High-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast using readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI
|
|
|
- Eustace Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 High-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast using readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI Objective: Compared to dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), image quality in diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DW-MRI) is generally poor because of low image spatial resolution and distortion. Readout-segmented EPI (RS-EPI) is a recently-developed technique to obtain high resolution DW-MRI with less distortion. The study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of high-resolution DW-MRI of the breast, using RS-EPI and single-shot EPI (SS-EPI). Methods: With IRB approval, 26 patients with clinically suspected breast cancer were prospectively enrolled. Breast MRI was performed on a 3.0 T scanner using a 16-channel breast coil. Sequences include T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) with fat saturation, a 3D DCE-MRI series and DW-MRI (b values of 0 and 850 s/mm2 for RS-EPI and SS-EPI). To evaluate image distortion, the antero-posterior (AP) extent of the mammary gland on DW-MRI with RS-EPI and SS-EPI were measured and differences from values obtained from T2WI were calculated. The artefacts on both sequences were scored. Diagnostic performance of lesions on both sequences was assessed using BI-RADS classification and the category was compared to that determined by DCE-MRI. Results: The average difference in the measured AP extent on DW-MRI with RS-EPI was significantly less than that on DW-MRI with SS-EPI (2.3 ± 2.0 versus 12.5 ± 4.7 mm, respectively, p<0.01). Distortion artefacts were significantly lower on DW-MRI with RS-EPI than that with SS-EPI in all cases. The sensitivity of DW-MRI with RS-EPI was higher than that with SS-EPI (88.9 and 77.8%, respectively). Conclusion: DW-MRI with RS-EPI has an advantage of less distortion compared to that with SS-EPI. KEYWORDS: breast cancer magnetic resonance imaging diffusion weighted imaging readout segmented echo planner imaging single shot echo planner imaging Introduction MRI of the breast is a study that requires the administration of a gadolinium-containing contrast agent during the study. Non-contrast diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DW-MRI) is expected to increase the diagnostic accuracy of detecting breast cancer due to excellent lesion conspicuity [1,2]. However, compared to dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI), the image quality of DW-MRI is generally poor because of low spatial resolution and image distortion, particularly around the nipple or breast-air interface. According to the Guidelines of the European Society of Breast Imaging, the spatial resolution of DCE-MRI should be at least mm [3]. If DW-MRI is used to evaluate breast lesion, it would be ideal to achieve a high spatial resolution equivalent to that of DCE-MRI, with minimal image distortion. Single-shot echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI) has been established as the method of choice for performing DW-MRI [4]. SS-EPI has the advantage of a short scan time and high signal- to-noise ratio compared to other techniques, but has the disadvantage of geometric distortion, signal dropout, and image blurring from field inhomogeneity and eddy currents [5]. On the other hand, readout segmented EPI (RS-EPI), with 2D navigator echoes for reduced sensitivity to motion-induced phase errors, is a recentlydeveloped technique to obtain high resolution DW-MRI with less geometric distortion, image blurring, and ghosting artefacts [6]. The advantages of RS-EPI have already been reported for a number of anatomical regions, including the breast [7-9], the skull base [10] and the head and neck region [11], demonstrating that the reduction of distortion is important to identify anatomical structure correctly. The objective of our study was to evaluate the feasibility of high resolution DW-MRI (special resolution of mm) of the breast, using RS-EPI and SS-EPI. Image distortion and artefacts on RS-EPI and SS-EPI images were evaluated. Diagnostic performances of these two high resolution DW-MRI sequences were estimated and compared with that of DCE-MRI. Shotaro Kanao* 1, Masako Kataoka 1, Mami Iima1, Ayami Ohno 1, Rena Sakaguchi 1, Akane Ohashi1, Maya Honda 1, Masakazu Toi 2, David A Porter 3 & Kaori Togashi 1 1 Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan 2 Department of Breast Surgery, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan 3 Fraunhofer Mevis Institute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen, Germany *Author for correspondence: kanaos@kuhp.kyoto-u.ac.jp ISSN Imaging Med. (2017) 9(6) 185
2 Kanao, Kataoka, Iima, Ohno, Sakaguchi, et al. Materials and methods Patient population With IRB approval, 26 patients who underwent DCE-MRI of the breast with clinically suspected breast cancer were prospectively enrolled between January and November General written informed consent was obtained for each patient. Exclusion criteria were as follows: those who had received presurgical systemic therapy; those who had already had an MR scan due to post-treatment follow-up; those whose diagnosis was not pathologically confirmed. Image acquisition Breast MRI was performed on a 3.0 T scanner (MAGNETOM Trio, A Tim System, Siemens AG) with a 16-channel breast coil. Sequences were as follows: axial T1-weighted images (T1WI), T2-weighted images (T2WI) with fat saturation, a 3D dynamic DCE- MRI series and DW-MRI. The 3.0-T MRI parameters were set as follows: T2-weighted images (whole breast; axial orientation; 2D turbo spin echo with fat suppression; repetition time/echo time [TR/TE], 5500/77 ms; FOV, mm; matrix, ; thickness, 3.0 mm), T1-weighted images (whole breast; axial orientation; 3D volumetric interpolated breath-hold examination [VIBE]; TR/TE, 4.83/2.45; FOV, mm; matrix, ; thickness, 1.5 mm), T1-weighted DCE images scanned pre-contrast and at 0-1, 1-2 and 5-6 min after gadolinium injection (whole breast; axial orientation; 3D-VIBE with fat suppression; TR/TE, 3.70/1.36 ms; flip angle [FA], 15; FOV, mm; matrix, ; thickness, 1.0 mm), contrast-enhanced T1-weighted images at high spatial resolution at min after gadolinium injection (whole breast; coronal orientation; 3D-VIBE with fat suppression; TR/TE, 4.01/1.63 ms; FA, 15; FOV, mm; matrix, ; thickness, 0.8 mm). Sagittal, unilateral breast DW-MRI at b values 0 and 850 s/mm 2 were obtained using the following parameters: 1) RS-EPI: TR/TE=6800/60 ms, FOV= mm, matrix= , 2.5 mm thickness, 40 slices, resolution of mm NEX=1, integrated parallel acquisition techniques (ipat) 2, 3 min 32 s, seven shots. 2) SS-EPI: TR/TE=8400/69 ms, FOV= mm, matrix= , 2.5 mm thickness, 40 slices, resolution of mm, NEX=5, ipat 2, 3 min 30 s. Both DW-MRI sequences were work-in-progress sequences and used a modified monopolar diffusion scheme [12] and fat suppression with gradient reversal technique [13]. A summary of sequence parameters used for DW-MRI is shown in TABLE l. The infused Gadolinium contrast medium was Gadoteridol (ProHance, Eisai Inc., Table 1. Sequence parameters for single-shot and readout-segmented echo-planar imaging. Single-Shot Echo-planar Imaging Readout-Segmented Echo-planar Imaging Diffusion directions Three-direction trace Three-direction trace Diffusion schema modified monopolar modified monopolar b value (s/mm 2 ) 0, 850 0,850 Fat suppression SPAIR with gradient reversal SPAIR with gradient reversal Repetition time (ms) Echo time (ms) Field of view (mm) Matrix No. of sections Section thickness (mm) Intersection gap (%) 0 0 Parallel Imaging Factor 2 2 Phase-encoding direction Antero-posterior Antero-posterior Readout segments 1 7 Average 5 1 Acquisition time 3 min 32 s 3 min 32 s 186 Imaging Med. (2017) 9(6)
3 High-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast using readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI RESEARCH PAPER Tokyo, Japan) for 0.2 ml/kg power injected at the speed of 2.0 ml/s and flashed with 20 ml of saline at the same rate. Image evaluation Image distortion and artefacts To evaluate the degree of image distortion, the antero-posterior (AP) extent of the mammary gland was measured on sagittal DW-MRI acquired with RS-EPI and SS-EPI (b=0 s/mm 2 ). The AP extent measured on sagittal T2WI was used as a reference. The AP extent was measured as the maximum distance between the mammary gland border on DWI image and T2WI. Distortion artefacts and ghost artefacts was also scored separately using RS-EPI and SS- EPI (b=0 and 850 s/mm 2 ), and evaluated by one board-certified radiologist using a fourpoint scale (0=no artifact, 1=small artifact, 2=moderate artefact, 3=severe artefact). Diagnostic performance To evaluate the diagnostic performance of each sequence in breast cancer, lesions on RS- EPI/SS-EPI DW-MRI (b=850 s/mm 2 ) and DCE-MRI were categorized based on Breast Imaging Report and Data System (BI-RADS) MRI. ADC maps were calculated on a pixel-bypixel basis, according to the equation: ADC=ln [S1/S0]/(b1-b0), where S0 and S1 are the signal intensities in the region-of-interest (ROI) obtained at two b-values, b1 and b0 (b0=0 s/ mm 2 and b1=850 s/mm 2 ). For quantitative evaluation, the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of background mammary gland and lesions were measured by one board-certified radiologist. Statistical analysis Statistical Analysis was performed using EZR (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University [14] which is a graphical user interface for R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, version 3.2.2). The image quality scores of the two DW-MRI sequences were compared using the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. The ADC values of lesions and background parenchyma were compared using paired Student t test. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05 for all tests. For diagnostic performance based on BI- RADS classification, the five categories were used for Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. Sensitivity and specificity of three sequences were evaluated using category 4 and 5 as positive for malignancy. Results Among 26 patients, 18 patients were pathologically confirmed as having breast cancer including 15 invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), one mucinous carcinoma and two ductal carcinomas in situ (DCIS). Relative to the reference value provided by T2WI, the average difference in the AP extent of the mammary gland on DW-MRI with RS- EPI (2.3 ± 2.0 mm) was significantly less than that on DW-MRI with SS-EPI (12.5 ± 4.7 mm, p<0.01) (TABLE 2 and FIGURE 1). Distortion artefacts were significantly lower on DW-MRIs with RS-EPI than those with SS-EPI in all cases, while no significant difference of ghost artefacts was observed between the two sequences (p=0.83) (TABLE 2). The sensitivity of DW-MRI with RS-EPI was higher than that with SS-EPI (88.9 versus 77.8%), while that of DCE-MRI was 94.4%. Specificity of these three sequences was 85.7 % for all. ROC analysis was performed (FIGURE 2) and the area under the curve for RS-EPI and Table 2. Evaluation of the image distortion on DW-MRIs with RS-EPI and SS-EPI. RS-EPI SS-EPI AP distance of mammary gland (compared to T2WI) 2.3 ± 2.0 mm 12.5 ± 4.7 mm p<0.01 Distortion Artifact 1.04 ± ± 0.37 p<0.01 Ghost Artifact 1.31 ± ± 0.55 p=0.83 Abbreviations DW-MRI: diffusion weighted MRI; RS-EPI: readout segmented echo planner imaging; SS-EPI: single shot echo planner imaging; AP: antero-posterior Distortion and ghost artifacts using a four-point score (0=no artifact, 1=small artifact, 2=moderate artifact, 3=severe artifact) Imaging Med. (2017) 9(6) 187
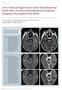
4 Kanao, Kataoka, Iima, Ohno, Sakaguchi, et al. A B C Figure 1. Normal breast of 30 year old female. (A) Sagittal reformatted T2WI of the right breast. Anteroposterior distance of mammary gland was measured (white arrow). (B) Sagittal DW-MRI using RS- EPI (b=0 s/mm 2 ). There are some distortion artifacts around the nipple. Antero-posterior distance of mammary gland was slightly shorter than T2WI (white arrow). (C) Sagittal DW-MRI using SS-EPI (b=0 s/mm 2 ). Compared to T2WI, the AP extent of the mammary gland was reduced on the SS-EPI image. Visualization of the nipple was also very poor. 1 ROC Curve for BI-RADS assessment 0.8 TPF SS-EPI RS-EPI DCE FPF Figure 2. Receiver operating characteristic curves for BBI-RADS assessment. Area under the curve for DCE, RS-EPI and SS-EPI were 0.976, and 0.906, respectively. BI-RADS: breast imaging reporting and data system; SS-PEI: single shot echo planner imaging; RS- EPI: readout segmented echo planner imaging; DCE: dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging SS-EPI was and respectively, while that of DCE-MRI was The false negative case on DW-MRI with RS-EPI and SS-EPI, and DCE-MRI was mucinous carcinoma with minimal enhancement and very high ADC. Typical case of IDC with DCIS was shown in (FIGURE 3). The false negative cases only by DW-MRI with SS-EPI were DCIS with small volume (FIGURE 4). Average ADC values of the mammary gland by RS-EPI and SS-EPI were 2.12 ± 0.24 and 1.47 ± mm 2 /s, respectively (p<0.01) and those of breast cancer were 1.04 ± 0.36 and 0.87 ± mm 2 /s, respectively (p<0.01). Discussion In our study, most of the breast cancers were picked up by both high-resolution DW-MRI of the breast using RS-EPI and SS-EPI with the same specificity. We also showed that DW-MRI with RS-EPI has less image distortion, which is probably related to the improved sensitivity compared to DW-MRI with SS-EPI. The results suggest that there is a promising role for RS- EPI, despite known advantages of SS-EPI over RS-EPI including established clinical experience with extensive data relating to ADC for various lesion types [4,15,16]. Our results regarding the lower distortion 188 Imaging Med. (2017) 9(6)
5 High-resolution diffusion-weighted MRI of the breast using readout-segmented EPI and single-shot EPI RESEARCH PAPER A B C D Figure year old female with invasive ductal carcinoma and ductal carcinoma in situ. (A) Sagittal reformatted image of the post-contrast enhanced MRI (120 s). There is linear, non-mass-enhancement with a clumped pattern. Histopatology of surgical specimen showed invasive ductal carcinoma and ductal carcinoma in situ. (B) Sagittal DW-MRI using RS-EPI (b=850). There are high signal non-mass lesions corresponding to post contrast MRI. (C) ADC map of DW-MRI using RE-EPI (b=0, 850). DCIS showed low ADC values. (D) Sagittal DW-MRI using SS-EPI (b=850). We can pick up abnormal signal intensity but the shape of the lesion was distorted. A B C Figure year old female with ductal carcinoma in situ. (A) Sagittal reformatted image of the DCE MRI (120 s after injection of contrast media). There is linear, non-mass-enhancement with a clumped pattern. Histopatology of surgical specimen showed ductal carcinoma in situ. (B) Sagittal DW-MRI using RS-EPI (b=850). There are high signal non-mass lesions corresponding to post contrast MRI. (C) Sagittal DW-MRI using SS-EPI (b=850). There is high signal but no confidence of significant finding because of imaging distortion. with RS-EPI agree with previous reports that RS-EPI tends to delineate anatomic detail better than SS-EPI because T2* blurring is reduced [7]. There are several previous DWI studies in the breast using RS-EPI [7-9,17]. In 2012, Bogner et al. reported the advantage of RS-EPI compared to SS-EPI. In this study, spatial resolution of both images was about 2.0 mm in plane [7]. In 2014, Wisner et al. reported the advantage of RS-EPI with spatial resolution about 1.8 mm in plane [17]. In 2015, one study reported the advantage of unilateral Zoomed EPI (single shot EPI with reduced FOV technique) compared to RS-EPI of both breasts. But in this study, spatial resolution of RS-EPI and Zoomed EPI were not matched (1.7 mm, 0.58 mm, respectively) [8]. Recently, Bogner et al. reported the 7.0 T breast DW-MRI using RS-EPI with spatial resolution about 0.9 mm [9]. These papers have a common point that diagnostic performance is better with higher spatial resolution and if the spatial resolution is the same, RS-EPI has the advantage of less distortion. Our study is, to our knowledge, the first paper that compares SS-EPI and RS-EPI in breast MRI using the same high spatial resolution of 1.0 mm for both sequences. For quantitative evaluation, the ADC value is recognized as an important parameter in the interpretation of DW-MRI images. Regarding the comparison of SS-EPI and RS-EPI, some papers have reported no significant difference among them [7,11]. But Wisner et al. reported a higher ADC value in background breast parenchyma that is similar to the result of our study [17]. Ihalainen et al also reported a higher ADC using RS-EPI in a phantom study [18]. With these mixed results, we should be cautious when performing quantitative evaluation of DW-MRI using RS-EPI in comparison to those obtained using SS-EPI. One reason for the difference is likely to be due to the effect of calculating modulus images before signal averaging to avoid motion-induced phase errors with SS-EPI. There are some limitations to this study. One limitation is the small population, making Imaging Med. (2017) 9(6) 189
6 Kanao, Kataoka, Iima, Ohno, Sakaguchi, et al. it difficult to identify significant differences in diagnostic performance between the two sequences. Another limitation is related to the version of the sequences used in the study. Because we used works-in-progress sequences, we have the latitude of choice about TR/TE. To the contrary, in the commercial version of DW- MRI, we cannot scan with high resolution or very long time. In this situation, there are some solution about two sequence that is the zoomed EPI technique [8] for SS-EPI and partial Fourier technique [19] for RS-EPI. The ultimate goal of breast DW-MRI is to allow breast MR examinations to be performed without contrast medium. For patient with renal dysfunction, past allergic history for gadolinium contrast medium and asthma, breast MR examination without contrast medium is desirable. Meta-analysis of diagnostic performance comparing DW- MRI with SS-EPI and DCE-MRI showed lower sensitivity despite higher specificity of DW-MRI [16], with problems in diagnosing non-mass lesions [20]. In order to improve the diagnostic performance of DW-MRI, high resolution DW-MRI with less distortion using RS-EPI is a possible way to achieve this goal. Another important role of DWI is to provide complementary information about the lesion compared to that provided by DCE-MRI, such as cell density. Again, less-distorted images are essential in order to match cell density information from DW-MRI with perfusion information from DCE-MRI. Conclusion High resolution DW-MRI using RS-EPI has the advantage of reduced distortion compared to SS-EPI. REFERENCES 1. Guo Y, Cai YQ, Cai ZL et al. Differentiation of clinically benign and malignant breast lesions using diffusion weighted imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 16, (2002). 2. Partridge SC, Rahbar H, Murthy R et al. Improved diagnostic accuracy of breast MRI through combined apparent diffusion coefficients and dynamic contrast-enhanced kinetics. Magn. Reson. Med. 65, (2011). 3. Mann RM, Kuhl CK, Kinkel K et al. Breast MRI: guidelines from the European Society of Breast Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 18, (2008). 4. Wenkel E, Geppert C, Schulz WR et al. Diffusion weighted imaging in breast MRI: Comparison of two different pulse sequences. Acad. Radiol. 14, (2007). 5. Porter DA, Calamante F, Gadian DG et al. The effect of residual Nyquist ghost in quantitative echo-planar diffusion imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 42, (1999). 6. Porter DA, Heidemann RM. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readoutsegmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn. Reson. Med. 62, (2009). 7. Bogner W, Pinker DK, Bickel H et al. Readoutsegmented echo-planar imaging improves the diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR breast examinations at 3.0 T. Radiology. 263, (2012). 8. Park JY, Shin HJ, Shin KC et al. Comparison of readout segmented echo planar imaging (EPI) and EPI with reduced field-of-view diffusionweighted imaging at 3t in patients with breast cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 42, (2015). 9. Bogner W, Pinker K, Zaric O et al. Bilateral diffusion-weighted MR imaging of breast tumors with submillimeter resolution using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging at 7 T. Radiology. 274, (2015). 10. Iima M, Yamamoto A, Brion V et al. Reduceddistortion diffusion MRI of the craniovertebral junction. AJNR. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 33, (2012). 11. Koyasu S, Iima M, Umeoka S et al. The clinical utility of reduced-distortion readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in the head and neck region: initial experience. Eur. Radiol. 24, (2014). 12. Morelli JN, Runge VM, Feiweier T et al. Evaluation of a modified Stejskal-Tanner diffusion encoding scheme, permitting a marked reduction in TE, in diffusion-weighted imaging of stroke patients at 3 T. Invest. Radiol. 45, (2010). 13. Park HW, Kim DJ, Cho ZH. Gradient reversal technique and its applications to chemical-shiftrelated NMR imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 4, (1987). 14. Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software EZR for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 48, (2013). 15. Tsushima Y, Takahashi TA, Endo K. Magnetic resonance (MR) differential diagnosis of breast tumors using apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) on 1.5-T. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 30, (2009). 16. Chen X, Li WL, Zhang Y et al. Meta-analysis of quantitative diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the differential diagnosis of breast lesions. BMC. Cancer. 10, 693 (2010). 17. Wisner DJ, Rogers N, Deshpande VS et al. High-resolution diffusion-weighted imaging for the separation of benign from malignant BI- RADS 4/5 lesions found on breast MRI at 3T. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging. 40, (2014). 18. Ihalainen T, Kuusela L, Soikkeli M et al. A body-sized phantom for evaluation of diffusionweighted MRI data using conventional, readoutsegmented, and zoomed echo-planar sequences. Acta. Radiol. 57, (2015). 19. Frost R, Porter DA, Miller KL et al. Implementation and assessment of diffusionweighted partial Fourier readout-segmented echo-planar imaging. Magn. Reson. Med. 68, (2012). 20. Tozaki M, Fukuma E. 1H MR spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted imaging of the breast: Are they useful tools for characterizing breast lesions before biopsy? AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 193, (2009). 190 Imaging Med. (2017) 9(6)
Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI
 Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI Poster No.: C-1974 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Y. Kanda 1, S. Kanao 2, M. Kataoka 2, K. Togashi 2 ; 1 Kyoto City/JP,
Categorical Classification of Spiculated Mass on Breast MRI Poster No.: C-1974 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit Y. Kanda 1, S. Kanao 2, M. Kataoka 2, K. Togashi 2 ; 1 Kyoto City/JP,
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Disclosures. Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck. Learning objectives ???
 Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures Diffusion and Perfusion Imaging in the Head and Neck Ashok Srinivasan, MD Associate Professor Director of Neuroradiology University of Michigan Health System
Comparison of 1.5 T Tesla and 3.0 T Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluating Local Extension of Endometrial Cancer
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 27 1, 21 28, March 2015 Original Comparison of 1.5 T Tesla and 3.0 T Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluating Local Extension of Endometrial Cancer Naomi YAGI, Masanori HIROSE,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 27 1, 21 28, March 2015 Original Comparison of 1.5 T Tesla and 3.0 T Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluating Local Extension of Endometrial Cancer Naomi YAGI, Masanori HIROSE,
Advances in MRI for Radiation Therapy
 Advances in MRI for Radiation Therapy Jing Cai, PhD, DABR Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology Duke University Medical Center, Durham NC Advances in MRI Structural Imaging Fast Imaging
Advances in MRI for Radiation Therapy Jing Cai, PhD, DABR Associate Professor Department of Radiation Oncology Duke University Medical Center, Durham NC Advances in MRI Structural Imaging Fast Imaging
The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses
 The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses Poster No.: C-1749 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: U. Aksoy Ozcan 1, A. Öz 2, S.
The role of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and relative ADC in the evaluation of breast masses Poster No.: C-1749 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: U. Aksoy Ozcan 1, A. Öz 2, S.
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
3D high-resolution MR imaging can provide reliable information
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
BioMatrix Tuners: CoilShim
 MAGNETOM Vida special issue Head and Neck Imaging Clinical 11 BioMatrix Tuners: CoilShim Miriam R. Keil, Ph.D.; Jörg Rothard; Carmel Hayes, Ph.D. Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany A cervical spine
MAGNETOM Vida special issue Head and Neck Imaging Clinical 11 BioMatrix Tuners: CoilShim Miriam R. Keil, Ph.D.; Jörg Rothard; Carmel Hayes, Ph.D. Siemens Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany A cervical spine
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
High-resolution, Anatomically-accurate Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Orbital and Sinonasal Lesions with RESOLVE
 52 Clinical Head-and-Neck Imaging MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/2017 High-resolution, Anatomically-accurate Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Orbital and Sinonasal Lesions with RESOLVE Yan Sha 1 ; Hailin Wan 1 ; Menglong
52 Clinical Head-and-Neck Imaging MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/2017 High-resolution, Anatomically-accurate Diffusion-weighted Imaging of Orbital and Sinonasal Lesions with RESOLVE Yan Sha 1 ; Hailin Wan 1 ; Menglong
Response Evaluation of Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Dynamic MRI vs. FDG-PET
 Response Evaluation of Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Dynamic MRI vs. FDG-PET Poster No.: C-2065 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Torii, S. Kanao, M.
Response Evaluation of Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Dynamic MRI vs. FDG-PET Poster No.: C-2065 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit M. Torii, S. Kanao, M.
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
Spiculated breast masses on MRI: Which category should we choose, 4 or 5?
 Spiculated breast masses on MRI: Which category should we choose, 4 or 5? Poster No.: C-1394 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Onishi, S. Kanao, M. Kataoka, M. Kawai, M. Iima, A.
Spiculated breast masses on MRI: Which category should we choose, 4 or 5? Poster No.: C-1394 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: N. Onishi, S. Kanao, M. Kataoka, M. Kawai, M. Iima, A.
European Journal of Radiology
 European Journal of Radiology 83 (2014) 1728 1733 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Usefulness of free-breathing readout-segmented
European Journal of Radiology 83 (2014) 1728 1733 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Usefulness of free-breathing readout-segmented
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process
 ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
imri 2017;21:
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:154-161 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.154 Diagnostic Performance of Diffusion- Weighted Steady-State Free Precession in Differential Diagnosis of
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:154-161 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.154 Diagnostic Performance of Diffusion- Weighted Steady-State Free Precession in Differential Diagnosis of
OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER
 OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER By Dr. John Feller, MD, Radiologist Desert Medical Imaging, Palm Springs, CA MRI is clinically accepted as the best imaging modality for displaying anatomical
OASIS 1.2T: MULTIPARAMETRIC MRI OF PROSTATE CANCER By Dr. John Feller, MD, Radiologist Desert Medical Imaging, Palm Springs, CA MRI is clinically accepted as the best imaging modality for displaying anatomical
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS
 Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS Poster No.: C-0412 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Breast H. G. Toonen, R. Mann, H. Huisman, J. Veltman, C. Boetes; Nijmegen/NL
Pharmacokinetic evaluation of DCIS Poster No.: C-0412 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit Breast H. G. Toonen, R. Mann, H. Huisman, J. Veltman, C. Boetes; Nijmegen/NL
Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications?
 Original Article Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications? Shinya Yamamoto, Takashi Chishima Department of Breast Surgery, Yokohama Rosai Hospital, Yokohama 222-0036,
Original Article Can magnetic resonance imaging obviate the need for biopsy for microcalcifications? Shinya Yamamoto, Takashi Chishima Department of Breast Surgery, Yokohama Rosai Hospital, Yokohama 222-0036,
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
6/23/2009. Inversion Recovery (IR) Techniques and Applications. Variations of IR Technique. STIR, FLAIR, TI and TI Null. Applications of IR
 The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results
 Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Oak foundation for donating the 3T Siemens Verio scanner. Board of directors BBH and Frh Hospitals for supporting the
 Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
8/4/2016. MRI for Radiotherapy: MRI Basics. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Wilson Miller
 MRI for Radiotherap: MRI asics Wilson Miller Universit of Virginia Department of Radiolog & Medical Imaging AAPM 2016 August 4, 2016 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Magnetic resonance images are created using
MRI for Radiotherap: MRI asics Wilson Miller Universit of Virginia Department of Radiolog & Medical Imaging AAPM 2016 August 4, 2016 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Magnetic resonance images are created using
Non Contrast MRA. Mayil Krishnam. Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine
 Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy
 DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
DTI fiber tracking at 3T MR using b-1000 value in the depiction of periprostatic nerve before and after nervesparing prostatectomy Poster No.: C-2328 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors:
ACR MRI Accreditation Program. ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update. Educational Objectives. ACR accreditation. History. New Modular Program
 ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
Breast MRI Update. Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR Yale University School of Medicine
 Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
Breast MRI Update Jeffrey C. Weinreb, MD, FACR jeffrey.weinreb@yale.edu Yale University School of Medicine I disclose the following financial relationships with relevant commercial interests: Bracco Bayer
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Handzettel 1. Multiparametric Functional Imaging in Radiation Therapy. Functional and Quantitative Imaging with MR
 Multiparametric Functional Imaging in Radiation Therapy Himanshu Bhat, Ph.D. Siemens Healthcare MR in RT Adding valuable information on tissue properties CT provides: Geometric accuracy Delineation of
Multiparametric Functional Imaging in Radiation Therapy Himanshu Bhat, Ph.D. Siemens Healthcare MR in RT Adding valuable information on tissue properties CT provides: Geometric accuracy Delineation of
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
D. J. Margolis 1, S. Natarajan 2, D. Kumar 3, M. Macairan 4, R. Narayanan 3, and L. Marks 4
 Biopsy Tracking and MRI Fusion to Enhance Imaging of Cancer Within the Prostate D. J. Margolis 1, S. Natarajan 2, D. Kumar 3, M. Macairan 4, R. Narayanan 3, and L. Marks 4 1 Dept. of Radiology, UCLA, Los
Biopsy Tracking and MRI Fusion to Enhance Imaging of Cancer Within the Prostate D. J. Margolis 1, S. Natarajan 2, D. Kumar 3, M. Macairan 4, R. Narayanan 3, and L. Marks 4 1 Dept. of Radiology, UCLA, Los
The Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Values for Breast Tumors
 The Role of iffusion-weighted Imaging and the Apparent iffusion Coefficient (AC) Values for Breast Tumors Mi Jung Park, M Eun Suk Cha, M Bong Joo Kang, M Yon Kwon Ihn, M Jun Hyun Baik, M Index terms: iffusion-weighted
The Role of iffusion-weighted Imaging and the Apparent iffusion Coefficient (AC) Values for Breast Tumors Mi Jung Park, M Eun Suk Cha, M Bong Joo Kang, M Yon Kwon Ihn, M Jun Hyun Baik, M Index terms: iffusion-weighted
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Magnetic resonance (MR) diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) is
 Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
Diagn Interv Radiol DOI 10.4261/1305-3825.DIR.3892-10.1 Turkish Society of Radiology 2010 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla: normative values and repeatability
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience
 African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer
 Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer Disclosure Information Vikas Kundra, M.D, Ph.D. No financial relationships to disclose. Education Goals and Objectives To describe the utility of diffusion-weighted
Diffusion Weighted Imaging in Prostate Cancer Disclosure Information Vikas Kundra, M.D, Ph.D. No financial relationships to disclose. Education Goals and Objectives To describe the utility of diffusion-weighted
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo
 Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis
 In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
Recently, prostate-specific antigen (PSA) has been identified as a
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2011; 17:243 248 Turkish Society of Radiology 2011 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prostate cancer detection with MRI: is dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging necessary in addition
Diagn Interv Radiol 2011; 17:243 248 Turkish Society of Radiology 2011 ABDOMINAL IMAGING ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prostate cancer detection with MRI: is dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging necessary in addition
Computed Diffusion-Weighted Image in the Abdomen
 Computed Diffusion-Weighted Image in the Abdomen Poster No.: C-0234 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Yoshikawa 1, N. Aoyama 1, Y. Ohno 1, K. Kyotani 1, Y. Kassai 2, K. Sofue 1, M.
Computed Diffusion-Weighted Image in the Abdomen Poster No.: C-0234 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: T. Yoshikawa 1, N. Aoyama 1, Y. Ohno 1, K. Kyotani 1, Y. Kassai 2, K. Sofue 1, M.
Successful Breast MRI Program : The ingredients
 Successful Breast MRI Program : The ingredients Dr. Smriti Hari Associate Professor Deptt. Of Radiology All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi How to perform Breast MRI Breast MRI descriptors
Successful Breast MRI Program : The ingredients Dr. Smriti Hari Associate Professor Deptt. Of Radiology All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi How to perform Breast MRI Breast MRI descriptors
Effects of magnetic field strength and b value on the sensitivity and specificity of quantitative breast diffusion-weighted MRI
 Original Article Effects of magnetic field strength and b value on the sensitivity and specificity of quantitative breast diffusion-weighted MRI Mohammad Eghtedari 1, Jingfei Ma 2, Patricia Fox 3, Inanc
Original Article Effects of magnetic field strength and b value on the sensitivity and specificity of quantitative breast diffusion-weighted MRI Mohammad Eghtedari 1, Jingfei Ma 2, Patricia Fox 3, Inanc
Diffusion-weighted Imaging of the Breast: Principles and Clinical Applications 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. BREAST IMAGING Diffusion-weighted
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. BREAST IMAGING Diffusion-weighted
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans
 Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY
 A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
Dynamic contrast enhanced breast MRI at 7T and 3T: an intra individual comparison study
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1654-7 RESEARCH Open Access Dynamic contrast enhanced breast MRI at 7T and 3T: an intra individual comparison study Gisela L. G. Menezes *, Bertine L. Stehouwer, Dennis W. J. Klomp,
DOI 10.1186/s40064-015-1654-7 RESEARCH Open Access Dynamic contrast enhanced breast MRI at 7T and 3T: an intra individual comparison study Gisela L. G. Menezes *, Bertine L. Stehouwer, Dennis W. J. Klomp,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion
 Acta Med Kindai Univ Vol.43, No.1 1-8, 2018 1 MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion Shojiro Hidaka 1,2,
Acta Med Kindai Univ Vol.43, No.1 1-8, 2018 1 MR cholangiopancreatography; Predicting imaging findings for differentiation of malignant bile ductal obstruction versus benign lesion Shojiro Hidaka 1,2,
Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma
 Journal of Health Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma Fuad Julardžija*,
Journal of Health Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Comparison of magnetic resonance diffusionweighted imaging characteristics between cystic lesions and normal pancreatic parenchyma Fuad Julardžija*,
Feasibility and initial dosimetric findings for a randomized trial using dose painted multi-parametric-mri defined targets in prostate cancer
 Feasibility and initial dosimetric findings for a randomized trial using dose painted multi-parametric-mri defined targets in prostate cancer Thoughts on the use of MRI in the treatment of prostate cancer
Feasibility and initial dosimetric findings for a randomized trial using dose painted multi-parametric-mri defined targets in prostate cancer Thoughts on the use of MRI in the treatment of prostate cancer
ASL BASICS II. Learning Objectives. Outline. Acquisition. M. A. Fernández-Seara, Ph. D. Arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI: basic theory
 Acquisition ASL BASICS II M. A. Fernández-Seara, Ph. D. Neuroimaging Laboratory Center for Applied Medical Research University of Navarra Pamplona, Spain Outline Arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI: basic
Acquisition ASL BASICS II M. A. Fernández-Seara, Ph. D. Neuroimaging Laboratory Center for Applied Medical Research University of Navarra Pamplona, Spain Outline Arterial spin labeled perfusion MRI: basic
Computer-aided IVIM/Kurtosis Diffusion MRI for breast lesions: comparison with BI-RADS MRI categories
 Computer-aided IVIM/Kurtosis Diffusion MRI for breast lesions: comparison with BI-RADS MRI categories Poster No.: C-1494 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Iima, M. Kataoka, Y. Nakanishi,
Computer-aided IVIM/Kurtosis Diffusion MRI for breast lesions: comparison with BI-RADS MRI categories Poster No.: C-1494 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Iima, M. Kataoka, Y. Nakanishi,
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Fat Suppression in the Abdomen
 Clinical How I do it? Fat Suppression in the Abdomen Wilhelm Horger Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany Introduction Due to the different chemical environment, hydrogen nuclei in - and in -tissue
Clinical How I do it? Fat Suppression in the Abdomen Wilhelm Horger Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany Introduction Due to the different chemical environment, hydrogen nuclei in - and in -tissue
Preoperative prediction of the malignancy or benignancy of
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Eida M. Sumi N. Sakihama H. Takahashi T. Nakamura Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of Salivary Gland Tumors: Prediction of the Benignancy and Malignancy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Eida M. Sumi N. Sakihama H. Takahashi T. Nakamura Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Mapping of Salivary Gland Tumors: Prediction of the Benignancy and Malignancy BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
Optimizing Your Breast MRI Technique. Nola Hylton, Ph.D. Department of Radiology, University of California, San Francisco
 Optimizing Your Breast MRI Technique Nola Hylton, Ph.D. Department of Radiology, University of California, San Francisco Introduction Breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is finding wider application
Optimizing Your Breast MRI Technique Nola Hylton, Ph.D. Department of Radiology, University of California, San Francisco Introduction Breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is finding wider application
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program - DRAFT
 ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program - DRAFT Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics Educational Objectives Provide an overview of the ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program (BMRAP)
ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program - DRAFT Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics Educational Objectives Provide an overview of the ACR Breast MRI Accreditation Program (BMRAP)
CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]
![CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE] CT and conventional MR imaging (using spin-echo [SE]](/thumbs/86/94270487.jpg) ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Srinivasan R. Dvorak K. Perni S. Rohrer S.K. Mukherji Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Pathology in the Head and Neck Using 3T Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Values: Early Experience
Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 101 106, 2011 MAJOR PAPER Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 10, No. 2, pp. 101 106, 2011 MAJOR PAPER Visualization of Endolymphatic Hydrops after Intratympanic Injection of Gd-DTPA: Comparison of 2D and 3D Real Inversion Recovery Imaging
Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods
 Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods Subjects The experiment included twelve subjects: ten sighted subjects and two blind. Five of the ten sighted subjects were expert users of a visual-to-auditory
Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods Subjects The experiment included twelve subjects: ten sighted subjects and two blind. Five of the ten sighted subjects were expert users of a visual-to-auditory
Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Mediastinal and Pulmonary Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 153-158, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 153-158, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of MRI Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Quantification in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant
PI-RADS classification: prognostic value for prostate cancer grading
 PI-RADS classification: prognostic value for prostate cancer grading Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Platzek, A. Borkowetz, T. Paulus, T. Brauer, M. Wirth, M.
PI-RADS classification: prognostic value for prostate cancer grading Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: I. Platzek, A. Borkowetz, T. Paulus, T. Brauer, M. Wirth, M.
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR Imaging
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors
 Eur Radiol (2011) 21:2475 2483 DOI 10.1007/s00330-011-2210-7 BREAST Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors Christian Sohns & Martin Scherrer
Eur Radiol (2011) 21:2475 2483 DOI 10.1007/s00330-011-2210-7 BREAST Value of the BI-RADS classification in MR-Mammography for diagnosis of benign and malignant breast tumors Christian Sohns & Martin Scherrer
Computer Aided Detection (CAD) for Breast MRI
 Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment ISSN 1533-0346 Volume 4, Number 1, February (2005) Adenine Press (2005) Computer Aided Detection (CAD) for Breast MRI www.tcrt.org Since 1999, there has been a
Technology in Cancer Research & Treatment ISSN 1533-0346 Volume 4, Number 1, February (2005) Adenine Press (2005) Computer Aided Detection (CAD) for Breast MRI www.tcrt.org Since 1999, there has been a
ORIGINAL PAPER. Background parenchymal enhancement in preoperative breast MRI
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 373 ~ 382, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER Background parenchymal enhancement in preoperative breast MRI Satoko Kohara 1, Satoko Ishigaki 1, Hiroko Satake 1, Akiko Kawamura 1, Hisashi Kawai
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 77. 373 ~ 382, 2015 ORIGINAL PAPER Background parenchymal enhancement in preoperative breast MRI Satoko Kohara 1, Satoko Ishigaki 1, Hiroko Satake 1, Akiko Kawamura 1, Hisashi Kawai
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Evaluation of Prostate Cancer: Optimal B Value at 3T
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.61 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2013;14(1):61-69 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Evaluation of Prostate
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.1.61 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2013;14(1):61-69 Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Evaluation of Prostate
Region of interest standardisation for diffusion-weighted imaging of breast malignancies
 Region of interest standardisation for diffusion-weighted imaging of breast malignancies Award: Poster No.: C-2765 Magna Cum Laude Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Wielema, M. D.
Region of interest standardisation for diffusion-weighted imaging of breast malignancies Award: Poster No.: C-2765 Magna Cum Laude Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. Wielema, M. D.
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body
 Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Normal and Abnormal Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics Evaluated by Optimized Cine Phase-contrast MR Imaging
 Chin J Radiol 2000; 25: 191-195 191 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Normal and Abnormal Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics Evaluated by Optimized Cine Phase-contrast MR Imaging LUNG-HUI GIIANG 1,3 CHENG-YU CHEN 1 MING-YEN
Chin J Radiol 2000; 25: 191-195 191 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Normal and Abnormal Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics Evaluated by Optimized Cine Phase-contrast MR Imaging LUNG-HUI GIIANG 1,3 CHENG-YU CHEN 1 MING-YEN
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive
 Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Speed, Comfort and Quality with NeuroDrive Echelon Oval provides a broad range of capabilities supporting fast, accurate diagnosis of brain conditions and injuries. From anatomical depiction to vascular
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
Clinical application of 3.0 T proton MR spectroscopy in evaluation of pancreatic diseases
 Clinical application of 3.0 T proton MR spectroscopy in evaluation of pancreatic diseases Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1762 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Su, E. Jin; Beijing/CN
Clinical application of 3.0 T proton MR spectroscopy in evaluation of pancreatic diseases Award: Cum Laude Poster No.: C-1762 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: T. Su, E. Jin; Beijing/CN
2D and 3D MR imaging in the assessment of Fallopian tube features
 2D and 3D MR imaging in the assessment of Fallopian tube features Poster No.: C-1292 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit Genitourinary Authors: J. Takahama, S. Kitano, N. Marugami, A. Takahashi,
2D and 3D MR imaging in the assessment of Fallopian tube features Poster No.: C-1292 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Topic: Scientific Exhibit Genitourinary Authors: J. Takahama, S. Kitano, N. Marugami, A. Takahashi,
WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TELL US ABOUT TRUST AND DISTRUST? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1
 SPECIAL ISSUE WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TE US ABOUT AND DIS? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1 By: Angelika Dimoka Fox School of Business Temple University 1801 Liacouras Walk Philadelphia, PA
SPECIAL ISSUE WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TE US ABOUT AND DIS? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1 By: Angelika Dimoka Fox School of Business Temple University 1801 Liacouras Walk Philadelphia, PA
ACR Accreditation Update in MRI
 ACR Accreditation Update in MRI Whole Body Systems Extremity (MSK) Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Dedicated Breast MRI Accreditation Update 1. ACR MRI Accreditation: Overview,
ACR Accreditation Update in MRI Whole Body Systems Extremity (MSK) Ron Price Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN Dedicated Breast MRI Accreditation Update 1. ACR MRI Accreditation: Overview,
FieldStrength. Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images
 FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
FieldStrength Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 33 December 2007 Achieva 3.0T enables cutting-edge applications, best-in-class MSK images Palo Alto Medical Clinic Sports Medicine Center employs
High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning. Dr. med. M. Golatta
 The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
The latest developments - Automated Breast Volume Scanning Dr. med. M. Golatta Automated Breast Volume US: Why? o Mammography is limited in dense breasts: high false negative rate o Many of these tumors
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR
 High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
High Signal Intensity of the Infundibular Stalk on Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery MR Yutaka Araki, Ryuichirou Ashikaga, Satoru Takahashi, Jun Ueda, and Osamu Ishida PURPOSE: To determine the MR imaging
Vacuum-assisted breast biopsy using computer-aided 3.0 T- MRI guidance: diagnostic performance in 173 lesions
 Vacuum-assisted breast biopsy using computer-aided 3.0 T- MRI guidance: diagnostic performance in 173 lesions Poster No.: C-2870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Pozzetto, L. Camera,
Vacuum-assisted breast biopsy using computer-aided 3.0 T- MRI guidance: diagnostic performance in 173 lesions Poster No.: C-2870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Pozzetto, L. Camera,
