Decreased glutathione biosynthesis contributes to EGFR T790M-driven. erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
|
|
|
- Amos Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMEARY DATA Decreased glutathione iosynthesis contriutes to EGFR T79M-driven erlotini resistance in non-small cell lung cancer Hongde Li #, William Stokes #, Emily Chater #, Rajat Roy #, Elza de Bruin, Yili Hu, Zhigang Liu, Egert F. Smit &, Guus J.J.E. Heynen, Julian Downward, Michael J. Seckl, Yulan Wang,Huiru Tang, Olivier E. Pardo State Key Laoratory of Genetic Engineering, Ministry of Education Key Laoratory of Contemporary Anthropology, Collaorative Innovation Centre for Genetics and Development, Shanghai International Centre for Molecular Phenomics, Metaonomics and Systems Biology Laoratory, School of Life Sciences, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, 2438, China. Key Laoratory of Magnetic Resonance in Biological Systems, National Centre for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, State Key Laoratory of Magnetic Resonance and Atomic and Molecular Physics, Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan 437, China. Division of Cancer, Department of Surgery and Cancer, Imperial College, Hammersmith Hospital, Du Cane Road, London W2 NN, UK. Signal Transduction laoratory, CRUK London Research Institute, London, UK. & Dept. Pulmonary Diseases, VU University Medical Centre and Section of molecular carcinogenesis, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Collaorative Innovation Centre for Diagnosis and Treatment of Infectious Diseases, Hangzhou, China. AstraZeneca, Personalised Healthcare & Biomarkers, Molecular Diagnostics, Darwin, Building 3, Camridge Science Park, Milton Road, Camridge CB4 WG, UK. # These authors have contriuted equally to the work. Corresponding authors: o.pardo@imperial.ac.uk, huiru_tang@fudan.edu.cn, m.seckl@imperial.ac.uk
2 SUPPLEMEARY TABLES Supplementary Tale : NMR data for metaolites identified and assigned. Keys refer to the peaks laelled on Figure A. Both the chemical shifts for proton (δ H) and caron (δ 3 C) NMR are taulated. a Multiplicity: singlet(s), doulet(d), triplet(t), quartet(q), doulet of doulets(dd), doule of triplets (dt), multiplet(m). The signals or the multiplicities were not determined. Supplementary Tale 2: Metaolites showed statistically significant differences in oth cell line pairs etween erlotini-resistant and erlotini-sensitive cells. "decrease" or "increase" meant statistically significant such differences were detected in the erlotini-resistant cells as compared to sensitive ones. Keys refer to the peaks laelled on Figure B and C. The chemical shifts for the identified metaolites and the OPLS-DA coefficient for oth cell line pairs are shown. SUPPLEMEARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure : (A and C) ER and H975 cells are resistant to the EGFR TKIs., ER, and H975 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of erlotini (A) or (C) for 48 h efore crystal violet staining. (B) and ER cells do not display differential sensitivity to classical chemotherapeutic agents. and ER cells were treated with increasing concentrations of cisplatin, taxol and etoposide for 48 hours prior to crystal violet staining. Results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data are average ± SEM of quadruplicates, P <.. Supplementary Figure 2: (A-C) Schematic representation of additional metaolic pathways differentially modulated in erlotini-resistant and sensitive cells. Red; metaolites with increased and Blue; decreased levels in resistant cells as compared to their sensitive counterparts. (D) Representative H-NMR spectra from the cell culture media of, ER, and H975 cells. Cells were grown for 4 days in complete medium. The media were then collected and analysed y NMR for their GSH content. The spectra are zoomed onto the chemical shifts area corresponding to GSH and GSSG. The top line corresponds to a purchased GSH/GSSG mixture internal control. The spectra shown are representative of replicates per cell lines. Supplementary Figure 3: qpcr controls for -mediated silencing of GSH metaolic enzymes and accompanying changes in GSH levels. (A) and ER cells were transfected with s targeting the indicated enzymes. 48 h later, transfected cells were sujected to RT-qPCR to assess the down-regulation of the target mrnas. Data are shown are average of quadruplicates ± SEM. (B) GSH levels were measured y colorimetric assay in or ER cells downstream of the silencing of selected targets. Data are shown are representative of at least three experiments. Results are average of quadruplicates ± SEM. (B) Statistical analysis, Student t-test with taken as reference. P <.5, P <.. (C) H975 cells were transfected with s for the indicated enzymes or a non-targeting sequence () prior to treatment with the IC 5 concentration of erlotini for cells. Cell survival was determined y crystal violet staining and normalised to that of the condition. (D) Intracellular GSH levels were measured in H975 cells treated with or without mercaptosuccinate (MS) using a colorimetric assay. (E) H975 cells were incuated in the presence or asence of MS for 2 h prior to treatment with or without erlotini for 48 h. Cell
3 viaility was assessed y crystal violet staining. Results shown are representative of experiments performed at least three times. Data are average of quadruplicates ± SEM. Statistical analysis: (C- D) t-test, (E) ANOVA. P <., P <., P <.5. Supplementary Figure 4: ER cells treated with or without Ethacrynic Acid (EA) were exposed to varying doses of Gefitini for 48 hours and cell survival monitored y crystal violet staining (A). Fold change in cell survival at the IC5 dose was determined and data normalised to the cell viaility with Gefitini alone (B). Fold change in GSH was measured in cells treated with or without Gefitini, EA or comination (C). P <., P <.. Supplementary Figure 5: Three replicates for the Western lots shown in Fig 4A and B were quantified using the optical densitometry function in ImageJ and the results otained for (A) NRF2, (B) KEAP, (C) SQSTM and (D) PALB2 normalised to the corresponding control cell line and plotted. (E-F) mrna level of SQSTM was quantified for 4 cell lines and results were normalised to the corresponding control cell line. Results shown are representative of experiments performed at least three times. Data are average of triplicates ± SEM. For ER, cells were used as control while for H975, were used for normalisation. Statistical analysis: t-test. P <., P <.,P <.5. Supplementary Figure 6: (A, C and E) qpcr controls for silencing of NRF2, SQSTM and KEAP in the indicated cell lines. (B, D and F) Accompanying changes in the mrna levels for GSH synthesising enzymes as determined y qpcr. Data shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. Results are average of quadruplicates ± SEM. Statistical analysis: t-test, P <.5, P <.. Supplementary Figure 7: Silencing of PALB2 in cells does not modulate their sensitivity to erlotini. (A and B) Cells were transfected with targeting PALB2 or with a non-targeting control for 48 h prior to exposure to a dose range of erlotini for 2 days (A) or GSH levels measurements using a colorimetric assay (B). Cell survival was assessed using crystal violet staining. Results shown are representative of experiments performed in triplicate. Data are average of quadruplicates ± SEM. Silencing of T79M-EGFR using selective does only modify EGFR expression in T79M-EGFR containing cells as assessed y qpcr. and ER cells were transfected with non-targeting () or two separate T79M-targeting s (C and D) and sujected to qpcr for EGFR using primers detecting equally T79M and non-t79m EGFRs. Results shown are normalised to the corresponding condition. Statistical analysis: Student t-test, P <., P <.. (E) Response to erlotini during systemic EA administration in mouse xenografts. Nude mice (n=/condition) were injected sucutaneously with cells and treatment started when tumours reached mm 3. Tumour volume was monitored for 2 weeks.
4 Supplementary Tale : NMR data for metaolites identified and assigned. Keys refer to the peaks laelled on Figure A. Both the chemical shifts for proton (δ H) and caron (δ 3 C) NMR are taulated. a Multiplicity: singlet(s), doulet(d), triplet(t), quartet(q), doulet of doulets(dd), doule of triplets (dt), multiplet(m). The signals or the multiplicities were not determined. Key Metaolites Assignment δ H(multiplicity a ) δ 3 C.92(s) 26. Acetate CH 3 COO Adenosine CH-ring CH-ring CH-riose C2H-riose C4H-riose C3H-riose C5H-riose 8.34(s) 8.78(s) 6.8(d) / Alanine (Ala) α-ch β-ch 3 4 Aspartate (Asp) α-ch β-ch β -CH γ 3.78(q).48(d) 3.9(m) 2.69(dd) 2.8(dd) Choline α-ch 2 β-ch 2 N-CH (s) Creatine CH 3 CH 2 N=C 3.4(s) 3.93(s) Formate H COO (s) 6.52(s) Fumarate C2,3H COO - 9 Glutamate (Glu) α-ch β-ch 2 γ-ch 2 δco 3.76(t) 2.8(m) 2.35(m) Glycerophosphocho line(gpc) -CH 2 2-CH 3-CH 2 α-ch 2 β-ch 2 N-CH 3 3.6(dd) 3.89(m) 3.72(dd) 4.32(t) 3.68(t) 3.23(s) 56.7 Glycine (Gly) α-ch (s) Glycogen 5.4(road peak)
5 3 Guanosine CH-ring CH-riose C3H-riose C4H-riose C5H-riose 4 Histidine (His) C4H,ring C2H,ring 5 Inosine CH-ring CH-ring CH-riose C2H-riose C3H-riose C4H-riose C5H-riose 6 Inosine-5 - monophosphate(im P) CH-ring CH-ring CH-riose C2H-riose C3H-riose C4H-riose C5H-riose 7 Isoleucine (Ile) α-ch β-ch γ-ch γ -CH δ-ch 3 3- CH 3 8 Lactate α-ch β-ch 3 COO - 9 Leucine(Leu) α-ch β-ch 2 γ-ch δ-ch 3 δ -CH 3 2 Myo-inositol C,3H C2H C5H C4,6H 2 N-acetyl Aspartate α-ch β-ch β -CH CH 3 22 NAD N5ring N4ring N2ring (s) 5.92(d) 4.4(dd) 4.24(dt) (s) 7.85(s) 8.35(s) 8.24(s) 6.(d) (s) 8.24(s) 6.4(d) (m).98(m).27(m).47(m).94(t).(d) 4.(q).33(d) 3.73(t).72(m).69(m).97(d).96(d) 3.54(dd) 4.6(t) 3.26(t) 3.62(t) 4.39(dd) 2.68(dd) 2.49(dd) 2.2(s) 8.2(m) 8.83(d) 9.34(s)
6 23 Oxidative Glutathione (GSSG) N6ring A2Hring A8H ring A4ring A H N H S-CH2 CH CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 C=O COOH 24 Phenylalanine (Phe) α-ch β-ch β -CH C,ring C2,6,ring C3,5,ring C4,ring 25 Phosphocholine (PC) 26 Reduced Glutathione (GSH) α-ch 2 β-ch 2 N-CH 3 Glu α Glu β Glu γ Cys α Cys β Gly α C=O 9.4(d) 8.(s) 8.43(s) 6.9(d) (dd)/2.98(dd) (m) 2.6(m) 2.5(m) 3.99(dd) 3.3(dd) 3.27(dd) 7.33(m) 7.42(m) 7.38(m) 3.6(m) 4.7(m) 3.22(s) 3.78(t) 2.6(m) 2.56(m) 4.57(dd) 2.94(m) , (s) Succinate CH 2 COO Taurine N-CH 2 S-CH (t) 3.42(t) Tyrosine (Tyr) C3,5H,ring C2,6H,ring C,ring α-ch β-ch 2 6.9(d) 7.9(d) 3.94(dd) Uridine 5 - diphosphate (UDP) 3 UDP-glucose (UDPG) CH-ring CH-ring CH-riose C3H-riose C2H-riose C4H-riose C5H-riose G-H C6,ring C5,ring 7.99(d) 5.97(d) 5.96(road,s) 4.43(t) 4.39(t) 4.27(m) 4.23(c) (d) 5.98(d)
7 C H,riose C2 3 H,riose C4,riose C5 H,riose G2-H G6-H G3-H G4-H G5-H 5.99(d) 4.38(m) 4.29(m) 4.26/4.2(m) / / UDP-N-acetyl glucosamine C6,ring C H,riose C5,ring C2 3 H,riose C5 H,riose C4 H,riose C2,ring G-H G2-H G3-H G4-H G5-H NA-H NA-C=O 7.96(d) 5.98(d) 5.97(d) 4.37(m) 4.23/4.7(m) 4.29(m) 5.52(dd) / UDP-N-Acetyl Galactosamine G-H G2-H G3-H G4-H G5-H G6-H C2 3 H,riose C4,riose C5 H,riose NA-H C H,riose C5,ring C6,ring 5.55(dd) 4.5(m) 3.97(dd) 3.76(m) (m) 4.29(m) 4.25/4.9(m) 2.89(s) 5.99(d) 5.97(d) 7.96(d) Uracil C5H C6H 5.8(d) 7.54(d) 35 Uridine C6,ring C H,riose C5,ring C3 H,riose C5 H,riose C4 H,riose C2,ring 7.87(d) 5.92(d) 5.9(d) 4.34(t) 4.2(q) 4.23(t) Valine (Val) α-ch β-ch γ-ch 3 γ -CH 3 3.6(d) 2.28(m).99(d).4(d)
8 Supplementary Tale 2: Metaolites showed statistically significant differences in oth cell line pairs etween erlotini-resistant and erlotini-sensitive cells. "decrease" or "increase" meant statistically significant such differences were detected in the erlotini-resistant cells as compared to sensitive ones. Keys refer to the peaks laelled on Figure B and C. The chemical shifts for the identified metaolites and the OPLS-DA coefficient for oth cell line pairs are shown. Key Metaolite Variation tendency Chemical shift Coefficient vs ER Coefficient 975 vs Adenosine Decrease Aspartate Decrease Choline Increase Inosine Decrease Isoleucine Increase Leucine Increase N-acetyl aspartate Decrease GSSG Decrease Phosphocholine Increase GSH Decrease UDP Increase UDPG Increase Uridine Increase Valine Increase
9 Supplementary Figure A. B Cell numer (fold) Cell numer (fold) ER Erlotini (nm) ER Cisplatin (µm) Cell numer (fold) H975 ER Taxol ( M) Erlotini (nm) ER Etoposide ( M) C. Cell numer (fold) ER Cell numer (fold) H EGFRI (µm) EGFRI (µm)
10 A. -ketoisocaproate Leu Val Ile 4-methyl-2- oxopentanoate 3-methyl-2- oxoutanoate Isoutyryl-CoA 3-methyl-2- oxopentanoate 3-methylutanoyl -CoA Branched chain fatty acid 2-methylutanoyl-CoA B. Acetylcholine Phosphocholine Choline Betaine aldehyde Betaine Dimethylglycine CDP-choline Gly Sarcosine Phosphatidyl choline Glycerophospho choline Guanidinoacetate Creatine C. N-acetylaspartate Uridine Ala Asp N-caramoyl- Asp UMP UDP UDPG Asn PRPP IMP Inosine Adenosine AMP D GSH GSSG ER ER H chemical shift (ppm)
11 Supplementary Figure 3 A. Relative mrna levels GPX GPX GSTpi GSPpi GSS GSS GCLC GCLC GSR GSR ER ER ER ER ER B. Relative GSH levels (fold) ER GSTpi Relative GSH levels (fold) ER GPX Relative GSH levels (fold) ER GGT Relative GSH levels (fold) GSS Relative GSH levels (fold) GSR Relative GSH levels (fold) GCLC C. Relative cell survival GGT H975 GPX GSTpi D. E. H975 GSH levels (fold) MS - + Relative cell survival Erlo MS H
12 Supplementary Figure 4 A ER B. IC 5 R e l a t i v e s u r v i v a l ( % ) F o ld c h a n g e Log [Gefitini]. G e f it in i G e f it in i + E A C G S H le v e l F o ld c h a n g e N o t r e a t m e n t G e f it in i G e f it in i + E A Gefitini Gefitini + EA
13 Supplementary Figure 5 A. B. NRF2 levels (fold OD) Cyto n.s. ER Nuclear n.s. H975 ER H975 KEAP levels (fold OD) ER H975 C. D. SQSTM levels (fold) ER H975 PALB2 levels (fold) ER H975 E. F. mrna levels (fold) SQSTM..5 ER mrna levels (fold) SQSTM H975
14 Supplementary Figure 6 A. NRF2 mrna levels (fold).5 NRF2 B. mrna levels (fold).5.5 sinrf2 GCLC GSR GSS C. SQSTM mrna (fold).5 SQSTM D. mrna levels (fold).5 GCLC sisqstm GSR GSS E. mrna levels (fold) ER F. mrna (Fold) sikeap KEAP GCLC GSR GSS
15 Supplementary Figure 7 A. Relative Survival (%) sipalb B. GSH levels (fold) Erlotini (nm).2 PALB2 C. D. EGFR mrna levels (fold) T79M # ER EGFR mrna levels (fold) T79M #2 E. 8 Tumour Volume ( mm 3 ) Con EA ER ER+EA Days
Supporting information for. Time-dependent Responses of Earthworms to Soil. Contaminated with Low Levels of Lead as Detected using 1 H
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information for Time-dependent Responses of Earthworms to Soil Contaminated with
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Supporting information for Time-dependent Responses of Earthworms to Soil Contaminated with
Supplementary Materials: Decrease in Circulating Fatty Acids is Associated with Islet Dysfunction in Chronically Sleep-Restricted Rats
 S of S6 Supplementary Materials: Decrease in Circulating Fatty Acids is Associated with Islet Dysfunction in Chronically Sleep-Restricted Rats Shanshan Zhan, Yangyang Wu, Peng Sun, Haiyan Lin, Yunxia Zhu
S of S6 Supplementary Materials: Decrease in Circulating Fatty Acids is Associated with Islet Dysfunction in Chronically Sleep-Restricted Rats Shanshan Zhan, Yangyang Wu, Peng Sun, Haiyan Lin, Yunxia Zhu
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Effects of Histidine Supplementation on Global Serum and Urine 1 H NMR-based. Metabolomics and Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Obese Women from a
 Supporting information for Effects of Histidine Supplementation on Global Serum and Urine 1 H NMR-based Metabolomics and Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Obese Women from a Randomized Controlled Study Shanshan
Supporting information for Effects of Histidine Supplementation on Global Serum and Urine 1 H NMR-based Metabolomics and Serum Amino Acid Profiles in Obese Women from a Randomized Controlled Study Shanshan
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice.
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure 1. Body weight and fat mass of AdicerKO mice. Twelve week old mice were subjected to ad libitum (AL) or dietary restriction (DR) regimens for three months. (A) Body
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Dr.Diala
 number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
number 32 Done by Mousa Salah Corrected by Bahaa Najjar Doctor Dr.Diala 1 P a g e In the last lecture we talked about the common processes between all amino acids which are: transamination, deamination,
AMINO ACID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Dept. of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Amino acids derived from dietary protein absorbed from intestine through blood taken up by tissues used for biosynthesis
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an
 Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Amino acids-incorporated nanoflowers with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity Zhuo-Fu Wu 1,2,+, Zhi Wang 1,+, Ye Zhang 3, Ya-Li Ma 3, Cheng-Yan He 4, Heng Li 1, Lei Chen 1, Qi-Sheng Huo 3, Lei Wang 1,*
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Correlations of Fecal Metabonomic and Microbiomic Changes Induced by High-fat Diet in the Pre-Obesity State
 Supplementary data Correlations of Fecal Metabonomic and Microbiomic Changes Induced by High-fat Diet in the Pre-Obesity State Hong Lin #, Yanpeng An #, Fuhua Hao, Yulan Wang,, and Huiru Tang * CAS Key
Supplementary data Correlations of Fecal Metabonomic and Microbiomic Changes Induced by High-fat Diet in the Pre-Obesity State Hong Lin #, Yanpeng An #, Fuhua Hao, Yulan Wang,, and Huiru Tang * CAS Key
Classification of amino acids: -
 Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Page 1 of 8 P roteinogenic amino acids, also known as standard, normal or primary amino acids are 20 amino acids that are incorporated in proteins and that are coded in the standard genetic code (subunit
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Evolution Name: Period Date :
 LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
LAB#23: Biochemical Evidence of Name: Period Date : Laboratory Experience #23 Bridge Worth 80 Lab Minutes If two organisms have similar portions of DNA (genes), these organisms will probably make similar
The human DEK oncogene: metabolic reprogramming of engineered epidermis
 The human DEK oncogene: metabolic reprogramming of engineered epidermis Markey Cancer Center, CESB, University of Kentucky 218 Metabolomics Symposium NMR Based Metabolomics Core CESB Co-director, UKY Marion
The human DEK oncogene: metabolic reprogramming of engineered epidermis Markey Cancer Center, CESB, University of Kentucky 218 Metabolomics Symposium NMR Based Metabolomics Core CESB Co-director, UKY Marion
Biology. Lectures winter term st year of Pharmacy study
 Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Biology Lectures winter term 2008 1 st year of Pharmacy study 3 rd Lecture Chemical composition of living matter chemical basis of life. Atoms, molecules, organic compounds carbohydrates, lipids, proteins,
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
1. Describe the relationship of dietary protein and the health of major body systems.
 Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Food Explorations Lab I: The Building Blocks STUDENT LAB INVESTIGATIONS Name: Lab Overview In this investigation, you will be constructing animal and plant proteins using beads to represent the amino acids.
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Supplementary Information Flux balance analysis predicts essential genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma metabolism
 Supplementary Information Flux balance analysis predicts essential genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma metabolism Francesco Gatto #, Heike Miess #, Almut Schulze, Jens Nielsen. 1 Supplementary Figures
Supplementary Information Flux balance analysis predicts essential genes in clear cell renal cell carcinoma metabolism Francesco Gatto #, Heike Miess #, Almut Schulze, Jens Nielsen. 1 Supplementary Figures
NMR ANNOTATION. Rémi Servien Patrick Tardivel Marie Tremblay-Franco Cécile Canlet 01/06/2017 v 1.0.0
 NMR ANNOTATION Rémi Servien Patrick Tardivel Marie Tremblay-Franco Cécile Canlet 01/06/2017 v 1.0.0 WHY DO WE NEED AN AUTOMATED NMR ANNOTATION TOOL 2 Metabolomic workflow Control mice Exposed mice Metabolites
NMR ANNOTATION Rémi Servien Patrick Tardivel Marie Tremblay-Franco Cécile Canlet 01/06/2017 v 1.0.0 WHY DO WE NEED AN AUTOMATED NMR ANNOTATION TOOL 2 Metabolomic workflow Control mice Exposed mice Metabolites
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011
 Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications - Acids. Data No. Column Data Title Solutes Eluent Detection Data No.
 GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)7 3205 1209
GL Science Inertsearch for LC Inertsil Applications: Acids For complete Product Description, Chromatograms Price & Delivery in Australia & New Zealand contact info@winlab.com.au or call 61 (0)7 3205 1209
Metabolomics approach reveals metabolic disorders and potential. biomarkers associated with the developmental toxicity of
 Supplementary information for Metabolomics approach reveals metabolic disorders and potential biomarkers associated with the developmental toxicity of tetrabromobisphenol A and tetrachlorobisphenol A Guozhu
Supplementary information for Metabolomics approach reveals metabolic disorders and potential biomarkers associated with the developmental toxicity of tetrabromobisphenol A and tetrachlorobisphenol A Guozhu
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules. Biological Macromolecules. Lipids
 Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Biological Macromolecules Much larger than other par4cles found in cells Made up of smaller subunits Found in all cells Great diversity of func4ons Four Classes of Biological Macromolecules Lipids Polysaccharides
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
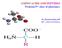 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM
 SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
SIMPLE BASIC METABOLISM When we eat food such as a tuna fish sandwich, the polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are digested to smaller molecules that are absorbed into the cells of our body. As these
Metabonomics and MRS BCMB/CHEM 8190
 Metabonomics and MRS BCMB/CHEM 8190 Metabolomics, Metabonomics, Metabolic Profiling! Definition: The quantitative measurement of the dynamic multi parametric metabolic response of living systems to physiological
Metabonomics and MRS BCMB/CHEM 8190 Metabolomics, Metabonomics, Metabolic Profiling! Definition: The quantitative measurement of the dynamic multi parametric metabolic response of living systems to physiological
CHM333 LECTURE 6: 1/25/12 SPRING 2012 Professor Christine Hrycyna AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID:
 AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
AMINO ACIDS II: CLASSIFICATION AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH AMINO ACID: - The R group side chains on amino acids are VERY important. o Determine the properties of the amino acid itself o Determine
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Midterm 2. Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98. Standard Deviation: 17.7
 Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
1. (38 pts.) 2. (25 pts.) 3. (15 pts.) 4. (12 pts.) 5. (10 pts.) Bonus (12 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2010 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination #5: Section Five May 4, 2010 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Cells N5 Homework book
 1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
1 Cells N5 Homework book 2 Homework 1 3 4 5 Homework2 Cell Ultrastructure and Membrane 1. Name and give the function of the numbered organelles in the cell below: A E B D C 2. Name 3 structures you might
Decreased glutathione biosynthesis contributes to EGFR T790M-driven erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
 OPEN ARTICLE Citation: Cell Discovery (2016) 2, 16031; doi:10.1038/celldisc.2016.31 www.nature.com/celldisc Decreased glutathione biosynthesis contributes to EGFR T790M-driven erlotinib resistance in non-small
OPEN ARTICLE Citation: Cell Discovery (2016) 2, 16031; doi:10.1038/celldisc.2016.31 www.nature.com/celldisc Decreased glutathione biosynthesis contributes to EGFR T790M-driven erlotinib resistance in non-small
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Midterm 1 Last, First
 Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Midterm 1 BIS 105 Prof. T. Murphy April 23, 2014 There should be 6 pages in this exam. Exam instructions (1) Please write your name on the top of every page of the exam (2) Show all work for full credit
Decreased glutathione biosynthesis contributes to EGFR T790M-driven. erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer
 2 Decreased glutathione biosynthesis contributes to EGFR T79M-driven erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer 3 4 5 Hongde Li #, William Stokes #, Emily Chater #, Rajat Roy #, Elza de Bruin,
2 Decreased glutathione biosynthesis contributes to EGFR T79M-driven erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung cancer 3 4 5 Hongde Li #, William Stokes #, Emily Chater #, Rajat Roy #, Elza de Bruin,
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Introduction to Peptide Sequencing
 Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Introduction to Peptide equencing Quadrupole Ion Traps tructural Biophysics Course December 3, 2014 12/8/14 Introduction to Peptide equencing - athan Yates 1 Why are ion traps used to sequence peptides?
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Practice Problems 3. a. What is the name of the bond formed between two amino acids? Are these bonds free to rotate?
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 3 1. Draw the oligopeptide for Ala-Phe-Gly-Thr-Asp. You do not need to indicate the stereochemistry of the sidechains. Denote with arrows the bonds formed between the
(30 pts.) 16. (24 pts.) 17. (20 pts.) 18. (16 pts.) 19. (5 pts.) 20. (5 pts.) TOTAL (100 points)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2009 Instructor: Professor Torres Examination # 5: Section Five April 30, 2009 ame: (print) ame: (sign) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection
 Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
Introduction to Protein Structure Collection Teaching Points This collection is designed to introduce students to the concepts of protein structure and biochemistry. Different activities guide students
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 ANSWERS For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination #5: Section Five December 7, Name: (print) Section:
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
METABOLITE CHARACTERIZATION IN SERUM SAMPLES FROM NORMAL HEALTHY HUMAN SUBJECTS BY 1 H AND 13 C NMR SPECTROSCOPY. Divya Misra * and Usha Bajpai
 , 211-221. ISSN 1011-3924 Printed in Ethiopia 2009 Chemical Society of Ethiopia METABOLITE CHARACTERIZATION IN SERUM SAMPLES FROM NORMAL HEALTHY HUMAN SUBJECTS BY 1 H AND 13 C NMR SPECTROSCOPY Divya Misra
, 211-221. ISSN 1011-3924 Printed in Ethiopia 2009 Chemical Society of Ethiopia METABOLITE CHARACTERIZATION IN SERUM SAMPLES FROM NORMAL HEALTHY HUMAN SUBJECTS BY 1 H AND 13 C NMR SPECTROSCOPY Divya Misra
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Proximate composition, amino acid and fatty acid composition of fish maws. Department of Biology, Lingnan Normal University, Zhanjiang, , China
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Proximate composition, amino acid and fatty acid composition of fish maws Jing Wen a, Ling Zeng b *, Youhou Xu c, Yulin Sun a, Ziming Chen b and Sigang Fan d a Department of Biology,
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Proximate composition, amino acid and fatty acid composition of fish maws Jing Wen a, Ling Zeng b *, Youhou Xu c, Yulin Sun a, Ziming Chen b and Sigang Fan d a Department of Biology,
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Examination #5 PRACTICE 1 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Supplementary files. Tissue metabolomics study to reveal the toxicity of a Traditional Tibetan. medicines Renqing Changjue in rat
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary files Tissue metabolomics study to reveal the toxicity of a Traditional Tibetan
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary files Tissue metabolomics study to reveal the toxicity of a Traditional Tibetan
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Introduction to proteins and protein structure
 Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Introduction to proteins and protein structure The questions and answers below constitute an introduction to the fundamental principles of protein structure. They are all available at [link]. What are
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis. Chemistry M3LC
 Protein and Amino Acid Analysis Chemistry M3LC Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine
Protein and Amino Acid Analysis Chemistry M3LC Proteins Proteins are made up of amino acids: H2N-CHR-COOH + H3N-CHR-COO - neutral form zwitterionic form There are twenty standard amino acids: A ala alanine
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية
 قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
قسم الكيمياء الحيوية د.دولت على سالمه استاذ الكيمياءالحيوية ٢٠١٥-٢٠١٤ الرمز الكودي : ٥١٢ المحاضرة األولى ١ Content : Definition of proteins Definition of amino acids Definition of peptide bond General
glpx Rv1100 Probe 4.4 kb 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda 25 kda 20 kda
 PvuI 2.0 k PvuI PvuI Rv1101c Rv1100 glpx fum 4.4 k PvuI PvuI ΔglpX Rv1101c Rv1100 HygR fum ΔglpX 5 k 4 k 3 k c 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda GLPX Δ Δ/C GLPX 2 k 1.5 k 25 kda 20 kda PRCB 1 k 0.5 k Supplementary
PvuI 2.0 k PvuI PvuI Rv1101c Rv1100 glpx fum 4.4 k PvuI PvuI ΔglpX Rv1101c Rv1100 HygR fum ΔglpX 5 k 4 k 3 k c 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda GLPX Δ Δ/C GLPX 2 k 1.5 k 25 kda 20 kda PRCB 1 k 0.5 k Supplementary
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Loss of succinate dehydrogenase activity results in dependency on pyruvate carboxylation for cellular anabolism
 Loss of succinate dehydrogenase activity results in dependency on pyruvate carboxylation for cellular anabolism Charlotte Lussey-Lepoutre, Kate ER Hollinshead, Christian Ludwig, Mélanie Menara, Aurélie
Loss of succinate dehydrogenase activity results in dependency on pyruvate carboxylation for cellular anabolism Charlotte Lussey-Lepoutre, Kate ER Hollinshead, Christian Ludwig, Mélanie Menara, Aurélie
Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple quadrupole mass spectrometer
 Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple ASMS 2012 ThP11-251 Zanariah Hashim 1 ; Yudai Dempo1; Tairo Ogura 2 ; Ichiro Hirano 2 ; Junko Iida
Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple ASMS 2012 ThP11-251 Zanariah Hashim 1 ; Yudai Dempo1; Tairo Ogura 2 ; Ichiro Hirano 2 ; Junko Iida
Nitrogen Metabolism. Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chaleckis et al. 10.1073/pnas.1603023113 SI Materials and Methods Human Subject Characteristics. Thirty healthy male and female volunteers participated in this study (Table S2).
Supporting Information Chaleckis et al. 10.1073/pnas.1603023113 SI Materials and Methods Human Subject Characteristics. Thirty healthy male and female volunteers participated in this study (Table S2).
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy G. A. Nagana Gowda Northwest Metabolomics Research Center University of Washington, Seattle, WA 1D NMR Blood Based Metabolomics Histidine Histidine Formate
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy G. A. Nagana Gowda Northwest Metabolomics Research Center University of Washington, Seattle, WA 1D NMR Blood Based Metabolomics Histidine Histidine Formate
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2*
 Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Analysis of L- and D-Amino Acids Using UPLC Yuta Mutaguchi 1 and Toshihisa Ohshima 2* 1 Department of Biotechnology, Akita Prefectural University, Akita City, Japan; 2 Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis leaves
 Environ. Chem. 216, 13, 877 887 doi:1.171/en165_ac CSIRO 216 Supplementary material Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis
Environ. Chem. 216, 13, 877 887 doi:1.171/en165_ac CSIRO 216 Supplementary material Proteins are a major component of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) leached from terrestrially aged Eucalyptus camaldulensis
2. Which of the following is NOT true about carbohydrates
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Examination #5 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response questions
Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Examination #5 For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response questions
Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular
 Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular weight markers (M). Supplementary Figure-2. Overlay of
Supplementary Figure-1. SDS PAGE analysis of purified designed carbonic anhydrase enzymes. M1-M4 shown in lanes 1-4, respectively, with molecular weight markers (M). Supplementary Figure-2. Overlay of
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
 Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides BINF 6101/8101, Spring 2018 Outline 1. Overall amino acid structure 2. Amino acid stereochemistry 3. Amino acid sidechain structure & classification 4. Non-standard
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Nitrogen Metabolism. Overview
 Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Nitrogen Metabolism Pratt and Cornely Chapter 18 Overview Nitrogen assimilation Amino acid biosynthesis Nonessential aa Essential aa Nucleotide biosynthesis Amino Acid Catabolism Urea Cycle Juicy Steak
Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds
 Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds Julie Kowalski, Michelle Misselwitz and Jack Cochran Restek
Investigating GCxGC separations using selective column chemistry and compound derivatization pairings for common metabolomics chemical compounds Julie Kowalski, Michelle Misselwitz and Jack Cochran Restek
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Introduction. Basic Structural Principles PDB
 BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
BCHS 6229 Protein Structure and Function Lecture 1 (October 11, 2011) Introduction Basic Structural Principles PDB 1 Overview Main Goals: Carry out a rapid review of the essentials of protein structure
Maha AbuAjamieh. Tamara Wahbeh. Mamoon Ahram
 12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
Glycolysis. Cellular Respiration
 Glucose is the preferred carbohydrate of cells. In solution, it can change from a linear chain to a ring. Energy is stored in the bonds of the carbohydrates. Breaking these bonds releases that energy.
Glucose is the preferred carbohydrate of cells. In solution, it can change from a linear chain to a ring. Energy is stored in the bonds of the carbohydrates. Breaking these bonds releases that energy.
LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a Novel Mixed-Mode HPLC Column
 Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry SSI-LCMS-022 LC-MS Analysis of Amino Acids on a ovel Mixed-Mode PLC Column LCMS-8040 Background There are four established methods for analyzing amino acids: prelabeled,
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes
 Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Amino acid metabolism II
 Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
Amino acid metabolism II Fates of amino acid carbon skeleton degradation to common intermediates pyruvate, intermediates of citric acid cycle, acetyl-coa Glucogenic AA precursors of glucose - degradation
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements.
 Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor

 Supplementary Figure 1 a OD c. 1. 1... Time [min] 1 p
Supplementary Figure 1 a OD c. 1. 1... Time [min] 1 p