Quality assurance program for prototype stereotactic system developed for Neptun 10 PC linac
|
|
|
- Alan Stevenson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2005; 3 (2): Quality assurance program for prototype stereotactic system developed for Neptun 10 PC linac A.R. Khoshbin Khoshnazar 1*, M.T. Bahreyni Toossi 2, A.R. Hashemiyan 2, M.H. Bahreyni Toossi 2,R.Salek 3 1 Medical Physics and Biochemistry Deptartment, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran 2 Medical Physics Department, Faculty of Medicine, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran 3 Radiotherapy Department of Imam Reza Hospital, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, Mashhad, Iran Background: A prototype stereotactic radiosurgery set was designed and constructed for a Neptun 10 PC linac that is currently being used at Imam Reza hospital in Mashhad. Materials and Methods: A complete quality assurance program was designed and performed for the constructed system including isocentric accuracy test, localization accuracy test, dose delivery accuracy test and leakage radiation test. Target simulator, control alignment device and plexiglass phantom which were parts of the developed hardware were used to fulfill quality assurance program. Results: The average isocentric shift resulted from the gantry rotation and couch turning were respectively obtained to be 1.4 and 2 mm. The average localization error in the three coordinates was found to be 2.2 mm. The total treatment uncertainty due to all of the probable errors in the system was equal to 4.32 mm. The dose delivery accuracy test was carried out, the result indicated a 3-7% difference between the given and measured dose. Conclusion: The quality assurance tests showed consistent performance of the constructed system within the accepted limits; however, some inconsistency might exist in certain cases. The safety of SRS method is increased when the overall uncertainty is minimized and the treatment of the lesions adjacent to critical organs is avoided. Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2005; 3 (2): Keywords: Quality assurance, stereotactic radiosurgery system, linac. INTRODUCTION Stereotactic radiosurgery was initially introduced by a Swedish neurosurgeon, Leksell in 1951 (1). In this method, a high radiation dose is delivered to a small defined volume. Stereotactic radiosurgery (single fraction dose) and radiotherapy (fractionated) are two step processes: 1. Accurately defining the shape, size and location of a lesion in a reference stereotactic frame using CT, MRI or angiography modalities. 2. Performing planned treatment. With certain modifications, available linear accelerators can be used for stereotactic treatment (2). The required instruments for stereotactic radiosurgery/radiotherapy include collimators (to limit the radiation field), patient docking device (to affix patient's head to treatment couch), head rings (to attach patient's head to the localizer and centering box), and finally quality assurance devices all of which were designed and constructed in our department. The spatial accuracy of treatment generally depends on several parameters, which are as follow (3) : a. Rigidity and immobilization of the stereotactic frame. b. Image slices thickness and the dimensions of its pixels. c. Spatial or isocentric accuracy of the linear accelerator. d. Displacement of head between the imaging and the treatment setup. Small radiation field and high radiation dose used in stereotactic treatments have drawn attention to the issue of the quality assurance more than any other treatment modalities (4). We have performed quality assurance test as acceptance program for constructed hardware. MATERIALS AND METHODS Neptun 10 PC linear accelerator with 9 MV X-ray was used in this study. The hardware needed for stereotactic treatment was designed according to the physical and *Corresponding author: Dr. Alireza Khoshbin Khoshnazar, Department of Medical Physics and Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran. Fax: akhoshbin@yahoo.com
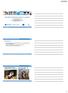
2 A.R. Khoshbin Khoshnazar, M.T. Bahreyni Toossi, et al. geometric properties of the linac. Arc therapy option (software and hardware) was installed on the linac enabling the delivery of radiation within the range of 1-8 cgy/deg. Target simulator This device as a part of the quality assurance set is composed of a base plate with four couplings, a plexiglass plate within which a 3 mm diameter steel sphere is embedded, a rotating and a stationary column (figure 1). Figure 1. Target simulator used for isocentric accuracy test. Control alignment device This device, also as a part of the quality assurance set, is composed of one vertical bar and two rectangular rings to hold the verification film. The proximal end of the bar is attached to collimator assembly and its distal end to the rings (figure 2). Figure 2. Isocentric alignment control along with target simulator. Plexiglass head phantom The main cylindrical body of the phantom is made of plexiglass, 200 mm in height and 140 mm in diameter, including 15, 10 and 5 mm thick slabs. The alignment of the slabs is accomplished by two vertical threaded rods of plexiglass which are fixed at the top with two screws of the same material (figure 3). The head phantom contains two main slabs namely the localization and dosimetry slab. The first one is composed of two 15 mm thick layer Figure 3. Plexiglass head phantom. which accommodates three circular, rectangular and triangular objects. A total of one hundred and fifty holes (1 mm in depth and 2 mm in diameter) were machined into the dosimetry layer to accommodate calibrated TLD microchips. These holes were arranged in concentric radii and 3 mm apart to minimize perturbation of dose distribution and to maintain a suitable resolution (5). The localization and dosimetry slabs can be placed in every desired height in the head phantom. The upper most slab of the phantom is semispherical in shape to resemble human's head. The phantom can be attached to the patient docking device through a plexiglass base plate. Treatment planning software An ERGO (V 3.1) system provided by 3D Line International s.r.l from Italy was used for treatment planning. Isocentric accuracy test The most important factor affecting the accuracy of stereotactic treatment is the isocentric accuracy of linear accelerator (6). Isocentric accuracy denotes the space where the collimator, gantry and couch rotation axis meet. Dimensions of this space are to be measured in this test. Practically, the target is placed stereotactically on the mechanical isocenter of the linear accelerator, the point where both the ceiling and wall lasers in the treatment room intersect. Although the emerging beams of the linear accelerator might not necessarily intersect this point, but they intersect another point namely the radiation isocenter. The accuracy of the treatment depends on the proximity of these two points (3). According to AAPM report no.54 the 74 Iran. J. Radiat. Res.; Vol. 3, No. 2, September 2005
3 Quality assurance program for Neptun 10 PC linac gantry, couch and collimator rotation axis has to meet within a sphere of 2 mm in diameter. The isocentric accuracy test was performed by examining the alignment of telemeter with the isocenter of the the linac, the room laser and the mechanical isocenter. The largest collimator was mounted on the head of the gantry and the target simulator was connected to the patient docking device by the means of four couplings. The collimator was then aligned horizontally by adjustment of its rotational screws. The proximal end of the vertical bar of the alignment control device was connected to the collimator holder and its distal end to the rectangular rings to hold radiotherapy verification film (figure 2). Finally, radiographs of the steel ball were taken at twelve different gantry positions, created angles, by 30 degree rotation intervals and four angles of couch turning in steps of 45 degrees. The radiographs were taken using 100 MU. The distance between the center of the radiation field and the steel ball image was taken as the isocenter shift in each angle (figure 4). performed by digitizing the fiducial markers observed on the CT images. Figure 5. CT scan taken from the localization layer of the phantom. Dose delivery accuracy test As it has already been stated, the plexiglass phantom contains a dosimetry slab accommodating TLD microcubes. Initially, the center of the localization slab was localized and defined as the center of the target. Treatment planning was performed delivering 15 Gy to the target. Finally the radiosurgery treatment was simulated on the plexiglass phantom (figure 6). Irradiation was performed using the 25 mm collimator and five arcs of 180 degrees. The TLD chips were read after the treatment simulation was completed. Figure 4. Radiographs taken in isocentric alignment control. Localization test To perform the localization test, the localization slab of the plexiglass phantom was placed at a known height which provides the exact coordinates of the three objects. The phantom was attached to the head ring via its base plate which was followed by mounting the localizer on the head ring. Finally the 5 mm thick CT slices were taken using the plexiglass phantom. The field of view (FOV) has to be selected in a way that it accommodates all the rods of the localizer in the topogram, which in turn allows fiducial markers to be seen in the CT slices. The CT images were then transferred to the treatment planning software (figure 5). The localization of the three objects was Figure 6. Simulated stereotactic treatment of the head phantom in the dose delivery accuracy test. Headring displacement test Headring is a device used to hold the localizer and the centering box on it and it will be connected to the patient's head, and also to the patient docking device by means of Iran. J. Radiat. Res.; Vol. 3, No. 2, September
4 A.R. Khoshbin Khoshnazar, M.T. Bahreyni Toossi, et al. four couplings to keep the head firmly inside the head frame. Thermoplastic mask and dental mold should be custom made for each patient. Tattoos are marked on patient's face and the corresponding parts of thermoplastic mask are also marked, hence any headring displacement between the imaging and treatment could be detected and measured. Leakage radiation test This test was performed during the simulation of the radiosurgery treatment on the plexiglass phantom. The TLD chips were placed on the phantom corresponding the approximate location of the eyes and thyroid. The dose received by these two critical organs was measured and compared against the dose (15 Gy) delivered to the target. RESULTS Table 1 shows the isocenter shifts under two conditions; couch stationary-gantry rotating and gantry stationary-couch rotating. The average isocenter shift due to the gantry rotation was found to be 1.4 mm with the maximum and minimum values of 2.8 and 0 mm respectively (SD = mm). The average isocenter shift due to the couch rotating was equal to mm with the maximum and minimum values of 2.5 and 1.4 mm respectively (SD = mm). Finally, the average isocenter shift due to the gantry and couch was mm where 0.99 mm represents one standard deviation. Assuming a normal distribution for the individual isocenter shift, the uncertainty should be less than 3.17 mm (= ) in 95% of the time. The localization was repeated three times for each individual object. Table 2 shows the results of the localization accuracy test. The values are the average error with one standard deviation. The total localization error in three orthogonal coordinates is derived from the following equation: Using the above equation the total localization error was found to be mm. Therefore, by assuming normal distribution, the error associated with the Table 1. Isocenter shifts resulted from gantry rotation and couch turning. Gantry rotation Couch angle Isocenter shift (mm) Average mm Average mm Table 2. Localization errors for x, y and z coordinates. x-coordinate y-coordinate z-coordinate mm mm mm localization should be less than 4.23 mm ( ) in 95% of the time. For the three simulated stereotactic treatments delivering 15 Gy to the center of the target, there was a difference of 0.4, 0.7 and 1 Gy between the prescribed and measured dose. The results suggested that average error in the dose delivery was 4.6% with 2% standard deviation. Therefore, assuming normal distribution, the uncertainty in the spatial dose delivery will be less than 3.95 mm ( ) in 95% of the time. During the three actual treatments the average displacement of the headring and the stereotactic frame was equal to mm consequently. The dose received by the eyes and thyroid from the three simulated stereotactic treatments was equal to 13.5 and 6.5 cgy 76 Iran. J. Radiat. Res.; Vol. 3, No. 2, September 2005
5 Quality assurance program for Neptun 10 PC linac respectively. Therefore, the two organs received 0.9 and 0.4 percent of the prescribed dose. DISCUSSION Using 1 and 3 mm thick CT slices would result in a total treatment uncertainty of 2.4 and 3 mm respectively (3). Therefore, even under the best condition, applying 5 mm thick CT slices a spatial uncertainty better than 4 mm should not be expected. Being aware of the total spatial uncertainty in the treatment, the diameter of the selected collimator could easily be determined (6). The localization uncertainty depends on the imaging modality matrix size, the thickness of the image slices and to some extent the type of the localizer being used (3). Matrix size of the CT slices was and the corresponding pixel size was 0.7 mm which is ideal for localization. Having in mind the minimum used CT slice thickness of 5 mm, a localization error of 4.23 mm (with accuracy of 95%) could be acceptable. The isocentric uncertainty depends on the mechanical properties of the linear accelerator. The measured value of the isocentric uncertainty (3.17 mm with accuracy of 95%) is not exactly equal to the value recommended by AAPM report no.54. The headring displacement of 1.8 mm for the constructed non-invasive system is acceptable as compared with the traditional ones (7). The total spatial uncertainty (TSU) is calculated according to the sum of the squares law as following: attached to the headring, the condition is similar to the invasive fixation method. Therefore, the headring displacement should be taken into consideration for calculating the total spatial uncertainty in the noninvasive method. According to the sum of the squares law the uncertainty is as following: The above value is not in agreement with the recommendation of AAPM report no. 54. The dose delivery accuracy test also shows an uncertainty of 7.9% for the absorbed dose (with accuracy of 95%), which exceeds the 5% limit recommended by AAPM. The main reason for the difference may be due to the fact that the measurements were performed in plexiglass with higher electron density than water. Therefore, correction should be made for the difference in the electron density (5). Another reason for the uncertainty is that TLD chips normally show a supralinear response to the doses above 1 Gy. Even though a dose-response curve was obtained for the TLD chips in the 0-15 Gy region and all of the measured values were corrected for supralinearity, the incomplete fitness of the obtained correction function to the actual absorbed dose may be a substantial factor for this difference (8, 9). The leakage radiation test showed that the eyes and thyroid respectively received 0.9 and 0.4 percent of the prescribed dose which is in agreement with the values obtained from a similar measurement made for the traditional systems (3). The results verified the necessary radiation protection provided by the constructed instruments. In spite of the above fact, the result of the dose delivery test does not verify the calculated value. The measured value of the spatial uncertainty (3.95 mm) is close to the localization uncertainty of 4.23 mm. In other words, it seems that the linac isocentric shifts have no effect on the total uncertainty. This situation may only occur when the isocentric shifts happen randomly and it does not necessarily add to the localization uncertainty (3). Regarding the type of the performed dose delivery test, in which the phantom is rigidly CONCLUSION The direct outcome of the quality assurance program is to make the decision whether to begin stereotactic radiosurgery treatment. The isocentric uncertainty behaves randomly and does not necessarily add to the total uncertainty. Since there is some difference between the acceptable limits and the measured value, the following recommendations are suggested: 1. Minimizing the errors by making the possible corrections. Iran. J. Radiat. Res.; Vol. 3, No. 2, September
6 A.R. Khoshbin Khoshnazar, M.T. Bahreyni Toossi, et al. 2. Using thinner CT slices. 3. Making the thermoplast mask and the dental mold in order to precisely fit the patient contour carefully. 4. Not treating the lesions that are in close proximity to the critical organs such as the optic nerve and brain stem. 5. Fractionating the applied dose in order to increase the tolerance dose level for the critical organs when possible. 6. Determining the local acceptable level after a trial period. 7. Limiting the effect of isocentric uncertainty by translating the intersection of the room lasers to the radiation isocenter for the error resulted from the gantry. It is also possible to limit the effect of the isocentric uncertainty by moving the linac table in the opposite direction for the errors resulted from the couch angle. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors would like to extend their special thanks to Engineer Nader Salehi and Dr. Marco Luzzara at 3DLine society of Italy for their generous and invaluable help in making this project possible. All the support provided by the office of vice president for research affairs and Imam Reza radiotherapy department staff are greatly appreciated. REFERENCES 1. Leksell L (1951) The stereotactic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand, 182: Betti O and Derechinsky V (1983) Irradiation stereotaxique multifaisceux. Neurochriurgie, 29: AAPM (American Association of Physicists in Medicine) (1995) Report No. 54. Stereotactic radiosurgery. 4. Yeung D, Palta J, Fountanesi J, Kun L (1993) Systematic analysis of error in target localization and treatment delivery in stereotactic radiosuregery (SR). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 28: Bazioglu M A, Theodorou K, Kappas C, Kalef-Ezra J, (2002) A multi purpose head phantom for stereotactic radiotherapy. Physica Medica, 18: Lutz W, Winston K, Maleki N (1988) A system for stereotactic radiosurgery with a linear accelerator. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 14: Kooy HM, Dunbar SF, Tarbell NJ, Mannarino E, Ferraro N, Shusterman S, et al. (1994) Adaptation and verification of the relocatable Gill-Thomas-Cosman frame in stereotactic radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 30: Ertl A, Hartl RFE, Zenetmayer M, Kitz K, Griffit W(1996) TLD array for precise dose measurement in stereotactic radiation techniques. Phys Med Biol, 41: Treuer H, Hoevels M, Luyken K, Gierich A, Kocher M, Muler RP, Sturm V( 2000) On isocenter adjustment and quality control in linear accelerator based radiosurgery with circular collimator and room lasers. Phys Med Biol, 45: Iran. J. Radiat. Res.; Vol. 3, No. 2, September 2005
Nuclear Associates
 Nuclear Associates 37-013 GARD Users Manual March 2005 Manual No. 37-013-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. All product names are trademarks of their respective
Nuclear Associates 37-013 GARD Users Manual March 2005 Manual No. 37-013-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in U.S.A. All product names are trademarks of their respective
Unrivaled, End-to-End
 PHANTOMS Unrivaled, End-to-End Stereotactic QA Industry-leading 0.1mm accuracy minimizes errors at each link in the stereotactic quality assurance chain. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is governed by
PHANTOMS Unrivaled, End-to-End Stereotactic QA Industry-leading 0.1mm accuracy minimizes errors at each link in the stereotactic quality assurance chain. Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is governed by
Can we hit the target? Can we put the dose where we want it? Quality Assurance in Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy
 Quality Assurance in Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy David Shepard, Ph.D. Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Timothy D. Solberg, Ph.D. University of Texas Southwestern
Quality Assurance in Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy David Shepard, Ph.D. Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Timothy D. Solberg, Ph.D. University of Texas Southwestern
SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties
 SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties Sonja Dieterich, PhD Linac/CyberKnife Technological Uncertainties 1 Linac Mechanical/Radiation Isocenters Depuydt, Tom, et al. "Computer aided analysis
SRS Uncertainty: Linac and CyberKnife Uncertainties Sonja Dieterich, PhD Linac/CyberKnife Technological Uncertainties 1 Linac Mechanical/Radiation Isocenters Depuydt, Tom, et al. "Computer aided analysis
A new geometric and mechanical verification device for medical LINACs
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2002 A new geometric and mechanical verification device for medical LINACs Keith T. Welsh,* Robert A. Wlodarczyk, and L. E. Reinstein
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2002 A new geometric and mechanical verification device for medical LINACs Keith T. Welsh,* Robert A. Wlodarczyk, and L. E. Reinstein
Implementing New Technologies for Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 Implementing New Technologies for Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Implementation of radiosurgery and SBRT requires a fundamentally sound approach Errors don t blur out
Implementing New Technologies for Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Implementation of radiosurgery and SBRT requires a fundamentally sound approach Errors don t blur out
Radiosurgery. Most Important! 8/2/2012. Stereotactic Radiosurgery: State of the Art Technology and Implementation Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery
 Therapy SAM Symposium: WE-A-BRCD-1 Stereotactic Radiosurgery: State of the Art Technology and Implementation Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery Kamil M. Yenice, PhD Associate Professor Chief of Clinical Physics
Therapy SAM Symposium: WE-A-BRCD-1 Stereotactic Radiosurgery: State of the Art Technology and Implementation Linear Accelerator Radiosurgery Kamil M. Yenice, PhD Associate Professor Chief of Clinical Physics
Quality Assurance of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy. Zuofeng Li, D.Sc. Murty S. Goddu, Ph.D. Washington University St.
 Quality Assurance of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy Zuofeng Li, D.Sc. Murty S. Goddu, Ph.D. Washington University St. Louis, Missouri Typical Applications of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy
Quality Assurance of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy Zuofeng Li, D.Sc. Murty S. Goddu, Ph.D. Washington University St. Louis, Missouri Typical Applications of Ultrasound Imaging in Radiation Therapy
Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI)
 Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI) Tagreed AL-ALAWI Medical Physicist King Abdullah Medical City- Jeddah Aim 1. Simplify and standardize
Treatment Planning Evaluation of Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) for Craniospinal Irradiation (CSI) Tagreed AL-ALAWI Medical Physicist King Abdullah Medical City- Jeddah Aim 1. Simplify and standardize
Evaluation of accuracy in determination of stereotactical isocenter: from image acquisition to treatment.
 Evaluation of accuracy in determination of stereotactical isocenter: from image acquisition to treatment. ANNA SARDO 1, EUGENIA MADON 1, EDOARDO TREVISIOL 1, DANILO SANTUARI 1, VERONICA RICHETTO 1, ROBERTO
Evaluation of accuracy in determination of stereotactical isocenter: from image acquisition to treatment. ANNA SARDO 1, EUGENIA MADON 1, EDOARDO TREVISIOL 1, DANILO SANTUARI 1, VERONICA RICHETTO 1, ROBERTO
ph fax
 This product is available through: JRT Associates www.standardimaging.com 800-261-4446. ph 608-831-0025. fax 608-831-2202 5 Nepperhan Avenue, Suite 2B 3120 Deming Way Middleton WIElmsford, 53562-1461 NY
This product is available through: JRT Associates www.standardimaging.com 800-261-4446. ph 608-831-0025. fax 608-831-2202 5 Nepperhan Avenue, Suite 2B 3120 Deming Way Middleton WIElmsford, 53562-1461 NY
A Patient s Guide to SRS
 A Patient s Guide to SRS Stereotactic Radiosurgery 230 Nebraska St. Sioux City, IA 51101 NOTES 230 Nebraska St. Sioux City, IA 51101 Contents page Introduction 1 SRS and how it works 2 The technology involved
A Patient s Guide to SRS Stereotactic Radiosurgery 230 Nebraska St. Sioux City, IA 51101 NOTES 230 Nebraska St. Sioux City, IA 51101 Contents page Introduction 1 SRS and how it works 2 The technology involved
SHIELDING TECHNIQUES FOR CURRENT RADIATION THERAPY MODALITIES
 SHIELDING TECHNIQUES FOR CURRENT RADIATION THERAPY MODALITIES MELISSA C. MARTIN, M.S., FACR, FAAPM PRESIDENT AAPM - 2017 PRESIDENT - THERAPY PHYSICS INC., GARDENA, CA MELISSA@THERAPYPHYSICS.COM AAPM Spring
SHIELDING TECHNIQUES FOR CURRENT RADIATION THERAPY MODALITIES MELISSA C. MARTIN, M.S., FACR, FAAPM PRESIDENT AAPM - 2017 PRESIDENT - THERAPY PHYSICS INC., GARDENA, CA MELISSA@THERAPYPHYSICS.COM AAPM Spring
X-Ray Guided Robotic Radiosurgery for Solid Tumors
 X-Ray Guided Robotic Radiosurgery for Solid Tumors Mohan Bodduluri Accuray Incorporated 570 Del Rey Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94085 USA and J. M. McCarthy Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
X-Ray Guided Robotic Radiosurgery for Solid Tumors Mohan Bodduluri Accuray Incorporated 570 Del Rey Avenue Sunnyvale, CA 94085 USA and J. M. McCarthy Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
Work partially supported by VisionRT
 Work partially supported by VisionRT Background of frameless intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery UCSD SRS/SRT procedure Clinical Results Summary Total prescribed doses : order of 10 50 Gy Planning targets
Work partially supported by VisionRT Background of frameless intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery UCSD SRS/SRT procedure Clinical Results Summary Total prescribed doses : order of 10 50 Gy Planning targets
Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery. Linear accelerators. Basic technique. Indications of SRS
 Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
Stereotactic Radiosurgery Extracranial Stereotactic Radiosurgery Annette Quinn, MSN, RN Program Manager, University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Using stereotactic techniques, give a lethal dose of ionizing
Assessment of variation of wedge factor with depth, field size and SSD for Neptun 10PC Linac in Mashhad Imam Reza Hospital
 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2004; 2 (2): 53-58 Assessment of variation of wedge factor with depth, field size and SSD for Neptun 10PC Linac in Mashhad Imam Reza Hospital M. Hajizadeh Saffar 1*, M.R. Ghavamnasiri
Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2004; 2 (2): 53-58 Assessment of variation of wedge factor with depth, field size and SSD for Neptun 10PC Linac in Mashhad Imam Reza Hospital M. Hajizadeh Saffar 1*, M.R. Ghavamnasiri
Chapters from Clinical Oncology
 Chapters from Clinical Oncology Lecture notes University of Szeged Faculty of Medicine Department of Oncotherapy 2012. 1 RADIOTHERAPY Technical aspects Dr. Elemér Szil Introduction There are three possibilities
Chapters from Clinical Oncology Lecture notes University of Szeged Faculty of Medicine Department of Oncotherapy 2012. 1 RADIOTHERAPY Technical aspects Dr. Elemér Szil Introduction There are three possibilities
IROC Liver Phantom. Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Liver Phantom. Revised July 2015
 IROC Liver Phantom Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Liver Phantom. Revised July 2015 The study groups are requests that each institution keep the phantom for no more than 2 weeks. During
IROC Liver Phantom Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Liver Phantom. Revised July 2015 The study groups are requests that each institution keep the phantom for no more than 2 weeks. During
4 Essentials of CK Physics 8/2/2012. SRS using the CyberKnife. Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest
 SRS using the CyberKnife Sonja Dieterich, PhD, DABR Associate Professor University of California Davis Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest Consulting agreements with Broncus Medical and CyberHeart, Inc. Scientific
SRS using the CyberKnife Sonja Dieterich, PhD, DABR Associate Professor University of California Davis Disclaimer/Conflict of Interest Consulting agreements with Broncus Medical and CyberHeart, Inc. Scientific
Quality Assurance in Stereotactic. Radiotherapy. Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA
 Quality Assurance in Stereotactic iosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy David Shepard, Ph.D. Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Timothy D. Solberg, Ph.D. University of Texas Southwestern
Quality Assurance in Stereotactic iosurgery and Fractionated Stereotactic Radiotherapy David Shepard, Ph.D. Swedish Cancer Institute Seattle, WA Timothy D. Solberg, Ph.D. University of Texas Southwestern
STEREOTACTIC DOSE VERIFICATION PHANTOM VERSATILE STEREOTACTIC QA PHANTOMS
 PHANTOMS VERSATILE STEREOTACTIC QA For fast and accurate commissioning of Accuray CyberKnife treatment systems and patient specific dose verification plans STEREOTACTIC DOSE VERIFICATION PHANTOM Stereotactic
PHANTOMS VERSATILE STEREOTACTIC QA For fast and accurate commissioning of Accuray CyberKnife treatment systems and patient specific dose verification plans STEREOTACTIC DOSE VERIFICATION PHANTOM Stereotactic
Verification of treatment planning system parameters in tomotherapy using EBT Radiochromic Film
 Verification of treatment planning system parameters in tomotherapy using EBT Radiochromic Film E.B.Rajmohan¹, Pratik Kumar¹, Bhudatt Paliwal,² David Westerly², N.Gopishankar³, R.K.Bisht³, D.Tewatia²,
Verification of treatment planning system parameters in tomotherapy using EBT Radiochromic Film E.B.Rajmohan¹, Pratik Kumar¹, Bhudatt Paliwal,² David Westerly², N.Gopishankar³, R.K.Bisht³, D.Tewatia²,
Traceability and absorbed dose standards for small fields, IMRT and helical tomotherapy
 Traceability and absorbed dose standards for small fields, IMRT and helical tomotherapy Simon Duane, Hugo Palmans, Peter Sharpe NPL, UK Stefaan Vynckier UCL, Brussels, Belgium LNE-LNHB / BIPM workshop,
Traceability and absorbed dose standards for small fields, IMRT and helical tomotherapy Simon Duane, Hugo Palmans, Peter Sharpe NPL, UK Stefaan Vynckier UCL, Brussels, Belgium LNE-LNHB / BIPM workshop,
MAX-HD SRS PHANTOM THE COMPREHENSIVE END-TO-END SRS PHANTOM SCAN PLAN LOCALIZE TREAT. distributed by:
 SRS PHANTOM SCAN PLAN LOCALIZE TREAT THE COMPREHENSIVE END-TO-END SRS PHANTOM distributed by: Tel: +33 (0) 42 88 68 41 info@orion-france.com www.orion-france.com 2, Avenue du General Balfourier 75016 Paris,
SRS PHANTOM SCAN PLAN LOCALIZE TREAT THE COMPREHENSIVE END-TO-END SRS PHANTOM distributed by: Tel: +33 (0) 42 88 68 41 info@orion-france.com www.orion-france.com 2, Avenue du General Balfourier 75016 Paris,
Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, Pamela Myers, Ph.D.
 Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, 2014 Pamela Myers, Ph.D. Introduction o o o o o Outline GRID compensator Purpose of SFRT/GRID therapy Fractionation
Spatially Fractionated Radiation Therapy: GRID Sponsored by.decimal Friday, August 22, 2014 Pamela Myers, Ph.D. Introduction o o o o o Outline GRID compensator Purpose of SFRT/GRID therapy Fractionation
Lung Spine Phantom. Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Spine Phantom. MARCH 2014
 Lung Spine Phantom Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Spine Phantom. MARCH 2014 The study groups are requesting that each institution keep the phantom for no more than 2 week. During this
Lung Spine Phantom Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Spine Phantom. MARCH 2014 The study groups are requesting that each institution keep the phantom for no more than 2 week. During this
RPC Liver Phantom Highly Conformal Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy
 RPC Liver Phantom Highly Conformal Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the RPC Liver Phantom. Revised Dec 2005 Credentialing for this protocol requires four steps:
RPC Liver Phantom Highly Conformal Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the RPC Liver Phantom. Revised Dec 2005 Credentialing for this protocol requires four steps:
IMRT QUESTIONNAIRE. Address: Physicist: Research Associate: Dosimetrist: Responsible Radiation Oncologist(s)
 IMRT QUESTIONNAIRE Institution: Date: / / Address: Physicist: e-mail: Telephone: Fax: Research Associate: email: Telephone: Fax: Dosimetrist: email: Telephone: Fax: Responsible Radiation Oncologist(s)
IMRT QUESTIONNAIRE Institution: Date: / / Address: Physicist: e-mail: Telephone: Fax: Research Associate: email: Telephone: Fax: Dosimetrist: email: Telephone: Fax: Responsible Radiation Oncologist(s)
Leksell Gamma Knife Icon A New User s Perspective
 Leksell Gamma Knife Icon A New User s Perspective Steve Herchko, DMP 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2017 MFMER slide-2 Outline Icon Overview Mayo Clinic Experience Frame-Based System Mask-Based System
Leksell Gamma Knife Icon A New User s Perspective Steve Herchko, DMP 2017 MFMER slide-1 Disclosures None 2017 MFMER slide-2 Outline Icon Overview Mayo Clinic Experience Frame-Based System Mask-Based System
CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy. Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017
 CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017 Objectives Components and work flow of CyberKnife Motion management of CyberKnife
CyberKnife Technology in Ablative Radiation Therapy Jun Yang PhD Cyberknife Center of Philadelphia Drexel University Jan 2017 Objectives Components and work flow of CyberKnife Motion management of CyberKnife
Normal tissue doses from MV image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) using orthogonal MV and MV-CBCT
 Received: 28 September 2017 Revised: 17 November 2017 Accepted: 28 December 2017 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12276 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Normal tissue doses from MV image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) using
Received: 28 September 2017 Revised: 17 November 2017 Accepted: 28 December 2017 DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12276 RADIATION ONCOLOGY PHYSICS Normal tissue doses from MV image-guided radiation therapy (IGRT) using
Disclosure. Outline. Machine Overview. I have received honoraria from Accuray in the past. I have had travel expenses paid by Accuray in the past.
 Clinical Implementation of the CyberKnife Disclosure I have received honoraria from Accuray in the past. I have had travel expenses paid by Accuray in the past. Mary Ellen Masterson-McGary McGary CyberKnife
Clinical Implementation of the CyberKnife Disclosure I have received honoraria from Accuray in the past. I have had travel expenses paid by Accuray in the past. Mary Ellen Masterson-McGary McGary CyberKnife
Canadian Partnership for Quality Radiotherapy. Technical Quality Control Guidelines for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. A guidance document on behalf of:
 Canadian Partnership for Quality Radiotherapy Technical Quality Control Guidelines for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery A guidance document on behalf of: Canadian Association of Radiation Oncology Canadian Organization
Canadian Partnership for Quality Radiotherapy Technical Quality Control Guidelines for Gamma Knife Radiosurgery A guidance document on behalf of: Canadian Association of Radiation Oncology Canadian Organization
Dosimetric characterization with 62 MeV protons of a silicon segmented detector for 2D dose verifications in radiotherapy
 Dosimetric characterization with 62 MeV protons of a silicon segmented detector for 2D dose verifications in radiotherapy C. Talamonti M. Bruzzi,M. Bucciolini, L. Marrazzo, D. Menichelli University of
Dosimetric characterization with 62 MeV protons of a silicon segmented detector for 2D dose verifications in radiotherapy C. Talamonti M. Bruzzi,M. Bucciolini, L. Marrazzo, D. Menichelli University of
S. Derreumaux (IRSN) Accidents in radiation therapy in France: causes, consequences and lessons learned
 S. Derreumaux (IRSN) Accidents in radiation therapy in France: causes, consequences and lessons learned MEDICAL LINEAR ACCELERATORS Electron beam (MeV) Photon beam (MV) PRECISION REQUIRED IN RADIOTHERAPY
S. Derreumaux (IRSN) Accidents in radiation therapy in France: causes, consequences and lessons learned MEDICAL LINEAR ACCELERATORS Electron beam (MeV) Photon beam (MV) PRECISION REQUIRED IN RADIOTHERAPY
Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for pediatric patients with retinoblastoma
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 7, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2006 Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for pediatric patients with retinoblastoma Patrick D. Higgins, 1,a Bruce J. Gerbi, 1
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 7, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2006 Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for pediatric patients with retinoblastoma Patrick D. Higgins, 1,a Bruce J. Gerbi, 1
Diode calibration for dose determination in total body irradiation
 Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2008; 6 (1): 43-50 Diode calibration for dose determination in total body irradiation M.Allahverdi 1*, Gh. Geraily 1, M. Esfehani 3,A. Sharafi 2,A. Shirazi 1 1 Department of Medical
Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2008; 6 (1): 43-50 Diode calibration for dose determination in total body irradiation M.Allahverdi 1*, Gh. Geraily 1, M. Esfehani 3,A. Sharafi 2,A. Shirazi 1 1 Department of Medical
M. J. Maryanski, Three Dimensional BANG Polymer Gel Dosimeters AAPM'99, CE Course
 Three Dimensional BANG Polymer Gel Dosimeters Marek J. Maryanski MGS Research, Inc. Guilford, CT Educational objectives: Describe the need for high-resolution 3D dosimetry in 3D CRT. Explain the physics
Three Dimensional BANG Polymer Gel Dosimeters Marek J. Maryanski MGS Research, Inc. Guilford, CT Educational objectives: Describe the need for high-resolution 3D dosimetry in 3D CRT. Explain the physics
Dosimetry of the Gamma Knife TM
 Dosimetry of the Gamma Knife TM Sheridan Griffin Meltsner, Ph.D. Aurora Health Care St. Luke s Medical Center NCCAAPM Spring Meeting Outline Introduction to stereotactic radiosurgery Elekta Gamma Knife
Dosimetry of the Gamma Knife TM Sheridan Griffin Meltsner, Ph.D. Aurora Health Care St. Luke s Medical Center NCCAAPM Spring Meeting Outline Introduction to stereotactic radiosurgery Elekta Gamma Knife
IROC Lung Phantom 3D CRT / IMRT. Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Lung Phantom. Revised Dec 2015
 IROC Lung Phantom 3D CRT / IMRT Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Lung Phantom. Revised Dec 2015 The IROC requests that each institution keep the phantom for no more than 2 weeks. During
IROC Lung Phantom 3D CRT / IMRT Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC Lung Phantom. Revised Dec 2015 The IROC requests that each institution keep the phantom for no more than 2 weeks. During
Dosimetric characterization with 62 MeV protons of a silicon segmented detector for 2D dose verifications in radiotherapy
 Dosimetric characterization with 62 MeV protons of a silicon segmented detector for 2D dose verifications in radiotherapy C. Talamonti a*, M. Bucciolini a, L. Marrazzo a, D. Menichelli a. a) Department
Dosimetric characterization with 62 MeV protons of a silicon segmented detector for 2D dose verifications in radiotherapy C. Talamonti a*, M. Bucciolini a, L. Marrazzo a, D. Menichelli a. a) Department
Delivery Quality Assurance with a High Resolution Liquid Filled Ion Chamber Array for Robotic Radiosurgery
 Adamczyk S, Chan M, Stelljes T, Schmitt D, Skrobala A, Poppinga D, Adamczyk M, Pawalowski B, Hildebrandt G, Poppe B, Blanck O Dr. Oliver Blanck University Clinic Lübeck, Germany Phone: +491728033815 E-Mail:
Adamczyk S, Chan M, Stelljes T, Schmitt D, Skrobala A, Poppinga D, Adamczyk M, Pawalowski B, Hildebrandt G, Poppe B, Blanck O Dr. Oliver Blanck University Clinic Lübeck, Germany Phone: +491728033815 E-Mail:
Intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) for treatment of post-operative high grade glioma in the right parietal region of brain
 1 Carol Boyd March Case Study March 11, 2013 Intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) for treatment of post-operative high grade glioma in the right parietal region of brain History of Present Illness:
1 Carol Boyd March Case Study March 11, 2013 Intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) for treatment of post-operative high grade glioma in the right parietal region of brain History of Present Illness:
Extracranial doses in stereotactic and conventional radiotherapy for pituitary adenomas
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 7, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2006 Extracranial doses in stereotactic and conventional radiotherapy for pituitary adenomas Thomas Samuel Ram, a Paul B. Ravindran,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 7, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2006 Extracranial doses in stereotactic and conventional radiotherapy for pituitary adenomas Thomas Samuel Ram, a Paul B. Ravindran,
Radiosurgery by Leksell gamma knife. Josef Novotny, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague
 Radiosurgery by Leksell gamma knife Josef Novotny, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague Radiosurgery - Definition Professor Lars Leksell The tools used by the surgeon must be adapted to the task and where the human
Radiosurgery by Leksell gamma knife Josef Novotny, Na Homolce Hospital, Prague Radiosurgery - Definition Professor Lars Leksell The tools used by the surgeon must be adapted to the task and where the human
Linac or Non-Linac Demystifying And Decoding The Physics Of SBRT/SABR
 Linac or Non-Linac Demystifying And Decoding The Physics Of SBRT/SABR PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FASTRO Department of Radiation Oncology Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, IN, USA Indra J. Das,
Linac or Non-Linac Demystifying And Decoding The Physics Of SBRT/SABR PhD, FAAPM, FACR, FASTRO Department of Radiation Oncology Indiana University School of Medicine Indianapolis, IN, USA Indra J. Das,
7/10/2015. Acknowledgments. Institution-specific TG-142? AAPM:Task Group-142. Failure-Mode & Effects Analysis
 Acknowledgments Thanks to Saiful Huq for an illuminating conversation about the application of TG-100 Jennifer O Daniel, Ph.D. & Fang-Fang Yin, Ph.D. Duke University Medical Center Annual AAPM Meeting,
Acknowledgments Thanks to Saiful Huq for an illuminating conversation about the application of TG-100 Jennifer O Daniel, Ph.D. & Fang-Fang Yin, Ph.D. Duke University Medical Center Annual AAPM Meeting,
Patient-specific quality assurance for intracranial cases in robotic radiosurgery system
 JBUON 2018; 23(1): 179-184 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Patient-specific quality assurance for intracranial cases in robotic
JBUON 2018; 23(1): 179-184 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Patient-specific quality assurance for intracranial cases in robotic
Verification of Relative Output Factor (ROF) Measurement for Radiosurgery Small Photon Beams
 Verification of Relative Output Factor (ROF) Measurement for Radiosurgery Small Photon Beams Reduan A a, Mazurawati M b, Nur Iziana M a, Nik Ruzman NI b, Ahmad Z a and Ahmad Lutfi Y b a School of Health
Verification of Relative Output Factor (ROF) Measurement for Radiosurgery Small Photon Beams Reduan A a, Mazurawati M b, Nur Iziana M a, Nik Ruzman NI b, Ahmad Z a and Ahmad Lutfi Y b a School of Health
Brain Tumor Radiosurgery. Gabor Fichtinger, PhD
 Brain Tumor Radiosurgery Gabor Fichtinger, PhD Surgical CAD/CAM Preoperative Computerassisted planning Surgical Intraoperative Update Model Update Plan Surgical CAD CAM Patient-specific Model Computer-
Brain Tumor Radiosurgery Gabor Fichtinger, PhD Surgical CAD/CAM Preoperative Computerassisted planning Surgical Intraoperative Update Model Update Plan Surgical CAD CAM Patient-specific Model Computer-
I. Equipments for external beam radiotherapy
 I. Equipments for external beam radiotherapy 5 linear accelerators (LINACs): Varian TrueBeam 6, 10 & 18 MV photons, 6-18 MeV electrons, image-guided (IGRT) and intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT),
I. Equipments for external beam radiotherapy 5 linear accelerators (LINACs): Varian TrueBeam 6, 10 & 18 MV photons, 6-18 MeV electrons, image-guided (IGRT) and intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT),
8/2/2018. Disclosure. Online MR-IG-ART Dosimetry and Dose Accumulation
 Online MR-IG-ART Dosimetry and Dose Accumulation Deshan Yang, PhD, Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology, School of Medicine Washington University in Saint Louis 1 Disclosure Received research
Online MR-IG-ART Dosimetry and Dose Accumulation Deshan Yang, PhD, Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology, School of Medicine Washington University in Saint Louis 1 Disclosure Received research
Application(s) of Alanine
 Application(s) of Alanine Simon Duane Radiotherapy Standards User Group, 5 June 2007 Outline Alanine/EPR dosimetry characteristics, usage (dis)advantages for reference dosimetry Traceable dosimetry for
Application(s) of Alanine Simon Duane Radiotherapy Standards User Group, 5 June 2007 Outline Alanine/EPR dosimetry characteristics, usage (dis)advantages for reference dosimetry Traceable dosimetry for
Case Study. Institution Farrer Park Hospital
 Case Study Single isocenter high definition dynamic radiosurgery (HDRS) for multiple brain metastases HDRS with Monaco, Versa HD and HexaPOD allows multiple brain metastases treatment within standard 15-minute
Case Study Single isocenter high definition dynamic radiosurgery (HDRS) for multiple brain metastases HDRS with Monaco, Versa HD and HexaPOD allows multiple brain metastases treatment within standard 15-minute
IMRT/IGRT Patient Treatment: A Community Hospital Experience. Charles M. Able, Assistant Professor
 IMRT/IGRT Patient Treatment: A Community Hospital Experience Charles M. Able, Assistant Professor Disclosures I have no research support or financial interest to disclose. Learning Objectives 1. Review
IMRT/IGRT Patient Treatment: A Community Hospital Experience Charles M. Able, Assistant Professor Disclosures I have no research support or financial interest to disclose. Learning Objectives 1. Review
) and the localizer(iso loc. I. Introduction
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 14, NUMBER 4, 2013 A phantom study of the immobilization and the indications for using virtual isocenter in stereoscopic X-ray image guidance system
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 14, NUMBER 4, 2013 A phantom study of the immobilization and the indications for using virtual isocenter in stereoscopic X-ray image guidance system
Varian Edge Experience. Jinkoo Kim, Ph.D Henry Ford Health System
 Varian Edge Experience Jinkoo Kim, Ph.D Henry Ford Health System Disclosures I participate in research funded by Varian Medical Systems. Outline of Presentation Review advanced imaging in Varian Edge Linear
Varian Edge Experience Jinkoo Kim, Ph.D Henry Ford Health System Disclosures I participate in research funded by Varian Medical Systems. Outline of Presentation Review advanced imaging in Varian Edge Linear
SBRT fundamentals. Outline 8/2/2012. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Quality Assurance Educational Session
 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Quality Assurance Educational Session J Perks PhD, UC Davis Medical Center, Sacramento CA SBRT fundamentals Extra-cranial treatments Single or small number (2-5) of
Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Quality Assurance Educational Session J Perks PhD, UC Davis Medical Center, Sacramento CA SBRT fundamentals Extra-cranial treatments Single or small number (2-5) of
RADIATION ONCOLOGY RESIDENCY PROGRAM Competency Evaluation of Resident
 Resident s Name: RADIATION ONCOLOGY RESIDENCY PROGRAM Competency Evaluation of Resident Rotation: PHYS 703: Clinical Rotation 2 Inclusive dates of rotation: Feb. 26, 2016 Aug. 25, 2016 Director or Associate
Resident s Name: RADIATION ONCOLOGY RESIDENCY PROGRAM Competency Evaluation of Resident Rotation: PHYS 703: Clinical Rotation 2 Inclusive dates of rotation: Feb. 26, 2016 Aug. 25, 2016 Director or Associate
DOSE DISTRIBUTION ANALYZE OF THE BODY STI USED MONTE CARLO METHOD
 Proceedings of the Tenth EGS4 Users' Meeting in Japan, KEK Proceedings 2002-18, p.65-73 DOSE DISTRIBUTION ANALYZE OF THE BODY STI USED MONTE CARLO METHOD N. Tohyama, H. Saitoh, T. Fujisaki 1, S. Abe 1
Proceedings of the Tenth EGS4 Users' Meeting in Japan, KEK Proceedings 2002-18, p.65-73 DOSE DISTRIBUTION ANALYZE OF THE BODY STI USED MONTE CARLO METHOD N. Tohyama, H. Saitoh, T. Fujisaki 1, S. Abe 1
Learning Objectives. Clinically operating proton therapy facilities. Overview of Quality Assurance in Proton Therapy. Omar Zeidan
 Overview of Quality Assurance in Proton Therapy Omar Zeidan AAPM 2012 Charlotte, NC July 30 st, 2012 Learning Objectives Understand proton beam dosimetry characteristics and compare them to photon beams
Overview of Quality Assurance in Proton Therapy Omar Zeidan AAPM 2012 Charlotte, NC July 30 st, 2012 Learning Objectives Understand proton beam dosimetry characteristics and compare them to photon beams
IMRT QA: Point Dose Measurements or 2D Array?
 QA for IMRT IMRT QA: Point Dose Measurements or D Array? General Linac QA for IMRT MLC checks Dose linearity at low MU Patient-specific measurements Performed using various methods Purpose is to verify
QA for IMRT IMRT QA: Point Dose Measurements or D Array? General Linac QA for IMRT MLC checks Dose linearity at low MU Patient-specific measurements Performed using various methods Purpose is to verify
Stereotaxy. Outlines. Establishing SBRT Program: Physics & Dosimetry. SBRT - Simulation. Body Localizer. Sim. Sim. Sim. Stereotaxy?
 Establishing SBRT Program: Physics & Dosimetry Lu Wang, Ph.D. Radiation Oncology Department Fox Chase Cancer Center Outlines Illustrate the difference between SBRT vs. CRT Introduce the major procedures
Establishing SBRT Program: Physics & Dosimetry Lu Wang, Ph.D. Radiation Oncology Department Fox Chase Cancer Center Outlines Illustrate the difference between SBRT vs. CRT Introduce the major procedures
Additional Questions for Review 2D & 3D
 Additional Questions for Review 2D & 3D 1. For a 4-field box technique, which of the following will deliver the lowest dose to the femoral heads? a. 100 SSD, equal dmax dose to all fields b. 100 SSD, equal
Additional Questions for Review 2D & 3D 1. For a 4-field box technique, which of the following will deliver the lowest dose to the femoral heads? a. 100 SSD, equal dmax dose to all fields b. 100 SSD, equal
such as lung cancer or breast cancer
 Assessing Dosimetric Accuracy with Lucy 3D QA Phantom Victoria Honetschlager, Department of Physics, Minnesota State University Moorhead, Moorhead, MN 56563 ABSTRACT Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is
Assessing Dosimetric Accuracy with Lucy 3D QA Phantom Victoria Honetschlager, Department of Physics, Minnesota State University Moorhead, Moorhead, MN 56563 ABSTRACT Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is
Quality Assurance of TPS: comparison of dose calculation for stereotactic patients in Eclipse and iplan RT Dose
 Petrovic B Comparison of dose calculation algorithms for stereotaxy Quality Assurance of TPS: comparison of dose calculation for stereotactic patients in and RT Dose Borislava Petrovic 1, Aleksandra Grządziel
Petrovic B Comparison of dose calculation algorithms for stereotaxy Quality Assurance of TPS: comparison of dose calculation for stereotactic patients in and RT Dose Borislava Petrovic 1, Aleksandra Grządziel
Leila E. A. Nichol Royal Surrey County Hospital
 2 nd UK and Ireland Dosimetry Check User Meeting Symposium Clatterbridge Cancer Centre, 24 th October 2012 Leila E. A. Nichol Royal Surrey County Hospital Leila.Nichol@nhs.net *My experience with Dosimetry
2 nd UK and Ireland Dosimetry Check User Meeting Symposium Clatterbridge Cancer Centre, 24 th October 2012 Leila E. A. Nichol Royal Surrey County Hospital Leila.Nichol@nhs.net *My experience with Dosimetry
Original Date: April 2016 Page 1 of 7 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines STEREOTACTIC RADIATION THERAPY: STEREO RADIOSURGERY (SRS) AND STEREOTACTIC BODY RADIATION THERAPY (SBRT) CPT4 Codes: Please refer to pages 5-6 LCD
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines STEREOTACTIC RADIATION THERAPY: STEREO RADIOSURGERY (SRS) AND STEREOTACTIC BODY RADIATION THERAPY (SBRT) CPT4 Codes: Please refer to pages 5-6 LCD
Strategies and Technologies for Cranial Radiosurgery Planning: Gamma Knife
 Conflicts of Interest Strategies and Technologies for Cranial Radiosurgery Planning: Gamma Knife David Schlesinger, Ph.D. Research support: Elekta Instruments, AB Lars Leksell Gamma Knife Center University
Conflicts of Interest Strategies and Technologies for Cranial Radiosurgery Planning: Gamma Knife David Schlesinger, Ph.D. Research support: Elekta Instruments, AB Lars Leksell Gamma Knife Center University
Amendment No. 2. Item No. 2 (Rfx/ Event number )
 Amendment 2 Sub: Amendment to the Document 06.12.2018 Ref.: Notice Inviting Bid ref. HITES/PCD/NCI-AIIMS/36/18-19 dated 26.09.2018 read with its Amendment no. 1 dated 19.11.18 The following changes have
Amendment 2 Sub: Amendment to the Document 06.12.2018 Ref.: Notice Inviting Bid ref. HITES/PCD/NCI-AIIMS/36/18-19 dated 26.09.2018 read with its Amendment no. 1 dated 19.11.18 The following changes have
Leksell Gamma Knife Icon. Treatment information
 Leksell Gamma Knife Icon Treatment information You may be feeling frightened or overwhelmed by your recent diagnosis. It can be confusing trying to process a diagnosis, understand a new and challenging
Leksell Gamma Knife Icon Treatment information You may be feeling frightened or overwhelmed by your recent diagnosis. It can be confusing trying to process a diagnosis, understand a new and challenging
Special Procedures Rotation I/II SBRT, SRS, TBI, and TSET
 University of Michigan Department of Radiation Oncology Division of Radiation Physics Special Procedures Rotation I/II SBRT, SRS, TBI, and TSET Resident: Rotation staff mentor/ advisor: _Scott Hadley,
University of Michigan Department of Radiation Oncology Division of Radiation Physics Special Procedures Rotation I/II SBRT, SRS, TBI, and TSET Resident: Rotation staff mentor/ advisor: _Scott Hadley,
Verification of performance of Acuros XB Algorithm (AXB) Implemented on Eclipse Planning System
 Original Article Research in Oncology 2018; Vol. 14, No. 1: 34-38. DOI: 10.21608/resoncol.2018.3026.1047 Verification of performance of Acuros XB Algorithm (AXB) Implemented on Eclipse Planning System
Original Article Research in Oncology 2018; Vol. 14, No. 1: 34-38. DOI: 10.21608/resoncol.2018.3026.1047 Verification of performance of Acuros XB Algorithm (AXB) Implemented on Eclipse Planning System
Phantom Positioning Variation in the Gamma Knife Perfexion Dosimetry
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Phantom Positioning Variation in the Gamma Knife Perfexion Dosimetry To cite this article: N A Costa et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 733 012098 View
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Phantom Positioning Variation in the Gamma Knife Perfexion Dosimetry To cite this article: N A Costa et al 2016 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 733 012098 View
Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Acoustic Neuromas (CyberKnife) UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Acoustic Neuromas (CyberKnife) UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Stereotactic Radiotherapy for Acoustic Neuromas (CyberKnife) UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Technical Study. Institution University of Texas Health San Antonio. Location San Antonio, Texas. Medical Staff. Daniel Saenz. Niko Papanikolaou.
 Technical Study Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Elekta Versa HD and Monaco Accuracy of a single isocenter, multiple brain metastases VMAT plan delivered to a pseudo-patient dosimetric gel phantom Institution
Technical Study Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Elekta Versa HD and Monaco Accuracy of a single isocenter, multiple brain metastases VMAT plan delivered to a pseudo-patient dosimetric gel phantom Institution
A simple technique for craniospinal radiotherapy in the supine position
 Radiotherapy and Oncology 78 (2006) 217 222 www.thegreenjournal.com Craniospinal radiotherapy A simple technique for craniospinal radiotherapy in the supine position William A. Parker a, *, Carolyn R.
Radiotherapy and Oncology 78 (2006) 217 222 www.thegreenjournal.com Craniospinal radiotherapy A simple technique for craniospinal radiotherapy in the supine position William A. Parker a, *, Carolyn R.
A quality assurance procedure to evaluate cone-beam CT image center congruence with the radiation isocenter of a linear accelerator
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 11, NUMBER 4, fall 2010 A quality assurance procedure to evaluate cone-beam CT image center congruence with the radiation isocenter of a linear accelerator
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 11, NUMBER 4, fall 2010 A quality assurance procedure to evaluate cone-beam CT image center congruence with the radiation isocenter of a linear accelerator
Quanitative and qualitative analysis of Image Quality and Imaging Dose of KV CBCT from XVI Elekta Linac.
 IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep. - Oct. 2017), PP 46-52 www.iosrjournals.org Quanitative and qualitative analysis of Image Quality and Imaging
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP) e-issn: 2278-4861.Volume 9, Issue 5 Ver. IV (Sep. - Oct. 2017), PP 46-52 www.iosrjournals.org Quanitative and qualitative analysis of Image Quality and Imaging
Production and dosimetry of simultaneous therapeutic photons and electrons beam by linear accelerator: a monte carlo study
 Production and dosimetry of simultaneous therapeutic photons and electrons beam by linear accelerator: a monte carlo study Navid Khledi 1, Azim Arbabi 2, Dariush Sardari 1, Mohammad Mohammadi 3, Ahmad
Production and dosimetry of simultaneous therapeutic photons and electrons beam by linear accelerator: a monte carlo study Navid Khledi 1, Azim Arbabi 2, Dariush Sardari 1, Mohammad Mohammadi 3, Ahmad
A comparison of dose distributions measured with two types of radiochromic film dosimeter MD55 and EBT for proton beam of energy 175 MeV
 A comparison of dose distributions measured with two types of radiochromic film dosimeter MD55 and EBT for proton beam of energy 175 MeV M. Mumot, G. V. Mytsin, Y. I. Luchin and A. G. Molokanov Medico-Technical
A comparison of dose distributions measured with two types of radiochromic film dosimeter MD55 and EBT for proton beam of energy 175 MeV M. Mumot, G. V. Mytsin, Y. I. Luchin and A. G. Molokanov Medico-Technical
Measurement of Dose to Implanted Cardiac Devices in Radiotherapy Patients
 Measurement of Dose to Implanted Cardiac Devices in Radiotherapy Patients Moyed Miften, PhD Professor and Chief Physicist University of Colorado Chester Reft, PhD Associate Professor University of Chicago
Measurement of Dose to Implanted Cardiac Devices in Radiotherapy Patients Moyed Miften, PhD Professor and Chief Physicist University of Colorado Chester Reft, PhD Associate Professor University of Chicago
EORTC Member Facility Questionnaire
 Page 1 of 9 EORTC Member Facility Questionnaire I. Administrative Data Name of person submitting this questionnaire Email address Function Phone Institution Address City Post code Country EORTC No Enter
Page 1 of 9 EORTC Member Facility Questionnaire I. Administrative Data Name of person submitting this questionnaire Email address Function Phone Institution Address City Post code Country EORTC No Enter
IROC Head and Neck Phantom. Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC IMRT Phantom. Revised MARCH 2014
 IROC Head and Neck Phantom Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC IMRT Phantom. Revised MARCH 2014 The study groups are requesting that each institution keep the phantom for a period of time
IROC Head and Neck Phantom Guidelines for Planning and Irradiating the IROC IMRT Phantom. Revised MARCH 2014 The study groups are requesting that each institution keep the phantom for a period of time
Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy - Patient Specific QA
 Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy - Patient Specific QA Daliang Cao, PhD, DABR Swedish Cancer Institute, Seattle, WA VMAT plan QA methods Composite dose measurement Film & ion chamber diode array Mapcheck
Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy - Patient Specific QA Daliang Cao, PhD, DABR Swedish Cancer Institute, Seattle, WA VMAT plan QA methods Composite dose measurement Film & ion chamber diode array Mapcheck
Evaluation of Monaco treatment planning system for hypofractionated stereotactic volumetric arc radiotherapy of multiple brain metastases
 Evaluation of Monaco treatment planning system for hypofractionated stereotactic volumetric arc radiotherapy of multiple brain metastases CASE STUDY Institution: Odette Cancer Centre Location: Sunnybrook
Evaluation of Monaco treatment planning system for hypofractionated stereotactic volumetric arc radiotherapy of multiple brain metastases CASE STUDY Institution: Odette Cancer Centre Location: Sunnybrook
Quality Assurance of Helical Tomotherapy Machines
 Quality Assurance of Helical Tomotherapy Machines Wolfgang Tomé 1,2, Hazim Jaradat 2, David Westerly 1, John Fenwick 3, Nigel Orton 2, Rock Mackie 1,2, and Bhudatt Paliwal 1,2 1 Human Oncology and 2 Medical
Quality Assurance of Helical Tomotherapy Machines Wolfgang Tomé 1,2, Hazim Jaradat 2, David Westerly 1, John Fenwick 3, Nigel Orton 2, Rock Mackie 1,2, and Bhudatt Paliwal 1,2 1 Human Oncology and 2 Medical
Stereotactic radiotherapy for meningiomas using CyberKnife
 Stereotactic radiotherapy for meningiomas using CyberKnife Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Stereotactic radiotherapy for meningiomas using CyberKnife Delivering the best in care UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm
Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung
 Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung Jamie Marie Harris, MS DABR Avera McKennan Radiation Oncology September 25, 2015 Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy - Clinical Dose/Fractionation - Normal
Image Guided Stereotactic Radiotherapy of the Lung Jamie Marie Harris, MS DABR Avera McKennan Radiation Oncology September 25, 2015 Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy - Clinical Dose/Fractionation - Normal
Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL
 Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL Conflict of Interest Disclaimer Employee of Aspirus Wausau
Implementation of the 2012 ACR CT QC Manual in a Community Hospital Setting BRUCE E. HASSELQUIST, PH.D., DABR, DABSNM ASPIRUS WAUSAU HOSPITAL Conflict of Interest Disclaimer Employee of Aspirus Wausau
To Reduce Hot Dose Spots in Craniospinal Irradiation: An IMRT Approach with Matching Beam Divergence
 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY To Reduce Hot Dose Spots in Craniospinal Irradiation: An IMRT Approach with Matching Beam Divergence Alburuj R. Rahman*, Jian Z. Wang, Dr. Z. Huang, Dr. J. Montebello Department of
SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY To Reduce Hot Dose Spots in Craniospinal Irradiation: An IMRT Approach with Matching Beam Divergence Alburuj R. Rahman*, Jian Z. Wang, Dr. Z. Huang, Dr. J. Montebello Department of
Assessing Heterogeneity Correction Algorithms Using the Radiological Physics Center Anthropomorphic Thorax Phantom
 Assessing Heterogeneity Correction Algorithms Using the Radiological Physics Center Anthropomorphic Thorax Phantom David Followill, Ph.D. Associate Director Radiological Physics Center RPC History Lesson
Assessing Heterogeneity Correction Algorithms Using the Radiological Physics Center Anthropomorphic Thorax Phantom David Followill, Ph.D. Associate Director Radiological Physics Center RPC History Lesson
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Technical Review Vol. 51 No. 1 (March 2014)
 The Challenge of Innovative Cancer Treatments Enabled by Vero4DRT -Development of High-precision Dose Delivery Features for Reducing Radiation Exposure of Healthy Tissue- 76 YASUNOBU SUZUKI *1 KUNIO TAKAHASHI
The Challenge of Innovative Cancer Treatments Enabled by Vero4DRT -Development of High-precision Dose Delivery Features for Reducing Radiation Exposure of Healthy Tissue- 76 YASUNOBU SUZUKI *1 KUNIO TAKAHASHI
Quality assurance in external radiotherapy
 Quality assurance in external radiotherapy dr. Marius Laurikaitis medical physicist Oncological Hospital of Kaunas Medical University Hospital Kaunas, 2010-10-14 Acceptance and Commissioning Acceptance
Quality assurance in external radiotherapy dr. Marius Laurikaitis medical physicist Oncological Hospital of Kaunas Medical University Hospital Kaunas, 2010-10-14 Acceptance and Commissioning Acceptance
FETUS ABSORBED DOSE EVALUATION IN HEAD AND NECK RADIOTHERAPY PROCEDURES OF PREGNANT PATIENTS
 FETUS ABSORBED DOSE EVALUATION IN HEAD AND NECK RADIOTHERAPY PROCEDURES OF PREGNANT PATIENTS Etieli Camargo da Costa 1, Luiz Antonio Ribeiro da Rosa 2 Delano Valdivino Santos Batista 3 1 Instituto de Radioproteção
FETUS ABSORBED DOSE EVALUATION IN HEAD AND NECK RADIOTHERAPY PROCEDURES OF PREGNANT PATIENTS Etieli Camargo da Costa 1, Luiz Antonio Ribeiro da Rosa 2 Delano Valdivino Santos Batista 3 1 Instituto de Radioproteção
Topics covered 7/21/2014. Radiation Dosimetry for Proton Therapy
 Radiation Dosimetry for Proton Therapy Narayan Sahoo Department of Radiation Physics University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Proton Therapy Center Houston, USA Topics covered Detectors used for to
Radiation Dosimetry for Proton Therapy Narayan Sahoo Department of Radiation Physics University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Proton Therapy Center Houston, USA Topics covered Detectors used for to
Verification of micro-beam irradiation
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Verification of micro-beam irradiation To cite this article: Qiongge Li et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 573 012047 View the article online for updates
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Verification of micro-beam irradiation To cite this article: Qiongge Li et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 573 012047 View the article online for updates
Current Concepts and Trends in Spinal Radiosurgery. Edward M. Marchan
 Current Concepts and Trends in Spinal Radiosurgery Edward M. Marchan Spinal Neoplasia The spine is the most common site of skeletal metastatic disease. (70%) 40% of bony metastases involve the vertebrae
Current Concepts and Trends in Spinal Radiosurgery Edward M. Marchan Spinal Neoplasia The spine is the most common site of skeletal metastatic disease. (70%) 40% of bony metastases involve the vertebrae
