Detection of gastric cancer and its histological type based on iodine concentration in spectral CT
|
|
|
- Lora McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Detection of gastric cancer and its histological type based on iodine concentration in spectral CT Rui Li 1, Jing Li 2, Xiaopeng Wang 1, Pan Liang 1 and Jianbo Gao 1* Abstract Background: Computed tomography (CT) imaging is the most common imaging modality for the diagnosis and staging of gastric cancer. The aim of this study is was to prospectively explore the ability of quantitative spectral CT parameters in the detection of gastric cancer and its histologic types. Methods: A total of 87 gastric adenocarcinoma (43 poorly and 44 well-differentiated) patients and 36 patients with benign gastric wall lesions (25 inflammation and 11 normal), who underwent dual-phase enhanced spectral CT examination, were retrospectively enrolled in this study. Iodine concentration (IC) and normalized iodine concentration (nic) during arterial phase (AP) and portal venous phase (PP) were measured thrice in each patient by two blinded radiologists. Moreover, intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to assess the interobserver reproducibility. Differences of IC and nic values between gastric cancer and benign lesion groups were compared using Mann-Whitney U test. Furthermore, the gender, age, location, thickness and histological types of gastric adenocarcinoma were analyzed by Mann-Whitney U test or Kruskal-Wallis H test. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of IC and nic values, and the optimal cut-off value was calculated with Youden J. Results: An excellent interobserver agreement (ICC > 0.6) was achieved for IC. Notably, the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp were significantly higher in gastric cancer group (Z = 5.870, 3.894, and , respectively; P < 0.05) than those in benign lesion group. Additionally, the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp were significantly higher in poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma group (Z = 4.118, 5.637, and 2.950, respectively; P < 0.005) than those in well-differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma group. There were no statistically significant differences in the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp between age, gender, tumor thickness and tumor location. Furthermore, the area under the curve (AUC) values of ICAP, nicap, ICPP and nicpp were 0.745, 0.584, 0.662, and 0.932, respectively, for gastric cancer detection; while 0.756, 0.919, and 0.684, respectively, in discriminating poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma. Conclusion: IC values exhibited great potential in the preoperative and non-invasive diagnosis of gastric cancer and its histological types. In particular, nicpp is more effective for the identification of gastric cancer, whereas nicap is more effective in discriminating poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma. Keywords: Gastric, Adenocarcinoma, Spectral CT imaging, Iodine concentration, Histological degree * Correspondence: gaojianbo_cancer@163.com 1 Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, No. 1, East Jianshe Road, Zhengzhou , Henan, China Full list of author information is available at the end of the article The Author(s) Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 2 of 10 Background Gastric cancer is the fifth most common cancer and the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide [1]. Gastric adenocarcinoma comprises 95% of all gastric cancers [2]. The incidence and mortality rates associated with gastric adenocarcinoma are both the highest among all malignant tumors of the digestive tract in China [3, 4], representing an emerging threat to human health. The mean survival time of patients with advanced gastric cancer is less than 1 year [5]. Therefore, early detection, diagnosis and treatment are advocated to improve the clinical outcomes and quality of life in patients with gastric cancer. Histological grading has been considered a predictor of lymph node metastasis and poor survival in gastric cancer [6]. Hence, accurate assessment of histological types is crucial for individualizing patient management [7]. Gold standard for the diagnosis of gastric cancer and its histological types can be obtained through preoperative endoscopic biopsy in clinical practice. However, endoscopic biopsy is an invasive procedure, and may posses unavoidable sampling bias and incoincident with histological diagnosis during surgery [8]. As compared to invasive endoscopic biopsy, preoperative imaging technique offers many advantages as its non-invasive detection and histologic evaluation of tumors, as well as the assessment of regional or distant lymph node metastasis. Conventional contrast-enhanced CT imaging is the first-line imaging modality for the detection and staging of gastric cancer. Its combination with multiple planar reconstruction and virtual endoscopy has proven to be effective for the diagnosis of gastric wall invasion in patients with gastric cancer [9]. However, this technique relies solely on the morphological criteria, and lack of parameters for quantitative analysis. Spectral CT provides material decomposition (MD) images that can quantitatively map the iodine concentration (IC) in the enhanced images of tissues. This IC value has been found to be strongly correlated with the actual IC in the phantom [10]. Preliminary studies have reported the use of IC value in differentiating benign from malignant lesions, evaluating tumor, node, and metastasis (TNM) staging and determining the efficacy of anticancer therapy [11 16]. However, to the best of our knowledge, only a few studies have employed IC value in discriminating the histological types of gastric adenocarcinoma [12, 17], and the results are inconsistent with respect to arterial phase (AP) and portal venous phase (PP). Indeed, the application of IC values for the discrimination of gastric cancer and its histological types is still in the exploratory stage. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of IC values for the detection of gastric cancer and its histological type, and to investigate their correlations with clinical data. Methods Patients Ethical approval was obtained from the institutional ethics review board, but the requirement of informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study. A total of 153 patients with gastric cancer and 45 patients with preoperative endoscopic biopsy-diagnosed benign gastric wall lesions (30 gastric inflammation and 15 normal gastric wall) who underwent spectral CT scans and surgical intervention were retrospectively enrolled from June 2013 to June Considering that the conditions of gastric wall beyond the sampling site are not accessible, the patients with gastric inflammation and normal gastric wall were grouped together. The exclusion criteria included pathologically-confirmed non-adenocarcinomas, history of preoperative therapy (such as radiotherapy and chemotherapy), severe artifacts on CT images, non-measurable lesions and incomplete clinical data. All the included patients completed the entire CT exam, and their gastric cavities were well distended on cross-sectional CT images without artifacts, and the gastric adenocarcinomas were clearly distinguished from normal gastric wall. Clinical data of patients, such as age, gender tumor thickness, tumor location and tumor differentiation were also documented. CT scan protocol After fasting for 8 h, patients were asked to consume 1000 ml of warm water and then injected with 20 mg of scopolamine (Specifications: 10 mg/ml; Hangzhou Minsheng Pharmaceutical Group Co.,Ltd.Hangzhou,China) 10 min prior to examination. Patients were placed in the supine position, and scanned on GE Discovery CT750 HD scanner (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) with gemstone spectral imaging (GSI) mode. Dual-energy CT images were acquired using a single x-ray source switches rapidly between 80 kvp and 140 kvp at less than 5 millisecond speed. The other acquisition parameters were as follows: 5 mm slice thickness, 40 mm detector coverage, helical pitch, 630 ma tube current, 0.6 s rotation time, matrix, and cm field of view. AP and PP contrast-enhanced CT scans were performed with 40 and 70 s delays, respectively, after intravenous injection of ml (1.5 ml per kg of body weight) iodinated contrast material (Ultravist 370, Bayer Schering Pharma, Berlin, Germany) at a rate of 3.0 ml/s through pump injector (Ulrich REF XD 2060-Touch, Ulrich Medical, Ulm, Germany). Contrast-enhanced CT images were reconstructed by using a standard kernel and 2.5 mm section thickness. The value of CT dose index volume (CTDIvol) for dual energy spectral mode in the abdomen was mgy. Image analysis All data were transferred to GE AW 4.6 workstation (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA), and interpreted
3 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 3 of 10 by two radiologists with 6 and 10 years of experience in gastrointestinal radiology. Data analysis was carried out independently using GSI Viewer software (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) with a standard soft-tissue window (WL 40 and WW 400). Regions of interest (ROI) were drawn on the solid part of the tumor (about two-thirds of the area), with the exclusion of peripheral fat, visible vessel, calcification and cystic/necrotic areas. A circular ROI was placed into the aortic arch within the same CT slice, after the exclusion of calcified atherosclerotic plaque. Subsequently, the thickness of tumour was measured and recorded. In order to reduce the individual variation between patients, IC value was normalized by dividing the IC of lesion to that of aorta (nic=iclesion/icaorta) [12]. All IC values were repeatedly measured three times, and the average value was then calculated. Similarly, ROI of the three gastric regions (fundus, body and antrum) was measured for three times, and their average values were calculated. Statistical analysis All statistical analyses were performed with MedCalc v (Frank Schoonjans, Broekstraat 52,B-9030 Mariakerke, Belgium). P values of less than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Interobserver agreement for IC and nic values was evaluated using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), which classified as poor (< 0.40), fair ( ), good ( ), or excellent ( ). The values of IC and nic at both AP and PP were expressed as median (P25, P75). Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the IC values between cancer and benign gastric wall group, as well as the IC values among age, gender, tumor thickness and histological types. Kruskal-Wallis H test was used to compare the differences of IC and nic values between different tumour sites, including funtus, body and antrum. Furthermore, ROC curves were used to evaluate the diagnostic values of IC and nic in discriminating gastric cancer and its histological type. Results Clinical data A total of 87 (57%) out of 153 gastric cancer patients and 36 (80%) out of 45 patients with benign gastric wall lesions were ultimately included in the study. Among the excluded patients, 18 of them were diagnosed as non-adenocarcinoma by surgical pathology, 12 patients with poor image quality (severe artifacts) evaluated by two radiologists in consensus, and 8 patients received preoperative therapy. A further 9 patients with benign gastric wall lesions and 28 gastric cancer patients were excluded from analysis due to the non-measurable lesions on enhanced CT images. Overall, clinical data of 87 gastric adenocarcinoma patients and 36 patients with benign gastric wall lesions were used for final analyses. The clinical characteristics of all included patients are summarized in Table 1, while the images of gastric adenocarcinoma patients at different sites are shown in Fig. 1. Interobserver agreement The interobserver agreement of IC measurement between two readers was ranked from good to excellent. In particular, the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp in were 0.664, 0.755, and 0.980, respectively, in gastric cancer group and 0.694, 0.713, 0.897, 0.910, respectively, in benign gastric wall lesions group. The mean difference between the two observers was used for further analysis. Comparison of IC and nic values between benign gastric wall lesions and gastric cancer As shown in Fig. 2 and Table 2, the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp in benign gastric wall lesions group were (7.497, ) 100 μg/ml, (14.448, ) 100 μg/ml, (0.076, 0.141) and (0.068, 0.328), respectively. On the other hand, the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp in gastric cancer group were (11.508, ) 100 μg/ml, (18.623, ) 100 μg/ml, (0.105, 0.141) Table 1 Clinical characteristics of 87 patients with gastric adenocarcinomas and 36 patients with benign gastric wall lesions Characteristics Statistics(mean, range) Cancer peoples 87 Age (years) 55 (29 74) Gender(M/F) 60/27 Tumor thickness (cm) 3.1 ( ) Tumor site Fundus 29 (33.3%) Body 28 (32.3%) Antrum 27 (31%) Whole stomach 3 (3.4%) Histological differentiation degree Highly differentiated adenocarcinoma 4 (4.6%) Moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma 40 (46.0%) Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma 43 (49.4%) Benign lesion peoples 36 Age (years) 53 (32 72) Gender(M/F) 22/14 Gastric wall Inflammation 25(69%) Normal 11(31%) Abbreviations:M Male, F Female
4 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 4 of 10 Fig. 1 Spectral CT images of patients with poorly and moderately differentiated gastric adenocarcinomas at different sites. a AP image shows moderate enhancement of fundal wall thickening in a 67-year-old male patient. The maximum thickness is mm, and ICAP is (100 μg/ml). b PP image demonstrates a ICPP value of (100 μg/ml) in the same patient. c Photomicrograph of histological specimen indicates a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma [hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain; original magnification 100]. d AP image shows irregular wall thickening of the gastric body in a 41-year-old female patient. The maximum thickness is mm, and ICAP is (100 μg/ml). e PP image demonstrates a ICPP value of (100 μg/ml) in the same patient. f Photomicrograph of histological specimen indicates a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. (H&E stain; original magnification 100). g AP image shows antrum wall thickening with surface ulcers in a 56-year-old male patient. The maximum thickness is mm and ICAP is (100 μg/ml). h PP image demonstrates a ICPP value of (100 μg/ml) in the same patient. i Photomicrograph of histological specimen indicates a moderately differentiated adenocarcinoma (H&E stain; original magnification 100) Fig. 2 Differences in IC and nic values between between gastric cancer and benign lesion groups. Box-and-whisker plots (box: 25, 75%; centreline: medium; whisker: min, max) reveal that (a) ICAP, ICPP, (b) nicap and nicpp of gastric adenocarcinoma group were significantly higher than benign gastric wall group, with P < , P = , P = and P < , respectively
5 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 5 of 10 Table 2 Comparison of IC and nic values between gastric cancer and benign lesion groups Group Number ICAP(100 μg/ml) ICPP(100 μg/ml) nicap nicpp Benign (7.497, ) Cancer (11.508, ) (14.448, ) (18.623, ) (0.076, 0.141) (0.105, 0.141) (0.068, 0.328) (0.392, 0.453) Z value P value < = = < Abbreviations: ICAP arterial phase iodine concentration, ICPP portal venous phase iodine concentration, nicap normalized arterial phase iodine concentration, nicpp normalized portal venous phase iodine concentration and (0.392, 0.453), respectively. Notably, these values were significantly higher in gastric cancer group than those in benign gastric wall lesions group [Z =5.870 (ICAP), (ICPP), (nicap) and (nicpp); P <0.005]. Comparison of IC and nic values between gender, age, thickness, location and histological types of gastric adenocarcinoma As compared to female patients, the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp were slightly higher in male patients (Table 3). However, none of these differences were statistically significant [Z = (ICAP), (ICPP), (nicap) and (nicpp); P > 0.05]. All gastric cancer patients were divided into young ( 55 years old) and older (> 55 years old) groups according to the mean age of 55 years old. The values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp in young group were slightly higher than those in older group, but the differences were not statistically significant (Z = 0.613, 1.066, and 0.583, respectively; P > 0.05). In addition, the patients were divided into small ( 3.1 cm) and large (> 3.1 cm) tumor groups according to the mean thickness of 3.1 cm. The values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp in small tumor group were slightly higher than those in large tumor group, but not significantly different (Z = 1.083, 0.706, and 1.272, respectively; P > 0.05). Similarly, the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp were not significantly different among the three tumor location groups (H values = 0.205, 4.221, and 4.836, respectively; P > 0.05). Furthermore, the moderately and well-differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma groups were combined into a single group, due to the limited numbers of cases in well-differentiated tumor group (n =4). As shown in Figure 3, the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp were significantly higher in poorly differentiated group than those in well-differentiated group (Z =4.118, 5.637, and 2.950, respectively; P <0.05). Diagnostic accuracy of IC values in detecting gastric cancer The AUC values of ICAP, nicap, ICPP and nicpp for the gastric cancer detection were 0.745, 0.584, and 0.923, respectively (Fig. 4 and Table 4). Of note, nicpp demonstrated the greatest ability in discriminating gastric cancer. Besides, the optimal cut-off values of ICAP, nicap, ICPP and nicpp were , 0.089, and 0.364, respectively. The sensitivities of ICAP, nicap, ICPP and nicpp were 95.40, 96.55, and 91.95%, respectively; while the specificities were 58.33, 37.04, and 87.96%, respectively. Diagnostic accuracy of IC values in discriminating the histological types of gastric adenocarcinoma The AUC values of ICAP, nicap, ICPP, and nicpp in discriminating poorly and well-differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma were 0.756, 0.919, and 0.684, respectively (Fig. 4 and Table 4). Of note, nicap demonstrated the greatest ability in discriminating the histological types of gastric adenocarcinoma, whereas nicpp showed the lowest. The optimal cut-off values of ICAP, nicap, ICPP and nicpp were , 0.125, and 0.431, respectively. The sensitivities of ICAP, nicap, ICPP, and nicpp were 53.49, 79.07, and 60.47%, respectively; while the specificities were 93.18, 97.73, and 79.55%, respectively. Discussion Spectral CT extends the capabilities of conventional CT, which uses a rapid kilovoltage switching technique to acquire monochromatic images of tissues, in a similar way to those obtained from a single X-ray source [18 20]. Subsequent elemental decomposition analysis can be performed to obtain iodinated contrast attenuation map, thereby allowing iodine density to be calculated [21, 22]. As a result, this can assist the radiologists to address diagnostic errors. Hence, the present study investigated the role of quantitative spectral CT parameters for the discrimination of gastric cancer and its histological types, and examined their correlations with clinical features. The major findings of this study were as follow: (1) IC values in gastric cancer were higher than benign gastric wall lesions, in which nicpp demonstrated the greatest diagnostic efficacy; (2) IC values in poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma were higher than in well-differentiated caners, in which nicap showed the highest diagnostic efficacy; and (3) IC values were not significantly different between age, gender, tumor thickness and tumor location.
6 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 6 of 10 Table 3 Comparison of IC and nic values between gender, age, location, thickness and histological types of gastric adenocarcinoma Clinical features Number of cases ICAP (100 μg/ml) ICPP (100 μg/ml) nicap nicpp Gender Male (11.511, 15,780) Female (11.456, ) (18.843, ) (18.635, ) (0.108, 0.147) (0.105, 0.136) (0.398, 0.462) (0.389, 0.443) Z value P value > 0.05 > 0.05 > 0.05 > 0.05 Age Young( 55 y) (11.483, ) Older (> 55 y) (11.450, ) (18.868, ) (18.780, ) (0.108, 0.153) (0.107, 0.136) (0.400, 0.455) (0.389, 0.463) Z value P value > 0.05 > 0.05 > 0.05 > 0.05 Sites Fundus (11.543, ) Body (11.465, ) Antrum (11.930, ) (18.742, ) (19.815, ) (19.253, ) (0.106, 0.147) (0.115, 0.151) (0.111,0.141) (0.394, 0.435) ( ) (0.399, 0.472) H value P value > 0.05 > 0.05 > 0.05 > 0.05 Thickness Small ( 3.1 cm) Large (> 3.1 cm) (11.890, ) (11.111, ) (19.022, ) (18.783, ) (0.109, 0.142) (0.107, 0.147) (0.393, 0.468) (0.396, 0.433) Z value P value > 0.05 > 0.05 > 0.05 > 0.05 Differentiation Poorly (13.168, ) Well-differentiated (11.240, ) (20.030, ) (17.270, ) (0.127, 0.155) (0.100, 0.113) (0.411, 0.472) (0.391, 0.431) Z value P value < < < = Abbreviations: ICAP arterial phase iodine concentration, ICPP portal venous phase iodine concentration, nicap normalized arterial phase iodine concentration, nicpp normalized portal venous phase iodine concentration Iodine concentration reflects the vessel density and the blood volume in different tissue regions during a contrast-enhanced CT scan. Tang et al. [15] reported a high consistency between spectral CT-measured IC and actual IC, and thus it is a useful parameter to indicate the physiological function. The growth and progression of solid tumors depend upon the formation of new blood vessels, which is different from normal tissues or benign lesions. Several studies have reported that CT imaging is useful for distinguishing small hepatocellular carcinoma from other hepatic lesions [23, 24], small intrahepatic mass-forming cholangiocarcinoma from small liver abscess [25], malignant from benign pulmonary nodules [26], and gastric cancer from benign gastric mucosal lesions [11]. Indeed, the quantitative IC measurement is significantly higher in cancerous lesions compared to benign lesions, and its accuracy is greater than that of conventional CT. In addition, Liu et al. examined the patients with papillary thyroid cancer, and their results suggested that nic measured during AP and PP are significantly higher in metastatic lymph nodes as compared to benign lesions [27]. Taken together, our results
7 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 7 of 10 Fig. 3 Differences in IC and nic values between poorly and well-differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma groups. Box-and-whisker plots (box: 25, 75%; centreline: medium; whisker: min, max) indicate that (a) ICAP, ICPP, (b) nicap and nicpp of poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma group were significantly higher than well-differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma group, with P <0.0001,P <0.0001,P < and P = , respectively Fig. 4 ROC curves for ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp. The ROC curves of (a) ICAP, ICPP, (b) nicap and nicpp between gastric cancer and benign gastric wall lesions groups. nicpp has the highest AUC value, followed by ICAP, ICPP and nicap. The ROC curves of (c) ICAP,ICPP,(d) nicap and nicpp between poorly and well-differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma groups. nicap has the highest AUC value, followed by ICPP, ICAP and nicpp
8 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 8 of 10 Table 4 The ROC curves of IC and nic values ROC ICAP ICPP nicap nicpp Cancer AUC sensitivity 95.40% 98.85% 96.55% 91.95% specificity 58.33% 43.52% 37.04% 87.96% Optimum cutoff values Youden index Poorly differentiated AUC sensitivity 53.49% 69.77% 79.07% 60.47% specificity 93.18% 90.91% 97.73% 79.55% Optimum cutoff values Youden index Abbreviations: ROC Receiver operating characteristic curves, AUC area under the curve, ICAP arterial phase iodine concentration, ICPP portal venous phase iodine concentration, nicap normalized arterial phase iodine concentration, nicpp normalized portal venous phase iodine concentration are consistent with the aforementioned studies, in which the values of IC are higher in cancer than in benign lesions, due to the increased angiogenesis during tumor development, leading to their enhancement in CT scan [28]. The degree of tumor differentiation is a predictive and prognosis biomarker for patients with gastric cancer [29], which can be distinguished quantitatively by dual-energy spectral CT (DESCT). Pan et al. [12] evaluated the clinical usefulness of DESCT in the classification and staging of gastric cancer. Their findings indicated that monochromatic images obtained from DESCT can be used to improve the accuracy of preoperative staging, and quantitative IC measurement is helpful in distinguishing the poorly and well-differentiated gastric carcinoma, as well as the metastatic and non-metastatic lymph nodes. A similar pattern of results was obtained, where IC and nic values were significantly lower in well-differentiated gastric cancer compared to poorly differentiated ones, which can be explained by the differences in tumor angiogenesis. Du et al. [30] have suggested that vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and microvessel density (MVD) are closely correlated with histological degree, in which their levels are reduced in early stage gastric carcinoma compared to progressive carcinoma. Chang et al. [31] have reported that MVD is significantly associated with poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma. Moreover, Hu et al. [32] demonstrated that the nic value of three-phase enhanced CT scan is positively correlated with MVD. Additionally, Chen et al. reported that poorly differentiated gastric cancer exhibited higher MVD and nic value, and a positive correlation between them [33]. A CT perfusion study on gastric cancer has revealed that the lower the degree of tumor differentiation, the higher the permeability surface area [34]. These findings indicate that poorly differentiated tumors may increase vasopermeability and immature endothelial cells, thereby explaining the high values of IC and MVD in gastric patients with poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. nic can minimize the effects of individual variability, such as contrast dose, injection rate and individual differences in circulation, and thereby it is more efficacy than IC. Both nicap and nicpp were found to be significantly different between gastric cancer group and benign gastric wall lesions group, as well as between poorly differentiated group and well-differentiated group. In particular, nicap demonstrated a higher efficiency in the diagnosis of poorly differentiated gastric adenocarcinoma, with AUC, sensitivity and specificity of 0.896, and 95.45%, respectively. Meanwhile, nicpp showed a higher efficacy for the detection of gastric cancer, with AUC, sensitivity and specificity of 0.923, and 87.96%, respectively. These results can be partly explained by different functional roles of nicap and nicpp. nicap mainly reflects the capillary density and the blood supply of gastric carcinomas, while nicpp may indicate the flow of blood supply and the retention of contrast agent in intrasvasular and extravascular space following AP. It is noticeable that venous phase enhancement is more prominent in gastric cancer, suggesting that PP enhancement characteristics are more useful for the detection of gastric cancer. Besides, the reason why PP is less effective than AP in distinguishing histological types may be due to the influence of blood flow. In addition, nicpp has been reported to exert a high sensitivity in differentiating malignant gastric mucosal lesions from normal gastric mucosa [11]. Furthermore, studies on the diagnostic efficacy of tumor differentiation degree are inconsistent [35, 36], which may be due to the different biological behaviors of tumors and degrees of differentiation. A previous study has found that the values of IC and nic of poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma are not significantly different compared to those of moderately and well-differentiated adenocarcinomas in AP [17]. These inconsistent results may be attributed to different patient populations and scan protocol. In that study, patients were subjected to triple-phase CT imaging, including AP at 25 s, which are different from ours. In sum, DESCT is more useful in evaluating gastric cancer with a delay AP scan protocol. Apart from that, Karim et al. [37] reported that younger age is correlated with the histology grade of gastric cancer. However, the histology grade is not correlated with gender and tumor location [38]. In addition, Wang et al. [38] demonstrated that tumour size is a prognostic factor in patients with advanced gastric cancer. In the present study, no significant differences were found in the values of ICAP, ICPP, nicap and nicpp between age, gender, tumor thickness and tumor location. There are some unavoidable limitations in this preliminary study. First, DESCT scans were performed on the
9 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 9 of 10 first-generation Discovery CT750 HD scanner with a fixed ma value of 600 ma. This yielded a CTDIvol of mgy, which is considerably high in current clinical practise settings. With the introduction of the second-generation CT750 HD scanner, the radiation dose has been reduced to 30% in GSI mode, and further dose reduction is forthcoming. Second, this is a retrospective study, and the sample size was relatively small, especially the number of patients with well-differentiated adenocarcinoma was too low to to allow a statistical comparison with moderately and poorly differentiated ones. Third, only patients with gastric adenocarcinoma were enrolled in this study, patients with other histological types of gastric cancer were not taken into account. Moreover, it was difficult to obtain pathologic confirmation of the entire gastric wall in non-cancer patients, and the patients with gastric inflammation and normal gastric wall were grouped together. Finally, since DESCT is a relatively new technique for gastric cancer, it may hinder the adaptation process based on these preliminary results. Conclusions In conclusion, this preliminary study compared the quantitative spectral CT parameters between benign lesion and gastric cancer groups, as well as different histological types of gastric adenocarcinoma. IC values can be used to accurately identify gastric cancer and quantitatively assess the degree of differentiation, without being affected by age, gender, tumor thickness and tumor location. These findings may improve the preoperative staging of gastric cancer, and lay the foundations for modern functional imaging in oncology. However, further studies with larger sample sizes are needed to draw a firm conclusion. Abbreviations AP: Arterial phase; AUC: Area under the curve; CT: Computed tomography; CTDIvol: CT dose index volume; DEsCT: Dual-energy spectral CT; IC: Iodine concentration; ICC: Intraclass correlation coefficient; MD: Material decomposition; MVD: Microvessel density; nic: Normalized iodine concentration; PP: Portal venous phase; ROC: Receiver-operating characteristics analysis; ROI: Regions-of-interest; SD: Standard deviation; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor Acknowledgements None. Funding National Natural and Science Fund of China (NO ). Availability of data and materials Please contact author for data requests. Authors contributions RL: manuscript preparation, literature research, data analysis, statistical analysis and manuscript editing; JL: data acquisition and statistical analysis; PL: literature research and data analysis; XP W: data acquisition; JB G: study conception and design, manuscript review and guarantor of integrity of the entire study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Ethics approval and consent to participate The study protocol was approved by Institutional Review Board of our institution, and written informed consent was obtained from each participant in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication Not applicable. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Publisher s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Author details 1 Department of Radiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, No. 1, East Jianshe Road, Zhengzhou , Henan, China. 2 Department of Radiology, the Affiliated Cancer Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Henan Cancer Hospital, No. 127, Dongming Road, Zhengzhou , Henan, China. Received: 24 August 2018 Accepted: 29 October 2018 References 1. Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65: Dicken BJ, Bigam DL, Cass C, et al. Gastric adenocarcinoma: review and considerations for future directions. Ann Surg. 2005;241: Wong BC, Lam SK, Wong WM, et al. Helicobacter pylori eradication to prevent gastric cancer in a high-risk region of China: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2004;291: Yan SY, Hu Y, Fan JG, et al. Clinicopathologic significance of HER-2/neu protein expression and gene amplification in gastric carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17: Bang YJ, Kang YK, Kang WK, et al. Phase II study of sunitinib as second-line treatment for advanced gastric cancer. Investig New Drugs. 2011;29: Sekiguchi M, Oda I, Taniguchi H, et al. Risk stratification and predictive riskscoring model for lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2016;51: Sasaki T, Koizumi W, Higuchi K, et al. Therapeutic strategy for type 4 gastric cancer from the clinical oncologist standpoint. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2007; 34: Liu S, Liu Song, Ji C, et al. Application of CT texture analysis in predicting histopathological characteristics of gastric cancers. Eur Radiol. 2017;27: Shen Y, Kang HK, Jeong YY, et al. Evalution of early gastric cnncer at multidetector CT with multiplanar reformation and virtual endoscopy. Radiographics. 2011;31: Lv P, Lin X, Gao J, Chen K. Spectral CT: preliminary studies in the liver cirrhosis. Korean J Radiol. 2012;13: Meng X, Ni C, ShenY HX, et al. Differentiating malignant from benign gastric mucosal lesions with quantitative analysis in dual energy spectral computed tomography: Initial experience. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96:e Pan Z, Pang L, Ding B, et al. Gastric cancer staging with dual energy spectral CT imaging. PLoS One. 2013;8:e Li C, Shi C, Zhang H, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis for preoperative invasion depth of gastric Cancer with dual-energy spectral CT imaging. Acad Radiol. 2015;22: Li C, Zhang S, Zhang H, et al. Using the K-nearest neighbor algorithm for the classification of lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer. Compu Math Methods Med. 2012;2012: Tang L, Li ZY, Li ZW, et al. Evaluating the response of gastric carcinomas to neoadjuvant chemotherapy using iodine concentration on spectral CT: a comparison with pathological regression. Clin Radiol. 2015;70: Li J, Fang M, Wang R, et al. Diagnostic accuracyof dual-energy CT-based nomograms to predict lymph node. Eur Radiol /s [Epub ahead of print]. 17. Chen LH, Xue YJ, Duan Q. Spectral CT imaging in quantitative evaluation on histological degree of gastric cancers. Chin J Med Imaging Technol. 2013;29: Chinese. 18. Hurrell MA, Butler AP, Cook NJ, et al. Spectral Hounsfield units: a new radiological concept. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:1008e Tang L, Zhang XP, Sun YS, et al. Spectral CT in the demonstration of the gastrocolic ligament: a comparison study. Surg Radiol Anat. 2013;35:539e45.
10 Li et al. Cancer Imaging (2018) 18:42 Page 10 of Li XH, Zhao R, Liu B, et al. Determination of urinary stone composition using dual-energy spectral CT: initial in vitro analysis. Clin Radiol. 2013;68:e370e Matsumoto K, Jinzaki M, Tanami Y, et al. Virtual monochromatic spectral imaging with fast kilovoltage switching: improved image quality as compared with that obtained with conventional 120-kVp CT. Radiology. 2011;259: Silva AC, Morse BG, Hara AK, et al. Dual-energy (spectral) CT: applications in abdominal imaging. Radiographics. 2011;31: Lv P, Lin XZ, Li J, et al. Differentiation of small hepatic hemangioma from small hepatocellular carcinoma: recently introduced spectral CT method. Radiology. 2011;259: Wang Q, Shi G, Qi X, et al. Quantitative analysis of the dual-energy CT virtual spectral curve for focal liver lesions characterization. Eur J Radiol. 2014;83: Kim JE, Kim HO, Bae K, et al. Differentiation of small intrahepatic massforming cholangiocarcinoma from small liver abscess by dual source dualenergy CT quantitative parameters. Eur J Radiol. 2017;92: Zhang Y, Cheng J, Hua X, et al. Can spectral CT imaging improve the differentiation between malignant and benign solitary pulmonary nodules? PLoS One. 2016;11:e Liu X, Ouyang D, Li H, et al. Papillary thyroid cancer: dual-energy spectral CT quantitative parameters for preoperative diagnosisof metastasis to the cervical lymph nodes. Radiology. 2015;275: Miles KA. Tumour angiogenesis and its relation to contrast enhancement on computed tomography: a review. Eur J Radiol. 1999;30: Haist T, Pritzer H, Pauthner M, et al. Prognostic risk factors of early gastric cancer-a western experience. Langenbeck's Arch Surg. 2016;401: Du JR, Jiang Y, Zhang YM, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor and microvascular density in esophageal and gastric carcinomas. World J Gastroenterol. 2003;9: Chang Y, Niu W, Lian PL, et al. Endocan-expressing microvessel density as a prognostic factor for survival in human gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22: Hu S, Huang W, Chen Y, et al. Spectral CT evaluation of interstitial brachytherapy in pancreatic carcinoma xenografts: preliminary animal experience. Eur Radiol. 2014;24: Chen XH, Ren K, Liang P, et al. Spectral computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer: can iodine concentration non-invasively assess angiogenesis? World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23: Lee DH, Kim SH, Joo I, et al. CT perfusion evaluation of gastric cancer: correlation with histologic type. Eur Radiol. 2018;28: Lin LY, Zhang Y, Suo ST, et al. Correlation between dual-energy spectral CT imaging parameters and pathological grades of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Radiol. 2018;73:412.e Chuang-Bo Y, Tai-Ping H, Hai-Feng D, et al. Quantitative assessment of the degree of differentiation in colon cancer with dual-energy spectral CT. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017;42: Karim S. Clinicopathological and p53 gene alteration comparison between young and older patients with gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014; 15: Wang HM, Huang CM, Zheng CH, et al. Tumor size as a prognostic factor in patients with advancer gastric cancer in the lower third of the stomach. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:
Fused monochromatic imaging acquired by single source dual energy CT in hepatocellular carcinoma during arterial phase: an initial experience
 Original Article Fused monochromatic imaging acquired by single source dual energy CT in hepatocellular carcinoma during arterial phase: an initial experience Shun-Yu Gao, Xiao-Peng Zhang, Yong Cui, Ying-Shi
Original Article Fused monochromatic imaging acquired by single source dual energy CT in hepatocellular carcinoma during arterial phase: an initial experience Shun-Yu Gao, Xiao-Peng Zhang, Yong Cui, Ying-Shi
Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis
 GE Healthcare Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis CT clinical case study lesion characterization Desiree Morgan, MD Vice Chair of Clinical Research Professor
GE Healthcare Gemstone Spectral Imaging quantifies lesion characteristics for a confident diagnosis CT clinical case study lesion characterization Desiree Morgan, MD Vice Chair of Clinical Research Professor
Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches
 Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
Dual-Energy CT: The Technological Approaches Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org Disclosure
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging Decisions Start Here SM
 Owing to its high resolution and wide anatomic coverage, dynamic first-pass perfusion 320-detector-row CT outperforms PET/CT for distinguishing benign from malignant lung nodules, researchers from Japan
Owing to its high resolution and wide anatomic coverage, dynamic first-pass perfusion 320-detector-row CT outperforms PET/CT for distinguishing benign from malignant lung nodules, researchers from Japan
Liver, Liver Fat, Fibrosis and HCC Screening with DECT
 Liver, Liver Fat, Fibrosis and HCC Screening with DECT Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org
Liver, Liver Fat, Fibrosis and HCC Screening with DECT Dushyant Sahani, M.D Director of CT Associate Professor of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School Email-dsahani@partners.org
Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma in China
 1663 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2016; 7(12): 1663-1667. doi: 10.7150/jca.15216 Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous
1663 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2016; 7(12): 1663-1667. doi: 10.7150/jca.15216 Prognostic Value of Plasma D-dimer in Patients with Resectable Esophageal Squamous
8/3/2016. Consultant for / research support from: Astellas Bayer Bracco GE Healthcare Guerbet Medrad Siemens Healthcare. Single Energy.
 U. Joseph Schoepf, MD Prof. (h.c.), FAHA, FSCBT-MR, FNASCI, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director, Division of Cardiovascular Imaging Consultant for / research support from: Astellas
U. Joseph Schoepf, MD Prof. (h.c.), FAHA, FSCBT-MR, FNASCI, FSCCT Professor of Radiology, Medicine, and Pediatrics Director, Division of Cardiovascular Imaging Consultant for / research support from: Astellas
Diffuse high-attenuation within mediastinal lymph nodes on non-enhanced CT scan: Usefulness in the prediction of benignancy
 Diffuse high-attenuation within mediastinal lymph nodes on non-enhanced CT scan: Usefulness in the prediction of benignancy Poster No.: C-1785 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Diffuse high-attenuation within mediastinal lymph nodes on non-enhanced CT scan: Usefulness in the prediction of benignancy Poster No.: C-1785 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer
 He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples. VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė
 Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė Stomach Computerized Tomography gastroente rologist Oncologist
Stomach Computerized Tomography indications, technique, examples VUH SK Radiology and nuclear medicine center Radiologist Dileta Rutkauskaitė Stomach Computerized Tomography gastroente rologist Oncologist
Spectral CT imaging as a new quantitative tool? Assessment of perfusion defects of pulmonary parenchyma in patients with lung cancer
 Original Article Spectral CT imaging as a new quantitative tool? Assessment of perfusion defects of pulmonary parenchyma in patients with lung cancer Ying-Shi Sun, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Yong Cui, Lei Tang, Xiao-Ting
Original Article Spectral CT imaging as a new quantitative tool? Assessment of perfusion defects of pulmonary parenchyma in patients with lung cancer Ying-Shi Sun, Xiao-Yan Zhang, Yong Cui, Lei Tang, Xiao-Ting
Comparison of gastric vascular anatomy by monochromatic and polychromatic dual-energy spectral computed tomography imaging
 Research Report Comparison of gastric vascular anatomy by monochromatic and polychromatic dual-energy spectral computed tomography imaging Journal of International Medical Research 2014, Vol. 42(1) 26
Research Report Comparison of gastric vascular anatomy by monochromatic and polychromatic dual-energy spectral computed tomography imaging Journal of International Medical Research 2014, Vol. 42(1) 26
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Abdominal CT protocol s influence on postoperative follow-up of lesions detection associated with gastrointestinal tumours
 Original Article on Translational Imaging in Cancer Patient Care Abdominal CT protocol s influence on postoperative follow-up of lesions detection associated with gastrointestinal tumours Jing-Feng Zhang
Original Article on Translational Imaging in Cancer Patient Care Abdominal CT protocol s influence on postoperative follow-up of lesions detection associated with gastrointestinal tumours Jing-Feng Zhang
Ultrasound. Computed tomography. Case studies. Utility of IQon Spectral CT in. cardiac imaging
 Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Ultrasound Computed tomography Case studies Utility of IQon Spectral CT in cardiac imaging Cardiac imaging is a challenging procedure where it is necessary to image a motion-free heart. This requires a
Pre-Operative Assesment of Lymphocyte Monocyte Ratio in Ovarian Neoplasms. Athulya Krishna Kumar K.T*, Krishnaraj Upadhyaya and Vineeth G Nair
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1919 Pre-Operative Assesment of Lymphocyte Monocyte Ratio in Ovarian Neoplasms Athulya Krishna Kumar K.T*, Krishnaraj Upadhyaya and Vineeth G Nair Department of Pathology,
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1919 Pre-Operative Assesment of Lymphocyte Monocyte Ratio in Ovarian Neoplasms Athulya Krishna Kumar K.T*, Krishnaraj Upadhyaya and Vineeth G Nair Department of Pathology,
Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 560712, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/560712 Case Report Five-Year Survival after Surgery for Invasive Micropapillary Carcinoma of the Stomach Shigeo
Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer
 IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer To cite this article: J Sembiring et al 2018
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science PAPER OPEN ACCESS Diagnostic test pepsinogen I and combination with tumor marker CEA in gastric cancer To cite this article: J Sembiring et al 2018
Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose??
 Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose?? William P. Shuman MD, FACR FSCBTMR Department of Radiology University of Washington SCBTMR Annual Course Boston, October 10, 2012 Conflict of Interest
Dual Energy CT Aortography: Can We Reduce Iodine Dose?? William P. Shuman MD, FACR FSCBTMR Department of Radiology University of Washington SCBTMR Annual Course Boston, October 10, 2012 Conflict of Interest
Evaluation of energy spectrum CT for the measurement of thyroid iodine content
 Shao et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2016) 16:47 DOI 10.1186/s12880-016-0151-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of energy spectrum CT for the measurement of thyroid iodine content Weiguang Shao, Jingang
Shao et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2016) 16:47 DOI 10.1186/s12880-016-0151-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Evaluation of energy spectrum CT for the measurement of thyroid iodine content Weiguang Shao, Jingang
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule
 Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Original Article Comparison of three mathematical prediction models in patients with a solitary pulmonary nodule Xuan Zhang*, Hong-Hong Yan, Jun-Tao Lin, Ze-Hua Wu, Jia Liu, Xu-Wei Cao, Xue-Ning Yang From
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Index. Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Surg Oncol Clin N Am 16 (2007) 465 469 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adjuvant therapy, preoperative for gastric cancer, staging and, 339 B Breast cancer, metabolic
Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer
 Original Article Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer Gil-Su Jang 1 *, Min-Jeong Kim 2 *, Hong-Il Ha 2, Jung Han Kim
Original Article Comparison of RECIST version 1.0 and 1.1 in assessment of tumor response by computed tomography in advanced gastric cancer Gil-Su Jang 1 *, Min-Jeong Kim 2 *, Hong-Il Ha 2, Jung Han Kim
Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): 321-326 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info The logistic regression analysis of ultrasonographic features in differential diagnosis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis
Biomedical Research 2014; 25(3): 321-326 ISSN 0970-938X http://www.biomedres.info The logistic regression analysis of ultrasonographic features in differential diagnosis of cervical lymph nodes metastasis
International Journal of Current Medical Sciences- Vol. 6, Issue,, pp , June, 2016 A B S T R A C T
 ISSN: 2320-8147 International Journal of Current Medical Sciences- Vol. 6, Issue,, pp. 122-126, June, 2016 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN HEPATIC METASTASES Ananthakumar P and Adaikkappan M., Available online
ISSN: 2320-8147 International Journal of Current Medical Sciences- Vol. 6, Issue,, pp. 122-126, June, 2016 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN HEPATIC METASTASES Ananthakumar P and Adaikkappan M., Available online
Embolotherapy for Cholangiocarcinoma: 2016 Update
 Embolotherapy for Cholangiocarcinoma: 2016 Update Igor Lobko,MD Chief, Division Vascular and Interventional Radiology Long Island Jewish Medical Center GEST 2016 Igor Lobko, M.D. No relevant financial
Embolotherapy for Cholangiocarcinoma: 2016 Update Igor Lobko,MD Chief, Division Vascular and Interventional Radiology Long Island Jewish Medical Center GEST 2016 Igor Lobko, M.D. No relevant financial
A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (2): 365-370 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A study on clinicopathological features and prognostic factors of patients with upper gastric cancer and middle and lower gastric
Cytokeratin 5/6 expression in bladder cancer: association with clinicopathologic parameters and prognosis
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3319-4 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH NOTE Open Access Cytokeratin 5/6 expression in bladder cancer: association with clinicopathologic parameters and prognosis Atif Ali
https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-018-3319-4 BMC Research Notes RESEARCH NOTE Open Access Cytokeratin 5/6 expression in bladder cancer: association with clinicopathologic parameters and prognosis Atif Ali
HRCT features distinguishing minimally invasive adenocarcinomas from invasive adenocarcinomas appearing as mixed ground-glass nodules
 Original Article HRCT features distinguishing minimally invasive adenocarcinomas from invasive adenocarcinomas appearing as mixed ground-glass nodules Wei Yu 1, Zhaoyu Wang 2, Liyong Qian 2, Shanjun Wang
Original Article HRCT features distinguishing minimally invasive adenocarcinomas from invasive adenocarcinomas appearing as mixed ground-glass nodules Wei Yu 1, Zhaoyu Wang 2, Liyong Qian 2, Shanjun Wang
Acknowledgments. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Lung Nodule Detection. A Specific Diagnostic Task: Chest CT Protocols. Chest CT Protocols
 Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Personalization of Pediatric Imaging in Terms of Needed Indication-Based Quality Per Dose Acknowledgments Duke University Medical Center Ehsan Samei, PhD Donald Frush, MD Xiang Li PhD DABR Cleveland Clinic
Utility of 18 F-FDG PET/CT in metabolic response assessment after CyberKnife radiosurgery for early stage non-small cell lung cancer
 Utility of F-FDG PET/CT in metabolic response assessment after CyberKnife radiosurgery for early stage non-small cell lung cancer Ngoc Ha Le 1*, Hong Son Mai 1, Van Nguyen Le 2, Quang Bieu Bui 2 1 Department
Utility of F-FDG PET/CT in metabolic response assessment after CyberKnife radiosurgery for early stage non-small cell lung cancer Ngoc Ha Le 1*, Hong Son Mai 1, Van Nguyen Le 2, Quang Bieu Bui 2 1 Department
Impact of conversion during laparoscopic gastrectomy on outcomes of patients with gastric cancer
 JBUON 2017; 22(4): 926-931 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of conversion during laparoscopic gastrectomy on outcomes of
JBUON 2017; 22(4): 926-931 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of conversion during laparoscopic gastrectomy on outcomes of
performed to help sway the clinician in what the appropriate diagnosis is, which can substantially alter the treatment of management.
 Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Hello, I am Maura Polansky at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I am a Physician Assistant in the Department of Gastrointestinal Medical Oncology and the Program Director for Physician
Nonfunctioning Islet Cell Tumors of the Pancreas: Computed Tomography Findings
 Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 239-243 239 Nonfunctioning Islet Cell Tumors of the Pancreas: Computed Tomography Findings CHAO-HSUAN YEN 1 JEN-HWEY CHIANG 1 JEN-I HUANG 3 CHENG-SHI SU 2 YI-YOU CHIOU 1 CHENG-YEN
Chin J Radiol 2002; 27: 239-243 239 Nonfunctioning Islet Cell Tumors of the Pancreas: Computed Tomography Findings CHAO-HSUAN YEN 1 JEN-HWEY CHIANG 1 JEN-I HUANG 3 CHENG-SHI SU 2 YI-YOU CHIOU 1 CHENG-YEN
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1
 Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Intrahepatic Sarcomatoid Cholangiocarcinoma with Portal Vein Thrombosis: A Case Report 1 Jae-Hoon Lim, M.D., Jin Woong Kim, M.D., Suk Hee Heo, M.D., Yong Yeon Jeong, M.D., Heoung Keun Kang, M.D. A 53-year-old
Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Chinese Journal of Cancer Original Article Cancer incidence and patient survival rates among the residents in the Pudong New Area of Shanghai between 2002 and 2006 Xiao-Pan Li 1, Guang-Wen Cao 2, Qiao
Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories
 Original Article Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories Wu Song, Yulong He, Shaochuan Wang, Weiling
Original Article Significance of the lymph nodes in the 7th station in rational dissection for metastasis of distal gastric cancer with different T categories Wu Song, Yulong He, Shaochuan Wang, Weiling
Upper GI Malignancies Imaging Guidelines for the Management of Gastric, Oesophageal & Pancreatic Cancers 2012
 Upper GI Malignancies Imaging Guidelines for the Management of Gastric, Oesophageal & Pancreatic Cancers 2012 Version Control This is a controlled document please destroy all previous versions on receipt
Upper GI Malignancies Imaging Guidelines for the Management of Gastric, Oesophageal & Pancreatic Cancers 2012 Version Control This is a controlled document please destroy all previous versions on receipt
Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT
 GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
GE Healthcare Case studies Combined Anatomical and Functional Imaging with Revolution * CT Jean-Louis Sablayrolles, M.D. Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Saint-Denis, France Case 1 Whole Brain Perfusion and
Analysis of the outcome of young age tongue squamous cell carcinoma
 Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Jeon et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0139-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Analysis of the outcome of
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 Final Pathology:
 Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Abstracting Upper GI Cancer Incidence and Treatment Data Quiz 1 Multiple Primary and Histologies Case 1 A 74 year old male with a history of GERD presents complaining of dysphagia. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer
 Feng et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:737 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3738-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer Fan Feng 1, Yangzi
Feng et al. BMC Cancer (2017) 17:737 DOI 10.1186/s12885-017-3738-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Diagnostic and prognostic value of CEA, CA19 9, AFP and CA125 for early gastric cancer Fan Feng 1, Yangzi
With recent advances in diagnostic imaging technologies,
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Management of Ground-Glass Opacity Lesions Detected in Patients with Otherwise Operable Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Hong Kwan Kim, MD,* Yong Soo Choi, MD,* Kwhanmien Kim, MD,* Young Mog
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Management of Ground-Glass Opacity Lesions Detected in Patients with Otherwise Operable Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Hong Kwan Kim, MD,* Yong Soo Choi, MD,* Kwhanmien Kim, MD,* Young Mog
Xiaohuan Pan 1,2 *, Xinguan Yang 1,2 *, Jingxu Li 1,2, Xiao Dong 1,2, Jianxing He 2,3, Yubao Guan 1,2. Original Article
 Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection
 Original Article Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection Mingjian Yang 1,2, Hongdian Zhang 1,2, Zhao Ma 1,2, Lei Gong 1,2, Chuangui Chen
Original Article Log odds of positive lymph nodes is a novel prognostic indicator for advanced ESCC after surgical resection Mingjian Yang 1,2, Hongdian Zhang 1,2, Zhao Ma 1,2, Lei Gong 1,2, Chuangui Chen
Justification of the use of CT for individual health assessment of asymptomatic people: the Chinese experience
 Justification of the use of CT for individual health assessment of asymptomatic people: the Chinese experience Liang Wang, MD, PhD Professor, attending radiologist wang6@tjh.tjmu.edu.cn Dept. of Radiology
Justification of the use of CT for individual health assessment of asymptomatic people: the Chinese experience Liang Wang, MD, PhD Professor, attending radiologist wang6@tjh.tjmu.edu.cn Dept. of Radiology
An Introduction to Dual Energy Computed Tomography
 An Introduction to Dual Energy Computed Tomography Michael Riedel University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Introduction The idea of computed tomography (CT) was first introduced in the
An Introduction to Dual Energy Computed Tomography Michael Riedel University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Introduction The idea of computed tomography (CT) was first introduced in the
The improved cure fraction for esophageal cancer in Linzhou city
 Liu et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:949 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4867-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The improved cure fraction for esophageal cancer in Linzhou city Shuzheng Liu 1, Lanwei Guo 1,
Liu et al. BMC Cancer (2018) 18:949 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4867-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The improved cure fraction for esophageal cancer in Linzhou city Shuzheng Liu 1, Lanwei Guo 1,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): ISSN X
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9497-9501 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis of relevant risk factor and recurrence prediction model construction of thyroid cancer after surgery. Shuai Lin 1#,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9497-9501 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Analysis of relevant risk factor and recurrence prediction model construction of thyroid cancer after surgery. Shuai Lin 1#,
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach
 Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting and Stone Visualization in Urolithiasis
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Learning Objectives. 1. Identify which patients meet criteria for annual lung cancer screening
 Disclosure I, Taylor Rowlett, DO NOT have a financial interest /arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context
Disclosure I, Taylor Rowlett, DO NOT have a financial interest /arrangement or affiliation with one or more organizations that could be perceived as a real or apparent conflict of interest in the context
Developing a Statistical Method of Quantifying Vascular Response after Radiotherapy Co-supervised by Dr. Glenn Bauman and Dr.
 6 Week Project Developing a Statistical Method of Quantifying Vascular Response after Radiotherapy Co-supervised by Dr. Glenn Bauman and Dr. Slav Yartsev Michal Stankiewicz April 9, 2013 Medical Biophysics,
6 Week Project Developing a Statistical Method of Quantifying Vascular Response after Radiotherapy Co-supervised by Dr. Glenn Bauman and Dr. Slav Yartsev Michal Stankiewicz April 9, 2013 Medical Biophysics,
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations. Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital
 Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Chapter 6. Hester Gietema Cornelia Schaefer-Prokop Willem Mali Gerard Groenewegen Mathias Prokop. Accepted for publication in Radiology
 Chapter 6 Interscan variability of semiautomated volume measurements in intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules using multidetector-row computed tomography: Influence of inspirational level, nodule size and
Chapter 6 Interscan variability of semiautomated volume measurements in intraparenchymal pulmonary nodules using multidetector-row computed tomography: Influence of inspirational level, nodule size and
Dual Energy Spectral CT of Focal Liver Lesions in Advanced Cirrhosis: Early Experience
 Dual Energy Spectral CT of Focal Liver Lesions in Advanced Cirrhosis: Early Experience William P. Shuman MD, FACR University of Washington SCBTMR Annual Course Washington DC, October 23-26, 2011 Conflict
Dual Energy Spectral CT of Focal Liver Lesions in Advanced Cirrhosis: Early Experience William P. Shuman MD, FACR University of Washington SCBTMR Annual Course Washington DC, October 23-26, 2011 Conflict
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in IBD: An Update Ethan A. Smith, MD Section of Pediatric Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan ethans@med.umich.edu Disclosures Royalties from Elsevier
ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes
 ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes Poster No.: B-0158 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper F. Houari, O. Lucidarme, J. Gabarre, F. Charlotte, C. Pellot- Barakat, M. Lefort,
ShearWave elastography in lymph nodes Poster No.: B-0158 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Paper F. Houari, O. Lucidarme, J. Gabarre, F. Charlotte, C. Pellot- Barakat, M. Lefort,
Case Scenario 1. The patient has now completed his neoadjuvant chemoradiation and has been cleared for surgery.
 Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
Case Scenario 1 July 10, 2010 A 67-year-old male with squamous cell carcinoma of the mid thoracic esophagus presents for surgical resection. The patient has completed preoperative chemoradiation. This
PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions
 PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions General Q: Is FDG PET specific for cancer? A: No, it is a marker of metabolism. In general, any disease that causes increased metabolism can result in increased FDG uptake
PET/CT Frequently Asked Questions General Q: Is FDG PET specific for cancer? A: No, it is a marker of metabolism. In general, any disease that causes increased metabolism can result in increased FDG uptake
Association between spectral computed tomography images and clinicopathological features in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma
 6664 Association between spectral computed tomography images and clinicopathological features in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma XIAOHUA CHEN 1*, KE REN 2*, PAN LIANG 1, JIAYIN LI 1, KUISHENG CHEN 3 and
6664 Association between spectral computed tomography images and clinicopathological features in advanced gastric adenocarcinoma XIAOHUA CHEN 1*, KE REN 2*, PAN LIANG 1, JIAYIN LI 1, KUISHENG CHEN 3 and
Purpose. Methods and Materials
 Comparison of iterative and filtered back-projection image reconstruction techniques: evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography Poster No.: C-1644 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific
Comparison of iterative and filtered back-projection image reconstruction techniques: evaluation of heavily calcified vessels with coronary CT angiography Poster No.: C-1644 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Supplementary Information Prognostic Impact of Signet Ring Cell Type in Node Negative Gastric Cancer Pengfei Kong1,4,Ruiyan Wu1,Chenlu Yang1,3,Jianjun Liu1,2,Shangxiang Chen1,2, Xuechao Liu1,2, Minting
Improved image quality of low-dose thoracic CT examinations with a new postprocessing software*
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 11, NUMBER 3, Summer 2010 Improved image quality of low-dose thoracic CT examinations with a new postprocessing software* Anne Catrine Traegde Martinsen,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 11, NUMBER 3, Summer 2010 Improved image quality of low-dose thoracic CT examinations with a new postprocessing software* Anne Catrine Traegde Martinsen,
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors
 CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD. Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China. Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine
 GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD EDUCATION Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine Ph.D. student specialized in pancreatic cancer, from
GUOPEI LUO, PhD, MD EDUCATION Shanghai Cancer Center, Shanghai, China Joint-trained Ph.D. student, from 2008 to 2009, University of California, Irvine Ph.D. student specialized in pancreatic cancer, from
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma
 Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Comparison of multidetector-row computed tomography findings of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis and cholangiocarcinoma Poster No.: C-0245 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Yata,
Endoscopic Ultrasonography Assessment for Ampullary and Bile Duct Malignancy
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Endoscopy, Vol. 3, pp. 35-40 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 1996 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) Amsterdam B.V.
Functional CT imaging techniques for the assessment of angiogenesis in lung cancer
 Perspective Functional CT imaging techniques for the assessment of angiogenesis in lung cancer Thomas Henzler 1, Jingyun Shi 2, Hashim Jafarov 1, Stefan O. Schoenberg 1, Christian Manegold 3, Christian
Perspective Functional CT imaging techniques for the assessment of angiogenesis in lung cancer Thomas Henzler 1, Jingyun Shi 2, Hashim Jafarov 1, Stefan O. Schoenberg 1, Christian Manegold 3, Christian
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
 Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds
 Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds Imaging in jaundice and 2ww pathway Image protocol Staging Limitations Pancreatic cancer 1.2.4 Refer people using a suspected
Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds Imaging in jaundice and 2ww pathway Image protocol Staging Limitations Pancreatic cancer 1.2.4 Refer people using a suspected
Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases
 Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Thoracic Cancer ISSN 1759-7706 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Characteristics and prognostic factors of synchronous multiple primary esophageal carcinoma: A report of 52 cases Mei Li & Zhi-xiong Lin Department of Radiation
Perfusion Physics. ICMRI2018 March 29-31, 2018 Grand Hilton Hotel, Seoul, Korea. Asian Forum Ⅱ: Perfusion MRI SY24-1.
 SY24-1 Perfusion Physics Hiroyuki Kabasawa MR Collaborations and Development, GE Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan Perfusion is referred as the blood supply to micro capillary in tissue. Perfusion parameter such
SY24-1 Perfusion Physics Hiroyuki Kabasawa MR Collaborations and Development, GE Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan Perfusion is referred as the blood supply to micro capillary in tissue. Perfusion parameter such
The clinicopathological features and treatment modalities associated with survival of neuroendocrine cervical carcinoma in a Chinese population
 Zhang et al. BMC Cancer (2019) 19:22 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5147-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The clinicopathological features and treatment modalities associated with survival of neuroendocrine
Zhang et al. BMC Cancer (2019) 19:22 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5147-2 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The clinicopathological features and treatment modalities associated with survival of neuroendocrine
Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients
 Yonago Acta medica 2012;55:57 61 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients Hiroaki Saito, Seigo Takaya, Yoji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Shigeru Tatebe and Masahide
Yonago Acta medica 2012;55:57 61 Clinicopathologic Characteristics and Prognosis of Gastric Cancer in Young Patients Hiroaki Saito, Seigo Takaya, Yoji Fukumoto, Tomohiro Osaki, Shigeru Tatebe and Masahide
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients
 128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI
 Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA
 Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2018, 34: 785 DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA PATIENTS JING-LI
Acta Medica Mediterranea, 2018, 34: 785 DIAGNOSTIC SIGNIFICANCE OF CHANGES IN SERUM HUMAN EPIDIDYMIS EPITHELIAL SECRETORY PROTEIN 4 AND CARBOHYDRATE ANTIGEN 125 IN ENDOMETRIAL CARCINOMA PATIENTS JING-LI
PET CT for Staging Lung Cancer
 PET CT for Staging Lung Cancer Rohit Kochhar Consultant Radiologist Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have financial relationships with commercial organizations that may have a direct
PET CT for Staging Lung Cancer Rohit Kochhar Consultant Radiologist Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have financial relationships with commercial organizations that may have a direct
Clinical significance and diagnostic value of serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA72-4 in patients with gastric cancer
 /, Vol. 7, No. 31 Clinical significance and diagnostic value of serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA72-4 in patients with gastric cancer Yao Liang 1,*, Wei Wang 1,*, Cheng Fang 1,*, Seeruttun Sharvesh Raj 1, Wan-Ming
/, Vol. 7, No. 31 Clinical significance and diagnostic value of serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA72-4 in patients with gastric cancer Yao Liang 1,*, Wei Wang 1,*, Cheng Fang 1,*, Seeruttun Sharvesh Raj 1, Wan-Ming
Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose?
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Ji-Feng Feng 1,2*, Ying Huang 3 and Qi-Xun Chen 1,2 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY
 Feng et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:58 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Preoperative platelet lymphocyte ratio (PLR) is superior to neutrophil lymphocyte ratio
Feng et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:58 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Preoperative platelet lymphocyte ratio (PLR) is superior to neutrophil lymphocyte ratio
American Journals of Cancer Case Reports. A Rare Case of Rectal Metastasis from Sarcomatoid Variant of Urothelial Carcinoma: A Case Report
 American Journals of Cancer Case Reports Lin JYJ et al. American Journals of Cancer Case Reports 2014, 3:1-5 http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr Page 1 of 5 Vol 3 Article ID 20140539, 5 pages Case Report
American Journals of Cancer Case Reports Lin JYJ et al. American Journals of Cancer Case Reports 2014, 3:1-5 http://ivyunion.org/index.php/ajccr Page 1 of 5 Vol 3 Article ID 20140539, 5 pages Case Report
Hepatobiliary Malignancies Retrospective Study at Truman Medical Center
 Hepatobiliary Malignancies 206-207 Retrospective Study at Truman Medical Center Brandon Weckbaugh MD, Prarthana Patel & Sheshadri Madhusudhana MD Introduction: Hepatobiliary malignancies are cancers which
Hepatobiliary Malignancies 206-207 Retrospective Study at Truman Medical Center Brandon Weckbaugh MD, Prarthana Patel & Sheshadri Madhusudhana MD Introduction: Hepatobiliary malignancies are cancers which
Construction and external validation of a nomogram that predicts lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer patients using preoperative parameters
 Original Article Construction and external validation of a nomogram that predicts lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer patients using preoperative parameters Yinan Zhang 1*, Yiqiang Liu 2*, Ji
Original Article Construction and external validation of a nomogram that predicts lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer patients using preoperative parameters Yinan Zhang 1*, Yiqiang Liu 2*, Ji
Accepted Manuscript. Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming?
 Accepted Manuscript Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming? Qing-Lei Zeng, Zhi-Qin Li, Hong-Xia Liang, Guang-Hua Xu, Chun-Xia
Accepted Manuscript Unexpected high incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in the era of DAAs: too alarming? Qing-Lei Zeng, Zhi-Qin Li, Hong-Xia Liang, Guang-Hua Xu, Chun-Xia
Scientific Exhibit. Authors: D. Takenaka, Y. Ohno, Y. Onishi, K. Matsumoto, T.
 The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
Multiple Primary Quiz
 Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Multiple Primary Quiz Case 1 A 72 year old man was found to have a 12 mm solid lesion in the pancreatic tail by computed tomography carried out during a routine follow up study of this patient with adult
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS
 Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Exercise 15: CSv2 Data Item Coding Instructions ANSWERS CS Tumor Size Tumor size is the diameter of the tumor, not the depth or thickness of the tumor. Chest x-ray shows 3.5 cm mass; the pathology report
Nasopharynx. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology
 Nasopharynx 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology The nasopharynx is the uppermost, nasal part of the pharynx. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate.
Nasopharynx 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology The nasopharynx is the uppermost, nasal part of the pharynx. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate.
Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2
 Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2 The Committee for Management of CT-screening-detected Pulmonary Nodules 2009-2011 The Japanese Society of CT Screening
Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2 The Committee for Management of CT-screening-detected Pulmonary Nodules 2009-2011 The Japanese Society of CT Screening
BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam
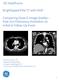 GE Healthcare BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam Michael Swack, MD Diagnostic Radiologist Irvington Radiologists, PC
GE Healthcare BrightSpeed Elite CT with ASiR: Comparing Dose & Image Quality Rule Out Pulmonary Embolism on Initial & Follow-Up Exam Michael Swack, MD Diagnostic Radiologist Irvington Radiologists, PC
Usefulness of spectral computed tomography for evaluation of intestinal activity and severity in ileocolonic Crohn s disease
 668309TAG0010.1177/1756283X16668309Therapeutic Advances in GastroenterologyJC Peng, Q Feng research-article2016 Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology Original Research Usefulness of spectral computed
668309TAG0010.1177/1756283X16668309Therapeutic Advances in GastroenterologyJC Peng, Q Feng research-article2016 Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology Original Research Usefulness of spectral computed
Title: What is the role of pre-operative PET/PET-CT in the management of patients with
 Title: What is the role of pre-operative PET/PET-CT in the management of patients with potentially resectable colorectal cancer liver metastasis? Pablo E. Serrano, Julian F. Daza, Natalie M. Solis June
Title: What is the role of pre-operative PET/PET-CT in the management of patients with potentially resectable colorectal cancer liver metastasis? Pablo E. Serrano, Julian F. Daza, Natalie M. Solis June
