Original Article Signet-ring cell in papilloma virus type 6 and 16-related non-neoplastic squamous cell lesion
|
|
|
- Rosamund Reeves
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1): /ISSN: /IJCEP Original Article Signet-ring cell in papilloma virus type 6 and 16-related non-neoplastic squamous cell lesion Meng-Meng Wang 1*, Nong-Rong Wang 1*, Lian-Rui Deng 1*, Jun Deng 2, Sheng-Liang Zhou 1, Jiang-Xia Xu 1, Lv Zhou 3, Jin-Ping Hu 3, Hua Cheng 1, Huan Deng 1,3,4 1 Molecular Medicine and Genetics Center, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China; 2 Department of Emergency, The First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China; 3 Department of Pathology, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang, China; 4 Renmin Institute of Forensic Medicine, Nanchang, China. * Equal contributors. Received August 13, 2015; Accepted September 22, 2015; Epub January 1, 2016; Published January 15, 2016 Abstract: Signet-ring cell has been used largely to refer to adenocarcinoma. Primary squamous cell lesions with signet-ring cell morphology are extremely uncommon. We reported the first case of condyloma acuminate with signet-ring cell of perianal skin in a 34-year-old Chinese woman. Typical signet-ring cells and gray-blue material were observed in parabasal and intermediate stratum. The large cytoplasmic vacuoles of signet-ring cell were negative for periodic-acid Schiff (), Alcian blue (AB), mucicarmin, AE1/AE3, EMA, MUC2, MUC5ac, HMB45, p16 INK4a and CEA. EMA and AE1/AE3 immunopositivity draw the outline of signet-ring cells. The gray-blue material and septum of small vacuoles also expressed AE1/AE3, indicating that they might contain intermediate filaments. The blocking staining pattern of p16 INK4a encouraged the diagnosis of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion which carries a significant risk of invasive cancer development if not treated. HPV type 6 and 16 s were confirmed by Hybrid Capture HPV test. Due to the similarities in molecular profiles it is conceived that signet-ring cell in HPV-related squamous cell lesion may represent a rare variant of koilocyte. Keywords: Signet-ring cell, HPV, squamous cell lesion, immunohistochemistry, condyloma acuminate Introduction Signet-ring cell is used to describe cells with an eccentric nucleus that is compressed to the cellular border by a large cytoplasmic vacuole [1]. The presence of signet-ring cell has been traditionally associated with mucin-producing adenocarcinomas, most commonly of gastric, colonic or mammary origin [2-4]. Primary squamous cell lesion with signet-ring cell morphology is very rare. The importance of recognizing it lies mainly in differentiating it from several other cutaneous and metastatic neoplasms which have the capacity to show signet-ring cell changes, including but not limited to, basal cell carcinoma (BCC), malignant melanoma, metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma and breast carcinoma [5]. There is now convincing evidence that signet-ring cell can be observed in primary squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) [6, 7]. Although the exact etiology of primary SCC with signetring cell is still unknown, human papilloma virus (HPV) appears to be one of the most potent inducers [8]. Here, we report the first case of HPV type 6 and 16-related non-neoplasia squamous cell lesion with signet-ring cell morphology. Case presentation A 34-year-old healthy Chinese woman (gravida 1, para 1) presented to the gynecology clinic with a 3-month history of nodal lesion in perianal skin, which had been increased in size in the past 3 weeks. Physical examination revealed a 7 mm diameter polypoid lesion. The nodule was resected under local anesthesia and then processed together with other routine biopsy materials from cervix to avoid the artifactual nature of the vacuolization. The formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue sections were studied by using hematoxylin and eosin staining, histochemistry, immunohistochemistry and HPV type-specific PCR and
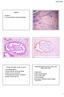
2 Figure 1. Histopathologic examination showed koilocytes in the superficial layer of squamous cell (A. original magnification 100; inserts 400). Typical signet-ring cells were observed (B. original magnification 100; inserts 400), and some of them (black arrows) contained hyperchromatic nuclei (C. original magnification 400). In the parabasal stratum of squamous cell, gray-blue material (black arrows) was detected in the cytoplasm (D. original magnification 400). genotyping. Evaluation of all results was performed by two independent pathologists who were blinded regarding patient details. Histopathology Epithelial cell hyperchromasia and crowding were seen. Some superficial and intermediate squamous cells exhibited enlarged nucleus with raisin-like nuclear membrane and prominent perinuclear vacuolation, characteristics of koilocyte (Figure 1A). Noteworthy, diffuse signet-ring cells were observed in the intermediate or parabasal stratum (Figure 1B). These signet-ring cells contained prominent vacuoles, which were sharply demarcated and appeared empty. However, most of signet-ring cells in this case are different from the malignant counterparts in their relative normal nuclei, the others scattered in the superficial stratum contained enlarged and hyperchromatic nuclei (Figure 1C). Another intriguing finding is that cytoplasm of some parabasal cells contained basophilic material (Figure 1D). Histochemistry and immunohistochemistry The paraffin-embedded sections were stained with periodic-acid Schiff (), Alcian blue, mucicarmin to explore the nature of signetring cell and gray-blue material. However, both of them were negative for the three histochemical staining, suggesting that neither mucin and mucopolysaccharides nor glycogen existed (Figure 2A-C). Signet-ring cells and koilocytes were positive for EMA (Figure 2D) but negative for MUC2, MUC5ac, HMB45 and CEA (data not shown). The scoring of p16 INK4a generally includes both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining, and is classified as negative, discontinu- 396 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):
3 397 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):
4 Figure 2. The signet-ring cells were negative for, Alcian Blue and mucicarmin (A-C. original magnification 400). They expressed EMA rather than MUC2, MUC5ac, HMB45 and CEA (D. original magnification 400). The block staining pattern of p16 INK4a was similar to that in high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion of cervix (E, F. original magnification 400). Ki-67 immunopositivity was detected in most of koilocytes and signet-ring cells (G. original magnification 400). A strongly positive staining for cytokeratin AE1/AE3 was obtained in septum of small vacuoles and gray-blue material (H. original magnification 400; inserts 400). Figure 3. HPV type-specific PCR and genotyping result showed HPV type 6 and 16 s. ous, or diffuse/continuous [9-11]. At the periphery of the lesion, p16 INK4a was negative (Figure 2E). Strong and diffuse block pattern of p16 INK4a was observed in the area composed of atypical epithelial cells (Figure 2E, 2F). Nuclear staining observed in epithelial cells above the parabasal layer was considered Ki-67 positivity. More than 50% of signet-ring cells and koilocytes in the middle and upper one-third of the epithelium expressed Ki-67 (Figure 2G). Cytokeratin AE1/AE3 drew the outlines of signet-ring cells and septum of small vacuoles (Figure 2H). The gray-blue cytoplasmic material also showed positivity for AE1/AE3 (Figure 2H). CK7 and CK20 were negative in this specimen (data not shown). HPV type-specific PCR and genotyping DNA was extracted and purified from FFPE tissue sections by using TIANamp FFPE DNA Kit (TIANGEN, Beijing, China). The operation was performed according to the manufacturer s protocol. Subsequently, HPV DNA was amplified with the L1 consensus HPV PGMY09/PGMY11 primer set as described previously [12]. PCR was performed with a 25 μl reaction system, which contained 1 ul DNA template and 0.75 μl DNA Taq polymerase. Amplification was carried out for 40 cycles in the CFX96 Touch TM Real- Time PCR Detection System (BIO-RAD, USA). HPV genotyping was performed by using HPV GenoArray test kit (Hybribio, Chaozhou, China), which makes use of flow-through hybridization and gene chips to identify 15 high-risk HPV types (HPV type 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 53, 56, 58, 59, 66 and 68) and 6 low-risk HPV types (HPV type 6, 11, 42, 43, 44 and 81). The result of genotypes indicated that this patient was co-infected with HPV type 6 and 16 (Figure 3). Discussion To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of HPV-related non-neoplasia squamous cell lesion with signet-ring cell morphology. Increasing evidence has shown that signet-ring cell is no longer restricted to adenocarcinoma. A set of malignant or benign lesions of squamous cell origin has been demonstrated to exhibit signet-ring cell morphology (Table 1) [1, 5, 7, 8, 13-18]. The exact etiology of SRC-containing lesion is still unknown. However, accumulating evidence indicate the particularly strong association between HPV and squamous cell neoplasia. 398 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):
5 Table 1. Summary of primary squamous cell lesions with signet-ring cell morphology Case Age/ Sex Pathologic Diagnosis Location HC Positive Negative Positive Negative IHC Etiology EM Reference 1 69/M SRSCC Forehead N/A Kreyberg Stain keratin N/A N/A N/A [13] 2 N/A SRSCC Pyriform Sinus N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A [14] 3 74/F SCC Cervix No AB, Mucicarmine, 4 84/F SCC Cervix No AB, Mucicarmine, 5 35/F CIN3 Cervix No AB, Mucicarmine, 6 37/F CIN3 Cervix No AB, Mucicarmine,, Giemsa 7 50/M SRSCC Neck (septum between vacuoles) Mucicarmine, (vacuoles) AE1/AE3, MAK 6 Ker, Ker 903, CAM 5.2, CEA (weak), EMA (weak), Ki-67 Leu M1, S-100, HMB- 45, Actin, Vimentin, SMA Empty spaces [7] Empty spaces Moderately electron-dense flocculent material/empty spaces Not done Not done Rough ER cisternal dilatation [15] 8 79/F SCC Right cheek No Colloical iron, cytokeratin No Not done no stained material [5] 9 82/M SCC Left temple No Colloical iron, cytokeratin No Not done no stained material 10 83/M SCC Right ear No Colloical iron, cytokeratin No Not done no stained material 11 80/M SCC Forehead No Colloical iron, cytokeratin No Not done no stained material 12 87/M SCC Frontal scalp No Colloical iron, cytokeratin No Not done no stained material 13 N/A SCC N/A No Colloical iron, cytokeratin No Not done no stained material 14 76/M SCC Forehead No Colloical iron, cytokeratin No Not done no stained material 15 84/F SRSCC Upper lip No Mucicarmine, keratin, P63, EMA No Not done Not done [16] 16 66/F SCC Sole AB, Colloidal iron 17 67/M SCC Left lateral canthus No AE1/AE3, EMA, CK5/6 CK7, CK20, CEA, BerEP4, S100, Her2- neu, ER, Ki-67 AB, Mucicarmine, 18 83/M SRSCC Left hand Not done Not done No CK20, CEA, vimentin, HMB45, Melan A, desmin 19 64/M SRSCC Left lung No AB, CK5/6, p16, p40, p63, EMA TTF-1, Napsin A, calretinin, WT-1, D2-40, CD56, SYN 20 34/F Condyloma acuminata Perianal skin No AB, Mucicarmine, HPV 18 Not done [8] CK5/6, p63, EMA CK7, Ck20, CEA Not done Not done [1] AE1/AE3, p16 INK4a, Ki-67, EMA CEA, MUC2, MUC5ac, CK7, CK20, HMB45 Not done Not done [17] No HPV Not done [18] HPV type 6 and 16 Not done present study SRSCC: signet-ring squamous cell carcinoma; SCC: squamous cell carcinoma; CIN: cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; HC: histochemistry; IHC: immunohistochemistry; AB: Alcian Blue; : periodic-acid Schiff; ER: endoplasmic reticulum. 399 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):
6 HPV type-6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 35 and 39 are most commonly observed in squamous cell lesions [19]. Including the present study, three cases have been submitted to HPV genotyping, and HPV type 6/16 and type 18 s are confirmed in two of them respectively [8, 18]. The HPV proteins E6 and E7 are thought to play an important role in this process by their interaction with the P53 protein and the RBsusceptibility gene product [125, 159, 169]. Consistent with previous studies, our case also exhibited overexpression of p16 INK4a (block staining pattern) and a high Ki-67 index, which indicate a high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion [9, 10]. Although there are no significant differences in histological appearance, signet-ring cell in squamous cell lesion clearly distinct from their counterparts in adenocarcinoma because of negativity for, AB, and mucicarmine or colloical iron (Table 1). The results of electron microscopy reveal that most of vacuoles contain moderate electron-dense flocculent material, others are empty [7]. Study further demonstrates that dilated endoplasmic reticulum serves as one of the most important components of vacuoles [15]. The septum of vacuoles includes intermediate filaments, which is in agreement with positivity for AE1/AE3 [15]. In contradiction to above-mentioned findings, an elaborate study suggests that signet-ring cell in SCC with mucinous metaplasia is positive for AB and colloidal iron rather than [8]. However, these signet-ring cells also show reactivity for AE1/AE3, EMA and CK5/6 and negativity for CEA, which denote a squamous cell origin phenotype [8]. Mature squamous cells do not contain mucinous. However, human epidermal stem cells are capable of differentiation into both keratinocytes and mucin producing cells in vitro [20]. We hypothesize that persistent HPV can trigger the epidermal stem cell to differentiate toward mucinous producing cells. During this process, the genomic changes may increase susceptibility of these transitioning cells to the harmful microenvironment, which inhibit the normal cell cycle and then create a pool of self-renewing cells that no longer enter a postmitotic differentiated state. Further accumulation of other alterations eventually leads to malignant transformation of signet-ring cells. Several studies of signet-ring cell generally encourage this view. There is now convincing evidence that cervical squamous cell can serve as a cellular source of signet-ring cell [7]. In an adenosquamous carcinoma of cervix, it is tempting to speculate that signetring cell may be derived from multipotential immature cells because neoplastic cells express both squamous and adenocarcinoma hallmarks, including low molecular weight cytokeratin, high molecular weight cytokeratin, MUC5AC and p63 [21]. Furthermore, HPV DNA is detected in several cases of primary cervical adenocarcinoma with signet-ring cell morphology [6, 22, 23]. Our study provides the first analysis of signet-ring cell in HPV-related benign squamous cell lesion. Koilocyte and signet-ring cell express the same panel of immunohistochemical markers, raising the possibility that the later may represent a rare variant of koilocyte. However, further experimentation will be required to determine the details of the relationship between signet-ring cell and koilocyte. Acknowledgements This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No ), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province, China (No BAB205037, 20151BAB215008, 20151BBG ), and Foundation of Jiangxi Educational Committee (No. GJJ14192), Foundation of Health and Family Planning Commission of Jiangxi Province (No , ). Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Huan Deng, Department of Pathology, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, 133 South Guangchang Road, Nanchang , China. beandeng@hotmail.com References [1] Lortscher DN, Satter EK and Romero LS. Signet ring-like cells: no longer a signature of glandular differentiation. Dermatol Online J 2012; 18: 3. [2] el-zimaity HM, Itani K and Graham DY. Early diagnosis of signet ring cell carcinoma of the stomach: role of the Genta stain. J Clin Pathol 1997; 50: [3] Makino T, Tsujinaka T, Mishima H, Ikenaga M, Sawamura T, Nakamori S, Fujitani K, Hirao M, 400 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):
7 Kashiwazaki M, Masuda N, Takeda M and Mano M. Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the colon and rectum: report of eight cases and review of 154 Japanese cases. Hepatogastroenterology 2006; 53: [4] Merino MJ and Livolsi VA. Signet ring carcinoma of the female breast: a clinicopathologic analysis of 24 cases. Cancer 1981; 48: [5] Bastian BC, Kutzner H, Yen T and LeBoit PE. Signet-ring cell formation in cutaneous neoplasms. J Am Acad Dermatol 1999; 41: [6] Giordano G, Pizzi S, Berretta R and D Adda T. A new case of primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the cervix with prominent endometrial and myometrial involvement: Immunohistochemical and molecular studies and review of the literature. World J Surg Oncol 2012; 10: 7. [7] Kupryjanczyk J and Kujawa M. Signet-ring cells in squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix and in non-neoplastic ectocervical epithelium. Int J Gynecol Cancer 1992; 2: [8] Caputo V, Colombi R, Ribotta M and Rongioletti F. Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma with mucinous metaplasia on the sole associated with high-risk human papillomavirus type 18. Am J Dermatopathol 2011; 33: [9] Bean SM, Eltoum I, Horton DK, Whitlow L and Chhieng DC. Immunohistochemical expression of p16 and Ki-67 correlates with degree of anal intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Surg Pathol 2007; 31: [10] Bergeron C, Ordi J, Schmidt D, Trunk MJ, Keller T and Ridder R. Conjunctive p16ink4a testing significantly increases accuracy in diagnosing high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Clin Pathol 2010; 133: [11] Galgano MT, Castle PE, Atkins KA, Brix WK, Nassau SR and Stoler MH. Using biomarkers as objective standards in the diagnosis of cervical biopsies. Am J Surg Pathol 2010; 34: [12] Gravitt PE, Peyton CL, Alessi TQ, Wheeler CM, Coutlee F, Hildesheim A, Schiffman MH, Scott DR and Apple RJ. Improved amplification of genital human papillomaviruses. J Clin Microbiol 2000; 38: [13] Cramer SF and Heggeness LM. Signet-ring squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol 1989; 91: [14] Klijanienko J, Micheau C, Ponzio-Prion A and Azli N. Signet-ring squamous cell carcinoma of the pyriform sinus. Am J Clin Pathol 1990; 93: [15] McKinley E, Valles R, Bang R and Bocklage T. Signet-ring squamous cell carcinoma: a case report. J Cutan Pathol 1998; 25: [16] El Demellawy D, Onuma K and Alowami S. Signet ring squamous cell carcinoma--the forgotten variant: case report and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol 2011; 38: [17] Nakajima K, Kaneko T, Aizu T, Nakano H, Matsuzaki Y and Sawamura D. Signet-ring cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma arising on the back of the finger. Case Rep Dermatol 2013; 5: [18] Park HS, Lee S. Acantholytic squamous cell carcinoma of the lung showing significant signet ring cell component. Histopathology 2015; [Epub ahead of print]. [19] Puy-Montbrun T, Denis J, Ganansia R, Mathoniere F, Lemarchand N and Arnous-Dubois N. Anorectal lesions in human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients. Int J Colorectal Dis 1992; 7: [20] Papini S, Cecchetti D, Campani D, Fitzgerald W, Grivel JC, Chen S, Margolis L and Revoltella RP. Isolation and clonal analysis of human epidermal keratinocyte stem cells in long-term culture. Stem Cells 2003; 21: [21] Moritani S, Ichihara S, Kushima R, Sugiura F, Mushika M and Silverberg SG. Combined signet ring cell and glassy cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix arising in a young Japanese woman: a case report with immunohistochemical and histochemical analyses. Pathol Int 2004; 54: [22] Balci S, Saglam A and Usubutun A. Primary signet-ring cell carcinoma of the cervix: case report and review of the literature. Int J Gynecol Pathol 2010; 29: [23] Haswani P, Arseneau J and Ferenczy A. Primary signet ring cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix: A clinicopathologic study of two cases with review of the literature. Int J Gynecol Cancer 1998; 8: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box?
 When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
Applications of IHC. Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin
 Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Table of Contents. 1. Overview. 2. Interpretation Guide. 3. Staining Gallery Cases Negative for CINtec PLUS
 Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
Staining Atlas Table of Contents 1. Overview 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Role of p16 INK4a 1.3 Role of Ki-67 1.4 Molecular Pathogenesis 1.5 p16 INK4a Expression in Cervical Dysplasia 1.6 The Concept of CINtec
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology
 New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
New Diagnoses Need New Approaches: A Glimpse into the Near Future of Gynecologic Pathology United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology 102 nd Annual Meeting Baltimore, Maryland Christina S. Kong, M.D.
The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix
 The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix Prof. Ben Davidson, MD PhD Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix Prof. Ben Davidson, MD PhD Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium
 chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium CHAPTER 1 All squamous cervical cancer (and probably all cervical adenocarcinoma) is associated with oncogenic HPV, and the absence
chapter 4. The effect of oncogenic HPV on transformation zone epithelium CHAPTER 1 All squamous cervical cancer (and probably all cervical adenocarcinoma) is associated with oncogenic HPV, and the absence
1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal
 Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Diseases of cervix I. Inflammations 1.Acute and Chronic Cervicitis - At the onset of menarche, the production of estrogens by the ovary stimulates maturation of the cervical and vaginal squamous mucosa
Thin HSIL of the Cervix: Detecting a Variant of High-grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions With a p16 INK4a Antibody
 International Journal of Gynecological Pathology 00:1 5, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore r 2016 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Original Article Thin HSIL of the Cervix: Detecting
International Journal of Gynecological Pathology 00:1 5, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore r 2016 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Original Article Thin HSIL of the Cervix: Detecting
PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals
 PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals Historical Named after George Papanicolaou, a Greek American Studied cervical epithelium in menstrual cycle of guinea
PAP SMEAR by Dr.Shantha Krishnamurthy MD Senior Consultant Pathology Fortis Hospitals Historical Named after George Papanicolaou, a Greek American Studied cervical epithelium in menstrual cycle of guinea
p16 Cervical HISTOLOGY Histology Compendium & Staining Atlas
 p16 Cervical HISTOLOGY Histology Compendium & Staining Atlas Chapter 1: An Introduction to p16...... 3 Normal Cervical Epithelium and the Cell Cycle....4 HPV Infection and Cervical Disease......................................
p16 Cervical HISTOLOGY Histology Compendium & Staining Atlas Chapter 1: An Introduction to p16...... 3 Normal Cervical Epithelium and the Cell Cycle....4 HPV Infection and Cervical Disease......................................
TEST MENU BY SPECIALTY
 1 TEST MENU BY SPECIALTY Breast Pathology Surgical excisions, needle core biopsies, and plastic surgery accepted from all sites Assessment of margins Axillary lymph node dissections Sentinel lymph nodes
1 TEST MENU BY SPECIALTY Breast Pathology Surgical excisions, needle core biopsies, and plastic surgery accepted from all sites Assessment of margins Axillary lymph node dissections Sentinel lymph nodes
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Tissue-based Immunohistochemical Biomarker Expression in Malignant Glandular Lesions of the Uterine Cervix: a Systematic Review
 Tissue-based Immunohistochemical Biomarker Expression in Malignant Glandular Lesions of the Uterine Cervix: a Systematic Review Sandra Lee MD, FRCPC 1 *, Vikrant V. Sahasrabuddhe, MBBS, DrPH 2 *, Diana
Tissue-based Immunohistochemical Biomarker Expression in Malignant Glandular Lesions of the Uterine Cervix: a Systematic Review Sandra Lee MD, FRCPC 1 *, Vikrant V. Sahasrabuddhe, MBBS, DrPH 2 *, Diana
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih
 Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Prepared By Jocelyn Palao and Layla Faqih The structure of the suspected atypical cell should always be compared to the structure of other similar, benign, cells which are present in the smears. The diagnosis
Title: PRIMARY SIGNET RING CELL CARCINOMA OF THE CERVIX: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 Accepted Manuscript Title: PRIMARY SIGNET RING CELL CARCINOMA OF THE CERVIX: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Author: Veysel Sal Ilker Kahramanoglu Hasan Turan Nedim Tokgozoglu Tugan Bese Ovgu
Accepted Manuscript Title: PRIMARY SIGNET RING CELL CARCINOMA OF THE CERVIX: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Author: Veysel Sal Ilker Kahramanoglu Hasan Turan Nedim Tokgozoglu Tugan Bese Ovgu
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98
 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2011 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 98 Radiology / Pathology Conference February 2011 Brooke Koltz, Cytopathology Resident Presentation
Enterprise Interest None
 Enterprise Interest None Invasive Stratified Mucin-producing Carcinoma (ismile) of the Cervix A Study in Morphology, Immunohistochemistry and Human Papillomavirus Status Kay J. Park, MD Memorial Sloan
Enterprise Interest None Invasive Stratified Mucin-producing Carcinoma (ismile) of the Cervix A Study in Morphology, Immunohistochemistry and Human Papillomavirus Status Kay J. Park, MD Memorial Sloan
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens
 How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
How to Recognize Gynecologic Cancer Cells from Pelvic Washing and Ascetic Specimens Wenxin Zheng, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Gynecology University of Arizona zhengw@email.arizona.edu http://www.zheng.gynpath.medicine.arizona.edu/index.html
HPV and Lower Genital Tract Disease. Simon Herrington University of Edinburgh, UK Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, UK
 HPV and Lower Genital Tract Disease Simon Herrington University of Edinburgh, UK Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, UK Conflict of interest/funding X None Company: Product royalties Paid consultant Research
HPV and Lower Genital Tract Disease Simon Herrington University of Edinburgh, UK Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, UK Conflict of interest/funding X None Company: Product royalties Paid consultant Research
Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. and invasive lobular carcinoma
 Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Case 3 - GYN. History: 66 year old, routine Pap test. Dr. Stelow
 Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
Case 3 - GYN History: 66 year old, routine Pap test Dr. Stelow Case 3 66 year year old woman Routine Pap Test Cytologic Features 3 dimensional clusters of cells with small to moderate amount of
Case history: Figure 1. H&E, 5x. Figure 2. H&E, 20x.
 1 Case history: A 49 year-old female presented with a 5 year history of chronic anal fissure. The patient s past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On digital rectal examination there was a very
1 Case history: A 49 year-old female presented with a 5 year history of chronic anal fissure. The patient s past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On digital rectal examination there was a very
ACCME/Disclosures. Diagnosing Mesothelioma in Limited Tissue Samples. Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology Companion Meeting March 12 th, 2016
 Diagnosing Mesothelioma in Limited Tissue Samples Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology Companion Meeting March 12 th, 2016 Sanja Dacic, MD, PhD University of Pittsburgh ACCME/Disclosures GENERAL RULES
Diagnosing Mesothelioma in Limited Tissue Samples Papanicolaou Society of Cytopathology Companion Meeting March 12 th, 2016 Sanja Dacic, MD, PhD University of Pittsburgh ACCME/Disclosures GENERAL RULES
BSD 2015 Case 19. Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is:
 BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21. Nodule on forehead. The best diagnosis is: A. mixed tumour of skin B. porocarcinoma C. nodular hidradenoma D. metastatic adenocarcinoma BSD 2015 Case 19 Female 21 Nodule on
Intravascular Endometrium Mimicking Vascular Invasion
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 A Papanicolau, G Lin Citation A Papanicolau, G Lin.. The Internet Journal of Pathology. 2010 Volume 12 Number 1. Abstract Intravascular endometrium
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 A Papanicolau, G Lin Citation A Papanicolau, G Lin.. The Internet Journal of Pathology. 2010 Volume 12 Number 1. Abstract Intravascular endometrium
Ascitic Fluid and Use of Immunocytochemistry. Mercè Jordà, University of Miami
 Ascitic Fluid and Use of Immunocytochemistry Mercè Jordà, University of Miami Is It Malignant? Yes? No Ascitic Fluid Cytomorphologic Useful Findings Tight clusters with smooth borders Cellular and nuclear
Ascitic Fluid and Use of Immunocytochemistry Mercè Jordà, University of Miami Is It Malignant? Yes? No Ascitic Fluid Cytomorphologic Useful Findings Tight clusters with smooth borders Cellular and nuclear
p16ink4a expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
 Original Article Brunei Int Med J. 2013; 9 (3): 165-171 p16ink4a expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer Kalpana KUMARI 1 and Akhila Arcot VADIVELAN 2 1 Department of Pathology,
Original Article Brunei Int Med J. 2013; 9 (3): 165-171 p16ink4a expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer Kalpana KUMARI 1 and Akhila Arcot VADIVELAN 2 1 Department of Pathology,
The LAST Guidelines in Clinical Practice. Implementing Recommendations for p16 Use
 AJCP / Original Article The LAST Guidelines in Clinical Practice Implementing Recommendations for p16 Use Lani K. Clinton, MD, PhD, 1,2 Kyle Miyazaki, 1 Asia Ayabe, 1 James Davis, PhD, 2 Pamela Tauchi-Nishi,
AJCP / Original Article The LAST Guidelines in Clinical Practice Implementing Recommendations for p16 Use Lani K. Clinton, MD, PhD, 1,2 Kyle Miyazaki, 1 Asia Ayabe, 1 James Davis, PhD, 2 Pamela Tauchi-Nishi,
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000
 Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Hyperchromatic Crowded Groups: What is Your Diagnosis? Session 3000 Thomas A. Bonfiglio, M.D. Professor Emeritus, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Rochester Disclosures In the past 12 months,
Cutaneous metastases. Thaddeus Mully. University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology
 Cutaneous metastases Thaddeus Mully University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Thaddeus Mully Course C005 Essential
Cutaneous metastases Thaddeus Mully University of California, San Francisco Professor, Departments of Pathology and Dermatology DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY Thaddeus Mully Course C005 Essential
Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 386921, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/386921 Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma Deba P. Sarma, 1 Daniel Olson, 1 Jennifer Olivella, 1 Tracey
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Volume 2011, Article ID 386921, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/386921 Case Report Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma Deba P. Sarma, 1 Daniel Olson, 1 Jennifer Olivella, 1 Tracey
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
BAP-oma & BEYOND MICHAEL A NOWAK, MD
 BAP-oma & BEYOND MICHAEL A NOWAK, MD CONFLICTS No conflicts with the content of this lecture BAP-oma Wiesner 2011: Families with multiple tan dome-shaped papules of head, neck, trunk, and extremities.
BAP-oma & BEYOND MICHAEL A NOWAK, MD CONFLICTS No conflicts with the content of this lecture BAP-oma Wiesner 2011: Families with multiple tan dome-shaped papules of head, neck, trunk, and extremities.
New Developments in Immunohistochemistry for Gynecologic Pathology
 New Developments in Immunohistochemistry for Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Gynecologic Oncology Immunohistochemistry in Gynecologic Pathology Majority
New Developments in Immunohistochemistry for Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Professor, Departments of Pathology and Gynecologic Oncology Immunohistochemistry in Gynecologic Pathology Majority
DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY)
 Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Translation from Romanian UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA THE FACULTY OF MEDICINE DOCTORAL THESIS (SUMMARY) Scientific coordinator Prof. Dr. Laurentiu MOGOANTA PhD student, Dr. Madalin IONILA
Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(1): 80-84
 80 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(1): 80-84 Letter to the Editor Assessing the Effectiveness of a Cervical Cancer Screening Program in a Hospital-based Study* YANG Yi1, LANG Jing He1, WANG You Fang1, CHENG
80 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(1): 80-84 Letter to the Editor Assessing the Effectiveness of a Cervical Cancer Screening Program in a Hospital-based Study* YANG Yi1, LANG Jing He1, WANG You Fang1, CHENG
Cervical FISH Testing for Triage and Support of Challenging Diagnoses: A Case Study of 2 Patients
 Cervical FISH Testing for Triage and Support of Challenging Diagnoses: A Case Study of 2 Patients Richard Hopley, MD, Alexandra Gillespie, MD* Laboratory Medicine 47:1:52-56 CLINICAL HISTORY Patients:
Cervical FISH Testing for Triage and Support of Challenging Diagnoses: A Case Study of 2 Patients Richard Hopley, MD, Alexandra Gillespie, MD* Laboratory Medicine 47:1:52-56 CLINICAL HISTORY Patients:
Signet-Ring Cell Change in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - A Rare Case Report
 Article ID: WMC00688 ISSN 2046-1690 Signet-Ring Cell Change in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - A Rare Case Report Author(s):Dr. Pallavi Bhuyan, Dr. Smita Mahapatra, Dr. Sujata Pujari, Dr. Jayasree Rath
Article ID: WMC00688 ISSN 2046-1690 Signet-Ring Cell Change in Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia - A Rare Case Report Author(s):Dr. Pallavi Bhuyan, Dr. Smita Mahapatra, Dr. Sujata Pujari, Dr. Jayasree Rath
Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery
 Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery Robert Glinert, MD and Song Q. Zhao, MD, Ph.D., MPH Department
Mapping Basal Cell and Squamous Carcinoma By 10 Min CK5 Direct Immunohistochemistry on Frozen Section Skin Tissues during Mohs Micrographic Surgery Robert Glinert, MD and Song Q. Zhao, MD, Ph.D., MPH Department
3/27/2017. Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships. Clinical History:
 Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Pulmonary Pathology Specialty Conference Saul Suster, M.D. Medical College of Wisconsin Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position
Colposcopy. Attila L Major, MD, PhD
 Colposcopy Attila L Major, MD, PhD Histology Colposcopy Cytology It has been estimated that annual Pap smear testing reduces a woman s chance of dying of cervical cancer from 4 in 1000 to about 5 in 10,000
Colposcopy Attila L Major, MD, PhD Histology Colposcopy Cytology It has been estimated that annual Pap smear testing reduces a woman s chance of dying of cervical cancer from 4 in 1000 to about 5 in 10,000
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
Differential diagnosis of HCC
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Quest for an Ideal Immunohistochemical Panel Sanjay Kakar, MD UCSF Differential diagnosis of HCC Hepatocellular lesions Adenoma, FNH, HG dysplasia Adenocarcinoma CholangioCA, metastasis
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Quest for an Ideal Immunohistochemical Panel Sanjay Kakar, MD UCSF Differential diagnosis of HCC Hepatocellular lesions Adenoma, FNH, HG dysplasia Adenocarcinoma CholangioCA, metastasis
INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES. 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH)
 INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH) Biopsy-Indications Diffuse/multifocal lesions (neoplastic, inflammatory, etc) Etiology of the
INTRODUCTION TO PATHOLOGICAL TECHNIQUES 1. Types of routine biopsy procedures 2. Special exams (IHC, FISH) Biopsy-Indications Diffuse/multifocal lesions (neoplastic, inflammatory, etc) Etiology of the
A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1878 A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre Rachana L Y, S.S. Hiremath*, Prabhu M H, S.S
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1878 A Study on Diagnostic Accuracy of Cervical Pap Smear by Correlating with Histopathology in a Tertiary Care Centre Rachana L Y, S.S. Hiremath*, Prabhu M H, S.S
Review and Updates of Immunohistochemistry in Selected Salivary Gland and Head and Neck Tumors
 Review and Updates of Immunohistochemistry in Selected Salivary Gland and Head and Neck Tumors. Monophasic tumors : myoepithelioma, acinic cell carcinoma, and salivary duct carcinoma. Biphasic tumors includes
Review and Updates of Immunohistochemistry in Selected Salivary Gland and Head and Neck Tumors. Monophasic tumors : myoepithelioma, acinic cell carcinoma, and salivary duct carcinoma. Biphasic tumors includes
Cytological Sub-classification of Lung Cancer: Morphologic and Molecular Characteristics. Mercè Jordà, University of Miami
 Cytological Sub-classification of Lung Cancer: Morphologic and Molecular Characteristics Mercè Jordà, University of Miami Mortality Lung cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer incidence and mortality
Cytological Sub-classification of Lung Cancer: Morphologic and Molecular Characteristics Mercè Jordà, University of Miami Mortality Lung cancer is the most frequent cause of cancer incidence and mortality
Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas
 Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Early Online Release Publication: Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 12/18/2017 Overview
Human Papillomavirus Testing in Head and Neck Carcinomas Guideline from the College of American Pathologists Early Online Release Publication: Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine 12/18/2017 Overview
A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy.
 November 2015 Case of the Month A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy. Contributed by: Rasha Salama, M.D., IU Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
November 2015 Case of the Month A 53 year-old woman with a lung mass, right hilar mass and mediastinal adenopathy. Contributed by: Rasha Salama, M.D., IU Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
CERVIX. MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb.
 CERVIX MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb. CERVIX Most cervical lesions are: Most are Cervicitis. cancers ( common in women worldwide). CERVICITIS Extremely
CERVIX MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L12 : Dr. Ali Eltayb. CERVIX Most cervical lesions are: Most are Cervicitis. cancers ( common in women worldwide). CERVICITIS Extremely
Gynaecological Malignancies
 Gynaecological Malignancies Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Overview Genital tract tumors
Gynaecological Malignancies Dr Rodney Itaki Lecturer Anatomical Pathology Discipline University of Papua New Guinea Division of Pathology School of Medicine & Health Sciences Overview Genital tract tumors
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
History A 89 year old gentleman presenting with a scalp/forehead nodule. Patient had squamous cell carcinoma 18 m at same site, excised. Outside diagn
 Case III History A 89 year old gentleman presenting with a scalp/forehead nodule. Patient had squamous cell carcinoma 18 m at same site, excised. Outside diagnoses: Squamous cell carcinoma. R/O: SCC, Melanoma,
Case III History A 89 year old gentleman presenting with a scalp/forehead nodule. Patient had squamous cell carcinoma 18 m at same site, excised. Outside diagnoses: Squamous cell carcinoma. R/O: SCC, Melanoma,
LESION AT PACIFIC MEDICAL COLLEGE, UDAIPUR. 1. Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Pacific Medical college and hospital, Udaipur.
 International Journal of Medical Science and Education An official Publication of Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) Original Research Article HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND CYTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS
International Journal of Medical Science and Education An official Publication of Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) Original Research Article HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND CYTOLOGICAL ANALYSIS
A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube
 A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube Kate Madhuri S 1, Gulhane Sushma R 2, Mane Sheetal V 3 1 Professor and Head, 2 Specialist cum
A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube Kate Madhuri S 1, Gulhane Sushma R 2, Mane Sheetal V 3 1 Professor and Head, 2 Specialist cum
Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms
 Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms Current Clinical Pathology ANTONIO GIORDANO, MD, PHD SERIES EDITOR For further titles published in this series, go to http://www.springer.com/springer/series/7632
Cytology and Surgical Pathology of Gynecologic Neoplasms Current Clinical Pathology ANTONIO GIORDANO, MD, PHD SERIES EDITOR For further titles published in this series, go to http://www.springer.com/springer/series/7632
Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma
 Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Anatomic Pathology / CYTOKERATINS 7 AND 20 IN PROSTATE AND BLADDER CARCINOMAS Coordinate Expression of Cytokeratins 7 and 20 in Prostate Adenocarcinoma and Bladder Urothelial Carcinoma Nader H. Bassily,
Case 18. M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is:
 Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Case 18 M75. Excision of mass on scalp. Clinically SCC. The best diagnosis is: A. Pilomatrical carcinoma B. Adnexal carcinoma NOS C. Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma D.Primary squamous cell carcinoma
Clinically Microscopically Pathogenesis: autoimmune not lifetime
 Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Vulvar Diseases: Can be divided to non-neoplastic and neoplastic diseases. The neoplastic diseases are much less common. Of those, squamous cell carcinoma is the most common. most common in postmenopausal
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Cytology/Biopsy/Leep Gynecologic Correlation: Practical Considerations and Approaches.
 Cytology/Biopsy/Leep Gynecologic Correlation: Practical Considerations and Approaches. Fadi W. Abdul-Karim MD MEd. Professor of Pathology. Vice chair for education. Robert Tomsich Pathology and Lab Med
Cytology/Biopsy/Leep Gynecologic Correlation: Practical Considerations and Approaches. Fadi W. Abdul-Karim MD MEd. Professor of Pathology. Vice chair for education. Robert Tomsich Pathology and Lab Med
Oncocytic-Appearing Salivary Gland Tumors. Oncocytic, Cystic, Mucinous, and High Grade Salivary Gland Tumors SALIVARY GLAND FNA: PART II
 William C. Faquin, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Harvard Medical School Director of Head and Neck Pathology Massachusetts Eye and Ear Massachusetts General Hospital SALIVARY GLAND FNA: PART II Oncocytic,
William C. Faquin, MD, PhD Professor of Pathology Harvard Medical School Director of Head and Neck Pathology Massachusetts Eye and Ear Massachusetts General Hospital SALIVARY GLAND FNA: PART II Oncocytic,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
HPV Genotyping: A New Dimension in Cervical Cancer Screening Tests
 HPV Genotyping: A New Dimension in Cervical Cancer Screening Tests Lee P. Shulman MD The Anna Ross Lapham Professor in Obstetrics and Gynecology and Chief, Division of Clinical Genetics Feinberg School
HPV Genotyping: A New Dimension in Cervical Cancer Screening Tests Lee P. Shulman MD The Anna Ross Lapham Professor in Obstetrics and Gynecology and Chief, Division of Clinical Genetics Feinberg School
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
4/12/2018. MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, Jesse K. McKenney, MD
 MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, 2018 Jesse K. McKenney, MD 1 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation 2 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation Recognition as
MUSC Pathology Symposium Kiawah Island April 18, 2018 Jesse K. McKenney, MD 1 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation 2 Urothelial Carcinoma with Alternative Differentiation Recognition as
Lessons From Cases of Screened Women Who Developed Cervical Carcinoma
 Lessons From Cases of Screened Women Who Developed Cervical Carcinoma R. Marshall Austin MD,PhD Magee-Womens Hospital of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center raustin@magee.edu Why Focus Study On Cases
Lessons From Cases of Screened Women Who Developed Cervical Carcinoma R. Marshall Austin MD,PhD Magee-Womens Hospital of University of Pittsburgh Medical Center raustin@magee.edu Why Focus Study On Cases
Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions
 Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Disclosure Select problems in cystic pancreatic lesions Five Prime Therapeutics shareholder Adicet Bio shareholder Bristol-Meyer Squibb advisory board grace.kim@ucsf.edu Pancreatic cystic lesions Intraductal
Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Lebanon Neuroendocrine Neoplasms of H&N Nov /7/2011. Broad Classification:
 H&N Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Classification and Diagnostic Considerations Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas Broad Classification: A. Epithelial:
H&N Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: Classification and Diagnostic Considerations Adel K. El-Naggar, M.D., Ph.D. The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas Broad Classification: A. Epithelial:
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H)
 SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
SQUAMOUS CELLS: Atypical squamous cells (ASC) - of undetermined significance (ASC-US) - cannot exclude HSIL (ASC-H) ASC refers to cytologic changes suggestive of SIL, which are qualitativley or quantitatively
Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8568-8572 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010093 Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(7):8568-8572 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010093 Case Report A case of matrix-producing carcinoma of the breast with micoglandular adenosis and review of literature
Basal cell carcinoma 5/28/2011
 Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Goal of this Presentation A practical approach to the diagnosis of cutaneous carcinomas and their mimics Thaddeus Mully, MD University of California San Francisco To review common non-melanoma skin cancers
Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng
 ADS Dermatopathology Meeting 2014 Selected Adnexal Tumors Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng Associate Professor, Dermatology & Pathology Director of Dermatopathology (Dermatology) University of Colorado School
ADS Dermatopathology Meeting 2014 Selected Adnexal Tumors Whitney A. High, MD, JD, MEng Associate Professor, Dermatology & Pathology Director of Dermatopathology (Dermatology) University of Colorado School
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Iulia Bârsan, MD, Lien Hoang, MD, Cristina Terinte, MD, Anna Pesci, MD, Sarit Aviel-Ronen, MD, Takako Kiyokawa, MD, Isabel Alvarado- Cabrero, MD, Esther Oliva, MD,
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Iulia Bârsan, MD, Lien Hoang, MD, Cristina Terinte, MD, Anna Pesci, MD, Sarit Aviel-Ronen, MD, Takako Kiyokawa, MD, Isabel Alvarado- Cabrero, MD, Esther Oliva, MD,
CK17 and p16 expression patterns distinguish (atypical) immature squamous metaplasia from high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN III)
 Histopathology 2007, 50, 629 635. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02652.x CK17 and p16 expression patterns distinguish (atypical) immature squamous metaplasia from high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Histopathology 2007, 50, 629 635. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2007.02652.x CK17 and p16 expression patterns distinguish (atypical) immature squamous metaplasia from high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Squamous entities of the thyroid: Reactive to Neoplastic Michelle D. Williams Associate Professor Dept of Pathology, Head & Neck Section University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosure of Relevant
Squamous entities of the thyroid: Reactive to Neoplastic Michelle D. Williams Associate Professor Dept of Pathology, Head & Neck Section University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Disclosure of Relevant
Thyroid pathology Practical part
 Thyroid pathology Practical part My Algorithm After a good macroscopy and a microscopic overview of the lesion, I especially look at the capsule and the thyroid just above and just beneath the capsule.
Thyroid pathology Practical part My Algorithm After a good macroscopy and a microscopic overview of the lesion, I especially look at the capsule and the thyroid just above and just beneath the capsule.
Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K)
 Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
LGM International, Inc.
 Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Liqui-PREP TM Cytology Atlas Preface The following pictures are examples with descriptions of cytology slides processed with the Liqui-PREP TM System.. The descriptions are reviewed by Pathologists. It
Hemorrhoidal disease is the consequence of distal displacement
 Pagetoid Dyskeratosis Is a Frequent Incidental Finding in Hemorrhoidal Disease J. Fernando Val-Bernal, MD, PhD; Jesús Pinto, MD Background. Pagetoid dyskeratosis is considered a selective keratinocytic
Pagetoid Dyskeratosis Is a Frequent Incidental Finding in Hemorrhoidal Disease J. Fernando Val-Bernal, MD, PhD; Jesús Pinto, MD Background. Pagetoid dyskeratosis is considered a selective keratinocytic
Immunohistochemical Expression of Cytokeratin 5/6 in Gynaecological Tumors.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Immunohistochemical Expression of Cytokeratin 5/6 in Gynaecological Tumors. A Baghla, S Choudhry, A Kataria Citation A Baghla, S Choudhry,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 13 Number 2 Immunohistochemical Expression of Cytokeratin 5/6 in Gynaecological Tumors. A Baghla, S Choudhry, A Kataria Citation A Baghla, S Choudhry,
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT
 Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Maligna Melanoma and Atypical Fibroxanthoma: An Unusual Collision Tumour G Türkcü 1, A Keleş 1, U Alabalık 1, D Uçmak 2, H Büyükbayram 1 ABSTRACT Two different neoplasia in the same biopsy material called
Histopathological diagnosis of CUP
 Histopathological diagnosis of CUP Dr Karin Oien karin.oien@glasgow.ac.uk Disclosure slide Dr Karin Oien has no financial interests in any company mentioned in this presentation. Dr Karin Oien is conducting
Histopathological diagnosis of CUP Dr Karin Oien karin.oien@glasgow.ac.uk Disclosure slide Dr Karin Oien has no financial interests in any company mentioned in this presentation. Dr Karin Oien is conducting
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007
 International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
International Society of Gynecological Pathologists Symposium 2007 Anais Malpica, M.D. Department of Pathology The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Grading of Ovarian Cancer Histologic grade
Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors. Thomas Brenn
 Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors Thomas Brenn Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumours Wide morphological and biological spectrum Myofibroblastic, smooth muscle, neural, vascular, apidocytic, undifferentiated;
Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors Thomas Brenn Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumours Wide morphological and biological spectrum Myofibroblastic, smooth muscle, neural, vascular, apidocytic, undifferentiated;
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017
 Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Urinary Bladder: WHO Classification and AJCC Staging Update 2017 Houston Society of Clinical Pathologists 58 th Annual Spring Symposium Houston, TX April 8, 2017 Jesse K. McKenney, MD Classification
Immunohistochemistry on Fluid Specimens: Technical Considerations
 Immunohistochemistry on Fluid Specimens: Technical Considerations Blake Gilks Dept of Pathology University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada Disclosures None Learning Objectives At the end of
Immunohistochemistry on Fluid Specimens: Technical Considerations Blake Gilks Dept of Pathology University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada Disclosures None Learning Objectives At the end of
Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa
 BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
BDIAP London, November 2010 School of Clinical Dentistry University of Sheffield Diagnostic difficulties with lesions of the oral mucosa Paul M Speight Dept Oral & Maxillofacial Pathology University of
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Primary enteric adenocarcinoma with predominantly signet ring features of the lung: A case report with clinicopathological and molecular findings
 CASE REPORT Primary enteric adenocarcinoma with predominantly signet ring features of the lung: A case report with clinicopathological and molecular findings Makoto Nagashima 1, Ayako Moriyama 1, Yasuo
CASE REPORT Primary enteric adenocarcinoma with predominantly signet ring features of the lung: A case report with clinicopathological and molecular findings Makoto Nagashima 1, Ayako Moriyama 1, Yasuo
A cyto-histopathological correlation study of lesions of uterine cervix
 Original Research Article Mandakini B. Tengli 1,*, Mohammed Mateen Ahmed 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pathology, KBNIMS, Gulbarga *Corresponding Author: Email: mandakinibt@gmail.com
Original Research Article Mandakini B. Tengli 1,*, Mohammed Mateen Ahmed 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pathology, KBNIMS, Gulbarga *Corresponding Author: Email: mandakinibt@gmail.com
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
