Angiogenesis and Metastasis
|
|
|
- Jasper Bradford
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Angiogenesis and Metastasis 10/31/2017 Tariq Bhat (Ph.D.)
2 Definition of Angiogenesis: Formation of new blood vessels/capillaries from the pre-existing vessels/capillaries Involves - sprouting - splitting - Remodeling (of the existing vessels) Why is it important??? - supply of oxygen and nutrients to tissues/organs - removal of waste products from tissues/organs - fuels tumor growth, progression and metastasis
3 Types of new vessel/ capillary formation Vasculogenesis: - Blood vessel formation by endothelial cells (ECs) that differentiate from stem cells - Seen during embryonic development (primary vasculature) Angiogenesis: - New capillaries or vessels from the pre-existing vessels - Seen during the embryonic development and in adult life - Physiologic stimuli (wound/injury Or reproductive cycle in women) Arteriogenesis - Growth of large arteries from pre-existing small vessels/capillaries Lymphangiogenesis - Formation of the lymphatic vasculature
4
5 Tumor angiogenesis
6 Vasculogenesis: Vessels formation by ECs differentiating from angioblasts in the yolk sac of embryo - differentiation and proliferation of ECs in a non-vascularized tissue - leads to formation of a primitive tubular network - undergoes angiogenic remodeling to stabilize vascular system
7 Postnatal vasculogenesis Hemangioblast Angioblast Endothelial cell (EC)
8 Structure of vessels and capillaries Small artery: Monocellular layer of endothelial cells
9 Angiogenesis is a multi-step process: 4 major steps by endothelial cells during angiogenesis 1. Breaking through of the basal lamina that envelops existing blood vessels 2. Migration toward a source signal (chemotactic signal) 3. Proliferation (cell division) 4. Formation of tubes
10 Conti Angiogenesis- multistep process: Key Stage Markers Stage One: Endothelial cell activation in response to angiogenic factors. Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (bfgf): a potent stimulatory factor for endothelial cell migration and proliferation. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF): initiates cell proliferation and migration. Stage Two: Degradation of the capillary wall by extracellular proteinases. Stage Three: Formation of a branch point in the vessel wall. Stage Four: Migration of endothelial cells into the extracellular matrix towards the angiogenic stimulus. Stage Five: Reorganisation of endothelial cells to form tubules with a central lumen. Stage Six: Interconnection of the new tubules to form a network (anastomosis). Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs): MMP1 (a collagenase) and MMP2 are expressed during angiogenesis and act to degrade extracellular matrix components. Integrins: expressed on newly forming vessels. Integrins: allow migrating endothelial cells to interact with specific components of the surrounding matrix. MMPs and urokinase: aid migration of endothelial cells into the surrounding matrix. Angiopoietin (Ang 1): produced by surrounding stromal cells; facilitates endothelial cell survival and stabilisation of new capillary tubes. Platelet Derived Growth Factor (PDGF): produced by endothelial cells of the new capillaries; recruits pericytes which stabilize the new vessels.
11 Life time of endothelial cells (major players): - Months (lung, liver) to Years (brain, muscle) - Slow repair and renewal of vascular wall New vessel formation: - Embryo, growth to adulthood, - In uterus, during menstruation cycle - Wound repair - Tumor angiogenesis
12 TYPE Sprouting angiogenesis Intussusceptive angiogenesis
13 Sprouting angiogenesis Non-sprouting angiogenesis A) Sprouting angiogenesis: formation of blood vessels is a multi-step process, which includes: (i) angiogenic chemoattractant signals (yellow spot) activate endothelial cells (EC) (ii) retraction of pericytes from the abluminal surface of capillary and secretion of proteases from activated EC (aec) to degrade ECM (green dash-line) (iii) chemotactic migration of EC under the angiogenic stimulators (iv) proliferation of EC and formation of lumen/canalisation by fusion of formed vessels with formation of tight junctions B) Non-sprouting angiogenesis intussusceptive microvascular growth: It is initiated by (i) protrusion of opposing capillary walls towards the lumen (ii) perforation of the EC bilayer and formation of many transcapillaries with interstitial core (red arrow) (iii) formation of the vascular tree from intussusceptive pillar formation and pillar fusion and elongation of capillaries (green arrows) (v) recruitment of pericytes and deposition of new basement membrane and initiation of blood flow.
14 stem tip cell Angiogenic factor production (VEGF, bfgf), secretion of proteases, resolution of basal lamina, migration towards chemotactic gradient, proliferation, tube formation
15 Capillaries sprouting in the retina of an embryonic mouse
16
17
18 VEGF
19 Chorioallantoic Membrane Assay (CAM) Serum free-media Serum free-media plus VEGF
20 Flt- FMS-like tyrosine kinase KDR- Kinase insert domain receptor (KDR, a type III receptor tyrosine kinase)
21 VEGF-VEGFR signaling Angiogenesis EC proliferation, survival, migration and invasion
22 VEGF Is a Key Mediator of Angiogenesis Upstream activators of VEGF synthesis Downstream signaling pathways
23 Hypoxia and Angiogenesis Hypoxia induces Angiogenesis: - during embryonic development - tumor growth - ischemia How??? Hypoxia induces Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)
24 Role of hypoxia in angiogenesis: (Hypoxia - HIF VEGF module) Angiogenic Switch Or Mutant VHL E3-ubiquitin Ligase complex Like VEGF VBC: Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)- containing VHL-elongin B/C and cullin-2
25 Role of hypoxia in angiogenesis: (Hypoxia - HIF VEGF module) conti HIF: hypoxia inducible factor VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor
26 Von Hippel-Lindau Tumor Suppressor, HIF and VEGF
27 Angiogenesis-dependent diseases Excess: Cancer Infantile hemangiomas Autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis Psoriasis Age-related macular degeneration Atherosclerosis Deficiency: Limb ischemia Myocardial ischemia
28 Angiogenic inhibitors: During the process of wound healing, the burst of angiogenesis must be shut down once the newly formed capillaries have reached a certain density. TSP-1 produced by stromal fibroblasts, ECs and immune cells suppresses tumor progression by inhibiting angiogenesis through direct effects on EC migration and survival and through indirect effects on growth factor mobilization.
29
30
31
32 Inhibits EC migration, proliferation and induces EC apoptosis
33 Tumor angiogenesis Judah Folkman (1971)- Angiogenesis is a pre-requisite process for tumor growth and metastatic progression Angioprevention- Targeting angiogenesis advocated for cancer therapy
34
35 Tumor growth and angiogenesis Solid tumors can grow in size up to ~1-2 mm diameter by simple diffusion of nutrients and gaseous exchange. However, beyond this size limit they require active supply of such components for tumor growth and progression. Angiogenic Switch Hypoxia Stabilization of HIF-alpha HR-gene expression (VGF) Growth, proliferation, survival and migration of ECs Sprouting, tube formation and tumor vasculature formation Tumor growth and metastatic progression
36 Carcinogenesis process
37 Features of tumor angiogenesis Extreme and chaotic expression of angiogenic factors Disorganized vascular structure and Low adhesion and pericyte coverage Hypoxic stress, metabolic changes, cancer cell intravasation and lesser effects of chemotherapy
38 What Is Tumor Angiogenesis? Tumor angiogenesis Proliferation of a network of blood vessels that penetrates into cancerous growths. Function Supplying nutrients and oxygen and removing waste products. Mechanism Cancer cells release molecules that send signals to surrounding normal host tissue. This signaling activates certain genes in the host tissue that, in turn, make proteins to encourage growth of new blood vessels.
39 Stroma contributes to tumor angiogenesis Tumor Microenvironment (Tumor-associated stroma): induced by cytokines and chemokines secreted from tumor cells Macrophage: Tumor- Associated Macrophages (TAMs) Fibroblast: Carcinoma- Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) Myeloid cell: Bone Marrow Derived Cells (BMDCs) Extracellular matrix (ECM) Tumor microenvironment complexity and degree of infiltration of various components correlates with the tumor angiogenesis and invasiveness
40 Macrophage and tumor angiogenesis
41 Anti-angiogenic therapy Dr. Judah Folkman proposed the concept of anti-angiogenic therapy (NEJM.1971).
42
43 Antiangiogenic Therapies Potential Targets: Block pro-angiogenic molecules (e.g., VEGF) Using anti-angiogenic agents (e.g. angiostatin, endostatin, TSP-1) Inhibit stroma-degrading enzymes (e.g., MMPIs) Target vascular antigens (e.g., avb3 integrin) Attack pericytes
44
45
46 Limitations of Anti-angiogenic therapy Resistance: expression of alternative angiogenic factors such as bfgf and PDGF Toxicity and dosage (off target effects) Normalize disorganized tumor blood vessels Side effects (high blood pressure, bleeding and coronary artery disease)
47
48 Metastasis
49 When does metastasis begin? Commitment to the metastatic phenotype: How early does it occur? Can it be reversed? Progenitor lesions: What are the key progenitor lesions? What is the efficiency of transition to invasion? Are all metastasis precursors clonal?
50 What is the role of the host? Under what conditions does the host drive or suppress the process? Does the transition from pre-invasive to invasive lesions require host participation? If so what are the molecular and cellular players that are functionally important? The circuitry of the tumor host communication may be the key to prevention of invasion.
51 Physiologic basis of metastasis Is metastasis a normal physiologic program which is disregulated or inappropriately activated? Does a physiologic motility and invasion program exist for development, angiogenesis morphogenesis and wound healing? Is metastasis colony formation a natural ongoing process conducted by stem cells?
52 What is the driving force? Is the metastatic phenotype pre determined within the primary tumor? Within the host microenvironment? Are malignant cells a product of adaptation and selection? What is the selection factor? If malignant cells are survival of the fittest, then what is the fitness test? Is cell survival in a foreign (non home) tissue the ultimate selection factor?
53 Metastasis Pre-1900 Pre-cellular theory of invasion and metastasis: recognition of malignant tumors and localized versus metastatic disease LeDran 1757: Noted that malignant tumors begin as localized disease, then spread to regional lymph nodes and then enter the circulation to subsequently appear in the lung Bichat 1801: Tumors contain both parenchyma and stroma Recamier 1829 : Used the term Metastases
54 Validation of the cellular theory of cancer metastasis
55 The organ pattern of metastasis is characteristic of the tumor type and tissue of origin. Potential molecular mechanisms: a) Preferential adhesion in the vessels of the target organ b) Selective extravasation c) Organ attractants d) Organ specific survival and growth
56 Pre-metastatic niche formation Something secreted from primary tumor and changing the behavior of host tissue at distant sites
57 Cancer develops through gradual changes in cell morphology and properties benign tumor malignant tumor
58 Where do they go? Metastatic tropism Figure The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
59 Metastasis- a stepwise process Figure 14.17b The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
60 An organ is composed of several tissues Epithelial cells Connective tissue Muscle tissue
61 Cancer cells change their epithelial properties, lose their adhesion and penetrate through physical barriers basal lamina connective tissue
62 Intravasation
63 Once lodged in the blood vessels of various tissues, cancer cells must escape from the lumina of these vessels and penetrate into the surrounding tissue- the step termed extravasation.
64 Platelet-mediated tumor cell extravasation Formation of microthrombus (attachment of platelets) and Proliferation in the lumen of the capillary
65 The blood: a hostile environment - Cells are normally anchorage-dependent (anoikis) - Shear forces tear cells apart Figure 14.7b The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
66 After extravasation what next???
67 Chemokines regulate leukocyte recirculation and trafficking to sites of inflammation and infection
68 The CXCR4/CXCL12 axis is one of the most studied chemokine receptor axis and has been shown to play a vital role in metastasis Metastatic breast cancers selectively express chemokine receptor CXCR4 and migrate to organs that express high levels of its respective ligand CXCL12, also known as SDF-1. Chemokine receptor CXCR4 is consistently upregulated in metastatic breast cancer cell lines, lymph node metastases, and liver metastases while expression levels are undetectable in normal epithelial cells. Its ligand CXCL12, meanwhile, is preferentially expressed in the most common sites of breast cancer metastasis, lung, brain, lymph nodes, liver, and bone marrow.
69 Premise: Metastasis homing is dictated by relative abundance of chemokines and cognate receptors on the tumor cell. Why do the tumor cells express the chemokine receptors in the primary tumor prior to dissemination? Therapeutic utility is limited because dissemination has already occurred at the time of diagnosis
70 Colonization First, micrometastases Figure 14.10a The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
71 Dormant micrometastases are viable Figure The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007) Figure 14.50a The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
72 Eventually: macrometastases Intravasation Latency Angiogenesis Colonization Steeg Nature Med 06
73 Nguyen, Nature Rev. Cancer 2009
74 Metastatic inefficiency A sequence of inefficient steps Figure Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008)
75 Metastasis Promoting Genes - I Gene Tissue Site Function ARM-1 Lymphoma Promotes adhesion of tumor cells to the endothelium ATX Breast, Liver, Lung, Melanoma, Teratocarcinoma cytoskeletal reorganization and motility; G- protein coupled receptor activation CD44 Multiple sites cell-cell interactions; activates HGF/c-Met pathway Cox2 Breast, Colorectal, Gastric Prostaglandin synthase; induces VEGF Cyr61 Breast Mediates adhesion; Erb-B2/3/4 pathway Ezrin HMG-I(Y) Liver, Ovary, Pancreas, Prostate, Uterus Breast, Cervical, Colorectal, Prostate, Skin, Thyroid, Uterus Membrane-cytoskeletal linker; RHO and RAC interactions Regulated by EGF and MMP-9 Laminin-5 Multiple sites EGF and TGF-a induce expression of laminin subunits; cell adhesion, motility c-met Multiple sites Activated by HGF; Modulates Ras and PI3 kinase
76 Metastasis Promoting Genes - II Gene Tissue Site Function MTA1 Breast, Cervix, Melanoma, Ovary Neucleosome remodeling; histone deacetylase complex Oncostatin M Lung Activates PKA-dependent pathway PP2A Not determined Activated by p38/mapk; inhibits MEK1, MEK2, and MMP-1 RAGE Gastric, Lung, Pancreatic, Renal transmembrane receptor; activates p21, MAPKs, NF-6B, cdc42/rac S100A4 Breast, Colorectal, Prostate Calcium-binding protein; activates c-erbb-2 S100A9 Colon, Gastric, Skin Calcium-binding protein; Modulates Mac-1 integrin receptor through G-protein Semaphorins Gastric, Leukemia, Lung, Skin cell-cell interactions; Receptor crosstalk with c-met binding semaphorin receptor, plexin Thymosin-b15 Prostate actin binding; motility Wnt-5a Breast, Colon, Lung, Melanoma, Pancreas, Prostate PKC activation with associated changes in cytoskeleton, cell adhesion, and motility
77 Metastasis Suppressor Genes - I Gene Tissue Site Function Annexin7 Prostate calcium-dependent GTPase; substrate for PKC and other kinases associated with proliferation BRMS1 Breast, Melanoma gap-junctional communication CC3 Colon, Lung serine/threonine kinase CEACAM1-4S Breast, Colon Bax pathway CRSP3 Melanoma transcriptional co-activator DAP-kinase Multiple sites calcium/calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine kinase; pro-apoptotic pathway E-cadherin Multiple sites Wnt signaling; cytoskeleton; cell-cell adhesion HEPSIN Ovarian, Prostate, Renal transmembrane serine protease HPI HSa Breast non-histone heterochromatin-associated protein KAI-1 Breast, Prostate Transmembrane tetraspondin; role in adhesion, motility, growth regulation, and differentiation; integrin interaction KiSS1 Breast, Melanoma Modulates Rho, Rac, and MAPK signaling Maspin Breast, Colon, Oral Squamous Cell, Prostate Serine protease inhibitor; binds collagen and can modulate integrins Melastatin Melanoma Calcium channel protein
78 Metastasis Suppressor Genes - II Gene Tissue Site Function MKK4 Ovary, Prostate MAPK; phosphorylates and activates p38 and JNK kinases NESH Lung, Prostate src homology 3 adapter protein; down regulates p21 pathway NM23-H1 Breast, Colon, Melanoma, Oral Squamous Cell histidine kinase; phosphorylates KSR, which might reduce ERK 1/2 activation PTEN Multiple sites phosphatase; growth regulation, cell motility RhoGD12 Bladder Inhibits GTP binding; regulates RHO and RAC SFRP1 Breast, Colorectal Modulates Wnt signaling pathway SHPS-1 Breast, Leukemia glycoprotein; may regulate RAS-MAPK signaling; suppresses anchorage independent growth Syk Breast, Colon, Pancreas, Skin Tyrosine kinase; inhibits PI3 kinase; necessary for MAPK activation TSP-1 Multiple sites inhibits endothelial cell proliferation and migration; c-myc expression inhibits TSP-1 tropomyosins Breast interacts with e-cadherin/catenin complex VDUP1 Melanoma Thioredoxin inhibitor; upregulates KiSS1; interacts with CRSPs
79 How do cells become invasive???
80 EMT Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition sea urchin embryo Figure 14.13a The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
81 Major changes during EMT - Loss of E-cadherin - Cell shape changes driven by Rho GTPases - MMPs
82
83
84 EMT in Tumor Progression
85 Adopting changes typical to EMT Twist plays an essential role in cancer metastasis. Over-expression of Twist is common in metastatic carcinomas. Figure 14.15b The Biology of Cancer ( Garland Science 2007)
86 MMPs (matrix metalloproteinases) help the cancer cells to invade the ECM
87 Signals from stroma controlling EMT
88 Snail or Slug functions Epithelial Markers Proliferation Mesenchymal markers Cell shape changes Cell movements, invasion Survival E-cadherin Claudins Occludins Desmoplakin Cytokeratins Cyclin D CDK4 Rb phosph p21 Fibronectin Vitronectin Vimentin RhoB MMPs PI3K activity ERK activity Caspases P53 BID
89 Small GTPase family plays a key role of cancer cell motility Cytokines Chemokines Extracellular matrix Rho family Rho Rac Cdc42 Stress fiber Focal adhesion Lamellipodia Filopodia
90 EMT and cancer progression Correlation between EMT inducing TFs with the malignant behavior in cancer patients
91
92 What we learn today!!! Angiogenesis (role of VEGF etc.) Tumor Angiogenesis Metastasis and role of Tumor Angiogenesis Invasion and migration EMT process Angioprevention OR anti-angiogenic therapy in preventing tumor metastasis Targeting Tumor Metastasis
93
Positive and Negative Regulators of Metastasis
 Positive and Negative Regulators of Metastasis J. Carl Barrett Laboratory of Biosystems and Cancer Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute TIME SCALE OF TUMOR PROGRESSION CHEMOPREVENTION PERIOD
Positive and Negative Regulators of Metastasis J. Carl Barrett Laboratory of Biosystems and Cancer Center for Cancer Research National Cancer Institute TIME SCALE OF TUMOR PROGRESSION CHEMOPREVENTION PERIOD
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
1. The metastatic cascade. 3. Pathologic features of metastasis. 4. Therapeutic ramifications. Which malignant cells will metastasize?
 1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
!!! Oncology for Scientists (RPN 530) Metastasis and Angiogenesis Chapter 13 and 14 Oct. 28 th 2014
 Oncology for Scientists (RPN 530) Metastasis and Angiogenesis Chapter 13 and 14 Oct. 28 th 2014 Department of Cancer Genetics Masashi Muramatsu, Ph.D. About Exam First, think and understand the concepts.
Oncology for Scientists (RPN 530) Metastasis and Angiogenesis Chapter 13 and 14 Oct. 28 th 2014 Department of Cancer Genetics Masashi Muramatsu, Ph.D. About Exam First, think and understand the concepts.
Cancer Biology Course. Invasion and Metastasis
 Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Tissue repair. (3&4 of 4)
 Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 21 Done by Ahmad Rawajbeh Corrected by Omar Sami Doctor Maha Shomaf Ability to Invade and Metastasize The metastatic cascade can be subdivided into two phases: 1-invasion of ECM and vascular dissemination:
number 21 Done by Ahmad Rawajbeh Corrected by Omar Sami Doctor Maha Shomaf Ability to Invade and Metastasize The metastatic cascade can be subdivided into two phases: 1-invasion of ECM and vascular dissemination:
Heterotypy and Angiogenesis
 Heterotypy and Angiogenesis Tumors are perpetual wounds 1. Normally stroma and epithelia converse at a distance. 2. Juxtaposition of stroma and epithelia is indicative of tissue damage. 4. Activate strategies
Heterotypy and Angiogenesis Tumors are perpetual wounds 1. Normally stroma and epithelia converse at a distance. 2. Juxtaposition of stroma and epithelia is indicative of tissue damage. 4. Activate strategies
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis
 Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
Processing of VEGF-C and -D by the Proprotein Convertases: Importance in Angiogenesis, Lymphangiogenesis, and Tumorigenesis
 Processing of VEGF-C and -D by the Proprotein Convertases: Importance in Angiogenesis, Lymphangiogenesis, and Tumorigenesis ii Colloquium Digital Library of Life Sciences This e-book is an original work
Processing of VEGF-C and -D by the Proprotein Convertases: Importance in Angiogenesis, Lymphangiogenesis, and Tumorigenesis ii Colloquium Digital Library of Life Sciences This e-book is an original work
Chapter 6. Villous Growth
 Core Curriculum in Perinatal Pathology Chapter 6 Villous Growth Overview of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis Vasculogenesis Extraembryonic Vasculogenesis Angiogenesis Branching angiogenesis Sprouting angiogenesis
Core Curriculum in Perinatal Pathology Chapter 6 Villous Growth Overview of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis Vasculogenesis Extraembryonic Vasculogenesis Angiogenesis Branching angiogenesis Sprouting angiogenesis
The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer
 Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Tissue renewal and Repair. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science
 Tissue renewal and Repair Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Email: nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science Topic Objectives 1. Describe processes of tissue repair, regeneration
Tissue renewal and Repair Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Email: nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science Topic Objectives 1. Describe processes of tissue repair, regeneration
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance
 Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century.
 Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century. In The Distribution Of Secondary Growths In Cancer Of The Breast Paget presents and analyzes 735 fatal cases of breast cancer, complete
Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century. In The Distribution Of Secondary Growths In Cancer Of The Breast Paget presents and analyzes 735 fatal cases of breast cancer, complete
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA
 PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
Oncolytic Virotherapy: Targeting Cancer Stem Cells
 Oncolytic Virotherapy: Targeting Cancer Stem Cells Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) or Cancer Initiating Cells (CICs) A consensus of five defining criteria has been established to affirm the existence of CICs:
Oncolytic Virotherapy: Targeting Cancer Stem Cells Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) or Cancer Initiating Cells (CICs) A consensus of five defining criteria has been established to affirm the existence of CICs:
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto Apr 2010 Skin tumor in a 10-year-old Rottweiler. Considering the external appearance and
The Hallmarks of Cancer
 The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Review. Endothelial Extracellular Matrix: Biosynthesis, Remodeling, and Functions During Vascular Morphogenesis and Neovessel Stabilization
 Review This Review is part of a thematic series on Vascular Cell Diversity, which includes the following articles: Heart Valve Development: Endothelial Cell Signaling and Differentiation Molecular Determinants
Review This Review is part of a thematic series on Vascular Cell Diversity, which includes the following articles: Heart Valve Development: Endothelial Cell Signaling and Differentiation Molecular Determinants
Cancer as a disease of development; Developmental therapies: Anti- Angiogenesis; Stem cells and tissue regeneration.
 Cancer as a disease of development; Developmental therapies: Anti- Angiogenesis; Stem cells and tissue regeneration Mitesh Shrestha What is Cancer? Unrestricted cell growth: tumor cell population 1x10^9
Cancer as a disease of development; Developmental therapies: Anti- Angiogenesis; Stem cells and tissue regeneration Mitesh Shrestha What is Cancer? Unrestricted cell growth: tumor cell population 1x10^9
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice
 Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Healing & Repair. Tissue Regeneration
 Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Mechanisms of Resistance to Antiangiogenic. Martin J. Edelman, MD University of Maryland Greenebaum Cancer Center Dresden, 2012
 Mechanisms of Resistance to Antiangiogenic Agents Martin J. Edelman, MD University of Maryland Greenebaum Cancer Center Dresden, 2012 Angiogenesis: A fundamental attribute of cancer Premise of Anti-angiogenic
Mechanisms of Resistance to Antiangiogenic Agents Martin J. Edelman, MD University of Maryland Greenebaum Cancer Center Dresden, 2012 Angiogenesis: A fundamental attribute of cancer Premise of Anti-angiogenic
The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis
 The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis Domenico Ribatti The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis Domenico Ribatti Department of Basic Medical Sciences,
The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis Domenico Ribatti The Role of Microenvironment in the Control of Tumor Angiogenesis Domenico Ribatti Department of Basic Medical Sciences,
SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons
 SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons 6/18/08 Akeila Bellahcène and Vincent Castronovo of the Metastasis Research laboratory of the University of Liège are among the first researchers to have discovered
SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons 6/18/08 Akeila Bellahcène and Vincent Castronovo of the Metastasis Research laboratory of the University of Liège are among the first researchers to have discovered
Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th Edition by Kumar
 Link full download:https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-robbinsand-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-by-kumar Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th
Link full download:https://getbooksolutions.com/download/test-bank-for-robbinsand-cotran-pathologic-basis-of-disease-9th-edition-by-kumar Test Bank for Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease 9th
Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis: Signaling pathways
 PhD program N090/N094 Vascular Biology Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis: Signaling pathways Erhard Hofer Department of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research Center for Biomolecular
PhD program N090/N094 Vascular Biology Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis: Signaling pathways Erhard Hofer Department of Vascular Biology and Thrombosis Research Center for Biomolecular
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CELL JUNCTIONS AND TISSUES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-CELL ADHESION Cells must be able to bind and interact with nearby cells in order to have functional and strong tissues Cells can in two main ways - Homophilic interactions
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-CELL ADHESION Cells must be able to bind and interact with nearby cells in order to have functional and strong tissues Cells can in two main ways - Homophilic interactions
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER
 THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
THE HALLMARKS OF CANCER ONCOGENES - Most of the oncogenes were first identified in retroviruses: EGFR (ErbB), Src, Ras, Myc, PI3K and others (slightly more than 30) - Mutated cellular genes incorporated
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES. Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr.
 BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
BL-8040: BEST-IN-CLASS CXCR4 ANTAGONIST FOR TREATMENT OF ONCOLOGICAL MALIGNANCIES Overview and Mechanism of Action Dr. Leah Klapper, CSO 88 BL-8040: Novel CXCR4 Antagonist For Hematological Cancers Indications:
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#5:(October-18-2010) Cancer and Signals Outline 1 2 Outline 1 2 Cancer is a disease of malfunctioning cells. Cell Lineage: Adult
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#5:(October-18-2010) Cancer and Signals Outline 1 2 Outline 1 2 Cancer is a disease of malfunctioning cells. Cell Lineage: Adult
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20
 Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
Genetics and Cancer Ch 20 Cancer is genetic Hereditary cancers Predisposition genes Ex. some forms of colon cancer Sporadic cancers ~90% of cancers Descendants of cancerous cells all cancerous (clonal)
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
Healing and Repair. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Healing and Repair Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD 1 ILOs Know the classification of human cells according to their ability for proliferation. Understand the mechanism of cellular regeneration. Identify the types
Healing and Repair Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD 1 ILOs Know the classification of human cells according to their ability for proliferation. Understand the mechanism of cellular regeneration. Identify the types
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia!
 Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia! Lorenz Poellinger! Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology! Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden! Normoxia - O 2 availability is in balance
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia! Lorenz Poellinger! Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology! Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden! Normoxia - O 2 availability is in balance
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy. Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI
 A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
A holistic approach to targeting breast cancer part II: Micronutrient synergy Presented by: Dr. Neha Shanker DRRI Overview of the previous webinar In the last presentation we talked about: Increase in
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CANCER.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF CANCER Cancer is a disease which is primarily caused from misregulated cell division, which form There are two types of tumors - Benign tumors remain confined
Angiogenesis in Human Development. Vascular Development
 Angiogenesis in Human Development Jan Kitajewski ICRC 217B, ph 851-4688, email: jkk9 BACKGROUND READING: Vascular Development Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan. Science 277:
Angiogenesis in Human Development Jan Kitajewski ICRC 217B, ph 851-4688, email: jkk9 BACKGROUND READING: Vascular Development Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan. Science 277:
Basic tumor nomenclature
 Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
Jonas Nilsson jonas.a.nilsson@surgery.gu.se Sahlgrenska Cancer Center Bilder gjorda av Per Holmfeldt och Jonas Nilsson Benign tumor Basic tumor nomenclature Malignant tumor = cancer Metastasis Carcinoma:
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Intercellular indirect communication
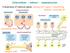 Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#10:(November-22-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 1 Micro-Environment Story How does the rest of our body influences the cancer cell?
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#10:(November-22-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 1 Micro-Environment Story How does the rest of our body influences the cancer cell?
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY. Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University
 CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University Padang 18 Mei 2013 INTRODUCTION Tumor: cells that continue to replicate, fail to differentiate into specialized cells, and become
CANCER IMMUNOPATHOLOGY Eryati Darwin Faculty of Medicine Andalas University Padang 18 Mei 2013 INTRODUCTION Tumor: cells that continue to replicate, fail to differentiate into specialized cells, and become
- A cancer is an uncontrolled, independent proliferation of robust, healthy cells.
 1 Cancer A. What is it? - A cancer is an uncontrolled, independent proliferation of robust, healthy cells. * In some the rate is fast; in others, slow; but in all cancers the cells never stop dividing.
1 Cancer A. What is it? - A cancer is an uncontrolled, independent proliferation of robust, healthy cells. * In some the rate is fast; in others, slow; but in all cancers the cells never stop dividing.
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 3 Rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Molecular basis of cancer (normal cell-cycle and cellular proliferation). Enrique
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 3 Rate of growth, local invasion, and metastasis. Molecular basis of cancer (normal cell-cycle and cellular proliferation). Enrique
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber
 Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors MCB 5068 November 12, 2013 Jason Weber jweber@dom.wustl.edu Oncogenes & Cancer DNA Tumor Viruses Simian Virus 40 p300 prb p53 Large T Antigen Human Adenovirus p300 E1A
Role of Cancer Microenvironment in Metastasis: Focus on Colon Cancer
 Cancer Microenvironment (2008) 1:69 83 DOI 10.1007/s12307-008-0007-2 REVIEW PAPER Role of Cancer Microenvironment in Metastasis: Focus on Colon Cancer Stéphanie Gout & Jacques Huot Received: 22 December
Cancer Microenvironment (2008) 1:69 83 DOI 10.1007/s12307-008-0007-2 REVIEW PAPER Role of Cancer Microenvironment in Metastasis: Focus on Colon Cancer Stéphanie Gout & Jacques Huot Received: 22 December
Contents. Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX
 Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Contents Preface XV Acknowledgments XXI List of Abbreviations XXIII About the Companion Website XXIX 1 General Aspects of Signal Transduction and Cancer Therapy 1 1.1 General Principles of Signal Transduction
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Name Chapter 9, Part 1: Biology of Cancer and Tumor Spread I. Cancer Characteristics and Terminology Neoplasm new growth, involves the overgrowth of tissue to form a neoplastic mass (tumor).
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis. Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval
 Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Biochemistry of Carcinogenesis Lecture # 35 Alexander N. Koval What is Cancer? The term "cancer" refers to a group of diseases in which cells grow and spread unrestrained throughout the body. It is difficult
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Tumor Associated Macrophages as a Novel Target for Cancer Therapy
 Tumor mass Tumor Associated Macrophage Tumor Associated Macrophages as a Novel Target for Cancer Therapy This booklet contains forward-looking statements that are based on Amgen s current expectations
Tumor mass Tumor Associated Macrophage Tumor Associated Macrophages as a Novel Target for Cancer Therapy This booklet contains forward-looking statements that are based on Amgen s current expectations
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PhD SCHOOL. PhD THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PhD SCHOOL PhD THESIS THE IMPORTANCE OF TUMOR ANGIOGENESIS IN CEREBRAL TUMOR DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY ABSTRACT PhD COORDINATOR: Prof. univ. dr. DRICU Anica PhD
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PhD SCHOOL PhD THESIS THE IMPORTANCE OF TUMOR ANGIOGENESIS IN CEREBRAL TUMOR DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY ABSTRACT PhD COORDINATOR: Prof. univ. dr. DRICU Anica PhD
OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene
 OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene hsa-let-7a-1 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-2 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-3 Breast Cancer, Lung
OncoMir Library Cancer Type Target Gene hsa-let-7a-1 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-2 Breast Cancer, Lung Cancer H RAS, HMGA2, CDK6, NRAS hsa-let-7a-3 Breast Cancer, Lung
Cell Polarity and Cancer
 Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
Cell Polarity and Cancer Pr Jean-Paul Borg Email: jean-paul.borg@inserm.fr Features of malignant cells Steps in Malignant Progression Cell polarity, cell adhesion, morphogenesis and tumorigenesis pathways
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression
 Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Immunological Lung Diseases
 Emphysema and Fibrosis Universitätsklinik für Pneumologie Prof. Thomas Geiser Head Div. of Pulmonary Medicine and Laboratory of Lung Research, MU50 thomas.geiser@insel.ch The healthy lung: The pathway
Emphysema and Fibrosis Universitätsklinik für Pneumologie Prof. Thomas Geiser Head Div. of Pulmonary Medicine and Laboratory of Lung Research, MU50 thomas.geiser@insel.ch The healthy lung: The pathway
EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition
 EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition A phenotypic change that is characteristic of some developing tissues and certain forms of cancer. This is a multistep, key process in embryonic development and metastasis
EMT: Epithelial Mesenchimal Transition A phenotypic change that is characteristic of some developing tissues and certain forms of cancer. This is a multistep, key process in embryonic development and metastasis
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers. A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs
 Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1796 (2009) 293 308 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbacan Review Metastasis mechanisms Thomas
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1796 (2009) 293 308 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbacan Review Metastasis mechanisms Thomas
Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension
 Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension K. R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, USA Prominent Fibroproliferative Changes are Observed in the Lung Vasculature of Infants With Pulmonary Arterial
Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension K. R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, USA Prominent Fibroproliferative Changes are Observed in the Lung Vasculature of Infants With Pulmonary Arterial
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century. Linda Lowe-Krentz
 Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
Cancer and Oncogenes Bioscience in the 21 st Century Linda Lowe-Krentz December 1, 2010 Just a Few Numbers Becoming Cancer Genetic Defects Drugs Our friends and family 25 More mutations as 20 you get older
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Maha Shomaf
 number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
number 19 Done by Waseem Abo-Obeida Corrected by Abdullah Zreiqat Doctor Maha Shomaf Carcinogenesis: the molecular basis of cancer. Non-lethal genetic damage lies at the heart of carcinogenesis and leads
Invasion And Metastasis. Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncologist Surgery Department Andalas Medical Schoool
 Invasion And Metastasis Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncologist Surgery Department Andalas Medical Schoool Biology of tumor growth The natural history of malignant tumors can be divided into four phase:
Invasion And Metastasis Wirsma Arif Harahap Surgical Oncologist Surgery Department Andalas Medical Schoool Biology of tumor growth The natural history of malignant tumors can be divided into four phase:
Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease
 Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease Shu Chien Dept. of Bioengineering & Medicine UC, San Diego Presented by Ming-Shaung Ju Dept. of Mech. Eng., NCKU, Tainan Background
Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease Shu Chien Dept. of Bioengineering & Medicine UC, San Diego Presented by Ming-Shaung Ju Dept. of Mech. Eng., NCKU, Tainan Background
Supplementary Figure 1: Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points
 A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
General Pathology VPM 152. Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer
 General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto http://people.upei.ca/eaburto Winter 2015 Molecular Basis of Cancer Fundamental principles
General Pathology VPM 152 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Lecture 4 Molecular basis of cancer Enrique Aburto http://people.upei.ca/eaburto Winter 2015 Molecular Basis of Cancer Fundamental principles
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
The 5th International Conference on Tumor Microenvironment: Progression, Therapy and Prevention Versailles, France, October 20 24, 2009
 Cancer Microenvironment (2010) 3:1 5 DOI 10.1007/s12307-010-0039-2 EDITORIAL The 5th International Conference on Tumor Microenvironment: Progression, Therapy and Prevention Versailles, France, October
Cancer Microenvironment (2010) 3:1 5 DOI 10.1007/s12307-010-0039-2 EDITORIAL The 5th International Conference on Tumor Microenvironment: Progression, Therapy and Prevention Versailles, France, October
Cell signaling. How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings?
 Cell signaling How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings? Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are largely independent and autonomous. In multicellular organisms there is a
Cell signaling How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings? Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are largely independent and autonomous. In multicellular organisms there is a
肿瘤信息学 徐鹰佐治亚大学生化系 吉林大学计算机学院
 肿瘤信息学 徐鹰佐治亚大学生化系 吉林大学计算机学院 2 Lecture V Biology of cancer metastasis and metastatic cancers 3 Metastatic Cancer Metastatic cancers are responsible for 90% of cancer related death Currently metastatic cancer
肿瘤信息学 徐鹰佐治亚大学生化系 吉林大学计算机学院 2 Lecture V Biology of cancer metastasis and metastatic cancers 3 Metastatic Cancer Metastatic cancers are responsible for 90% of cancer related death Currently metastatic cancer
stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products
 stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products Stem Cell Qualified Extracellular Matrix Proteins Stem cell research requires the finest
stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products Stem Cell Qualified Extracellular Matrix Proteins Stem cell research requires the finest
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation. Thursday Jan 26th, 2017
 Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
Lymphoid architecture & Leukocyte recirculation Thursday Jan 26th, 2017 Topics The life of immune cells Where are they born? Where are they educated? Where do they function? How do they get there? The
THE BIOLOGY OF PLATELET-GEL THERAPY
 THE BIOLOGY OF PLATELET-GEL THERAPY The synopsis of normal healing includes a well known sequence of coordinated phases. The unique process leading to healing is ontologically partitioned in three sequential
THE BIOLOGY OF PLATELET-GEL THERAPY The synopsis of normal healing includes a well known sequence of coordinated phases. The unique process leading to healing is ontologically partitioned in three sequential
Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenesis in Hematological Malignancies
 Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenesis in Hematological Malignancies Domenico Ribatti Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenesis in Hematological Malignancies 1 3 Domenico Ribatti Department of Basic Medical Sciences
Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenesis in Hematological Malignancies Domenico Ribatti Angiogenesis and Anti-Angiogenesis in Hematological Malignancies 1 3 Domenico Ribatti Department of Basic Medical Sciences
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells. Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari
 Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
Editor Journal of Allergy and Therapy
 Editor Journal of Allergy and Therapy Biography Prof. Domenico Ribatti was awarded his MD degree on October 1981 with full marks. His present position is of a full-time professor of Human Anatomy at the
Editor Journal of Allergy and Therapy Biography Prof. Domenico Ribatti was awarded his MD degree on October 1981 with full marks. His present position is of a full-time professor of Human Anatomy at the
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. No conflicts of interest
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST No conflicts of interest University Heart Centre Tübingen Angiogenic actions of platelets Meinrad Gawaz, MD, FESC Tübingen, Germany ESC 2011 Paris GPIb GPIb GPVI TxA2
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST No conflicts of interest University Heart Centre Tübingen Angiogenic actions of platelets Meinrad Gawaz, MD, FESC Tübingen, Germany ESC 2011 Paris GPIb GPIb GPVI TxA2
C) The graph should look exactly like the graph on the left (Mut1 cells + Mating Pheromone for 3 hours at 25 degrees). The cells arrest in G1.
 706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
706-2000-Exam 4 Answer Key 1) The question asks you to explain peaks A and B in the top graph. The other two graphs were there to give you hints. The question did not ask for these other two graphs to
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Cancer. Questions about cancer. What is cancer? What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage?
 Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Questions about cancer What is cancer? Cancer Gil McVean, Department of Statistics, Oxford What causes unregulated cell growth? What regulates cell growth? What causes DNA damage? What are the steps in
Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies. Traditional Hypothesis Stress
 3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
2.1 Introduction. George E. Davis, Amber N. Stratman, and Anastasia Sacharidou
 Chapter 2 Molecular Control of Vascular Tube Morphogenesis and Stabilization: Regulation by Extracellular Matrix, Matrix Metalloproteinases, and Endothelial Cell Pericyte Interactions George E. Davis,
Chapter 2 Molecular Control of Vascular Tube Morphogenesis and Stabilization: Regulation by Extracellular Matrix, Matrix Metalloproteinases, and Endothelial Cell Pericyte Interactions George E. Davis,
