Neuro - imaging. Sella. ssregypt.com
|
|
|
- Amos Adams
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuro - imaging Sella ssregypt.com
2 Bony Sella AP diameter Depth Contents 16mm 14mm Pituitary gland, part of infundibular stalk, CSF
3 CT Technique 5 mm slices Axial and coronal Contrast injection Bone and soft tissue windows
4 Axial
5 CORONAL
6 MRI Technique 3 mm thickness slices Sagittal and coronal T1 weighted images Pre and post contrast injection Axial T2 for brain
7 Normal CT AND MRI Normal size and shape of the sella Concave upper border of pituitary gland Homogenous enhancement of the pituitary gland showing normal height [ less than 8mm] and regular contour Midline infundibular stalk Clear suprasellar cistern MR shows isointense signal of the pituitary gland to the brain parenchyma in T1 and T2 WIs
8
9 Pituitary gland Anterior pituitary [ adenohypophysis ] 75% of the pituitary volum Growth Hormone GH Adreno Cortico-trophic Hormone ACTH Thyroid Stimulating Hormone TSH Follicle Stimulating Hormone FSH Luteinizing Hormone LH Melanophore Stimulating Hormone Prolactine
10 Pituitary gland Posterior pituitary 25% of volume Neurohypophysis = posterior pituitary + infundibular stalk + hypothalamic nuclei [ Supra optic, Para ventricular nuclei ] Hypothalamus Oxytocin + vasopressin Coupled by proteins and enveloped by phospholipids vesicles hypothalamo - hypophyseal tracks posterior pituitary high signal in T1 WIs
11 Absence of high signal of the posterior pituitary in T1 WIs is usually, but not always, associated with diabetes insipidus
12 Intrasellar Pathology Empty sella Very common variant The sella is partially filled with CSF The infundibulum is dipping in the sella The pituitary is flattened against the sellar floor Two types primary and secondary Secondary type Post operative Sheehan syndrome [post partum circulatory collapse pituitary necrosis]
13 M 26Y
14 F 73Y M 50Y Empty sella
15 Intrasellar lesions Small or absent gland and stalk [primary panhypopituitarism] Ectopic neurohypophysis [suprasellar hot spot] Duplicated pituitary stalk
16 Intrasellar lesions Incidentally found pituitary lesion more than 3mm should represent micro adenoma or Rathke s Cleft cyst Causes: Pituitary cyst Artifacts Pituitary micro adenoma
17 Pituitary cysts Non neoplastic pituitary cysts are found in about 20% of autopsy specimens F 22Y
18 Pituitary adenoma The most common Intrasellar tumor in adults Pituitary adenoma is rare below the age of 18 years [ 3% ] Adenomas measuring 10mm or less are called microadenomas Adenomas larger than 10mm are called macroadenomas
19 Microadenoma 75% are functioning tumors 50% of active adenomas are prolactinomas Normal serum prolactin < 20ng/ml Serum prolactin above 150 ng/ml is diagnostic of adenoma MRI 95% of adenoma are hypointense in T1 Hyperintensity due to hemorrhage 20-30% of adenomas, these tumors are usually cystic with intracystic blood 50% of adenoma are hyperintense in T2
20 M 34Y
21 Microadenoma F 24Y Focal nonenhancing lesion within pituitary gland Surface bulge superior or inferior Convex upper border of pituitary gland Contra lateral stalk deviation NB Tilt of the pituitary stalk may be normal variant
22 F 24Y F 52Y
23 F 25Y F 28Y
24 F 30Y +C Microadenoma
25 F 23Y
26 F 52Y
27 Microadenoma Dynamic study
28
29 Microadenoma MR sensitivity 90% M 17Y Good clinical and biochemical evidence of adenoma Coronal non contrast T1 WIs Immediate coronal T1 WIs after contrast injection Dynamic scanning in coronal T1 WIs after contrast injection Delayed minutes after contrast injection [enhancing adenoma after contrast washout from the normal gland] Petrosal venous sampling for ACTH adenoma Locates the site of the lesion [not so accurate?!] Differentiates pituitary from adrenal cause [100% accuracy]
30 Microadenoma Dynamic study F 18Y
31 Follow up interval for microprolactinoma should not be more often than every several years [ 32 month ]
32 Macroadenoma Suprasellar extension of pituitary adenoma 30-50% of masses Homogenous or heterogeneous enhancement Calcification is rare 1-2% Hemorrhage, cyst formation, postoperative changes may change the findings
33 Macroadenoma F 54Y CT : MRI : Relatively hyper dense lesion Heterogeneous enhancement Cystic changes 5-18% T1 isointense signal T2 hyperintense signal
34
35 Macroadenoma Imaging should fulfill Suprasellar extension * filling the cistern * reaching the chiasm * reaching hypothalamus Parasellar extension into cavernous sinus Infrasellar extension into sphenoid sinus Intra tumoral hemorrhage
36 F 41Y
37 F 55Y Pituitary adenoma with supra- sellar extension
38 Macroadenoma Intratumoral hemorrhage 20-30% of adenomas High signal in T1 + variable signal in T2 DD craniopharyngioma cyst [ High signal in T1] The presence of fluid level in the lesion suggests hemorrhage
39 Macroadenoma Abnormal tissue between the lateral wall of the sinus and the carotid artery Cavernous sinus invasion Asymmetry between cavernous sinuses Serum prolactin above 1000 ng /ml Extension of the lesion to the sagittal plane of the intracavernous carotid artery is not a reliable indicator of sinus invasion
40 NB Constriction or occlusion of the carotid artery by pituitary adenoma is very rare while in meningiomas it is not uncommon
41 M 34Y
42 M 27Y
43 F 29Y Macroadenoma
44 Macroadenoma with hemorrhage M 34Y
45 Invasive adenoma M 48Y
46 M 47 Y
47 M 20Y
48 M 40Y
49 M 35Y
50 Pituitary abscess Symptoms similar to adenoma rather than infection Cystic lesion with marginal enhancement DD pituitary adenoma with cystic changes. Marginal enhancement supports the diagnosis of an abscess M 42Y
51 Pituitary abscess : This patient developed fever, headache, and diabetes insipidus following transsphenoidal resection of adenoma.
52 Choriostoma [Granular cell tumor, myoblastoma] Masses of normal tissues in aberrant site may occur intra or para-sellar o inside IAC Presents with pituitary endocrine dysfunction Intrasellar lesion similar to pituitary adenoma Differentiating points : Posteriorly located lesion Loss of the normal posterior lobe hyperintensity The lesion is very vascular [trans sphenoidal approach is hazardous]
53 Choristoma Sagittal T1 -weighted image shows a posterior pituitary mass which is hyperintense with absence of the normal thin hyperintensity, which corresponds to posterior lobe in normal glands. (B) The tumor is heterogeneous on Sagittal T2-weighted image [ Kucharczyk et al., 1996]
54 Rathke s cleft cyst Cubiodal or columnar epithelial lining A sellar lesion with suprasellar extension May occur suprasellar DD crainopharyngioms Calcification is uncommon Variable signal on MR [ colloid ] No solid component Marginal enhancement Displaces in stalk anterior The cyst is isointense relative to the cerebrospinal fluid, as shown on this coronal PD weighted image. The mass effect on the optic chiasm is well depicted.
55 Rathke s cleft arise from the craniopharyngeal duct [an epithelial structure connects the nasopharynx with 3 rd ventricle, involutes during fetal life] Coronal T1-weighted contrast-enhanced image shows a nonenhancing hypointense Rathke s cleft cyst within the homogeneously enhancing pituitary gland
56 T1-weighted sagittal image obtained before contrast enhancement demonstrates a well-defined Rathke s cleft cyst in the sella that is isointense relative to the CSF. Note the normal high signal intensity in the posterior pituitary, which is draped over the dorsal aspect of the cyst.
57 M 12Y Rathke s cleft cyst
58 Metastases 1% - 5% cancer patients Mostly occur suprasellar, parasellar, infrasellar Intrasellar deposits are uncommon Most of malignant pituitary lesions are metastases from extra cranial primaries [pituitary carcinoma is rare ] Symptoms include diabetes insipidus (rare with adenomas), panhypopituitarism, cranial nerve palsy III, IV, VI ( common with deposits) M 72Y
59 M 67 Y Sellar and Infrasellar deposits
60 Suprasellar anatomy &pathology
61 Suprasellar Structures Diaphragma sellae Suprasellar cistern and circle of Willis Optic nerves and chiasm Upper part of infundibular stalk Hypothalamus Anterior 3 rd ventricle and its recesses Mammellary bodies Tuber cenerium
62 Optic chiasm Hypothalamus Mammellary bodies Tuber cenerium
63 Hypothalamus
64 Suprasellar lesions Adult Child Extension of pituitary adenoma Suprasellar meningioma Craniopharyngioma Hypothalamic glioma Aneurysms 80% of the lesions
65 Craniopharyngioma 1.2-3% of intracranial tumors Occurs only in the region of the sella Epithelial origin [adamantinomatous, squamous- papillary, mixed] Two peaks Children 6-10 years Adults 50 years 50% of suprasellar tumors in children are craniopharyngiomas Symptoms of increased intracranial pressure
66 Craniopharyngioma Item Incidence Calcium Cyst Shape Age Vascular encasement Recurrence Adamantinomatous More common Common Always present Lobulated Common in children Positive Usually Squamous - papillary Less common Less likely Usually solid Rounded Common in adults Negative Rare
67 Craniopharyngioma M 16Y Lobulated suprasellar mass with cystic component The cystic component is hyperintense in T1 [protinacious contents] In T2 WIs the cyst may be hyper or hypointense The solid component shows strong enhancement Calcification is common Vascular encasement in the adamantinomatous type not seen in other types
68 M 5Y
69 Craniopharyngioma M 18Y 421 HU
70 Craniopharyngioma, MRI M 13Y
71 Craniopharyngioma, MRI
72 Rathke s cleft cyst Craniopharyngioma Cubiodal or columnar lining Not a pure suprasellar lesion Calcification is uncommon CSF signal on MR No solid component Marginal enhancement Displaces in stalk anterior Squamous or basal cell lining Usually occur suprasellar Common Hyperintense in T1 Solid component is present Enhancement of solid part Displaces the stalk posterior
73 Suprasellar lesions Adult Child Extension of pituitary adenoma Suprasellar meningioma Craniopharyngioma Hypothalamic glioma Aneurysms 80% of the lesions
74 Optic and hypothalamic glioma 25% of pediatric suprasellar neoplasms 75% of tumors occur in 1 st decade M=F 20-50% of patients with neurofibromatosis type I will develop hypothalamic glioma The tumors are often large at presentation (slow growth) May infiltrate the thalamus and brain stem
75 Optic and hypothalamic glioma CT calcification MRI Isodense suprasellar mass no Strong enhancement T1 isointense T2 hyperintense No hemorrhage Enhancement similar to CT
76 Hypothalamic glioma F 8Y
77 Hypothalamic glioma M 10Y
78 Hypothalamic glioma M 10Y
79 Hypothalamic glioma Solid lesion No Calcification Low signal on T1 Heterogeneous / Homogenous enhancement Infiltrates the visual tracts, brainstem and thalami 20-50% associated with NF1 Craniopharyngioma A cystic part is present Calcification is common Hyperintense in T1 Intense enhancement of the solid part NO NO
80 Neurofibromatosis Type I Autosomal dominant disorder About 50% of patients had family history 1:2500 births More than 50% of patients with NFI have abnormal neuroimaging The main lesions include hamartomas and gliomas in the orbit and brain Multifocal lesions in the optic nerves, brain stem, basal ganglia, dentate nuclei and periventricular white matter [Low T1, high T2 signals] To differentiate hamartomas from gliomas No edema No mass effect = Hamartomas No enhancement
81 Neurofibromatosis Type I
82 Infiltrating glioma of the optic nerve in NFI
83 Infiltrating glioma of the optic nerve in NFI
84 Optic chiasm glioma Coronal T1-weighted MR images before and after contrast enhancement showing marked enlargement of the right side of the optic chiasm with a clear plane of separation between the chiasm and the hypothalamus [Kucharczyk et al., 1996]
85 Optic neuritis
86 Small chiasmatic glioma versus optic neuritis Neuritis is painful while tumor is not Neuritis regress in follow up studies
87 Suprasellar lesions Adult Child Extension of pituitary adenoma Suprasellar meningioma Craniopharyngioma Hypothalamic glioma Aneurysms 80% of the lesions
88
89 Supra- sellar extension of pituitary adenoma M 30Y
90 M 26Y
91 Suprasellar meningioma 15-25% of meningiomas The 2 nd common Suprasellar tumor in adults Origin: Sphenoid ridge, diaphragma sellae, tuberculum sellae Usually present in middle aged females Shows lobulated outlines, strong enhancement Calcification 20 % and hyperostosis are seen Dural tail enhancement? Not specific Vascular encasement
92 Tuberculum sellae meningioma F 45Y
93 Suprasellar meningioma F 55Y F 51Y
94 F 53Y Suprasellar meningioma
95 F 51Y Suprasellar meningioma
96 M 30Y
97 Adenoma versus Meningioma Meningioma is separate from the pituitary Phosphorus MRS can differentiates adenomas which have a higher phosphate monoester peak than meningiomas
98 Suprasellar lesions Adult Child Extension of pituitary adenoma Suprasellar meningioma Craniopharyngioma Hypothalamic glioma Aneurysms 80% of the lesions
99 Suprasellar aneurysm The circle of Willis is present in the suprasellar cistern usually clinically silent until rapture subarachnoid hemorrhage CT: Hyper dense rounded lesion with marginal calcification usually off the midline Homogenous enhancement [large aneurysm may contain thrombus] Bilateral internal carotid aneurysms
100
101 Suprasellar aneurysm
102 Ruptured suprasellar aneurysm Subarachnoid hemorrhage and communicating hydrocephalus
103 MRI aneurysm] Suprasellar aneurysm - Signal void in all pulse sequences [patent - Signal misregistration artifacts in the phase encoding direction due to pulsitile flow - Laminated internal architecture of thrombosed aneurysm [T2]
104 MR I Well defined lesion with mixed signal intensities Patent lumen [ signal void] Thrombosed lumen [Laminated thrombus of mixed stages] Perianeurysmal hemorrhage and edema
105 Thrombosed aneurysm Multiple laminae of variable signals representing the blood products in the thrombus, the most recent thrombus is present centrally After contrast the patent lumen may enhance (slow flow), part of the thrombus and aneurysm wall may also enhance MR angiography
106 Suprasellar dermoid cyst % of intracranial tumors Inclusion of epithelium during embryogenesis Suprasellar is more common than vermian Benign, slowly growing, cystic midline lesion CT: Fat density + calcification MR: Fat signal [ Fat saturation technique] Assess for rupture into ventricles or CSF M 39Y
107 Dermoid tumor. The high signal intensity areas in the subarachnoid space of the Sylvian fissures and ambient cisterns represent lipid material from the tumor that has contaminated the CSF (Haughton and Peebles, 2002)
108 Suprasellar epidermiod cyst Located away from the midline CSF like contents on CT, MRI DD arachnoid cyst FLAIR intermediate signal of epidermoid cyst Diffusion WIs Free diffusion of water molecules in CSF Low signal in arachnoid cyst while restricted diffusion by protein macro moelecules in epidermoid cyst high signal Calcification is uncommon. No enhancement % of intracranial tumors
109
110 Tuber cinereum hamartoma Slowly growing non neoplastic lesion Boys > Girls Presents with precocious puberty, Seizures or both CT: Small (2cm) isodense lesion No calcification MR: Isointense in T1, Hyper intense in T2 No enhancement Mammellary bodies Tuber cenerium
111 Tuber cinereum hamartoma
112 Hypothalamic hamartoma M 16Y
113 Suprasellar arachnoid cyst 15% of arachnoid cysts occur in the sellar region CT: well defined, cystic, CSF containing suprasellar lesion No calcification No enhancement MRI: CSF signal in all pulse sequences Suprasellar arachnoid cyst compressing the third ventricle and displacing the brainstem posteriorly [Haughton and Peebles, 2002]
114 Colloid cyst 2% of all glial neoplasms Characteristic site anterior 3 rd ventricle Characteristic contents dense viscid mucoid material (old blood, cholesterol crystals, CSF, various ions) CT: hyper dense midline lesion no enhancement F 31Y
115 Colloid cyst 2% of all glial neoplasms MRI any signal depending on the contents T1 hyperintense or hypo intense T2 hyperintense or hypo intense No enhancement [CT, MRI] Solid enhancement should suspect other lesion Intermittent herniation into the foramina of Monro causes hydrocephalus
116 Colloid cyst
117 Colloid cyst
118 F 45Y Colloid cyst
119 Suprasellar germinoma Synchronous Suprasellar and pineal germ cell tumors occur in 6-12% of cases 80% of germinomas occur in the pineal body region, 20% Suprasellar Midline lesion with homogenous enhancement. Cystic changes are rare Subependymal spread enhancing nodules in the wall of the 3 rd and lateral ventricles Other germ cell carcinoma Embryonal cell carcinoma Yolk sac tumor Choriocarcinoma Teratomas
120 Pineal body and suprasellar germinomas Arise from the primitive germ cells in the suprasellar region Usually present with diabetes insipidus, hypo- pituitarism, visual changes
121 Suprasellar lipoma 0.1% of intracranial tumors Fat density (CT) or signal (MRI) No enhancement Adjacent to the mammillary bodies Fat saturation MR techniques are helpful in diagnosis
122 Suprasellar lipoma F 21Y
123 Sarcoidosis Suprasellar granuloma Chronic inflammatory disease of unknown cause 3rd 4th decades Diabetes insipidus + cranial nerve affection, mainly visual disturbance Leptomeningeal thickening and enhancement along hypothalamus, tuber cinereum, mammillary bodies Thickened enhanced infundibular stalk
124 Sarcoidosis F 34Y
125 F 23Y
126 Suprasellar Hot Spot nal focus on unenhanced T1 WIs Craniopharyngioma Subacuate hemorrhage (thrombosed vessels) Ectopic neurohypophysis Lipoma Dermoid Ectopic neurohypophysis
127 Supra and Infrasellar metastases The most common 1ry lesions are lung, breast, melanoma Multiple lesions in the sellar region affecting any anatomic structure CT usually hypodense- Hyper dense deposits [melanoma, hemorrhage] MRI signal depends on the cellularity and hemorrhage Solitary lesion is common [known primary is essential for diagnosis]
128 Suprasellar deposits of breast cancer F 60Y
129 Parasellar anatomy &pathology
130 Cavernous sinus contents Internal carotid artery Cranial nerves III, IV, V (ophthalmic, maxillary divisions), VI Dura Bones
131 Parasellar lesions Points to be assessed Anterior extension into the orbital apex Medial extension into the sella Posterior extension into the prepontine cistern Assessment of the orbit is important for: Tumor extension Proptosis Dilated veins
132 Para-sellar meningioma 10% of meningiomas occur in the Parasellar region Arise in the cavernous sinus or extend from optic nerve, sphenoid wing All features of meningiomas by CT and MRI Homogenous enhancement Dural base and Dural tail [ Dove s tail ] Calcification Bone sclerosis Vascular encasement F 40Y
133 Para-sellar meningioma M 45Y
134 Para-sellar meningioma F 50Y
135 Para-sellar meningioma F 33Y
136 Trigeminal nerve schwannoma The 2 nd common after acoustic Schwannoma Facial pain, weak muscles of mastication Follow the course of the nerve CT: Heterogeneously enhancing para-sellar mass MRI: T1 isointense T2 hyperintense Diagnostic landmarks Involvement of the Gasserian ganglion Dumble configuration with posterior fossa component
137 Trigeminal neuroma Involvement of the Gasserian ganglion
138 Trigeminal neuroma Dumble configuration with posterior fossa component M 36Y
139 Trigeminal neuroma Extension through the widened skull base foramina M 19Y
140 M 6Y
141 Para-sellar chordoma 0.2% of intracranial tumors M = F A common lesion arising from notochord remnants Infrasellar or para-sellar Benign, may be locally invasive CT: Mass with bone destruction MRI: T1 hypo, 25% isointense 75% T2 marked hyper intensity similar to fluids with septations in 70% Gd- DTPA heterogeneous enhancement Vascular enhancement without narrowing
142 Para-sellar chordoma F 26Y
143 Para sellar carotid- cavernous fistula Abnormal communication between the artery and cavernous sinus Patients present by proptosis (pulsating), motility disorders Most cases are due to trauma Spontaneous cases may be due to Arteriosclerosis Congenital defect in the media of the artery Rapture of carotid aneurysm inside the sinus The affected sinus is enlarged + dilated ophthalmic vein on CT MRI will show signal void in the sinus and ophthalmic vein and can detect thrombosis Angiography is diagnostic
144 Carotid cavernous fistula M 20Y
145 M 20Y Carotid cavernous fistula
146 F 47Y Carotid cavernous fistula
147 Aneurysms of the intra-cavernous portion of the ICA
148 Aneurysms of the intra-cavernous portion of the ICA M 30Y
149 Cavernous sinus thrombosis F 25Y A rare lesion caused by infection starting in the face, ear or sinuses specially the sphenoid Peri -orbital pain, proptosis, venous congestion and ophthalmoplegia[ cranial nerve affection] CT: Filling defect in the sinus with increased densities anterior to the globe MRI: Signal of subacute blood in the sinus with attenuated carotid artery Diagnostic landmarks Enlarged sinus with loss of normal enhancement Inflammatory orbital changes
150 Cavernous sinus thrombosis M 11Y
151 Cavernous sinus thrombosis
152 Parasellar deposits of melanoma
153 Quiz cases Colloid cyst
154 QPituitary adenoma M 40Y
155 QCraino-pharyngiomaoma F 20Y
156 QPituitary adenoma M 53Y
157 Q
158 QPituitary micro-adenoma
159 Q F 56Y Neuro - sarcoidosis
160 QCraino-pharyngiomaoma Squamous papillary type F 41Y
161 Q Tuber sinereum hamartoma F 8Y
162 Q Supra-sellar partially thrombosed aneurysm
163 Q Carotid cavernous fistula F 47 Y
164 Q Rathke s cleft cyst / adenoma
165 QSupra-sellar meningioma F 41Y
166 Q Pituitary micro-adenoma F 19Y
167 سبحانك اللهم و بحمدك نشهد ان ال اله اال انت نستغفرك و نتوب اليك ssr-eg.net Thank you Mamdouh Mahfouz MD
168 Q
169 Q
170 F 42Y?
171 ?
172 F 24Y?
173 F 34Y?
174 F 30Y?
175 ?
176 ? F 22Y
177 ?
178 M 40Y?
179 M 59Y?
180 M 36Y?
181 ?
182 F 40Y
183 F 45Y
184
185
186
187
188 M 42Y
189 Teratoma A- SagittalT1 WI showing markedly heterogonous intensity of a large suprasellar mass lesion B Axial post contrast scan showing intense heterogeneous enhancement of the lesion with central necrotic areas. (Yock, 1995)
190 Recurrent Chiasmatic glioma
191 Craniopharyngioma
192 M 36Y
193
194 F 41Y
195 Suprasellar lesions [ Granuloma ] Eosinophilic granuloma Proliferation of histeocytes Childhood disease Diabetes insipidus + lytic bony + lesions+ exophthalmos Nodular enhancement in the hypothalamus Thickened enhanced infundibular stalk Sarcoidosis Chronic inflammatory disease, unknown cause 3 rd 4 th decades Diabetes insipidus + cranial nerve affection visual disturbance Leptomeningeal thickening and enhancement along hypothalamus, tuber cinereum, mammillary bodies Thickened enhanced infundibular stalk
196 Carotid-cavernous fistula : Digital subtraction angiogram showing cortical venous drainage pathways over the right convexity to the superior sagittal sinus in a patient with a carotid-cavernous fistula
197
198 F 26Y
199 F 24Y
200 F 48Y
201 F 13Y
202 M 18Y
203 M 32Y
204
205 F 1Y
206
207 M 10Y Hypothalamic glioma
208 Hypothalamic glioma
209 M 6Y
210 Suprasellar aneurysm F 70Y
211
212 Colloid cyst
213 +C Rathke s cleft cyst, extending into the suprasellar cistern. Note that the mass has homogeneous high signal intensity in T1, intermediate T2 with no enhancement after contrast injection
214 M 59Y Infrasellar deposits
215 M 62Y Infrasellar deposits
216 F 50Y
217
218 M 30Y
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS. Kim Learned, MD
 PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
Metastasis. 57 year old with progressive Headache and Right Sided Visual Loss
 Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
Metastasis 1% of sellar/parasellar masses Usually occurs with known primary Can involve third ventricle, hypothalamus, infundibular stalk May be both supra-, intrasellar 57 year old with progressive Headache
Laurie A. Loevner, MD
 Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Laurie A. Loevner, MD Chief, Division of Neuroradiology UPHS Professor of Radiology, Otorhinolaryngology: Head & Neck Surgery, Neurosurgery, and Ophthalmology University of Pennsylvania Health System Disclosures
Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region. Child thirsty, increased urination. Imaging. Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) No Disclosures
 Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region No Disclosures 2018 Head and Neck Imaging Conference Child thirsty, increased urination Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) Midline Pineal >> Suprasellar > Other
Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region No Disclosures 2018 Head and Neck Imaging Conference Child thirsty, increased urination Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) Midline Pineal >> Suprasellar > Other
EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
 EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Sellar Region Anne G. Osborn, M.D. DISCLOSURE: Published RSNA 2008 SELLA, PITUITARY: Normal Gross, 3T Anatomy SELLA, PITUITARY: Anatomically-Based Differential Diagnoses
EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Sellar Region Anne G. Osborn, M.D. DISCLOSURE: Published RSNA 2008 SELLA, PITUITARY: Normal Gross, 3T Anatomy SELLA, PITUITARY: Anatomically-Based Differential Diagnoses
Where Has My Vision Gone? Evaluation of Sellar Lesions. Caleb Stowell,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD November 2008
 Where Has My Vision Gone? Evaluation of Sellar Lesions Caleb Stowell,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD November 2008 Objectives Present a case highlighting the clinical presentation and evaluation of a sellar
Where Has My Vision Gone? Evaluation of Sellar Lesions Caleb Stowell,, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD November 2008 Objectives Present a case highlighting the clinical presentation and evaluation of a sellar
Imaging The Turkish Saddle. Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman
 Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
Imaging The Turkish Saddle Russell Goodman, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman Learning Objectives Review the anatomy of the sellar region Discuss the differential diagnosis of sellar masses Discuss typical
RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA
 RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA O.BAKKACHA, H.MALAJATI, M.RHISSASSI, H. BENCHAABOUNE, N.CHAKIR, My R. EL HASSANI,M.JIDDANE Department of Neuroradiology specialties Hospital. Rabat Objective: New imaging
RADIOANATOMY OF SELLA TURCICA O.BAKKACHA, H.MALAJATI, M.RHISSASSI, H. BENCHAABOUNE, N.CHAKIR, My R. EL HASSANI,M.JIDDANE Department of Neuroradiology specialties Hospital. Rabat Objective: New imaging
Part II - Revising the sellar and parasellar region: differential diagnosis of a sellar region mass
 Part II - Revising the sellar and parasellar region: differential diagnosis of a sellar region mass Poster No.: C-1390 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Candelaria, C. Figueira,
Part II - Revising the sellar and parasellar region: differential diagnosis of a sellar region mass Poster No.: C-1390 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Candelaria, C. Figueira,
Brain Imaging. IC calcifications. Mamdouh mahfouz MD
 Brain Imaging IC calcifications www.ssregypt.com Mamdouh mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com CT Hyper dense [ more than100 HU ] MRI Low signal in T1 and T2 WIs [non mobile protons] Exceptions Minute calcifications
Brain Imaging IC calcifications www.ssregypt.com Mamdouh mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com CT Hyper dense [ more than100 HU ] MRI Low signal in T1 and T2 WIs [non mobile protons] Exceptions Minute calcifications
TABLES. Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging. Conclusions. Author (Year) Classification Process/Evid ence Class
 TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
Imaging pituitary gland tumors
 November 2005 Imaging pituitary gland tumors Neel Varshney,, Harvard Medical School Year IV Two categories of presenting signs of a pituitary mass Functional tumors present with symptoms due to excess
November 2005 Imaging pituitary gland tumors Neel Varshney,, Harvard Medical School Year IV Two categories of presenting signs of a pituitary mass Functional tumors present with symptoms due to excess
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Craniopharyngioma. Michael Gottschalk, MD,PhD University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital
 Craniopharyngioma Michael Gottschalk, MD,PhD University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital Objectives Incidence Clinical Presentation Treatment Options Perioperative concerns Long-term endocrine
Craniopharyngioma Michael Gottschalk, MD,PhD University of California San Diego Rady Children s Hospital Objectives Incidence Clinical Presentation Treatment Options Perioperative concerns Long-term endocrine
HEPATO-BILIARY IMAGING
 HEPATO-BILIARY IMAGING BY MAMDOUH MAHFOUZ MD PROF.OF RADIOLOGY CAIRO UNIVERSITY mamdouh.m5@gmail.com www.ssregypt.com CT ABDOMEN Indications Patient preparation Patient position Scanogram Fasting 4-6 hours
HEPATO-BILIARY IMAGING BY MAMDOUH MAHFOUZ MD PROF.OF RADIOLOGY CAIRO UNIVERSITY mamdouh.m5@gmail.com www.ssregypt.com CT ABDOMEN Indications Patient preparation Patient position Scanogram Fasting 4-6 hours
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A
 Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
Cross sectional imaging of Intracranial cystic lesions Abdel Razek A Department of Radiology. Mansoura Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura. Egypt. arazek@mans.edu.eg Introduction Intracranial cystic lesions
DISCLOSURES LEARNING OBJECTIVES WE WILL NOT DISCUSS. CSB: Birdseye View MESSAGE NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE
 NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE Christopher P. Hess, M.D., Ph.D. DISCLOSURES Research Support, General Electric SLIDES: http://www.radiology.ucsf.edu/research/meetings/rsna LEARNING OBJECTIVES
NAVIGATING THE SELLA AND CENTRAL SKULL BASE Christopher P. Hess, M.D., Ph.D. DISCLOSURES Research Support, General Electric SLIDES: http://www.radiology.ucsf.edu/research/meetings/rsna LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Head&Neck Imaging. ssregypt.com. Parapharyngeal Spaces. Mamdouh mahfouz MD
 Head&Neck Imaging Parapharyngeal Spaces ssregypt.com Mamdouh mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com Definitio n Fat filled triangular space lateral the pharynx Extends from the skull base to the oropharynx Parapharyngeal
Head&Neck Imaging Parapharyngeal Spaces ssregypt.com Mamdouh mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com Definitio n Fat filled triangular space lateral the pharynx Extends from the skull base to the oropharynx Parapharyngeal
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Transplanum Approach for Suprasellar pathology
 Transplanum Approach for Suprasellar pathology Omar A. El-Banhawy Prof. of otorhinolaryngology El Menoufyia University, Egypt Why Endoscopic Approach For Suprasellar Pathology Constant improvements in
Transplanum Approach for Suprasellar pathology Omar A. El-Banhawy Prof. of otorhinolaryngology El Menoufyia University, Egypt Why Endoscopic Approach For Suprasellar Pathology Constant improvements in
Year 2003 Paper two: Questions supplied by Tricia
 question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
question 43 A 42-year-old man presents with a two-year history of increasing right facial numbness. He has a history of intermittent unsteadiness, mild hearing loss and vertigo but has otherwise been well.
Radiology of hypothalamic lesions: A pictorial essay depicting characteristic hypothalamic pathologies
 Radiology of hypothalamic lesions: A pictorial essay depicting characteristic hypothalamic pathologies Poster No.: C-2713 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: A. J. B. Baxi,
Radiology of hypothalamic lesions: A pictorial essay depicting characteristic hypothalamic pathologies Poster No.: C-2713 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: A. J. B. Baxi,
Brain Tumors. Medulloblastoma. Pilocytic astrocytoma: Ahmed Koriesh, MD. Pathological finding
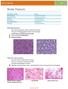 NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
NeuroPathology Page 8 Brain Tumors Pathological finding Pseudorosette Rosenthal fibers Rosettes Wet Keratin Psammoma bodies Fried egg Tumor Ependymoma, SEGA Pilocytic astrocytoma Medulloblastoma Craniopharyngioma
Sellar and Parasellar Lesions: over and above adenomas.
 Sellar and Parasellar Lesions: over and above adenomas. Poster No.: C-2052 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Paz Maya, P. Lemercier, I. lópez blasco, D. Soriano Mena, J. P. Ruiz
Sellar and Parasellar Lesions: over and above adenomas. Poster No.: C-2052 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Paz Maya, P. Lemercier, I. lópez blasco, D. Soriano Mena, J. P. Ruiz
Spinal Imaging. ssregypt.com. Mamdouh Mahfouz MD
 Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
Spinal Imaging Degenerative diseases ssregypt.com Mamdouh Mahfouz MD mamdouh.m5@gmail.com MRI Open MRI Closed Extremity MRI Dynamic MRI Dynamic MRI The bed rotates from Upright to Recumbent, stopping at
ANATOMY AND IMAGING APPEARANCES OF COMMON PATHOLOGIES OF THE PITUITARY REGION: A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 ANATOMY AND IMAGING APPEARANCES OF COMMON PATHOLOGIES OF THE PITUITARY REGION: A PICTORIAL REVIEW Sitheeque F 1, Udupihille JJKH 2, Amarasinghe VGPS 1 1 Department of Radiology and Medical Imaging, Teaching
ANATOMY AND IMAGING APPEARANCES OF COMMON PATHOLOGIES OF THE PITUITARY REGION: A PICTORIAL REVIEW Sitheeque F 1, Udupihille JJKH 2, Amarasinghe VGPS 1 1 Department of Radiology and Medical Imaging, Teaching
What we will cover. Evaluation of the Child with Suspected Pituitary Disease. ituitary
 Evaluation of the Child with Suspected Pituitary Disease Craig Alter, MD University of Pennsylvania Children s Hospital of Philadelphia What we will cover * What laboratory tests to order * MRI: common
Evaluation of the Child with Suspected Pituitary Disease Craig Alter, MD University of Pennsylvania Children s Hospital of Philadelphia What we will cover * What laboratory tests to order * MRI: common
Visual pathways in the chiasm
 Visual pathways in the chiasm Intracranial relationships of the optic nerve Fixation of the chiasm Chiasmatic pathologies The function of the optic chiasm may be altered by the presence of : 4) Artero
Visual pathways in the chiasm Intracranial relationships of the optic nerve Fixation of the chiasm Chiasmatic pathologies The function of the optic chiasm may be altered by the presence of : 4) Artero
panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013
 panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013 PITUITARY GLAND (HYPOPHYSIS CEREBRI) The master of endocrine glands master of endocrine glands It is a small oval
panhypopituitarism Pattawan Wongwijitsook Maharat Nakhon Ratchasima hospital 17 Nov 2013 PITUITARY GLAND (HYPOPHYSIS CEREBRI) The master of endocrine glands master of endocrine glands It is a small oval
Imaging of Hearing Loss
 Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Original Research Paper
 Original Research Paper Radiology Dr. Abhishek J. Arora Dr. Richa Arora Dr. Jyotsna Yarlagadda Magnetic Resonance Evaluation of Non Vascular and Non Cystic Sellar, Suprasellar and Parasellar lesions Assistant
Original Research Paper Radiology Dr. Abhishek J. Arora Dr. Richa Arora Dr. Jyotsna Yarlagadda Magnetic Resonance Evaluation of Non Vascular and Non Cystic Sellar, Suprasellar and Parasellar lesions Assistant
Intrasphenoidal Rathke's Cleft Cyst: Case presentation and review of the literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 4 2016 October - December Article Intrasphenoidal Rathke's Cleft Cyst: Case presentation and review of the literature Umit Kocaman, Muhammet Bahadir Yilmaz, Hakan
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXX Number 4 2016 October - December Article Intrasphenoidal Rathke's Cleft Cyst: Case presentation and review of the literature Umit Kocaman, Muhammet Bahadir Yilmaz, Hakan
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
MRI findings in childhood neurohypophyseal germinomas
 MRI findings in childhood neurohypophyseal germinomas Poster No.: C-1587 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Laganâ, S. I. Sirvent, M. A. Lopez-Pino, G. Albi, I. Solis Muniz, E. García
MRI findings in childhood neurohypophyseal germinomas Poster No.: C-1587 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Laganâ, S. I. Sirvent, M. A. Lopez-Pino, G. Albi, I. Solis Muniz, E. García
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland
 Anatomy of Pituitary Gland Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Anatomy of Pituitary Gland Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings
 Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings Robert J Sevick, MD, FRCPC, FACR Professor, Radiology and Clinical Neurosciences Cumming School of Medicine University of Calgary Learning objectives:
Adult Brain Tumours: an approach based on imaging findings Robert J Sevick, MD, FRCPC, FACR Professor, Radiology and Clinical Neurosciences Cumming School of Medicine University of Calgary Learning objectives:
MRI of the Pituitary Gland
 MRI of the Pituitary Gland Jean- François Bonneville Fabrice Bonneville Françoise Cattin Sonia Nagi MRI of the Pituitary Gland With a Foreword by A. Beckers Jean-François Bonneville, MD Department of
MRI of the Pituitary Gland Jean- François Bonneville Fabrice Bonneville Françoise Cattin Sonia Nagi MRI of the Pituitary Gland With a Foreword by A. Beckers Jean-François Bonneville, MD Department of
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours. Colin Kennedy March 2015
 Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
MR Imaging of the ellar and Juxtasellar
 .... S MR Imaging of the ellar and Juxtasellar. 1,: Regions DavidE.Jobnsen, MD. William W. Woodruff MD Ira S. Allen, MD PeterJ. Cera, MD George R. Funkbouser, MD Linda L. Coleman, MD. Multiplanar capability
.... S MR Imaging of the ellar and Juxtasellar. 1,: Regions DavidE.Jobnsen, MD. William W. Woodruff MD Ira S. Allen, MD PeterJ. Cera, MD George R. Funkbouser, MD Linda L. Coleman, MD. Multiplanar capability
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Pituitary gland diseases
 Pituitary gland diseases Pituitary Gland Weight 600 mg Is located within the sella turcica Anatomically and functionally distinct anterior and posterior lobes Pituitary Development The pituitary originate
Pituitary gland diseases Pituitary Gland Weight 600 mg Is located within the sella turcica Anatomically and functionally distinct anterior and posterior lobes Pituitary Development The pituitary originate
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review
 Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Posterior fossa tumors: clues to differential diagnosis with case-based review Poster No.: C-0323 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. A. Aboughalia, M. Abdelhady; Doha/QA Keywords:
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
NANOS Patient Brochure
 NANOS Patient Brochure Pituitary Tumor Copyright 2015. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for informational
NANOS Patient Brochure Pituitary Tumor Copyright 2015. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for informational
PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT
 PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and
PITUITARY: JUST THE BASICS PART 2 THE PATIENT DISCLOSURE Relevant relationships with commercial entities none Potential for conflicts of interest within this presentation none Steps taken to review and
Case Studies in the Skull Base
 Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
Non-Functioning Tumours and Pituitary Hormone Testing. Miguel Debono Consultant in Endocrinology
 Non-Functioning Tumours and Pituitary Hormone Testing Miguel Debono Consultant in Endocrinology Agenda Pituitary masses Non functioning pituitary adenomas Testing pituitary function Pituitary Hormone Replacement
Non-Functioning Tumours and Pituitary Hormone Testing Miguel Debono Consultant in Endocrinology Agenda Pituitary masses Non functioning pituitary adenomas Testing pituitary function Pituitary Hormone Replacement
Imaging of Petrous Apex: Anatomy and Pathology
 University of Utah Head and Neck Conference 2018 Petrous apex Imaging of Petrous Apex: Anatomy and Pathology Philip Chapman MD University of Alabama, Birmingham Good News PAs tend to be symmetric A quick
University of Utah Head and Neck Conference 2018 Petrous apex Imaging of Petrous Apex: Anatomy and Pathology Philip Chapman MD University of Alabama, Birmingham Good News PAs tend to be symmetric A quick
Diseases of pituitary gland
 Diseases of pituitary gland A brief introduction Anterior lobe = adenohypophysis Posterior lobe = neurohypophysis The production of most pituitary hormones is controlled in large part by positively and
Diseases of pituitary gland A brief introduction Anterior lobe = adenohypophysis Posterior lobe = neurohypophysis The production of most pituitary hormones is controlled in large part by positively and
Lecture 03. Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018
 Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Lecture 03 Hyophyseal Cerebri or Pituitary Gland By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 16 th March. 2018 The pituitary gland Also called as Hypophyseal Cerebri. Hypo.Under. Physis..Growth Cerebri Cerebrum. Small
Meningioma tumor. Meningiomas are named according to their location (Fig. 1) and cause various symptoms: > 1
 Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Meningioma tumor Overview A meningioma is a type of tumor that grows from the protective membranes, called meninges, which surround the brain and spinal cord. Most meningiomas are benign (not cancer) and
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity
 Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
Supra- and infratentorial brain tumors from childhood to maternity What to expect? I am going to show you the characteristic imaging findings of following tumors: Thierry A.G.M. Huisman, MD, FICIS, EQNR
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Pituitary Macroadenoma with Superior Orbital Fissure Syndrome
 1 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Pituitary Macroadenoma with Superior Orbital Fissure Syndrome Tapan Nagpal, Ankit Singhania ABSTRACT Introduction: Pituitary adenomas are benign tumours which arise within the
1 CASE REPORT OPEN ACCESS Pituitary Macroadenoma with Superior Orbital Fissure Syndrome Tapan Nagpal, Ankit Singhania ABSTRACT Introduction: Pituitary adenomas are benign tumours which arise within the
Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis
 Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis Schwannomas (also called neurinomas or neurilemmomas) constitute the most common primary cranial nerve tumors. They are benign slow-growing
Dr. T. Venkat Kishan Asst. Prof Department of Radiodiagnosis Schwannomas (also called neurinomas or neurilemmomas) constitute the most common primary cranial nerve tumors. They are benign slow-growing
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Contents. Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Nodule Characteristics
 Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
 www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
www.oralradiologists.com CONE BEAM CT REPORT CASE ---- Case Information Referring Doctor: - Patient Name: - Scan Date: December 1, 2015 Patient DOB: - Reason for Exam: - Study Details: icat Flex, 160x160x112
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Case Studies in CPA/IAC
 Outline Case Studies in CPA/IAC Atul K Mallik MD PhD Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA Case based review of cerebellopontine
Outline Case Studies in CPA/IAC Atul K Mallik MD PhD Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA Case based review of cerebellopontine
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN. Scalp, Skull. Anatomically Based Differentials. Skull Normal Variants. Scalp Mass, Child.
 Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
Pathology of pituitary gland. By: Shifaa Qa qa
 Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Making Sense of Sellar Region Pathology: Image-Based Diagnostic Algorithm
 Volume 38 Number 22 October 31, 2015 Making Sense of Sellar Region Pathology: Image-Based Diagnostic Algorithm Ammar A. Chaudhry, MD, Rajesh Gupta, MD, Luboslav Woroch, DO, Alexander Filatov, MD, Robert
Volume 38 Number 22 October 31, 2015 Making Sense of Sellar Region Pathology: Image-Based Diagnostic Algorithm Ammar A. Chaudhry, MD, Rajesh Gupta, MD, Luboslav Woroch, DO, Alexander Filatov, MD, Robert
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands
 Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands A Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri) Hypo means below, and physis means growth, so it is the gland that grows from below because it is located below the brain.
Gross Morphology of the Endocrine Glands A Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis Cerebri) Hypo means below, and physis means growth, so it is the gland that grows from below because it is located below the brain.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF SELLAR MASSES
 ~~ ~~ ~ ADVANCES IN PITUITARY TUMOR THERAPY 0889-8529/99 $8.00 +.OO DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF SELLAR MASSES Pamela U. Freda, MD, and Kalmon D. Post, MD Pituitary adenomas are the most common cause of a
~~ ~~ ~ ADVANCES IN PITUITARY TUMOR THERAPY 0889-8529/99 $8.00 +.OO DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF SELLAR MASSES Pamela U. Freda, MD, and Kalmon D. Post, MD Pituitary adenomas are the most common cause of a
Neuroimaging Core Curriculum
 Neuroimaging Core Curriculum Program Content The purpose of the training program is to prepare the physician for the independent practice of neuroimaging. Neuroimaging is the subspecialty of Neurology
Neuroimaging Core Curriculum Program Content The purpose of the training program is to prepare the physician for the independent practice of neuroimaging. Neuroimaging is the subspecialty of Neurology
Cavernous sinus síndrome. Diferencial diagnosis.
 Cavernous sinus síndrome. Diferencial diagnosis. Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. M. Vilela, H. C. Marques, L. L. Macedo, R. V. Leite, L. C. 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 Campos,
Cavernous sinus síndrome. Diferencial diagnosis. Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. M. Vilela, H. C. Marques, L. L. Macedo, R. V. Leite, L. C. 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 Campos,
Hypothalamic glioma masquerading as craniopharyngioma
 1 di 7 24/01/2014 18.58 J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013 Jul-Sep; 4(3): 323 325. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.118790 PMCID: PMC3821425 Hypothalamic glioma masquerading as craniopharyngioma Sameer Vyas, Nidhi Prabhakar,
1 di 7 24/01/2014 18.58 J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2013 Jul-Sep; 4(3): 323 325. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.118790 PMCID: PMC3821425 Hypothalamic glioma masquerading as craniopharyngioma Sameer Vyas, Nidhi Prabhakar,
Endocrine System. Dr. Rajaa Ali
 Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
Endocrine System Dr. Rajaa Ali Structure and Function of the Pituitary Gland Anterior Lobe of the Pituitary Gland (Adenohypophysis) The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland regulates other endocrine glands.
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: OBJECTIVES OSTEOLOGY. Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD
 Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Stephen A. Gudas, PT, PhD Cranial Cavity REFERENCES: Moore and Agur, Essential Clinical Anatomy (ECA), 3rd ed., pp. 496 498; 500 507; 512 514 Grant s Atlas 12 th ed., Figs 7.6; 7.19 7.30. Grant s Dissector
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Skullbase Lesions. Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic. Choice Of Surgical Approaches 12/28/2015. Skullbase Surgery: Evolution
 Skullbase Lesions Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic Prof Asim Mahmood,FRCS,FACS,FICS,FAANS, Professor of Neurosurgery Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, MI, USA Anterior Cranial Fossa Subfrontal meningioma
Skullbase Lesions Skullbase Surgery Open vs endoscopic Prof Asim Mahmood,FRCS,FACS,FICS,FAANS, Professor of Neurosurgery Henry Ford Hospital Detroit, MI, USA Anterior Cranial Fossa Subfrontal meningioma
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland
 Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
Hypothalamus & Pituitary Gland Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland The hypothalamus and pituitary gland form a unit that exerts control over the function of several endocrine glands (thyroid, adrenals, and
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Cysts Arachnoid Cyst (also called Leptomeningeal Cyst)
 Cysts This article was provided to us by David Schiff, MD, Co-Director of the Neuro-Oncology Center and Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Medicine at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
Cysts This article was provided to us by David Schiff, MD, Co-Director of the Neuro-Oncology Center and Professor of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Medicine at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, et al. Incidental findings
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Vernooij MW, Ikram MA, Tanghe HL, et al. Incidental findings
CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad
 CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Many thanks to Drs. Heiken, Narra & Menias (MIR) Dr. Sahani (MGH) for sharing images Benign Liver Tumors:
CT & MRI of Benign Liver Neoplasms Srinivasa R Prasad No financial disclosures Acknowledgements Many thanks to Drs. Heiken, Narra & Menias (MIR) Dr. Sahani (MGH) for sharing images Benign Liver Tumors:
Sellar and Parasellar pathologies: a comprehensive review on MRI
 Sellar and Parasellar pathologies: a comprehensive review on MRI Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Sahni, K. Saggar, K. GUPTA, C. Kakkar, A. Banerjee ; 1 1 2 2
Sellar and Parasellar pathologies: a comprehensive review on MRI Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Sahni, K. Saggar, K. GUPTA, C. Kakkar, A. Banerjee ; 1 1 2 2
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Blue-domed cyst with optic nerve compression
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 987-991 Blue-domed cyst with optic nerve compression MITCHELL D. BURNBAUM, JOHN W. HARBISON, JOHN B. SELHORST, AND HAROLD F. YOUNG From the
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1978, 41, 987-991 Blue-domed cyst with optic nerve compression MITCHELL D. BURNBAUM, JOHN W. HARBISON, JOHN B. SELHORST, AND HAROLD F. YOUNG From the
Pituitary gland Pituitary fossa Mass: 5 gms DIMENSIONS 7mm (Ht) 9mm (AP) 11m(transverse) originates from Rathke s pouch and infundibulum
 Pituitary gland Pituitary fossa Mass: 5 gms DIMENSIONS 7mm (Ht) 9mm (AP) 11m(transverse) originates from Rathke s pouch and infundibulum Cell type hormone Clinical syndrome Tumor type Somatotroph Growth
Pituitary gland Pituitary fossa Mass: 5 gms DIMENSIONS 7mm (Ht) 9mm (AP) 11m(transverse) originates from Rathke s pouch and infundibulum Cell type hormone Clinical syndrome Tumor type Somatotroph Growth
Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
