three forms: c-cbl, CBLb and CBL-3) MDM2, MDMX and SCF Fbxo11
|
|
|
- Rodney Andrews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary information S1 (table) Reported Neddylation Substrates Target protein Biological function of target Effect of neddylation E2 E3 Regulation of neddylation Cullins RING ubiquitin E3 ligases Activation of ubiquitin UBC12, RBX1/RBX2 Enhanced by DCNLs, transfer activity UBE2F Tfb3 (budding yeast) and ubiquitylation substrates, reversed by the CSN complex SMURF1 HECT Ubiquitin E3 ligase Activation of ubiquitin transfer activity TGFβRII TGF-β signal transduction, inhibition of proliferation TGFβRII stabilization, thus promoting the antiproliferative effect of TGF-β Neddylated lysines (method) Human CUL1: Lys720 Human CUL2: Lys689 Human CUL3: Lys712 Human CUL4A: Lys705 Human CUL4B: Lys859 Human CUL5: Lys724 UBC12 SMURF1 Not known Lys324, Lys495, Lys545, Lys558, Lys559, and Lys667 (mass spectrometry) UBC12 c-cbl c- CBL- mediated neddylation depends on TGFβRII kinase activity; reversed by DEN1 Lys556, Lys567 (mass spectrometry and mutagenesis) Addressed criteria* Reference s 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 1 1, 2, 4, 5 2 1, 2, 4, 5 3 EGFR Growth factor signal transduction Enhanced ubiquitylation and subsequent lysosomal degradation TP53 Transcription factor Inhibition of transcription activity, cytoplasmic localization TP73 Transcription factor Inhibition of transcription activity, cytoplasmic localization Not studied Not studied CBL (all three forms: c-cbl, CBLb and CBL-3) MDM2, MDMX and SCF Fbxo11 Stimulated by EGF Reversed by DEN1; inhibited by TIP60. NUB1 decreases TP53 neddylation Not studied MDM2 Reversed by DEN1. Only full length TP73 but not the N- terminally truncated isoform is neddylated Multiple lysines in tyrosine kinase domain Lys370, Lys372 and Lys373 1, 5 4 1, 2, 4, Not known 1, 2, 5 11
2 E2F (E2F-1, -2, -3, -4 and DP1) IKKγ (also known as NEMO) BCA3 (also known as AKIP1) Transcription factor, regulating the G1/S phase cell cycle transition Regulatory subunit of the IKK complex Regulator of NF-κB transcription Down- regulation of transcriptional activity; destabilization Inhibition of NF-κB signalling Inhibition of NF-κB transcription Mainly UBE2F MDM2 RING E3 ligase Stabilization Not studied MDM2 (autoneddylation) Not identified Reversed by DEN1; inhibited by TIP60 Reversed by DEN1. SET7/9-mediated methylation promotes neddylation Not studied TRIM40 Neddylation is higher in normal gastric epithelium than in gastric cancer tissue Not studied Not studied Reversed by DEN1; inhibited by ostrogen Not known 1, 5 5,12 Mainly Lys residues in the DNA-binding domain (Lys117, Lys120, Lys125, Lys182, Lys183 and Lys 185) 1, 3, 5 13,14 Not identified 1, 5 15 All 11 Lys residues 1, 2, 5 16 BRAP2 RING E3 regulating the Ras- MAPK pathway; associated with inflammatory dysfunction; suppressor of NF- κb signalling No effect for inhibition of NF-κB Not studied Not studied Not studied Lys HIF1α /HIF2α VHL HIF transcription factor component; survival signalling under hypoxia Substrate receptor of a CRL2 E3 ligase; regulating hypoxia signalling through degradation of HIF1α; positive regulator of fibronectin-mediated extracellular matrix assembly Stabilization in both normoxia and hypoxia Prevents CUL2 and fibronectin binding; might trigger the switch from CUL2 to fibronectin Not studied Not studied Not studied PAS-B domain (truncation) Not studied Not studied Not studied All three available Lys residues (Lys159, Lys171 and Lys196) with Lys159 as the major acceptor 1, 2, , 2 19,20
3 APP (amyloid precursor protein) intracellular domain (AICD) Component of a transcription factor Inhibition of transcription activity Not studied Not studied Not studied All 7 Lys residues (Lys612, Lys624, Lys , Lys676 and Lys688); Lys676 and Lys688 are sites in AICD 1 21 Parkin RING-in-between-RING E3 ligase; regulator of mitophagy; mutated in Parkinson s disease Increased E3 ligase activity PINK1 Protein kinase, activator of Parkin Stabilization of its 55 kda fragment Histone H4 Core nucleosome component; Polyneddylation recruits multiple post-translational RNF168 and facilitates modifications regulate repair chromatin state and DNA repair drice D. melanogaster homologue Inhibition of caspase of capsase 7; effector caspase activity in apoptosis signalling RPL11 Ribosomal protein Stabilization and nucleolar localization; non-neddylated form activates TP53 by binding to MDM2 RPS14 Ribosomal protein Stabilization and nucleolar localization; neddylated form activates TP53 by binding to MDM2 Not studied Not studied Reversed by DEN1 Multiple Lys residues, along the entire protein. Lys76 was detected by mass spectrometry from Parkinson s disease patients brain samples. 1, 2, 5 22,23 Not studied Not studied Reversed by DEN1 Not studied 1 22 UBC12 RNF111 Triggered by DNA damage Not studied Drosophila IAP1 Reversed by DEN1 N-terminal Lys residues All 9 surface exposed Lys residues Not studied MDM2 Reversed by DEN1 All 16 Lys residues 1, 2, 4, , 2, , 2, Not studied MDM2 Reversed by DEN1 Not studied 1, 2, 5 31
4 HuR RCAN1 mrna stabilization; cell dedifferentiation; proliferation Inhibitor of calcineurin signaling HuR stabilization; nuclear localization Enhanced stability; increased binding to calcineurin Not studied MDM2 Reversed by DEN1 Lys283, Lys313 and Lys326 Not studied Not studied Endogenous neddylation observed in mouse embryonic brain but not adult; reduced by oxidative stress Lys96, Lys104 and Lys170 1, , 2, 5 33 *The criteria for a genuine neddylation target are: 1, covalent attachment of NEDD8 through its C- terminal glycine to a Lys residue in the target protein; 2, detectable neddylation under homeostatic conditions and at endogenous levels of NEDD8 and substrate expression; 3, neddylation of the proposed target is sensitive to MLN4924 treatment under conditions that block cullin neddylation but not ubiquitylation, and NEDD8 is thus activated by NAE. Ideally, studies of a neddylation target should further define: 4, the specific NEDD8 E2 and E3 enzyme(s); 5, the regulation and biological consequences of neddylation. References 1. Bennett, E. J., Rush, J., Gygi, S. P. & Harper, J. W. Dynamics of cullin- RING ubiquitin ligase network revealed by systematic quantitative proteomics. Cell 143, (2010). 2. Xie, P. et al. The covalent modifier Nedd8 is critical for the activation of Smurf1 ubiquitin ligase in tumorigenesis. Nat Commun 5, 3733 (2014). 3. Zuo, W. et al. c- Cbl- mediated neddylation antagonizes ubiquitination and degradation of the TGF- β type II receptor. Mol Cell 49, (2013). 4. Oved, S. et al. Conjugation to Nedd8 instigates ubiquitylation and down- regulation of activated receptor tyrosine kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 281, (2006). 5. Xirodimas, D. P., Saville, M. K., Bourdon, J.- C., Hay, R. T. & Lane, D. P. Mdm2- mediated NEDD8 conjugation of p53 inhibits its transcriptional activity. Cell 118, (2004). 6. Dohmesen, C., Koeppel, M. & Dobbelstein, M. Specific inhibition of Mdm2- mediated neddylation by Tip60. Cell Cycle 7, (2008). 7. Singh, R. K., Iyappan, S. & Scheffner, M. Hetero- oligomerization with MdmX rescues the ubiquitin/nedd8 ligase activity of RING finger mutants of Mdm2. J. Biol. Chem. 282, (2007).
5 8. Abida, W. M., Nikolaev, A., Zhao, W., Zhang, W. & Gu, W. FBXO11 promotes the Neddylation of p53 and inhibits its transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 282, (2007). 9. Liu, G. & Xirodimas, D. P. NUB1 promotes cytoplasmic localization of p53 through cooperation of the NEDD8 and ubiquitin pathways. Oncogene 29, (2010). 10. Leidecker, O., Matic, I., Mahata, B., Pion, E. & Xirodimas, D. P. The ubiquitin E1 enzyme Ube1 mediates NEDD8 activation under diverse stress conditions. Cell Cycle 11, (2012). 11. Watson, I. R., Blanch, A., Lin, D. C. C., Ohh, M. & Irwin, M. S. Mdm2- mediated NEDD8 modification of TAp73 regulates its transactivation function. J. Biol. Chem. 281, (2006). 12. Watson, I. R. et al. Chemotherapy induces NEDP1- mediated destabilization of MDM2. Oncogene 29, (2010). 13. Loftus, S. J., Liu, G., Carr, S. M., Munro, S. & La Thangue, N. B. NEDDylation regulates E2F- 1- dependent transcription. EMBO Rep 13, (2012). 14. Aoki, I., Higuchi, M. & Gotoh, Y. NEDDylation controls the target specificity of E2F1 and apoptosis induction. Oncogene 32, (2013). 15. Noguchi, K. et al. TRIM40 promotes neddylation of IKKγ and is downregulated in gastrointestinal cancers. Carcinogenesis 32, (2011). 16. Gao, F., Cheng, J., Shi, T. & Yeh, E. T. H. Neddylation of a breast cancer- associated protein recruits a class III histone deacetylase that represses NFkappaB- dependent transcription. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, (2006). 17. Takashima, O. et al. Brap2 regulates temporal control of NF- κb localization mediated by inflammatory response. PLoS ONE 8, e58911 (2013). 18. Ryu, J.- H. et al. Hypoxia- inducible factor α subunit stabilization by NEDD8 conjugation is reactive oxygen species- dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 286, (2011). 19. Stickle, N. H. et al. pvhl modification by NEDD8 is required for fibronectin matrix assembly and suppression of tumor development. Mol Cell Biol 24, (2004). 20. Russell, R. C. & Ohh, M. NEDD8 acts as a molecular switch defining the functional selectivity of VHL. EMBO Rep 9, (2008). 21. Lee, M.- R., Lee, D., Shin, S. K., Kim, Y. H. & Choi, C. Y. Inhibition of APP intracellular domain (AICD) transcriptional activity via covalent conjugation with Nedd8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 366, (2008). 22. Choo, Y. S. et al. Regulation of parkin and PINK1 by neddylation. Hum. Mol. Genet. 21, (2012). 23. Um, J. W. et al. Neddylation positively regulates the ubiquitin E3 ligase activity of parkin. J. Neurosci. Res. 90, (2012).
6 24. Ma, T. et al. RNF111- dependent neddylation activates DNA damage- induced ubiquitination. Mol Cell 49, (2013). 25. Broemer, M. et al. Systematic in vivo RNAi analysis identifies IAPs as NEDD8- E3 ligases. Mol Cell 40, (2010). 26. Xirodimas, D. P. et al. Ribosomal proteins are targets for the NEDD8 pathway. EMBO Rep 9, (2008). 27. Ebina, M. et al. Myeloma Overexpressed 2 (Myeov2) Regulates L11 Subnuclear Localization through Nedd8 Modification. PLoS ONE 8, e65285 (2013). 28. Mahata, B., Sundqvist, A. & Xirodimas, D. P. Recruitment of RPL11 at promoter sites of p53- regulated genes upon nucleolar stress through NEDD8 and in an Mdm2- dependent manner. Oncogene 31, (2012). 29. Sun, X.- X., Wang, Y.- G., Xirodimas, D. P. & Dai, M.- S. Perturbation of 60 S ribosomal biogenesis results in ribosomal protein L5- and L11- dependent p53 activation. J. Biol. Chem. 285, (2010). 30. Sundqvist, A., Liu, G., Mirsaliotis, A. & Xirodimas, D. P. Regulation of nucleolar signalling to p53 through NEDDylation of L11. EMBO Rep 10, (2009). 31. Zhang, J., Bai, D., Ma, X., Guan, J. & Zheng, X. hcinap is a novel regulator of ribosomal protein- HDM2- p53 pathway by controlling NEDDylation of ribosomal protein S14. Oncogene 33, (2012). 32. Embade, N. et al. Murine double minute 2 regulates Hu antigen R stability in human liver and colon cancer through NEDDylation. Hepatology 55, (2012). 33. Noh, E. H. et al. Covalent NEDD8 conjugation increases RCAN1 protein stability and potentiates its inhibitory action on calcineurin. PLoS ONE 7, e48315 (2012).
Post-translational modifications of proteins in gene regulation under hypoxic conditions
 203 Review Article Post-translational modifications of proteins in gene regulation under hypoxic conditions 1, 2) Olga S. Safronova 1) Department of Cellular Physiological Chemistry, Tokyo Medical and
203 Review Article Post-translational modifications of proteins in gene regulation under hypoxic conditions 1, 2) Olga S. Safronova 1) Department of Cellular Physiological Chemistry, Tokyo Medical and
Protein methylation CH 3
 Protein methylation CH 3 methionine S-adenosylmethionine (SAM or adomet) Methyl group of the methionine is activated by the + charge of the adjacent sulfur atom. SAM S-adenosylhomocysteine homocysteine
Protein methylation CH 3 methionine S-adenosylmethionine (SAM or adomet) Methyl group of the methionine is activated by the + charge of the adjacent sulfur atom. SAM S-adenosylhomocysteine homocysteine
The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein
 THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2
 p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
Research Article Targeting the Neddylation Pathway to Suppress the Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells: Therapeutic Implication for the Men s Cancer
 BioMed Research International Volume 14, Article ID 97439, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/97439 Research Article Targeting the Neddylation Pathway to Suppress the Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells:
BioMed Research International Volume 14, Article ID 97439, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/14/97439 Research Article Targeting the Neddylation Pathway to Suppress the Growth of Prostate Cancer Cells:
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I. Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017
 Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Cell Cycle I Ron Bose, MD PhD November 14, 2017 CELL DIVISION CYCLE M G2 S G1 DISCOVERY AND NAMING OF CYCLINS A protein (called cyclin ) was observed to increase as cells
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
Chapter 18 Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development and is responsible for differences
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Degrading the Barriers to Drug Discovery in Ubiquitin E3 Ligase Pathways
 Degrading the Barriers to Drug Discovery in iquitin E3 Ligase Pathways Blaine N. Armbruster, PhD. Sr. Manager - Discovery & Development Solutions EMD Millipore 1 Oct, 2012 Outline Introduction ti to EMD
Degrading the Barriers to Drug Discovery in iquitin E3 Ligase Pathways Blaine N. Armbruster, PhD. Sr. Manager - Discovery & Development Solutions EMD Millipore 1 Oct, 2012 Outline Introduction ti to EMD
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression. Chromatin Array of nuc
 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: (chapter 13 pp276) Chromatin structure affects gene expression Chromatin Array of nuc 1 Transcriptional control in Eukaryotes: Chromatin undergoes structural changes
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
BIO360 Quiz #1. September 14, Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points)
 Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Name: BIO360 Quiz #1 September 14, 2012 1. Name five of the six Hallmarks of Cancer (not emerging hallmarks or enabling characteristics ): (5 points) 2. The controversial hypothesis that only a small subset
Apoptosis Oncogenes. Srbová Martina
 Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
Apoptosis Oncogenes Srbová Martina Cell Cycle Control point Cyclin B Cdk1 Cyclin D Cdk4 Cdk6 Cyclin A Cdk2 Cyclin E Cdk2 Cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) have to bind a cyclin to become active Regulation
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals?
 The Virtual Free Radical School NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals? Emily Ho, Ph.D Linus Pauling Institute Scientist Department of Nutrition and Food Management Oregon State University 117
The Virtual Free Radical School NFκB What is it and What s the deal with radicals? Emily Ho, Ph.D Linus Pauling Institute Scientist Department of Nutrition and Food Management Oregon State University 117
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Identification and characterization of genes responsive to apoptosis: Application of DNA chip technology and mrna differential display
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 1271-1 284 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and H istopat hology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Revie W Identification and characterization of genes
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 1271-1 284 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and H istopat hology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Revie W Identification and characterization of genes
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Alex Cioffi June 22 nd 2013
 Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Alex Cioffi June 22 nd 2013 Implications in Human Disease Adenovirus Early Region 1A (E1A) and Cancer α-synuclein and Parkinson s Disease Amyloid β and Alzheimer s Disease
Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Alex Cioffi June 22 nd 2013 Implications in Human Disease Adenovirus Early Region 1A (E1A) and Cancer α-synuclein and Parkinson s Disease Amyloid β and Alzheimer s Disease
Einführung in die Genetik
 Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Einführung in die Genetik Prof. Dr. Kay Schneitz (EBio Pflanzen) http://plantdev.bio.wzw.tum.de schneitz@wzw.tum.de Prof. Dr. Claus Schwechheimer (PlaSysBiol) http://wzw.tum.de/sysbiol claus.schwechheimer@wzw.tum.de
Study of different types of ubiquitination
 Study of different types of ubiquitination Rudi Beyaert (rudi.beyaert@irc.vib-ugent.be) VIB UGent Center for Inflammation Research Ghent, Belgium VIB Training Novel Proteomics Tools: Identifying PTMs October
Study of different types of ubiquitination Rudi Beyaert (rudi.beyaert@irc.vib-ugent.be) VIB UGent Center for Inflammation Research Ghent, Belgium VIB Training Novel Proteomics Tools: Identifying PTMs October
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler
 Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer
 Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
Chapt 15: Molecular Genetics of Cell Cycle and Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe the cell cycle: steps taken by a cell to duplicate itself = cell division; Interphase (G1, S and G2), Mitosis.
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Silver staining and immunoblotting of the purified TAK1 kinase complex. The TAK1 kinase complex was purified through tandem affinity methods (Protein A and FLAG), and aliquots of the purified
Figure S1. Silver staining and immunoblotting of the purified TAK1 kinase complex. The TAK1 kinase complex was purified through tandem affinity methods (Protein A and FLAG), and aliquots of the purified
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3073 LATS2 Binding ability to SIAH2 Degradation by SIAH2 1-160 161-402 403-480 -/ 481-666 1-666 - - 667-1088 -/ 1-0 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic drawing of LATS2 deletion mutants and
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3073 LATS2 Binding ability to SIAH2 Degradation by SIAH2 1-160 161-402 403-480 -/ 481-666 1-666 - - 667-1088 -/ 1-0 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic drawing of LATS2 deletion mutants and
Cell Cycle. Trends in Cell Biology
 Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
Cell Cycle Trends in Cell Biology Cell Cycle The orderly sequence of events by which a cell duplicates its contents and divides into two Daughter Cells Activities of a cell from one cell division to the
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function mutation.
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
 Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
Eukaryotic Gene Regulation Chapter 19: Control of Eukaryotic Genome The BIG Questions How are genes turned on & off in eukaryotes? How do cells with the same genes differentiate to perform completely different,
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2)
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Prof. R. V. Skibbens November 22, 2010 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality - clocks go in only one direction G1 doesn t have replication-inducing
Histones modifications and variants
 Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Histones modifications and variants Dr. Institute of Molecular Biology, Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz www.imb.de Lecture Objectives 1. Chromatin structure and function Chromatin and cell state Nucleosome
Emerging Role of the Ubiquitin-proteasome System as Drug Targets
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.org Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2013, 19, 000-000 1 Emerging Role of the Ubiquitin-proteasome System as Drug Targets Gozde Kar 1, Ozlem Keskin 1, Franca
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.org Current Pharmaceutical Design, 2013, 19, 000-000 1 Emerging Role of the Ubiquitin-proteasome System as Drug Targets Gozde Kar 1, Ozlem Keskin 1, Franca
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
The ubiquitin-proteasome system. in bone biology. University of Nottingham. ECTS PhD Training July 5 th Dr Rob Layfield
 The ubiquitin-proteasome system in bone biology Dr Rob Layfield University of Nottingham ECTS PhD Training July 5 th 2009 Images reproduced from: http://www.bostonbiochem.com/overview.php?prod=ubchains
The ubiquitin-proteasome system in bone biology Dr Rob Layfield University of Nottingham ECTS PhD Training July 5 th 2009 Images reproduced from: http://www.bostonbiochem.com/overview.php?prod=ubchains
UbcH (E2) Enzyme Kit. Catalog Number K-980B. This kit contains reagents for the qualitative analysis of UbcH Enzyme usage.
 UbcH (E2) Enzyme Kit Catalog Number K-980B This kit contains reagents for the qualitative analysis of UbcH Enzyme usage. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product. For
UbcH (E2) Enzyme Kit Catalog Number K-980B This kit contains reagents for the qualitative analysis of UbcH Enzyme usage. This package insert must be read in its entirety before using this product. For
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Complexity DNA. Genome RNA. Transcriptome. Protein. Proteome. Metabolites. Metabolome
 DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
Multistep nature of cancer development. Cancer genes
 Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Multistep nature of cancer development Phenotypic progression loss of control over cell growth/death (neoplasm) invasiveness (carcinoma) distal spread (metastatic tumor) Genetic progression multiple genetic
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem
 Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Removal of Shelterin Reveals the Telomere End-Protection Problem DSB Double-Strand Breaks causate da radiazioni stress ossidativo farmaci DSB e CROMATINA Higher-order chromatin packaging is a barrier to
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Tumor suppressor genes D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L
 Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Tumor suppressor genes 1 D R. S H O S S E I N I - A S L What is a Tumor Suppressor Gene? 2 A tumor suppressor gene is a type of cancer gene that is created by loss-of function mutations. In contrast to
Stochastic Simulation of P53, MDM2 Interaction
 Human Journals Research Article May 2017 Vol.:6, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by B.Odgerel et al. Stochastic Simulation of P53, MDM2 Interaction Keywords: DNA damage, P53, MDM2 interactions, propensity,
Human Journals Research Article May 2017 Vol.:6, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by B.Odgerel et al. Stochastic Simulation of P53, MDM2 Interaction Keywords: DNA damage, P53, MDM2 interactions, propensity,
A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect. suppressor gene products can release cells. hyperproliferation.
 Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
Tumor Suppressor Genes A class of genes that normally suppress cell proliferation. p53 and Rb..ect Mutations that inactivate the tumor suppressor gene products can release cells from growth suppression
HIV-1 genome organization
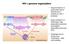 HIV-1 genome organization Gag encodes for a polyprotein that is cleaved into 4 proteins by HIV-1 protease. Gag is present in 2 transcripts: Gag polyprotein precursor and GagPol polyprotein precursor (5%).
HIV-1 genome organization Gag encodes for a polyprotein that is cleaved into 4 proteins by HIV-1 protease. Gag is present in 2 transcripts: Gag polyprotein precursor and GagPol polyprotein precursor (5%).
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES. Molecular Oncology Michael Lea
 TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES Molecular Oncology 2011 Michael Lea TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES - Lecture Outline 1. Summary of tumor suppressor genes 2. P53 3. Rb 4. BRCA1 and 2 5. APC and DCC 6. PTEN and PPA2 7. LKB1
TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES Molecular Oncology 2011 Michael Lea TUMOR-SUPPRESSOR GENES - Lecture Outline 1. Summary of tumor suppressor genes 2. P53 3. Rb 4. BRCA1 and 2 5. APC and DCC 6. PTEN and PPA2 7. LKB1
Alternative splicing. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6
 Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
Alternative splicing Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 6 Function(s) of RNA splicing Splicing of introns must be completed before nuclear RNAs can be exported to the cytoplasm. This led to early
oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes)
 Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Special topics in tumor biochemistry oncogenes-and- tumour-suppressor-genes) Speaker: Prof. Jiunn-Jye Chuu E-Mail: jjchuu@mail.stust.edu.tw Genetic Basis of Cancer Cancer-causing mutations Disease of aging
Review Article Regulation of T cell receptor complex-mediated signaling by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications
 Am J Clin Exp Immunol 2014;3(3):107-123 www.ajcei.us /ISSN:2164-7712/AJCEI0002062 Review Article Regulation of T cell receptor complex-mediated signaling by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications Samantha
Am J Clin Exp Immunol 2014;3(3):107-123 www.ajcei.us /ISSN:2164-7712/AJCEI0002062 Review Article Regulation of T cell receptor complex-mediated signaling by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like modifications Samantha
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Review. Ageing 2: Cancer! Review: Mutations. Mutations 2/14/11. The Raw Material for Evolution. The Double Edged Sword
 Ageing 2: Cancer! Review: The force of natural selection declines with ageing due to increase in extrinsic mortality (= weakening of natural selection) and reduction in reproduction with age (selection
Ageing 2: Cancer! Review: The force of natural selection declines with ageing due to increase in extrinsic mortality (= weakening of natural selection) and reduction in reproduction with age (selection
Introduction to Cancer Biology
 Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
Introduction to Cancer Biology Robin Hesketh Multiple choice questions (choose the one correct answer from the five choices) Which ONE of the following is a tumour suppressor? a. AKT b. APC c. BCL2 d.
The ubiquitin proteasome system in cardiovascular disease Basic mechanisms
 ECS Congress 2010 Stockholm, Sweden 28 Aug 2010 01 Sep 2010 The ubiquitin proteasome system in cardiovascular disease Basic mechanisms Saskia Schlossarek Department of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology
ECS Congress 2010 Stockholm, Sweden 28 Aug 2010 01 Sep 2010 The ubiquitin proteasome system in cardiovascular disease Basic mechanisms Saskia Schlossarek Department of Experimental and Clinical Pharmacology
(A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939 (5 µm)
 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Tankyrase inhibition suppresses cell proliferation in an axin/β-catenin independent manner. (A) SW480, DLD1, RKO and HCT116 cells were treated with DMSO or XAV939
PUBLICATIONS. cells. J. Physiol. (London) 517P:91P (Manchester, England, UK).
 277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1
 BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
BIO360 Fall 2013 Quiz 1 Name: Key 1. Examine the diagram below. There are two homologous copies of chromosome one and the allele of YFG carried on the light gray chromosome has undergone a loss-of-function
Effects of Second Messengers
 Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Effects of Second Messengers Inositol trisphosphate Diacylglycerol Opens Calcium Channels Binding to IP 3 -gated Channel Cooperative binding Activates Protein Kinase C is required Phosphorylation of many
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure
 Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure Frederick E. Domann, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology The University of Iowa Iowa City,
Biochemical Determinants Governing Redox Regulated Changes in Gene Expression and Chromatin Structure Frederick E. Domann, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Radiation Oncology The University of Iowa Iowa City,
REGULATION OF MDM2 MEDIATED NFκB2 PATHWAY IN HUMAN LUNG CANCER
 Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2008 REGULATION OF MDM2 MEDIATED NFκB2 PATHWAY IN HUMAN LUNG CANCER Lathika Mohanraj Virginia Commonwealth
Virginia Commonwealth University VCU Scholars Compass Theses and Dissertations Graduate School 2008 REGULATION OF MDM2 MEDIATED NFκB2 PATHWAY IN HUMAN LUNG CANCER Lathika Mohanraj Virginia Commonwealth
Supplementary Discussion 1: The mechanistic model of NIK1-mediated antiviral
 doi:10.1038/nature14171 SUPPLEMENTARY DISCUSSION Supplementary Discussion 1: The mechanistic model of NIK1-mediated antiviral signaling 1. Stress-induced oligomerization of the extracellular domain of
doi:10.1038/nature14171 SUPPLEMENTARY DISCUSSION Supplementary Discussion 1: The mechanistic model of NIK1-mediated antiviral signaling 1. Stress-induced oligomerization of the extracellular domain of
Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs
 Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs Not just quite interesting - really interesting! A cell must be able to degrade proteins when their activity is no longer required. Many eukaryotic proteins are
Cbl ubiquitin ligase: Lord of the RINGs Not just quite interesting - really interesting! A cell must be able to degrade proteins when their activity is no longer required. Many eukaryotic proteins are
Screening for E3-Ubiquitin ligase inhibitors: challenges and opportunities
 /, Vol. 5, No. 18 Screening for E3-Ubiquitin ligase inhibitors: challenges and opportunities Vivien Landré 1, Barak Rotblat 1, Sonia Melino 2, Francesca Bernassola 2 and Gerry Melino 1,2 1 Medical Research
/, Vol. 5, No. 18 Screening for E3-Ubiquitin ligase inhibitors: challenges and opportunities Vivien Landré 1, Barak Rotblat 1, Sonia Melino 2, Francesca Bernassola 2 and Gerry Melino 1,2 1 Medical Research
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
doi: /journal.pone
 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065285 Myeloma Overexpressed 2 (Myeov2) Regulates L11 Subnuclear Localization through Nedd8 Modification Manato Ebina., Fuminori Tsuruta*., Megumi C. Katoh, Yu Kigoshi, Akie
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065285 Myeloma Overexpressed 2 (Myeov2) Regulates L11 Subnuclear Localization through Nedd8 Modification Manato Ebina., Fuminori Tsuruta*., Megumi C. Katoh, Yu Kigoshi, Akie
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway
 Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway S1 Oleksi Petrenko and Ute M. Moll Figure S1. MIF-Deficient Cells Have Reduced Transforming Ability (A) Soft
Supplemental Data Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor MIF Interferes with the Rb-E2F Pathway S1 Oleksi Petrenko and Ute M. Moll Figure S1. MIF-Deficient Cells Have Reduced Transforming Ability (A) Soft
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment
 Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Overview: Conducting the Genetic Orchestra Prokaryotes and eukaryotes alter gene expression in response to their changing environment In multicellular eukaryotes, gene expression regulates development
Introduction. Cancer Biology. Tumor-suppressor genes. Proto-oncogenes. DNA stability genes. Mechanisms of carcinogenesis.
 Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
Cancer Biology Chapter 18 Eric J. Hall., Amato Giaccia, Radiobiology for the Radiologist Introduction Tissue homeostasis depends on the regulated cell division and self-elimination (programmed cell death)
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7)
 Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled
 Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Protein Targeting Objectives 1. to understand how proteins find their destination in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. to know how proteins are bio-recycled As a protein is being synthesized, decisions
Cellular functions of protein degradation
 Protein Degradation Cellular functions of protein degradation 1. Elimination of misfolded and damaged proteins: Environmental toxins, translation errors and genetic mutations can damage proteins. Misfolded
Protein Degradation Cellular functions of protein degradation 1. Elimination of misfolded and damaged proteins: Environmental toxins, translation errors and genetic mutations can damage proteins. Misfolded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature23267 Discussion Our findings reveal unique roles for the methylation states of histone H3K9 in RNAi-dependent and - independent heterochromatin formation. Clr4 is the sole S. pombe enzyme
doi:10.1038/nature23267 Discussion Our findings reveal unique roles for the methylation states of histone H3K9 in RNAi-dependent and - independent heterochromatin formation. Clr4 is the sole S. pombe enzyme
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Chapter 9. Cellular Signaling
 Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Ubiquitin modifications
 REVIEW Ubiquitin modifications Cell Research (2016) :1-24. www.nature.com/cr npg Kirby N Swatek 1, David Komander 1 1 Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge,
REVIEW Ubiquitin modifications Cell Research (2016) :1-24. www.nature.com/cr npg Kirby N Swatek 1, David Komander 1 1 Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Francis Crick Avenue, Cambridge,
ubiquitinylation succinylation butyrylation hydroxylation crotonylation
 Supplementary Information S1 (table) Overview of histone core-modifications histone, residue/modification H1 H2A methylation acetylation phosphorylation formylation oxidation crotonylation hydroxylation
Supplementary Information S1 (table) Overview of histone core-modifications histone, residue/modification H1 H2A methylation acetylation phosphorylation formylation oxidation crotonylation hydroxylation
VII SYNOPSIS. Cancer is a disease, causes due to failure of control of growth and. cell proliferation mechanisms. There are genetic control systems,
 VII SYPSIS Cancer is a disease, causes due to failure of control of growth and cell proliferation mechanisms. There are genetic control systems, regulate the balance between cell birth and death in response
VII SYPSIS Cancer is a disease, causes due to failure of control of growth and cell proliferation mechanisms. There are genetic control systems, regulate the balance between cell birth and death in response
Gene Expression DNA RNA. Protein. Metabolites, stress, environment
 Gene Expression DNA RNA Protein Metabolites, stress, environment 1 EPIGENETICS The study of alterations in gene function that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence. Epigenetic gene regulatory
Gene Expression DNA RNA Protein Metabolites, stress, environment 1 EPIGENETICS The study of alterations in gene function that cannot be explained by changes in DNA sequence. Epigenetic gene regulatory
Cancer Genetics. What is Cancer? Cancer Classification. Medical Genetics. Uncontrolled growth of cells. Not all tumors are cancerous
 Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Session8 Medical Genetics Cancer Genetics J avad Jamshidi F a s a U n i v e r s i t y o f M e d i c a l S c i e n c e s, N o v e m b e r 2 0 1 7 What is Cancer? Uncontrolled growth of cells Not all tumors
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Prof. R. V. Skibbens December 2, 2011 BIOS 10: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and Cancer (Part 2) Directionality The Cell Cycle clock goes in only one direction S-phase cells
Drug discovery in the ubiquitin proteasome system
 Drug discovery in the ubiquitin proteasome system Grzegorz Nalepa*, Mark Rolfe and J. Wade Harper* Abstract Regulated protein turnover via the ubiquitin proteasome system (UP) underlies a wide variety
Drug discovery in the ubiquitin proteasome system Grzegorz Nalepa*, Mark Rolfe and J. Wade Harper* Abstract Regulated protein turnover via the ubiquitin proteasome system (UP) underlies a wide variety
Prof. R. V. Skibbens
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Prof. R. V. Skibbens September 8, 2017 BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell growth and division What are the goals? I Cell Cycle what is this? response to
Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS. D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH
 E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
E6 2006-2007: 2007: Molecular Biology of Cancer DEREGULATION OF CELL CYCLE CONTROL IN ONCOGENESIS D. Kardassis Division of Basic Sciences University of Crete Medical School and IMBB-FORTH Literature *
The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 52: 1081-1094, 2018 The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review) Zhi-Jian Han 1, Yan-Hu Feng 1, Bao-Hong Gu 2, Yu-Min Li 2 and Hao Chen 2 1 Key
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 52: 1081-1094, 2018 The post-translational modification, SUMOylation, and cancer (Review) Zhi-Jian Han 1, Yan-Hu Feng 1, Bao-Hong Gu 2, Yu-Min Li 2 and Hao Chen 2 1 Key
Proteasomes. When Death Comes a Knock n. Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001
 Proteasomes When Death Comes a Knock n Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001 I. Introduction Introduction The central dogma Genetic information is used to make proteins. DNA RNA Proteins Proteins are the
Proteasomes When Death Comes a Knock n Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001 I. Introduction Introduction The central dogma Genetic information is used to make proteins. DNA RNA Proteins Proteins are the
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II. Prof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department
 Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Genetics of Cancer Lecture 32 Cancer II rof. Bevin Engelward, MIT Biological Engineering Department Why Cancer Matters New Cancer Cases in 1997 Cancer Deaths in 1997 Genetics of Cancer: Today: What types
Cancer. Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions.
 Cancer Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions. Should it divide? Yes No--> Should it differentiate? Yes No-->Should it die? Yes-->Apoptosis
Cancer Throughout the life of an individual, but particularly during development, every cell constantly faces decisions. Should it divide? Yes No--> Should it differentiate? Yes No-->Should it die? Yes-->Apoptosis
Epigenetics. Lyle Armstrong. UJ Taylor & Francis Group. f'ci Garland Science NEW YORK AND LONDON
 ... Epigenetics Lyle Armstrong f'ci Garland Science UJ Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO 3.2 CHROMATIN ARCHITECTURE 21 THE STUDY OF EPIGENETICS 1.1 THE CORE
... Epigenetics Lyle Armstrong f'ci Garland Science UJ Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO 3.2 CHROMATIN ARCHITECTURE 21 THE STUDY OF EPIGENETICS 1.1 THE CORE
