Production and Use of the Radiopharmaceuticals ( 18 F-FDG and 18 F-NaF) in Nuclear Medicine in Kazakhstan
|
|
|
- Cornelius Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NUCLEAR THEORY, Vol. 34 (2015) eds. M. Gaidarov, N. Minkov, Heron Press, Sofia Production and Use of the Radiopharmaceuticals ( 18 F-FDG and 18 F-NaF) in Nuclear Medicine in Kazakhstan B.A. Prmantaeva 2, A. Ryskulov 2, G. Ryskulova 1, S.A. Nurkenov 1 1 JSC National Diagnostic Center of National Medical Holding, Astana, Kazakhstan 2 L.N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University, Astana, Kazakhstan Abstract. This paper presents the results of studies using radiotracer solution [18F] - fluorodeoxyglucose with the use of PET/CT method. Calibration studies were performed for PET/CT machine with 22 Na source; installation of PET/CT scanner was performed and the program Topas-Vicro was studied to eliminate artefacts arising during operation, the possibility of formation of artefacts was excluded in the study and definition of the ellipse of the head in brain research. On the basis of the application of labeled ultra-short living radionuclides ( 18 F-FDG), malignant tumours and metastases were identified in the bodies of patients. The article presents information about first experience of production and use of a new radiopharmaceutical 18 F-NaF in Kazakhstan for diagnosis of bone metastases of different aetiology by positron-emission/computed tomography (PET/CT). 1 Introduction The successes of atomic physics have great influence on the development of almost all branches of human knowledge [1,2]. Acquisition of atomic energy has given new means and methods of scientific research into the hands of scientists of diverse specialities. Possibility of scientific knowledge immeasurably increased. Since its inception, scientific medicine draws new ideas and tools for prevention and control over disease in physics and chemistry. It is worth recalling, for example, the opening X-rays at the end of the last century led to the fact that even a small hospital cannot do without X-ray machine now. Use of nuclear energy is of paramount importance for the medicine. This branch of science has been enriched with new, highly valuable methods for studying life processes, diagnosis and treatment of disease. The scope of the mass use of radionuclides is nuclear medicine. Radionuclides are used in nuclear medicine, mainly in the form of radiopharmaceuticals (RPCs) for the early diagnosis of diseases of various organs and for therapy. 72
2 Production and Use of the Radiopharmaceuticals ( 18 F-FDG and 18 F-NaF)... RPC is a chemical compound containing certain radioactive nuclide in the molecule allowed for administration to humans for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. At the same time, a distinctive feature of the diagnostic RPC is the lack of pharmacological effect [3,4]. Bone metastases are frequent complication of a whole number of tumour diseases, in the first place of breast cancer, prostate cancer, lung cancer, renal cancer, thyroid carcinoma. Bone metastases are one of the factors, which considerably lower the life quality, that is why their early detection and treatment remain actual problem in oncology up till now. Application of new RPC with high sensitivity and specificity to pathological changes of osseous tissue will extend limitations of cancer patients diagnosis. The aim of this work is the production and use of labeled positron-emitting ultra-short living radionuclides for the radioisotope diagnosis using the positron emission tomography. This paper presents the results on the production and use of RPC fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F in Astana on the basis of JSC National Diagnostic Center to diagnose complex oncological, neurological and cardiovascular diseases. RPC fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F is used as a diagnostic tool for the positron emission tomography (PET). The main indications for the study are: in oncology: the differential diagnosis of malignant tumours of different clinical forms and localization, including tumours of the brain, determining the prevalence and staging of malignant tumours, evaluation of tumour treatment; in cardiology: evaluation of myocardial viability in the planning of reconstructive surgery in patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular systolic dysfunction, monitoring the effectiveness of treatment of myocardium; in neurology: identifying hypometabolism in epilepsy centers, the differential diagnosis of parkinsonism, determining the degree of brain damage in traumatic brain injury and cerebrovascular disease, determining the effectiveness of treatment of neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases. Contraindications. Specific contraindication to the use of the drug was found. Using the RPC fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation. 2 Methodology of Research The main research method was the method of positron emission tomography (PET) the newest method based on the use of ultra-short living radioisotopes. PET is an essential component of a cyclotron, which yields labeled positronemitting RPCs [5]. 73
3 B.A. Prmantaeva, A. Ryskulov, G. Ryskulova, S.A. Nurkenov At present, the series of first experimental data on the production of the RPC ( 18 F-FDG) were obtained. Research is carried out using the methods of PET/CT and SPECT. Radionuclide of fluorine-18 is produced by irradiation of the nuclei of the isotope of oxygen-18 by beam of accelerated protons with an energy of 15 MeV according to the reaction: 18 O(p, n) 18 F. As a target substance, water enriched with oxygen-18 is used. Produced radionuclide of fluorine-18 is stabilized in the chemical form of fluoride, fluorine- 18 ([ 18 F], F). 2.1 Formation of radionuclides of nitrogen-13 and fluorine-17 With the indicated parameters of irradiation, oxygen-16 and oxygen-17, contained in the irradiated material as impurities, undergo nuclear reactions with the formation of radionuclides of nitrogen-13 (half-life - 9,96 min) and fluorine- 17 (half-life - 70 s), respectively: 16 O(p, α) 13 N 17 O(p, n) 17 F. Chemical forms of stabilization of nitrogen-13 is nitrogen gas [ 13 N]N 2. Radionuclide of fluorine-17 is stabilized in the chemical form of fluoride, fluorine- 17. The content of nitrogen-13 and fluorine-17 in preparation at the time of its manufacture cannot exceed 0.01% theoretically, which allows not identifying radionuclide impurities in the final product. Production of fluoride tetrabutylammonium, fluorine-18: (C 4 H 9 ) 4 N + HCO }{{}}{{ F } Tetrabutylammonium Fluoride, hydrocarbonate fluorine-18 M.m 303 A.m 18 H 2 O (C 4 H 9 ) 4 N +18 F }{{} Tetrabutylammonium fluoride, fluorine-18 M.m HCO 3 }{{} Hydrocarbonate M.m 61 74
4 Production and Use of the Radiopharmaceuticals ( 18 F-FDG and 18 F-NaF)... Adverse reaction. Formation of chloride tetrabutylammonium: (C 4 H 9 ) 4 N + HCO3 + }{{}}{{} Cl Tetrabutylammonium Chloride, hydrocarbonate A.m 35 M.m 303 H 2 O (C 4 H 9 ) 4 N + Cl }{{} Tetrabutylammonium chloride M.m 277 B.A. Prmantaeva, A. Ryskulov, G. Ryskulova, S.A. Nurkenov B.A. Prmantaeva, A. Ryskulov, G. Ryskulova, S.A. Nurkenov Preparation of 2-fluoro [ 18 F]-2-deoxy-D-glucose: Preparation of 2-fluoro [ 18 F]-2-deoxy-D-glucose: Preparation of 2-fluoro [ 18 F]-2-deoxy-D-glucose: + HCO 3 }{{} Hydrocarbonate M.m 61 The The formation of of 2-chloro-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranose: The formation of 2-chloro-2-deoxy-β-D-glucopyranose: The production and use of the radiopharmaceuticals ( 18 F-FDG and 18 F-NaF) in nuclear medicine in Kazakhstan The formation of D-glucose: The formation of D-glucose: Fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F Fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F is a nonspecific tumour-tropic RPC and accumulates in high quantities in the cells of malignant tumours and metastases due to their inherent hyperglycolysis [6-10]. 18 F fluorodeoxyglucose accumulation level in cancer cells correlates with the degree of their malignancy. The product also allows to evaluate the effect of the treatment, since the level of drug accumulation in tumours is reduced in effective treatment and it does not change or increases in ineffective one. 18 F fluorodeoxyglucose is actively transported into the cells by proteins-transporters, where it undergoes phosphorylation to form fluorodeoxyglucose-6-phosphate, 18 F, the product which does not enter further reactions and is retained in this form in the cells of malignant tumours. In the non-transformed cells of tissues and organs, dephosphorylation is observed to form fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F, which is derived from normal cells and can be redistributed. The best conditions for the detection of malignant tumours are the mild hypoglycaemia achieved by starvation for 4-6 hours, and the water load
5 B.A. Prmantaeva, A. Ryskulov, G. Ryskulova, S.A. Nurkenov 2.2 Fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F Fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F is a nonspecific tumour-tropic RPC and accumulates in high quantities in the cells of malignant tumours and metastases due to their inherent hyperglycolysis [6-10]. 18 F fluorodeoxyglucose accumulation level in cancer cells correlates with the degree of their malignancy. The product also allows to evaluate the effect of the treatment, since the level of drug accumulation in tumours is reduced in effective treatment and it does not change or increases in ineffective one. 18 F fluorodeoxyglucose is actively transported into the cells by proteins-transporters, where it undergoes phosphorylation to form fluorodeoxyglucose-6-phosphate, 18 F, the product which does not enter further reactions and is retained in this form in the cells of malignant tumours. In the non-transformed cells of tissues and organs, dephosphorylation is observed to form fluorodeoxyglucose, 18 F, which is derived from normal cells and can be redistributed. The best conditions for the detection of malignant tumours are the mild hypoglycaemia achieved by starvation for 4-6 hours, and the water load (intake of ml of water) after the introduction of the RPC. Patients are asked to empty the bladder several times. Starvation promotes increased glucose uptake by the cells, and water load accelerates the removal of the label from normal tissues in the urine, thereby reducing the level of radioactivity and radiation exposure. For patients with diabetes, it is necessary to control the blood glucose level before the study. PET study is only performed when the blood glucose level is normal or low. After intravenous administration of the drug, 18 F fluorodeoxyglucose quickly leaves the bloodstream and gradually builds up in organs and tissues. 18 F fluorodeoxyglucose is excreted by the kidneys to the bladder, so the pelvis of the kidneys, ureters and bladder are also visualized normally. More than 50% of the injected amount of radiotracer is excreted in the urine within the first 2 hours after injection. In the brain, increased accumulation of radiotracer is observed in the cortex and deeper structures, and the content of the RPC in the gray matter is 2 times higher than in white one. Accumulation of the drug in human myocardium is 3-4% of the administered one. Optimal ratio of organ/background in the study of infarction and brain is reached after minutes after the intravenous administration of the drug and continues for another minutes which is sufficient for positron emission tomography. Optimal ratio of tumour/normal tissue is observed minutes after drug administration and persists for another minutes after administration [11-13]. Glucose, containing radioactive atom, is used in PET/CT. The generated radioactivity is registered in special chamber. Since malignant cells have an increased metabolism, they consume large quantity of radioactive glucose. PET/CT with 18 F-FDG allows us to detect tumour in a whole body within one examination. In some cases given method makes it possible to separate benign and malignant tumours. Sometimes for better diagnosis of certain kinds of cancer PET is combined with CT (PET/CT method). However, PET/CT with the use of 18 F- 76
6 Production and Use of the Radiopharmaceuticals ( 18 F-FDG and 18 F-NaF)... FDG is mainly sensitive to osteolytic bone metastases. Osteoblastic metastases do not consume glucose. 2.3 PET/CT with 18 F-NaF PET/CT with 18 F-NaF bone scanning with the help of introduction of radioactive material NaF with isotope 18 18F is used for effective diagnosis of osteoblastic and osteolytic types of bone metastases, for determination of their disposition and size, for definition of spread of disease. This method allows us to carry out differential diagnosis between malignant and benign as well as other bone affections, such as: Backache or unexplainable bone pains: 1. Osteomyelitis; 2. Inflammatory and degenerative arthritises; 3. Aseptic necrosis; 4. Osteonecrosis of lower jaw; 5. Paget s disease; 6. Bone graft viability; 7. Joint implant complications. PET/CT scanning with 18 F-NaF has higher diagnostic accuracy than ordinary bone scanning with 99mTc, and also advantages are the major contraction of scanning time, diagnosis both osteoblastic and osteolytic types of bone metastases. All the skeletal system is scanned and bones image with high resolution is created during the PET/CT scanning with sodium fluoride injection. PET/CT with marker 18 F-NaF is applied for diagnosis of bone metastases. Advantages of this method in comparison with conventional skeletal scintigraphy are higher spatial resolution and 3D investigation technique, therefore 18 F-NaF PET/CT makes it possible to detect the smallest bone metastases. Table 1. Comparison characteristic of the methods Investigation method Sensitivity Specificity 1 Planar scintigraphy 54% 88% 2 Planar + SPEKT 92% 100% 3 18 F Fluoride PET 100% 100% 3 Results and Discussion As it is well known, more than 90% of the Positron Emission Tomography is performed with an analog of glucose fluorodeoxyglucose, in which a stable fluorine is replaced by the radioactive one, resulting in ultra-short living radiopharmaceutical of 18-fluorodeoxyglucose 18 FDG [I.G. Zubal et al, Ratio 77
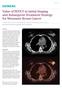
7 F isotope is produced in a cyclotron Cyclone 18/9 (IBA) using the nuclear action 18 O(p,n) 18 F. Niobium target with a volume of 2 ml, filled with water, 18 B.A. Prmantaeva, A. Ryskulov, G. Ryskulova, S.A. Nurkenov images calculated from interictal positron emission tomography and singlephoton emission computed tomography for quantification of the uncouplingof brain metabolismand perfusin in epilepsy, Epilepsia 41 (2000) ]. In this work, we have carried out a research with the PET/CT using the RPC solution [ 18 F] - fluorodeoxyglucose and intravenous maintenance for the diagnosis of complex oncological diseases by PET/CT according to the testimony. Calibration studies were performed for PET/CT machine with 22 Na source. PET scanner was installed and the program Topas-Vicro was studied to eliminate artefacts arising during the work. Any artefact was prevented in the study and definition of the ellipse of head in the studies of brain. TOPAS-VICRO toolkit was studied for smoothing model and experimental noise. Currently we perform a two-dimensional visualization of the original projections (sinogram) or the solution - tomograms. Herewith, one-dimensional graphics are built for any horizontal or vertical section of image. Solving problems on one-dimensional deconvolution is based on such components as onedimensional Fourier and wavelet analysis and filtering of external or internal (tomogram) matrices, two-dimensional Fourier analysis of the tomograms or external images, one-dimensional smoothing and differentiation over the rows or columns of the image. Reconstruction results are saved in the image and binary formats [14,15]. The investigation of patients was performed and corresponding PET/CT pictures of patients were obtained. The analysis and interpretation of these data were performed; appropriate conclusions were obtained and prepared: using ultra-short living tracer radionuclide ( 18 F-FDG), malignant tumours and metastases were detected in the bodies of patients. The resulting radionuclide based B.A. onprmantaeva, 18 F FDG reveals A. bone Ryskulov, metastases (PET-CT G. Ryskulova, picture). S.A. Nurkenov Figure 1. Patient P.P. Bone metastases: in the left acetabulum in the spinous process 4 of Figure - Patient P.P. in the left acetabulum in the spinous the lumbar vertebra. process 4 of the lumbar vertebra. 78 The Control Committee of Medical and Pharmaceutical activity of the Mintry of Healthcare and Social Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan gave ermission as of /6692 to production and use of new RPC - F-NaF..1 Production
8 Production and Use of the Radiopharmaceuticals ( 18 F-FDG and 18 F-NaF)... The Control Committee of Medical and Pharmaceutical activity of the Ministry of Healthcare and Social Development of the Republic of Kazakhstan gave permission as of /6692 to production and use of new RPC - 18 F-NaF. 3.1 Production 18 F isotope is produced in a cyclotron Cyclone 18/9 (IBA) using the nuclear reaction 18 O(p,n) 18 F. Niobium target with a volume of 2 ml, filled with water, enriched by the isotope 18 O, is irradiated by a proton beam with a current of 30 mka on the target. The solution, containing 18 F, is pumped into automated synthesis module Synthera (IBA), with prepared kit for production of Na 18 F (ABX). Ions of 18 F are trapped by column Sep Pak Light Accell Plus QMA, then the column is washed with 0.9% solution of NaCl. At the final stage, 2 ml Na 18 F moves into a sterile pyrogen-free vial through 0.22 micron filter. 3.2 Quality control The ph value of the solution Na 18 F is measured with the use of ph test strips (0-14), which change their color depending on ph-sample. The results are estimated by standard buffer solution with well-known ph. The radiochemical purity of the solution Na 18 F is estimated using thin-layer chromatography (TLC). Stationary phase of TLC is silica gel, mobile phase is mixture - acetonitrile : water (95:5% by volume). The peak of radioactivity is determined by scanning of a silica gel plate with a collimated detector (Minigita, Raytest). Radionuclidic purity is determined by gamma-ray spectrometer ( Mucha, Raytest). A half-life of the isotope 18 F is calculated after measuring the activity of the sample within 20 minutes ( Unidos 4, PTW Freiburg). 3.3 Procedure for examination A small amount of slightly radioactive substance ( 18 F-NaF) is injected intravenously to the patient. The scanning on PET/CT is started after 30 minutes, it takes about 20 minutes. And contrast medium is not injected. The dose for an adult is MBq (5-10 mci). The higher activity (370 MBq, 10 mci) can be used to obese patients. The radionuclide activity for children must be calculated on the basis of weight (2.22 MBq/kg, 0.06 mci/kg) with the use of minimum and maximum activity from 18.5 to 185 MBq (0.5 to 5 mci). The 19 examinations on PET/CT with the use of new RPC 18 F-NaF were carried out in the Department of Radionuclide diagnostics. All the patients were referred with the diagnosis: Breast cancer, prostate cancer, bone metastases without primary lesion, agnogenic bone pains. The 10 patients were examined on PET/CT with 18 F-FDG and the 9 patients were examined on gamma camera with the use of Tc-99m. It was revealed by investigation results: metastases in bones of skeleton are confirmed in 12 (63.1%) patients; degenerative or dystrophic changes of skeletal system are diagnosed in 7 (36.8%) patients. New pathological focuses were revealed in 5 (41.6%) of 12 patients. 79
9 without primary lesion, agnogenic bone pains. The 10 patients were examined on PET/CT with 18 F-FDG and the 9 patients were examined on gamma camera with the use of Tc-99m. It was revealed by investigation results: metastases in bones of skeleton are confirmed in 12 (63.1%) patients; degenerative or dystrophic changes of skeletal system are diagnosed in 7 (36.8%) patients. New pathological focuses were revealed in 5 (41.6%) of 12 patients. This is our first experience of production and application of new RPC for the diagnosis of bone lesions. However, even small amount of studies allowed us to assess the sensitivity and specificity of the drug in comparison with other RPCs. B.A. Prmantaeva, A. Ryskulov, G. Ryskulova, S.A. Nurkenov This is our first experience of production and application of new RPC for the diagnosis of bone lesions. However, even small amount of studies allowed us to assess the sensitivity and specificity of the drug in comparison with other RPCs. 4 Conclusions Thus, we have performed: calibration study of PET/CT machine with 22 Na source; installation of PET/CT scanner and studying the Topas-Vicro program to avoid artefacts arising at work; prevent any artefacts in the study and definition of a head ellipse in the study of a brain; malignant tumours and metastases in the bodies of patients were identified by applying labeled ultra-short living radionuclides ( 18 F-FDG) [16, 17]. Studying literary sources and relying on our first experience, we can conclude, that examinations on PET/CT with 18 F-sodium fluoride (NaF) have a number of advantages in comparison with conventional 99mTc on SPECT and PET/CT with 18 F-FDG, such as: 80 the higher accuracy in detection of osteolytic and osteoblastic metastases; differentiation between benign and malignant tumours; 9
10 Production and Use of the Radiopharmaceuticals ( 18 F-FDG and 18 F-NaF)... differentiation of degenerative and dystrophic changes from malignant; the higher sensitivity in comparison with 99mTc and 18 F-FDG; the higher specificity in comparison with 99mTc and 18 F-FDG; precise anatomic information, received from CT-component; three-dimensional and whole body scanning, similar to investigations on PET/CT with FDG; RPC 18 F-sodium fluoride (NaF) is easily available for use; the value of the achievements in the field of nuclear medicine is identifying the diseases not diagnosed by other methods at an early stage when the cure is possible, as well as improvement of the condition and extension of lives of seriously ill patients; in most cases, the use of radioisotope diagnosis helps to save lives of patients with such complex cancer as tumours of various etiologies including brain cancer, lymphoma, leukaemia, etc., when other means are not effective [18, 19]. References [1] H. Jones, Physics Radiology (Atomizdat, 1965). [2] I.A. Pereslegin, Yu.H. Sarkisian, Clinical Radiology IzdAT, Moscow (2000) 1973). [3] V.Yu. Baranov (Ed.), Isotopes: Properties, Production and Application (IzdAT, Moscow, 2000). [4] I.N. Bekman, Lectures Nuclear medicine. [5] F.M. Lyass, G.A. Zubovsky, Methodological Foundations of Gamma Topographic Studies (Medicine, Moscow, 1983). [6] O.S. Levin, I.A. Amosov, V.V. Potsybina, I.G. Smolentseva, D.Yu. Olyunin, Journal of Neurology XXXVII (2005) [7] O.E. Shlyginoy, A.R. Borisenko, Nuclear Medicine, Part I, (Sansam, Almaty, 2006). [8] V.I. Ivanov, Dosimetry of Ionizing Radiation (Atomizdat, 1964). [9] B.V. Zabrodin, V.N. Lomas, A.V.Motorny, Radionuclide Visualization: Manual (St. Petersburg State Polytechnic University, 2006). [10] K.D. Kalantarov, S.D. Kalashnikov, V.A. Kostylev, S.G. Kutuzov, A.E. Markov, B.Ya. Narkevich, V.V. Ponomarev, L.D. Soshin, Apparatus and Methods of Nuclear Medicine in Medicine (CJSC VNIIMP-VITA, New York, 2002). [11] K.V. Kotegov, O.N. Pavlov, V.P. Shvedov, Technetium (Atomizdat, 1965). [12] N.A. Figurovsky, The Discovery of Elements and the Origin of Their Names (Nauka, Moscow, 1970). [13] Yu.D. Tretyakov, L.I. Martynenko, A.N. Grigoriev, A.Yu. Tsivadze, Inorganic Chemistry, vol. 1, 2 (Chemistry, Moscow, 2001). 81
11 B.A. Prmantaeva, A. Ryskulov, G. Ryskulova, S.A. Nurkenov [14] M.A. Bagarodskaya, G.E. Kodina, Chemical Technology of Radiopharmaceutical (Moscow, 2010). [15] SEC EPI BPH NNC RK, Regulations on obtaining 99 mtc radiopharmaceutical. [16] F.D. Grant, F.H. Fahey, A.B. Packard, R.T. Davis, A. Alavi, S.T. Treves, J. Nucl. Med. 38 (2008) [17] H. Schirrmeister, et al., J. Nucl. Med. 40 (1999) [18] H. Schirrmeister, et al., J. Clin. Oncol. 17 (1999) [19] H. Schirrmeister, et al., J. Nucl. Med. 42 (2001)
Nuclear Medicine and PET. D. J. McMahon rev cewood
 Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
Nuclear Medicine and PET D. J. McMahon 150504 rev cewood 2018-02-15 Key Points Nuclear Medicine and PET: Imaging: Understand how Nuc Med & PET differ from Radiography & CT by the source of radiation. Be
45 Hr PET Registry Review Course
 45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
45 HR PET/CT REGISTRY REVIEW COURSE Course Control Document Timothy K. Marshel, MBA, R.T. (R), (N)(CT)(MR)(NCT)(PET)(CNMT) The PET/CT Training Institute, Inc. SNMMI-TS 028600-028632 45hr CEH s Voice Credits
PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5)
 PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5) 1. (a) A radioisotope is an isotope that is unstable and will emit particles from the nucleus
PHYSICS 2: HSC COURSE 2 nd edition (Andriessen et al) CHAPTER 20 Radioactivity as a diagnostic tool (pages 394-5) 1. (a) A radioisotope is an isotope that is unstable and will emit particles from the nucleus
Nuclear Medicine: Manuals. Nuclear Medicine. Nuclear imaging. Emission imaging: study types. Bone scintigraphy - technique
 Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Nuclear Medicine - Unsealed radioactive preparations the tracer mixes with the patients body fluids on a molecular level (e.g. after intravenous injection) - 3 main fields: - In vitro : measuring concentrations
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes
 Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
Medical imaging X-ray, CT, MRI, scintigraphy, SPECT, PET Györgyi Műzes Semmelweis University, 2nd Dept. of Medicine Medical imaging: definition technical process of creating visual representations about
Molecular Imaging and the Brain
 Molecular imaging technologies are playing an important role in neuroimaging, a branch of medical imaging, by providing a window into the living brain. Where CT and conventional MR imaging provide important
Molecular imaging technologies are playing an important role in neuroimaging, a branch of medical imaging, by providing a window into the living brain. Where CT and conventional MR imaging provide important
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry
 Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
Option D: Medicinal Chemistry Basics - unstable radioactive nuclei emit radiation in the form of smaller particles alpha, beta, positron, proton, neutron, & gamma are all used in nuclear medicine unstable
Bone Metastasis. Patient Management with PET/CT
 Bone Metastasis Patient Management with PET/CT Bone Metastasis Patient Management with PET/CT OVERVIEW Bone Metastasis is a process in which cancer cells from the original or primary tumor site break away
Bone Metastasis Patient Management with PET/CT Bone Metastasis Patient Management with PET/CT OVERVIEW Bone Metastasis is a process in which cancer cells from the original or primary tumor site break away
ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER
 ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER Bro. Dr. Collie Miller IARC/WHO Based on trends in the incidence of cancer, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and WHO
ADVANCES IN RADIATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER Bro. Dr. Collie Miller IARC/WHO Based on trends in the incidence of cancer, the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) and WHO
Molecular Imaging and Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Cancer Cancer causes one in every four deaths in the United States, second only to heart disease. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than 512,000
Molecular Imaging and Cancer Cancer causes one in every four deaths in the United States, second only to heart disease. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, more than 512,000
Radionuclides in Medical Imaging. Danielle Wilson
 Radionuclides in Medical Imaging Danielle Wilson Outline Definitions History and development Radionuclide applications & techniques in imaging Conclusion Definition #1 : Radionuclide An unstable nucleus
Radionuclides in Medical Imaging Danielle Wilson Outline Definitions History and development Radionuclide applications & techniques in imaging Conclusion Definition #1 : Radionuclide An unstable nucleus
Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* PET/CT Imaging
 Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* PET/CT Imaging for Prostate Cancer Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* ( 18 F NaF) PET/CT Imaging of Bone Metastases in Prostate Cancer About Prostate Cancer According to the
Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* PET/CT Imaging for Prostate Cancer Sodium Fluoride F 18 Injection* ( 18 F NaF) PET/CT Imaging of Bone Metastases in Prostate Cancer About Prostate Cancer According to the
Mobile PET Center Project
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Mobile PET Center Project To cite this article: O Ryzhikova et al 2017 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 784 012051 View the article online for updates and enhancements.
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Mobile PET Center Project To cite this article: O Ryzhikova et al 2017 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 784 012051 View the article online for updates and enhancements.
OTHER NON-CARDIAC USES OF Tc-99m CARDIAC AGENTS Tc-99m Sestamibi for parathyroid imaging, breast tumor imaging, and imaging of other malignant tumors.
 DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
DEFINITION OF CARDIAC RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL: A radioactive drug which, when administered for purpose of diagnosis of heart disease, typically elicits no physiological response from the patient. Even though
Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate)
 Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate) Overview Ga-68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (sstr2). It binds to cells that express
Austin Radiological Association Ga-68 NETSPOT (Ga-68 dotatate) Overview Ga-68 dotatate binds to somatostatin receptors, with highest affinity for subtype 2 receptors (sstr2). It binds to cells that express
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT)
 Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) What is Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Scanning? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare for
Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) What is Positron Emission Tomography Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Scanning? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare for
Whole body F-18 sodium fluoride PET/CT in the detection of bone metastases in patients with known malignancies: A pictorial review
 Whole body F-18 sodium fluoride PET/CT in the detection of bone metastases in patients with known malignancies: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1196 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Whole body F-18 sodium fluoride PET/CT in the detection of bone metastases in patients with known malignancies: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1196 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF) Overview Indication Sodium Fluoride F18 injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure PET SODIUM FLUORIDE BONE SCAN (F-18 NaF) Overview Indication Sodium Fluoride F18 injection is a radioactive diagnostic agent for positron emission
Medical Use of Radioisotopes
 Medical Use of Radioisotopes Therapy Radioisotopes prove to be useful in the application of brachytherapy, the procedure for using temporary irradiation close to the area of disease (i.e. cancer) 10% Medical
Medical Use of Radioisotopes Therapy Radioisotopes prove to be useful in the application of brachytherapy, the procedure for using temporary irradiation close to the area of disease (i.e. cancer) 10% Medical
Optimization of Production and Synthesis of the Radiopharmaceutical 18 F-FET in Kazakhstan for the Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
 NUCLEAR THEORY, Vol. 35 (2016) eds. M. Gaidarov, N. Minkov, Heron Press, Sofia Optimization of Production and Synthesis of the Radiopharmaceutical 18 F-FET in Kazakhstan for the Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
NUCLEAR THEORY, Vol. 35 (2016) eds. M. Gaidarov, N. Minkov, Heron Press, Sofia Optimization of Production and Synthesis of the Radiopharmaceutical 18 F-FET in Kazakhstan for the Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS (DTPA)
 CMR Group of Companies info@isotope-cmr.com www.isotope-cmr.com SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS (DTPA) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PENTATECH lyophilized powder for injection (DTPA) 2. QUALITATIVE
CMR Group of Companies info@isotope-cmr.com www.isotope-cmr.com SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS (DTPA) 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PENTATECH lyophilized powder for injection (DTPA) 2. QUALITATIVE
Using PET/CT in Prostate Cancer
 Using PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Legal Disclaimer These materials were prepared in good faith by MITA as a service to the profession and are believed to be reliable based on current scientific literature.
Using PET/CT in Prostate Cancer Legal Disclaimer These materials were prepared in good faith by MITA as a service to the profession and are believed to be reliable based on current scientific literature.
CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM
 Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 HU-RO-DOCS CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM Part 3 Modern imaging methods SPECT, PET, nmri History of Nuclear Medicine Starts with the invention of the X-ray 1946: radioactive
Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 HU-RO-DOCS CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM Part 3 Modern imaging methods SPECT, PET, nmri History of Nuclear Medicine Starts with the invention of the X-ray 1946: radioactive
Basics of nuclear medicine
 Basics of nuclear medicine Prof. dr. Davor Eterović Prof. dr. Vinko Marković Radioisotopes are used both in diagnostics and in therapy Diagnostics gamma emitters are used since gamma rays can penetrate
Basics of nuclear medicine Prof. dr. Davor Eterović Prof. dr. Vinko Marković Radioisotopes are used both in diagnostics and in therapy Diagnostics gamma emitters are used since gamma rays can penetrate
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors
 Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
Bone PET/MRI : Diagnostic yield in bone metastases and malignant primitive bone tumors Lars Stegger, Benjamin Noto Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to
POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPHY (PET)
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Radiology Policy Number: V-27 Effective Date: 08/27/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Radiology Policy Number: V-27 Effective Date: 08/27/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility
 Egyptian J. Nucl. Med., Vol. 8, No. 2, December 2013 1 Editorial Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility Taalab, Kh; and Mohsen, Z Department of Nuclear Medicine, International Medical Center;
Egyptian J. Nucl. Med., Vol. 8, No. 2, December 2013 1 Editorial Radiation Exposure to Staff Using PET/CT Facility Taalab, Kh; and Mohsen, Z Department of Nuclear Medicine, International Medical Center;
Nuclear Medicine in the Diabetic Foot
 26.11.2015, Uniklinik Balgrist Nuclear Medicine in the Diabetic Foot Martin Hüllner Nuklearmedizin und Neuroradiologie, USZ / UZH Outline A. Imaging modalities brief technical overview B. Nuclear medicine
26.11.2015, Uniklinik Balgrist Nuclear Medicine in the Diabetic Foot Martin Hüllner Nuklearmedizin und Neuroradiologie, USZ / UZH Outline A. Imaging modalities brief technical overview B. Nuclear medicine
Isotopes in Functional Cancer Imaging
 Seeing and Believing: i Medical Isotopes in Functional Cancer Imaging François Bénard, MD, FRCPC BCCancer Cancer Agency and University of British Columbia Nuclear Medicine 101 A radioactive atom is produced
Seeing and Believing: i Medical Isotopes in Functional Cancer Imaging François Bénard, MD, FRCPC BCCancer Cancer Agency and University of British Columbia Nuclear Medicine 101 A radioactive atom is produced
Radiopharmacy. Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL. CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı
 Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear Medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the use of radionuclides in the study and the diagnosis of diseases.
Prof. Dr. Çetin ÖNSEL CTF Nükleer Tıp Anabilim Dalı What is Nuclear Medicine? Nuclear Medicine is the branch of medicine concerned with the use of radionuclides in the study and the diagnosis of diseases.
Quantitative Theranostics in Nuclear Medicine
 Quantitative Theranostics in Nuclear Medicine M. Lassmann Klinik und Poliklinik für Nuklearmedizin Direktor: Prof. Dr. A. Buck Contents What is Theranostics? Potential Targets Basic Principles of Quantitative
Quantitative Theranostics in Nuclear Medicine M. Lassmann Klinik und Poliklinik für Nuklearmedizin Direktor: Prof. Dr. A. Buck Contents What is Theranostics? Potential Targets Basic Principles of Quantitative
Cardiac Imaging. Kimberly Delcour, DO, FACC. Mahi Ashwath, MD, FACC, FASE. Director, Cardiac CT. Director, Cardiac MRI
 Cardiac Imaging Kimberly Delcour, DO, FACC Director, Cardiac CT Mahi Ashwath, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Cardiac MRI Cardiac Imaging Discuss the clinical applications of and indications for: Cardiac CT Nuclear
Cardiac Imaging Kimberly Delcour, DO, FACC Director, Cardiac CT Mahi Ashwath, MD, FACC, FASE Director, Cardiac MRI Cardiac Imaging Discuss the clinical applications of and indications for: Cardiac CT Nuclear
GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION
 511945-0903 September 2003 USA Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging 331 Treble Cove Road N. Billerica, MA 01862 USA GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE DESCRIPTION: Gallium Citrate Ga 67
511945-0903 September 2003 USA Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging 331 Treble Cove Road N. Billerica, MA 01862 USA GALLIUM CITRATE Ga 67 INJECTION FOR DIAGNOSTIC USE DESCRIPTION: Gallium Citrate Ga 67
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours. Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany
 PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
PET-MRI in malignant bone tumours Lars Stegger Department of Nuclear Medicine University Hospital Münster, Germany Content From PET to PET/MRI General considerations Bone metastases Primary bone tumours
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
 1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE a) Axumin is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE a) Axumin is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) in men with suspected prostate cancer recurrence based on elevated blood prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels following
Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153
 APPROVED BY: Z. Yang Page 1 of 5 Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153 Primary Indications: Rationale: To treat bone pain resulting from osteoblastic metastases as defined by bone scan.
APPROVED BY: Z. Yang Page 1 of 5 Palliative treatment of bone metastases with samarium-153 Primary Indications: Rationale: To treat bone pain resulting from osteoblastic metastases as defined by bone scan.
Principles of nuclear metabolic imaging. Prof. Dr. Alex Maes AZ Groeninge Kortrijk and KULeuven Belgium
 Principles of nuclear metabolic imaging Prof. Dr. Alex Maes AZ Groeninge Kortrijk and KULeuven Belgium I. Molecular imaging probes A. Introduction - Chemical disturbances will precede anatomical abnormalities
Principles of nuclear metabolic imaging Prof. Dr. Alex Maes AZ Groeninge Kortrijk and KULeuven Belgium I. Molecular imaging probes A. Introduction - Chemical disturbances will precede anatomical abnormalities
Appendix A: Introduction to Imaging Modalities for Which Data Were Collected in the 2017 Imaging Inventory
 Appendix A: Introduction to Imaging Modalities for Which Data Were Collected in the 207 Imaging Inventory Computed Tomography Computed tomography (CT) employs X-rays as a source of ionizing radiation,
Appendix A: Introduction to Imaging Modalities for Which Data Were Collected in the 207 Imaging Inventory Computed Tomography Computed tomography (CT) employs X-rays as a source of ionizing radiation,
The Use of PET Scanning in Urologic Oncology
 The Use of PET Scanning in Urologic Oncology Dr Nicholas C. Buchan Uro-oncology Fellow 1 2 Aims To understand the basic concepts underlying PET scanning. Understand the emerging role of PET Scanning for
The Use of PET Scanning in Urologic Oncology Dr Nicholas C. Buchan Uro-oncology Fellow 1 2 Aims To understand the basic concepts underlying PET scanning. Understand the emerging role of PET Scanning for
COMENIUS-Project: SM&CLIL Radiation & Medicine
 Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to create images of the human body (or parts thereof) for clinical purposes. Thanks to modern mathematics and computer technology, medical imaging
Medical imaging refers to the techniques and processes used to create images of the human body (or parts thereof) for clinical purposes. Thanks to modern mathematics and computer technology, medical imaging
Joint Comments on Positron Emission Tomography (NaF-18) to Identify Bone Metastasis of Cancer (CAG-00065R1)
 July 2, 2009 Tamara Syrek Jensen, J.D. Acting Director, Coverage and Analysis Group Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services 7500 Security Blvd., Mail Stop C1-09-06 Baltimore, MD 21244 Re: Joint Comments
July 2, 2009 Tamara Syrek Jensen, J.D. Acting Director, Coverage and Analysis Group Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services 7500 Security Blvd., Mail Stop C1-09-06 Baltimore, MD 21244 Re: Joint Comments
Core SPC for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) March 2005
 Core SPC for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) March 2005 This FDG Core SPC has been prepared on the basis, and taking into account the available published scientific literature dated from more than 10 years. Then
Core SPC for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) March 2005 This FDG Core SPC has been prepared on the basis, and taking into account the available published scientific literature dated from more than 10 years. Then
Chapter 10. Summary, conclusions and future perspectives
 Chapter 10 Summary, conclusions and future perspectives 10.1 SUMMARY In this thesis, a new tumor imaging tracer in nuclear medicine is studied. This 123 tracer, L-3-[ I]Iodo-alpha-methyl-tyrosine (IMT),
Chapter 10 Summary, conclusions and future perspectives 10.1 SUMMARY In this thesis, a new tumor imaging tracer in nuclear medicine is studied. This 123 tracer, L-3-[ I]Iodo-alpha-methyl-tyrosine (IMT),
Typical PET Image. Elevated uptake of FDG (related to metabolism) Lung cancer example: But where exactly is it located?
 Typical PET Image Elevated uptake of FDG (related to metabolism) Lung cancer example: But where exactly is it located? PET/CT Oncology Imaging Anatometabolic fusion images are useful in the management
Typical PET Image Elevated uptake of FDG (related to metabolism) Lung cancer example: But where exactly is it located? PET/CT Oncology Imaging Anatometabolic fusion images are useful in the management
Cardiac Imaging Tests
 Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer
 Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
Molecular Imaging and Breast Cancer Breast cancer forms in tissues of the breast usually in the ducts, tubes that carry milk to the nipple, and lobules, the glands that make milk. It occurs in both men
General Nuclear Medicine
 General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
General Nuclear Medicine What is General Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles. Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine NUCLEAR MEDICINE Application of the radioactive isotopes in the diagnostics and in the
Itroduction to the Nuclear Medicine: biophysics and basic principles Zámbó Katalin Department of Nuclear Medicine NUCLEAR MEDICINE Application of the radioactive isotopes in the diagnostics and in the
F NaF PET/CT in the Evaluation of Skeletal Malignancy
 F NaF PET/CT in the Evaluation of Skeletal Malignancy Andrei Iagaru, MD September 26, 2013 School of of Medicine Ø Introduction Ø F NaF PET/CT in Primary Bone Cancers Ø F NaF PET/CT in Bone Metastases
F NaF PET/CT in the Evaluation of Skeletal Malignancy Andrei Iagaru, MD September 26, 2013 School of of Medicine Ø Introduction Ø F NaF PET/CT in Primary Bone Cancers Ø F NaF PET/CT in Bone Metastases
Theragnostics for bone metastases. Glenn Flux Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK
 Theragnostics for bone metastases Glenn Flux Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK NPL 2015 Ra-223 Biodistribution & dosimetry Ra-223: 11.4 days half-life, range of 100 µm Six
Theragnostics for bone metastases Glenn Flux Royal Marsden Hospital & Institute of Cancer Research Sutton UK NPL 2015 Ra-223 Biodistribution & dosimetry Ra-223: 11.4 days half-life, range of 100 µm Six
Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals
 Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals 1. Generator & Reactors 2. Cyclotrons & PET tracer 3. Quality control 4. Renal 5. GIT 6. CNS & Psychiatrics 7. Tumor Diagnosis & Treatment 8. Bones & joints 9. Thyroid
Radionuclide & Radiopharmaceuticals 1. Generator & Reactors 2. Cyclotrons & PET tracer 3. Quality control 4. Renal 5. GIT 6. CNS & Psychiatrics 7. Tumor Diagnosis & Treatment 8. Bones & joints 9. Thyroid
Page 1 of CONTRAINDICATIONS None (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AXUMIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AXUMIN. AXUMIN (fluciclovine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AXUMIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AXUMIN. AXUMIN (fluciclovine
Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region. Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine
 Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scintigraphy Parathyroid scintigraphy F18-FDG PET examinations in head and neck cancer
Nuclear Medicine Head and Neck Region Bán Zsuzsanna, MD University of Pécs, Department of Nuclear Medicine Thyroid scintigraphy Parathyroid scintigraphy F18-FDG PET examinations in head and neck cancer
Department of Nuclear Medicine with Positron Emission Tomography
 (PET) Unit [1] Contact information: Registration: +48 41 367 4850 Main office: +48 41 367 4860 Fax: +48 41 367 4887 e-mail: zmnsco@onkol.kielce.pl [2] Head of the Department: Professor Janusz Braziewicz
(PET) Unit [1] Contact information: Registration: +48 41 367 4850 Main office: +48 41 367 4860 Fax: +48 41 367 4887 e-mail: zmnsco@onkol.kielce.pl [2] Head of the Department: Professor Janusz Braziewicz
KEYWORDS: nuclear medicine; gamma camera; radiopharmaceutical activities.
 Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in the First Six Months of the Gamma Camera Use in the Clinical Center of Montenegro - Podgorica Nevenka Antovic
Radiopharmaceutical Activities Administered for Diagnostic Procedures in Nuclear Medicine in the First Six Months of the Gamma Camera Use in the Clinical Center of Montenegro - Podgorica Nevenka Antovic
Value of PET/CT in Initial Staging and Subsequent Treatment Strategy for Metastatic Breast Cancer
 Case Study Value of PET/CT in Initial Staging and Subsequent Treatment Strategy for Metastatic Breast Cancer By Dustin Osborne, PhD, and Yong Bradley, MD, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA Data
Case Study Value of PET/CT in Initial Staging and Subsequent Treatment Strategy for Metastatic Breast Cancer By Dustin Osborne, PhD, and Yong Bradley, MD, University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, USA Data
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure BONE MINERAL STUDY (Tc-99m-MDP, Tc-99m-HMDP)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure BONE MINERAL STUDY (Tc-99m-MDP, Tc-99m-HMDP) Overview The Bone Mineral Study, with either Tc-99m-MDP or Tc-99m-HMDP, depicts the distribution
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure BONE MINERAL STUDY (Tc-99m-MDP, Tc-99m-HMDP) Overview The Bone Mineral Study, with either Tc-99m-MDP or Tc-99m-HMDP, depicts the distribution
1. OVERVIEW 2. RADIOPHARMACEUTICAL UTILIZED
 1. OVERVIEW F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Injection is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in the following settings: a) Oncology: For assessment of abnormal glucose metabolism to assist
1. OVERVIEW F-18 Fluorodeoxyglucose Injection is indicated for positron emission tomography (PET) imaging in the following settings: a) Oncology: For assessment of abnormal glucose metabolism to assist
An investigation of the effect of ionising radiation on nurses and their patients during dialysis
 International Scholars Journals African Journal of Nursing and Midwifery ISSN 2198-4638 Vol. 2 (7), pp. 548-552, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
International Scholars Journals African Journal of Nursing and Midwifery ISSN 2198-4638 Vol. 2 (7), pp. 548-552, September, 2015. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International
Description of the consecutive stages (which took place from December 2002 to July 2003)
 Radiation Protection Issues in a PET/CT Installation M. Coronado 1, R. Plaza 2, R. Couto 1, MD. Marin 1, C. Huerga 2, J. Coya 1, LM Martin Curto 1, M. Téllez de Cepeda 2 1 Servicio de Medicina Nuclear,
Radiation Protection Issues in a PET/CT Installation M. Coronado 1, R. Plaza 2, R. Couto 1, MD. Marin 1, C. Huerga 2, J. Coya 1, LM Martin Curto 1, M. Téllez de Cepeda 2 1 Servicio de Medicina Nuclear,
of Bone Pain in Children
 Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Pictorial Essay Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Pictorial Essay Laura. rubach 1 Susan. onnolly 1 Edwin L. Palmer III 2 rubach L, onnolly S, Palmer EL III Keywords:
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Pictorial Essay Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging Pictorial Essay Laura. rubach 1 Susan. onnolly 1 Edwin L. Palmer III 2 rubach L, onnolly S, Palmer EL III Keywords:
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 TechneScan Gluceptate Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
TechneScan Gluceptate Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions. Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Cardiac Nuclear Medicine
 Cardiac Nuclear Medicine What is Cardiac Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
Cardiac Nuclear Medicine What is Cardiac Nuclear Medicine? What are some common uses of the procedure? How should I prepare? What does the equipment look like? How does the procedure work? How is the procedure
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 78300 Bone and/or joint imaging; limited area 78305 multiple areas 78306 whole body 78315 three phase study
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 78300 Bone and/or joint imaging; limited area 78305 multiple areas 78306 whole body 78315 three phase study
Physical Bases : Which Isotopes?
 Physical Bases : Which Isotopes? S. Gnesin Institute of Radiation Physics, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland 1/53 Theranostic Bruxelles, 2 Octobrer 2017 Theranostic : use of diagnostic
Physical Bases : Which Isotopes? S. Gnesin Institute of Radiation Physics, Lausanne University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland 1/53 Theranostic Bruxelles, 2 Octobrer 2017 Theranostic : use of diagnostic
RADIATION MONITORING EXPERIMENT USING THERMOLUMINESCENT DOSIMETER FOR THE TR 19 CYCLOTRON AREA IN NUCLEAR RESEARCH INSTITUTE
 RADIATION MONITORING EXPERIMENT USING THERMOLUMINESCENT DOSIMETER FOR THE TR 19 CYCLOTRON AREA IN NUCLEAR RESEARCH INSTITUTE A. STOCHIOIU, L. CRACIUN, F. MIHAI, I. TUDOR Horia Hulubei National Institute
RADIATION MONITORING EXPERIMENT USING THERMOLUMINESCENT DOSIMETER FOR THE TR 19 CYCLOTRON AREA IN NUCLEAR RESEARCH INSTITUTE A. STOCHIOIU, L. CRACIUN, F. MIHAI, I. TUDOR Horia Hulubei National Institute
Quantitation of Cerebral Glucose Utilization using the Arterial Input Function or the Standardized Uptake Value (SUV)
 Quantitation of Cerebral Glucose Utilization using the Arterial Input Function or the Standardized Uptake Value (SUV) Brian R. Moyer BRMoyer & Associates, LLC, Amherst, NH 03031 http://www.brmassocllc-org.com/
Quantitation of Cerebral Glucose Utilization using the Arterial Input Function or the Standardized Uptake Value (SUV) Brian R. Moyer BRMoyer & Associates, LLC, Amherst, NH 03031 http://www.brmassocllc-org.com/
Introduction to the Course and the Techniques. Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology
 Introduction to the Course and the Techniques Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology (jralger@ucla.edu) CTSI Neuroimaging April 2014 Rationale for the Course
Introduction to the Course and the Techniques Jeffry R. Alger, PhD Ahmanson-Lovelace Brain Mapping Center Department of Neurology (jralger@ucla.edu) CTSI Neuroimaging April 2014 Rationale for the Course
Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET
 Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET M. Soret, C. Riddell, S. Hapdey, and I. Buvat Abstract-- The influence of tumor diameter, tumor-tobackground activity ratio, attenuation, spatial resolution,
Biases affecting tumor uptake measurements in FDG-PET M. Soret, C. Riddell, S. Hapdey, and I. Buvat Abstract-- The influence of tumor diameter, tumor-tobackground activity ratio, attenuation, spatial resolution,
María del Pilar Garrido Ruiz Teresa Mendoza Dobaño Cristian Jesús Lucena Morales
 María del Pilar Garrido Ruiz Teresa Mendoza Dobaño Cristian Jesús Lucena Morales Index 1. Introduction. 2. Physical principles: annihilation reaction. 3. PET image creation. 4. Advantages of PET use. 5.
María del Pilar Garrido Ruiz Teresa Mendoza Dobaño Cristian Jesús Lucena Morales Index 1. Introduction. 2. Physical principles: annihilation reaction. 3. PET image creation. 4. Advantages of PET use. 5.
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs)
 Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs) Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Migration Study demonstrates the distribution
Austin Radiological Association Nuclear Medicine Procedure WHITE BLOOD CELL MIGRATION STUDY (In-111-WBCs, Tc-99m-HMPAO-WBCs) Overview Indications The White Blood Cell Migration Study demonstrates the distribution
Imaging Core Laboratory Standard Operating Procedure
 Imaging Core Laboratory Standard Operating Procedure Patient Preparation and FDG Administration Procedure for ACRIN FDG-PET Scans 1.0 PURPOSE To outline the procedure for patient preparation and for 18
Imaging Core Laboratory Standard Operating Procedure Patient Preparation and FDG Administration Procedure for ACRIN FDG-PET Scans 1.0 PURPOSE To outline the procedure for patient preparation and for 18
Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai.
 Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai. Topics covered Lymphomas including Burkitts Pediatric solid tumors (non CNS) Musculoskeletal Ewings & osteosarcoma. Neuroblastomas Nasopharyngeal carcinomas
Dr Sneha Shah Tata Memorial Hospital, Mumbai. Topics covered Lymphomas including Burkitts Pediatric solid tumors (non CNS) Musculoskeletal Ewings & osteosarcoma. Neuroblastomas Nasopharyngeal carcinomas
Prostate Cancer and PSMA:
 Prostate Cancer and PSMA: The Clinical Perspective from Liverpool. Dr. Christopher Mayes. Professor Sobhan Vinjamuri. Department of Nuclear Medicine Royal Liverpool University Hospital (BSUR 2016 Plymouth)
Prostate Cancer and PSMA: The Clinical Perspective from Liverpool. Dr. Christopher Mayes. Professor Sobhan Vinjamuri. Department of Nuclear Medicine Royal Liverpool University Hospital (BSUR 2016 Plymouth)
Core Summary of Product Characteristics for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F)
 Core Summary of Product Characteristics for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) This fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) Core SmPC has been prepared on the basis, and taking into account the available published scientific literature
Core Summary of Product Characteristics for Fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) This fludeoxyglucose ( 18 F) Core SmPC has been prepared on the basis, and taking into account the available published scientific literature
Ga68 Imaging. Roland HUSTINX Division of Nuclear Medicine and Oncologic Imaging Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Liège Belgium
 Ga68 Imaging Roland HUSTINX Division of Nuclear Medicine and Oncologic Imaging Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Liège Belgium 68 Ga Produced by a 68 Ge/ 68 Ga generator Decays by positron emission
Ga68 Imaging Roland HUSTINX Division of Nuclear Medicine and Oncologic Imaging Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Liège Belgium 68 Ga Produced by a 68 Ge/ 68 Ga generator Decays by positron emission
Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT)
 Scan for mobile link. Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Positron emission tomography (PET) uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera and
Scan for mobile link. Positron Emission Tomography - Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Positron emission tomography (PET) uses small amounts of radioactive materials called radiotracers, a special camera and
CARDIAC PET PERFUSION IMAGING with RUBIDIUM-82
 CARDIAC PET PERFUSION IMAGING with RUBIDIUM-82 Pr Denis AGOSTINI Président du Groupe de Cardiologie Nucléaire et IRM CHU Caen Bordeaux 2006 Cardiac Perfusion-Metabolism Mismatch with PET Cumulative Survival
CARDIAC PET PERFUSION IMAGING with RUBIDIUM-82 Pr Denis AGOSTINI Président du Groupe de Cardiologie Nucléaire et IRM CHU Caen Bordeaux 2006 Cardiac Perfusion-Metabolism Mismatch with PET Cumulative Survival
An Introduction to PET Imaging in Oncology
 January 2002 An Introduction to PET Imaging in Oncology Janet McLaren, Harvard Medical School Year III Basics of PET Principle of Physiologic Imaging: Allows in vivo visualization of structures by their
January 2002 An Introduction to PET Imaging in Oncology Janet McLaren, Harvard Medical School Year III Basics of PET Principle of Physiologic Imaging: Allows in vivo visualization of structures by their
1 Introduction. 2 Materials and methods. LI Na 1 LI Yaming 1,* YANG Chunming 2 LI Xuena 1 YIN Yafu 1 ZHOU Jiumao 1
 Nuclear Science and Techniques 20 (2009) 354 358 18 F-FDG PET/CT in diagnosis of skeletal metastases LI Na 1 LI Yaming 1,* YANG Chunming 2 LI Xuena 1 YIN Yafu 1 ZHOU Jiumao 1 1 Department of Nuclear Medicine,
Nuclear Science and Techniques 20 (2009) 354 358 18 F-FDG PET/CT in diagnosis of skeletal metastases LI Na 1 LI Yaming 1,* YANG Chunming 2 LI Xuena 1 YIN Yafu 1 ZHOU Jiumao 1 1 Department of Nuclear Medicine,
Philips Gemini TF camera (Philips, Cleveland OH), with an 18 cm coronal and a 57 cm axial
 Supplement Material 18 F-DCFBC PET/CT Imaging Protocol 18 F-DCFBC PET/CT imaging was performed on a 3D time of flight (TOF) mode Philips Gemini TF camera (Philips, Cleveland OH), with an 18 cm coronal
Supplement Material 18 F-DCFBC PET/CT Imaging Protocol 18 F-DCFBC PET/CT imaging was performed on a 3D time of flight (TOF) mode Philips Gemini TF camera (Philips, Cleveland OH), with an 18 cm coronal
SPECT-CT: Τι πρέπει να γνωρίζει ο Καρδιολόγος
 SPECT-CT: Τι πρέπει να γνωρίζει ο Καρδιολόγος Δρ Αναστασία Κίτσιου Διευθύντρια, Καρδιολογική Κλινική, Σισμανόγλειο ΓΝΑ Chair, Education Committee, Section on Nuclear Cardiology & Cardiac CT, EACVI, ESC
SPECT-CT: Τι πρέπει να γνωρίζει ο Καρδιολόγος Δρ Αναστασία Κίτσιου Διευθύντρια, Καρδιολογική Κλινική, Σισμανόγλειο ΓΝΑ Chair, Education Committee, Section on Nuclear Cardiology & Cardiac CT, EACVI, ESC
Fellows on this rotation are expected to attend nuclear conferences and multimodality imaging conference.
 Rotation: Imaging 1 Imaging 1 provides COCATS Level 1 experience for nuclear cardiology (including SPECT and PET) and cardiac CT. Fellows will administer, process, and read cardiac nuclear studies with
Rotation: Imaging 1 Imaging 1 provides COCATS Level 1 experience for nuclear cardiology (including SPECT and PET) and cardiac CT. Fellows will administer, process, and read cardiac nuclear studies with
PET IMAGING (POSITRON EMISSION TOMOGRAPY) FACT SHEET
 Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) When calling Anthem (1-800-533-1120) or using the Point of Care authorization system for a Health Service Review, the following clinical information may be needed to
Outline. Lifetime Attributable Risk 10 mgy in 100,000 exposed persons (BEIR VII 2006) SPECT/CT and PET/CT Dosimetry
 SPECT/CT and PET/CT Dosimetry Lifetime Attributable Risk 10 mgy in 100,000 exposed persons (BEIR VII 2006) All Solid Tumors Leukemia Frederic H. Fahey DSc Male Female Male Female Children s Hospital Boston
SPECT/CT and PET/CT Dosimetry Lifetime Attributable Risk 10 mgy in 100,000 exposed persons (BEIR VII 2006) All Solid Tumors Leukemia Frederic H. Fahey DSc Male Female Male Female Children s Hospital Boston
PET-CT for radiotherapy planning in lung cancer: current recommendations and future directions
 PET-CT for radiotherapy planning in lung cancer: current recommendations and future directions Gerry Hanna Centre for Cancer Research and Cell Biology Queen s University of Belfast @gerryhanna Talk Outline
PET-CT for radiotherapy planning in lung cancer: current recommendations and future directions Gerry Hanna Centre for Cancer Research and Cell Biology Queen s University of Belfast @gerryhanna Talk Outline
Brain Tumors. What is a brain tumor?
 Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
Scan for mobile link. Brain Tumors A brain tumor is a collection of abnormal cells that grows in or around the brain. It poses a risk to the healthy brain by either invading or destroying normal brain
A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
 Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Description MRI, TMJ C T Head Without Contrast C T Head With Contrast C T Head Without & With Contrast
 s Requiring Prior Authorization for the Advanced Imaging 70336 MRI, TMJ 70450 C T Head Without Contrast 70460 C T Head With Contrast 70470 C T Head Without & With Contrast 70480 C T Orbit Without Contrast
s Requiring Prior Authorization for the Advanced Imaging 70336 MRI, TMJ 70450 C T Head Without Contrast 70460 C T Head With Contrast 70470 C T Head Without & With Contrast 70480 C T Orbit Without Contrast
Scintillations. spect lab. A group of donkeys led by a lion can defeat a group of lions led by a donkey - Socrates. nuclear medicine services
 Scintillations A group of donkeys led by a lion can defeat a group of lions led by a donkey - Socrates solov - PETCT Volume III / Issue I January - March 2010 spect lab nuclear medicine services Visit
Scintillations A group of donkeys led by a lion can defeat a group of lions led by a donkey - Socrates solov - PETCT Volume III / Issue I January - March 2010 spect lab nuclear medicine services Visit
Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new
 Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new Dr B K S Sastry, MD, DM. CARE Hospitals, Hyderabad What is Viability Viability Dysfunctional myocardium subtended by diseased coronary arteries
Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new Dr B K S Sastry, MD, DM. CARE Hospitals, Hyderabad What is Viability Viability Dysfunctional myocardium subtended by diseased coronary arteries
Indications of PET/CT in oncology
 Monday, August 27, 2012 Session 1, 10:00-10:40 Indications of PET/CT in oncology Helle Westergren Hendel MD, PhD, assistant professor Bacelor in Leadership & Health Ecomomics Head of Clinical PET, Herlev
Monday, August 27, 2012 Session 1, 10:00-10:40 Indications of PET/CT in oncology Helle Westergren Hendel MD, PhD, assistant professor Bacelor in Leadership & Health Ecomomics Head of Clinical PET, Herlev
Nuclear Medicine in Australia. Shaun Jenkinson
 Nuclear Medicine in Australia Shaun Jenkinson Landmark Infrastructure for Australian Science OPAL Research Reactor Australian Synchrotron Camperdown Cyclotron Bragg Institute Centre for Accelerator Science
Nuclear Medicine in Australia Shaun Jenkinson Landmark Infrastructure for Australian Science OPAL Research Reactor Australian Synchrotron Camperdown Cyclotron Bragg Institute Centre for Accelerator Science
GLUCEPTATE. Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION
 27194 0001E m TM GLUCEPTATE Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain the sterile, non-pyrogenic, nonradioactive ingredients necessary to
27194 0001E m TM GLUCEPTATE Technetium Tc 99m Gluceptate Kit DIAGNOSTIC DESCRIPTION The kit consists of reaction vials which contain the sterile, non-pyrogenic, nonradioactive ingredients necessary to
Click Here to Continue. Click Here to Return to Table of Contents
 Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Hippuran I 131 Injection Package inserts are current as of January, 1997. Contact Professional Services, 1-888-744-1414, regarding possible revisions Click Here to Continue Click Here to Return to Table
Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 317e322. Available online at ScienceDirect
 Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 317e322 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences journal homepage:
Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences 8 (2015) 317e322 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Journal of Radiation Research and Applied Sciences journal homepage:
R: March, E D T P A. Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection. DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use
 R: March, 1998 27227 0002E m TM DESCRIPTION D T P A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use Each kit consists of reaction vials which contain the
R: March, 1998 27227 0002E m TM DESCRIPTION D T P A Kit for the Preparation of Technetium Tc 99m Pentetate Injection DIAGNOSTIC - For Intravenous Use Each kit consists of reaction vials which contain the
