Legionella pneumophila: an intracellular pathogen of phagocytes Prof. Craig Roy
|
|
|
- Joan James
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 an intracellular pathogen of phagocytes Section of Microbial Pathogenesis, Yale University School of Medicine 1 Legionella pneumophila Gram-negative bacterium Facultative intracellular pathogen Protozoa are natural hosts Aerosols can result in human infection Replication in macrophages Legionnaires' disease 2 Horwitz and colleagues define the Legionella lifecycle 3 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 1
2 The Shuman and Isberg laboratories independently identify the dot and icm genes Andrea Marra: Complementing an icm defect restores the ability of Legionella 25d to avoid fusion with lysosomes Karen Berger: The dota gene is essential for intracellular replication and avoiding lysosome fusion Joe Vogel and Gil Segal sequence a total of 24 dot and icm genes 4 The dot and icm genes define a new type IV secretion system Host cell plasma membrane Outer membrane Inner membrane Figure by Christie and Vogel A. tumefaciens virb type IVa L. pneumophila dot/icm type IVb 5 Why is the Dot/Icm system required for intracellular replication? Does Dot/Icm control nutrient acquisition into the vacuole? Does Dot/Icm poison the cell to make it generally permissive for bacterial replication? Does Dot/Icm interfere directly with vesicle transport? Are bacterial effector proteins translocated by the Dot/Icm system? 6 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 2
3 Endocytic membrane transport Endocytic membrane transport 7 The Dot/Icm system mediates rapid evasion of endocytic maturation 100% wild type dot/icm mutants hagosomes ining positive Ph stai 75% 50% 25% 5 min 15 min 30 min Early Endocytic Compartments Rab7 - LAMP-1 - Rab7 + LAMP-1-5 min 15 min 30 min Late Endocytic Compartments Rab7 + LAMP-1 + Rab7 - LAMP Understanding Dot/Icm function through coinfection of macrophages Wild type bacteria do not produce GFP dota mutants produce GFP Macrophages coinfected with wild type and dota mutants dota mutant transdominant over wild type Vacuoles traffic independently Wild type transdominant over dota mutant Joern Coers and Catherine Monahan 9 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 3
4 The Dot/Icm system controls transport of the Legionella-containing vacuole All bacteria dota mutant Merge-DIC All bacteria + nucleus dota mutant Merge 10 Legionella subverts vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi Inhibiting Golgi assembly and membrane transport in the late secretory pathway had no effect on Legionella replication Inhibiting membrane transport from the ER interfered with Legionella replication X X X Inhibiting membrane transport in the endocytic pathway enhanced Legionella replication Jonathan Kagan 11 Legionella replication requires vesicular transport out of the endoplasmic reticulum 12 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 4
5 ARF function is required for ER remodeling of the Legionella-containing vacuole ER labeled with YFP-KDEL No inhibition of ARF ER labeled with YFP-KDEL ARF function inhibited with Brefeldin A 13 ER-derived vesicles associate rapidly with the Legionella-containing vacuole 5 min post infection 15 min post infection Lew Tilney and Cam Robinson 14 Legionella utilize host ases for biogenesis of a vacuole that supports replication 15 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 5
6 The Dot/Icm system modulates Arf Legionella ARF1-GFP Merge dota wild type Jon Kagan 16 The Dot/Icm system modulates Rab1 GFP-Rab1a DNA GFP-Rab1a DNA anti-rab1b DNA anti-rab1b DNA Jon Kagan 17 Control of Arf and Rab ases cytosolic Arf1 GEF membrane associated Arf1 Effectors Coat proteins -COPI - AP-1 - AP-3 - GGAs Lipid modification enzymes -PLD -PI 4 K -PI 4 P 5 K Pi GAP Others - Arfaptin/POR1 - Arfophilins/FIPs - FAPPs 18 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 6
7 Can we identify Legionella proteins that modulate Arf and Rab1 function? Arf1 Putative Dot/Icm effector proteins Rab1 19 Identification of ralf (Recruitment of Arf to the Legionella phagosome) ralf wild type Legionella ARF1-GFP Hiroki Nagai ARF1-GFP 20 RalF is present on the cytosolic surface of the Legionella-containing vacuole anti-ralf Legionella anti-ralf Legionella anti-ralf Legionella anti-ralf Legionella 21 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 7
8 RalF is delivered into host cells by the Dot/Icm system upon uptake DNA anti-legionella (extracellular) ARF1 22 RalF defines a bacterial member of the Sec7 family of Arf exchange factors L. pneumophila RalF protein S. cerevisiae Sec7p Sec7 Domain RalF + Arf1 RalF + Arf6 RalF + Arf5 Richard Kahn 23 Activation of Arf by Legionella cytosolic RalF membrane associated Arf1 Arf1 Legionella Pi GAP Vacuole 24 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 8
9 Can Legionella modulate the function of other host ases? 25 Identification of DrrA: a Legionella effector protein that modulates Rab1 activity Legionella transposon insertion mutants Pick individual mutants Array mutants in 96-well dish 96-pin replicator Infect macrophages in 96-well glass-bottom dish Takahiro Murata Fix and stain for Rab1 Screened 3948 mutants Re-screened 441 mutants Rab defects 119 mutants Dot + /Rab1-9 mutants Score Rab1 recruitment Clean deletion 1 mutant by microscopy 26 DrrA is a novel protein that functions as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rab1 cytosolic DrrA (SidM) membrane associated Rab1 Rab1 Legionella GAP Pi Vacuole 27 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 9
10 Does Legionella have other effectors that target Rab1 specifically?? DrrA?? Alyssa Ingmundson 28 DrrA does not require other Legionella effectors to localize and activate Rab1 GFP-DrrA Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Microscopy (TIRFM) of plasma membrane 29 DrrA is able to dissociate GDI from Rab1 Pull-down Rab1-GDI complex from transfected cells Add purified DrrA Immunoblot supernatant to measure GDI release 30 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 10
11 DrrA has GDI displacement activity 31 DrrA modulates Rab1 function by removing GDI and stimulated for exchange DrrA (SidM) GDI Rab1 GDI Rab1 Legionella GAP Pi 32 LepB interacts specifically with Rab1-33 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 11
12 LepB interacts specifically with Rab1- (2) 34 LepB is a Rab1 GAP 35 Control of Rab1 membrane cycling by Legionella effector proteins Plasma membrane DrrA Rab1-GDI GDI Pi LepB Pi ER exit sites 36 The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 12
13 Legionella: the greatest cell biologist on Earth! Phagocytosis Trafficking Inhibit host defenses Estimated 150 effectors Egress Cell survival Modulate host transcription/ translation The screen versions of these slides have full details of copyright and acknowledgements 13
JCB. The road less traveled: transport of Legionella to the endoplasmic reticulum. Mini-Review. Craig R. Roy 1 and Lewis G.
 JCB Published Online: 29 July, 2002 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200205011 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 6, 2018 Mini-Review The road less traveled: transport of Legionella to the
JCB Published Online: 29 July, 2002 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200205011 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on November 6, 2018 Mini-Review The road less traveled: transport of Legionella to the
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport
 Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
Mechanism of Vesicular Transport Transport vesicles play a central role in the traffic of molecules between different membrane-enclosed enclosed compartments. The selectivity of such transport is therefore
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION In format provided by Isberg et al. (JANUARY 2008)
 Supplementary Table S1: Dot/Icm translocated substrates A: Substrates based on similarity to eukaryotic proteins LepA 1 lpg2793 coiled-coil domain/ bacterial egress CA, BLA LepB 1,2 lpg2490 coiled-coil
Supplementary Table S1: Dot/Icm translocated substrates A: Substrates based on similarity to eukaryotic proteins LepA 1 lpg2793 coiled-coil domain/ bacterial egress CA, BLA LepB 1,2 lpg2490 coiled-coil
Vesicle Transport. Vesicle pathway: many compartments, interconnected by trafficking routes 3/17/14
 Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Vesicle Transport Vesicle Formation Curvature (Self Assembly of Coat complex) Sorting (Sorting Complex formation) Regulation (Sar1/Arf1 GTPases) Fission () Membrane Fusion SNARE combinations Tethers Regulation
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
General aspects of this review - specific examples were addressed in class.
 General aspects of this review - specific examples were addressed in class. 1 Exam 1 Lecture 2: Discussed intracellular killing mechanisms Important maturation steps Rapid development into a microbicidal
General aspects of this review - specific examples were addressed in class. 1 Exam 1 Lecture 2: Discussed intracellular killing mechanisms Important maturation steps Rapid development into a microbicidal
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Rapid Escape of the dot/icm Mutants of Legionella pneumophila into the Cytosol of Mammalian and Protozoan Cells
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2007, p. 3290 3304 Vol. 75, No. 7 0019-9567/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00292-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Rapid Escape of the
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2007, p. 3290 3304 Vol. 75, No. 7 0019-9567/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00292-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Rapid Escape of the
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 17: Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about clathrin-coated vesicles is correct? Question #1 (A) There are
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Bringing host-cell takeover by pathogenic bacteria to center stage: Editorial
 Bringing host-cell takeover by pathogenic bacteria to center stage: Editorial Ron Dubreuil and Nava Segev University of Illinois at Chicago Abstract Intra-cellular pathogenic bacteria contrive processes
Bringing host-cell takeover by pathogenic bacteria to center stage: Editorial Ron Dubreuil and Nava Segev University of Illinois at Chicago Abstract Intra-cellular pathogenic bacteria contrive processes
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al.
 Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Intracellular Vesicular Traffic Chapter 13, Alberts et al. The endocytic and biosynthetic-secretory pathways The intracellular compartments of the eucaryotic ell involved in the biosynthetic-secretory
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, Please print your name: Instructions:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In class Exam 1 October 2, 2012 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your number
endomembrane system internal membranes origins transport of proteins chapter 15 endomembrane system
 endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
endo system chapter 15 internal s endo system functions as a coordinated unit divide cytoplasm into distinct compartments controls exocytosis and endocytosis movement of molecules which cannot pass through
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014
 Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
Homework Hanson section MCB Course, Fall 2014 (1) Antitrypsin, which inhibits certain proteases, is normally secreted into the bloodstream by liver cells. Antitrypsin is absent from the bloodstream of
Chapter 6. Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Chapter 6 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Generation of T-cell Receptor Ligands T cells only recognize Ags displayed on cell surfaces These Ags may be derived from pathogens that replicate within
Chapter 6 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Generation of T-cell Receptor Ligands T cells only recognize Ags displayed on cell surfaces These Ags may be derived from pathogens that replicate within
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic. Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18
 Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
Chapter 1: Vesicular traffic Biochimica cellulare parte B 2017/18 Major Protein-sorting pathways in eukaryotic cells Secretory and endocytic pathways Unifying principle governs all protein trafficking
1. endoplasmic reticulum This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Evidence that Dot-dependent and -independent factors isolate the Legionella pneumophila phagosome from the endocytic network in mouse macrophages
 Cellular Microbiology (2001) 3(2), 99±114 Evidence that Dot-dependent and -independent factors isolate the Legionella pneumophila phagosome from the endocytic network in mouse macrophages Amrita D. Joshi,
Cellular Microbiology (2001) 3(2), 99±114 Evidence that Dot-dependent and -independent factors isolate the Legionella pneumophila phagosome from the endocytic network in mouse macrophages Amrita D. Joshi,
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Lewis G. Tilney 1 *, Omar S. Harb 1, Patricia S. Connelly 1, Camenzind G. Robinson 2, and Craig R. Roy 2 SUMMARY
 RESEARCH ARTICLE 4637 How the parasitic bacterium Legionella pneumophila modifies its phagosome and transforms it into rough ER: implications for conversion of plasma membrane to the ER membrane Lewis
RESEARCH ARTICLE 4637 How the parasitic bacterium Legionella pneumophila modifies its phagosome and transforms it into rough ER: implications for conversion of plasma membrane to the ER membrane Lewis
A Bacterial Virulence Protein Suppresses Host Innate Immunity to Cause Plant Disease
 A Bacterial Virulence Protein Suppresses Host Innate Immunity to Cause Plant Disease Nomura, K., Debroy, S., Lee, Y.H., Pumplin, N., Jones, J., and He, S.Y. (2006). Science 313, 220-223. Presented by:
A Bacterial Virulence Protein Suppresses Host Innate Immunity to Cause Plant Disease Nomura, K., Debroy, S., Lee, Y.H., Pumplin, N., Jones, J., and He, S.Y. (2006). Science 313, 220-223. Presented by:
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 22, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 April 22, 2013 1 / 38 Outline Questions and answers Intracellular
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University April 22, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 33 April 22, 2013 1 / 38 Outline Questions and answers Intracellular
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Essential Cell Biology
 Alberts Bray Hopkin Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Essential Cell Biology FOURTH EDITION Chapter 15 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport Copyright Garland Science 2014 CHAPTER CONTENTS MEMBRANE-ENCLOSED
Alberts Bray Hopkin Johnson Lewis Raff Roberts Walter Essential Cell Biology FOURTH EDITION Chapter 15 Intracellular Compartments and Protein Transport Copyright Garland Science 2014 CHAPTER CONTENTS MEMBRANE-ENCLOSED
Laboratory 10 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena,
 BIO354: Cell Biology Laboratory 1 Laboratory 1 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena, I. Introduction A characteristic feature of all eukaryotic cells is the ability to pinch off portions of
BIO354: Cell Biology Laboratory 1 Laboratory 1 Factors Controlling Phagocytosis in Tetrahymena, I. Introduction A characteristic feature of all eukaryotic cells is the ability to pinch off portions of
Department of Microbial Pathogenesis, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, United States of America
 Effector Protein Translocation by the Coxiella burnetii Dot/Icm Type IV Secretion System Requires Endocytic Maturation of the Pathogen-Occupied Vacuole Hayley J. Newton*, Justin A. McDonough, Craig R.
Effector Protein Translocation by the Coxiella burnetii Dot/Icm Type IV Secretion System Requires Endocytic Maturation of the Pathogen-Occupied Vacuole Hayley J. Newton*, Justin A. McDonough, Craig R.
Antigen presenting cells
 Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Antigen recognition by T and B cells - T and B cells exhibit fundamental differences in antigen recognition - B cells recognize antigen free in solution (native antigen). - T cells recognize antigen after
Molecular Pathogenesis of Infections Caused by Legionella pneumophila
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2010, p. 274 298 Vol. 23, No. 2 0893-8512/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cmr.00052-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Molecular Pathogenesis
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Apr. 2010, p. 274 298 Vol. 23, No. 2 0893-8512/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cmr.00052-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Molecular Pathogenesis
THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS
 Research Foundation, 18 month progress report THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS Ekaterina Ivanova, doctoral student Elena Levtchenko, MD, PhD, PI Antonella
Research Foundation, 18 month progress report THE ROLE OF ALTERED CALCIUM AND mtor SIGNALING IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF CYSTINOSIS Ekaterina Ivanova, doctoral student Elena Levtchenko, MD, PhD, PI Antonella
Summary and Discussion antigen presentation
 Summary and Discussion antigen presentation 247 248 Summary & Discussion Summary and discussion: antigen presentation For a cell to communicate information about its internal health and status to the immune
Summary and Discussion antigen presentation 247 248 Summary & Discussion Summary and discussion: antigen presentation For a cell to communicate information about its internal health and status to the immune
The Journal of Experimental Medicine
 Legionella Subvert the Functions of Rab1 and Sec22b to Create a Replicative Organelle Jonathan C. Kagan, Mary-Pat Stein, Marc Pypaert, and Craig R. Roy Section of Microbial Pathogenesis, Boyer Center for
Legionella Subvert the Functions of Rab1 and Sec22b to Create a Replicative Organelle Jonathan C. Kagan, Mary-Pat Stein, Marc Pypaert, and Craig R. Roy Section of Microbial Pathogenesis, Boyer Center for
Maturation of the Legionella pneumophila-containing Phagosome into a Phagolysosome within Gamma Interferon-Activated Macrophages
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 2005, p. 3166 3171 Vol. 73, No. 5 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.5.3166 3171.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Maturation
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 2005, p. 3166 3171 Vol. 73, No. 5 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.5.3166 3171.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Maturation
1. This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
The machinery at endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact sites contributes to spatial regulation of multiple Legionella effector proteins
 University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 7-3-2014 The machinery at endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact sites
University of Massachusetts Medical School escholarship@umms Open Access Articles Open Access Publications by UMMS Authors 7-3-2014 The machinery at endoplasmic reticulum-plasma membrane contact sites
MCB130 Midterm. GSI s Name:
 1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson
 Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
Lysosomes and endocytic pathways 9/27/2012 Phyllis Hanson General principles Properties of lysosomes Delivery of enzymes to lysosomes Endocytic uptake clathrin, others Endocytic pathways recycling vs.
/searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1
 http://www.studiodaily.com/main /searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1 2011-2012 Cytology: science/study of cells To view cells: Light microscopy resolving power: measure of clarity Electron microscopy
http://www.studiodaily.com/main /searchlist/6850.html Tour of the Cell 1 2011-2012 Cytology: science/study of cells To view cells: Light microscopy resolving power: measure of clarity Electron microscopy
regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs;
 regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs; p.vandersluijs@umcutrecht.nl cytotoxic T cell recognizes complex of viral peptide with MHC class I and kills infected cell
regulation of polarized membrane transport by rab GTPases Peter van der Sluijs; p.vandersluijs@umcutrecht.nl cytotoxic T cell recognizes complex of viral peptide with MHC class I and kills infected cell
In the previous chapter we explored how proteins are targeted
 17 VESICULAR TRAFFIC, SECRETION, AND ENDOCYTOSIS Electron micrograph of clathrin cages, like those that surround clathrin-coated transport vesicles, formed by the in vitro polymerization of clathrin heavy
17 VESICULAR TRAFFIC, SECRETION, AND ENDOCYTOSIS Electron micrograph of clathrin cages, like those that surround clathrin-coated transport vesicles, formed by the in vitro polymerization of clathrin heavy
4 A Tour of the Cell CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS. Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Reece 4 A Tour of the Cell Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life All
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles. Hüseyin Çağsın
 Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Lysosomes, Peroxisomes and Centrioles Hüseyin Çağsın Lysosomes Outline Endosomes Molecule transport to the lysosomes Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Vacuoles Peroxisomes Centrioles Lysosomes Lysosomes
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
LidA, a Translocated Substrate of the Legionella pneumophila Type IV Secretion System, Interferes with the Early Secretory Pathway
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2005, p. 4370 4380 Vol. 73, No. 7 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.7.4370 4380.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. LidA, a
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, July 2005, p. 4370 4380 Vol. 73, No. 7 0019-9567/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.73.7.4370 4380.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. LidA, a
Intracellular vesicular traffic. B. Balen
 Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Intracellular vesicular traffic B. Balen Three types of transport in eukaryotic cells Figure 12-6 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) Endoplasmic reticulum in all eucaryotic cells Endoplasmic
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
General information. Cell mediated immunity. 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon. Anytime after class.
 General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
Subcellular biochemistry
 Department of Medical Biochemistry Semmelweis University Subcellular biochemistry February-March 2017 Subcellular biochemistry (biochemical aspects of cell biology) Miklós Csala Semmelweis University Dept.
Department of Medical Biochemistry Semmelweis University Subcellular biochemistry February-March 2017 Subcellular biochemistry (biochemical aspects of cell biology) Miklós Csala Semmelweis University Dept.
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
BIS2A T.M. Murphy Page 1
 BIS2A T.M. Murphy Page 1 CELL PROBLEMS A. Structure 1. Decide whether microscopy or cell fractionation would be the best way to answer each of the following questions. a. What is the nucleus made of? b.
BIS2A T.M. Murphy Page 1 CELL PROBLEMS A. Structure 1. Decide whether microscopy or cell fractionation would be the best way to answer each of the following questions. a. What is the nucleus made of? b.
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Barbara Heard, Atlantic Cape Community College Ninth Edition Human Anatomy & Physiology C H A P T E R 3 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images 2013 Pearson Education,
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human
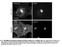 Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
Fig. S1. Subcellular localization of overexpressed LPP3wt-GFP in COS-7 and HeLa cells. Cos7 (top) and HeLa (bottom) cells expressing for 24 h human LPP3wt-GFP, fixed and stained for GM130 (A) or Golgi97
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Received 11 February 2008/Returned for modification 10 March 2008/Accepted 13 March 2008
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 2008, p. 2671 2677 Vol. 76, No. 6 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00185-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Acquisition of the
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 2008, p. 2671 2677 Vol. 76, No. 6 0019-9567/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.00185-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Acquisition of the
Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Principal Investigator: Project title:
 Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Gennaro Napolitano Principal Investigator: Sergio Daniel Catz Project title: Small molecule regulators of vesicular trafficking to enhance lysosomal exocytosis
Project report October 2012 March 2013 CRF fellow: Gennaro Napolitano Principal Investigator: Sergio Daniel Catz Project title: Small molecule regulators of vesicular trafficking to enhance lysosomal exocytosis
2.4 : Cell Transport
 2.4 : Cell Transport At the end of the lesson, you should be able to : Explain the various transport mechanisms across the membrane : Active transport - Sodium-Potassium Pump Endocytosis and Exocytosis
2.4 : Cell Transport At the end of the lesson, you should be able to : Explain the various transport mechanisms across the membrane : Active transport - Sodium-Potassium Pump Endocytosis and Exocytosis
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH INTRACELLULAR PROTEIN TRANSPORT.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: MEMBRANE ENCLOSED ORGANELLES Table of eukaryotic organelles and their functions Organelle Function % volume of cell Cytosol Aqueous fluid where metabolic pathways and chemical
A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Cell Theory 1 A Tour of the Cell Lecture 2, Part 1 Fall 2008 Cells are the basic unit of structure and function The lowest level of structure that can perform all activities required for life Reproduction
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis
 Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Module 3 Lecture 7 Endocytosis and Exocytosis Endocytosis: Endocytosis is the process by which cells absorb larger molecules and particles from the surrounding by engulfing them. It is used by most of
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic
 Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Chapter 13: Vesicular Traffic Know the terminology: ER, Golgi, vesicle, clathrin, COP-I, COP-II, BiP, glycosylation, KDEL, microtubule, SNAREs, dynamin, mannose-6-phosphate, M6P receptor, endocytosis,
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15
 Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Name: Key Trask Zool 3200: Cell Biology Exam 4 Part I 2/3/15 Answer each of the following questions in the space provided, explaining your answers when asked to do so; circle the correct answer or answers
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/334/rs4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Rapidly rendering cells phagocytic through a cell surface display technique and concurrent Rac activation Hiroki Onuma,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/334/rs4/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Rapidly rendering cells phagocytic through a cell surface display technique and concurrent Rac activation Hiroki Onuma,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Host cell death in Legionella pneumophila pathogenesis and immunity
 Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Dissertations Theses and Dissertations Fall 2014 Host cell death in Legionella pneumophila pathogenesis and immunity Wenhan Zhu Purdue University Follow this
Purdue University Purdue e-pubs Open Access Dissertations Theses and Dissertations Fall 2014 Host cell death in Legionella pneumophila pathogenesis and immunity Wenhan Zhu Purdue University Follow this
A Closer Look at Cell Membranes. Chapter 5 Part 2
 A Closer Look at Cell Membranes Chapter 5 Part 2 5.5 Membrane Trafficking By processes of endocytosis and exocytosis, vesicles help cells take in and expel particles that are too big for transport proteins,
A Closer Look at Cell Membranes Chapter 5 Part 2 5.5 Membrane Trafficking By processes of endocytosis and exocytosis, vesicles help cells take in and expel particles that are too big for transport proteins,
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation
 Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 3/8/2011 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 3/8/2011 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS
 BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
BACTERIAL PATHOGENESIS A pathogen is a microorganism that is able to cause disease. Pathogenicity is the ability to produce disease in a host organism. Virulence a term which refers to the degree of pathogenicity
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment
 Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
Overview of the immune system
 Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Overview of the immune system Immune system Innate (nonspecific) 1 st line of defense Adaptive (specific) 2 nd line of defense Cellular components Humoral components Cellular components Humoral components
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine
 Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation
 Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 2/21/17 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
Localization and Retention of Glycosyltransferases And the Role of Vesicle Trafficking in Glycosylation Richard Steet, Ph.D. 2/21/17 glycosylation is a non-template derived phenomenon - the presence of
AP Biology
 Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
Tour of the Cell (1) 2007-2008 Types of cells Prokaryote bacteria cells - no organelles - organelles Eukaryote animal cells Eukaryote plant cells Cell Size Why organelles? Specialized structures - specialized
17/01/2017. Protein trafficking between cell compartments. Lecture 3: The cytosol. The mitochondrion - the power plant of the cell
 ell biology 2017 version 13/1 2017 ote endosome vs lysosome handout Lecture 3: Text book Alberts et al.: hapter 12-14 (Topics covered by the lecture) A lot of reading! Focus on principles ell Biology interactive
ell biology 2017 version 13/1 2017 ote endosome vs lysosome handout Lecture 3: Text book Alberts et al.: hapter 12-14 (Topics covered by the lecture) A lot of reading! Focus on principles ell Biology interactive
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, Please print your name:
 Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, 2015 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Molecular Cell Biology 5068 In Class Exam 1 September 29, 2015 Exam Number: Please print your name: Instructions: Please write only on these pages, in the spaces allotted and not on the back. Write your
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology
 The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
The cell III. Renáta Schipp Gergely Berta Department of Medical Biology Size and Biology Biology is a visually rich subject many of the biological events and structures are smaller than the unaided human
Selective protection of an ARF1-GTP signaling axis by a bacterial scaffold induces bidirectional trafficking arrest.
 Selective protection of an ARF1-GTP signaling axis by a bacterial scaffold induces bidirectional trafficking arrest. Andrey S. Selyunin, L. Evan Reddick, Bethany A. Weigele, and Neal M. Alto Supplemental
Selective protection of an ARF1-GTP signaling axis by a bacterial scaffold induces bidirectional trafficking arrest. Andrey S. Selyunin, L. Evan Reddick, Bethany A. Weigele, and Neal M. Alto Supplemental
Cytoskeleton. Provide shape and support for the cell. Other functions of the cytoskeleton. Nucleolus. Nucleus
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Cytoskeleton The cytoskeleton is a network of fibers that organizes structures and activities in the cell. Microtubules (the largest) Intermediate fibers Microfilaments
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Introduction. Microbiology. Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Lecture 2
 Introduction to Microbiology Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Lecture 2 Cell structure / Eukaryotes 1. Nucleolus 2. Nucleus 3. Ribosome (80S) 4. Vesicle 5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum 6. Golgi apparatus (or
Introduction to Microbiology Anas Abu-Humaidan M.D. Ph.D. Lecture 2 Cell structure / Eukaryotes 1. Nucleolus 2. Nucleus 3. Ribosome (80S) 4. Vesicle 5. Rough endoplasmic reticulum 6. Golgi apparatus (or
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
(a) TEM of a plasma. Fimbriae. Nucleoid. Ribosomes. Plasma membrane. Cell wall Capsule. Bacterial chromosome
 0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
0 m m 0. m cm mm 00 µm 0 µm 00 nm 0 nm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Frog egg Most plant and animal cells Most bacteria Smallest bacteria Viruses Proteins Unaided eye Light
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #7
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #7 Introduction Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging from 1 1000 cubic
Cells. A typical animal cell THE CELL MEMBRANE FIRST STOP
 WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
WHAT ARE YOU MADE OF? A typical animal cell Cells Cells FIRST STOP The cell membrane THE CELL MEMBRANE The CELL MEMBRANE is the Gate Keeper It controls what goes in and out of the cell. The membrane is
Legionella pneumophila Is Internalized by a Macropinocytotic Uptake Pathway Controlled by the Dot/Icm System and the Mouse Lgn1 Locus
 Legionella pneumophila Is Internalized by a Macropinocytotic Uptake Pathway Controlled by the Dot/Icm System and the Mouse Lgn1 Locus Masahisa Watarai, 1, 2 Isabelle Derre, 2 James Kirby, 2 Joseph D. Growney,
Legionella pneumophila Is Internalized by a Macropinocytotic Uptake Pathway Controlled by the Dot/Icm System and the Mouse Lgn1 Locus Masahisa Watarai, 1, 2 Isabelle Derre, 2 James Kirby, 2 Joseph D. Growney,
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
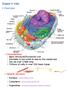 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department
 Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Renata Schipp Medical Biology Department Deffinition of cell The cell is the smallest structural and functional unit of all known living organisms The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665 and also
Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors
 Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors Federle, M. (2017). Lectures 4-5: Signal Transduction parts 1&2: nuclear receptors and GPCRs. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy,
Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors Federle, M. (2017). Lectures 4-5: Signal Transduction parts 1&2: nuclear receptors and GPCRs. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy,
