diffusion tensor visualization. Eur J Radiol 2003; 46: Melhem ER, Mori S, Mukundan G, Kraut MA, Pomper MG, van Zijl PC. tensor MR imaging of the brain and white matter tractography. AJR 2002; 178: Abe O, Aoki S, Hayashi N, et al. Normal aging in the central nervous system: quantitative MR diffusiontensor analysis. Neurobiol Aging 2002; 23: Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV, Hedehus M, Lim KO, Adalsteinsson E, Moseley M. Age-related decline in brain white matter anisotropy measured with spatially corrected echo-planar diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Med 2000; 44: Vital A, Vital C, Rigal B, Decamps A, Emeriau JP, Galley P. Morphological study of the aging human peripheral nerve. Clin Neuropathol 1990; 9: Wang FC, de Pasqua V, Delwaide PJ. Age-related changes in fastest and slowest conducting axons of thenar motor units. Muscle Nerve 1999; 22: Oh SJ. Physiologic factors affecting nerve conduction. In: Oh SJ, ed. Clinical electromyography: nerve conduction studies. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2003: AJR:189, October
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common peripheral
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:60 66 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging in carpal tunnel syndrome Neslihan Taşdelen, Bengi Gürses, Özgür Kılıçkesmez,
Diagn Interv Radiol 2012; 18:60 66 Turkish Society of Radiology 2012 MUSCULOSKELETAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging in carpal tunnel syndrome Neslihan Taşdelen, Bengi Gürses, Özgür Kılıçkesmez,
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Andreisek et al. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of Median Nerve Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gustav Andreisek 1,2 Lawrence M. White 1 Andrea Kassner 3 Marshall
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Andreisek et al. Diffusion Tensor Imaging of Median Nerve Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Gustav Andreisek 1,2 Lawrence M. White 1 Andrea Kassner 3 Marshall
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography
 Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
Patterns of Brain Tumor Recurrence Predicted From DTI Tractography Anitha Priya Krishnan 1, Isaac Asher 2, Dave Fuller 2, Delphine Davis 3, Paul Okunieff 2, Walter O Dell 1,2 Department of Biomedical Engineering
The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging
 In Practice The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging y Darryl. Sneag, MD, Assistant Attending Radiologist, and Hollis G. Potter, MD, Chairman and The Coleman Chair, MRI Research, Department
In Practice The Role of IDEAL and DTI in Peripheral Nerve MR Imaging y Darryl. Sneag, MD, Assistant Attending Radiologist, and Hollis G. Potter, MD, Chairman and The Coleman Chair, MRI Research, Department
Magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is
 Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 August 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010 August ; 143(2): 304 306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2010.03.012. Application of diffusion tensor imaging
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis
 In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy
 DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
DTI tractography of lumbosacral plexus and sciatic nerve: initial experience
 DTI tractography of lumbosacral plexus and sciatic nerve: initial experience Poster No.: C-2076 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: J. Broncano, P. Gomez-Angulo, I. Simon Yarza, G. Viteri,
DTI tractography of lumbosacral plexus and sciatic nerve: initial experience Poster No.: C-2076 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: J. Broncano, P. Gomez-Angulo, I. Simon Yarza, G. Viteri,
MSK Imaging Conference. 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology
 MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
MSK Imaging Conference 07/22/2016 Eman Alqahtani, MD, MPH R3/PGY4 UCSD Radiology A 51 years old female with chronic thumb pain, and inability to actively flex the thumb interphalyngeal joint Possible trigger
Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality
 The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), e279 e283 Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality C K KIM, MD,
The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), e279 e283 Diffusion tensor imaging of normal prostate at 3 T: effect of number of diffusion-encoding directions on quantitation and image quality C K KIM, MD,
2005 Elsevier Science. Reprinted with permission from Elsevier.
 Hiltunen, J., Suortti, T., Arvela, S., Seppä, M., Joensuu, R., and Hari, R. (2005). Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of distal peripheral nerves at 3 T. Clinical Neurophysiology, 116: 2315 2323.
Hiltunen, J., Suortti, T., Arvela, S., Seppä, M., Joensuu, R., and Hari, R. (2005). Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of distal peripheral nerves at 3 T. Clinical Neurophysiology, 116: 2315 2323.
Original Article Age-related changes of normal prostate: evaluation by MR diffusion tensor imaging
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(7):11220-11224 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0009871 Original Article Age-related changes of normal prostate: evaluation by MR diffusion tensor imaging Ji Zhang 1,2, Wei-Zhong
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(7):11220-11224 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0009871 Original Article Age-related changes of normal prostate: evaluation by MR diffusion tensor imaging Ji Zhang 1,2, Wei-Zhong
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Overview. Fundamentals of functional MRI. Task related versus resting state functional imaging for sensorimotor mapping
 Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Functional MRI and the Sensorimotor System in MS Nancy Sicotte, MD, FAAN Professor and Vice Chair Director, Multiple Sclerosis Program Director, Neurology Residency Program Cedars-Sinai Medical Center
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!!
 Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion tensor imaging of spinal cord as an emerging tool in neuroradiology!!! Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1049 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Agawane, M. R. Verma, D. P.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in brain tumours @MarionSmits, MD PhD Associate Professor of Neuroradiology Dept. of Radiology, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam (NL) Honorary Consultant and Reader UCLH National Hospital
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
AHMAD M. WAFAIE, M.D.*; KAREEM M. MOUSSA, M.D.*; HODA M. ABBAAS, M.Sc.*; LAMIA M. AFIFI, M.D.** and AYMAN M. MANSOUR, M.D.***
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 86, No. 1, March: 675-683, 2018 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Median Nerve in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Case Control Comparative
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 86, No. 1, March: 675-683, 2018 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Median Nerve in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Case Control Comparative
Acute radial nerve entrapment at the spiral groove: detection by DTI-based neurography
 Eur Radiol (2015) 25:1678 1683 DOI 10.1007/s00330-014-3562-6 MAGNETIC RESONANCE Acute radial nerve entrapment at the spiral groove: detection by DTI-based neurography Suren Jengojan & Florian Kovar & Julia
Eur Radiol (2015) 25:1678 1683 DOI 10.1007/s00330-014-3562-6 MAGNETIC RESONANCE Acute radial nerve entrapment at the spiral groove: detection by DTI-based neurography Suren Jengojan & Florian Kovar & Julia
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Optimal Parameters and Location for Diffusion-Tensor Imaging in the Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: A Prospective Matched Case-Control Study
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kwon et al. Diffusion-Tensor Imaging of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Bong Cheol Kwon 1 Sung Hye Koh 2 Su Yeon Hwang 3 Kwon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Kwon et al. Diffusion-Tensor Imaging of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Bong Cheol Kwon 1 Sung Hye Koh 2 Su Yeon Hwang 3 Kwon
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa
 Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa catorres@toh.on.ca None 1. Simplify the complex imaging anatomy of the BP using clear anatomical
Carlos Torres MD, FRCPC, Associate Professor of Radiology Department of Radiology, University of Ottawa catorres@toh.on.ca None 1. Simplify the complex imaging anatomy of the BP using clear anatomical
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION?
 WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
WHAT CAN ULTRASOUND SEE IN THE CARPAL TUNNEL REGION? Jay Smith, M.D. CMO, Sonex Health LLC June 2017 Modern day ultrasound (US) machines provide a powerful combination of submillimeter resolution and dynamic
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
In patients with degenerative lumbar disease, lumbar foraminal
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Eguchi S. Ohtori S. Orita H. Kamoda G. Arai T. Ishikawa M. Miyagi G. Inoue M. Suzuki Y. Masuda H. Andou M. Takaso Y. Aoki T. Toyone A. Watanabe K. Takahashi Quantitative Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Y. Eguchi S. Ohtori S. Orita H. Kamoda G. Arai T. Ishikawa M. Miyagi G. Inoue M. Suzuki Y. Masuda H. Andou M. Takaso Y. Aoki T. Toyone A. Watanabe K. Takahashi Quantitative Evaluation
The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
 Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 1, p. 11 17, 2004 MAJOR PAPER The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
Magnetic Resonance in Medical Sciences, Vol. 3, No. 1, p. 11 17, 2004 MAJOR PAPER The Optimal Trackability Threshold of Fractional Anisotropy for DiŠusion Tensor Tractography of the Corticospinal Tract
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity
 Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Ultrasonography of Peripheral Nerve -upper extremity Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Korea University Guro Hospital Korea University College of Medicine Yoon Joon Shik Normal median
Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
 Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Symptoms and Signs Thumb, index, middle, and radial aspect of ring finger Hand Pain Paresthesia Numbness Pins
Manual therapy approach to the Patient with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Symptoms and Signs Thumb, index, middle, and radial aspect of ring finger Hand Pain Paresthesia Numbness Pins
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology
 Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
Pearls and Pitfalls of MR Diffusion in Clinical Neurology Dr. Alberto Bizzi Neuroradiology Unit Fondazione IRCCS Istituto Neurologico Carlo Besta Milan, Italy Email: alberto_bizzi@fastwebnet.it Diffusion
MR neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves
 Publication for the Philips I Community ISSE 50 2014 / 1 neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves Shandong edical Imaging esearch Institute explores DWIBS for neurography in extremities
Publication for the Philips I Community ISSE 50 2014 / 1 neurography allows clear visualization of peripheral nerves Shandong edical Imaging esearch Institute explores DWIBS for neurography in extremities
Disclosure. Entrapment Neuropathies - Overview. Common mononeuropathy sites. Definitions. Common mononeuropathy sites. Common mononeuropathy sites
 Disclosure Entrapment Neuropathies - Overview I receive compensation from Wiley- Blackwell publishers for my work as Editor-in-Chief of Muscle & Nerve Lawrence H. Phillips, II, MD Definitions Mononeuropathy:
Disclosure Entrapment Neuropathies - Overview I receive compensation from Wiley- Blackwell publishers for my work as Editor-in-Chief of Muscle & Nerve Lawrence H. Phillips, II, MD Definitions Mononeuropathy:
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries. First Global Conflict Medicine Congress
 Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Management of Brachial Plexus & Peripheral Nerves Blast Injuries Joseph BAKHACH First Global Conflict Medicine Congress Hand & Microsurgery Department American University of Beirut Medical Centre Brachial
Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Peripheral Nervous System: General Considerations and Examination Technique
 Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Peripheral Nervous System: General Considerations and Examination Technique 2 Werner Judmaier Contents 2.1 General Considerations on Peripheral Nerve MRI...
Introduction to Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Peripheral Nervous System: General Considerations and Examination Technique 2 Werner Judmaier Contents 2.1 General Considerations on Peripheral Nerve MRI...
/13/$ IEEE
 Multivariate Discriminant Analysis of Multiparametric Brain MRI to Differentiate High Grade and Low Grade Gliomas - A Computer- Aided Diagnosis Development Study *, Zeynep Firat, Ilhami Kovanlikaya, Ugur
Multivariate Discriminant Analysis of Multiparametric Brain MRI to Differentiate High Grade and Low Grade Gliomas - A Computer- Aided Diagnosis Development Study *, Zeynep Firat, Ilhami Kovanlikaya, Ugur
Professional boxing is a controversial sport, and research
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH L. Zhang L.A. Heier R.D. Zimmerman B. Jordan A.M. Uluğ Diffusion Anisotropy Changes in the Brains of Professional s BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Professional boxing may result in brain injury.
Diffusion MRI explores new indications
 DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
DECEMBER 2001 Diffusion MRI finds new indications Neuroimaging expands with functional MRI 3-tesla MRI bests 1.5-tesla in body and brain Diffusion MRI explores new indications Diffusion tensor imaging
ajnr am j. neuroradiol apr; 28(4):
 ajnr am j. neuroradiol. 2007 apr; 28(4): 724-30 7 Diffusion tensor imaging-based fractional anisotropy quantification in the corticospinal tract of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a probabilistic
ajnr am j. neuroradiol. 2007 apr; 28(4): 724-30 7 Diffusion tensor imaging-based fractional anisotropy quantification in the corticospinal tract of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using a probabilistic
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Usefulness of DWI MR-neurography in the diagnosis of piriformis muscle syndrome
 Usefulness of DWI MR-neurography in the diagnosis of piriformis muscle syndrome Poster No.: P-0086 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit F. Caro Mateo 1, A. Luna Alcalá 2,
Usefulness of DWI MR-neurography in the diagnosis of piriformis muscle syndrome Poster No.: P-0086 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit F. Caro Mateo 1, A. Luna Alcalá 2,
3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions
 110 Rizea et al 3D diffuse tensor imaging for preoperative planning 3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions R.E. Rizea, A.V. Ciurea,
110 Rizea et al 3D diffuse tensor imaging for preoperative planning 3D diffuse tensor imaging important acquisition in diagnostic and preoperative planning of intracranial lesions R.E. Rizea, A.V. Ciurea,
Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients
 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Singapore Med Med J 2006; J 2006; 47(3) 47(3) : 198 : 1 Early experiences with diffusion tensor imaging and magnetic resonance tractography in stroke patients Parmar H, Golay
MR Neurography Technique & Brachial Plexus Evaluation. Avneesh Chhabra, MD
 MR Neurography Technique & Brachial Plexus Evaluation Avneesh Chhabra, MD Introduction The ventral rami of the C5-8 and T1 nerve root unite to form the brachial plexus. It is a network of nerve convergences
MR Neurography Technique & Brachial Plexus Evaluation Avneesh Chhabra, MD Introduction The ventral rami of the C5-8 and T1 nerve root unite to form the brachial plexus. It is a network of nerve convergences
Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:742 746 (2006) Clinical Note Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 23:742 746 (2006) Clinical Note Tendon and Neurovascular Bundle Displacement in the Palm With Hand Flexion and Extension: An MRI and Gross Anatomy Correlative Study
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 39 December 2009 32-channel coil boosts 3.0T neuro imaging at Kennedy Krieger Kennedy Krieger Institute sees significantly better fmri, DTI,
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Radiology, Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya, Japan ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 76. 285 ~ 291, 2014 ORIGINAL PAPER VISUALIZATION OF BRAIN WHITE MATTER TRACTS USING HEAVILY T2-WEIGHTED THREE-DIMENSIONAL FLUID-ATTENUATED INVERSION-RECOVERY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 76. 285 ~ 291, 2014 ORIGINAL PAPER VISUALIZATION OF BRAIN WHITE MATTER TRACTS USING HEAVILY T2-WEIGHTED THREE-DIMENSIONAL FLUID-ATTENUATED INVERSION-RECOVERY MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis. Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY A New Method for Assessing Tissue Alignment using Clinical MRI in Multiple Sclerosis by Shrushrita Sharma A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN PARTIAL FULFILMENT
MR Neurography: Cervical Plexus and Shoulder Girdle
 MR Neurography: Cervical Plexus and Shoulder Girdle Gustav Andreisek, MD, MBA 3rd MSK MRI Meeting 2016 Date: April 23th, 2016 Time: 11:10-11:30 AM Head MSK and MR Imaging Department of Radiology University
MR Neurography: Cervical Plexus and Shoulder Girdle Gustav Andreisek, MD, MBA 3rd MSK MRI Meeting 2016 Date: April 23th, 2016 Time: 11:10-11:30 AM Head MSK and MR Imaging Department of Radiology University
Diffusion Tensor Imaging 12/06/2013
 12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
12/06/2013 Beate Diehl, MD PhD FRCP University College London National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square London, UK American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure None Learning
The visualization of periprostatic nerve fibers using Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging with tractography
 The visualization of periprostatic nerve fibers using Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging with tractography Poster No.: C-0009 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Kitajima 1,
The visualization of periprostatic nerve fibers using Diffusion Tensor Magnetic Resonance Imaging with tractography Poster No.: C-0009 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Kitajima 1,
During human aging, the brain exhibits both macro- and
 Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Published November 5, 2009 as 10.3174/ajnr.A1862 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Q. Wang X. Xu M. Zhang Normal Aging in the Basal Ganglia Evaluated by Eigenvalues of Diffusion Tensor Imaging BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Spine Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Spine Neurosurgery Spine neurosurgeons treat
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Spine Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Spine Neurosurgery Spine neurosurgeons treat
Stereotactic Diffusion Tensor Tractography For Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis
 J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
J7ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1 996;60: 15-19 MRI dynamics of brain and spinal cord in progressive multiple sclerosis 1 5 D Kidd, J W Thorpe, B E Kendall, G J Barker, D H Miller,
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR Imaging
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Diffusion Tensor Imaging Assessment of Brain White Matter Maturation During the First Postnatal Year
 DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
DTI of White Matter in infants Neuroradiology Original Research James M. Provenzale 1 Luxia Liang 1,2 David DeLong 1 Leonard E. White 3 Provenzale JM, Liang L, DeLong D, White LE Keywords: anisotropy,
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Neurography
 Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Neurography Policy #: 177 Latest Review Date: June 2011 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: C Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue
Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Neurography Policy #: 177 Latest Review Date: June 2011 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: C Background/Definitions: As a general rule, benefits are payable under Blue
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
The clinical significance of bifid median nerve. Evaluation with ultrasonography
 The clinical significance of bifid median nerve. Evaluation with ultrasonography Poster No.: C-3364 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors: D. Papoutsi, E. Andipa, A.
The clinical significance of bifid median nerve. Evaluation with ultrasonography Poster No.: C-3364 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit Musculoskeletal Authors: D. Papoutsi, E. Andipa, A.
Enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces in a young man: a constrained spherical deconvolution tractography study
 Acta Biomed 2017; Vol. 88, N. 3: 319-324 DOI: 10.23750/abm.v%vi%i.5181 Mattioli 1885 Case report Enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces in a young man: a constrained spherical deconvolution tractography study Alberto
Acta Biomed 2017; Vol. 88, N. 3: 319-324 DOI: 10.23750/abm.v%vi%i.5181 Mattioli 1885 Case report Enlarged Virchow-Robin spaces in a young man: a constrained spherical deconvolution tractography study Alberto
MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution
 MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution microscopy coil Poster No.: P-0115 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords:
MRI of scapholunate ligament- comparison between direct MR arthrography and non-contrast examination with highresolution microscopy coil Poster No.: P-0115 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords:
Magnetic resonance imaging (MR!) provides
 0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
0 Wallerian Degeneration of the Pyramidal Tract in Capsular Infarction Studied by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Jesiis Pujol, MD, Josep L. Marti-Vilalta, MD, Carme Junqu6, PhD, Pere Vendrell, PhD, Juan Fernandez,
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
Functional MRI and Diffusion Tensor Imaging Andrew Steven March 23, 2018 Ochsner Neuroscience Symposium None Disclosure 1 Objectives Review basic principles of BOLD fmri and DTI. Discuss indications and
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
Interesting Case Series. The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve
 Interesting Case Series The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve Jeon Cha, Blair York, and John Tawfik The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney Eye Hospital, Sydney, Australia Correspondence:
Interesting Case Series The Recurrent Motor Branch of the Median Nerve Jeon Cha, Blair York, and John Tawfik The Sydney Hospital Hand Unit, Sydney Hospital and Sydney Eye Hospital, Sydney, Australia Correspondence:
Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 524096, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/524096 Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion
BioMed Research International, Article ID 524096, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/524096 Research Article Corticospinal Tract Change during Motor Recovery in Patients with Medulla Infarct: A Diffusion
A nimal experiments and post-mortem examinations have
 PAPER A prospective study of secondary degeneration following subcortical infarction using diffusion tensor imaging Zhijian Liang, Jinsheng Zeng, Sirun Liu, Xueying Ling, Anding Xu, Jian Yu, Li Ling...
PAPER A prospective study of secondary degeneration following subcortical infarction using diffusion tensor imaging Zhijian Liang, Jinsheng Zeng, Sirun Liu, Xueying Ling, Anding Xu, Jian Yu, Li Ling...
Wrist, Elbow Hand. Surface Recording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle
 Surface ecording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle Original Settings Sensitivity, duration of pulse, sweep speed, low-frequency filter, high- frequency filter, and the machine used were not
Surface ecording Technique, Study from Median Thenar (MT) Muscle Original Settings Sensitivity, duration of pulse, sweep speed, low-frequency filter, high- frequency filter, and the machine used were not
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection. Page inserted by evaluation version
 PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
PDFlib PLOP: PDF Linearization, Optimization, Protection Page inserted by evaluation version www.pdflib.com sales@pdflib.com Principal Diffusion Direction in Peritumoral Fiber Tracts Color Map Patterns
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries
 1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
1) Diffusion weighted imaging DWI is a term used to describe moving molecules due to random thermal motion. This motion is restricted by boundaries such as ligaments, membranes and macro molecules. Diffusion
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper
 Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Introduction to Ultrasound Examination of the Hand and upper Emil Dionysian, M.D. Ultrasound of upper ext. Upside Convenient Opens another exam dimension Can be like a stethoscope Helps 3-D D visualization
Traumatic injuries of the cervical spine are potentially catastrophic.
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Shanmuganathan R.P. Gullapalli J. Zhuo S.E. Mirvis Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging in Cervical Spine Trauma BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Our aim was to investigate the extent and severity of
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities
 Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
The use of Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Treatment of the Musculoskeletal System
 The use of Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Treatment of the Musculoskeletal System St. Joseph s Refresher Course March 2019 Kenneth Iles, DC John Finkenstadt, MD THIS WORKSHOP WILL FOCUS ON 2 MAIN TOPICS:
The use of Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Treatment of the Musculoskeletal System St. Joseph s Refresher Course March 2019 Kenneth Iles, DC John Finkenstadt, MD THIS WORKSHOP WILL FOCUS ON 2 MAIN TOPICS:
Value of DTI parameters to differentiate prostate cancer in central gland from benign prostate hyperplasia
 Value of DTI parameters to differentiate prostate cancer in central gland from benign prostate hyperplasia Poster No.: C-0129 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit T. GONG;
Value of DTI parameters to differentiate prostate cancer in central gland from benign prostate hyperplasia Poster No.: C-0129 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit T. GONG;
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the
 Supplementary Methods Materials & Methods Subjects Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the Dartmouth community. All subjects were native speakers of English,
Supplementary Methods Materials & Methods Subjects Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the Dartmouth community. All subjects were native speakers of English,
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Study of the CNS. Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David Norman Thomas H. Newton
 271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
271 Reproducibility of Relaxation Times and Spin Density Calculated from Routine MR Imaging Sequences: Clinical Study of the CNS Bent O. Kjos' Richard L. Ehman Michael Brant-Zawadzki William M. Kelly David
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound
 Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Normal Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound appearance: Hypoechoic
Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Normal Peripheral Nerve Ultrasound appearance: Hypoechoic
Diffusion Tensor Imaging To Assess Triceps Surae After Achilles Tenotomy In Rats.
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging To Assess Triceps Surae After Achilles Tenotomy In Rats. Yusuke Hara 1, Kazuya Ikoma, MD, PhD 1, Tsuyoshi Sukenari 1, Yuji Arai 1, Yasuo Mikami 1, Hiroyoshi Fujiwara 1, Takashi
Diffusion Tensor Imaging To Assess Triceps Surae After Achilles Tenotomy In Rats. Yusuke Hara 1, Kazuya Ikoma, MD, PhD 1, Tsuyoshi Sukenari 1, Yuji Arai 1, Yasuo Mikami 1, Hiroyoshi Fujiwara 1, Takashi
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Neurol Clin N Am 20 (2002) 605 617 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A ALS. See Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) active denervation
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. Nerve anatomy. Pathophysiology 6/14/2014. Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Justin Arnold MD Family Medicine Update 2014 Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity Increasing prevalence CTS 50/1000 subjects Up to
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Justin Arnold MD Family Medicine Update 2014 Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity Increasing prevalence CTS 50/1000 subjects Up to
Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민
 Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민 Contents US appearance of nerves Scanning technique Peripheral nerve pathology Nerves of arm Nerves of leg US Appearance of Nerve Multiple longitudinal hypoechoic
Anatomy of Peripheral Nerve 가톨릭대학교 재활의학과 김재민 Contents US appearance of nerves Scanning technique Peripheral nerve pathology Nerves of arm Nerves of leg US Appearance of Nerve Multiple longitudinal hypoechoic
Compound Action Potential, CAP
 Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry
 WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
WINDOWS TO THE BRAIN Robin A. Hurley, M.D., L. Anne Hayman, M.D., Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D. Section Editors The Future for Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Neuropsychiatry Katherine H. Taber, Ph.D., Carlo Pierpaoli,
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
