glpx Rv1100 Probe 4.4 kb 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda 25 kda 20 kda
|
|
|
- Philippa Roberta Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PvuI 2.0 k PvuI PvuI Rv1101c Rv1100 glpx fum 4.4 k PvuI PvuI ΔglpX Rv1101c Rv1100 HygR fum ΔglpX 5 k 4 k 3 k c 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda GLPX Δ Δ/C GLPX 2 k 1.5 k 25 kda 20 kda PRCB 1 k 0.5 k Supplementary Fig. 1. Generation and Validation of ΔglpX. (a) Strategy for deleting glpx (Rv1099c) y homologous recomination and validating ΔglpX candidates y PvuI digest and southern lot analysis. () Southern lot analysis of Mt and ΔglpX where genomic DNA was digested with PvuI. (c) Western lot analysis of Mt (), ΔglpX (Δ), and complemented strain ΔglpX/C (Δ/C) cell lysates with anti-glpx antiody. Molecular weight of GLPX is kda. Recominant His-tagged GLPX (GLPX, kda) was run as a positive control. Anti- PRCB was used to confirm equal loading.
2 Glucose G6P S7P F6P FBP GLPX DHAP G3P Glycerol GL3P PEP PYR Acetyl-CoA ASP OAA TCA Cycle α-kg Supplementary Fig. 2. Gluconeogenesis is not strictly dependent on GLPX. Aundance and 13 C laeling of metaolites in Mt and ΔglpX (Δ). Bacteria were grown on glycerol-containing plates for 5 days and then transferred to U- 13 C glycerol-containing plates for an additional 16h prior to harvesting. Data are means ± standard deviation of three iological replicates and are representative of two independent experiments. Data are reported as ion counts (IC) per mg total protein. *0.01<P 0.05, **0.001<P 0.01, ***P y Student s t-test. G6P: glucose 6- phosphate, S7P: sedoheptulose 7-phosphate, F6P: fructose 6-phosphate, FBP: fructose 1,6- isphosphate, DHAP: dihydroxyacetone phosphate, G3P: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, GL3P: glycerol 3-phosphate, PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate, PYR: pyruvate, OAA: oxaloacetate, ASP: aspartate α-kg: α-ketoglutarate.
3 DraIII 3.8 k BsI (glpx Msm ) 5240 (fum) 2.4 k DraIII DraIII BsI BsI 5238 Hyg 5240 (fum) c Δ GLPX Δ Δ/C 4 k 3 k 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda GLPX GLPX Msm 2 k 25 kda PRCB Supplementary Fig. 3. Generation and Validation of. (a) Strategy for deleting msmeg_5239 (glpx homolog in M. smegmatis) y homologous recomination and validating candidates y DraIII and BsI doule digest and southern lot analysis. () Southern lot analysis of Msm and where genomic DNA was digested with DraIII and BsI. (c) Western lot analysis of Msm (), (Δ), and complemented strain /C (glpx) (Δ/C) cell lysates with anti-glpx antiody. Molecular weight of GLPX Msm is kda. Molecular weight of GLPX is kda. Recominant His-tagged GLPX (GLPX, kda) was run as a positive control. Anti-PRCB was used to confirm equal loading.
4 0.1% Glucose 0.1% Glycerol 10 DglpX Msm DglpX Msm /C (glpx) OD 580 OD Time (hours) Time (hours) 1.5 mm FBP 12 mm FBP Enzymatic Activity (nmole/min/mg total protein) DglpX Msm DglpX Msm /C (glpx) Enzymatic Activity (nmole/min/mg total protein) LiCl (mm) LiCl (mm) Supplementary Fig. 4. DglpX Msm can grow on gluconeogenic caron sources and has detectale FBPase activity. (a) Growth of Msm (lack), DglpX Msm (red) and complemented strain DglpX Msm /C (glpx) (gray) in 7H9 media containing 0.1% glucose or 0.1% glycerol as the sole caron source. Data are representative of three independent experiments. () FBPase activity of Msm (lack), DglpX Msm (red) and complemented strain DglpX Msm /C (glpx) (gray) cell lysates in the asence or presence of lithium chloride using 1.5 mm F-1,6BP or 12 mm F-1,6BP as sustrate. Dashed line indicates limit of detection. Data are means ± standard deviation of three iological replicates.
5 2.5 k SpeI XhoI Rv3213c gpm2 entc 1.5 k SpeI SpeI XhoI Δgpm2 Rv3213c le gpm2 entc ΔΔ c ΔΔ ΔΔ/C d GPM2 ΔΔ ΔΔ/C 3 k 2 k 50 kda 37 kda GLPX 50 kda 37 kda ENO 1.5 k 1 k 25 kda 20 kda PRCB 25 kda 20 kda GPM2 Supplementary Fig. 5. Generation and Validation of Mt ΔglpXΔgpm2. (a) Strategy for deleting gpm2 (Rv3214) y homologous recomination and validating ΔglpXΔgpm2 candidates y SpeI and XhoI doule digest and southern lot analysis. () Southern lot analysis of Mt and ΔglpXΔgpm2 where genomic DNA was digested with SpeI and XhoI. (c) Western lot analysis of Mt (), ΔglpXΔgpm2 (ΔΔ), and complemented strain ΔglpXΔgpm2/C (glpx) (ΔΔ/C) cell lysates with anti-glpx antiody. Molecular weight of GLPX is kda. Anti-PRCB was used to confirm equal loading. (d) Western lot analysis of Mt (), ΔglpXΔgpm2 (ΔΔ), and complemented strain ΔglpXΔgpm2/C (gpm2) (ΔΔ/C) cell lysates with anti-gpm2 antiody. Molecular weight of GPM2 is kda. Recominant His-tagged GPM2 (GPM2, kda) was run as a positive control. Anti-ENO was used to confirm equal loading.
6 0.1% Acetate 0.2% Acetate OD DglpX DglpXDgpm2 DglpXDgpm2/C (glpx) DglpXDgpm2/C (gpm2) CFU per ml Time (days) Time (days) Supplementary Fig. 6. Mt DglpXDgpm2 does not grow on fatty acids as a sole caron source ut remains viale. (a) Growth of Mt (lack), DglpX (red), DglpXDgpm2 (orange) and complemented strains DglpXDgpm2/C (glpx) (purple) and DglpXDgpm2/C (gpm2) (lue) in Sauton's minimal media containing 0.1% acetate. Data are representative of three independent experiments. () Survival of DglpXDgpm2 in Sauton's minimal media containing 0.2% acetate. Data represent the mean CFU/mL of three iological replicates at different time points.
7 Glucose G6P S7P F6P FBP GLPX, GPM2 DHAP G3P PEP PYR Acetyl-CoA ASP OAA TCA Cycle Supplementary Fig. 7. Glycolysis is unpertured in Mt ΔglpXΔgpm2. Aundance and 13 C laeling of metaolites in Mt and ΔglpXΔgpm2 (ΔΔ). Bacteria were grown on glucosecontaining plates for 5 days and then transferred to U- 13 C glucose-containing plates for an additional 24h prior to harvesting. Data are means ± standard deviation of three iological replicates and are representative of two independent experiments. *0.01<P 0.05, **0.001<P 0.01, ***P y Student s t-test. ND indicates that the recovered level of FBP was elow the limit of detection (3.13 μm). G6P: glucose 6-phosphate, S7P: sedoheptulose 7- phosphate, F6P: fructose 6-phosphate, FBP: fructose 1,6-isphosphate, DHAP: dihydroxyacetone phosphate, G3P: glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, PEP: phosphoenolpyruvate, PYR: pyruvate, OAA: oxaloacetate, ASP: aspartate.
8 10 OD Time (days) 0.1% Acetate 0.1% Acetate + 0.2% Glucose 0.1% Acetate + 0.4% Glucose 0.4% Glucose Supplementary Fig. 8. Growth of Mt DglpXDgpm2 on glucose is enhanced y the presence of acetate. Growth of DglpXDgpm2 in Sauton's minimal media containing 0.1% acetate (red), 0.1% acetate and 0.2% glucose (lue) 0.1% acetate and 0.4% glucose (orange) or 0.4% glucose (lack) Data are representative of three independent experiments.
9 Supplementary Fig. 9. Mt ΔglpXΔgpm2 is attenuated in vivo Lung histopathology. (a) Gross pathology of left lung loes from infected C57BL/6 mice at Day 56 post-infection. () Hemotoxylin and eosin staining of sections from left lung loes of infected C57BL/6 mice at Day 56 post-infection. Top row of images show sections from four mice per group. Black ox indicates region magnified in the ottom row of images. The scale ar is 10 μm.
10 Purification Step Protein Concentration (mg/ml) Total Protein (mg) Activity (nmol/min) Specific Activity (nmol/min/mg protein x10 3 ) Fold Enrichment Total Protein Lysate Anion Exchange (Q Sepharose) Hydrophoic Interaction (Phenyl Sepharose) Gel Filtration (Superose 6) Anion Exchange (Mono Q) * * * 65.13* Supplementary Tale 1. Purification of second FBPase activity from ΔglpX cell lysate. Four purification steps were done in total. Initial FBPase activity and protein concentration for the total lysate sample are shown. After the anion exchange (Q Sepharose), hydrophoic interaction and gel filtration steps, the active fractions were pooled and the FBPase activity and protein concentration of were measured. After the anion exchange (Mono Q) step, the FBPase activity and protein concentration were measured for just the peak activity fraction (Fraction B15). Total protein, specific activity and fold enrichment of activity were determined for each sample accordingly. Asterisks indicate that the protein concentration of the anion exchange (Mono Q) sample was elow the limit of detection of the protein measurement assay used ( mg/ml). As a result, total protein, specific activity and fold enrichment values for this step are presented as minimum values ased on the limit of detection of the protein measurement assay. Peptide Sequence MH + (Da) HTGGTEVELTDTGR HGETAWSTLGR WVQLPLAEGSR ADSAVALALEHMSSR TQAELAGQLLGELELDDPIVICSPR QLAVLGLTGHPQPIAAG DVLFVSHGHFSR LAGLTVNEVTGLLAEWDYGSYEGLTTPQIR Supplementary Tale 2. GPM2 peptides identified y LC-MS/MS of 25 kda gel and from Figure 2.
11 Name Sequence Use in This Study JM17 5 TATACTTAAGCGGCGTTGCTCTGGGTCAAGCTCAG 3 JM18 5 AATACCTAGGGGCCAGGTTGCGGTCCGGGGCTTCC 3 JM19 5 TATAAAGCTTCACACCCACGACACACAAGGAACCC 3 JM20 5 ATATATGCATGGCGGCCAATGCGTCGTGCAGCTGC 3 UG1 5 ACCACGCACCAATGCTCTAC 3 UG2 5 CGGTGGTCAAGACCTGGTTC 3 5 GGGGACTGCTTTTTTGTACAAACTTGTGCCTCGGTTACCCGGACAAGTTC 3 5 GGGGACAACTTTGTATAGAAAAGTTGGTACTCGCTGGTGTCCGAGTTACG 3 5 GGGGACAGCTTTCTTGTACAAAGTGGACACCAACAAACAAGGGACGCAACAG 3 5 GGGGACAACTTTGTATAATAAAGTTGTTGACGAGCACCTCGACGACCTTG 3 UG3 5 TACGAGCTGGGCTTCATCGAC 3 UG4 5 TGGGATACTGGCAGGCATGAC 3 clo-glpx-attb2 JM33 UG17-SD 5 GGGGACAGCTTTCTTGTACAAAGTGGAAGGAGGACCAACCATGACAGCTGAGG GATCCGGTT 3 5 GGGGACAACTTTGTATAATAAAGTTGCTTAGGGCAATGGGTACACGGCGCTGCT GTCGC 3 5 GGGGACAGCTTTCTTGTACAAAGTGGAAGGAGGTGTCGGTATGGGCGTGCGCA ACCACCG 3 UG18 5 CTTATCGTCATCGTCCTTGTAGTCCCCGGCTGCGATCGGCTGCGGATGACC 3 KO-glpXsmattB1r KO-glpXsmattB4 KO-glpXsmattB2 KO-glpXsmattB3 OE-gpm2- attb1 (UG) OE-gpm2- attb2r KO-gpm2- attb4 KO-gpm2- attb1r KO-gpm2- attb2 KO-gpm2- attb3 5 GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTGGGCGTGCGCAACCACCGATTGC TAC 3 5 GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTTGTGCGCTCACCCGGCTGCGATCG GC 3 5 GGGGACAACTTTGTATAGAAAAGTTGGCGGTCGGCGACATCGAGCAACACG 3 5 GGGGACTGCTTTTTTGTACAAACTTGCCGACAGATTGTGCCCGACGACATC 3 5 GGGGACAGCTTTCTTGTACAAAGTGGTGGACGCACGGCTGCCCAGCTGGAG 3 5 GGGGACAACTTTGTATAATAAAGTTGTGAGGTCGACGAGATAGCCGTAAGC 3 UG20 5 ATACTGTTGGGCGCGTTGCCTTTC 3 UG21 5 TTGGCCGAACTGGCTAGTGC 3 ΔglpX Knockout ΔglpX Knockout ΔglpX Knockout ΔglpX Knockout ΔglpX Southern Blot ΔglpX Southern Blot Knockout Knockout Knockout Knockout Southern Blot Southern Blot glpx Complementation glpx Complementation gpm2 Complementation gpm2 Complementation 6xHis-Tagged GPM2 6xHis-Tagged GPM2 Δgpm2 Knockout Δgpm2 Knockout Δgpm2 Knockout Δgpm2 Knockout Δgpm2 Southern Blot Δgpm2 Southern Blot Supplementary Tale 3. List of primers used in this study.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 2 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17084 Metabolic anticipation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Hyungjin Eoh, Zhe Wang, Emilie Layre,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 2 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17084 Metabolic anticipation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Hyungjin Eoh, Zhe Wang, Emilie Layre,
Supplementary Information CAND1 controls in vivo dynamics of the Cullin 1-RING ubiquitin ligase repertoire
 Supplementary Information CAD1 controls in vivo dynamics of the Cullin 1-RIG uiquitin ligase repertoire Shuangding Wu, Wenhong Zhu, Tina han, Julia I. Toth, Matthew D. Petroski, Dieter A. Wolf 1 c knd1
Supplementary Information CAD1 controls in vivo dynamics of the Cullin 1-RIG uiquitin ligase repertoire Shuangding Wu, Wenhong Zhu, Tina han, Julia I. Toth, Matthew D. Petroski, Dieter A. Wolf 1 c knd1
0.40. Biochemistry of Carbohydrates
 0.40 Biochemistry of Carbohydrates Biochemistry of Carbohydrates ATP ADP Glycolysis The Breakdown of Glucose Primary Energy Source of Cells Central Metabolic Pathway All Reactions Occur in Cytoplasm Two
0.40 Biochemistry of Carbohydrates Biochemistry of Carbohydrates ATP ADP Glycolysis The Breakdown of Glucose Primary Energy Source of Cells Central Metabolic Pathway All Reactions Occur in Cytoplasm Two
Biochemistry of carbohydrates
 Biochemistry of carbohydrates الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Hanan Jamal لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ In the last lecture we talked about Pyruvate, pyruvate is a central intermediate;
Biochemistry of carbohydrates الفريق الطبي األكاديمي Done By: - Hanan Jamal لكية الطب البرشي البلقاء التطبيقية / املركز 6166 6102/ In the last lecture we talked about Pyruvate, pyruvate is a central intermediate;
Glycolysis. Intracellular location Rate limiting steps
 Glycolysis Definition Fx Fate Site Intracellular location Rate limiting steps Regulation Consume ATP Subs level phosphoryla tion Key reactions control points Nb Oxidation of glucose to give pyruvate (
Glycolysis Definition Fx Fate Site Intracellular location Rate limiting steps Regulation Consume ATP Subs level phosphoryla tion Key reactions control points Nb Oxidation of glucose to give pyruvate (
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis
 Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis 2007-2008 What s the point? The point is to make! 2007-2008 Glycolysis Breaking down glucose glyco lysis (splitting sugar) glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C In the cytosol?
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis 2007-2008 What s the point? The point is to make! 2007-2008 Glycolysis Breaking down glucose glyco lysis (splitting sugar) glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C In the cytosol?
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material HLA-DM Captures Partially Empty HLA-DR Molecules for Catalyzed Peptide Removal Anne-Kathrin Anders, Melissa J. Call, Monika-Sarah E. D. Schulze, Kevin D. Fowler, David A. Schuert,
Supplementary Material HLA-DM Captures Partially Empty HLA-DR Molecules for Catalyzed Peptide Removal Anne-Kathrin Anders, Melissa J. Call, Monika-Sarah E. D. Schulze, Kevin D. Fowler, David A. Schuert,
Gluconeogenesis. Gluconeogenesis / TCA 11/12/2009. Free energy changes in glycolysis 11/13/2009
 Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis / TCA 11/12/2009 Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the
Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis / TCA 11/12/2009 Gluconeogenesis is the process whereby precursors such as lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and amino acids are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the
[U- 13 C5] glutamine. Glutamate. Acetyl-coA. Citrate. Citrate. Malate. Malate. Isocitrate OXIDATIVE METABOLISM. Oxaloacetate CO2.
![[U- 13 C5] glutamine. Glutamate. Acetyl-coA. Citrate. Citrate. Malate. Malate. Isocitrate OXIDATIVE METABOLISM. Oxaloacetate CO2. [U- 13 C5] glutamine. Glutamate. Acetyl-coA. Citrate. Citrate. Malate. Malate. Isocitrate OXIDATIVE METABOLISM. Oxaloacetate CO2.](/thumbs/76/74112154.jpg) Supplementary Figures a. Relative mrna levels Supplementary Figure 1 (Christofk) 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 LAT1 Fumarate Succinate Palmitate Acetyl-coA Oxaloacetate OXIDATIVE METABOLISM α-ketoglutarate
Supplementary Figures a. Relative mrna levels Supplementary Figure 1 (Christofk) 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 LAT1 Fumarate Succinate Palmitate Acetyl-coA Oxaloacetate OXIDATIVE METABOLISM α-ketoglutarate
a b c d e C 3 ]Aspartate [ 20 minutes C 3 ]Hexose-P * * *
![a b c d e C 3 ]Aspartate [ 20 minutes C 3 ]Hexose-P * * * a b c d e C 3 ]Aspartate [ 20 minutes C 3 ]Hexose-P * * *](/thumbs/92/110334219.jpg) Supplemental Figure 1 Metabolic flux with [U- C]Lactate - [ 12 C]Glutamine in primary hepatocytes a b c d e [ C 3 ]Pyruvate [ C 3 ]Malate [ C 3 ]Aspartate [ C 3 ]Citrate [ C 2 ] -Ketoglutarate f g h [
Supplemental Figure 1 Metabolic flux with [U- C]Lactate - [ 12 C]Glutamine in primary hepatocytes a b c d e [ C 3 ]Pyruvate [ C 3 ]Malate [ C 3 ]Aspartate [ C 3 ]Citrate [ C 2 ] -Ketoglutarate f g h [
Information transmission
 1-3-3 Case studies in Systems Biology Goutham Vemuri goutham@chalmers.se Information transmission Fluxome Metabolome flux 1 flux flux 3 Proteome metabolite1 metabolite metabolite3 protein 1 protein protein
1-3-3 Case studies in Systems Biology Goutham Vemuri goutham@chalmers.se Information transmission Fluxome Metabolome flux 1 flux flux 3 Proteome metabolite1 metabolite metabolite3 protein 1 protein protein
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: (Glycolysis) AP Biology
 Cellular Respiration Stage 1: (Glycolysis) What s the point? The point is to make! Glycolysis: Breaking down glucose glyco lysis (splitting sugar) glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C In the cytosol? Why does that
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: (Glycolysis) What s the point? The point is to make! Glycolysis: Breaking down glucose glyco lysis (splitting sugar) glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C In the cytosol? Why does that
Integration & Hormone Regulation
 Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Integration Branchpoints in metabolism where metabolites can go several directions 1. Glucose 6-phosphate Energy needed (low energy charge): glycolysis Low blood sugar: high [glucagon], low [insulin] glycogen
Supplementary Figure 1: Detailed schematic of the synthetic biochemistry system for the conversion of glucose to monoterpenes.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Detailed schematic of the synthetic biochemistry system for the conversion of glucose to monoterpenes. Glycolytic and mevalonate enzymes are highlighted in blue and orange respectively.
Supplementary Figure 1: Detailed schematic of the synthetic biochemistry system for the conversion of glucose to monoterpenes. Glycolytic and mevalonate enzymes are highlighted in blue and orange respectively.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Keller et al. 10.1073/pnas.1222607110 MB1 Ori puc18 Ori AscI (8713) pdad downstream flank pdad PpdaD SphI (6970) Msed1993 ApaI (10721) Apr ApaLI (9115) NcoI (8) PmeI (8796) PvuI
Supporting Information Keller et al. 10.1073/pnas.1222607110 MB1 Ori puc18 Ori AscI (8713) pdad downstream flank pdad PpdaD SphI (6970) Msed1993 ApaI (10721) Apr ApaLI (9115) NcoI (8) PmeI (8796) PvuI
MITOCW watch?v=345wz_7crn4
 MITOCW watch?v=345wz_7crn4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
MITOCW watch?v=345wz_7crn4 The following content is provided under a Creative Commons license. Your support will help MIT OpenCourseWare continue to offer high-quality educational resources for free. To
Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection
 ## Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection Blood glucose (mm/l) 25 2 15 1 5 # 15 3 6 3+3 Time after glucose injection (min) # Figure S1B. α-kg levels in mouse livers after glucose
## Figure S1A. Blood glucose levels in mice after glucose injection Blood glucose (mm/l) 25 2 15 1 5 # 15 3 6 3+3 Time after glucose injection (min) # Figure S1B. α-kg levels in mouse livers after glucose
Supplementary Material. Contents include:
 Supplementary Material Contents include: 1. Supplementary Figures (p. 2-7) 2. Supplementary Figure Legends (p. 8-9) 3. Supplementary Tables (p. 10-12) 4. Supplementary Table Legends (p. 13) 1 Wellen_FigS1
Supplementary Material Contents include: 1. Supplementary Figures (p. 2-7) 2. Supplementary Figure Legends (p. 8-9) 3. Supplementary Tables (p. 10-12) 4. Supplementary Table Legends (p. 13) 1 Wellen_FigS1
What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP
 ATP Chapter 8 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Energy is stored in organic compounds Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins Heterotrophs eat
ATP Chapter 8 What s the point? The point is to make ATP! ATP Flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Energy is stored in organic compounds Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins Heterotrophs eat
(de novo synthesis of glucose)
 Gluconeogenesis (de novo synthesis of glucose) Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the biosynthesis of new glucose. The main purpose of gluconeogenesis is to maintain the constant blood Glc concentration.
Gluconeogenesis (de novo synthesis of glucose) Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the biosynthesis of new glucose. The main purpose of gluconeogenesis is to maintain the constant blood Glc concentration.
Journal of Cell Science Supplementary information. Arl8b +/- Arl8b -/- Inset B. electron density. genotype
 J. Cell Sci. : doi:.4/jcs.59: Supplementary information E9. A Arl8b /- Arl8b -/- Arl8b Arl8b non-specific band Gapdh Tbp E7.5 HE Inset B D Control al am hf C E Arl8b -/- al am hf E8.5 F low middle high
J. Cell Sci. : doi:.4/jcs.59: Supplementary information E9. A Arl8b /- Arl8b -/- Arl8b Arl8b non-specific band Gapdh Tbp E7.5 HE Inset B D Control al am hf C E Arl8b -/- al am hf E8.5 F low middle high
Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet
 Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-fundamentals-ofbiochemistry-4th-edition-by-voet/ Chapter 16: Glycogen
Link download full of Test Bank for Fundamentals of Biochemistry 4th Edition by Voet http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-fundamentals-ofbiochemistry-4th-edition-by-voet/ Chapter 16: Glycogen
Chapter 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism
 Chapter 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism Metabolism of Foods Food is broken down into carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins and sent through catabolic pathways to produce energy. Glycolysis glucose 2 P i 2 ADP
Chapter 13 Carbohydrate Metabolism Metabolism of Foods Food is broken down into carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins and sent through catabolic pathways to produce energy. Glycolysis glucose 2 P i 2 ADP
NC bp. b 1481 bp
 Kcna3 NC 11 178 p 1481 p 346 p c *** *** d relative expression..4.3.2.1 CD4 T cells Kcna1 Kcna2 Kcna3 Kcna4 Kcna Kcna6 Kcna7 Kcnn4 relative expression..4.3.2.1 CD8 T cells Kcna1 Kcna2 Kcna3 Kcna4 Kcna
Kcna3 NC 11 178 p 1481 p 346 p c *** *** d relative expression..4.3.2.1 CD4 T cells Kcna1 Kcna2 Kcna3 Kcna4 Kcna Kcna6 Kcna7 Kcnn4 relative expression..4.3.2.1 CD8 T cells Kcna1 Kcna2 Kcna3 Kcna4 Kcna
Review of Carbohydrate Digestion
 Review of Carbohydrate Digestion Glycolysis Glycolysis is a nine step biochemical pathway that oxidizes glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid. During this process, energy is released and some of it
Review of Carbohydrate Digestion Glycolysis Glycolysis is a nine step biochemical pathway that oxidizes glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid. During this process, energy is released and some of it
Exosomes function in antigen presentation during an in vivo Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection
 Exosomes function in antigen presentation during an in vivo Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection Victoria L. Smith, Yong Cheng, Barry R. Bryant and Jeffrey S. Schorey Supplementary Figure 1: Unprocessed
Exosomes function in antigen presentation during an in vivo Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection Victoria L. Smith, Yong Cheng, Barry R. Bryant and Jeffrey S. Schorey Supplementary Figure 1: Unprocessed
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Notes CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc1,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD,!! Sébastien!M.!
 SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD, SébastienM.Labbé,,MathildeMouchiroud,,AlexandreCaron,,BlandineSecco,, Elizaveta
SUPPLEMENTARY,INFORMATIONS,,,, mtorc,is,required,for,brown,adipose,tissue,recruitment,and, METABOLIC,ADAPTATION,TO,COLD, SébastienM.Labbé,,MathildeMouchiroud,,AlexandreCaron,,BlandineSecco,, Elizaveta
Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: Da. m/z. hrmif ( Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ Da. m/z.
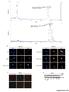 Intensity % Intensity % A Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: 12428.31 Da m/z hrmif (12428.31 Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ 12715.21 Da m/z B HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3 Merge HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3
Intensity % Intensity % A Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: 12428.31 Da m/z hrmif (12428.31 Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ 12715.21 Da m/z B HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3 Merge HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3
Metabolic Shifts in Carbohydrate Metabolism during Embryonic Development of Non-Diapause Eggs of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori
 Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology 73, 15-22 (2004) Metabolic Shifts in Carbohydrate Metabolism during Embryonic Development of Non-Diapause Eggs of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori Daisuke Sakano
Journal of Insect Biotechnology and Sericology 73, 15-22 (2004) Metabolic Shifts in Carbohydrate Metabolism during Embryonic Development of Non-Diapause Eggs of the Silkworm, Bombyx mori Daisuke Sakano
GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels
 GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels - Catabolic process degradative pathway - Energy stored in sugars (carbohydrates) released to perform biological work - Transforms GLUCOSE to PYRUVATE
GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels - Catabolic process degradative pathway - Energy stored in sugars (carbohydrates) released to perform biological work - Transforms GLUCOSE to PYRUVATE
Metabolic engineering some basic considerations. Lecture 9
 Metabolic engineering some basic considerations Lecture 9 The 90ties: From fermentation to metabolic engineering Recruiting heterologous activities to perform directed genetic modifications of cell factories
Metabolic engineering some basic considerations Lecture 9 The 90ties: From fermentation to metabolic engineering Recruiting heterologous activities to perform directed genetic modifications of cell factories
Moh Tarek. Razi Kittaneh. Jaqen H ghar
 14 Moh Tarek Razi Kittaneh Jaqen H ghar Naif Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis is making glucose from non-carbohydrates precursors. Although Gluconeogenesis looks like Glycolysis in many steps, it is not the simple
14 Moh Tarek Razi Kittaneh Jaqen H ghar Naif Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis is making glucose from non-carbohydrates precursors. Although Gluconeogenesis looks like Glycolysis in many steps, it is not the simple
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis (Ch. 6)
 Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis (Ch. 6) What s the point? The point is to make! 2007-2008 Harvesting stored energy Energy is stored in organic molecules carbohydrates, fats, proteins Heterotrophs
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis (Ch. 6) What s the point? The point is to make! 2007-2008 Harvesting stored energy Energy is stored in organic molecules carbohydrates, fats, proteins Heterotrophs
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES. Carbohydrate Metabolism
 ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES I. Glycolysis A. Pathway Regulation of glycolysis Hexokinase: Activated by glucose. Inhibited by G6P. 6-Phosphofructokinase: Inhibited by ATP, especially
ANSC 619 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIES I. Glycolysis A. Pathway Regulation of glycolysis Hexokinase: Activated by glucose. Inhibited by G6P. 6-Phosphofructokinase: Inhibited by ATP, especially
Carbohydrate. Metabolism
 Carbohydrate Metabolism Dietary carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose Mouth salivary amylase Summary of Carbohydrate Utilization Utilization for energy (glycolysis) ligosaccharides and disaccharides
Carbohydrate Metabolism Dietary carbohydrates (starch, glycogen, sucrose, lactose Mouth salivary amylase Summary of Carbohydrate Utilization Utilization for energy (glycolysis) ligosaccharides and disaccharides
Pathway overview. Glucose + 2NAD + + 2ADP +2Pi 2NADH + 2pyruvate + 2ATP + 2H 2 O + 4H +
 Glycolysis Glycolysis The conversion of glucose to pyruvate to yield 2ATP molecules 10 enzymatic steps Chemical interconversion steps Mechanisms of enzyme conversion and intermediates Energetics of conversions
Glycolysis Glycolysis The conversion of glucose to pyruvate to yield 2ATP molecules 10 enzymatic steps Chemical interconversion steps Mechanisms of enzyme conversion and intermediates Energetics of conversions
Supplementary Figure S1. TRAIL-induced necroptosis at acidic phe is dependent on
 Online supplementary information Supplementary Figure S1. TRAIL-induced necroptos at acidic phe is dependent on RIPK1 and RIPK3. (a) HT29 cells were tranently transfected with RIPK1, RIPK3, RIPK1/ RIPK3
Online supplementary information Supplementary Figure S1. TRAIL-induced necroptos at acidic phe is dependent on RIPK1 and RIPK3. (a) HT29 cells were tranently transfected with RIPK1, RIPK3, RIPK1/ RIPK3
Control 7 d cold 7 d CL
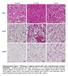 Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
How do we retain emphasis on function?
 Systems Biology Systems biology studies biological systems by systematically perturbing them (biologically, genetically, or chemically); monitoring the gene, protein, and informational pathway responses;
Systems Biology Systems biology studies biological systems by systematically perturbing them (biologically, genetically, or chemically); monitoring the gene, protein, and informational pathway responses;
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Dr. Mohnen s notes on GLUCONEOGENESIS
 Dr. Mohnen s notes on GLUCONEOGENESIS Note: Even though we did not get through all of these slides during lecture, I advise you to look them all through because they will be helpful to you as you learn
Dr. Mohnen s notes on GLUCONEOGENESIS Note: Even though we did not get through all of these slides during lecture, I advise you to look them all through because they will be helpful to you as you learn
Synthetic non-oxidative glycolysis (NOG) enables complete carbon conservation
 Synthetic non-oxidative glycolysis (NOG) enables complete carbon conservation Igor W. Bogorad, Tzu-Shyang Lin, James C. Liao Nature, vol 502, 2013 Presented by Elise Jyränoja, Kellen Leskinen and Tia Korhonen
Synthetic non-oxidative glycolysis (NOG) enables complete carbon conservation Igor W. Bogorad, Tzu-Shyang Lin, James C. Liao Nature, vol 502, 2013 Presented by Elise Jyränoja, Kellen Leskinen and Tia Korhonen
7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life Is Work Living
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life Is Work Living
Control vs. HFD-lipid
 Animals Control vs. T1D vs. T1D-leptin and Hyperinsulinemic-diabetic vs. hyperinsulinemic-diabetic-leptin STZ ± nicotinamide injection Leptin or saline 6 8 1 12 2 4 6 8 1 12 2 4 6 8 1 12 Control vs. HFD-lipid
Animals Control vs. T1D vs. T1D-leptin and Hyperinsulinemic-diabetic vs. hyperinsulinemic-diabetic-leptin STZ ± nicotinamide injection Leptin or saline 6 8 1 12 2 4 6 8 1 12 2 4 6 8 1 12 Control vs. HFD-lipid
BIOLOGY. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 9.2 Light energy
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 9.2 Light energy
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION. C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete loss of electrons Reduction: partial or complete gain of electrons
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete loss of electrons Reduction: partial or complete gain of electrons
BIOLOGY. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Life Is Work Living cells
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Life Is Work Living cells
BIOLOGY. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Life Is Work Living cells
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Life Is Work Living cells
Photosynthesis in chloroplasts. Cellular respiration in mitochondria ATP. ATP powers most cellular work
 Light energy ECOSYSTEM CO + H O Photosynthesis in chloroplasts Cellular respiration in mitochondria Organic molecules + O powers most cellular work Heat energy 1 becomes oxidized (loses electron) becomes
Light energy ECOSYSTEM CO + H O Photosynthesis in chloroplasts Cellular respiration in mitochondria Organic molecules + O powers most cellular work Heat energy 1 becomes oxidized (loses electron) becomes
7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life Is Work Living
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life Is Work Living
a Anti-Dab2 RGD Merge
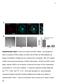 a Anti-Da Merge *** ** Percentage of cells adhered 8 6 4 RGE RAD RGE RAD Supplementary Figure Da are localized at clusters. (a) Endogenous Da is localized at clusters. (), ut not RGE nor RAD peptides can
a Anti-Da Merge *** ** Percentage of cells adhered 8 6 4 RGE RAD RGE RAD Supplementary Figure Da are localized at clusters. (a) Endogenous Da is localized at clusters. (), ut not RGE nor RAD peptides can
Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR-2B cells untreated (-) or stimulated (+) for 45 min
 Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR2B cells untreated () or stimulated () for 45 min with 5 ng/ml TGFβ or 10 ng/ml BMP4 were incubated with
Figure S1. Sorting nexin 9 (SNX9) specifically binds psmad3 and not psmad 1/5/8. Lysates from AKR2B cells untreated () or stimulated () for 45 min with 5 ng/ml TGFβ or 10 ng/ml BMP4 were incubated with
Notes CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions.
 I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions. These are some questions from doctor2015 med exam : 1. One of them isn t acute phase protein
I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions. These are some questions from doctor2015 med exam : 1. One of them isn t acute phase protein
I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions.
 I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions. These are some questions from doctor2015 med exam : 1. One of them isn t acute phase protein
I tried to put as many questions as possible, but unfortunately only answers were found without the questions. These are some questions from doctor2015 med exam : 1. One of them isn t acute phase protein
Development of efficient Escherichia coli succinate production strains
 Development of efficient Escherichia coli succinate production strains Ka-Yiu San Department of Bioengineering Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Rice University, Houston, Texas International
Development of efficient Escherichia coli succinate production strains Ka-Yiu San Department of Bioengineering Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Rice University, Houston, Texas International
METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI 1 METABOLISM Process of how cells acquire, transform, store and use energy Study of the chemistry, regulation and energetics
METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI 1 METABOLISM Process of how cells acquire, transform, store and use energy Study of the chemistry, regulation and energetics
Chromatin IP (Isw2) Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles.
 Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
Chromatin IP (Isw2) 7/01 Toshi last update: 06/15 Reagents Fix soln: 11% formaldehyde, 0.1 M NaCl, 1 mm EDTA, 50 mm Hepes-KOH ph 7.6. Freshly prepared. Do not store in glass bottles. 2.5 M glycine. TBS:
CH 7: Cell Respiration and Fermentation Overview. Concept 7.1: Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels
 CH 7: Cell Respiration and Fermentation Overview Living cells require energy from outside sources Some animals obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other organisms Energy flows into
CH 7: Cell Respiration and Fermentation Overview Living cells require energy from outside sources Some animals obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other organisms Energy flows into
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Carbohydrate Metabolism
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46451 1 Carbohydrate Metabolism OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m46451 1 Carbohydrate Metabolism OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
CIII Advances in Engineering Metabolism & Microbial Conversion
 CIII Advances in Engineering Metabolism & Microbial Conversion George Bennett, Ka-Yiu San, Rice University Manipulation and Balance of Reducing Equivalents to Enhance Productivity of Chemicals in E. coli
CIII Advances in Engineering Metabolism & Microbial Conversion George Bennett, Ka-Yiu San, Rice University Manipulation and Balance of Reducing Equivalents to Enhance Productivity of Chemicals in E. coli
BIOLOGY. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation CAMPBELL. Photosynthesis in chloroplasts. Light energy ECOSYSTEM. Organic molecules CO 2 + H 2 O
 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 9.1 Figure 9.2
9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 9.1 Figure 9.2
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table.
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tale. Type of file: VI Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description:
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Tale. Type of file: VI Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description:
7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life Is Work Living
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: Life Is Work Living
-ketoglutarate coordinates carbon and nitrogen utilization via Enzyme I inhibition
 -ketoglutarate coordinates carbon and nitrogen utilization via Enzyme I inhibition Christopher D Doucette, David J Schwab, Ned S Wingreen, and Joshua D Rabinowitz Supplementary Results 1. Supplementary
-ketoglutarate coordinates carbon and nitrogen utilization via Enzyme I inhibition Christopher D Doucette, David J Schwab, Ned S Wingreen, and Joshua D Rabinowitz Supplementary Results 1. Supplementary
Chapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway
 Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition Donald Voet Judith G. Voet harlotte W. Pratt hapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Page No. 47-490 Introduction Glucose: is major source of metabolic
Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition Donald Voet Judith G. Voet harlotte W. Pratt hapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Page No. 47-490 Introduction Glucose: is major source of metabolic
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Photosynthesis generates O 2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Photosynthesis generates O 2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism Learning Objectives: q Role in
CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism Learning Objectives: q Role in
The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry. Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013
 The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013 What is it? Hey! Look at that! Something is reacting in here! I just wish I knew what it
The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013 What is it? Hey! Look at that! Something is reacting in here! I just wish I knew what it
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Glycolysis is the sequence of reactions that metabolize one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate with the production of two molecules
 Glycolysis is the sequence of reactions that metabolize one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate with the production of two molecules of ATP Anaerobic no O 2 needed aerobic O 2 needed In
Glycolysis is the sequence of reactions that metabolize one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate with the production of two molecules of ATP Anaerobic no O 2 needed aerobic O 2 needed In
DATA. Miriah Meyer University of Utah. cs6964 January
 cs6964 January 19 212 DATA Miriah Meyer University of Utah slide acknowledgements: Tamara Munzner, University of British Columbia Hanspeter Pfister, Harvard University 2 LAST TIME 3 target translate design
cs6964 January 19 212 DATA Miriah Meyer University of Utah slide acknowledgements: Tamara Munzner, University of British Columbia Hanspeter Pfister, Harvard University 2 LAST TIME 3 target translate design
Mock Exam All of the following are oxidizing agents EXCEPT a. NADP+ b. NADH c. FAD d. e. cytochromes
 Mock Exam 2 1. The Calvin cycle differs from the citric acid cycle in that it a. produces ATP b. directly requires light to run c. depends on the products of an electron transport chain d. occurs in a
Mock Exam 2 1. The Calvin cycle differs from the citric acid cycle in that it a. produces ATP b. directly requires light to run c. depends on the products of an electron transport chain d. occurs in a
CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions
 CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions Glucose metabolism 1. Below is depicted glucose catabolism. Indicate on the pathways the following: A) which reaction(s) of glycolysis are irreversible B) where energy
CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions Glucose metabolism 1. Below is depicted glucose catabolism. Indicate on the pathways the following: A) which reaction(s) of glycolysis are irreversible B) where energy
TIGAR's promiscuity Bolaños, Juan P.
 TIGAR's promiscuity Bolaños, Juan P. TIGAR [TP53 (tumour protein 53)-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator] is an important survival factor for cancer cells. The enzymatic activity supported by sequence
TIGAR's promiscuity Bolaños, Juan P. TIGAR [TP53 (tumour protein 53)-induced glycolysis and apoptosis regulator] is an important survival factor for cancer cells. The enzymatic activity supported by sequence
Chapter 15 Homework Assignment
 Chapter 15 Homework Assignment The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 3, 5, 6, 8, 9 Chapter 15 1 Regulation of Metabolic Pathways Dynamic Steady State Fuels, such as glucose, enter
Chapter 15 Homework Assignment The following problems will be due once we finish the chapter: 3, 5, 6, 8, 9 Chapter 15 1 Regulation of Metabolic Pathways Dynamic Steady State Fuels, such as glucose, enter
Yield of energy from glucose
 Paper : Module : 05 Yield of Energy from Glucose Principal Investigator, Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Prof. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dept. of Biosciences, Saurashtra University, Rajkot - 360005
Paper : Module : 05 Yield of Energy from Glucose Principal Investigator, Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Prof. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dept. of Biosciences, Saurashtra University, Rajkot - 360005
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 20 Done by Corrected by Rana Ghassan Doctor Only 4 questions in the mid-term exam are based on the 4 lectures to be given by Dr Faisal. Dr Faisal will give us 10 lectures, the first 4 are included
number 20 Done by Corrected by Rana Ghassan Doctor Only 4 questions in the mid-term exam are based on the 4 lectures to be given by Dr Faisal. Dr Faisal will give us 10 lectures, the first 4 are included
Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3. Glycolysis is only the start. Cellular respiration. Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle.
 Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3 Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle AP 2006-2007 Biology Glycolysis is only the start Glycolysis glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C Pyruvate has more energy to yield 3 more C to strip
Cellular Respiration Stage 2 & 3 Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle AP 2006-2007 Biology Glycolysis is only the start Glycolysis glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C Pyruvate has more energy to yield 3 more C to strip
Cellular Respiration. The Details
 Cellular Respiration The Details LEARNING GOALS By the end of the lesson you will be able to; 1. Describe in detail the 4 stages of cellular respira;on 2. Track the crea;on of ATP and energy carrier molecules
Cellular Respiration The Details LEARNING GOALS By the end of the lesson you will be able to; 1. Describe in detail the 4 stages of cellular respira;on 2. Track the crea;on of ATP and energy carrier molecules
CELLULAR METABOLISM. Metabolic pathways can be linear, branched, cyclic or spiral
 CHM333 LECTURE 24 & 25: 3/27 29/13 SPRING 2013 Professor Christine Hrycyna CELLULAR METABOLISM What is metabolism? - How cells acquire, transform, store and use energy - Study reactions in a cell and how
CHM333 LECTURE 24 & 25: 3/27 29/13 SPRING 2013 Professor Christine Hrycyna CELLULAR METABOLISM What is metabolism? - How cells acquire, transform, store and use energy - Study reactions in a cell and how
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Integration of Metabolism
 Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Transport. Oxidation. Electron. which the en the ETC and. of NADH an. nd FADH 2 by ation. Both, Phosphorylation. Glycolysis Glucose.
 Electron Transport Chain and Oxidation Phosphorylation When one glucose molecule is oxidized to six CO 2 molecules by way of glycolysiss and TCA cycle, considerable amount of energy (ATP) is generated.
Electron Transport Chain and Oxidation Phosphorylation When one glucose molecule is oxidized to six CO 2 molecules by way of glycolysiss and TCA cycle, considerable amount of energy (ATP) is generated.
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Table S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample
 Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways
 METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways Metabolism Metabolism involves : Catabolic reactions that break down large, complex molecules to provide energy and smaller molecules. Anabolic reactions that use ATP energy
METABOLISM Biosynthetic Pathways Metabolism Metabolism involves : Catabolic reactions that break down large, complex molecules to provide energy and smaller molecules. Anabolic reactions that use ATP energy
Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy. Examples:
 Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy Examples: Energy can be transformed: Thermodynamics: First law of Thermodynamics: Second
Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy Examples: Energy can be transformed: Thermodynamics: First law of Thermodynamics: Second
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 5, part A Microbial Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L. Case Microbial
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 5, part A Microbial Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L. Case Microbial
ATP. Principles of Energy Harvest. Chapter 9~ The point is to make ATP! Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy. What s the point?
 Chapter 9~ Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy What s the point? The point is to make! 2006-2007 Principles of Energy Harvest Catabolic pathway Fermentation Cellular Respiration C6H126 + 62
Chapter 9~ Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy What s the point? The point is to make! 2006-2007 Principles of Energy Harvest Catabolic pathway Fermentation Cellular Respiration C6H126 + 62
incorporation into fructose-6-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate (F6P/G6P); 2-
 Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
Student Number: To form the polar phase when adsorption chromatography was used.
 Name: Student Number: April 14, 2001, 1:30 AM - 4:30 PM Page 1 (of 4) Biochemistry II Lab Section Final Examination Examiner: Dr. A. Scoot 1. Answer ALL questions in the space provided.. 2. The last page
Name: Student Number: April 14, 2001, 1:30 AM - 4:30 PM Page 1 (of 4) Biochemistry II Lab Section Final Examination Examiner: Dr. A. Scoot 1. Answer ALL questions in the space provided.. 2. The last page
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead

 Supplementary Figure 1 a OD c. 1. 1... Time [min] 1 p
Supplementary Figure 1 a OD c. 1. 1... Time [min] 1 p