Resolving Inflammation: Novel Control Pathways for Chronic Health Conditions
|
|
|
- Emil Collins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pre-Conference, New York, NY February 24, 216 Resolving Inflammation: Novel Control Pathways for Chronic Health Conditions Joan Clària Hospital Clínic of Barcelona Esther Koplowitz Research Center-IDIBAPS School of Medicine-University of Barcelona
2 Outline Unresolved inflammation in chronic health conditions (i.e. obese subjects and associated disorders) Specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators (SPM). Deficit of SPM in chronic metabolic diseases. Biological properties of SPM on insulin sensitive tissues. In vitro actions of SPM in adipocytes, macrophages and liver cells. Translational studies in patients with chronic metabolic disorders.
3 Prevalent obesity comorbidities INCREASED RISK: Type 2 diabetes (6-9%) Dyslipidemia (High LDL, TAG: 25-4%) Hypertension (>14/9: 7-8%) Vascular disease (CHD, stroke: 5-75%) "A Family", 1989 by Fernando Botero Liver disease (2-4%) Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Adapted from Carey et al. Diabetes 1996
4 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Prevalence in Obese Individuals: >4% >2% 5-1% Steatosis Steatohepatitis Fibrosis/Cirrhosis Fat accumulates in the liver Fat plus inflammation Scar tissue replaces liver cells Non-Alcoholic (NAFLD) Alcoholic (ALD)
5 Up-regulation of genes involved in the desaturation of fatty acids in patients with NASH CT NASH Biosynthesis of unsaturated fatty acids CT NASH FADS1 (D5 desaturase) SCD-1 (D9 desaturase) FADS2 (D6 desaturase) ELOVL6 ELOVL5 SC5DL desaturase 6 desaturase 9 desaturase Saturation Index (18:1/18:) Gene expression P<.5 Gene expression P<.1 Gene expression P<.1 Ratio P<.1 5 CT NASH 4 CT NASH 6 CT NASH CT NASH López-Vicario and Clària. Gut 214
6 Altered omega-6/omega-3 ratio in patients with NAFLD López-Vicario and Clària. Gut 214
7 Adipokines in Obesity Hormones: Leptin, adiponectin, resistin Cytokines: TNFα, IL-6, IL-8, IL-1, MCP-1 Obese Complement Factors: Adipsin, complement factor B Enzymes: PAI-1, ACE, LPL Growth Factors: VEGF, HGF Adiponectin Anti-inflammatory Insulin Sensitizing Leptin, TNFα, IL-6, MCP-1 Pro-inflammatory Insulin Resistant Unbalanced Adipokine Release Insulin Resistance NAFLD
8 Obesity Triggers Adipose Tissue Inflammation Lean Obese Adipocyte hypertrophy Hypoxia Exacerbated production of Inflammatory Mediators Recruitment of Macrophages Adapted from Wellen and Hotamisligil. J Clin Invest. 23
9 Unresolved inflamed Adipose Tissue = Target NAFLD
10 Resolution is Part of the Inflammatory Response Inflammation Pro-resolving mediators Modified from Meneghin and Hogaboam, J. Clin. Invest. 27
11 Lipidomic Analysis of Self-Resolving Exudates Zymosan A (1 mg intraperitoneal) peritonitis Various timepoints (time) Collect peritoneal exudates 72 h LC-MS/MS analysis Fatty acids (FA) FA oxygenated products Adapted from Bannenberg and Serhan, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 21
12 Fatty Acids Fatty Acids
13 Bioactive Lipid Mediators Lopategi and Clària, Mol Cell Endocrinol 215.
14 Lipid Mediators Derived from Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Omega-6 Omega-3 Arachidonic Acid 2:4n-6 DHA 22:6n-3 EPA 2:5n-3 First double bond at 6 carbons from methyl end First double bond at 3 carbons from methyl end SPM Inflammatory Mediators Prostaglandins and Leukotrienes Anti-inflammatory Mediators Resolvins, Protectins and Maresins
15 Serhan CN. Nature 214 Bioactive DHA Metabolome DHA 4-hydroperoxy- 17S-HDHA 4(5)-epoxy- 17S-HDHA 7-hydroperoxy- 17S-HDHA 7(8)-epoxy- 17S-HDHA 17S-HpDHA 5-LOX 5-LOX Epoxidation Hydrolysis 17S-HDHA MaR1 [N]PD1 17S-HpDHA 14S-HpDHA Hydrolase Epoxidation Hydrolysis MaR2 Peroxidase Peroxidase OH OH OH OH OH OH HO RvD5 HO HO RvD1 HO HO OH RvD2 OH OH HO RvD3 OH HO HO Hydrolysis Hydrolysis RvD6 OH OH HOOC RvD4 OH HOOC OH OH Acetylated COX-2 5-LOX AT-Resolvins Peroxidase 17R-HpDHA 15-LOX 15-LOX 12-LOX
16 Bioactive Lipid Mediators in Adipose Tissue Specialized Pro-resolving Mediators (SPM) Protectins, Resolvins, Maresins and Lipoxins Pro-inflammatory Lipid Mediators Prostaglandins Leukotrienes Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Endocrine Dysfunction in Obesity White Adipose Tissue Adipocytes Stromal Vascular Cells (pre-adipocytes, macrophages)
17 Increased Omega-6-derived Eicosanoids in Obesity Relative Intensity (%) 1 5 LXA 4 PGD 2 PGE 2 5-HETE 12-HETE 15-HETE LTB 4 pg/mg tissue LTB 4 P<.5 mrna expression (r.u.) FLAP 1.8 P< Time, min Horrillo and Clària. J. Immunol. 21
18 Deficit of Pro-resolving Mediators in Obese Adipose Tissue 5-LOX M C+ C- ALX/FPR2 1 RvD2 RvD1 PD1 12/15-LOX CYP45 GAPDH ChemR23 X1 X2 Relative Intensity (%) Time, min m>z 375> > >153 ALX/FPR2 ChemR23 Lean Obese C Lean Obese pg/mg tissue Lean Obese P<.5 P<.1 RvD1 RvD2 PD1 Relative Intensity (%) 1 RvD H O H O O H m/z, Da C O O H =M-H 357=M-H-H 2 O 339=M-H-2H 2 O 313=M-H-H 2 O-CO 2 331=M-H-CO 2 295=M-H-2H 2 O-CO 2 259=277-H 2 O 215=233-H 2 O Clària and Serhan. J. Immunol. 212
19 Impaired Formation of Pro-resolving Mediators in Patients with Peripheral Vascular Disease 5 Relative Intensity (%) Time, min HDHA 17-HDHA PD1 12-LOX DHA 14-HDHA 14-H(p)DHA 17-H(p)DHA 17-HDHA MaR1 5-LOX 15-LOX RvD1 RvD2 5-LOX PD1 7-HDHA MCP-1 PAI Resistin IL-8 Rel. Int. (%) HO 17-HDHA m/z, Da 343=M-H 325=M-H-H 2 O 299=M-H-CO 2 281=M-H-H 2 O-CO 2 21=245-CO 2 Rel. Int. (%) PD1 OH m/z, Da OH 359=M-H 297=M-H-H 2 O-CO 2 pg/g tissue Control PVD pg/g tissue Control PVD P<.1 Subcutaneous Spearman s correlation coeff. 18-HEPE (n=11), pg/g HDHA (n=11), pg/g.66.3 P P< HDHA 14-HDHA 17-HDHA RvD1 RvD2 PD1 Clària and Serhan. Am. J. Physiol. (Cell. Physiol.) 213
20 Anatomical heterogeneity in human fat depots Increased levels in self-resolving peri-wound human fat Control SC fat Peri-wound SC fat H&E Masson s Trichrome Monohydroxy Biomarkers from DHA Resolvins and Protectins from DHA Monohydroxy Biomarkers from DHA Resolvins and Protectins from DHA Subcutaneous Perivascular Control Peri-wound Clària and Serhan. Am. J. Physiol. (Cell. Physiol.) 213
21 Pro-resolving Mediators Reduce Adipose Tissue Inflammation ng/mg tissue Adiponectin P<.1 ng/mg tissue P<.5 Adiponectin P<.1 P<.5 P<.5 P<.1 ng/mg tissue Leptin P<.5 P<.1 Lean Obese. 8x1 6 4x1 6 TNFα IL-6 IL-12 IL-1 IL-1β P<.5 P<.5 P<.5 IL-4 LTB 4 4 P<.5 3 pg/g tissue P<.5 P<.5 P<.5 P<.5 % relative to control Monocyte Adhesion to Adipocytes V P<.5 P<.5 RvD1 RvD2 % relative to control Transadipose Migration V P<.5 P<.5 RvD1 RvD2 Clària and Serhan. J. Immunol. 212 LTB 4 LTB 4
22 RvD1 Promotes M2 Polarization of Adipose Tissue Macrophages Chow HFD HFD+DHA 16.3 % 29.6 % 26.4 % CD11b F4/8lo 23.3% F4/8hi 6.7% F4/8lo 26.8% F4/8hi 15.6% F4/8hi 9.3% F4/8lo 27.3% F4/8 Clària et al. Front. Immunol. 211 mrna expression (arbitrary units) Arginase RvD1 (nm) arbitrary units arbitrary units IFNγ/LPS IL-4 RvD1 TNFα 4 IL Relative expression (arbitrary units) Arg IL Ym1 RELMα ADP SVC ADP SVC ADP SVC ADP SVC CD26 ADP SVC Titos and Clària. J. Immunol. 211
23 Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Adapted from Adams et al. CMAJ 25 Pharmacological treatment Steatosis Steatohepatitis Fibrosis/Cirrhosis Life-style changes Calorie Restriction + Physical Exercise RvD1? Lipid accumulation? Inflammation Fat accumulates in the liver Fat plus inflammation Scar tissue replaces liver cells
24 RvD1 Actions on Hepatic Inflammation Design of the Study Chow CT Chow (Chow group, n=9) Switch from HFD to chow diet; calorie restriction (CR) HFD (CT group, n=13) CR+ Plb (CR group, n=8) CR+ RvD1 (3 ng/mouse day, n=7) Oil Red-O C57BL/6J weeks Chow CT CR CR+RvD1 Hematoxylin-eosin staining F4/8 staining CR Chow CR+RvD1 CT % Stained area Macrophage Infiltrate P<.1,c Chow CT CR CR+RvD1 GAPDH Protein expression (relative units) CCR CCR7 (M1 marker) Chow P<,5 CT CR CR + RvD1 Arg1 b-actin Protein expression (relative units) Arg1 (M2 marker) Chow, CT CR CR + RvD1 CR CR+RvD1 Rius and Clària. FASEB J. 214
25 RvD1 Anti-inflammatory Actions in Precision-Cut Liver Tissue Slices Resting 2h 21% O 2 5 µm Hypoxia mrna expression (arbitrary units) Precision-cut Liver Slices 21% O 2 Normoxia Veh Veh 1% O 2 Hypoxia Tissue collection RvD1 1 nm 18h Hypoxia + RvD1 % change vs control RvD COX-2 β-actin P<.1 P<.1 P<.5 IL-1β β-actin P<.5 Clodronate Liposomes (CLL) Rius and Clària. FASEB J COX-2 2. IL-1β 6 IL CCR7 mrna expression (arbitrary units) mrna expression (arbitrary units) mrna expression (arbitrary units) 4 2 mrna expression (arbitrary units) 1..5 Veh RvD1 CLL+Hypoxia. Veh RvD1 CLL+Hypoxia Veh RvD1 CLL+Hypoxia. Veh RvD1 CLL+Hypoxia
26 RvD1 Modulates Hepatic MicroRNA levels microrna array Placebo Group (n=6) RvD1 Group (n=6) 1 % expression vs Placebo Pre-miRNA Mature-miRNA Rius and Clària. FASEB J. 214
27 Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) Rius and Clària. FASEB J. 214 RvD1 IL-1 IL-6 IL-1 IL-1R CCR-7 HIF-1α
28 Fat-1 mice: transgenic expression of an omega-3 desaturase gene J X Kang. The Laboratory for Lipid Medicine and Technology, Harvard University. C. elegans Omega-3 desaturase Microinjection into fertilized egg Fat-1 mice Relative intensity 9 AA EPA AA EPA WT Fat-1 DPA DPA DHA DHA % Area Ratio ω-3 index CT Fat-1 ω-6/ω Retention Time (min) CT Fat-1 López-Vicario and Clària. Gut 214 White et al. Diabetes 21 Hudert et al. PNAS 26
29 Fat-1 mice are Protected from Hepatic Steatosis and Inflammation mg/dl ng/ml Body weight (g) Serum Insulin 3 a c c c c c c b a Total Cholesterol 25 c CT CT Fat-1 n3 Lean HFD CT CT Fat-1 n3 Lean HFD weeks mg/dl mg/dl c c c c c c c Triglycerides CT CT Fat-1 n3 Lean HFD Serum Glucose a a HFD-CT HFD-n3 CT CT Fat-1 n3 Lean HFD HFD-Fat-1 Lean Ratio P-JNK1 P-JNK2 JNK2 JNK1 a WT P-JNK1/JNK1. CT CT Fat-1 n3 Lean HFD Ratio Fat-1 Lean HFD CT CT Fat-1 n3 P-JNK2/JNK2 a. CT CT Fat-1 n3 Lean HFD Oil Red-O F4/8+ H&E F4/8+ Adipose tissue WT WT Liver Fat-1 Fat-1 López-Vicario and Clària. Gut 214
30 Increased omega-3 epoxides in Fat-1 mice López-Vicario and Clària. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 215 PLA2 Cell membrane AA DHA EPA CYP CYP 5,6-EET 8,9-EET O 11,12-EET O 14,15-EET 19,2-EDP 17,18-EEQ O O O O Omega-6 epoxides Omega-3 epoxides seh Inhibitor seh 5,6-DHET 8,9-DHET 11,12-DHET 14,15-DHET Inactive metabolites 19,2-DiHDPA 17,18-DiHETE
31 Omega-3 epoxides regulate autophagy and ER stress in hepatocytes López-Vicario and Clària. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 215
32 Summary of Metabolic Actions of Omega-3-derived Lipid Mediators López-Vicario and Clària. Eur J Pharmacol 215
33 Summary - Un-resolved inflammation is a common finding in chronic health conditions. - Chronic metabolic diseases have a remarkable deficit in SPM. - SPM are endogenous immunoresolvents promoting the resolution of inflammation. - SPM promote resolution by shifting macrophages toward a M2 phenotype and deactivating the inflammasome. - SPM exert protective actions by blocking ER stress and improving survival in parenchymal cells. - SPM are a promising discovery for chronic health conditions.
34 LAB MEMBERS Current Dr. Esther Titos Dr. Aritz Lopategi Dr. Cristina López-Vicario Dr. Naira Rico Bibiana Rius José Alcaraz Anabel Martínez Albert Salvatella Former Dr. Verónica García-Alonso Dr. Eva Morán-Salvador (Newcastle University) Dr. Natàlia Ferré (Universitat Rovira i Virgili) Dr. Marta López-Parra (Centro Nacional de Análisis Genómico) Dr. Anna Planagumà (Almirall) Dr. Ana González-Périz (Centro Nacional de Análisis Genómico) Dr. Raquel Horrillo (Grifols) Dr. Marcos Martínez-Clemente (Grifols) COLLABORATORS Dr. Charles N. Serhan (BWH/Harvard Univ.) Dr. Karsten Gronert (Univ. California Berkeley) Dr. Bruce Hammock (Uni. California Davis) Dr. Colin Funk (Queen s Univ.) Dr. Per-Johan Jakobsson (Karolinska Institutet) Dr. Mario Romano (Univ. Chieti)
Understanding How Allergic Responses End: The Allergy Resolvome. Lipid mediators
 Understanding How Allergic Responses End: The Allergy Resolvome Lipid mediators Koichiro Asano Tokai University School of Medicine, Kanagawa, JAPAN ko-asano@tokai-u.jp Resolution of granulocytic inflammation
Understanding How Allergic Responses End: The Allergy Resolvome Lipid mediators Koichiro Asano Tokai University School of Medicine, Kanagawa, JAPAN ko-asano@tokai-u.jp Resolution of granulocytic inflammation
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fish Oils
 Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fish Oils A. Macrophage Production of Eicosanoids B. w-3 PUFA Supplementation of Macrophages C. w-3 PUFA in IR & diabetes Oswald Quehenberger Departments of Medicine and Pharmacology
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Fish Oils A. Macrophage Production of Eicosanoids B. w-3 PUFA Supplementation of Macrophages C. w-3 PUFA in IR & diabetes Oswald Quehenberger Departments of Medicine and Pharmacology
Omega 3 and its impact on immune health:
 Omega 3 and its impact on immune health: exploring the potential of omega 3 Gerard Bannenberg November 20 th, 2014 Food Matters Live, London Session: Capitalising on the immunity 'super' trend Objectives
Omega 3 and its impact on immune health: exploring the potential of omega 3 Gerard Bannenberg November 20 th, 2014 Food Matters Live, London Session: Capitalising on the immunity 'super' trend Objectives
Differentiating omega-3 fatty acids from SPMs (specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators)
 NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre in nutrition Differentiating omega-3 fatty acids from SPMs (specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators) Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University
NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre in nutrition Differentiating omega-3 fatty acids from SPMs (specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators) Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of human carotid plaques. (a) Flash-frozen human plaques were separated into vulnerable (V) and stable (S),
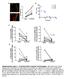 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of human carotid plaques. (a) Flash-frozen human plaques were separated into vulnerable (V) and stable (S), regions which were then quantified for mean fluorescence
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of human carotid plaques. (a) Flash-frozen human plaques were separated into vulnerable (V) and stable (S), regions which were then quantified for mean fluorescence
Involvement of n-3 PUFA-derived lipid mediators in the resolution of brain inflammation
 The 1 th Nutrition-Neuroscience meeting The 27 th of march 217 Involvement of n-3 PUFA-derived lipid mediators in the resolution of brain inflammation Charlotte Rey- PhD student Acute inflammatory response
The 1 th Nutrition-Neuroscience meeting The 27 th of march 217 Involvement of n-3 PUFA-derived lipid mediators in the resolution of brain inflammation Charlotte Rey- PhD student Acute inflammatory response
Disclosures for Charles N. Serhan
 IOM NAS Washington June 24 21 Resolvins & Protectins : SPM in & Organ Protection Charles N. Serhan Director & Prof. Center for Experimental Therapeutics BWH Harvard Medical School Prof. Dept Oral Medicine,
IOM NAS Washington June 24 21 Resolvins & Protectins : SPM in & Organ Protection Charles N. Serhan Director & Prof. Center for Experimental Therapeutics BWH Harvard Medical School Prof. Dept Oral Medicine,
FAPESP Week /21/2017
 Texas Tech University Dr Naima Moustaid-Moussa Texas Tech University FAPESP Week 2017 09/21/2017 University of Sao Paulo Dr Sonia Jancar ICB-USP Theresa Ramalho MS PhD candidate, Immunology ICB-USP Dr
Texas Tech University Dr Naima Moustaid-Moussa Texas Tech University FAPESP Week 2017 09/21/2017 University of Sao Paulo Dr Sonia Jancar ICB-USP Theresa Ramalho MS PhD candidate, Immunology ICB-USP Dr
Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human
 July 9, 2015, Ion Channel Retreat, Vancouver Ion Channel and Pain Targets Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Pain Research Division Department of Anesthesiology
July 9, 2015, Ion Channel Retreat, Vancouver Ion Channel and Pain Targets Modulation of TRP channels by resolvins in mouse and human Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Pain Research Division Department of Anesthesiology
T he resolution of acute inflammation is an active process temporally orchestrated by local-acting mediators
 SUBJECT AREAS: EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF DISEASE ACUTE INFLAMMATION INNATE IMMUNITY CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Received 5 March 2013 Accepted 13 May 2013 Published 5 June 2013 Correspondence and requests for materials
SUBJECT AREAS: EXPERIMENTAL MODELS OF DISEASE ACUTE INFLAMMATION INNATE IMMUNITY CHRONIC INFLAMMATION Received 5 March 2013 Accepted 13 May 2013 Published 5 June 2013 Correspondence and requests for materials
Emerging roles of pro-resolving lipid mediators in immunological and adaptive responses to exercise-induced muscle injury
 110 Exercise roles of bioactive lipid mediators Emerging roles of pro-resolving lipid mediators in immunological and adaptive responses to exercise-induced muscle injury James F. Markworth 1, Krishna Rao
110 Exercise roles of bioactive lipid mediators Emerging roles of pro-resolving lipid mediators in immunological and adaptive responses to exercise-induced muscle injury James F. Markworth 1, Krishna Rao
Resolution of Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes
 Resolution of Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Accessed Citable Link
Resolution of Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Accessed Citable Link
Goals. Chronic Wounds. Nutrition, the Often Forgotten Part of the Equation for Wound Healing. Nutritional Risk Factors for Impaired Wound Healing
 Goals Nutrition, the Often Forgotten Part of the Equation for Wound Healing Principles in wounds healing Critical Nutrients Marlene Grenon, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San
Goals Nutrition, the Often Forgotten Part of the Equation for Wound Healing Principles in wounds healing Critical Nutrients Marlene Grenon, MD Associate Professor of Surgery University of California San
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ
 ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different?
 Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different? Trevor A Mori, Ph.D., Professor, School of Medicine and Pharmacology, Royal Perth Hospital Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth,
Eicosapentaenoic Acid and Docosahexaenoic Acid: Are They Different? Trevor A Mori, Ph.D., Professor, School of Medicine and Pharmacology, Royal Perth Hospital Unit, University of Western Australia, Perth,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids?
 Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Denise Beaulieu Assistant Professor Animal & Poultry Science Introduction What are omega-3 fatty acids? Outline Why would we consider augmenting the diet of growing
Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Denise Beaulieu Assistant Professor Animal & Poultry Science Introduction What are omega-3 fatty acids? Outline Why would we consider augmenting the diet of growing
New therapeutic targets for T2DM
 New therapeutic targets for T2DM Targeting inflammation: NF- B, salsalate Gwanpyo Koh Department of Internal Medicine Jeju National University School of Medicine Introduction Obesity is occurring at epidemic
New therapeutic targets for T2DM Targeting inflammation: NF- B, salsalate Gwanpyo Koh Department of Internal Medicine Jeju National University School of Medicine Introduction Obesity is occurring at epidemic
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Anti-Inflammatory Diets for the Prevention of Chronic Disease
 Anti-Inflammatory Diets for the Prevention of Chronic Disease Jessica A. Miller, PhD R25T Cancer Prevention and Control Postdoctoral Fellow The University of Arizona Cancer Center May 9, 2013 Objectives
Anti-Inflammatory Diets for the Prevention of Chronic Disease Jessica A. Miller, PhD R25T Cancer Prevention and Control Postdoctoral Fellow The University of Arizona Cancer Center May 9, 2013 Objectives
Identification of novel omega-3 fatty acid-derived bioactive metabolites based on a targeted lipidomics approach
 Serial Review Advance Publication JCBN Journal 0912-0009 1880-5086 the Kyoto, jcbn14-18 10.3164/jcbn.14-18 Original Society Japan of Article Clinical for Free Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition
Serial Review Advance Publication JCBN Journal 0912-0009 1880-5086 the Kyoto, jcbn14-18 10.3164/jcbn.14-18 Original Society Japan of Article Clinical for Free Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition
h h h h h h h h h 5-HETE 11-HETE 19-HETE 20-HETE * * * *
 L ip id m e d ia to r (fo ld c h a n g e ) Figure S1 Figure S1. Oxylipin formation in acute inflammation and resolution. Mean fold change in (A) COX products: eicosanoids; (B) 5-, 11-, 19- and 2-HETE;
L ip id m e d ia to r (fo ld c h a n g e ) Figure S1 Figure S1. Oxylipin formation in acute inflammation and resolution. Mean fold change in (A) COX products: eicosanoids; (B) 5-, 11-, 19- and 2-HETE;
HSN301 Diet and Disease Entire Note Summary
 Topic 1: Metabolic Syndrome Learning Objectives: 1. Define obesity 2. Factors causing obesity 3. Obesity as a risk factor for metabolic syndrome 4. The pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome 5. Treatment of
Topic 1: Metabolic Syndrome Learning Objectives: 1. Define obesity 2. Factors causing obesity 3. Obesity as a risk factor for metabolic syndrome 4. The pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome 5. Treatment of
Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue. Rinke Stienstra
 Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue Rinke Stienstra Obesity promotes the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes County-level Estimates
Inflammasome-mediated caspase-1 activity Gatekeeper of inflammation in the adipose tissue Rinke Stienstra Obesity promotes the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes County-level Estimates
Endogenous Receptor Agonists: Resolving Inflammation
 Review Article Special Issue: Eicosanoid Receptors and Inflammation TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 1440 1462 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.188 Endogenous Receptor Agonists: Resolving Inflammation
Review Article Special Issue: Eicosanoid Receptors and Inflammation TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2007) 7, 1440 1462 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2007.188 Endogenous Receptor Agonists: Resolving Inflammation
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; Tel.: ; Fax:
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184-6223; doi:10.3390/ijms15046184 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications:
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184-6223; doi:10.3390/ijms15046184 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications:
Pro-resolving actions and stereoselective biosynthesis of 18S E-series resolvins in human leukocytes and murine inflammation
 Pro-resolving actions and stereoselective biosynthesis of 18S E-series resolvins in human leukocytes and murine inflammation Sungwhan F. Oh,, Rong Yang, Charles N. Serhan J Clin Invest. 2011;121(2):569-581.
Pro-resolving actions and stereoselective biosynthesis of 18S E-series resolvins in human leukocytes and murine inflammation Sungwhan F. Oh,, Rong Yang, Charles N. Serhan J Clin Invest. 2011;121(2):569-581.
Roadmap. Diabetes and the Metabolic Syndrome in the Asian Population. Asian. subgroups 8.9. in U.S. (% of total
 Diabetes and the Metabolic Syndrome in the Asian Population Alka Kanaya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, UCSF Feb 26, 2010 Roadmap 1. Diabetes in Asian Americans Prevalence in the U.S. Risk factors
Diabetes and the Metabolic Syndrome in the Asian Population Alka Kanaya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine, UCSF Feb 26, 2010 Roadmap 1. Diabetes in Asian Americans Prevalence in the U.S. Risk factors
 A real life example In human studies, we quantify ~120 plasma related proteins Monocytes MMP9 Macrophages TNFα IL1ß platelet derived growth factor IFNγ MMP1 MMP8 MMP13 Myeloid Related Protein14 CD40
A real life example In human studies, we quantify ~120 plasma related proteins Monocytes MMP9 Macrophages TNFα IL1ß platelet derived growth factor IFNγ MMP1 MMP8 MMP13 Myeloid Related Protein14 CD40
Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Diabetes: Making the Connections
 Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Diabetes: Making the Connections Alka M. Kanaya, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine & Epi/Biostats University of California, San Francisco February 26, 21 Roadmap 1.
Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Diabetes: Making the Connections Alka M. Kanaya, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine & Epi/Biostats University of California, San Francisco February 26, 21 Roadmap 1.
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
Metabolic Syndrome in Asians
 Metabolic Syndrome in Asians Alka Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine, UCSF Asian CV Symposium, November 17, 2007 The Metabolic Syndrome Also known as: Syndrome X Insulin Resistance Syndrome The Deadly
Metabolic Syndrome in Asians Alka Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine, UCSF Asian CV Symposium, November 17, 2007 The Metabolic Syndrome Also known as: Syndrome X Insulin Resistance Syndrome The Deadly
Innovation in Clinical Practice. Role of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs) in the Resolution of Chronic Inflammation. Jennifer Stagg, ND
 Innovation in Clinical Practice Role of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs) in the Resolution of Chronic Inflammation Jennifer Stagg, ND Innovation in Clinical Practice New News in Patient Care
Innovation in Clinical Practice Role of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators (SPMs) in the Resolution of Chronic Inflammation Jennifer Stagg, ND Innovation in Clinical Practice New News in Patient Care
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA
 PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Alena Buretić-Tomljanović 1, Jasminka Giacometti 1, Sergej Nadalin 1, Gordana Rubeša 2, Mirjana Vulin 3, Draško
PHOSPHOLIPID MEMBRANE ABNORMALITIES AND REDUCED NIACIN SKIN FLUSH RESPONSE IN SCHIZOPHRENIA Alena Buretić-Tomljanović 1, Jasminka Giacometti 1, Sergej Nadalin 1, Gordana Rubeša 2, Mirjana Vulin 3, Draško
METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE
 METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE 2. LF UK Prof. Rudolf Poledne, PhD. TYPES OF ADIPOSE TISSUE brown adipose tissue subcutaneous adipose tissue visceral adipose tissue ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTIONS: thermal isolation
METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE 2. LF UK Prof. Rudolf Poledne, PhD. TYPES OF ADIPOSE TISSUE brown adipose tissue subcutaneous adipose tissue visceral adipose tissue ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTIONS: thermal isolation
Measuring efficacy of dietary fatty acid intake using a proteomics approach. Baukje de Roos
 Measuring efficacy of dietary fatty acid intake using a proteomics approach Baukje de Roos Dietary fat and mammary tumors rodent models Strong tumor-enhancing effect for n-6 fatty acids Weaker tumor-enhancing
Measuring efficacy of dietary fatty acid intake using a proteomics approach Baukje de Roos Dietary fat and mammary tumors rodent models Strong tumor-enhancing effect for n-6 fatty acids Weaker tumor-enhancing
3/20/2011. Body Mass Index (kg/[m 2 ]) Age at Issue (*BMI > 30, or ~ 30 lbs overweight for 5 4 woman) Mokdad A.H.
![3/20/2011. Body Mass Index (kg/[m 2 ]) Age at Issue (*BMI > 30, or ~ 30 lbs overweight for 5 4 woman) Mokdad A.H. 3/20/2011. Body Mass Index (kg/[m 2 ]) Age at Issue (*BMI > 30, or ~ 30 lbs overweight for 5 4 woman) Mokdad A.H.](/thumbs/82/84935173.jpg) U.S. Adults: 1988 Nineteen states with 10-14% 14% Prevalence of Obesity (*BMI > 30, or ~ 30 lbs overweight for 5 4 woman) Metabolic John P. Cello, MD Professor of Medicine and Surgery, University of California,
U.S. Adults: 1988 Nineteen states with 10-14% 14% Prevalence of Obesity (*BMI > 30, or ~ 30 lbs overweight for 5 4 woman) Metabolic John P. Cello, MD Professor of Medicine and Surgery, University of California,
NASH Bench to Bedside
 NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
NASH Bench to Bedside October 2006 Anna Mae Diehl, M.D. Gastroenterology Division Duke University NonAlcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Common ~1/4-1/3 1/3 US adults Outcome highly variable Course indolent
Oils Rich in alpha-linolenic acid independently protect against characteristics of fatty liver disease in the delta-6 desaturase null mouse
 Oils Rich in alpha-linolenic acid independently protect against characteristics of fatty liver disease in the delta-6 desaturase null mouse By Jessica Monteiro A Thesis presented to The University of Guelph
Oils Rich in alpha-linolenic acid independently protect against characteristics of fatty liver disease in the delta-6 desaturase null mouse By Jessica Monteiro A Thesis presented to The University of Guelph
Supplementary Information. Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis.
 Supplementary Information Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis. Phillip J. White, Philippe St-Pierre, Alexandre Charbonneau, Patricia Mitchell,
Supplementary Information Protectin DX alleviates insulin resistance by activating a myokine-liver glucoregulatory axis. Phillip J. White, Philippe St-Pierre, Alexandre Charbonneau, Patricia Mitchell,
DM, NAFLD, and conjugated linoleic acid (omega 6); what is the link
 DM, NAFLD, and conjugated linoleic acid (omega 6); what is the link Mona Hegazy Professor of Internal Medicine Hepatology Department Cairo University Egypt Agenda Congugated lionleic fatty acid NAFLD
DM, NAFLD, and conjugated linoleic acid (omega 6); what is the link Mona Hegazy Professor of Internal Medicine Hepatology Department Cairo University Egypt Agenda Congugated lionleic fatty acid NAFLD
The Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on the Resolution of Inflammation in the Rodent Brain
 The Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on the Resolution of Inflammation in the Rodent Brain By Marc-Olivier Trépanier A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
The Effect of Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on the Resolution of Inflammation in the Rodent Brain By Marc-Olivier Trépanier A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of
Novel Lipid Mediators Promote Resolution of Acute Inflammation: Impact of Aspirin and Statins
 This Review is part of a thematic series on Lipid Oxidation and Cardiovascular Disease, which includes the following articles: Lipid Oxidation and Cardiovascular Disease: Introduction to a Review Series
This Review is part of a thematic series on Lipid Oxidation and Cardiovascular Disease, which includes the following articles: Lipid Oxidation and Cardiovascular Disease: Introduction to a Review Series
Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Baseline Levels of Inflammatory Markers in the General Population
 University of Central Florida Honors in the Major Theses Open Access Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Baseline Levels of Inflammatory Markers in the General Population 2017 Alex Nhan University
University of Central Florida Honors in the Major Theses Open Access Impact of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Supplementation on Baseline Levels of Inflammatory Markers in the General Population 2017 Alex Nhan University
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
The American University in Cairo. School of Science and Engineering
 The American University in Cairo School of Science and Engineering INFLUENCE OF DELTA-6-DESATURASE ON HEPATIC MEMBRANE COMPOSITION IN OBESITY/INSULIN RESISTANCE: IMPLICATIONS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF CARDIOMETABOLIC
The American University in Cairo School of Science and Engineering INFLUENCE OF DELTA-6-DESATURASE ON HEPATIC MEMBRANE COMPOSITION IN OBESITY/INSULIN RESISTANCE: IMPLICATIONS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF CARDIOMETABOLIC
University of California, San Diego La Jolla CA 92093
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0131 TITLE: Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jerrold Olefsky, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0131 TITLE: Role of Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mouse Models of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jerrold Olefsky, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University
Metabolic Syndrome: Bad for the Heart and Bad for the Brain? Kristine Yaffe, MD Univ. of California, San Francisco
 Metabolic Syndrome: Bad for the Heart and Bad for the Brain? Kristine Yaffe, MD Univ. of California, San Francisco Why would diabetes and obesity be bad for the brain? Insulin receptors in brain Insulin
Metabolic Syndrome: Bad for the Heart and Bad for the Brain? Kristine Yaffe, MD Univ. of California, San Francisco Why would diabetes and obesity be bad for the brain? Insulin receptors in brain Insulin
Roles of Lipids in the body
 Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Roles of Lipids in the body 1- Energy storage : Lipids contain a lot of calories in a small space. Since Lipids are generally insoluble in polar substances such as water, they are stored in special ways
Review Article Health Implications of High Dietary Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids
 Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism Volume 2012, Article ID 539426, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/539426 Review Article Health Implications of High Dietary Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids E. Patterson,
Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism Volume 2012, Article ID 539426, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/539426 Review Article Health Implications of High Dietary Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids E. Patterson,
Biomarkers of inflammation in human nutrition studies
 NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre in nutrition Biomarkers of inflammation in human nutrition studies Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University of Southampton The NIHR Southampton
NIHR Southampton Biomedical Research Centre in nutrition Biomarkers of inflammation in human nutrition studies Philip Calder Professor of Nutritional Immunology University of Southampton The NIHR Southampton
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
: Overview of EFA metabolism
 Figure 1 gives an overview of the metabolic fate of the EFAs when consumed in the diet. The n-6 and n-3 PUFAs when consumed in the form of dietary triglyceride from various food sources undergoes digestion
Figure 1 gives an overview of the metabolic fate of the EFAs when consumed in the diet. The n-6 and n-3 PUFAs when consumed in the form of dietary triglyceride from various food sources undergoes digestion
Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. Gijs Goossens, PhD
 Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity -The role of adipose tissue oxygenation - Gijs Goossens, PhD NUTRIM School of Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism Maastricht University Medical Centre
Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity -The role of adipose tissue oxygenation - Gijs Goossens, PhD NUTRIM School of Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism Maastricht University Medical Centre
Nutrition and Age-Associated Inflammation :Role of Nutritional Intervention Simin Nikbin Meydani, DVM, PhD.
 Nutrition and Age-Associated Inflammation :Role of Nutritional Intervention Simin Nikbin Meydani, DVM, PhD simin.meydani@tufts.edu Outline 1) Role of immune and inflammatory responses in age-related diseases
Nutrition and Age-Associated Inflammation :Role of Nutritional Intervention Simin Nikbin Meydani, DVM, PhD simin.meydani@tufts.edu Outline 1) Role of immune and inflammatory responses in age-related diseases
Preventing Collateral Damage Clinical Relevance of SPM s
 Preventing Collateral Damage Clinical Relevance of SPM s Robert G. Martindale MD, PhD Chief, Division of General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Medical Director Hospital Nutrition Service Oregon Health and
Preventing Collateral Damage Clinical Relevance of SPM s Robert G. Martindale MD, PhD Chief, Division of General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Medical Director Hospital Nutrition Service Oregon Health and
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
 Short-Term, High-Dose Fish Oil Supplementation Increases the Production of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Derived Mediators in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease (the OMEGA-PAD I Trial) The Harvard community
Short-Term, High-Dose Fish Oil Supplementation Increases the Production of Omega-3 Fatty Acid Derived Mediators in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease (the OMEGA-PAD I Trial) The Harvard community
The Relationship between Dietary Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Genes on the Obese Phenotype and Serum Lipids
 Nutrients 2013, 5, 1672-1705; doi:10.3390/nu5051672 Review OPEN ACCESS nutrients ISSN 2072-6643 www.mdpi.com/journal/nutrients The Relationship between Dietary Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Genes on the
Nutrients 2013, 5, 1672-1705; doi:10.3390/nu5051672 Review OPEN ACCESS nutrients ISSN 2072-6643 www.mdpi.com/journal/nutrients The Relationship between Dietary Fatty Acids and Inflammatory Genes on the
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome. and Type-2 Diabetes
 A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
Enzymatic oxidation of lipids: mechanisms and functions.
 Enzymatic oxidation of lipids: mechanisms and functions. Valerie B. O Donnell, PhD. Cardiff University. Enzymatic lipid oxidation: involves an enzyme catalyst, and gives very specific stereo- and regiospecific
Enzymatic oxidation of lipids: mechanisms and functions. Valerie B. O Donnell, PhD. Cardiff University. Enzymatic lipid oxidation: involves an enzyme catalyst, and gives very specific stereo- and regiospecific
HSN301 REVISION NOTES TOPIC 1 METABOLIC SYNDROME
 HSN301 REVISION NOTES TOPIC 1 METABOLIC SYNDROME What does the term Metabolic Syndrome describe? Metabolic syndrome describes a cluster of cardio-metabolic conditions that increase one's risk of developing
HSN301 REVISION NOTES TOPIC 1 METABOLIC SYNDROME What does the term Metabolic Syndrome describe? Metabolic syndrome describes a cluster of cardio-metabolic conditions that increase one's risk of developing
Morphogens: What are they and why should we care?
 Morphogens: What are they and why should we care? Historic, Theoretical Mechanism of Action Nucleoprotein: the specific trophic cellular material extracted from the cell nucleus. DNA and RNA which regulates
Morphogens: What are they and why should we care? Historic, Theoretical Mechanism of Action Nucleoprotein: the specific trophic cellular material extracted from the cell nucleus. DNA and RNA which regulates
Inflammation and Targeted Nutrition
 Inflammation and Targeted Nutrition Nutrition Masters Course Annalouise O Connor, PhD, RD Learning Objectives 1. Understand the two distinct phases of inflammation: initiation and resolution. 2. Learn
Inflammation and Targeted Nutrition Nutrition Masters Course Annalouise O Connor, PhD, RD Learning Objectives 1. Understand the two distinct phases of inflammation: initiation and resolution. 2. Learn
FROM ABSTRACT Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) improve on a vegetarian diet or supplementation with fish oil.
 Anti-inflammatory effects of a low arachidonic acid diet and fish oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatol Int (2003) 23: 27 36 Olaf Adam, Corinna Beringer, Thomas Kless, Christa Lemmen, Alexander
Anti-inflammatory effects of a low arachidonic acid diet and fish oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis Rheumatol Int (2003) 23: 27 36 Olaf Adam, Corinna Beringer, Thomas Kless, Christa Lemmen, Alexander
The Role of Lipid Mediators in Systemic Inflammation and Type 2 Diabetes. Ella Stephan. December 7, 2018
 The Role of Lipid Mediators in Systemic Inflammation and Type 2 Diabetes Ella Stephan The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Gillings School of Global Public Health A paper submitted to the faculty
The Role of Lipid Mediators in Systemic Inflammation and Type 2 Diabetes Ella Stephan The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill Gillings School of Global Public Health A paper submitted to the faculty
Robert G. Martindale MD, PhD
 Start the Resolution Robert G. Martindale MD, PhD Chief, Division of General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Medical Director Hospital Nutrition Service Oregon Health and Science University Portland, Oregon
Start the Resolution Robert G. Martindale MD, PhD Chief, Division of General and Gastrointestinal Surgery Medical Director Hospital Nutrition Service Oregon Health and Science University Portland, Oregon
Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease
 Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease Xin-Liang Ma, MD, PhD Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia, PA USA CVD As The #1 Causes of Death In USA Male Female Heart Disease and
Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease Xin-Liang Ma, MD, PhD Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia, PA USA CVD As The #1 Causes of Death In USA Male Female Heart Disease and
3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids?
 Conference on Food Structure and Food Quality 3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids? Rolf K. Berge rolf.berge@med.uib.no Fatty acids- Essential cellular metabolites Concentrations must
Conference on Food Structure and Food Quality 3-Thia Fatty Acids A New Generation of Functional Lipids? Rolf K. Berge rolf.berge@med.uib.no Fatty acids- Essential cellular metabolites Concentrations must
Resolvins and Protectins: Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Inflammation and Organ Protection: Metabolomics of Catabasis
 Resolvins and Protectins: Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Inflammation and Organ Protection: Metabolomics of Catabasis Charles N. Serhan 1 INTRODUCTION A highly regulated inflammatory response and
Resolvins and Protectins: Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Inflammation and Organ Protection: Metabolomics of Catabasis Charles N. Serhan 1 INTRODUCTION A highly regulated inflammatory response and
Lipoatrophic Diabetes: What can zebras teach us about horses? Ranganath Muniyappa, MD, PhD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Obesity Branch NIDDK, NIH
 Lipoatrophic Diabetes: What can zebras teach us about horses? Ranganath Muniyappa, MD, PhD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Obesity Branch NIDDK, NIH Objectives 1. Describe the clinical manifestations of abnormal
Lipoatrophic Diabetes: What can zebras teach us about horses? Ranganath Muniyappa, MD, PhD Diabetes, Endocrinology, and Obesity Branch NIDDK, NIH Objectives 1. Describe the clinical manifestations of abnormal
Facts on Fats. Ronald P. Mensink
 Facts on Fats Ronald P. Mensink Department of Human Biology NUTRIM, School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism Maastricht University Maastricht The Netherlands Outline of the Presentation Saturated
Facts on Fats Ronald P. Mensink Department of Human Biology NUTRIM, School for Nutrition, Toxicology and Metabolism Maastricht University Maastricht The Netherlands Outline of the Presentation Saturated
Targeting Inflammation in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis
 Targeting Inflammation in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis Clifford Hudis, M.D. Chief, Breast Cancer Medicine Service Attending Physician, MSKCC Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College August 7,
Targeting Inflammation in Breast Cancer Pathogenesis Clifford Hudis, M.D. Chief, Breast Cancer Medicine Service Attending Physician, MSKCC Professor of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College August 7,
Supplementary Figure S1
 Lipidomic-based investigation into the regulatory effect of Schisandrin B on palmitic acid level in non-alcoholic steatotic livers Hiu Yee Kwan 1,2, Xuyan Niu 3, Wenlin Dai 4, Tiejun Tong 4, Xiaojuan Chao
Lipidomic-based investigation into the regulatory effect of Schisandrin B on palmitic acid level in non-alcoholic steatotic livers Hiu Yee Kwan 1,2, Xuyan Niu 3, Wenlin Dai 4, Tiejun Tong 4, Xiaojuan Chao
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
Objectives 4/4/2013. Healing with Fats and Fatty Acids-- an Integrative approach. Inflammation Nation. A silent attack on the modern human race
 Healing with Fats and Fatty Acids-- an Integrative approach Tracy S. Hunter, RPh, MS, PhD Professor Wingate University School of Pharmacy Charlotte Metro-area, NC 1 Objectives Explain the relationship
Healing with Fats and Fatty Acids-- an Integrative approach Tracy S. Hunter, RPh, MS, PhD Professor Wingate University School of Pharmacy Charlotte Metro-area, NC 1 Objectives Explain the relationship
NOTES. Developed by Fabio Comana, MA., MS., All rights Reserved Page 1
 Session 455: Core Essentials in Science Fabio Comana, MA, MS, NASM CPT, CES & PES; ACE CPT & LWMC; ACSM HFS, NSCA CSCS; CISSN National Academy of Sports Medicine fabio.comana@nasm.org NOTES Developed by
Session 455: Core Essentials in Science Fabio Comana, MA, MS, NASM CPT, CES & PES; ACE CPT & LWMC; ACSM HFS, NSCA CSCS; CISSN National Academy of Sports Medicine fabio.comana@nasm.org NOTES Developed by
Empower Preventive Medicine. Timothy J. McCormick, DO, MPH 4221 Baymeadows Suite 6 Jacksonville, FL
 Empower Preventive Medicine Timothy J. McCormick, DO, MPH 4221 Baymeadows Suite 6 Jacksonville, FL 32217 904-367-4005 Drtim@emprevmed.com Obesity Medicine Old paradigm: Obesity was a matter of willpower,
Empower Preventive Medicine Timothy J. McCormick, DO, MPH 4221 Baymeadows Suite 6 Jacksonville, FL 32217 904-367-4005 Drtim@emprevmed.com Obesity Medicine Old paradigm: Obesity was a matter of willpower,
LIPID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
Fats, Cholesterol, and Hormones
 Fats, Cholesterol, and Hormones 1 Types of Fats Lipids biological origin sparingly soluble in water Main classes of lipids Fatty Acids long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid on one end Triacylglycerols
Fats, Cholesterol, and Hormones 1 Types of Fats Lipids biological origin sparingly soluble in water Main classes of lipids Fatty Acids long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid on one end Triacylglycerols
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic
 Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Update on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Kathleen E Corey, MD, MPH, MMSc Director, Mass General Fatty Liver Clinic Outline Defining the phenotypes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD Diagnostics
Resolvin D1 and Resolvin D2 Govern Local Inflammatory Tone in Obese Fat
 This information is current as of June 19, 2018. Resolvin D1 and Resolvin D2 Govern Local Inflammatory Tone in Obese Fat Joan Clària, Jesmond Dalli, Stephanie Yacoubian, Fei Gao and Charles N. Serhan J
This information is current as of June 19, 2018. Resolvin D1 and Resolvin D2 Govern Local Inflammatory Tone in Obese Fat Joan Clària, Jesmond Dalli, Stephanie Yacoubian, Fei Gao and Charles N. Serhan J
METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM HCV
 METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE HCV Steatosis Insulin resistance Arun J Sanyal M.D. Chairman, Div. of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond,
METABOLIC SYNDROME AND HCV: FROM THEORY TO PRACTICE HCV Steatosis Insulin resistance Arun J Sanyal M.D. Chairman, Div. of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond,
Atherosclerosis is an Inflammatory Disease: Does it Matter? Atherosclerosis is an Inflammatory Disease: Does it Matter?
 12 th Annual Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Symposium February 8, 2013 Atherosclerosis is an Inflammatory Disease: Does it Matter? Ira Tabas, M.D., Ph.D. Richard J. Stock Professor of Medicine, Cell
12 th Annual Cardiovascular Disease Prevention Symposium February 8, 2013 Atherosclerosis is an Inflammatory Disease: Does it Matter? Ira Tabas, M.D., Ph.D. Richard J. Stock Professor of Medicine, Cell
The Metabolic Syndrome Update The Metabolic Syndrome: Overview. Global Cardiometabolic Risk
 Update 2013 Marc Cornier, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes Anschutz Health and Wellness Center University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver Health
Update 2013 Marc Cornier, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes Anschutz Health and Wellness Center University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver Health
The true cost of inpatient obesity impact on inflammatory stress and morbidity.
 The true cost of inpatient obesity impact on inflammatory stress and morbidity. Professor Bob Grimble, Institute of Human Nutrition, Institute of Developmental Sciences Building, University of Southampton
The true cost of inpatient obesity impact on inflammatory stress and morbidity. Professor Bob Grimble, Institute of Human Nutrition, Institute of Developmental Sciences Building, University of Southampton
Arachidonic Acid (AA) is the source of eicosanoids, a. The Eicosanoids, Redox-Regulated Lipid Mediators in Immunometabolic Disorders
 ANTIOXIDANTS & REDOX SIGNALING Volume 29, Number 3, 2018 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7332 FORUM REVIEW ARTICLE The Eicosanoids, Redox-Regulated Lipid Mediators in Immunometabolic Disorders
ANTIOXIDANTS & REDOX SIGNALING Volume 29, Number 3, 2018 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/ars.2017.7332 FORUM REVIEW ARTICLE The Eicosanoids, Redox-Regulated Lipid Mediators in Immunometabolic Disorders
Research in IBD at University of Colorado Denver
 Research in IBD at University of Colorado Denver Blair Fennimore, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology UCH Crohn s and Colitis Center Mucosal Inflammation Program
Research in IBD at University of Colorado Denver Blair Fennimore, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology UCH Crohn s and Colitis Center Mucosal Inflammation Program
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases
 Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
Cholesterol and Cholesterol Oxides on Coronary Heart Diseases Trends in egg consumption in U.S. and the reason A. Egg Consumption: - 403 in 1945-234 in 1993 (176 Table eggs, 58 Processed eggs) - 256 in
LIPOCALIN 2 DEFICIENCY INFLUENCES TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β EFFECT ON INFLAMMATION AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX REMODELING IN INGUINAL ADIPOCYTES
 LIPOCALIN 2 DEFICIENCY INFLUENCES TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β EFFECT ON INFLAMMATION AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX REMODELING IN INGUINAL ADIPOCYTES A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA
LIPOCALIN 2 DEFICIENCY INFLUENCES TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β EFFECT ON INFLAMMATION AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX REMODELING IN INGUINAL ADIPOCYTES A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Regulation of angiotensinogen in adipocytes by polyunsaturated fatty acids
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 5-2010 Regulation of angiotensinogen in adipocytes by polyunsaturated fatty acids Sarah
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 5-2010 Regulation of angiotensinogen in adipocytes by polyunsaturated fatty acids Sarah
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes
 Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
EICOSANOID METABOLISM
 1 EICOSANOID METABOLISM EICOSANOIDS C20 polyunsaturated fatty acids e.g. Arachidonic acid Eicosanoids physiologically, pathologically and pharmacologically active compounds PG Prostaglandins TX - Thromboxanes
1 EICOSANOID METABOLISM EICOSANOIDS C20 polyunsaturated fatty acids e.g. Arachidonic acid Eicosanoids physiologically, pathologically and pharmacologically active compounds PG Prostaglandins TX - Thromboxanes
Outline. Fitting Nutrition into Your Genes. Martha A. Belury, Ph.D., R.D. Martha A. Belury Sept 2018
 Fitting Nutrition into Your Genes, Ph.D., R.D. Human Nutrition The Ohio State University Outline I. History (abridged) of the Study of Genetics and Nutrition II. The Skinny on Fats & Genes III. How Dietary
Fitting Nutrition into Your Genes, Ph.D., R.D. Human Nutrition The Ohio State University Outline I. History (abridged) of the Study of Genetics and Nutrition II. The Skinny on Fats & Genes III. How Dietary
ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL FATTY ACID METABOLISM CAUSED BY VITAMIN E DEFICIENCY
 ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL FATTY ACID METABOLISM CAUSED BY VITAMIN E DEFICIENCY Bonnie Buckingham Faculty Mentor: Dr. Maret Traber Linus Pauling Institute HHMI Summer 2011 Outline Significance Background Hypothesis
ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL FATTY ACID METABOLISM CAUSED BY VITAMIN E DEFICIENCY Bonnie Buckingham Faculty Mentor: Dr. Maret Traber Linus Pauling Institute HHMI Summer 2011 Outline Significance Background Hypothesis
For Asian individuals the BMI numbers are 27.5 and 25 respectively These values are from the NICE guidelines of 2014
 Ken Cathcart DO FACE We need to define several things to start the talk Obesity is defined medically as a BMI of greater than 30 or a BMI >27 with co-morbidities such as hypertension, type 2 DM, dyslipidemia,
Ken Cathcart DO FACE We need to define several things to start the talk Obesity is defined medically as a BMI of greater than 30 or a BMI >27 with co-morbidities such as hypertension, type 2 DM, dyslipidemia,
University of Groningen. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba
 University of Groningen Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Sheedfar, Fareeba IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
