Bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OMVs)
|
|
|
- Whitney Montgomery
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bacterial outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) PhD student: Wei TAN Supervisor: Prof. Guoping Zhao Deparment of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine The Chinese University of Hong Kong Date: 1 Dec 2016
2 Outline Introduction of OMVs Formation mechanism and content of OMVs Entry mechanism into host cells of OMVs Functions of OMVs Application: OMV-based vaccines Conclusions and perspectives
3 Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) Bacterial OMVs: nano sized spherical structures nm in diameter derived from the bacterial cell envelopes produced by of almost all Gram negative bacteria during all growth phases and in all environmental conditions Pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria OMV TEM image of OMVs in Aeromonas hydrophila Meta J. Kuehn and Nicole C. Kesty. Genes Dev, 2005 Andrea Guerrero Mandujano, et al. EC Microbiology, 2015
4 How do bacteria produce OMVs? ----a general mechanism of OMVs formation
5 OMVs formation VacJ/Yrb transport system: highly conserved in Gram-negative bacteria affects the migration of membrane phospholipids phospholipid VacJ/Yrb-mediated phospholipids migration Prevention of phospholipids accumulation in the outer leaflet of the outer membrane Sandro Roier, et al. Nature Communications, 2016
6 OMVs formation mechanism Step 3: The released OMV is enriched in phospholipids incorporated into the outer leaflet of the vesicle membrane. Step 1: Inhibition of VacJ/Yrb system-related genes expression results in phospholipids accumulation in the outer leaflet of the outer membrane, thus initiates an outward bulging of the outer membrane through the asymmetric expansion of the outer leaflet. Step 2: Further enrichment of positive and negative curvature-inducing phospholipids in both leaflets supports the budding of the outer membrane, which finally pinches off to form an OMV. Sandro Roier, et al. Nature Communications, 2016
7 Structure and content of OMVs Detailed proteomic and biochemical analyses have shown that OMVs contain diverse components derived from the parent bacteria: lipopolysaccharide (LPS), periplasmic and membrane-bound proteins, enzymes, toxins, DNA, RNA A secretion and delivery system Maria Kaparakis-Liaskos and Richard L. Ferrero. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2015
8 How do OMVs enter host cells?
9 Mechanisms of OMVs entry Four main pathways of endocytosis have all been implicated in mediating OMVs entry into host cells. Clathrindependent Caveolindependent Host epithelial cell Maria Kaparakis-Liaskos and Richard L. Ferrero. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2015
10 Eloise J. O'Donoghue and Anne Marie Krachler. Cellular Microbiology, 2016 Inhibition of OMVs entry Pharmacological inhibition of key components of the endocytic pathways prevents OMVs entry:
11 Functions of OMVs in bacterial physiology and pathogenesis
12 Stress response >>>> bacterial survival Quinolone antibiotics Carmen Schwechheimer and Meta J. Kuehn. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2015
13 Nutrient acquisition >>>> bacterial survival Carmen Schwechheimer and Meta J. Kuehn. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2015
14 Defense and resistance >>>> bacterial pathogenicity decoy Carmen Schwechheimer and Meta J. Kuehn. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2015
15 Delivery of virulence factors >>>> bacterial pathogenicity Pathogenic bacteria can use OMVs to mediate the delivery of virulence factors, such as toxins, into host cells, including immune cells. Carmen Schwechheimer and Meta J. Kuehn. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2015
16 OMVs-related virulence factors Over 30 virulence factors Sangyong Lim and Hyunjin Yoon. J Bacteriol Virol, 2015
17 association with biofilm formation >>>> bacterial pathogenicity Species Factor Effect Helicobacter pylori 22-kDa protein Plays an important role in biofilm formation. Francisella OMV Involved in biofilm formation and forming part of biofilm matrix. Pseudomonas aeruginosa Vibrio cholerae Pseudomonas putida CPA OMV-associated protein DegP OMV Its absence causes structural defects which limit the development of mature biofilms. Required for the secretion of biofilm matrix components and the activity strongly influences biofilm formation. Lead to an increased hydrophobicity of cells surface which enhanced their ability to form biofilms OMVs have been shown to participate in biofilm formation. Wendong Wang, et al. FEMS Microbiology Letters, 2015 Carmen Schwechheimer and Meta J. Kuehn. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2015
18 Application: OMV-based vaccines OMVs are attractive vaccine candidates: 1. high immunogenicity closely reflect the native conformation of their parent bacteria that induce both innate and adaptive immunity after entering eukaryotic cells 2. non-replicative and hence safe A success: OMV-based vaccine against serogroup B Neisseria meningitides (approved by the European Commission) The OMV-based 4CMenB vaccine contains three highly immunogenic proteins that induce protective antibody responses. Maria Kaparakis-Liaskos and Richard L. Ferrero. Nature Reviews Immunology, 2015 Sophie M Andrews and Andrew J Pollard. Lancet Infect. Dis, 2014
19 Conclusions and perspectives 1. The production of OMVs in Gram-negative bacteria allows bacteria to interact with a wide area of their environment. 2. OMVs play important roles in bacterial physiology and pathogenesis, ranging from secretion and delivery of biomolecules over stress response and biofilm formation to immunomodulation and adherence to host cells. 3. Due to the multifunctional activities, OMVs have been an attractive platform for bioengineering applications. (OMV-based vaccines, drug delivery vehicles)
20 Conclusions and perspectives Some aspects of OMVs need to be illustrated What is the energy source for the vesiculation process in Gramnegative bacteria? How do bacteria regulate OMVs formation? How is protein cargo selected? Gram-positive bacteria also release membrane vesicles: Staphylococcus aureus and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. biogenesis mechanisms? functions in bacterial physiology and pathogenesis??
21 Thank you
Production of Outer Membrane Vesicles in a Clinical Strain of Aeromonas hydrophila
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS MICROBIOLOGY Research Article Production of Outer Membrane Vesicles in a Clinical Strain of Aeromonas hydrophila Andrea Guerrero M 1, Edgar Oliver Lopez V 2, Aurora Longa B 3 and Graciela
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS MICROBIOLOGY Research Article Production of Outer Membrane Vesicles in a Clinical Strain of Aeromonas hydrophila Andrea Guerrero M 1, Edgar Oliver Lopez V 2, Aurora Longa B 3 and Graciela
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
Mechanisms of Pathogenicity The Microbes Fight Back Medically important bacteria Salmonella Bacillus anthracis Shigella dysenteriae Campylobacter Shigella sonnei Clostridium botulinum Staphylococcus aureus
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS
 BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology
 Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Definitions Path- means disease. Pathogenesis The steps or mechanisms involved in the development of a disease. Infection The presence
Host Parasite Relationship. Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU
 Host Parasite Relationship Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU OBJECTIVES Define core terms important in host-parasite relationship. Know host response to parasite invasion
Host Parasite Relationship Prof. Hanan Habib Department of Pathology, College of Medicine,KSU OBJECTIVES Define core terms important in host-parasite relationship. Know host response to parasite invasion
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms 1 Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure
 Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
Prokaryotic Cell Structure Chapter 3 Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes DNA Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Organelles Size & Organization Kingdoms Where do viruses fit in? Acellular microorganisms Cannot reproduce outside
1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE?
 1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
1 Microm 301 Final Exam 2012 Practice Questions and Key 1. Which of the following statements concerning Plasmodium vivax is TRUE? A. It infects all stages of erythrocytes (immature, mature, and senescent).
Role of Outer Membrane Vesicles of Bacteria
 Role of Outer Membrane Vesicles of Bacteria MVJagannadhamandMKChattopadhyay Outer membrane vesicles are nano-sized spheres produced predominantly by gram-negative bacteria. They play a significant role
Role of Outer Membrane Vesicles of Bacteria MVJagannadhamandMKChattopadhyay Outer membrane vesicles are nano-sized spheres produced predominantly by gram-negative bacteria. They play a significant role
Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells
 Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS
 PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
PATHOGENICITY OF MICROORGANISMS Some microorganisms are : 1- Harmless microorganism, as normal flora 2- Harmfull microorganism, as pathogenic. A pathogenic microorganism is defined as one that causes or
Cell Structure. Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell. Cytoplasmic Membrane 4/6/2011. Chapter 3. Cytoplasmic membrane
 Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Quiz Student:
 Quiz 5 080911 Student: 1. The enveloped viruses typically obtain their envelope A. from the host plasma membrane. B. as they exit the host. C. from a newly constructed viral-derived membrane. D. from the
Quiz 5 080911 Student: 1. The enveloped viruses typically obtain their envelope A. from the host plasma membrane. B. as they exit the host. C. from a newly constructed viral-derived membrane. D. from the
Pathogens and the immune system
 Pathogens and the immune system Veronica Leautaud, Ph.D. vl2@ rice.edu Keck Hall 224 / 232-lab Lecture 8 BIOE 301-Bioengineering and World Health Review of lecture 7 Science Science is the human activity
Pathogens and the immune system Veronica Leautaud, Ph.D. vl2@ rice.edu Keck Hall 224 / 232-lab Lecture 8 BIOE 301-Bioengineering and World Health Review of lecture 7 Science Science is the human activity
3/10/14. Ultrastructural organization. Gram Stain. Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation. Gram negative.
 Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Infection leads to production of inducers of inflammation or dendritic cell Inflammatory mediators: Complex and many, but include: Lipids and Proteins (cytokines/chemokines) TNF Others Ultrastructural
Lahore University of Management Sciences. BIO 314- Microbiology and Virology (Spring 2018)
 BIO 314- Microbiology and Virology (Spring 2018) Instructor Shaper Mirza Room No. 9-318A Office Hours TBA Email Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu ; shaper.mirza@lums.edu.pk Telephone 8413 Secretary/TA No TA Office
BIO 314- Microbiology and Virology (Spring 2018) Instructor Shaper Mirza Room No. 9-318A Office Hours TBA Email Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu ; shaper.mirza@lums.edu.pk Telephone 8413 Secretary/TA No TA Office
Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease
 Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease Normal Flora Virulence and Pathogenicity Toxicity vs. Invasiveness WE ARE NOT ALONE! We are outnumbered. The average human contains about 10 trillion cells. On
Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease Normal Flora Virulence and Pathogenicity Toxicity vs. Invasiveness WE ARE NOT ALONE! We are outnumbered. The average human contains about 10 trillion cells. On
Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology
 Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology PJL:2011 Bacterial Overview: Morphology, Structure, Jargon General Features Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria Spirochaetes Firmicutes Actinobacteria No nuclear membrane
Veterinary Bacteriology and Mycology PJL:2011 Bacterial Overview: Morphology, Structure, Jargon General Features Domain Bacteria Proteobacteria Spirochaetes Firmicutes Actinobacteria No nuclear membrane
Lahore University of Management Sciences. BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015)
 BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015) Instructor Room. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Shaper Mirza and Sadia Hamera Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu Course
BIO314 Virology and Microbiology (Spring 2015) Instructor Room. Office Hours Email Telephone Secretary/TA TA Office Hours Course URL (if any) Shaper Mirza and Sadia Hamera Shaper.Mirza@uth.tmc.edu Course
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Portals of Entry Mucous membranes Conjunctiva Respiratory tract: Droplet inhalation of moisture and dust particles. Most common portal of entry. GI tract: food, water,
Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Portals of Entry Mucous membranes Conjunctiva Respiratory tract: Droplet inhalation of moisture and dust particles. Most common portal of entry. GI tract: food, water,
Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease
 Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease Normal Flora Virulence and Pathogenicity Toxicity vs. Invasiveness WE ARE NOT ALONE! We are outnumbered. The average human contains about 10 trillion cells. On
Microbes as Agents of Infectious Disease Normal Flora Virulence and Pathogenicity Toxicity vs. Invasiveness WE ARE NOT ALONE! We are outnumbered. The average human contains about 10 trillion cells. On
MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN. Chapter 14. Pathogenicity
 MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 14 Pathogenicity Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Pathogenicity -The ability to cause disease Virulence - The extent of pathogenicity Virulence Factors Adhesion
MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 14 Pathogenicity Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Pathogenicity -The ability to cause disease Virulence - The extent of pathogenicity Virulence Factors Adhesion
Where are we heading?
 Unit 4: Where are we heading? Unit 4: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
Unit 4: Where are we heading? Unit 4: Introduction Unit 1: Why should we care about infectious diseases? Unit 2: What does it mean to have an infectious disease? Unit 3: When does a microbe become a pathogen?
PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether each of the following statements are true or false.
 MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
MCB 55 Plagues and Pandemics Midterm I Practice questions Read each question carefully. All the questions can be answered briefly, in the space allotted. PART A. True/False. Indicate in the space whether
Bacterial Diseases IMMUNITY TO BACTERIAL INFECTIONS. Gram Positive Bacteria. Gram Negative Bacteria. Many Infectious agents and many diseases
 IMMUNITY TO BACTERIAL INFECTIONS Chapter 18 Bacterial Diseases Many Infectious agents and many diseases Bacteria can Infect any part of the body Cause disease due to Growth of the microbe in a tissue Produce
IMMUNITY TO BACTERIAL INFECTIONS Chapter 18 Bacterial Diseases Many Infectious agents and many diseases Bacteria can Infect any part of the body Cause disease due to Growth of the microbe in a tissue Produce
Study Guide 23, 24 & 47
 Study Guide 23, 24 & 47 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 23-3 Bacteria and Humans Name Period Date 1. One bacterial disease that is transmitted by contaminated drinking water is a. Lyme disease b. gonorrhea c. tuberculosis
Study Guide 23, 24 & 47 STUDY GUIDE SECTION 23-3 Bacteria and Humans Name Period Date 1. One bacterial disease that is transmitted by contaminated drinking water is a. Lyme disease b. gonorrhea c. tuberculosis
Bacterial Secreted Proteins: Secretory Mechanisms And Role In Pathogenesis READ ONLINE
 Bacterial Secreted Proteins: Secretory Mechanisms And Role In Pathogenesis READ ONLINE If you are looking for the ebook Bacterial Secreted Proteins: Secretory Mechanisms and Role in Pathogenesis in pdf
Bacterial Secreted Proteins: Secretory Mechanisms And Role In Pathogenesis READ ONLINE If you are looking for the ebook Bacterial Secreted Proteins: Secretory Mechanisms and Role in Pathogenesis in pdf
Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers. EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3
 Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring
Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring
Foundations in Microbiology
 Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Foundations in Microbiology Fifth Edition Talaro Chapter 13 Microbe Human Interactions: Infection and Disease Chapter 13 2 3 Infection a condition in which pathogenic microbes penetrate host defenses,
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles
 Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles Topics: External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms Prokaryotes include two small groups
Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles Topics: External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms Prokaryotes include two small groups
LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK. How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication
 DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
DEFINITIONS OF TERMS Eukaryotic: Non-bacterial cell type (bacteria are prokaryotes).. LESSON 4.4 WORKBOOK How viruses make us sick: Viral Replication This lesson extends the principles we learned in Unit
Biology Multiple Choice, 2 pt each.
 Biology 3340 Spring 2007 Name Exam 1, Version A Write your name on both the exam booklet and the mark sense sheet. On the upper left corner of the mark sense sheet in the Key ID box, mark the version letter
Biology 3340 Spring 2007 Name Exam 1, Version A Write your name on both the exam booklet and the mark sense sheet. On the upper left corner of the mark sense sheet in the Key ID box, mark the version letter
Fig. LPS in Gram negative bacteria
 Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Structure of bacterial cell Dentistry college - first class Medical biology- Lec.3 Lecturer D. Hanan S A- Cell wall ***Chemical composition of the cell wall Bacteria are divided into two separated groups
Pre-Lec. + Questions
 Sheet 14 (part 2) made by : Majd abu-fares corrected by: Shatha khtoum date:8/11/2016 Pre-Lec. + Questions *Pus: secretion of {WBCs + product of WBCs + product of M.O} *WBCs can produce enzymes cytokines
Sheet 14 (part 2) made by : Majd abu-fares corrected by: Shatha khtoum date:8/11/2016 Pre-Lec. + Questions *Pus: secretion of {WBCs + product of WBCs + product of M.O} *WBCs can produce enzymes cytokines
Bio Microbiology - Spring 2010 Study Guide 21
 Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2010 Study Guide 21 Factors in Microbial Disease Host Parasite Interactions are Dynamic Evolution effects both Parasite and Host Pathogenic Properties of Bacteria Microorganisms
Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2010 Study Guide 21 Factors in Microbial Disease Host Parasite Interactions are Dynamic Evolution effects both Parasite and Host Pathogenic Properties of Bacteria Microorganisms
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3)
 Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Topic 03 Prokaryotes (3.3) Topics Characteristics (comparison) External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification 1 Relative size of bacterial cell
Unit One Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infection Pathogenesis of bacterial infection includes the mechanisms that lead to the development of signs and
 Unit One Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infection Pathogenesis of bacterial infection includes the mechanisms that lead to the development of signs and symptoms of disease. Characteristics of bacteria that
Unit One Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infection Pathogenesis of bacterial infection includes the mechanisms that lead to the development of signs and symptoms of disease. Characteristics of bacteria that
18.2 Viruses and Prions
 KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
Product Development for Public Health & Emerging Infections
 Product Development for Public Health & Emerging Infections Michael G Kurilla, MD-PhD Director, Office of BioDefense Research Affairs Division of Microbiology & Infectious Diseases Associate Director,
Product Development for Public Health & Emerging Infections Michael G Kurilla, MD-PhD Director, Office of BioDefense Research Affairs Division of Microbiology & Infectious Diseases Associate Director,
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year )
 BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
BACTERIOLOGY PROGRAMME AND PLAN OF TEACHING 3 rd Semester (academic year 2012-2013) 19. 10. 2012. Introduction in microbiology, bacterial taxonomy, general bacterial prop Bacterial structures, biosynthesis
MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview
 MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview Hieucam Phan, MD Pediatrics St. Luke s Hospital San Francisco, CA Microbiology 6/01 1 Introduction Major Achievements of Medical Sciences in the 20th Century Microbiology DNA
MICROBIOLOGY - An Overview Hieucam Phan, MD Pediatrics St. Luke s Hospital San Francisco, CA Microbiology 6/01 1 Introduction Major Achievements of Medical Sciences in the 20th Century Microbiology DNA
Chapter 39 Viruses. Viruses are tiny. They are much smaller (50 times) than a bacterium.
 Chapter 39 Viruses Viruses are tiny. They are much smaller (50 times) than a bacterium. They are not made of cellsand cannot reproduceon their own. Therefore they are not alive according to our rules.
Chapter 39 Viruses Viruses are tiny. They are much smaller (50 times) than a bacterium. They are not made of cellsand cannot reproduceon their own. Therefore they are not alive according to our rules.
Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity
 Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
Part 1 Disease causing organisms Resistance Immunity Bacteria Most common pathogens Anthrax Cholera Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteria Bacterial diseases Tuberculosis Cholera Bubonic Plague Tetanus Effects
8/13/2009. Diseases. Disease. Pathogens. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. Bacteria Shapes. Domain Bacteria Characteristics
 Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
5/6/17. Diseases. Disease. Pathogens. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Pathogens are disease-causing organisms
 5/6/17 Disease Diseases I. II. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Biol 105 Chapter 13a Pathogens Pathogens are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic.
5/6/17 Disease Diseases I. II. Bacteria Viruses (including HIV) Biol 105 Chapter 13a Pathogens Pathogens are disease-causing organisms Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic.
Contents The Cytokine System The Discovery of the Brain Immunomodulators
 Contents 1 The Cytokine System... 1 1.1 Inducible Character of Cytokine Formation and Reception... 1 1.2 Locality of Cytokine Action... 2 1.3 Superfluity of Cytokine System... 2 1.4 Interrelationship and
Contents 1 The Cytokine System... 1 1.1 Inducible Character of Cytokine Formation and Reception... 1 1.2 Locality of Cytokine Action... 2 1.3 Superfluity of Cytokine System... 2 1.4 Interrelationship and
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com. Question Number. 1. prevents viruses attaching to {uninfected / eq} host cells / eq ; 2. by binding to receptors / eq ;
 1(a) 1. prevents viruses attaching to {uninfected / eq} host cells / eq ; 2. by binding to receptors / eq ; 3. (therefore) preventing virus from entering cell / eq ; 4. (therefore) viruses cannot replicate
1(a) 1. prevents viruses attaching to {uninfected / eq} host cells / eq ; 2. by binding to receptors / eq ; 3. (therefore) preventing virus from entering cell / eq ; 4. (therefore) viruses cannot replicate
Biology of Neisseria meningitidis: implications for vaccine development Richard Moxon: University of Oxford
 Biology of Neisseria meningitidis: implications for vaccine development Richard Moxon: University of Oxford Biology of N.meningitidis infection Within hours, the disease may progress to shock with multi-organ
Biology of Neisseria meningitidis: implications for vaccine development Richard Moxon: University of Oxford Biology of N.meningitidis infection Within hours, the disease may progress to shock with multi-organ
Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance
 Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance I. Symbiosis relationship in which 2 organisms spend a portion or all of their lifecycles associated with one another A. Commensalism
Chapter 29 Lecture Notes: Parasitism, pathogenicity and resistance I. Symbiosis relationship in which 2 organisms spend a portion or all of their lifecycles associated with one another A. Commensalism
Microbial Pathogenesis. How do bacteria cause disease? How do E.coli become pathogens? Commensal flora
 Microbial Pathogenesis How do E.coli become pathogens? Commensal flora Acquire genes that cause disease How do bacteria cause disease? 1- Direct toxic effects proteases flesh eating bacteria 2- Activation
Microbial Pathogenesis How do E.coli become pathogens? Commensal flora Acquire genes that cause disease How do bacteria cause disease? 1- Direct toxic effects proteases flesh eating bacteria 2- Activation
ILOs. 10/10/2016 Maha Fathy 2
 ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
ILOs 1- List different components of bacterial cell. 2-Describe structure of cell wall of Gram +ve and ve bacteria 3-Recognize role of cell wall and cytoplasmic membrane in survival and growth of bacterial
KOMAR UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (KUST) Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016
 Course Title Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016 Medical Bacteriology Course Code MLS3330 No. of Credits Department Medical Laboratory Science (MLS) College Science Pre-requisites Course
Course Title Medical Bacteriology Syllabus (Theory) Spring 2016 Medical Bacteriology Course Code MLS3330 No. of Credits Department Medical Laboratory Science (MLS) College Science Pre-requisites Course
Overview of the Immune System
 Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Overview of the Immune System Immune System Innate (Nonspecific) Adaptive (Specific) Cellular Components Humoral Components Cell-Mediated Humoral (Ab) Antigens Definitions Immunogen Antigen (Ag) Hapten
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Microbial Pathogenesis
 Microbial Pathogenesis September 15, 2008 by David E. Briles dbriles@uab.edu 934-6595 Whether a pathogen is able to cause symptoms (disease) is dependent on the interaction of the pathogen with the host.
Microbial Pathogenesis September 15, 2008 by David E. Briles dbriles@uab.edu 934-6595 Whether a pathogen is able to cause symptoms (disease) is dependent on the interaction of the pathogen with the host.
Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases
 Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases HOST DISEASE TRIAD PATHOGEN ENVIRONMENT OTHER MICROBES Microbial Interactions KOCH'S POSTULATES Four criteria that were established
Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases Pathogenicity of Infectious Diseases HOST DISEASE TRIAD PATHOGEN ENVIRONMENT OTHER MICROBES Microbial Interactions KOCH'S POSTULATES Four criteria that were established
Bacterial Infec-on. November 9, 2018 Time pm. Yaowarin Nakornpakdee, Ph.D. (Lect.)
 SCBM341 General Pathology Bacterial Infec-on November 9, 2018 Time 01.00-04.00 pm Yaowarin Nakornpakdee, Ph.D. (Lect.) Email: yaowarin.nak@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objec-ves Explain the virulence factors involving
SCBM341 General Pathology Bacterial Infec-on November 9, 2018 Time 01.00-04.00 pm Yaowarin Nakornpakdee, Ph.D. (Lect.) Email: yaowarin.nak@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objec-ves Explain the virulence factors involving
Biodefense / Human Threats and Mass Spectrometry Applications. German Henostroza MD Division of Infectious Diseases and International Medicine
 Biodefense / Human Threats and Mass Spectrometry Applications German Henostroza MD Division of Infectious Diseases and International Medicine SARS(Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) Colera Colera Gram
Biodefense / Human Threats and Mass Spectrometry Applications German Henostroza MD Division of Infectious Diseases and International Medicine SARS(Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) Colera Colera Gram
Legionella pneumophila: an intracellular pathogen of phagocytes Prof. Craig Roy
 an intracellular pathogen of phagocytes Section of Microbial Pathogenesis, Yale University School of Medicine 1 Legionella pneumophila Gram-negative bacterium Facultative intracellular pathogen Protozoa
an intracellular pathogen of phagocytes Section of Microbial Pathogenesis, Yale University School of Medicine 1 Legionella pneumophila Gram-negative bacterium Facultative intracellular pathogen Protozoa
I. Bacteria II. Viruses including HIV. Domain Bacteria Characteristics. 5. Cell wall present in many species. 6. Reproduction by binary fission
 Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including are disease-causing organisms Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Disease Diseases I. Bacteria II. Viruses including are disease-causing organisms Biol 105 Lecture 17 Chapter 13a Domain Bacteria Characteristics 1. Domain Bacteria are prokaryotic 2. Lack a membrane-bound
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences
 Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Section VII. Pathogenesis and Host Defense Mechanisms Burton's Microbiology for the Health Sciences Chapter 14. Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases 1 Chapter
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
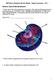 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
Chapter 15. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Chapter 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity I. Entry of a Microorganism into the Host A. Portals of Entry 1. Mucous Membranes Conjunctiva, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts Important
Chapter 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity I. Entry of a Microorganism into the Host A. Portals of Entry 1. Mucous Membranes Conjunctiva, respiratory, gastrointestinal, and genitourinary tracts Important
Are you ready for SK320?
 SK320 Infectious disease and public health Are you ready for SK320? Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Suggested prior study 2 3 Module content 2 4 Key concepts for SK320 4 4.1 Cell structure and function 4 4.2
SK320 Infectious disease and public health Are you ready for SK320? Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Suggested prior study 2 3 Module content 2 4 Key concepts for SK320 4 4.1 Cell structure and function 4 4.2
Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Disease
 Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Disease INFECTIOUS AGENTS AND PATHOGENESIS Series Editors: Allen L. Honeyman and Herman Friedman, University South Florida College of Medicine Mauro Bendinelli, University
Staphylococcus aureus Infection and Disease INFECTIOUS AGENTS AND PATHOGENESIS Series Editors: Allen L. Honeyman and Herman Friedman, University South Florida College of Medicine Mauro Bendinelli, University
Bacterial growth, physiology & metabolism
 2 nd year Medical Students - JU Bacterial growth, physiology & metabolism Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi Associate Professor of Medical Microbiology. MBBS / J.U.S.T MSc, PhD/ UK Bacterial physiology, metabolism and
2 nd year Medical Students - JU Bacterial growth, physiology & metabolism Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi Associate Professor of Medical Microbiology. MBBS / J.U.S.T MSc, PhD/ UK Bacterial physiology, metabolism and
Lecture 17: Attack by Complement and Counterattack by Microbes
 Lecture 17: Attack by Complement and Counterattack by Microbes 2 Review Concepts of Complement Complement was addressed in Lecture 3 Major first line of defense (innate immunity) Major functions: Opsonization
Lecture 17: Attack by Complement and Counterattack by Microbes 2 Review Concepts of Complement Complement was addressed in Lecture 3 Major first line of defense (innate immunity) Major functions: Opsonization
Questions in Cell Biology
 Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Bacterial growth, physiology & metabolism
 2 nd year Medical Students - JU Bacterial growth, physiology & metabolism Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi Associate Professor of Medical Microbiology. MBBS / J.U.S.T MSc, PhD/ UK Bacterial physiology, metabolism and
2 nd year Medical Students - JU Bacterial growth, physiology & metabolism Dr. Hamed Al Zoubi Associate Professor of Medical Microbiology. MBBS / J.U.S.T MSc, PhD/ UK Bacterial physiology, metabolism and
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and Function Topics External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification An Infectious Exam Patient with Tuberculosis
Cell Structure and Function Cell Structure and Function Topics External Structures Cell Envelope Internal Structures Cell Shapes, Arrangement, and Sizes Classification An Infectious Exam Patient with Tuberculosis
Microbiology / Active Lecture Questions Chapter 15 / Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity 1 Chapter 15 / Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 1 2 The removal of plasmids reduces virulence in which of the following organisms? a. Clostridium tetani b. Escherichia coli c. Staphylococcus aureus d. Streptococcus mutans e. Clostridium botulinum 3
1 2 The removal of plasmids reduces virulence in which of the following organisms? a. Clostridium tetani b. Escherichia coli c. Staphylococcus aureus d. Streptococcus mutans e. Clostridium botulinum 3
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral sizes and structures. Workbook Lesson 1.4
 Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Normal Flora PROF. HANAN HABIB DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, KSU
 Normal Flora PROF. HANAN HABIB DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, KSU Objectives 1. Define the terms: Normal Flora, Resident flora, Transient flora and carrier state 2. Know the origin of normal
Normal Flora PROF. HANAN HABIB DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY COLLEGE OF MEDICINE, KSU Objectives 1. Define the terms: Normal Flora, Resident flora, Transient flora and carrier state 2. Know the origin of normal
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Ch 15. Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity
 Ch 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Student Learning Outcomes Identify the principal portals of entry and exit. Using examples, explain how microbes adhere to host cells. Explain how capsules and
Ch 15 Microbial Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Student Learning Outcomes Identify the principal portals of entry and exit. Using examples, explain how microbes adhere to host cells. Explain how capsules and
Symbiosis to live together symbiotic relationships with microorganisms Main kinds of symbiosis:
 Topic 6 (15): Microbe Mechanisms of Pathogenicity - Infection and Disease Topics Human Host Disease Classifications of Disease Infection Progress stages Koch s Postulates Virulence Factors Prokaryotic
Topic 6 (15): Microbe Mechanisms of Pathogenicity - Infection and Disease Topics Human Host Disease Classifications of Disease Infection Progress stages Koch s Postulates Virulence Factors Prokaryotic
DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE
 DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE COURSE OUTLINE WINTER 2018 MI 2950 INFECTION & IMMUNITY 3 Credits (3-0-0) 45 hours 15 weeks INSTRUCTOR: Philip Johnson PHONE: 780-539-2863 OFFICE: J224 E-MAIL: PJohnson@gprc.ab.ca
DEPARTMENT OF SCIENCE COURSE OUTLINE WINTER 2018 MI 2950 INFECTION & IMMUNITY 3 Credits (3-0-0) 45 hours 15 weeks INSTRUCTOR: Philip Johnson PHONE: 780-539-2863 OFFICE: J224 E-MAIL: PJohnson@gprc.ab.ca
New genomic typing method MLST
 New genomic typing method MLST Bon KIMURA fingerprinting PFGE DNA multilocus sequence typingmlst alleles PFGE MLST 1990 PCR 1 PCR DNA PFGE 1 PFGE RAPDrandomly amplified polymorphic DNA 3 AFLPAmplified
New genomic typing method MLST Bon KIMURA fingerprinting PFGE DNA multilocus sequence typingmlst alleles PFGE MLST 1990 PCR 1 PCR DNA PFGE 1 PFGE RAPDrandomly amplified polymorphic DNA 3 AFLPAmplified
Module Contact: Dr Gary Rowley, BIO Copyright of the University of East Anglia Version 1
 UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2014-2015 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY BIO-3C28 Time allowed: 3 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A and ONE question from
UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA School of Biological Sciences Main Series UG Examination 2014-2015 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY BIO-3C28 Time allowed: 3 hours Answer ALL questions in Section A and ONE question from
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan. Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan Immunology and Serology (DVT2153) By Dr. Erkihun Aklilu 1 Immune Response AgAinst Various infectious agents Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Universiti Malaysia Kelantan Immunology and Serology (DVT2153) By Dr. Erkihun Aklilu 1 Immune Response AgAinst Various infectious agents Immunology and Serology (DVT2153)
Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenesis
 Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenesis Pin Ling ( 凌斌 ), Ph.D. Department of Microbiology & Immunology, NCKU ext 5632 lingpin@mail.ncku.edu.tw References: 1. Chapter 19 in Medical Microbiology (Murray, P.
Mechanisms of Bacterial Pathogenesis Pin Ling ( 凌斌 ), Ph.D. Department of Microbiology & Immunology, NCKU ext 5632 lingpin@mail.ncku.edu.tw References: 1. Chapter 19 in Medical Microbiology (Murray, P.
AREAS OF CONCENTRATION
 Dr. Shruti Mehta, Director The development of antibiotics, improved access to safe food, clean water, sewage disposal and vaccines has led to dramatic progress in controlling infectious diseases. Despite
Dr. Shruti Mehta, Director The development of antibiotics, improved access to safe food, clean water, sewage disposal and vaccines has led to dramatic progress in controlling infectious diseases. Despite
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Hamed Alzoubi
 number 4 Done by Tasneem Mountaj Saad Hayek Corrected by حسام أبو عوض Doctor Hamed Alzoubi Bacterial growth, physiology and metabolism Bacteria, like all living species, need to grow and replicate in order
number 4 Done by Tasneem Mountaj Saad Hayek Corrected by حسام أبو عوض Doctor Hamed Alzoubi Bacterial growth, physiology and metabolism Bacteria, like all living species, need to grow and replicate in order
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System
 Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
Necrotizing Enterocolitis: The Role of the Immune System Patricia Denning, M.D. Associate Professor in Pediatrics Division of Neonatology Emory University School of Medicine What is NEC? What is NEC? Necrotizing
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology
 علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
Patient: Ima Sample. Accession: Shiloh Rd, Ste 101. Collected: 2/10/2018. Received: 2/12/2018 Alpharetta GA
 GI-MAP TM DNA Stool Analysis Patient: Ima Sample Accession: 20180212-0001 5895 Shiloh Rd, Ste 101 Collected: 2/10/2018 Received: 2/12/2018 Alpharetta GA 30005 877-485-5336 DOB: 7/11/1981 Completed: Ordered
GI-MAP TM DNA Stool Analysis Patient: Ima Sample Accession: 20180212-0001 5895 Shiloh Rd, Ste 101 Collected: 2/10/2018 Received: 2/12/2018 Alpharetta GA 30005 877-485-5336 DOB: 7/11/1981 Completed: Ordered
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses
 Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Medical Virology Immunology. Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University
 Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
Medical Virology Immunology Dr. Sameer Naji, MB, BCh, PhD (UK) Head of Basic Medical Sciences Dept. Faculty of Medicine The Hashemite University Human blood cells Phases of immune responses Microbe Naïve
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Meningococcal vaccines and Herd protection. Potential Role, Coverage and Impact on carriage of the New Serogroup B protein vaccines in the Region
 Meningococcal vaccines and Herd protection. Potential Role, Coverage and Impact on carriage of the New Serogroup B protein vaccines in the Region Ricardo Rüttimann Pediatric Infectious Diseases FUNCEI
Meningococcal vaccines and Herd protection. Potential Role, Coverage and Impact on carriage of the New Serogroup B protein vaccines in the Region Ricardo Rüttimann Pediatric Infectious Diseases FUNCEI
Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host
 Module 10 Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host The concept of immunity Immunity: ability to protect against from microbes and their o Aka, Susceptibility: vulnerability or lack
Module 10 Chapter 16 Innate Immunity: Nonspecific Defenses of the Host The concept of immunity Immunity: ability to protect against from microbes and their o Aka, Susceptibility: vulnerability or lack
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate
 Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Shirin Abadi, B.Sc.(Pharm.), ACPR, Pharm.D. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist & Pharmacy Education Coordinator, BC Cancer Agency Clinical Associate Professor of Pharmacy & Associate Member of Medicine, UBC
Chain of Infection Agent Mode of transmission Contact (direct, indirect, droplet spread) Airborne Common-vehicle spread Host
 Goals Microbiology of Healthcare-associated Infections William A. Rutala, Ph.D., M.P.H. Director, Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology and Research Professor of Medicine, University
Goals Microbiology of Healthcare-associated Infections William A. Rutala, Ph.D., M.P.H. Director, Statewide Program for Infection Control and Epidemiology and Research Professor of Medicine, University
4. The most common cause of traveller s diarrheoa is a. Rotavirus b. E coli c. Shigella d. Giardia e. Salmonella
 INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
INFECTIOUS DISEASE 1. Mumps virus is a a. Adenovirus b. Herpes virus c. Paramyxovirus d. Pox virus e. Picornavirus 2. All of the following cause a clinical effect via the production of exotoxin except
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 4.1 What is a Cell? Each cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus (in eukaryotic cells) or a nucleoid (in prokaryotic cells) 1 Nucleoid concentrated DNA
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 4.1 What is a Cell? Each cell has a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus (in eukaryotic cells) or a nucleoid (in prokaryotic cells) 1 Nucleoid concentrated DNA
Protein Modeling Event
 Protein Modeling Event School Name: School Number: Team Member 1: Team Member 2: : Pre-Build Score: On-Site Build Score: Test Score: Tie Breaker: Total: Final Rank: Part I: Pre-Build (40% of total score)
Protein Modeling Event School Name: School Number: Team Member 1: Team Member 2: : Pre-Build Score: On-Site Build Score: Test Score: Tie Breaker: Total: Final Rank: Part I: Pre-Build (40% of total score)
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care. Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK
 Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Topical antimicrobial agents in wound care Professor Val Edwards-Jones Manchester Metropolitan University UK Antimicrobial agents Antibacterial agents Antifungal agents Antiviral agents Antiparasitic agents?others
Current Strategies in HIV-1 Vaccine Development Using Replication-Defective Adenovirus as a Case Study
 Note: I have added some clarifying comments to the slides -- please click on Comments under View to see them. Current Strategies in HIV-1 Vaccine Development Using Replication-Defective Adenovirus as a
Note: I have added some clarifying comments to the slides -- please click on Comments under View to see them. Current Strategies in HIV-1 Vaccine Development Using Replication-Defective Adenovirus as a
