The Beauty of the Skin
|
|
|
- Cori Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Beauty of the Skin Rose-Anne Romano, Ph.D Assistant Professor Department of Oral Biology School of Dental Medicine State University of New York at Buffalo
2 The Big Question How do approximately 50 trillion cells, each one with the SAME genetic information, co-ordinate to make all the different tissues of the human body
3 Identifying the cues necessary for proper skin development
4 Dermis Epidermis Skin Functions: -Regulation of body temperature -Prevents dehydration -Protects from toxic substances & radiation -Protects against mechanical stress and trauma -Immunological functions -Sensory organ
5 Skin Epidermis Cornified layer Granular layer Loricrin Spinous layer K1/K10 Self-renewing Keratinocytes- major cell type Other cell types: Melanocytes, Langerhans cells Basal layer K5/K14
6 Skin Epidermis Cornified layer Granular layer Loricrin Spinous layer K1/K10 Basal layer K5/K14 Pilosebaceous Unit Hair follicle Sebaceous Gland
7 Epithelial Specification Commitment to Stratification Commitment to Differentiation Commitment to Terminal Differentiation Embryonic Skin Development Ectodermal Progenitor Cells E7.5 B Sp B K8/18 E9.5 K5/14 E13.5 K1/10 E17 Loricrin Gr Sp B K8 K5 K5/K10 K5/Lor
8 Stages of Hair Follicle Development E13.5 E14.5 E16.5 Epidermis Dermis Dermal signals initiate hair follicle formation Epidermal signals organize the mesenchyme Dermal signals coordinate growth and differentiation
9 Hair Follicle Cycling Anagen Catagen Telogen Return to Anagen
10 How Does the Skin Self-renew? Stratum Corneum Granular Layer Terminally Differentiated Keratinocyte Basement Membrane Spinous Layer Basal Layer TA cell TA Cells -Daughter stem cells that divide for a limited number of times and then undergo terminal differentiation SCs Location: Basal Layer -Express Keratin5 and Keratin14 Stem cell Proliferative Potential Stem Cells (SCs) -potential to develop into many different cell types in the body -can divide an unlimited number of times -each new cell has the potential to either remain a stem cell or to become a Transit Amplifying (TA) Cell
11 Epithelial Specification Commitment to an epithelial lineage Early Stages of Epithelial Development Mammary Gland Ectodermal Progenitor Cells Skin K8/18 K8 Bladder Ureter
12 Epithelial Specification Commitment to an epithelial lineage Early Stages of Epithelial Development Ectodermal Progenitor Cells E7.5 K8/18 B K5/14 K8 K5
13 Dermis Epidermis p63 is expressed in the proliferating cells of the epidermis and hair follicle p63/dapi Romano et al. Development 2010
14 Transcription factor p63 Belongs to the p53 family of proteins Mutations of p63 associated with several human developmental syndromes: EEC Syndrome (Ectrodactyly, Ectodermal Dysplasia, and cleft lip/palate) AEC Syndrome (Ankyloblepharon, ectodermal defects-cleft lip/palate)
15 The different roles of each p53 family member Growth arrest Apoptosis Morphogenesis, Epithelial development/ differentiation Neurogenesis, Neuronal development/ differentiation
16 p63 P1 (TA) P2( N) p63 genomic locus TAp63 Isoforms DNA Binding Oligo SAM TID DNA Binding Oligo SAM TID Np63 Isoforms
17 Loss of p63: We Have a Major Problem TAp63 ΔNp63 TA DNA binding Oligo DNA binding Oligo p63 +/- p63 -/- p63 +/- p63 -/- Yang et al. Nature 1999 Mills et al. Nature 1999
18 Epidermal Specification Commitment to Stratification Biological Function of p63 +/+ -/- McKeon Lab Roop Lab +/+ +/+ +/+ -/- -/- -/- E17 Lor E17 Lor Self Renewal Terminal Differentiation Ectodermal Progenitor Cells Stem Cell Yang et al. Nature (1999). Mills et al. Nature (1999). K8/K18 K5/K14
19 Loss of p63: We Have a Major Problem TAp63 ΔNp63 TA DNA binding Oligo DNA binding Oligo p63 +/- p63 -/- Which Isoform is Important? p63 +/- p63 -/-
20 Roles for TAp63 TAp63 TA DBD OLIGO SAM In Vitro K14/p63 TAp63 Np63 TAp63 Np63 Ptk2 Cells Roop et al. Genes Dev. 2004
21 Which p63 Isoform Is Critical In the Skin? H&E Np63 p63 K5 K14 TAp63 E10.5 E11.5 E14.5 E18.5 Romano et al. PLoS One 2009
22 Both TAp63 and Np63 Induce K14 Expression DAPI HA K14 MERGE DNA binding domain Oligo SAM HA-TAp63 DNA binding domain Oligo SAM HA- Np63 DNA binding domain Oligo HA- Np63 DNA binding domain Oligo HA- Np63 (R249W) DNA binding domain Oligo SAM HA- Np63MT Romano, R.A. et al. JID (2007) Ptk2 Cells
23 Epithelial Specification Commitment to an epithelial lineage Early Stages of Epithelial Development Ectodermal Progenitor Cells E7.5 K8/18 B K5/14 K8 K5
24 Tet-inducible Expression of Np63 in Transgenic Mice Keratin 5 Promoter tta TRE HA Np63 Tet driver Tet responder K5 Bitransgenic Mouse + Dox - Dox TRE HA Np63 TRE HA Np63
25 Phenotype of Np63 Expressing Mice BG (P30)
26 Phenotype of Np63 Expressing Mice Epidermal Hyperplasia Hypertrophic Hair Follicles
27 Follicular Transformation K14/K10/DAPI Hair Shaft Epidermis Sebaceous Gland Bulge ORS- K14 +,K10 - IRS Matrix Derma Papilla WT BG (P28) Romano, et al. Development, 2010
28 Follicular Transformation K14/Fil/DAPI Hair Shaft Epidermis Sebaceous Gland Bulge ORS- K14 +, Fil - IRS Matrix Derma Papilla WT BG (P28) Romano, et al. Development, 2010
29 Expression of Np63 in Lung Epithelium Np63 Bronchi p63 (null) K5 (null) K14 (null) Human SPC Promoter tta TRE HA Np63 Tet driver Tet responder Bitransgenic Mouse (BG)
30 Expression of Np63 in Lung Epithelium Human SPC Promoter tta TRE HA Np63 Tet driver Tet responder Bitransgenic Mouse (BG) WT BG
31 Np63 Can Direct Cell Lineage Commitment and Induce Stratification SPC Promoter tta TRE HA Np63 Bronchi Np63 WT Np63 (BG) WT Np63 (BG) DAPI DAPI K1/HA K1/HA Np63 (BG) Np63 (BG) WT Np63 (BG) K5/HA K14/HA K10/HA K10/HA
32 p63 and Epithelial Cell Fate Ectodermal Progenitor Cells Epithelial Specification Commitment to Stratification K8/18 K5/14 E7.5 E9.5 Np63 Np63 regulates basal keratinocyte-specific gene expression Np63 Bronchi Np63 directs epithelial cell fate K5/HA K14/HA How Can We Confirm This?
33 Np63GFP Knock-in mice: P1 Isoform Specific Knockout P2 p63 genomic locus P1 (TAp63) P2 ( Np63) P1 (TAp63) P2 ( Np63) p63 gene egfp Np63GFP
34 P1 Validation P2 p63 genomic locus Np63 TAp63 GAPDH /+ +/- -/- Np63GFP +/- Np63GFP -/- Np63/K5/DAPI Np63/K5/DAPI Np63eGFP +/- (E14.5) Day 4
35 Loss of Np63: Major Problems Np63 +/+ Np63 gfp/gfp Np63 +/+ (E18.5) Np63 gfp/gfp (E18.5) E18.5 Romano, et al. Development, 2012
36 Np63 Knockout Mice Np63GFP +/- Np63GFP -/- Np63GFP +/+ Np63GFP -/- Tongue Palate E18.5 E18.5 Buccal Mucosa
37 Keratinocytes lacking Np63: Should I Commit? Epithelial Specification Commitment to Stratification Np63 E7.5 K8/18 E9.5 K5/14 Romano, et al. Development, 2012
38 Loss of Np63 Results in Premature Keratinocyte Differentiation Np63 +/+ Np63 gfp/gfp Np63 +/+ Np63 gfp/gfp E15.5 K5/DAPI K5/DAPI K1/DAPI K1/DAPI K10/DAPI K10/DAPI Lor/DAPI Lor/DAPI Fil/DAPI Fil/DAPI Romano, et al. Development, 2012
39 Compromised Basement Membrane BASAL CELL Np63 +/+ Np63 gfp/gfp DERMIS Romano, et al. Development, 2012
40 Compromised Integrin Expression Np63 +/+ Np63 gfp/gfp BASAL CELL 6/K5/DAPI 6/K5/DAPI 4/K5/DAPI 4/K5/DAPI DERMIS 1/K5/DAPI 1/K5/DAPI Romano, et al. Development, 2012
41 Compromised Cell Adhesion Np63 +/+ Np63 gfp/gfp Dsg1/K5/DAPI Dsg1/K5/DAPI Dsg2/K5/DAPI Dsg2/K5/DAPI Pkp2/K5/DAPI Pkp2/K5/DAPI
42 Loss of Np63: Major Issues K8/18 K5/14 Block in Squamous Switch Altered Differentiation Cell-Cell & Cell-Basement Membrane Contacts
43 Knockout Mice Mice in which researchers have disrupted or knocked out an existing gene by replacing it with a foreign piece of DNA. The loss of the gene often causes a phenotypic change in the mouse which includes appearance or behaviour
44 How are Knockout Mice Made? Pick your favourite gene What genomic region to target? LoxP sites Design a targeting vector Must have 5 and 3 homologous (identical) sequences and selection marker (Neo) Targeting vector is electroporated into Embryonic Stem (ES) cells Can select for positive clones that are Neo resistant Positive ES cells are then injected into a blastocyst and transferred into a pseudopregnant foster mouse to generate chimera mice Breed mice with Cre Recombinase mice DNA between LoxP sites is removed in cells expressing Cre, generating KO mice
45
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS
 Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
Lab 7: Integumentary System Hamilton ANSWERS TO PRE- LAB ASSIGNMENTS Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. epidermis b. dermis c. hypodermis d. adipose tissue e. hair f. sebaceous gland g. sweat gland 2. a Pre-Lab
This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur.
 Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Background Knowledge Functions of normal skin Background Knowledge This section covers the basic knowledge of normal skin structure and function required to help understand how skin diseases occur. Learning
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9
 Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
Skin (Integumentary System) Wheater, Chap. 9 Skin (Integument) Consists of skin and associated derivatives Largest organ of body (21 ft 2 ; 9 lbs.; has 11 miles of blood vessels) Functions: Protection
ANAT3231: lectures overview
 ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
ANAT3231: lectures overview Stem Cell Biology Stem Cell Technology Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/cell biology/ Essential Cell Biology 3 rd edition Alberts Dr Annemiek Beverdam School of Medical
Development of the skin and its derivatives
 Development of the skin and its derivatives Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School
Development of the skin and its derivatives Resources: http://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ Larsen s Human Embryology The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology Dr Annemiek Beverdam School
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System. Integumentary System. Page 1
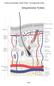 Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Anatomy and Physiology I Student Outline The Integumentary System Integumentary System Page 1 Have a very clear understanding of the each particular tissue and their unique functions in each layer of the
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) i. Organ of the Integument. Connective Tissues. Epithelial Tissues
 Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Integumentary System 1. Introduction (Open your text to the image of a cross section of skin) A. Integumentary System i. Organ of the Integument a. Tissues Connective Tissues * Tissue / Location Relationships
Stem Cells. Induced Stem Cells
 Induced Stem Cells Stem Cells Mouse and human somatic cells can either be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state or converted to another lineage with a combination of transcription factors suggesting that
Induced Stem Cells Stem Cells Mouse and human somatic cells can either be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state or converted to another lineage with a combination of transcription factors suggesting that
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Plikus et al. 10.1073/pnas.1215935110 SI Text Movies S1, S2, S3, and S4 are time-lapse recordings from individually cultured Period2 Luc vibrissa follicles show that circadian cycles
Supporting Information Plikus et al. 10.1073/pnas.1215935110 SI Text Movies S1, S2, S3, and S4 are time-lapse recordings from individually cultured Period2 Luc vibrissa follicles show that circadian cycles
B. Incorrect! The ectoderm does not produce the dermis. C. Incorrect! The dermis is derived from the mesoderm.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 04: The Integumentary System Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper as 1. From the inner cell
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY. Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations
 DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
DEBRIDEMENT: ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Professor Donald G. MacLellan Executive Director Health Education & Management Innovations ANATOMY and PHYSIOLOGY Epidermal Layers ECM Structure Dermis Structure Skin
Cytological and Histological Study of Adult and Neonate Epidermis in Thick and Thin Skin of Various Anatomical Sites
 Available online on www.ijpqa.com International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance 218; 9(2); 174-179 doi: 1.25258/ijpqa.v9i2.13642 ISSN 975 956 Research Article Cytological and Histological Study
Available online on www.ijpqa.com International Journal of Pharmaceutical Quality Assurance 218; 9(2); 174-179 doi: 1.25258/ijpqa.v9i2.13642 ISSN 975 956 Research Article Cytological and Histological Study
Integumentary System. Integumentary System
 1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
1. General aspects a. The integumentary system consists of several organs major organ of the system is the skin other organs are relatively small and they can be considered as specialized structures of
Integument. Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Melanoma. Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors
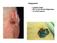 Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
Squamous Cell Carcinoma Integument Largest organ 30% of all clinical diagnoses 1/3 of all tumors Melanoma Epidermis Stratified, squamous keratinized epithelium Derived from ectoderm Appendages hair follicles
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY
 CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
CHAPTER 5 INTEGUMENTARY skin under the skin other stuff cutaneous layer hypodermis (subcutaneous) accessory structures Cutaneous layer = skin epithelial layers = connective tissue layer = dermis Subcutaneous
Chapter 5: Integumentary System
 Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
Chapter 5: Integumentary System I. Overview of the Integumentary System A. List the five major functions of the integumentary system: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Il. Skin A. Epidermis 1. The epidermis consists of 2.
The Integumentary System: An Overview
 The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System: An Overview Functions: Protective covering Helps regulate body temperature Retards water loss from deeper tissues Houses sensory receptors Synthesizes biochemicals Excretes small
The Integumentary System : Embryology & Genetic Bases. Purnomo Soeharso Department of Medical Biology FMUI
 The Integumentary System : Embryology & Genetic Bases Purnomo Soeharso Department of Medical Biology FMUI Tissue organization of the skin (integumentum) : - Epidermis stratified epithelium on the outer
The Integumentary System : Embryology & Genetic Bases Purnomo Soeharso Department of Medical Biology FMUI Tissue organization of the skin (integumentum) : - Epidermis stratified epithelium on the outer
Multipotency, Differentiation and Malfunction of Epidermal Stem Cells
 Cover Multipotency, Differentiation and Malfunction of Epidermal Stem Cells Francisca Peixoto 1 Acknowledgments I would like to thank Salvador Aznar-Benitah for his outstanding supervision. Writing this
Cover Multipotency, Differentiation and Malfunction of Epidermal Stem Cells Francisca Peixoto 1 Acknowledgments I would like to thank Salvador Aznar-Benitah for his outstanding supervision. Writing this
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System
 Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Anatomy Ch 6: Integumentary System Introduction: A. Organs are body structures composed of two or more different tissues. B. The skin and its accessory organs make up the integumentary system. Types of
Chapter 4 Opener Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
Chapter 4 Opener Introduction The integumentary system is composed of: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands Mammary glands The skin is the most visible organ of the body Clinicians can tell a lot about
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis PHL 212 1 Function
Skin. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
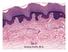 Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Skin Kristine Krafts, M.D. Skin Lecture Objectives Describe the functions of skin. Describe the structure, location and function of the cell types found in epidermis: keratinocytes, melanocytes, Langerhans
Introduction. Skin and Body Membranes. Cutaneous Membranes Skin 9/14/2017. Classification of Body Membranes. Classification of Body Membranes
 Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Introduction Skin and Body Membranes Body membranes Cover surfaces Line body cavities Form protective and lubricating sheets around organs Classified in 5 categories Epithelial membranes 3 types- cutaneous,
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System. Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system
 Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Integumentary System (Script) Slide 1: Integumentary System Slide 2: An overview of the integumentary system Skin is the body s largest and heaviest organ making up 15% of body weight. Most skin is 1 to
Skin. Lecture #14. Ref:
 Skin Lecture #14 Ref: http://www.ccunix.ccu.edu.tw/~chenmsl/tea/skin_910721.htm Structure of Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutis 4. Hair follicle 5. Sebaceous gland 6. Sweat gland Skin Largest human
Skin Lecture #14 Ref: http://www.ccunix.ccu.edu.tw/~chenmsl/tea/skin_910721.htm Structure of Skin 1. Epidermis 2. Dermis 3. Subcutis 4. Hair follicle 5. Sebaceous gland 6. Sweat gland Skin Largest human
Unit 4 The Integumentary System
 Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Unit 4 The Integumentary System I. Classification of Body Membranes A. Epithelial Membranes (3) 1. Cutaneous Membrane > Stratified Squamous > Sits on Dense Connective Tissue > Skin: Epidermis & Dermis
Integumentary System
 Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Integumentary System Overview Functions 1. Protection 2. Excretion of wastes 3. Maintenance of T b 4. Synthesis of vitamin D 3 5. Storage of lipids 6. Detection of sensory stimuli Epidermis Tissue types
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 5 The Integumentary System Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails,
Ch 5: Integumentary System
 Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Ch 5: Integumentary System You gotta have skin; All you really need is skin. Skin's the thing, that if you've got it outside, It helps keep your insides in. Alan Sherman (1924-1973) Developed by John Gallagher,
Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 3
 Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 3 Please note that this study guide is a listing of objectives that you are required to master for this course. However, items mentioned in class or in laboratory as
Study Guide for Bio 101 Lecture Exam 3 Please note that this study guide is a listing of objectives that you are required to master for this course. However, items mentioned in class or in laboratory as
Figure 6.1 Transparency Master 37
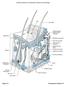 Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Pore Hair shaft Epidermis Dermal papillae (papillary layer of dermis) Meissner s corpuscle Dermis Free nerve ending Reticular layer of dermis Sebaceous (oil) gland Arrector pili muscle Sensory nerve fiber
Histology of Skin. dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008
 Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008 1 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16%
Histology of Skin dr. Alya Amila Fitrie, M.Kes dr. Radita Nur Anggraeni Department of Histology Medical Faculty University of North Sumatera 2008 1 INTRODUCTION The heaviest single organ of the body, 16%
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 6
Histology of Integumentary System
 Histology of Integumentary System CONTENT / Topics Integumentary System Skin, thick - Major Layers Epidermis Dermis Hair Skin, hairy and Hair Follicle Sebaceous Glands Sebaceous Gland Sweat Glands Merocrine
Histology of Integumentary System CONTENT / Topics Integumentary System Skin, thick - Major Layers Epidermis Dermis Hair Skin, hairy and Hair Follicle Sebaceous Glands Sebaceous Gland Sweat Glands Merocrine
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
Levels of Organization Oklahoma Laws Violators can be fined, arrested or jailed for making ugly faces at a dog. Females are forbidden from doing their own hair without being licensed by the state. Dogs
ABCD rule. apocrine glands. arrector pili. ceruminous glands. contact dermatitis
 ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
ABCD rule assessing moles: asymmetric, broder irregularity, color, diameter (larger than 6mm) apocrine glands arrector pili sweat glands in the pubic and underarm areas that secrete thicker sweat, that
Multiple Roles of Notch Signaling in the Regulation of Epidermal Development
 Article Multiple Roles of Notch Signaling in the Regulation of Epidermal Development Mariko Moriyama, 1 André-Dante Durham, 2 Hiroyuki Moriyama, 1 Kiyotaka Hasegawa, 1 Shin-Ichi Nishikawa, 3 Freddy Radtke,
Article Multiple Roles of Notch Signaling in the Regulation of Epidermal Development Mariko Moriyama, 1 André-Dante Durham, 2 Hiroyuki Moriyama, 1 Kiyotaka Hasegawa, 1 Shin-Ichi Nishikawa, 3 Freddy Radtke,
Basal cell carcinomas in mice arise from hair follicle stem cells and multiple epithelial progenitor populations
 Research article Basal cell carcinomas in mice arise from hair follicle stem cells and multiple epithelial progenitor populations Marina Grachtchouk, 1 Joanna Pero, 1 Steven H. Yang, 1,2 Alexandre N. Ermilov,
Research article Basal cell carcinomas in mice arise from hair follicle stem cells and multiple epithelial progenitor populations Marina Grachtchouk, 1 Joanna Pero, 1 Steven H. Yang, 1,2 Alexandre N. Ermilov,
4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide
 Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Name: SKIN AND BODY MEMBRANES: 4 Skin and Body Membranes Study Guide Period: Body membranes, which cover body surfaces, line its cavities, and form protective sheets around organs, fall into two major
Ex. 7: Integumentary
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2401 Ex. 7: Integumentary. Skin or Integument Consists of three major regions Epidermis outermost superficial region Dermis middle region Hypodermis (superficial fascia)
Review Article Delineating Molecular Mechanisms of Squamous Tissue Homeostasis and Neoplasia: Focus on p63
 Journal of Skin Cancer Volume 2013, Article ID 632028, 14 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/632028 Review Article Delineating Molecular Mechanisms of Squamous Tissue Homeostasis and Neoplasia: Focus
Journal of Skin Cancer Volume 2013, Article ID 632028, 14 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/632028 Review Article Delineating Molecular Mechanisms of Squamous Tissue Homeostasis and Neoplasia: Focus
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 5 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Haematopoietic stem cells
 Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System. Skin Cells. Layers of Skin. Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer beneath dermis not part of skin
 Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Chapter 6 Skin and the Integumentary System Composed of several tissues Maintains homeostasis Protective covering Retards water loss Regulates body temperature Houses sensory receptors Contains immune
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 4
 *We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
*We are revisiting Ch 3B on body tissues (Connective) prior to our study of Ch 4 Integumentary. Start on p.90 I. Connective Tissue A. Functions of Connective 1. Protection 2. Support 3. Binding Together
Keratinocyte Stem Cells, Label-Retaining Cells and Possible Genome Protection Mechanisms
 Keratinocyte Stem Cells, Label-Retaining Cells and Possible Genome Protection Mechanisms Christopher S. Potten EpiStem Ltd., Incubator Building, Manchester, UK Stem cells are the crucial cells upon which
Keratinocyte Stem Cells, Label-Retaining Cells and Possible Genome Protection Mechanisms Christopher S. Potten EpiStem Ltd., Incubator Building, Manchester, UK Stem cells are the crucial cells upon which
Integumentary System. 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1
 Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
Integumentary System 2/20/02 S. Davenport 1 Functions of Skin Protection Temperature regulation Sensation Excretion Vitamin D production 2/20/02 S. Davenport 2 Protection A Barrier Three types of barriers:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
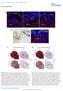 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2535 Figure S1 SOX10 is expressed in human giant congenital nevi and its expression in human melanoma samples suggests that SOX10 functions in a MITF-independent manner. a, b, Representative
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2535 Figure S1 SOX10 is expressed in human giant congenital nevi and its expression in human melanoma samples suggests that SOX10 functions in a MITF-independent manner. a, b, Representative
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6
 AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
AP I f2014 E3 c_5 & 6 Student: Multiple choice questions choose the best answer. True/false answer A for true and B for false 1. The layer within the epidermis that acts as the foundation providing new
Overview of the Integumentary System. Lab #7. Layers of the epidermis are known as strata. Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the Epidermis
 Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Overview of the Integumentary System Lab #7 Integumentary System Organization of the Epidermis: Layers of the epidermis are known as strata Figure 5 2 Layers of the Epidermis Top: Free surface of skin
Ch 4. Skin and Body Membranes
 Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
Ch 4 Skin and Body Membranes TITLE HISTOLOGY SLIDES & NOTES ESSENTIAL QUESTION What tissues compose the integumentary system? Stratified Squamous Epithelium Stratified = several layers; Squamous = shape
11/8/2012. Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Skin = Integument = Cutaneous Membrane. The Structure of Skin. Epidermis
 Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
Chapter 6 Part 1 Objectives: Define organ, and associate the skin as an organ of the integumentary system. List the general functions of the skin. Describe the structure of the layers of the skin. Summarize
TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0325 TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Valerie Boka CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Health Science
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0325 TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Valerie Boka CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Health Science
The Cardiovascular System (Part II)
 The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 1 Aortic arch derivatives Aortic arches 2 Pharyngeal and aortic arches 4 th week 3 (1st, 2nd pairs disappeared) 6 th week (37 days) 4 8th week: transformed into the
The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 1 Aortic arch derivatives Aortic arches 2 Pharyngeal and aortic arches 4 th week 3 (1st, 2nd pairs disappeared) 6 th week (37 days) 4 8th week: transformed into the
Epidermis. Integumentary system
 Epidermis the doctor mentioned at the begging of the lecture that the slides is from different sources and has information and details that is enough for us so we don t have to go back and read from the
Epidermis the doctor mentioned at the begging of the lecture that the slides is from different sources and has information and details that is enough for us so we don t have to go back and read from the
Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel,
 Name: Period: Date: Adapted from: Akkaraju, Liachovitzky Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel, 2010-11 Objectives Checklist. After completion of this packet you should be able to: list the general
Name: Period: Date: Adapted from: Akkaraju, Liachovitzky Integumentary System Practice & McDaniel, 2010-11 Objectives Checklist. After completion of this packet you should be able to: list the general
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument. Mikrogeo. com
 SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
SKIN HISTOLOGY the microscopic anatomy of the Integument Mikrogeo. com Hair follicles, sweat glands, sebaceous glands (even teeth) are products of the epidermis,embryologically speaking ectododerm, that
A classification of epithelial tissues
 A classification of epithelial tissues Ramray Bhat Molecular Reproduction Development and Genetics ramray@iisc.ac.in Textbooks for my portion Molecular Biology of the Cell (Bruce Alberts) 6 th Edition
A classification of epithelial tissues Ramray Bhat Molecular Reproduction Development and Genetics ramray@iisc.ac.in Textbooks for my portion Molecular Biology of the Cell (Bruce Alberts) 6 th Edition
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep to it Two distinct regions Epidermis Dermis
The Integumentary System
 The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
The Integumentary System The Integumentary System Integument is skin Skin and its appendages make up the integumentary system (See if you can name some appendages) A fatty layer (hypodermis) lies deep
All the Rest. What is All the Rest? Integumentary System. First are the FUNCTI0NS. THERMOREGULATION function. PROTECTION function 10/12/16
 What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
What is All the Rest? Integumentary System All the Rest Integumentary System Homeostatic Imbalances Skin Cancer Burns First are the FUNCTI0NS Chemical, Physical/Mechanical, Biological Thermoregulation
****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ****************************************************************************************************** INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM ******************************************************************************************************
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS
 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM PART I: FUNCTIONS & EPIDERMIS Integumentary System Cutaneous membrane Epidermis (5-layers) made up of epithelial tissue only Dermis (2-layers) contains connective tissue, vessels,
Index. derm.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adhesion and migration, the diverse functions of the laminin a3 subunit, 79 87 Alopecia in epidermolysis bullosa, 165 169 Amblyopia and inherited
Integumentary System. Remember: Types of Membranes: Bio 250
 Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
Integumentary System Bio 250 Remember: Tissue: Group of cells that are similar in appearance and perform similar function Organ: Two or more tissues grouped together and performing a specialized function
...if the bulge does not support interfollicular epidermis, how is this compartment maintained?
 Perspectives S t e m c e l l s o p i n i o n Epidermal homeostasis: do committed progenitors work while stem cells sleep? Philip Jones and Benjamin D. Simons Abstract Tracking the fate of cells in murine
Perspectives S t e m c e l l s o p i n i o n Epidermal homeostasis: do committed progenitors work while stem cells sleep? Philip Jones and Benjamin D. Simons Abstract Tracking the fate of cells in murine
Epithelial stem cells in the skin: definition, markers, localization and functions
 Exp Dermatol 1999: 8: 80 88 Copyright C Munksgaard 1999 Printed in Denmark All rights reserved Controversies in Experimental Dermatology Section Editor: Ralf Paus, Berlin ISSN 0906-6705 Epithelial stem
Exp Dermatol 1999: 8: 80 88 Copyright C Munksgaard 1999 Printed in Denmark All rights reserved Controversies in Experimental Dermatology Section Editor: Ralf Paus, Berlin ISSN 0906-6705 Epithelial stem
Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Chapter 5 The Integumentary System Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Introduction The organs of the integumentary system include the skin and its accessory structures including hair, nails, and
Skin and Body Membranes
 4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
4 Skin and Body Membranes PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Skin and Body Membranes
Loss of RhoA promotes skin tumor formation. Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization. a. Representative IF images of F-actin staining of big and small control (left) and RhoA ko tumors
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of RhoA does not impair F-actin organization. a. Representative IF images of F-actin staining of big and small control (left) and RhoA ko tumors
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT
 ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
ACTIVITY 2: HISTOLOGY AND INTEGUMENT Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 4 and 5, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify each tissue (26 tissues)
SKIN. 3. How is the skin structured around the finger joints to allow for flexible movement of the fingers?
 SKIN Objectives for Exam #1: 1. List various skin structures and describe their functions. 2. Describe skin responses to increases and decreases in body temperature. 3. Provide examples of various skin
SKIN Objectives for Exam #1: 1. List various skin structures and describe their functions. 2. Describe skin responses to increases and decreases in body temperature. 3. Provide examples of various skin
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Figure S1: Follicular melanocytes in the wound peripheral area migrate to the epidermis in response to wounding stimuli. Dorsal skin of Trp2-LacZ mice stained with X-gal and analyzed
Supplementary Information Figure S1: Follicular melanocytes in the wound peripheral area migrate to the epidermis in response to wounding stimuli. Dorsal skin of Trp2-LacZ mice stained with X-gal and analyzed
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis
 Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Chapter 5: The Integumentary System - Introduction and Epidermis The Integument Means Covering Composed: Skin Hair Nails Sweat glands Oil glands The Integument Thickness 1.5 4 mm (or more) Weight 9 11
Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful.
 SKIN SCIENCE Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful. Dr. Des Fernandes Copyright 2016 Environ Skin Care (Pty)
SKIN SCIENCE Skin is a complex organ, but by understanding its structure and function it becomes easier to create skin that is Reborn Beautiful. Dr. Des Fernandes Copyright 2016 Environ Skin Care (Pty)
Transcription factor p63 bookmarks and regulates dynamic enhancers during epidermal differentiation
 Published online: June 1, 15 Article Transcription factor p63 bookmarks and regulates dynamic enhancers during epidermal differentiation Evelyn N Kouwenhoven 1,, Martin Oti, Hanna Niehues 3, Simon J van
Published online: June 1, 15 Article Transcription factor p63 bookmarks and regulates dynamic enhancers during epidermal differentiation Evelyn N Kouwenhoven 1,, Martin Oti, Hanna Niehues 3, Simon J van
Epidermal Stem Cells of the Skin
 I ANRV288-CB22-14 ARI 22 June 2006 19:51 R E V I E W S First published online as a Review in Advance on July 11, 2006 E C N A D V A N Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006. 22:339 73 The Annual Review of Cell
I ANRV288-CB22-14 ARI 22 June 2006 19:51 R E V I E W S First published online as a Review in Advance on July 11, 2006 E C N A D V A N Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006. 22:339 73 The Annual Review of Cell
Epidermal Label-Retaining Cells: Background and Recent Applications
 Epidermal Label-Retaining Cells: Background and Recent Applications KristinM.BraunandFionaM.Watt Keratinocyte Laboratory, Cancer Research UK London Research Institute, London, UK Epidermal label-retaining
Epidermal Label-Retaining Cells: Background and Recent Applications KristinM.BraunandFionaM.Watt Keratinocyte Laboratory, Cancer Research UK London Research Institute, London, UK Epidermal label-retaining
Notch signaling in bulge stem cells is not required for selection of hair follicle fate
 RESEARCH REPORT 891 Development 136, 891-896 (2009) doi:10.1242/dev.030700 Notch signaling in bulge stem cells is not required for selection of hair follicle fate Shadmehr Demehri and Raphael Kopan* Notch
RESEARCH REPORT 891 Development 136, 891-896 (2009) doi:10.1242/dev.030700 Notch signaling in bulge stem cells is not required for selection of hair follicle fate Shadmehr Demehri and Raphael Kopan* Notch
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
 CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
CH 05 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM This system consists of skin and its derivatives. The skin is one of the largest organs of the body in terms of surface area. The functions of the integumentary system include:
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Eleventh Edition. Chapter 6
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 6 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Referred to as Cutaneous Membrane
Oral histology. How is the oral mucosa different from skin?
 Oral histology Lec.13 Oral mucosa: Dr.Nada AL.Ghaban The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth and consists of stratified squamous epithelium termed oral epithelium and an underlying
Oral histology Lec.13 Oral mucosa: Dr.Nada AL.Ghaban The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth and consists of stratified squamous epithelium termed oral epithelium and an underlying
Skin and Body Membranes
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 4 Skin and Body Membranes Slides 4.1 4.32 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Skin and Body Membranes Function
Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands
 Integumentary system - skin and adnexa Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands Skin (cutis): structure epidermis stratified squamous keratinized
Integumentary system - skin and adnexa Skin and adnexa Skin Adnexa (derivatives): hair nail sebaceous glands sweat glands mammary glands Skin (cutis): structure epidermis stratified squamous keratinized
INTEGUMENTARY 1-Epidermis, 2-Dermis, Structure of thick and thin skin I- Epidermis . Stratum basale
 INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
INTEGUMENTARY The skin (integument, cutis ) and its derivatives constitute the integumentary system. It form the external covering of the body and is the largest organ of the body. The skin consists of
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer
 Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer Aom Isbell http://www2.massgeneral.org/cancerresourceroom/types/gi/index.asp Spring/Summer 1, 2012 Alexandros Tzatsos, MD PhD Bardeesy Lab: Goals and Objectives
Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer Aom Isbell http://www2.massgeneral.org/cancerresourceroom/types/gi/index.asp Spring/Summer 1, 2012 Alexandros Tzatsos, MD PhD Bardeesy Lab: Goals and Objectives
Mitosis Models 3-5. Chromosome. #1 Prophase. #2 Prophase. 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids. 2n = 4
 MITOSIS Mitosis Models 3-5 Chromosome #1 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids #2 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids Mitosis Models 3-5 Astral Rays Chromosomes Chromosome Chromosome Spindle
MITOSIS Mitosis Models 3-5 Chromosome #1 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids #2 Prophase 2n = 4 4 Chromosomes 8 Chromatids Mitosis Models 3-5 Astral Rays Chromosomes Chromosome Chromosome Spindle
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM. Body Membranes & Skin
 THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Body Membranes & Skin TYPES OF MEMBRANES Epithelial Membranes includes layer of epithelial cells and connective tissue Serous Cutaneous Mucous Connective Tissue Membranes solely
The Integumentary System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Meg Flemming Austin Community College C H A P T E R 5 The Integumentary System Chapter 5 Learning Outcomes 5-1 5-2 5-3 5-4 5-5 Describe the main structural features
Keratinocyte stem cells: targets for cutaneous carcinogens
 Keratinocyte stem cells: targets for cutaneous carcinogens Rebecca J. Morris J Clin Invest. 2000;106(1):3-8. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci10508. Perspective A skin cancer seen in the clinic is in reality
Keratinocyte stem cells: targets for cutaneous carcinogens Rebecca J. Morris J Clin Invest. 2000;106(1):3-8. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci10508. Perspective A skin cancer seen in the clinic is in reality
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs
 Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin and Body Membranes Body Membranes Function of body membranes Cover body surfaces Line body cavities Form protective sheets around organs Classification of Body Membranes Epithelial membranes Cutaneous
Skin human skin. cold, touch, pressure, vibration, and tissue injury
 Skin human skin multiple layers of ectodermal tissue hairy and glabrous skin, glabrous skin is hairless. It is found on fingers, palmar surfaces of hands, soles of feet, lips, labia minora and penis Functions:
Skin human skin multiple layers of ectodermal tissue hairy and glabrous skin, glabrous skin is hairless. It is found on fingers, palmar surfaces of hands, soles of feet, lips, labia minora and penis Functions:
