Radiation Safety. Page 1. Introduction. Radiation is ENERGY IN TRANSIT in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves.
|
|
|
- Egbert Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Radiation Safety Introduction Radiation is ENERGY IN TRANSIT in the form of high speed particles and electromagnetic waves. NOTE: We encounter electromagnetic ti waves every day. They make up our visible light, radio and television waves, ultra violet (UV), and microwaves with a spectrum of energies. These examples of electromagnetic waves do not cause ionizations of atoms because they do not carry enough energy to separate molecules or remove electrons from atoms. 2 Page 1
2 Introduction Ionizing radiation is radiation WITH enough energy so that during an interaction with an atom, it can remove tightly bound electrons from their orbits, causing the atom to become charged or ionized. Example is X-RAY Non-ionizing radiation is radiation WITHOUT enough energy to remove tightly bound electrons from their orbits around atoms. Example is LASER 3 Electromagnetic Spectrum 4 Page 2
3 Health Effects IONIZING DAMAGES chemical bonds NON-IONIZING Lower energy, CAN T DAMAGE bonds Alpha, Beta, Gamma, X-Ray Microwave, Infrared, Visible, Ultraviolet, Laser CUMULATIVE effects THRESHOLD effects damage from low levels damage occurs only of exposure that can addup over time no cumulative effects above a threshold level below threshold 5 Ionizing Radiation Types of Ionizing Radiation Alpha, Beta and Gamma rays from the decay of radioactive substances matter X-ray produced electronically by X-ray machines. X-ray machine emits radiation only when the machine is energised. Alpha Alpha decay is a radioactive process in which a particle with two neutrons and two protons is ejected from the nucleus of a radioactive atom. 6 Page 3
4 Ionizing Radiation Beta A beta is a high speed particle, identical to an electron, that is emitted from the nucleus of an atom. Gamma Gamma rays are electromagnetic waves or photons emitted from the nucleus (center) of an atom. 7 Ionizing Radiation X Ray X Rays are electromagnetic waves or photons not emitted from the nucleus, but normally emitted by energy changes in electrons. X-ray production OCCURS whenever electrons of high energy STRIKE a heavy metal target, like tungsten or copper. 8 Page 4
5 Penetrating Distances 9 Ionizing Radiation Dose Sievert (Sv), rem (roentgen-equivalent man) Old unit is rem where 1 Sv = 100 rem Sievert (Sv) is a unit of RADIATION DOSE due to ionizing radiation Express doses received by human beings Dose depends on ACTIVITY of radioactive source, distance, shielding and exposure time. Sievert is named after Rolf M. Sievert, a Swedish Physicist who was one of the pioneers in protection against ionizing radiation 10 Page 5
6 Effects Due To Ionizing Radiation Ionizing radiation can cause two main biological effects, namely Somatic effects (acute & chronic) in which the damage appears in the IRRADIATED PERSON HIMSELF, and Genetic effects which arise only in the OFFSPRING of the irradiated persons as a result of radiation damage to germ cells in the reproductive organs. 11 Acute Effects of Irradiation at Different Doses Dose (Sv) Effect 1,000 Spastic seizures; death in minutes. 100 Damage to central nervous system; death in hours. 10 Circulating changes; death in days. 1 Radiation sickness (nausea, vomiting, fatigue; following a short latent period epilation, loss of appetite, fever, diahorrea, rapid emaciation, and possible death); decrease in life expectancy and disease resistance; sterility, erythema reddening of the skin. 0.1 No obvious injury. 12 Page 6
7 Statistics for Chernobyl Accident Sv Casualties Deaths < Some Chronic Effects of Radiation Effect Mean Latent Period Evidence For Effect Leukemia 8-10 years Atomic bomb casualties, Medical X-ray treatmentt t Radium luminous dial Bone cancer 15 years painters Atomic bomb casualties, Thyroid cancer years Medical treatment Lung cancer years Mine workers Life shortening -- Experiments with mice Cataract 5-10 years Atomic bomb casualties 14 Page 7
8 Second Schedule - Part I Dose Limits For Radiation Workers (a) The dose from any medical or dental exposure as a patient, from the exposure to natural background radiation or from other exposures received by the radiation worker as a member of the public shall not be taken into account. Application Dose Limit per year (msv) Effective dose (whole body) 20 1 Equivalent dose in the lens of the eye the skin 2 the hands and feet (b) Where only a part or parts of the body are irradiated by external radiation, the effective dose received from external radiation shall be determined by calculating the sum W T H T over all organs and tissues irradiated, where ---- (i) H T is the equivalent dose received by any particular tissue or organ T; and (ii) W T is the weighting factor for that tissue or organ 1. The limit on effective dose (whole body) is 20 msv per year, averaged over defined periods of 5 years and with the further provision that the effective dose shall not exceed 50 msv in any single year. 2. The limit of 500 msv for skin is averaged over areas of no more than 1 cm 2 regardless of the area exposed 15 Second Schedule Part II Dose Limits For Individual Members Of The Public Application Effective dose (whole body) Equivalent dose in Dose Limit per year (msv) 1 1 the lens of the eye 15 the skin In special circumstances, a higher value of effective dose for the whole body is allowed in a single year provided that the average over 5 years does not exceed 1 msv per year. The limit shall apply to the sum of the relevant doses from the external exposure in the specified period and the committed effective dose 2. The limit of 50 msv for skin is averaged over areas of no more than 1 cm 2 regardless of the area exposed 16 Page 8
9 Control of Ionizing Radiation Exposure Whole body effective dose limit for radiation worker should not be more than 20 msv a year for whole body exposure and 1 msv a year for public members All unjustifiable doses should be avoided High dose accumulation is to be avoided for women of reproductive capacity 17 Reduction of Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Time Shielding Distance 18 Page 9
10 Reduction of Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Distance - keeping a RESPECTFUL distance from a radiation source is often the most effective way of REDUCING dose (moving from 1 m to 10 m from strong radioactive source reduce radiation dose received by 100 times). Shielding INCREASE the amount of shielding will DECREASE the amount of exposure. Time - radiation dose is directly proportional to exposure time. Keep exposure time to as SHORT as possible. 19 Control Measures Engineering Controls X-ray machine adequately shielded so that radiation level anywhere outside the enclosure when the X-ray machine is energized is within legal limit. Effective safety interlocks shall be provided so that when the X-ray machine has to be switched off before any enclosure door can be opened and cannot be switched on so long as the door is opened. Adequate warning to everyone in the vicinity i it shall be given by appropriate light or audible signals or both while X-ray machine is energized. 20 Page 10
11 Control Measures Example of Electrical Safety Lockout/Tagout (LOTO) Reproductive Health Hazard Radiation Safety 21 Operating a X-ray machine Licenses Apply for required licenses, L3 (machine), L5 (Supervision of R1 holder) and/or R1 (Radiation Worker) from National Environment Agency (NEA) Applicant must be at least 18 years old Medical Examination Before beginning radiation work. Must be certified fit for radiation work by registered medical doctor. If there is directive from NEA. 22 Page 11
12 Site Monitoring A monitoring survey is required after installation of a new X-ray machine, move a X-ray machine or modify a X- ray machine Geiger counter Scintillation counter Training All radiation worker must be adequately trained on operation of X-ray machine and know the hazards associated with the work. 23 Warning Label 24 Page 12
13 Safety Guides Follow the recommended safety guidelines from the equipment manufacturer Report any abnormal situation to immediate supervisor, Radiation Safety Officer and/or Safety Department Test interlocks at the frequency required for your particular type of X-ray machine Document and understand alignment procedures for the X-ray machine you own or use Pregnant radiation worker shall declare pregnancy to their immediate supervisor and managers so that arrangement can be made to exempt them from working X-ray machine during the pregnancy. 25 Personal Dosimeters Thermoluminescent Dosimeter (TLD) is used to measure the estimated radiation dose absorbed thru skin and body. TLD consists of TLD card and holder, also known as TLD badge. 26 Page 13
14 Personal Dosimeters TLD card provide early warning TLD card is issued bi-monthly TLD card is tested individually, data is retained forever (by NEA) After the TLD cards are processed, a dose report is generated Measures exposure in msv Identifies radiation energy, type, and direction 27 TLD Badge Do s and Don ts DO Put in TLD card properly in TLD holder with name appearing on window Wearer name should be against the wearer when TLD badge is worn Wear TLD at chest level when working around X-ray machine Keep TLD at workplace DON T Place TLD on X-ray machine Deliberately expose TLD to radiation Wear TLD during medical tests Expose TLD to heat 28 Page 14
15 Establish System for Reporting When Acquire a X-ray machine Dispose a X-ray machine Suspect an abnormal condition Move a X-ray machine Modify a X-ray machine Return a X-ray machine to service 29 Statutory Requirement Radiation Protection Act Radiation Protection (Ionizing Radiation) Licenses required for manufacture, possess, use and import, and sale of radioactive and irradiation apparatus Radiation workers must not be younger than 18 yrs old, required to register, go for medical examination, instructed to do radiation work and wear personal dosimeter. Not allowed to receive excess of annual dose limit in 2nd Schedule 30 Page 15
16 Statutory Requirement Radiation Protection (Ionizing Radiation) Regulations Medical examination include full blood examination & certified fit by approved registered doctor before engaged in radiation work Radiation worker has been adequately trained Transfer record in approved form for employees who had left the company Radioactive materials, irradiating apparatus and radiation areas must be appropriately labeled Safe storage and accounting of radiation sources Design aspects such as shielding, interlocks, warning devices, layout, instrumentation, ventilation must meet applicable requirements 31 Statutory Requirement Radiation Protection (Ionizing Radiation) Regulations Penalty for individual not exceeding $2000 Appropriate procedures in dealing with radiation accidents Calibration of area monitors and dosimeters L3 - license to keep or possess an irradiating apparatus (company) L5 -license to use irradiating at apparatus atus (individual) dua R1 - license to register as a radiation worker (individual using ionizing irradiating apparatus under supervision of licensee L5) 32 Page 16
17 Non-Ionizing Radiation Types of Non-Ionizing Radiation Electromagnetic radiation & fields with wavelengths greater than 100 nm & acoustic radiation & fields with frequencies above 16 KHz, Microwave Radiation Infrared Radiation Visible Radiation Ultraviolet Radiation Ultrasound Laser 33 Laser LASER is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation LASER light differs from ordinary light in three ways, Monochromatic (single wavelength) Coherent (in-phase) Directional 34 Page 17
18 Laser Laser can pose more of a hazard than ordinary light because they can focus a lot of energy onto a small area LASERS ARE POINT SOURCES OF LIGHT LASER (POINT SOURCE) INCANDESCENT LIGHT BULB (EXTENDED SOURCE) 35 Laser Design Lasing media (gas, liquid, solid, semiconductor) Excitation mechanism (power supply, flash lamp, laser) Feedback mechanism (mirror, grating) Output coupler (partially reflecting mirror) Lasing medium Feedback mechanism Output Coupler Excitation mechanism 36 Page 18
19 Types of Laser Lasers are generally classified according to the materials used Gas (CO 2, Argon) Solid (Nd:YAG, Ti:Sa) Semiconductor (Gallium-Arsenide) Dye Mode of Operation Continuous Wave; Pulsed Wave; Q-switched Wavelength UV; Visible to Near IR; Mid to Far IR 37 Laser Hazards Beam Hazards Eye Skin Non Beam Hazards Chemical Electrical l Explosion Fire 38 Page 19
20 Laser Hazards Eye Hazards Risk for retinal injury is dependent on wavelength and/or total power entering the eye For wavelengths that focus on the retina, the optical gain of the eye is about 100,000 times! If the irradiance entering the eye is 1mW/cm 2, then the irradiance at the retina will be 100 W/cm 2 39 Laser Hazards Skin Hazard Skin injury from laser energy is primarily THERMAL (except for UV). Highly dependent d on: Beam Irradiance Exposure Duration 40 Page 20
21 Laser Hazards Non-beam Hazards Chemical Hazards - from dyes; from solvents used to clean optics Electrical Hazards from high voltage power supplies Explosion Hazards from high pressure arc lamps, from compressed gases Fire Hazards from electrical circuit, ignition of gases, flammable solvents BOOM 41 Laser Classification Class Description 1 Lasers that are inherently safe & incapable of producing dangerous levels of emissions 2 Do not normally present a hazard because of normal human bright-light aversion response. May present potential eye hazard if viewed directly for long time, 3a 3b Would not injure the eye if viewed for only momentary periods with the unaided eye, Eye damage possible if viewed with collection optics Hazardous under direct viewing or a reflected beam is viewed. 4 Hazardous under all viewing conditions, may produce significant skin hazards as well as fire hazards. 42 Page 21
22 Engineering Controls Protective housing that prevents human access during operation to laser Enclosed beam path Safety Interlocks Remote control firing Key actuated master control Beam stops and attenuators 43 Control Measures Example of Electrical Safety Lockout/Tagout t (LOTO) Radiation Safety 44 Page 22
23 Licenses Apply for required licenses, N2 (machine) and/or N3 (laser worker) from National Environment Agency Applicant must be at least 18 years old Medical Examination Before beginning laser work. Must be certified fit for laser work by registered medical doctor. Training All radiation worker must be adequately trained on operation of X-ray machine and know the hazards associated with the work. 45 Protective Eyewear Appropriate for all wavelengths in use Sufficient attenuation (Optical Density) at wavelengths in use Good visible light transmission Good field of viewing Comfortable to wear 46 Page 23
24 Warning Label LASER RADIATION DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM OR VIEW TYPE OF LASER POWER & WAVELENGTH CLASS 2 LASER PRODUCT Class 2 Laser Product LASER RADIATION DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM OR VIEW DIRECTLY WITH OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS TYPE OF LASER POWER & WAVELENGTH CLASS 3A LASER PRODUCT Class 3a Laser Product 47 Warning Label LASER RADIATION AVOID EXPOSURE TO BEAM TYPE OF LASER POWER & WAVELENGTH CLASS 3b LASER PRODUCT Class 3b Laser Product LASER RADIATION AVOID EYE OR SKIN EXPOSURE TO DIRECT OR SCATTERED RADIATION TYPE OF LASER POWER & WAVELENGTH CLASS 4 LASER PRODUCT Class 4 Laser Product 48 Page 24
25 Safety Guides Do not attempt to operate systems with enclosures open Do not defeat or tamper with safety interlocks Do not operate machine if enclosures are damaged Follow the recommended laser safety guidelines of the equipment manufacturer as in the user/service manual 49 For Repair Work Control access to the equipment during service e.g. Laser curtains, barriers, closing entranceways Post NOTICE sign at entranceway into controlled area After maintenance or servicing, Remove NOTICE sign Remove unnecessary objects from the vicinity of the laser Checked to confirm all safety interlocks are operating effectively NOTICE LASER REPAIR IN PROGRESS Laser Safety Eyewear Required 50 Page 25
26 Laser should be discharged in a non-reflective & fire resistant background Area should be cleared of personnel for a reasonable distance on all sides of laser beam Looking into the primary laser beam, specular reflections of the beam, including those from lens surface, should be avoided at all times Avoid aiming laser into eye to prevent looking along the axis of the beam which increases the hazard from reflections 51 Laser work should be carried out in areas of high general illuminations to keep pupils constricted thus limiting the energy which might inadvertently enter the eyes Personnel should be instructed on potential eye hazards & the importance of limiting unnecessary exposure Safety eyewear designed to filter off specific frequencies & to provide protection should be worn at all times. Binoculars or aiming telescopes should not be used to view direct laser beam or reflected beam from mirrors unless the beam intensities are greatly below safety levels. 52 Page 26
27 Statutory Requirement Radiation Protection Act The Radiation Protection (Non-Ionizing Radiation) Regulations Apply to the following non-ionizing i i apparatus: a) ultraviolet sunlamps (for irradiating living human body) ; b) microwave ovens ; c) medical and industrial ultrasound apparatus; d) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus; e) entertainment lasers; and f) high power lasers N2 - license to keep or possess for use of class 3b & 4 lasers & ultrasound N3 - license to use class 3b & 4 lasers 53 Statutory Requirement The Radiation Protection (Non-Ionizing Radiation) Regulations Detail requirements in dealing with NIR Requirements on shielding, interlocks, warning devices Appropriately labeled to give adequate warning Worker must be at least 18 yrs old to perform laser radiation work, adequately trained & holds a license for class 3b or 4 lasers 54 Page 27
28 Thank You Page 28
UQ X-ray Safety Training Module
 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module 23 January 2018, v2 1 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module Course Overview: This training module has been developed for workers at the University of Queensland, and forms part
UQ X-ray Safety Training Module 23 January 2018, v2 1 UQ X-ray Safety Training Module Course Overview: This training module has been developed for workers at the University of Queensland, and forms part
RELIANT HOLDINGS LTD AND ITS AFFILIATES Safety Management System. Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: CEO Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 5
 Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: CEO Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 5 Purpose The purpose of this program is to protect employees who may encounter ionizing radiation and its hazards while performing
Preparation: Safety Mgr Authority: CEO Issuing Dept: Safety Page: Page 1 of 5 Purpose The purpose of this program is to protect employees who may encounter ionizing radiation and its hazards while performing
Radiation Safety Guide. Analytical X-Ray Equipment
 Radiation Safety Guide Analytical X-Ray Equipment Table of Content Page 1. Radiation 2 A. Radiation Quantities 2 B. Background Radiation 2 C. Biological Effect of Radiation 3 D. Radiation Injury To The
Radiation Safety Guide Analytical X-Ray Equipment Table of Content Page 1. Radiation 2 A. Radiation Quantities 2 B. Background Radiation 2 C. Biological Effect of Radiation 3 D. Radiation Injury To The
Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students
 Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students John Vetter, PhD Medical Physics Department UW School of Medicine & Public Health Background and Purpose of This Training This is intended as
Radiation Safety for New Medical Physics Graduate Students John Vetter, PhD Medical Physics Department UW School of Medicine & Public Health Background and Purpose of This Training This is intended as
Radioactivity. Alpha particles (α) :
 Radioactivity It is the property of an element that causes it to emit radiation Discovered by Becquerel (1896) Radiation comes from the nucleus of the atom There are three types of radiation : alpha particles
Radioactivity It is the property of an element that causes it to emit radiation Discovered by Becquerel (1896) Radiation comes from the nucleus of the atom There are three types of radiation : alpha particles
RADIOACTIVITY & RADIATION CHARACTERISTICS
 CEMP TRAINING SESSION 15-17 JULY 2013 RADIOACTIVITY & RADIATION CHARACTERISTICS Instructor: Gary M. Sandquist, PhD, CHP 2013 Training Session Slide 1 Occupational Dose Equivalent Limits General Public
CEMP TRAINING SESSION 15-17 JULY 2013 RADIOACTIVITY & RADIATION CHARACTERISTICS Instructor: Gary M. Sandquist, PhD, CHP 2013 Training Session Slide 1 Occupational Dose Equivalent Limits General Public
PAGE 1 OF 5 HEALTH, SAFETY & ENVIROMENTAL MANUAL PROCEDURE: S560 Radiation Safety REV /14/2012
 PAGE 1 OF 5 RADIATION SAFETY PURPOSE: A wide usage of x-ray machines and isotopes for examination of steel plate fabricated and erected structures require a knowledge of the radiation hazard and the precautionary
PAGE 1 OF 5 RADIATION SAFETY PURPOSE: A wide usage of x-ray machines and isotopes for examination of steel plate fabricated and erected structures require a knowledge of the radiation hazard and the precautionary
Radiologic Units: What You Need to Know
 Radiologic Units: What You Need to Know TODD VAN AUKEN M.ED. RT (R)(MR) Agenda Greys, Sieverts, Coulombs per kg, & Becquerel's Conventional Units Other Concepts (LET, Q-Factor, Effective Dose, NCRP Report
Radiologic Units: What You Need to Know TODD VAN AUKEN M.ED. RT (R)(MR) Agenda Greys, Sieverts, Coulombs per kg, & Becquerel's Conventional Units Other Concepts (LET, Q-Factor, Effective Dose, NCRP Report
Radiation Safety Manual
 King Abdulaziz University Faculty of Dentistry Radiation Safety Manual FOR X-RAY EQUIPMENT OPERATORS October 2009 Radioactivity and Radiation All matter in our environment is made of atoms. Most atoms
King Abdulaziz University Faculty of Dentistry Radiation Safety Manual FOR X-RAY EQUIPMENT OPERATORS October 2009 Radioactivity and Radiation All matter in our environment is made of atoms. Most atoms
Radiation Safety Bone Densitometer
 Radiation Safety Bone Densitometer Outline I. State Regulations II. Fundamentals of Radiation Safety III. IV. i. Characteristics of x-ray radiation ii. Units of radiation dose iii. Biological effects iv.
Radiation Safety Bone Densitometer Outline I. State Regulations II. Fundamentals of Radiation Safety III. IV. i. Characteristics of x-ray radiation ii. Units of radiation dose iii. Biological effects iv.
Basic radiation protection & radiobiology
 Basic radiation protection & radiobiology By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient care & management 202 Wednesday, October 13, 2010 Ionizing radiation. Discussion issues Protecting the patient. Protecting the radiographer.
Basic radiation protection & radiobiology By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Patient care & management 202 Wednesday, October 13, 2010 Ionizing radiation. Discussion issues Protecting the patient. Protecting the radiographer.
RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N & B I O L O G Y - R H O D E S
 RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES 10-526- 1 9 7 R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N & B I O L O G Y - R H O D E S DETECTION AND MEASUREMENT OF IONIZING RADIATION Dosimeter Dose-measuring device Two classifications:
RADIATION MONITORING DEVICES 10-526- 1 9 7 R A D I A T I O N P R O T E C T I O N & B I O L O G Y - R H O D E S DETECTION AND MEASUREMENT OF IONIZING RADIATION Dosimeter Dose-measuring device Two classifications:
Code of Practice for Radiation Protection in Dentistry. Code of Practice For Radiation Protection in Dentistry
 Code of Practice for Radiation Protection in Dentistry Code of Practice For Radiation Protection in Dentistry 10 OCTOBER 2017 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 1.0 CITATION... 3 1.1 BACKGROUND... 3 1.2 PURPOSE
Code of Practice for Radiation Protection in Dentistry Code of Practice For Radiation Protection in Dentistry 10 OCTOBER 2017 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 3 1.0 CITATION... 3 1.1 BACKGROUND... 3 1.2 PURPOSE
Chapter 8. Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation
 Chapter 8 Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation Learning Objectives By the end of the chapter the reader will be able to: Define the terms ionizing radiation and nonionizing radiation State the differences
Chapter 8 Ionizing and Non-Ionizing Radiation Learning Objectives By the end of the chapter the reader will be able to: Define the terms ionizing radiation and nonionizing radiation State the differences
Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/11/09
 Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/11/09 Health Physics NRC Dose Limits The NRC has established the following annual dose limits. Organ NRC Limit (mrem/year) Comments Whole Body 5000 (50 msv/yr) Lens of the Eye
Chem 481 Lecture Material 3/11/09 Health Physics NRC Dose Limits The NRC has established the following annual dose limits. Organ NRC Limit (mrem/year) Comments Whole Body 5000 (50 msv/yr) Lens of the Eye
Laboratory Safety 197/405. Types of Radiation 198/405
 Laboratory Safety 197/405 Types of Radiation 198/405 Particle Radiation Alpha He nucleus (heavy particle) +2 charge Internal hazard only Beta Electron -1 charge Internal and external hazard Neutron 199/405
Laboratory Safety 197/405 Types of Radiation 198/405 Particle Radiation Alpha He nucleus (heavy particle) +2 charge Internal hazard only Beta Electron -1 charge Internal and external hazard Neutron 199/405
Radiation Safety. - Orientation Session - Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit
 Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit Radiation Safety - Orientation Session - Mohamad Houssam Tamim University Radiation Safety Officer B.E. Communications and Electronics
Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit Radiation Safety - Orientation Session - Mohamad Houssam Tamim University Radiation Safety Officer B.E. Communications and Electronics
Radiation Safety for Safety Wardens
 Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit Radiation Safety for Safety Wardens - Orientation Session - Mohamad Houssam Tamim University Radiation Safety Officer B.E. Communications
Environmental Health, Safety & Risk Management Health Physics Services Unit Radiation Safety for Safety Wardens - Orientation Session - Mohamad Houssam Tamim University Radiation Safety Officer B.E. Communications
RADIATION SAFETY. Junior Radiology Course
 RADIATION SAFETY Junior Radiology Course Expectations for the Junior Radiology Course Medical School wants students to learn basic principles, factual knowledge, safety info, etc. Medical Students want
RADIATION SAFETY Junior Radiology Course Expectations for the Junior Radiology Course Medical School wants students to learn basic principles, factual knowledge, safety info, etc. Medical Students want
Radiation Safety For Anesthesiologists. R2 Pinyada Pisutchareonpong R2 Nawaporn Sateantantikul Supervised by Aj Chaowanan Khamtuicrua
 Radiation Safety For Anesthesiologists R2 Pinyada Pisutchareonpong R2 Nawaporn Sateantantikul Supervised by Aj Chaowanan Khamtuicrua Modern World Non Ionizing VS Ionizing Non Ionizing Harmless Ex. visible
Radiation Safety For Anesthesiologists R2 Pinyada Pisutchareonpong R2 Nawaporn Sateantantikul Supervised by Aj Chaowanan Khamtuicrua Modern World Non Ionizing VS Ionizing Non Ionizing Harmless Ex. visible
ALBERTA REGULATION 182/2003 RADIATION PROTECTION REGULATION
 Us (Consolidated up to 74/2004) Radiation Protection Act Table of Contents ALBERTA REGULATION 182/2003 RADIATION PROTECTION REGULATION 1 Interpretation Part 1 General Provisions 2 Prohibited radiation
Us (Consolidated up to 74/2004) Radiation Protection Act Table of Contents ALBERTA REGULATION 182/2003 RADIATION PROTECTION REGULATION 1 Interpretation Part 1 General Provisions 2 Prohibited radiation
Principles of Radiation
 RADIOACTIVE AGENTS Principles of Radiation 2 types of radiation Non-ionizing (no tissue damage) Ionizing (tissue damage) 2010 MGH International Disaster Institute 1 2010 MGH International Disaster Institute
RADIOACTIVE AGENTS Principles of Radiation 2 types of radiation Non-ionizing (no tissue damage) Ionizing (tissue damage) 2010 MGH International Disaster Institute 1 2010 MGH International Disaster Institute
CHAPTER 28 RADIATION CONTROL
 CHAPTER 28 RADIATION CONTROL BOARD OF HEALTH ROLE AT A GLANCE Be aware of radioactive materials in the community and request technical assistance in response to incidents involving the possession, handling,
CHAPTER 28 RADIATION CONTROL BOARD OF HEALTH ROLE AT A GLANCE Be aware of radioactive materials in the community and request technical assistance in response to incidents involving the possession, handling,
Quality Assurance and Radiation Protection Manual for Non-Human Use Radiation Generating Equipment
 Quality Assurance and Radiation Protection Manual for Non-Human Use Radiation Generating Equipment DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT RECORD OF REVISION PAGE Revision # Date of Revision Change Entered Original 9/15/1998
Quality Assurance and Radiation Protection Manual for Non-Human Use Radiation Generating Equipment DRAFT DRAFT DRAFT RECORD OF REVISION PAGE Revision # Date of Revision Change Entered Original 9/15/1998
created by high-voltage devices Examples include medical and dental x-rays, light, microwaves and nuclear energy
 What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
What is radiation? Radiation is energy emitted from a source, that travels through space and can penetrate matter. Listed below are two types that we are exposed to and contribute to our overall radiation
Introduction. Chapter 15 Radiation Protection. Advisory bodies. Regulatory bodies. Main Principles of Radiation Protection
 Introduction Chapter 15 Radiation Protection Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. F.M. Khan, The Physics of Radiation Therapy, 4th ed., Chapter
Introduction Chapter 15 Radiation Protection Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. F.M. Khan, The Physics of Radiation Therapy, 4th ed., Chapter
Radiation physics and radiation protection. University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Radiation physics and radiation protection University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine Radiation doses to the population 1 Radiation doses to the population 2 Sources of radiation 1 Radiation we
Radiation physics and radiation protection University of Szeged Department of Nuclear Medicine Radiation doses to the population 1 Radiation doses to the population 2 Sources of radiation 1 Radiation we
The College of Dental Surgeons of Saskatchewan Radiation and Imaging Standard
 The College of Dental Surgeons of Saskatchewan Radiation and Imaging Standard Legislation Radiation safety has long been a priority in Saskatchewan. This province, the first in Canada to have radiation
The College of Dental Surgeons of Saskatchewan Radiation and Imaging Standard Legislation Radiation safety has long been a priority in Saskatchewan. This province, the first in Canada to have radiation
Diploma Unit B - Element B7 - Physical agents 2 - Radiation February RMS Publishing. Fourth Edition November 2013
 NEBOSH DIPLOMA IN OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY Licence details RMS Publishing Victoria House, Lower High Street, Stourbridge DY8 1TA RMS Publishing. Unit B Hazardous agents in the workplace Fourth Edition
NEBOSH DIPLOMA IN OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH AND SAFETY Licence details RMS Publishing Victoria House, Lower High Street, Stourbridge DY8 1TA RMS Publishing. Unit B Hazardous agents in the workplace Fourth Edition
MONITORING OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AT NUCLEAR FACILITIES
 GUIDE YVL 7.10 / 29 JANUARY 2002 MONITORING OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AT NUCLEAR FACILITIES 1 GENERAL 3 2 PROVISIONS OF THE RADIATION ACT AND DECREE 3 3 MONITORING OF RADIATION EXPOSURE 4 3.1 General requirements
GUIDE YVL 7.10 / 29 JANUARY 2002 MONITORING OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE AT NUCLEAR FACILITIES 1 GENERAL 3 2 PROVISIONS OF THE RADIATION ACT AND DECREE 3 3 MONITORING OF RADIATION EXPOSURE 4 3.1 General requirements
PERSONNEL MONITORING AND DOSIMETRY POLICIES
 PERSONNEL MONITORING AND DOSIMETRY POLICIES All individuals who are required to have their exposure to ionizing radiation monitored must be trained prior to using the source(s) of radiation. The radioactive
PERSONNEL MONITORING AND DOSIMETRY POLICIES All individuals who are required to have their exposure to ionizing radiation monitored must be trained prior to using the source(s) of radiation. The radioactive
ARRT Specifications Radiation Exposure & Monitoring
 Radiation Protection Review 15% (30) 11% (22) Gina Tice, MSRS, RT(R) Gadsden State Community College ARRT Specifications Radiation Exposure & Monitoring Radiation Protection (45) Biological Aspects of
Radiation Protection Review 15% (30) 11% (22) Gina Tice, MSRS, RT(R) Gadsden State Community College ARRT Specifications Radiation Exposure & Monitoring Radiation Protection (45) Biological Aspects of
a. If dosimeters should be issued; b. What type(s) will be used and; c. The frequency that dosimeters will be exchanged
 Monitoring Criteria for External Radiation RMSO Standard Operating Procedure Risk Management & Safety Main Office, Merica Hall Room 323 Phone: (307) 766-3277 Fax: (307)766-6116 Regulated Materials Management
Monitoring Criteria for External Radiation RMSO Standard Operating Procedure Risk Management & Safety Main Office, Merica Hall Room 323 Phone: (307) 766-3277 Fax: (307)766-6116 Regulated Materials Management
Radiation Monitoring Instruments
 Radiation Monitoring Instruments This set of slides is based on Chapter 4 authored byg. Rajan, J. Izewska of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers
Radiation Monitoring Instruments This set of slides is based on Chapter 4 authored byg. Rajan, J. Izewska of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Radiation Oncology Physics: A Handbook for Teachers
RADIATION HAZARDS AND SAFETY
 RADIATION HAZARDS AND SAFETY Dr. S. P. Tyagi All types of radiation produce changes in the living tissues. The resultant cellular injury causes physiological and pathological changes leading to Radiation
RADIATION HAZARDS AND SAFETY Dr. S. P. Tyagi All types of radiation produce changes in the living tissues. The resultant cellular injury causes physiological and pathological changes leading to Radiation
RADIATION SAFETY REFRESHER TRAINING FOR AUGUSTA UNIVERSITY USERS OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
 RADIATION SAFETY REFRESHER TRAINING FOR AUGUSTA UNIVERSITY USERS OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Environmental Health and Safety Division Course Content Radiation Safety Radiation Dose Limits and Dosimetry Postings
RADIATION SAFETY REFRESHER TRAINING FOR AUGUSTA UNIVERSITY USERS OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Environmental Health and Safety Division Course Content Radiation Safety Radiation Dose Limits and Dosimetry Postings
Survey of Radiation Dose Levels in Patients in X-Ray Units of Some Selected Hospitals in Jos Metropolis
 International Journal of Innovative Scientific & Engineering Technologies Research 6(4):1-9, Oct.-.Dec., 2018 SEAHI PUBLICATIONS, 2018 www.seahipaj.org ISSN: 2360-896X Survey of Radiation Dose Levels in
International Journal of Innovative Scientific & Engineering Technologies Research 6(4):1-9, Oct.-.Dec., 2018 SEAHI PUBLICATIONS, 2018 www.seahipaj.org ISSN: 2360-896X Survey of Radiation Dose Levels in
The x-rays produced penetrate the body which absorbs, refracts, or reflects the x-ray beam energy depending on the tissue. Bone
 Authors Sari Cohen, Poh Yan Lim, Merng Koon Wong, Siew Hong Lau, Donna Russell-Larson 1.6.2 Image intensifier Poh Yan Lim, Merng Koon Wong The discovery of x-rays had a profound impact on the diagnosis
Authors Sari Cohen, Poh Yan Lim, Merng Koon Wong, Siew Hong Lau, Donna Russell-Larson 1.6.2 Image intensifier Poh Yan Lim, Merng Koon Wong The discovery of x-rays had a profound impact on the diagnosis
Health & Safety, Edinburgh Napier University
 Health & Safety, Edinburgh Napier University Version number 2.0 Version date October 2018 Review Date 1 : 1 or earlier if change in legislation or on risk assessment Approval/Authorised Signature Distribution
Health & Safety, Edinburgh Napier University Version number 2.0 Version date October 2018 Review Date 1 : 1 or earlier if change in legislation or on risk assessment Approval/Authorised Signature Distribution
University of Cincinnati. Quality Assurance. and. Radiation Protection Manual. for. Non-Human Use. Radiation Generating. Equipment
 University of Cincinnati Quality Assurance and Radiation Protection Manual for Non-Human Use Radiation Generating Equipment RECORD OF REVISION PAGE Revision # Date of Revision Change Entered Original 9/15/1998
University of Cincinnati Quality Assurance and Radiation Protection Manual for Non-Human Use Radiation Generating Equipment RECORD OF REVISION PAGE Revision # Date of Revision Change Entered Original 9/15/1998
The Radiation Health and Safety Act, 1985
 1 The Radiation Health and Safety Act, 1985 Repealed by Chapter S-15.1 of the Statutes of Saskatchewan, 2013 (effective April 29, 2014) Formerly Chapter R-1.1 of the Statutes of Saskatchewan, 1984-85-86
1 The Radiation Health and Safety Act, 1985 Repealed by Chapter S-15.1 of the Statutes of Saskatchewan, 2013 (effective April 29, 2014) Formerly Chapter R-1.1 of the Statutes of Saskatchewan, 1984-85-86
Ionizing Radiation. Michael J. Vala, CHP. Bristol-Myers Squibb
 Ionizing Radiation Michael J. Vala, CHP Bristol-Myers Squibb michael.vala@bms.com 732-227-5096 2013 American Industrial Hygiene Association, New Jersey Section, Inc. Course Objectives At the end of this
Ionizing Radiation Michael J. Vala, CHP Bristol-Myers Squibb michael.vala@bms.com 732-227-5096 2013 American Industrial Hygiene Association, New Jersey Section, Inc. Course Objectives At the end of this
GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL
 RADIATION PROTECTION AUTHORITY OF ZIMBABWE (RPAZ) RADIATION PROTECTION ACT [CHAPTER 15:15] GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Compiled by Radiation
RADIATION PROTECTION AUTHORITY OF ZIMBABWE (RPAZ) RADIATION PROTECTION ACT [CHAPTER 15:15] GUIDELINES ON IONISING RADIATION DOSE LIMITS AND ANNUAL LIMITS ON INTAKE OF RADIOACTIVE MATERIAL Compiled by Radiation
in developing institutional policies, procedures, and /or protocols. The Canadian Society of
 1 TITLE: GUIDELINES FOR RADIATION SAFETY APPROVED; October 2015 REVISION DATE: February 2016 Disclaimer The Canadian Society of Gastroenterology Nurses and Associates present this guideline for use in
1 TITLE: GUIDELINES FOR RADIATION SAFETY APPROVED; October 2015 REVISION DATE: February 2016 Disclaimer The Canadian Society of Gastroenterology Nurses and Associates present this guideline for use in
Please refer to the body corporate s registered bylaws in relation to domestic noise.
 1 P a g e Noise Control Guide It is the responsibility of every occupant, owner, tenant, contractor, employee & visitor and ALL users of this facility to ensure they take all reasonably practical steps
1 P a g e Noise Control Guide It is the responsibility of every occupant, owner, tenant, contractor, employee & visitor and ALL users of this facility to ensure they take all reasonably practical steps
A Study of dose Distribution and Radiation Protection in Industrial Radiography in Ireland
 A Study of dose Distribution and Radiation Protection in Industrial Radiography in Ireland L. Currivan, J. T. Duffy, D. Spain and D. Pollard Radiological Protection Institute of Ireland, 3 Clonskeagh Square,
A Study of dose Distribution and Radiation Protection in Industrial Radiography in Ireland L. Currivan, J. T. Duffy, D. Spain and D. Pollard Radiological Protection Institute of Ireland, 3 Clonskeagh Square,
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden
 Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
Radiation Safety Information for Students in Courses given by the Nuclear Physics Group at KTH, Stockholm, Sweden September 2006 The aim of this text is to explain some of the basic quantities and units
Radiation in Everyday Life
 Image not found Rincón http://www.rinconeducativo.org/sites/default/files/logo.jpg Educativo Published on Rincón Educativo (http://www.rinconeducativo.org) Inicio > Radiation in Everyday Life Recursos
Image not found Rincón http://www.rinconeducativo.org/sites/default/files/logo.jpg Educativo Published on Rincón Educativo (http://www.rinconeducativo.org) Inicio > Radiation in Everyday Life Recursos
IONIZING RADIATION, HEALTH EFFECTS AND PROTECTIVE MEASURES
 May 2011 IONIZING RADIATION, HEALTH EFFECTS AND PROTECTIVE MEASURES KEY FACTS Ionizing radiation is a type of energy released by atoms in the form of electromagnetic waves or particles. People are exposed
May 2011 IONIZING RADIATION, HEALTH EFFECTS AND PROTECTIVE MEASURES KEY FACTS Ionizing radiation is a type of energy released by atoms in the form of electromagnetic waves or particles. People are exposed
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage
 Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Nature of Radiation and DNA damage Index 1. What is radiation? 2. Ionizing Radiation 3. Interaction of Gamma-radiation with Matter 4. Radiobiology 5. Direct and Indirect action of radiation 6. Steps of
Safety Services Guidance. Occupational Noise
 Occupational Noise Key word(s): Occupational noise, sound, hearing, decibel, noise induced hearing loss (NIHL), Noise at Work Regulations 2005 Target audience: Managers and staff with responsibility to
Occupational Noise Key word(s): Occupational noise, sound, hearing, decibel, noise induced hearing loss (NIHL), Noise at Work Regulations 2005 Target audience: Managers and staff with responsibility to
RADIATION SAFETY GUIDE FOR ANALYTICAL X-RAY SYSTEM USERS
 DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY RADIATION PROTECTION DIVISION MAY 2001 FOR ANALYTICAL X-RAY SYSTEM USERS I INTRODUCTION The Minnesota Department of Health has established rules for the registration
DEPARTMENT OF ENVIRONMENTAL HEALTH & SAFETY RADIATION PROTECTION DIVISION MAY 2001 FOR ANALYTICAL X-RAY SYSTEM USERS I INTRODUCTION The Minnesota Department of Health has established rules for the registration
Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 2 & 3 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy radiation
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 2 & 3 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy radiation
Table of Contents. Introduction 3. Background 4
 Training manual Table of Contents Introduction 3 Background 4 What are X-rays? 4 How are X-rays Generated? 5 Primary and Scatter Radiation 6 Interactions with Matter 6 Biological Effects of Radiation 7
Training manual Table of Contents Introduction 3 Background 4 What are X-rays? 4 How are X-rays Generated? 5 Primary and Scatter Radiation 6 Interactions with Matter 6 Biological Effects of Radiation 7
Radiation Health Effects
 Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
Radiation Health Effects Elena Buglova Incident and Emergency Centre Department of Nuclear Safety and Security Content Historical background Primary target for cell damage Deterministic effects Stochastic
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry
 Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
Radioactive Exposure. Abstract of Article:
 Radioactive Exposure Abstract of Article: All ionizing radiations, at sufficiently large exposures, can cause cancer. Many, in carefully controlled exposures, are also used for cancer therapy. Ionizing
Radioactive Exposure Abstract of Article: All ionizing radiations, at sufficiently large exposures, can cause cancer. Many, in carefully controlled exposures, are also used for cancer therapy. Ionizing
Utilize radiation safety principles to reduce the amount of radiation used to achieve desired clinical result.
 Minimizing Dose Understand the importance and methods of pre-procedure patient assessment including a review of previous radiologic exams, disease processes and anatomical considerations that may increase
Minimizing Dose Understand the importance and methods of pre-procedure patient assessment including a review of previous radiologic exams, disease processes and anatomical considerations that may increase
Section 7 ALARA Program
 Page 7-1 Section 7 ALARA Program Contents A. ALARA Principle... 7-2 1. Biological Basis... 7-2 2. Applied Practices... 7-3 3. Operational Dose Limits... 7-3 4. Collective Dose... 7-3 B. Radiation Safety
Page 7-1 Section 7 ALARA Program Contents A. ALARA Principle... 7-2 1. Biological Basis... 7-2 2. Applied Practices... 7-3 3. Operational Dose Limits... 7-3 4. Collective Dose... 7-3 B. Radiation Safety
3/26/2017. Personal Dosimetry Monitoring and Dose Measurements. Agenda. Dosimetric Terms and Definitions Dose Limits External Dosimetry
 Speaker David Pellicciarini, CHP, MBA Vice President, Pharmacy Safety, Practice and Technical Operations Cardinal Health Nuclear Pharmacy Services david.pellicciarini@cardinalhealth.com Personal Dosimetry
Speaker David Pellicciarini, CHP, MBA Vice President, Pharmacy Safety, Practice and Technical Operations Cardinal Health Nuclear Pharmacy Services david.pellicciarini@cardinalhealth.com Personal Dosimetry
Ionizing Radiation. Alpha Particles CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Ionizing Radiation Ionizing radiation is radiation that has sufficient energy to remove electrons from atoms. In this document, it will be referred to simply as radiation. One source of radiation
CHAPTER 1 Ionizing Radiation Ionizing radiation is radiation that has sufficient energy to remove electrons from atoms. In this document, it will be referred to simply as radiation. One source of radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF
 BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
BIOLOGICAL EFFECTS OF RADIATION Natural Sources of Radiation Natural background radiation comes from three sources: Cosmic Radiation Terrestrial Radiation Internal Radiation 2 Natural Sources of Radiation
UPPER MISSOURI DISTRICT HEALTH UNIT REGULATIONS FOR TANNING FACILITIES
 UPPER MISSOURI DISTRICT HEALTH UNIT REGULATIONS FOR TANNING FACILITIES Adopted by reference by the Upper Missouri District Health Unit. Except as amended in 33-42-01-10. ADOPTED: 01-29-2008 Article 33-42
UPPER MISSOURI DISTRICT HEALTH UNIT REGULATIONS FOR TANNING FACILITIES Adopted by reference by the Upper Missouri District Health Unit. Except as amended in 33-42-01-10. ADOPTED: 01-29-2008 Article 33-42
GUIDE TO THE APPLICATION TO POSSESS AND USE A SOURCE(S) FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS
 ATOMIC ENERGY COUNCIL GUIDE TO THE APPLICATION TO POSSESS AND USE A SOURCE(S) FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS Item Type of Application 1 Name and address of applicant 2 Radiation safety Officer (RSO) Guiding
ATOMIC ENERGY COUNCIL GUIDE TO THE APPLICATION TO POSSESS AND USE A SOURCE(S) FOR INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS Item Type of Application 1 Name and address of applicant 2 Radiation safety Officer (RSO) Guiding
Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units
 INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 3, 4 & 5 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy
INAYA MEDICAL COLLEGE (IMC) RAD 232 - LECTURE 3, 4 & 5 Biological Effects of Ionizing Radiation & Commonly Used Radiation Units DR. MOHAMMED MOSTAFA EMAM How does radiation injure people? - High energy
PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF RADIATION PROTECTION
 PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF RADIATION PROTECTION Lesson Outcomes At the end of the lesson, student should be able to: Define what is radiation protection (RP) Describe basic principles of RP Explain methods
PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF RADIATION PROTECTION Lesson Outcomes At the end of the lesson, student should be able to: Define what is radiation protection (RP) Describe basic principles of RP Explain methods
ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment
 ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment Badria Al Hatali, MD Medical Toxicologist Department of Environmental and Occupational Health MOH - Oman Objectives Provide a review of radiation basics
ACUTE RADIATION SYNDROME: Diagnosis and Treatment Badria Al Hatali, MD Medical Toxicologist Department of Environmental and Occupational Health MOH - Oman Objectives Provide a review of radiation basics
45 Hr PET Registry Review Course
 45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
NEW RADIATION LEGISLATION M M TREVOR
 NEW RADIATION LEGISLATION M M TREVOR RADIATION Aims to: Produce a working definition for the term Radiation Consider what types of radiation are present in the workplace Look at risk assessment of artificial
NEW RADIATION LEGISLATION M M TREVOR RADIATION Aims to: Produce a working definition for the term Radiation Consider what types of radiation are present in the workplace Look at risk assessment of artificial
Adult: > 18 Years ALARA: As low as reasonably achievable ALI:
 Health Physics Adult: > 18 Years ALARA: As low as reasonably achievable ALI: Annual Limit on Intake. The amount of an isotope that if taken into the body over the course of a year would result in in a
Health Physics Adult: > 18 Years ALARA: As low as reasonably achievable ALI: Annual Limit on Intake. The amount of an isotope that if taken into the body over the course of a year would result in in a
Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation
 Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Course Director, Conrad Daniel Volz, DrPH, MPH Assistant Professor, Environmental & Occupational Health, University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health
Lecture 14 Exposure to Ionizing Radiation Course Director, Conrad Daniel Volz, DrPH, MPH Assistant Professor, Environmental & Occupational Health, University of Pittsburgh, Graduate School of Public Health
Radiation Safety - Things You Need to Know
 Radiation Safety - Things You Need to Know Michael Casey Ph.D. Phlebotomy Autumn Seminar 13 th October 2012 Radiation is a form of energy transport What is Radiation? It is caused by electrical disturbances
Radiation Safety - Things You Need to Know Michael Casey Ph.D. Phlebotomy Autumn Seminar 13 th October 2012 Radiation is a form of energy transport What is Radiation? It is caused by electrical disturbances
IONISING RADIATION SAFETY MANUAL
 IONISING RADIATION SAFETY MANUAL Version 1 Area Radiation Safety Officers (RSO) (After hours call: Security 1 2880) Area RSO Contact # Biological Sciences Dr Peter Anderson 15269/13752 SCaPS Dr Rachel
IONISING RADIATION SAFETY MANUAL Version 1 Area Radiation Safety Officers (RSO) (After hours call: Security 1 2880) Area RSO Contact # Biological Sciences Dr Peter Anderson 15269/13752 SCaPS Dr Rachel
"The Good Side of Radiation: Medical Applications"
 "The Good Side of Radiation: Medical Applications" J. Battista, Ph.D. Medical Physicist London Regional Cancer Program LHSC http://www.macmillan.org.uk/images/cancerinfo Role of Medical Physicists Diagnostic
"The Good Side of Radiation: Medical Applications" J. Battista, Ph.D. Medical Physicist London Regional Cancer Program LHSC http://www.macmillan.org.uk/images/cancerinfo Role of Medical Physicists Diagnostic
University of Arizona Radiation Generating Machine Protection Reference Guide. Research Laboratory & Safety Services Revised January 8, 2018
 PO Box 245101 Tucson, AZ 85724-5101 Voice: (520) 626-6850 FAX: (520) 626-2583 rlss.arizona.edu University of Arizona Radiation Generating Machine Protection Reference Guide Research Laboratory & Safety
PO Box 245101 Tucson, AZ 85724-5101 Voice: (520) 626-6850 FAX: (520) 626-2583 rlss.arizona.edu University of Arizona Radiation Generating Machine Protection Reference Guide Research Laboratory & Safety
SECTION 1 - INTRODUCTION 2 PURPOSE 2 SCOPE 2 DEFINITIONS 2 LEGISLATIVE CONTEXT 3 RESPONSIBILITIES 4
 OHS Noise Procedure Name: Approved by: Noise Procedure Vice Chancellors Executive Group Last reviewed: 21 December 2010 SECTION 1 - INTRODUCTION 2 PURPOSE 2 SCOPE 2 DEFINITIONS 2 LEGISLATIVE CONTEXT 3
OHS Noise Procedure Name: Approved by: Noise Procedure Vice Chancellors Executive Group Last reviewed: 21 December 2010 SECTION 1 - INTRODUCTION 2 PURPOSE 2 SCOPE 2 DEFINITIONS 2 LEGISLATIVE CONTEXT 3
Nuclear Radiation Today
 CHAPTER 10 13 SECTION Nuclear Changes Nuclear Radiation Today KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: Where are some common sources of radiation? What are some beneficial uses
CHAPTER 10 13 SECTION Nuclear Changes Nuclear Radiation Today KEY IDEAS As you read this section, keep these questions in mind: Where are some common sources of radiation? What are some beneficial uses
What We Know and What We Don t Know About Radiation Health Effects
 What We Know and What We Don t Know About Radiation Health Effects An Educational Briefing By The HEALTH PHYSICS SOCIETY Specialists In Radiation Safety March 28, 2001 Presentation Agenda Radiation Exposure
What We Know and What We Don t Know About Radiation Health Effects An Educational Briefing By The HEALTH PHYSICS SOCIETY Specialists In Radiation Safety March 28, 2001 Presentation Agenda Radiation Exposure
Hearing Conservation Program
 Hearing Conservation Program Revised: September 2017 2009-2017. University of New Hampshire Office of Environmental Health and Safety. All rights reserved. The most current version of this document can
Hearing Conservation Program Revised: September 2017 2009-2017. University of New Hampshire Office of Environmental Health and Safety. All rights reserved. The most current version of this document can
Risk and Risk Reduction. Environmental Health and Safety. Radiation Safety. Radiation is all around us
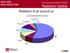 Risk and Risk Reduction Radiation is all around us Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Safety Risk and Risk Reduction Risk Webster s dictionary defines risk as the chance of injury, damage, or loss;
Risk and Risk Reduction Radiation is all around us Environmental Health and Safety Radiation Safety Risk and Risk Reduction Risk Webster s dictionary defines risk as the chance of injury, damage, or loss;
Radiation Generating Machines. Reference Guide
 THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Radiation Generating Machines Reference Guide October 2008 1717 E. Speedway Blvd. (Bldg. 151) Suite 1201 Tucson, AZ 85724 P.O. Box 245101 www.radcon.arizona.edu Phone (520) 626-6850
THE UNIVERSITY OF ARIZONA Radiation Generating Machines Reference Guide October 2008 1717 E. Speedway Blvd. (Bldg. 151) Suite 1201 Tucson, AZ 85724 P.O. Box 245101 www.radcon.arizona.edu Phone (520) 626-6850
78th OREGON LEGISLATIVE ASSEMBLY Regular Session. Enrolled. Senate Bill 280
 78th OREGON LEGISLATIVE ASSEMBLY--2015 Regular Session Enrolled Senate Bill 280 Printed pursuant to Senate Interim Rule 213.28 by order of the President of the Senate in conformance with presession filing
78th OREGON LEGISLATIVE ASSEMBLY--2015 Regular Session Enrolled Senate Bill 280 Printed pursuant to Senate Interim Rule 213.28 by order of the President of the Senate in conformance with presession filing
Dental Intraoral X-ray Systems
 Dental Intraoral X-ray Systems PROPOSED REVISIONS TO 4732.XXXX, 2.0 4732.#### DENTAL INTRAORAL X-RAY SYSTEMS; STATIONARY AND MOBILE. Commented [JC(1]: Based on part 4732.0880. Subpart 1. Applicability.
Dental Intraoral X-ray Systems PROPOSED REVISIONS TO 4732.XXXX, 2.0 4732.#### DENTAL INTRAORAL X-RAY SYSTEMS; STATIONARY AND MOBILE. Commented [JC(1]: Based on part 4732.0880. Subpart 1. Applicability.
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT
 RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
RADIATION RISK ASSESSMENT EXPOSURE and TOXITY ASSESSMENT Osipova Nina, associated professor, PhD in chemistry, Matveenko Irina, Associate professor, PhD in philology TOMSK -2013 The contents 1.What is
Dr. Mohammed T Omar Associate professor CAMS Mobile: Office: 2074
 INFRARED Therapy Dr. Mohammed T Omar Associate professor CAMS E-mail-momarar@ksu.edi.sa Dr.taher-M@yahoo.com Mobile: 0542115404 Office: 2074 Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student
INFRARED Therapy Dr. Mohammed T Omar Associate professor CAMS E-mail-momarar@ksu.edi.sa Dr.taher-M@yahoo.com Mobile: 0542115404 Office: 2074 Objectives Following completion of this lecture the student
Chapter 4: Radiation Monitoring Instruments
 Chapter 4: Radiation Monitoring Instruments Set of 107 slides based on the chapter authored by G. Rajan, J. Izewska of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A
Chapter 4: Radiation Monitoring Instruments Set of 107 slides based on the chapter authored by G. Rajan, J. Izewska of the IAEA publication (ISBN 92-0-107304-6): Review of Radiation Oncology Physics: A
Accelerator Laboratory GENERAL EMPLOYEE RADIATION TRAINING
 f Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory GENERAL EMPLOYEE RADIATION TRAINING Operated by Universities Research Association, Inc. under contract with the United States Department of Energy October, 1999
f Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory GENERAL EMPLOYEE RADIATION TRAINING Operated by Universities Research Association, Inc. under contract with the United States Department of Energy October, 1999
Understanding Radiation and Its Effects
 Understanding Radiation and Its Effects Prepared by Brooke Buddemeier, CHP University of California Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Presented by Jeff Tappen Desert Research Institute 1 Radiation
Understanding Radiation and Its Effects Prepared by Brooke Buddemeier, CHP University of California Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Presented by Jeff Tappen Desert Research Institute 1 Radiation
An update: Dealing with radiation as a hazard. WAJ Meintjes MBChB; DOM; FCPHM(SA) Occ Med; MMed (Occ Med)
 An update: Dealing with radiation as a hazard WAJ Meintjes MBChB; DOM; FCPHM(SA) Occ Med; MMed (Occ Med) Radiation The emission and propagation of energy in the form of rays Usually differentiate ionising
An update: Dealing with radiation as a hazard WAJ Meintjes MBChB; DOM; FCPHM(SA) Occ Med; MMed (Occ Med) Radiation The emission and propagation of energy in the form of rays Usually differentiate ionising
Sources of ionizing radiation Atomic structure and radioactivity Radiation interaction with matter Radiation units and dose Biological effects
 INTRODUCTION TO RADIATION PROTECTION Sources of ionizing radiation Atomic structure and radioactivity Radiation interaction with matter Radiation units and dose Biological effects 3/14/2018 1 Wilhelm C.
INTRODUCTION TO RADIATION PROTECTION Sources of ionizing radiation Atomic structure and radioactivity Radiation interaction with matter Radiation units and dose Biological effects 3/14/2018 1 Wilhelm C.
Santa Clarita Community College District HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM. Revised
 Santa Clarita Community College District HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM Revised March 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1 HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM...2 1.1 District Policy...2 1.2 Plan Review...2
Santa Clarita Community College District HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM Revised March 2018 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...1 HEARING CONSERVATION PROGRAM...2 1.1 District Policy...2 1.2 Plan Review...2
Radiation Safety in the Catheterization Lab
 SCAI FALL FELLOWS COURSE - 2015 Radiation Safety in the Catheterization Lab V. Vivian Dimas, MD, FSCAI Associate Professor Pediatrics, Cardiology UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas TX None Disclosures
SCAI FALL FELLOWS COURSE - 2015 Radiation Safety in the Catheterization Lab V. Vivian Dimas, MD, FSCAI Associate Professor Pediatrics, Cardiology UT Southwestern Medical Center Dallas TX None Disclosures
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 RA202 Rad protection class two True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Secondary radiation comes from scatter and leakage. 2. Grids are considered a protection device.
RA202 Rad protection class two True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. 1. Secondary radiation comes from scatter and leakage. 2. Grids are considered a protection device.
Practice and Risk at Medical Facilities in Agency Operations
 Practice and Risk at Medical Facilities in Agency Operations Igor Gusev Radiation Protection Unit IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency Outline What is medical radiation exposure? Radiation sources and
Practice and Risk at Medical Facilities in Agency Operations Igor Gusev Radiation Protection Unit IAEA International Atomic Energy Agency Outline What is medical radiation exposure? Radiation sources and
Module Rhodes
 Module 6 10-526-197 Rhodes Health Physicist Concerned with providing occupation radiation protection and minimizing radiation dose to the public. Diagnostic Imaging has changed our world Live longer Work
Module 6 10-526-197 Rhodes Health Physicist Concerned with providing occupation radiation protection and minimizing radiation dose to the public. Diagnostic Imaging has changed our world Live longer Work
2017 Course of the Nordic Association for Clinical Physics on occupational dosimetry in hospitals
 2017 Course of the Nordic Association for Clinical Physics on occupational dosimetry in hospitals 27 September 2017 Dr. Pedro Ortiz López Retired member of the ICRP and the IAEA 2 Pedro Ortiz López (Chair)
2017 Course of the Nordic Association for Clinical Physics on occupational dosimetry in hospitals 27 September 2017 Dr. Pedro Ortiz López Retired member of the ICRP and the IAEA 2 Pedro Ortiz López (Chair)
workplace includes, any land, premises, location, vessel or thing, at, in, upon, or near which, a worker is, in the course of employment.
 L.N. 25/2005 THE FACTORIES AND OTHER PLACES OF WORK (NOISE PREVENTION AND CONTROL) RULES 2005 Citation 1 These rules shall be cited as Factories and Other Places of Work (Noise Prevention and Control)
L.N. 25/2005 THE FACTORIES AND OTHER PLACES OF WORK (NOISE PREVENTION AND CONTROL) RULES 2005 Citation 1 These rules shall be cited as Factories and Other Places of Work (Noise Prevention and Control)
Ionising Radiations Regulations 2017
 Health and Safety Executive Ionising Radiations Regulations 2017 New Provisions etc. James Taylor Principal Specialist Inspector (Radiation) Tel: 07879 661820 email: james.taylor@hse.gov.uk Graded Approach
Health and Safety Executive Ionising Radiations Regulations 2017 New Provisions etc. James Taylor Principal Specialist Inspector (Radiation) Tel: 07879 661820 email: james.taylor@hse.gov.uk Graded Approach
(1) This standard applies to all indoor work areas where the temperature equals or exceeds 82 degrees Fahrenheit when employees are present.
 Heat Illness Prevention Draft Text draft revisions 1/29/19 compared to 10/24/18. Heat Illness Prevention in Indoor Places of Employment (a) Scope and Application. (1) This standard applies to all indoor
Heat Illness Prevention Draft Text draft revisions 1/29/19 compared to 10/24/18. Heat Illness Prevention in Indoor Places of Employment (a) Scope and Application. (1) This standard applies to all indoor
Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources)
 Vision and Light Vision Generators Transmitters (Light Sources) Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources) Receivers Decoder Encoders Interpreter (Eyes) (Brain) Sun, Discharge lamps, fluorescent
Vision and Light Vision Generators Transmitters (Light Sources) Modifiers and Retransmitters (Secondary Light Sources) Receivers Decoder Encoders Interpreter (Eyes) (Brain) Sun, Discharge lamps, fluorescent
