Limited long-term impact of insect venom immunotherapy on the micro-rna landscape in whole blood
|
|
|
- Vernon Baker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Limited long-term impact of insect venom immunotherapy on the micro-rna landscape in whole blood Short title: Limited impact of insect immunotherapy on the mirna in whole blood Karpinski P 1, * Kahraman M 2 *, Ludwig N 3, Skiba P 1, Kosinska M 4, Rosiek-Biegus M 4, Królewicz E 4, Panaszek B 4, Nittner-Marszalska M 4, Blin N 1, Keller A 2, Meese E 3, Malgorzata Sasiadek M 1 1 Department of Genetics; Wroclaw Medical University, Wroclaw, Poland 2 Chair for Clinical Bioinformatics, Saarland University, Saarbrücken, Germany 3 Institute of Human Genetics, Saarland University, Homburg, Germany 4 Department and Clinic of Internal Medicine and Allergology; Wroclaw Medical University, Poland Corresponding author : Pawel Karpinski Department of Genetics; Wroclaw Medical University ul. Marcinkowskiego 1; Wroclaw, Poland polemiraza@poczta.fm This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process, which may lead to differences between this version and the Version of Record. Please cite this article as
2 2 Abstract Objective: To perform a genome-wide characterization of changes of microrna (mirna) expression in the course of VIT (venom immunotherapy). Methods: mirna was isolated form in the whole-blood of 13 allergic patients and 14 controls, who showed no allergic reaction upon stings by honeybees and wasps. We analyzed 2549 different mirnas from whole blood of these patients prior to VIT and 12 months after the start of the VIT. Differential expression results obtained on microarray platform were confirmed by quantitative real -time PCR (qrt-pcr). Out of the 13 patients, eight were confirmed to show a negative allergic reaction upon VIT thus indicating a successful VIT. Results: By comparing time points prior and 12 month after ultra-rush venom immunotherapy (VIT), correlation and principal component analysis both indicate a limited effect of the VIT on the overall mirna expression pattern. Volcano blot analysis based on raw p-values revealed few deregulated mirnas with the majority of them being increasingly expressed after VIT as compared to prior VIT. Using the 50 most altered mirnas, there was no clear clustering according to the time points i.e. the time prior and the time after VIT. Conclusions: Our results indicate an overall low effect of VIT on the mirna expression pattern in whole blood. Keywords mirna, Whole genome, Blood, Expression, Venom immunotherapy Resumen Objetivo: realizar la caracterización genómica de los cambios en la expresión de microarn (miarn) en el curso de ITV (inmunoterapia con veneno). Métodos: Los microarns se analizaron en la sangre total de 13 pacientes alérgicos y 14 controles sin reacción alérgica a las picaduras de abejas y avispas. Se analizaron 2549 mirnas diferentes en la sangre total de estos pacientes antes de la ITV y 12 meses después del inicio de la ITV. Los resultados de expresión diferencial obtenidos en la plataforma de microarrays se confirmaron mediante PCR cuantitativa a tiempo real (qrt-pcr). De los 13 pacientes, se confirmó que ocho tenían una reacción alérgica negativa tras la ITV, lo que indicó una ITV exitosa. Resultados: al comparar los resultados de micrornas, previa IT y 12 meses después de la (ITV), la correlación y el análisis de componentes principales indican un efecto limitado de la ITV en el patrón de expresión general de miarn. El análisis de Volcano basado en los valores de p crudos, reveló la existencia de pocos mirnas desregulados estando la mayoría de ellos sobreexpresados tras la ITV en comparación con la previa. Utilizando los 50 mirnas que más se alteraban, no se observó una agrupación clara en función del tiempo, es decir, pre y post-itv. Conclusiones: Nuestros resultados indican que la ITV tiene poco efecto en el patrón de expresión de miarn en sangre completa. Palabras clave: miarn, genoma completo, sangre, expresión, inmunoterapia con veneno.
3 3 Introduction Stings by Hymenoptera, including honeybees and wasps, may cause systemic allergic reactions occurring with an estimated prevalence of 1 5 % in Europe [1]. Venom immunotherapy (VIT) is a frequently used procedure to effectively prevent further severe allergic reactions to insect stings in people who once had suffered such a complication [2-4]. While a number of immunologic alterations have been well characterized in the context of VIT, the underlying changes of gene expression and their relationship to the overall effectiveness of VIT still remain unclear [5]. Recently, microarrays have been used to identify venom allergy-associated modification of gene expression in peripheral blood (PB), even though PB is a heterogeneous mixture of different cell types [6-8]. A main goal of genome-wide gene expression research is to understand molecular triggers for venom allergy and identification of immunological pathways that are responsible for effective VIT response [9]. In the last decade, micrornas (mirnas) have emerged as key regulators in different human tissues and of diverse biological and pathological processes, including carcinogenesis, morphogenesis, apoptosis and cell differentiation [10-13]. MiRNAs are small single-stranded non-coding RNAs that anneal to the 3'-UTR of target mrnas to down-regulate gene expression by inhibiting translation or stimulating mrna degradation [14-17]. The involvement of mirnas in various human diseases makes them promising novel targets of research providing insights into the molecular mechanisms of and possible therapeutically approaches in human malignancies [15]. Previous reports implicated mirnas in the pathogenesis of several allergic diseases including asthma, food allergy, eosinophilic esophagitis, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis [18]. Most recently, several changes in mirna expression have been identified in the build-up phase of hymenoptera VIT by screening 740 mirnas [19]. In the present study, we studied the long-term effects of hymenoptera VIT by measuring the abundances of 2549 mirnas prior and one year after the VIT.
4 4 Materials and Methods Study group. The group of patients selected for mirna expression microarray consisted of 13 patients presenting severe allergic reactions (IIIo/IVo according to Mueller s classification) after bee or wasp sting (Vespula species). Patients were recruited from the Department and Clinic of Internal Medicine and Allergology; Wroclaw Medical University, Poland, EU. As reference we included 14 individuals that showed no allergic reactions after bee or wasp stings. The study has been approved by a Wroclaw Medical University ethics committee (internal number 521/2012). All patients gave their informed consent to participate in the study. Blood from each patient has been sampled two times (prior and after one year of VIT). Detailed characteristics of individuals recruited to this study is presented in table 1. Hymenoptera ultra-rush venom immunotherapy (VIT-UR) protocol: VIT-UR was performed in the same way for all study patients. VIT procedures were conducted according the ultra-rush protocol due to which treatment begins with the initial venom dose of 0.1 mcg and the summary dose of mcg is reached within 3.5 hours. A venous access with infusion of sodium chloride 0.9% was secured before the first injection. Standardized lyophilized venom allergen extract (Pharmalgen Alk Abello) was used for build-up phase of VIT, and aluminum hydroxide adsorbed insect venom (Alutard-Alk Abello) for maintenance phase of therapy. MiRNA isolation and microarray hybridization: Whole blood samples were collected in PAXgene Blood RNA Tubes (BD, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey, USA) and stored in -60 C. Total RNA containing mirna was isolated using PAXgene Blood mirna Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). MiRNA abundances were analyzed using mirna expression array (SurePrint G3 Unrestricted mirna 8x60K v21, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) encompassing 2549 known human mirnas. All procedures were carried out according to the manufacturer's recommendations: To generate fluorescently labeled RNAs, 100ng total RNA per sample was processed by the mirna Complete Labeling and Hyb Kit (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Samples were loaded onto the microarrays and incubated for 55 C for 20 hours with rotation. Subsequent to washing microarrays were scanned with the Agilent Microarray Scanner at 3 microns in double
5 5 path mode. Data were acquired using Agilent AGW Feature Extraction software version (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-pcr (RT-qPCR) analysis: Expression levels of 2 mirnas that displayed significant deregulation in T cells CD8 were analyzed on the prepared cdna using the miscript II RT Kit according to the manufacturer's recommendations (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Detection of amplification was performed on 5 ng of cdna on an LightCycler480 instrument (Roche, USA) using the miscript Starter PCR Kit (Qiagen) and mirna specific quantitative RT-PCR primer sets for the mirna of interest (Qiagen): hsa-mir-16-2 (cat.no: MS ) and hsa-mir-4516 (cat.no: MS ) and endogenous control RNU6-2 (included in the miscript Starter PCR Kit). Each qrt-pcr reaction was conducted in duplicate. Statistical analysis: We used the freely available R statistical environment v to analyze the differences of mirna abundance in VIT patients. After applying the Feature Extraction software, we computed the normalized total gene signal for each mirna by performing the RMA method (AgiMicroRna) based on quantile normalization [20]. The resulting expression values were transformed to log (base 2). Then the whole mirna set of 2,549 mirnas was reduced to 534 by filtering in that way that each marker was detected at least in 25% of the samples in one of the 3 groups (before, after and reference). Different levels of mirnas among the same probands before and after the wasp sting were analyzed with using a paired two-tailed t test. We carried out a hierarchical clustering approach on top 50 most altered mirnas (as revealed by raw p- values) to detect clusters of mirnas and blood samples. In detail, we applied bottom up complete linkage clustering and used the Euclidian distance measure. In addition, we carried out a standard principal component analysis (PCA) and provide scatter plots of the first versus second principal component [21]. Relative quantification of mirna expression and calculation of the range of confidence was performed using the REST 2009 Software [22]. Computation blood cell-specific differential expression: For computation of relative blood cell proportions, we used normalized gene expression data obtained from the same patients on the Affymetrix PrimeView platform (results to be published, raw data available from Geo Expression Omnibus: GSE92866). After data normalization, we
6 6 utilized CIBERSORT algorithm (1000 iterations) and LM22 gene signature to predict relative proportions 9 major cell types (B cells, T cells CD8, T cells CD4, T cells regulatory (Tregs), NK cells, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and neutrophils) [23]. Calculated proportions were used as an input to cssam package that allows the analysis of differential expression for each blood cell type [24]. Results The aim of the study was to provide a comprehensive comparison of mirnas derived from whole blood of patients prior and 12 months after the start of VIT treatment (referred to as after VIT ). In total, we compared the abundance of 2549 mirnas from 13 patients including 6 males and 7 females, each showing severe allergic reactions of grades IIIo or IVo according to Mueller s classification after bee or wasp stings. Detailed clinical characteristics of the patients are given in table 1. Out of the 13 patients, eight were challenged with insect venom after finishing therapy and all eight patients were negative for signs of allergy against Hymenoptera venom, indicating a successful VIT. The control group (7 males and 7 females) consisted of individuals without allergic reactions after bee or wasp sting (as revealed by skin prick test). We first compared the individuals tested based on the overall mirna expression pattern. The correlation analysis between the samples identified several samples with a reduced correlation (Figure 1). Principal component analysis (PCA) showed no signs of difference between the time points prior and 12 months after VIT (Figure 2). As for specific mirnas with abundances altered by VIT, volcano blot analysis based on raw p- values revealed few deregulated mirnas with the majority of them displaying a lower abundance level prior to VIT as compared to after VIT (Figure 3a). After p-value adjustment, the volcano blot analysis did not indicate any mirna with a significantly altered abundance between the time point prior and after VIT (Figure 3b). These results also point to an overall low effect of VIT on the mirna expression pattern in whole blood. Figure 4 presents exemplary results of ANOVA analysis between both time points and the controls. Based on the differences in mirna abundance between the time points prior and after VIT we performed a clustering analysis using the 50 most altered mirnas. Figure 4
7 7 shows the lack of clustering between two time points prior and after VIT. These data further indicate a rather limited impact of VIT-UR on mirna expression pattern in blood. Finally we computed differential expression for each blood cell type between two time points (prior and after VIT). Applying this approach we found 14 mirnas (4 downregulated / 10 upregulated) with a differential abundance in T CD8 lymphocytes and 2 differentially expressed mirnas in monocytes (adjusted p-value 0.25 as proposed by authors of cssam; see ref. (Shen-Orr, et al., 2010)) (Table 2). Subsequently, we selected two mirnas based on significant deregulation in T CD8 cells (hsa-mir p and hsa-mir-4516) to preform qrt-pcr in the whole blood (Figure 5). None of selected mirnas revealed significant alteration when comparing our study groups (prior and after VIT). Functional enrichment of genes targeted by up- or downregulated mirnas revealed a number of significantly deregulated pathways, however, none of them could be attributed to immunology- or allergy-related mechanisms (data not shown). Discussion Most recently, several changes in mirna expression have been identified in the build-up phase of hymenoptera VIT by screening 740 mirnas [19]. Here, we studied the longterm effects of hymenoptera VIT by measuring the abundances of 2549 mirnas one year after the VIT. While we found a limited effect on the overall mirna expression pattern, we nevertheless detected few mirnas that displayed an altered expression pattern one year after VIT. The influence of the VIT was sufficient to prevent clustering of the two samples that belong to a given patient. The difference in results of our and the study of Specijalski et al. (2016) can be explained the time points taken for the buildup phase of the immunotherapy: measuring of mirna changes 24 hours after VIT vs. 12 months, as in our study [19]. Further differences between both studies include the mode of blood drawing (PAXgene versus conventional blood collection), the numbers of mirnas analyzed (2549 mirnas vs 740 mirnas) and different methods used (array based approach vs qrt-pcr). While bearing these facts in mind the comparison of both studies indicates that the long and short term effects of VIT on the mirna pattern appear to be different. After 12 month upon VIT, the whole-blood
8 8 mirna expression pattern was largely similar to the pattern prior to venom immunotherapy. As in numerous previous studies we used the PAXGene system that allows immediate stabilization of intracellular RNA, thereby facilitating the generation of reproducible mirna expression data. A drawback of this approach is that the lysis of blood prevents to relate the identified mirna pattern to specific blood cells. In addition, even experimental cell sorting does not necessarily allow to detect the mirna pattern of specific cell type due to the stress effects on expression patterns as previously described by us and others [25,26]. To address this problem, we tested a deconvolution algorithm that allows to predict differently expressed mirnas in small cell subpopulations [27]. Using the deconvolution algorithm, we predicted the mirna abundance in B cells, T cells CD8, T cells CD4, T cells regulatory (Tregs), NK cells, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and neutrophils. We found 14 mirnas with a differential abundance in TCD8 lymphocytes and two mirnas in monocytes. The elevated number of mirnas predicted to be deregulated in T cells is consistent with previous studies suggesting that biochemical changes in CD8+ T-cell function may represent key events in successful T- cell immunotherapy [28]. As for the function of monocytes in course of VIT, there is less evidence linking changes of mirna abundance to VIT. Although the employed deconvolution algorithm indicates differently expressed mirnas in blood cell subpopulations, the influence on cell type specific mirna changes by VIT awaits experimental validation. Potential limitation of our study is the fact that that whole blood was used as the mirna source, whereas, significant expression changes in VIT revealed by deconvolution approach were specific to a small fraction of cells (e.g T cells CD8). Presence of large proportion of cells not determining subject condition in the context of VIT (e.g. neutrophils) may weaken cell-specific expression signals. In summary, we studied the influence of hymenoptera VIT on the mirna abundance in whole blood of Hymenoptera venom allergic patients and found evidence for expression changes of specific mirna in whole blood between patients prior and 1 year after VIT. The overall mirna pattern was, however, largely unaffected. Our results lay the ground to further study the role of a mirna-based regulation during the process of desensitization, including cell-type specific alteration of mirna abundances.
9 9 Funding This work was supported by the Polish National Science Centre (NCN) grant 2012/05/B/NZ6/00637 ( ). Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank all the patients that participated in this study. Conflicts of interest None to declare References 1. Alfaya Arias T, Soriano Gómis V, Soto Mera T, Vega Castro A, Vega Gutiérrez JM, Alonso Llamazares A, et al. Key Issues in Hymenoptera Venom Allergy: An Update. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2017;27(1): Nittner-Marszalska M, Liebhart J, Liebhart E, Dor A, Dobek R, Obojski A, et al. Prevalence of Hymenoptera venom allergy and its immunological markers current in adults in Poland. Med Sci Monit. 2004;10(7):CR Aeberhard J, Haeberli G, Müller UR, Helbling A. Specific Immunotherapy in Hymenoptera Venom Allergy and Concomitant Malignancy: A Retrospective Follow-up Focusing on Effectiveness and Safety. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2017;27(6): Sturm GJ, Varga EM, Roberts G, Mosbech H, Bilò MB, Akdis CA, et al. EAACI guidelines on allergen immunotherapy: Hymenoptera venom allergy. Allergy. 2018;73(4): Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy: multiple suppressor factors at work in immune tolerance to allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;133(3): Niedoszytko M, Bruinenberg M, de Monchy J, Wijmenga C, Platteel M, Jassem E, et al. Gene expression analysis in predicting the effectiveness of insect venom immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010;125(5): Niedoszytko M, Bruinenberg M, de Monchy J, Weersma RK, Wijmenga C, Jassem E, et al. Changes in gene expression caused by insect venom immunotherapy responsible for the long-term protection of insect venom-allergic patients. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2011;106(6): Niedoszytko M, Gruchała-Niedoszytko M, Jassem E. Gene expression analysis in allergology: the prediction of Hymenoptera venom allergy severity and treatment efficacy. Clin Transl Allergy. 2013;3(1): Niedoszytko M, Bonadonna P, Oude Elberink JN, Golden DB. Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment of Hymenoptera venom allergy in mastocytosis patients. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2014;34(2): Keller A, Leidinger P, Bauer A, Elsharawy A, Haas J, Backes C, et al. Toward the bloodborne mirnome of human diseases. Nat Methods. 2011;8(10): Leidinger P, Backes C, Meder B, Meese E, Keller A. The human mirna repertoire of different blood compounds. BMC Genomics. 2014;15: Keller A, Leidinger P, Vogel B, Backes C, ElSharawy A, Galata V, et al. mirnas can be generally associated with human pathologies as exemplified for mir-144. BMC Med. 2014;12:224.
10 Ludwig N, Leidinger P, Becker K, Backes C, Fehlmann T, Pallasch C, et al. Distribution of mirna expression across human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(8): Hart M, Rheinheimer S, Leidinger P, Backes C, Menegatti J, Fehlmann T, et al. Identification of mir-34a-target interactions by a combined network based and experimental approach. Oncotarget. 2016;7(23): Backes C, Meese E, Keller A. Specific mirna Disease Biomarkers in Blood, Serum and Plasma: Challenges and Prospects. Mol Diagn Ther. 2016;20(6): Backes C, Kehl T, Stöckel D, Fehlmann T, Schneider L, Meese E, et al. mirpathdb: a new dictionary on micrornas and target pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(D1):D90-D Backes C, Fehlmann T, Kern F, Kehl T, Lenhof HP, Meese E, et al. mircarta: a central repository for collecting mirna candidates. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46(D1):D160-D Dissanayake E, Inoue Y. MicroRNAs in Allergic Disease. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016;16(9): Specjalski K, Maciejewska A, Pawłowski R, Chełmińska M, Jassem E. Changes in the Expression of MicroRNA in the Buildup Phase of Wasp Venom Immunotherapy: A Pilot Study. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2016;170(2): López-Romero P. Pre-processing and differential expression analysis of Agilent microrna arrays using the AgiMicroRna Bioconductor library. BMC Genomics. 2011;12: Graffelman J, van Eeuwijk F. Calibration of multivariate scatter plots for exploratory analysis of relations within and between sets of variables in genomic research. Biom J. 2005;47(6): Pfaffl MW, Horgan GW, Dempfle L. Relative expression software tool (REST) for groupwise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002;30(9):e Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, et al. Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods ;12(5): Shen-Orr SS, Tibshirani R, Khatri P, Bodian DL, Staedtler F, Perry NM, et al. Cell typespecific gene expression differences in complex tissues. Nat Methods. 2010;7(4): Reynaud CA, Weill JC. Gene profiling of CD11b+ and CD11b B1 cell subsets reveals potential cell sorting artifacts. J Exp Med. 2012;209(3): Bukowska-Straková K, Baran J, Gawlicka M, Kowalczyk D. A false expression of CD8 antigens on CD4+ T cells in a routine flow cytometry analysis. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2006;44(3): Gaujoux R, Seoighe C. CellMix: a comprehensive toolbox for gene expression deconvolution. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(17): Schuerwegh AJ, De Clerck LS, Bridts CH, Stevens WJ. Wasp venom immunotherapy induces a shift from IL-4-producing towards interferon-gamma-producing CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001;31(5):740-6.
11 11 Patient s Number (A-prior, C-after, G - controls) Age Table 1. Demographic and clinical data Gender Grade of allergic reaction after sting According to Mueller scale Responsible insect IDT* with venom of responsible insect - concentration 10-6 g/l (mm) sige** with venom of responsible insect (concentration and class) Vesp v 1 (concentration and class) Vesp v 5 (concentration and class) Api m 1 (concentration and class) Results of sting challenge / field sting 11A/11C 45 F III Wasp 12x (2) 0.02 (0) 6.82 (3) (0) Negative 6A/6C 32 M IV Wasp 9x (2) 0.03 (0) 10.4 (3) 0.01 (0) Negative 2A/2C 45 M IV Wasp 10x (1) 0.07 (1) 0.33 (0) 0 (0) Negative 7A/7C 40 M IV Wasp 11x (3) 11.4 (3) 0.28 (0) 0 (0) Negative 19A/19C 37 M IV Wasp 8x (2) ND*** ND ND Negative 15A/15C 40 F III Wasp 10x (3) 0.61 (1) 3.47 (2) 0 (0) Negative 13A/13C 50 F IV Wasp 10x (3) 1.96 (2) 4.88 (3) 0.37 (1) ND 16A/16C 62 M III Bee 13x (3) ND ND ND Negative 1A/1C 38 F IV Wasp 7x9 5.2 (3) 0.01 (0) 3.12 (2) (0) ND 14A/14C 62 F IV Wasp 8x (0) (0) 1.59 (2) 0 (0) ND 18A/18C 56 F IV Wasp 7x (2) ND ND ND Negative 17A/17C 71 M III Bee 10x (3) 0 (0) 0 (0) 0.12 (0) ND 13A/13C 52 F III Wasp 10x (3) (2) 1.88 (3) 0.67 (0) ND 10G 23 M 11G 22 M 12G 25 M 13G 31 F 14G 22 M 1G 33 M 2G 27 M 3G 29 F 4G 26 F 5G NA F 6G 60 F 7G 18 M 8G 62 F 9G 28 F *IDT - intradermal test; ** sige specific IgE; ***ND - not determined
12 12 Table 2. Differentially regulated mirnas in blood cell types T CD8 Status Expression difference* FDR** (p-value) hsa-mir p downregulated hsa-mir-371b-5p upregulated hsa-mir-3960 upregulated hsa-mir-4286 downregulated hsa-mir-4466 upregulated hsa-mir-4516 upregulated hsa-mir p upregulated hsa-mir-6089 upregulated hsa-mir-638 upregulated hsa-mir-664a-3p downregulated hsa-mir p upregulated hsa-mir p downregulated hsa-mir p upregulated hsa-mir-8063 upregulated Monocytes hsa-mir p upregulated hsa-mir-494-3p upregulated * Expression difference=after - prior **FDR cutt off<=0.25
13 13 Figure Legends Figure 1. Correlation matrix. Pair-wise Pearson Correlation Coefficient of the mirna expression profile was computed for all samples. Yellow to blue colors indicate high or lower correlation coefficient values. The numbers indicate the different individuals, A and B denotes the time point of blood collection prior and after VIT, respectively. Controls are indicated by G.
14 14 Figure 2. Principal Component Analysis. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) of blood samples taken from patients before VIT and 12 months after VIT. The figure shows the first principal component (PC1) on the x-axis versus the second PC2 on the y-axis. The numbers indicate the different patients, A and B denotes the time point of blood collection prior (green) and after VIT (orange), respectively. Controls are indicated in blue and by G.
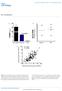
15 15 Figure 3. Differential expression of mirnas upon VIT. A - shows analysis based on raw values; B - shows data after adjustment of p-value for multiple testing. Volcano plots of all measured blood borne mirnas show the fold change of each mirna in logarythmic scale (base 2) on the x-axis, and the negative logarythmic p-value (base 10) on the y- axis. The mirna significantly overexpressed prior to IVT versus after IVT are indicated as red dots. MiRNAs with a significantly lower expression prior IVT are indicated as green dots.
16 16 Figure 4. Hierarchical clustering of samples before and after VIT based on top most altered 50 mirnas. The figure presents hierarchical clustering in patients prior VIT (green) and 12 months after the start of the VIT (orange). Controls are indicated in blue. Samples belonging to the same individual are indicated at the bottom of the heat map; mirnas used for the heat map are indicated at the right-hand side.
17 17 Figure 5. Expression of 2 selected mirna before and after VIT. A - derived from array based approach. B - derived from RT-qPCR. Box-whisker plots of mirnas differentially expressed in blood of patients prior IVT is indicated in red and 12 months after VIT indicated in green The boxes represent the 2 nd and 3 rd quartile, with the whiskers displaying minimum and maximum expression values. MiRNAs were selected based on significant deregulation in T cells CD8 (see table 2).
Basal Serum Tryptase Level Correlates With Severity of Hymenoptera Sting and Age
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Basal Serum Tryptase Level Correlates With Severity of Hymenoptera Sting and Age I Kucharewicz, 1 A Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, 1 W Szymanski, 1 B Mroczko, 2 M Szmitkowski 2 1 Department of Allergology
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Basal Serum Tryptase Level Correlates With Severity of Hymenoptera Sting and Age I Kucharewicz, 1 A Bodzenta-Lukaszyk, 1 W Szymanski, 1 B Mroczko, 2 M Szmitkowski 2 1 Department of Allergology
Preliminary Communication Cichocka-Jarosz, Dorynska, Pietrzyk & Spiewak
 For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com Laboratory markers of mast cell and basophil activation in monitoring rush immunotherapy in bee venom-allergic children Aim: To evaluate
For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com Laboratory markers of mast cell and basophil activation in monitoring rush immunotherapy in bee venom-allergic children Aim: To evaluate
11/5/2013. Insect Allergy Update. Diagnostic Testing for Insect Allergy. ACAAI Annual Meeting Nov , Baltimore. ACAAI 2013 Workshop
 ACAAI 2013 Workshop Insect Allergy Update Diagnostic Testing for Insect Allergy David B.K. Golden, M.D. Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest: Speakers Bureau Genentech / Novartis Mylan / Dey
ACAAI 2013 Workshop Insect Allergy Update Diagnostic Testing for Insect Allergy David B.K. Golden, M.D. Disclosures of Potential Conflicts of Interest: Speakers Bureau Genentech / Novartis Mylan / Dey
Allergy School on Investigating allergic effects of environmental exposures. Brindisi, Italy, 2-5 July Venom Allergy. M.
 Allergy School on Investigating allergic effects of environmental exposures Brindisi, Italy, 2-5 July 2014 Venom Allergy M.Beatrice Bilò Department of Internal Medicine Allergy Unit University Hospital,
Allergy School on Investigating allergic effects of environmental exposures Brindisi, Italy, 2-5 July 2014 Venom Allergy M.Beatrice Bilò Department of Internal Medicine Allergy Unit University Hospital,
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy and Field Stings R Lang, T Hawranek
 Original Article Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy and Field Stings R Lang, T Hawranek Department of Dermatology, Paracelsus Private Medical University, Salzburg, Austria Abstract. Background: Anaphylactic
Original Article Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy and Field Stings R Lang, T Hawranek Department of Dermatology, Paracelsus Private Medical University, Salzburg, Austria Abstract. Background: Anaphylactic
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits
 Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Cellecta Overview. Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA
 Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays
 Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
Supplementary Materials RASA: Robust Alternative Splicing Analysis for Human Transcriptome Arrays Junhee Seok 1*, Weihong Xu 2, Ronald W. Davis 2, Wenzhong Xiao 2,3* 1 School of Electrical Engineering,
ImmunoCAP Tryptase Product information
 ImmunoCAP Tryptase Product information 1 Clinical utility of ImmunoCAP Tryptase Risk marker for severe reactions elevated baseline levels indicate increased risk for severe reactions (1-3) in insect and
ImmunoCAP Tryptase Product information 1 Clinical utility of ImmunoCAP Tryptase Risk marker for severe reactions elevated baseline levels indicate increased risk for severe reactions (1-3) in insect and
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization
 A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
A novel and universal method for microrna RT-qPCR data normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle 4 th International qpcr Symposium Weihenstephan, March 1,
Allergy Update. because you depend upon results. Abacus ALS
 Allergy Update Abacus ALS ALS ImmunoCAP sigg measurement ImmunoCAP Specific IgG Measures antigen-specific IgG antibodies in human serum and plasma. Part of the natural defence system of the body and develop
Allergy Update Abacus ALS ALS ImmunoCAP sigg measurement ImmunoCAP Specific IgG Measures antigen-specific IgG antibodies in human serum and plasma. Part of the natural defence system of the body and develop
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification
 BD AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification Overview of BD AbSeq antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates. High-throughput
BD AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification Overview of BD AbSeq antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates. High-throughput
University of Groningen. Hymenoptera venom allergy Vos, Byrthe
 University of Groningen Hymenoptera venom allergy Vos, Byrthe IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Hymenoptera venom allergy Vos, Byrthe IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Total genomic DNA was extracted from either 6 DBS punches (3mm), or 0.1ml of peripheral or
 Material and methods Measurement of telomere length (TL) Total genomic DNA was extracted from either 6 DBS punches (3mm), or 0.1ml of peripheral or cord blood using QIAamp DNA Mini Kit and a Qiacube (Qiagen).
Material and methods Measurement of telomere length (TL) Total genomic DNA was extracted from either 6 DBS punches (3mm), or 0.1ml of peripheral or cord blood using QIAamp DNA Mini Kit and a Qiacube (Qiagen).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
doi:.38/nature8975 SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT Unique association of HOTAIR with patient outcome To determine whether the expression of other HOX lincrnas in addition to HOTAIR can predict patient outcome, we measured
RESEARCH Open Access Abstract Background: Methods: Results: Conclusions: Keywords: Background
 DOI 10.1186/s12948-016-0040-5 Clinical and Molecular Allergy RESEARCH Comparing the ability of molecular diagnosis and CAP inhibition in identifying the really causative in patients with positive tests
DOI 10.1186/s12948-016-0040-5 Clinical and Molecular Allergy RESEARCH Comparing the ability of molecular diagnosis and CAP inhibition in identifying the really causative in patients with positive tests
INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY. Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim
 INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim Definition Involves Administration of gradually increasing quantities of specific allergens to patients with IgE-mediated
INVESTIGATIONS & PROCEDURES IN PULMONOLOGY Immunotherapy in Asthma Dr. Zia Hashim Definition Involves Administration of gradually increasing quantities of specific allergens to patients with IgE-mediated
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers
 Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers Kai-Ming Jiang 1,2, Bao-Liang Lu 1,2, and Lei Xu 1,2,3(&) 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
Bootstrapped Integrative Hypothesis Test, COPD-Lung Cancer Differentiation, and Joint mirnas Biomarkers Kai-Ming Jiang 1,2, Bao-Liang Lu 1,2, and Lei Xu 1,2,3(&) 1 Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
RNA-seq Introduction
 RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
RNA-seq Introduction DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different functional RNAs Which RNAs (and sometimes then translated
CD30 Serum Levels and Response to Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE CD30 Serum Levels and Response to Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy FG Foschi, F Emiliani, S Savini, O Quercia, GF Stefanini Allergic Unit, Internal Medicine Department, Faenza Hospital,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE CD30 Serum Levels and Response to Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy FG Foschi, F Emiliani, S Savini, O Quercia, GF Stefanini Allergic Unit, Internal Medicine Department, Faenza Hospital,
Survey on practice of venom immunotherapy in France
 Public health Survey on practice of venom immunotherapy in France Charles Dzviga 1, Catherine Matevi 2, Philippe Bonniaud 3, François Lavaud 4, Bruno Girodet 5, Joelle Birnbaum 6, Claude Lambert 7, the
Public health Survey on practice of venom immunotherapy in France Charles Dzviga 1, Catherine Matevi 2, Philippe Bonniaud 3, François Lavaud 4, Bruno Girodet 5, Joelle Birnbaum 6, Claude Lambert 7, the
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Products for cfdna and mirna isolation. Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma
 MACHEREY-NAGEL Products for cfdna and mirna isolation Bioanalysis Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma n Flexible solutions for small and large blood plasma volumes n Highly efficient recovery
MACHEREY-NAGEL Products for cfdna and mirna isolation Bioanalysis Subhead Circulating Cover nucleic acids from plasma n Flexible solutions for small and large blood plasma volumes n Highly efficient recovery
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells. in the nasal mucosa. Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD,
 Radulovic 1 1 2 3 Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells in the nasal mucosa 4 5 6 7 Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD, Stephen R Durham MD, Kayhan T Nouri-Aria
Radulovic 1 1 2 3 Grass pollen immunotherapy induces Foxp3 expressing CD4 + CD25 + cells in the nasal mucosa 4 5 6 7 Suzana Radulovic MD, Mikila R Jacobson PhD, Stephen R Durham MD, Kayhan T Nouri-Aria
The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors
 Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
Department of Tumor Biology The clinical relevance of circulating, cell-free and exosomal micrornas as biomarkers for gynecological tumors cfdna Copenhagen April 6-7, 2017 Heidi Schwarzenbach, PhD Tumor
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc.
 Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc. Cellecta, Inc. Founded: April 2006 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA 12 SBIR Grants Custom Service Provider for Functional
Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc. Cellecta, Inc. Founded: April 2006 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA 12 SBIR Grants Custom Service Provider for Functional
Supplemental Information. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls. Monocyte Differentiation. into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages
 Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls Monocyte Differentiation into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages Christel Goudot, Alice Coillard, Alexandra-Chloé Villani,
Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls Monocyte Differentiation into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages Christel Goudot, Alice Coillard, Alexandra-Chloé Villani,
Single venom-based immunotherapy effectively protects patients with double positive tests to honey bee and Vespula venom
 Stoevesandt et al. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology 2013, 9:33 ALLERGY, ASTHMA & CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Single venom-based immunotherapy effectively protects patients with double
Stoevesandt et al. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology 2013, 9:33 ALLERGY, ASTHMA & CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY RESEARCH Open Access Single venom-based immunotherapy effectively protects patients with double
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
From reference genes to global mean normalization
 From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
From reference genes to global mean normalization Jo Vandesompele professor, Ghent University co-founder and CEO, Biogazelle qpcr Symposium USA November 9, 2009 Millbrae, CA outline what is normalization
Insect allergy PHILLIP L. LIEBERMAN, MD
 Insect allergy PHILLIP L. LIEBERMAN, MD Disclosure Consultant/Advisory Board: Genentech, Meda, Mylan, Teva Speaker: Genentech, Meda, Merck, Mylan, Teva Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session,
Insect allergy PHILLIP L. LIEBERMAN, MD Disclosure Consultant/Advisory Board: Genentech, Meda, Mylan, Teva Speaker: Genentech, Meda, Merck, Mylan, Teva Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session,
A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer
 Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
Poster # B4 A two-microrna signature in urinary exosomes for diagnosis of prostate cancer Anne Karin Ildor Rasmussen 1, Peter Mouritzen 1, Karina Dalsgaard Sørensen 3, Thorarinn Blondal 1, Jörg Krummheuer
IgE-Api m 4 Is Useful for Identifying a Particular Phenotype of Bee Venom Allergy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IgE-Api m 4 Is Useful for Identifying a Particular Phenotype of Bee Venom Allergy Ruiz B 1,2, Serrano P 1,2, Moreno C 1,2 1 Maimonides Biomedical Research Institute of Cordoba (IMIBIC)
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IgE-Api m 4 Is Useful for Identifying a Particular Phenotype of Bee Venom Allergy Ruiz B 1,2, Serrano P 1,2, Moreno C 1,2 1 Maimonides Biomedical Research Institute of Cordoba (IMIBIC)
Safety of specific immunotherapy using a four-hour ultra-rush induction scheme in bee and wasp allergy
 Original Article Safety of specific immunotherapy using a four-hour ultra-rush induction scheme in bee and wasp allergy A. Roll, G. Hofbauer, B.K. Ballmer-Weber, P. Schmid-Grendelmeier Allergy Unit, Department
Original Article Safety of specific immunotherapy using a four-hour ultra-rush induction scheme in bee and wasp allergy A. Roll, G. Hofbauer, B.K. Ballmer-Weber, P. Schmid-Grendelmeier Allergy Unit, Department
Practical Course Allergen Immunotherapy (AIT) How to be effective. Michel Dracoulakis HSPE- FMO São Paulo-SP Brazil
 Practical Course Allergen Immunotherapy (AIT) How to be effective Michel Dracoulakis HSPE- FMO São Paulo-SP Brazil Allergen immunotherapy - beginning Dunbar almost died with first inoculation 1911 Noon
Practical Course Allergen Immunotherapy (AIT) How to be effective Michel Dracoulakis HSPE- FMO São Paulo-SP Brazil Allergen immunotherapy - beginning Dunbar almost died with first inoculation 1911 Noon
developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success
 micrornas developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success Dr. Carola Wagner IMGM Laboratories GmbH Martinsried, Germany qpcr 2009 Symposium
micrornas developing new tools for diagnostics Join forces with IMGM Laboratories to make your mirna project a success Dr. Carola Wagner IMGM Laboratories GmbH Martinsried, Germany qpcr 2009 Symposium
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles
 On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
On the Reproducibility of TCGA Ovarian Cancer MicroRNA Profiles Ying-Wooi Wan 1,2,4, Claire M. Mach 2,3, Genevera I. Allen 1,7,8, Matthew L. Anderson 2,4,5 *, Zhandong Liu 1,5,6,7 * 1 Departments of Pediatrics
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplemental Data. Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature
 Supplemental Data Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature Jianfu Jiang 1, Xinna Liu 1, Guotian Liu, Chonghuih Liu*, Shaohuah Li*, and Lijun
Supplemental Data Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature Jianfu Jiang 1, Xinna Liu 1, Guotian Liu, Chonghuih Liu*, Shaohuah Li*, and Lijun
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo. Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale
 Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
Paternal exposure and effects on microrna and mrna expression in developing embryo Department of Chemical and Radiation Nur Duale Our research question Can paternal preconceptional exposure to environmental
A longitudinal study of hymenoptera stings in preschool children
 Received: 12 May 2018 Revised: 24 September 2018 Accepted: 24 September 2018 DOI: 10.1111/pai.12987 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Food Allergy & Anaphylaxis A longitudinal study of hymenoptera stings in preschool children
Received: 12 May 2018 Revised: 24 September 2018 Accepted: 24 September 2018 DOI: 10.1111/pai.12987 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Food Allergy & Anaphylaxis A longitudinal study of hymenoptera stings in preschool children
HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA LEO TUNKLE *
 CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
CERNA SEARCH METHOD IDENTIFIED A MET-ACTIVATED SUBGROUP AMONG EGFR DNA AMPLIFIED LUNG ADENOCARCINOMA PATIENTS HALLA KABAT * Outreach Program, mircore, 2929 Plymouth Rd. Ann Arbor, MI 48105, USA Email:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
IgE-Api m4 is useful to identify a particular phenotype of allergy to bee venom.
 1 IgE-Api m4 is useful to identify a particular phenotype of allergy to bee venom. Short title: Allergy to Api m 4 from bee venom. AUTHORS Berta Ruiz, MD. PhD. Department of Allergology. Hospital General
1 IgE-Api m4 is useful to identify a particular phenotype of allergy to bee venom. Short title: Allergy to Api m 4 from bee venom. AUTHORS Berta Ruiz, MD. PhD. Department of Allergology. Hospital General
Clinical Study Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy: Tolerance and Efficacy of an Ultrarush Protocol versus a Rush and a Slow Conventional Protocol
 Allergy Volume 2012, Article ID 192192, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/192192 Clinical Study Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy: Tolerance and Efficacy of an Ultrarush Protocol versus a Rush and a Slow Conventional
Allergy Volume 2012, Article ID 192192, 8 pages doi:10.1155/2012/192192 Clinical Study Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy: Tolerance and Efficacy of an Ultrarush Protocol versus a Rush and a Slow Conventional
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing
 Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing RNA sequencing applications RNA sequencing provides fundamental insights into how genomes are organized and regulated, giving us valuable information about the
Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing RNA sequencing applications RNA sequencing provides fundamental insights into how genomes are organized and regulated, giving us valuable information about the
Research Article Evaluation of a Novel Rapid Test System for the Detection of Specific IgE to Hymenoptera Venoms
 Allergy Volume 202, Article ID 862023, 7 pages doi:0.55/202/862023 Research Article Evaluation of a Novel Rapid Test System for the Detection of Specific IgE to Hymenoptera Venoms Nikolai Pfender, Ralf
Allergy Volume 202, Article ID 862023, 7 pages doi:0.55/202/862023 Research Article Evaluation of a Novel Rapid Test System for the Detection of Specific IgE to Hymenoptera Venoms Nikolai Pfender, Ralf
Specific Immunotherapy in Hymenoptera Venom Allergy and Concomitant Malignancy: A Retrospective Follow-up Focusing on Effectiveness and Safety
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Specific Immunotherapy in Hymenoptera Venom Allergy and Concomitant Malignancy: A Retrospective Follow-up Focusing on Effectiveness and Safety Aeberhard J 1, Haeberli G 1, Müller UR 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Specific Immunotherapy in Hymenoptera Venom Allergy and Concomitant Malignancy: A Retrospective Follow-up Focusing on Effectiveness and Safety Aeberhard J 1, Haeberli G 1, Müller UR 1,
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x
 Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
Supplementary Figure 1: TSLP receptor skin expression in dcssc. A: Healthy control (HC) skin with TSLP receptor expression in brown (10x magnification). B: Second HC skin stained for TSLP receptor in brown
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles
 Author's response to reviews Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles Authors: Julia Tchou (julia.tchou@uphs.upenn.edu) Andrew V Kossenkov (akossenkov@wistar.org)
Author's response to reviews Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles Authors: Julia Tchou (julia.tchou@uphs.upenn.edu) Andrew V Kossenkov (akossenkov@wistar.org)
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and
 Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Discovery of Novel Human Gene Regulatory Modules from Gene Co-expression and Promoter Motif Analysis Shisong Ma 1,2*, Michael Snyder 3, and Savithramma P Dinesh-Kumar 2* 1 School of Life Sciences, University
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks
 Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
Digitizing the Proteomes From Big Tissue Biobanks Analyzing 24 Proteomes Per Day by Microflow SWATH Acquisition and Spectronaut Pulsar Analysis Jan Muntel 1, Nick Morrice 2, Roland M. Bruderer 1, Lukas
Cytogenetics 101: Clinical Research and Molecular Genetic Technologies
 Cytogenetics 101: Clinical Research and Molecular Genetic Technologies Topics for Today s Presentation 1 Classical vs Molecular Cytogenetics 2 What acgh? 3 What is FISH? 4 What is NGS? 5 How can these
Cytogenetics 101: Clinical Research and Molecular Genetic Technologies Topics for Today s Presentation 1 Classical vs Molecular Cytogenetics 2 What acgh? 3 What is FISH? 4 What is NGS? 5 How can these
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping
 Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping Melanie Rae Simpson PhD candidate Department of Public Health and General Practice Norwegian University of
Human breast milk mirna, maternal probiotic supplementation and atopic dermatitis in offsrping Melanie Rae Simpson PhD candidate Department of Public Health and General Practice Norwegian University of
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER
 EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER Tom Hait Aviv Steiner Igor Ulitsky Chaim Linhart Amos Tanay Seagull Shavit Rani Elkon Adi Maron-Katz Dorit Sagir Eyal David Roded Sharan Israel Steinfeld Yossi Shiloh
EXPression ANalyzer and DisplayER Tom Hait Aviv Steiner Igor Ulitsky Chaim Linhart Amos Tanay Seagull Shavit Rani Elkon Adi Maron-Katz Dorit Sagir Eyal David Roded Sharan Israel Steinfeld Yossi Shiloh
APPLICATION NOTE. Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices
 APPLICATION NOTE Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices INTRODUCTION Preservation of tissue biopsies is a critical step to This
APPLICATION NOTE Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices INTRODUCTION Preservation of tissue biopsies is a critical step to This
Evaluation of the quality of life in subjects with a history of severe anaphylactic reaction to the Hymenoptera venom
 ORIGINAL PRACA ORYGINALNA RESEARCH Natalia Nowak 1, Stanisława Bazan-Socha 2, Grażyna Pulka 3, Karolina Pełka 3, Paulina Latra 3 1 University Hospital, Allergy and Clinical Immunology Department, Krakow,
ORIGINAL PRACA ORYGINALNA RESEARCH Natalia Nowak 1, Stanisława Bazan-Socha 2, Grażyna Pulka 3, Karolina Pełka 3, Paulina Latra 3 1 University Hospital, Allergy and Clinical Immunology Department, Krakow,
Supplemental Information. Systems Scale Interactive Exploration. Reveals Quantitative and Qualitative Differences
 Immunity, Volume 38 Supplemental Information Systems Scale Interactive Exploration Reveals Quantitative and Qualitative Differences in Response to Influenza and Pneumococcal Vaccines Gerlinde Obermoser,
Immunity, Volume 38 Supplemental Information Systems Scale Interactive Exploration Reveals Quantitative and Qualitative Differences in Response to Influenza and Pneumococcal Vaccines Gerlinde Obermoser,
Gene expression analysis. Roadmap. Microarray technology: how it work Applications: what can we do with it Preprocessing: Classification Clustering
 Gene expression analysis Roadmap Microarray technology: how it work Applications: what can we do with it Preprocessing: Image processing Data normalization Classification Clustering Biclustering 1 Gene
Gene expression analysis Roadmap Microarray technology: how it work Applications: what can we do with it Preprocessing: Image processing Data normalization Classification Clustering Biclustering 1 Gene
mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017
 mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017 Outline Introduction Circulating mirnas as potential biomarkers for pain Complex regional
mirna Biomarkers Seena K. Ajit PhD Pharmacology & Physiology Drexel University College of Medicine October 12, 2017 Outline Introduction Circulating mirnas as potential biomarkers for pain Complex regional
genomics for systems biology / ISB2020 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
Supplementary Figure 1: Experimental design. DISCOVERY PHASE VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) (N = 20) Healthy = 20. Healthy = 6. Endometriosis = 33
 DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
DISCOVERY PHASE (N = 20) Healthy = 6 Endometriosis = 7 EAOC = 7 Quantitative PCR (mirnas = 1113) a Quantitative PCR Verification of Candidate mirnas (N = 24) VALIDATION PHASE (N = 88) Healthy = 20 Endometriosis
BIMM 143. RNA sequencing overview. Genome Informatics II. Barry Grant. Lecture In vivo. In vitro.
 RNA sequencing overview BIMM 143 Genome Informatics II Lecture 14 Barry Grant http://thegrantlab.org/bimm143 In vivo In vitro In silico ( control) Goal: RNA quantification, transcript discovery, variant
RNA sequencing overview BIMM 143 Genome Informatics II Lecture 14 Barry Grant http://thegrantlab.org/bimm143 In vivo In vitro In silico ( control) Goal: RNA quantification, transcript discovery, variant
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Bayesian Inference for Single-cell ClUstering and ImpuTing (BISCUIT) Elham Azizi
 Bayesian Inference for Single-cell ClUstering and ImpuTing (BISCUIT) Elham Azizi BioC 2017: Where Software and Biology Connect Profiling Tumor-Immune Ecosystem in Breast Cancer Immunotherapy treatments
Bayesian Inference for Single-cell ClUstering and ImpuTing (BISCUIT) Elham Azizi BioC 2017: Where Software and Biology Connect Profiling Tumor-Immune Ecosystem in Breast Cancer Immunotherapy treatments
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
HHS Public Access Author manuscript J Invest Dermatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 January 01.
 RNA-seq Permits a Closer Look at Normal Skin and Psoriasis Gene Networks David Quigley 1,2,3 1 Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco,
RNA-seq Permits a Closer Look at Normal Skin and Psoriasis Gene Networks David Quigley 1,2,3 1 Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Specific Immunotherapy in Hymenoptera Venom Allergy and. concomitant Malignancies - A retrospective follow-up focusing on
 1 Specific Immunotherapy in Hymenoptera Venom Allergy and concomitant Malignancies - A retrospective follow-up focusing on efficacy and safety Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy & Cancer Aeberhard J 1, Haeberli
1 Specific Immunotherapy in Hymenoptera Venom Allergy and concomitant Malignancies - A retrospective follow-up focusing on efficacy and safety Hymenoptera Venom Immunotherapy & Cancer Aeberhard J 1, Haeberli
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Mastocytosis and Hymenoptera venom allergy Franziska Ruëff, Marianne Placzek and Bernhard Przybilla
 Mastocytosis and Hymenoptera venom allergy Franziska Ruëff, Marianne Placzek and Bernhard Przybilla Purpose of review Mastocytosis is a rare disease characterized by increased mast cells in skin and/or
Mastocytosis and Hymenoptera venom allergy Franziska Ruëff, Marianne Placzek and Bernhard Przybilla Purpose of review Mastocytosis is a rare disease characterized by increased mast cells in skin and/or
UNIVERSITY OF ZAGREB SCHOOL OF MEDICINE. Plan of the course. Basics of Pediatric Allergy. Academic year 2015/2016. Mirjana Turkalj
 UNIVERSITY OF ZAGREB SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Plan of the course Basics of Pediatric Allergy Academic year 2015/2016 I. COURSE AIMS COURSE OUTLINE The specialty of allergy involves the management of a wide range
UNIVERSITY OF ZAGREB SCHOOL OF MEDICINE Plan of the course Basics of Pediatric Allergy Academic year 2015/2016 I. COURSE AIMS COURSE OUTLINE The specialty of allergy involves the management of a wide range
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Joan & Sanford I. Weill Medical College of Cornell University New York, NY 10065
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0263 TITLE: Early Detection of NSCLC Using Stromal Markers in Peripheral Blood PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dingcheng Gao CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Joan & Sanford I. Weill Medical
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0263 TITLE: Early Detection of NSCLC Using Stromal Markers in Peripheral Blood PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dingcheng Gao CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Joan & Sanford I. Weill Medical
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes
 Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Ioana Agache Transylvania University Brasov. Precision medicine in allergy and asthma
 Ioana Agache Transylvania University Brasov Precision medicine in allergy and asthma Precision medicine and precision health Personalized care based on molecular, immunologic and functional endotyping
Ioana Agache Transylvania University Brasov Precision medicine in allergy and asthma Precision medicine and precision health Personalized care based on molecular, immunologic and functional endotyping
Micro-RNA web tools. Introduction. UBio Training Courses. mirnas, target prediction, biology. Gonzalo
 Micro-RNA web tools UBio Training Courses Gonzalo Gómez//ggomez@cnio.es Introduction mirnas, target prediction, biology Experimental data Network Filtering Pathway interpretation mirs-pathways network
Micro-RNA web tools UBio Training Courses Gonzalo Gómez//ggomez@cnio.es Introduction mirnas, target prediction, biology Experimental data Network Filtering Pathway interpretation mirs-pathways network
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers
 micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
micrornas (mirna) and Biomarkers Small RNAs Make Big Splash mirnas & Genome Function Biomarkers in Cancer Future Prospects Javed Khan M.D. National Cancer Institute EORTC-NCI-ASCO November 2007 The Human
QIAGEN's Growing Immuno-Oncology Testing Portfolio
 QIAGEN's Growing Immuno-Oncology Testing Portfolio QIAGEN Your Partner in Translational Medicine Current Biomarkers of Immuno-Oncology Focus: Immuno-Oncology Testing Portfolio Tumor mutation burden (TMB)
QIAGEN's Growing Immuno-Oncology Testing Portfolio QIAGEN Your Partner in Translational Medicine Current Biomarkers of Immuno-Oncology Focus: Immuno-Oncology Testing Portfolio Tumor mutation burden (TMB)
Public Assessment Report Scientific discussion. Alutard SQ Bigift (Apis mellifera) SE/H/1637/01-02/MR
 Public Assessment Report Scientific discussion Alutard SQ Bigift (Apis mellifera) SE/H/1637/01-02/MR This module reflects the scientific discussion for the approval of Alutard SQ Bigift. The procedure
Public Assessment Report Scientific discussion Alutard SQ Bigift (Apis mellifera) SE/H/1637/01-02/MR This module reflects the scientific discussion for the approval of Alutard SQ Bigift. The procedure
