DUGAN. Introduction. I s o l a t i o n of Fhospholipids
|
|
|
- Jason Cox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 98. PHOSPHOLIPIDS I N REAT H E T H O D S O F i S O 1 A T l O N A N D I N F L U E N C E OM F E A T C H A R A C T E R I S T I C S L. R. DUGAN Introduction The growing r e a l i z a t i o n of t h e influence of minor components on system p r o p e r t i e s and t h e advances i n s o p h i s t i c a t i o n and s e n s i t i v i t y of measurement of molecular moieties has drawn a t t e n t i o n t o a r e a s which long have been neglected i n food systems. One a r e a of t h i s nature i s t h a t of t h e phospholipids i n food systems and e s p e c i a l l y i n foods of animal o r i g i n. The presence of phospholipids has been recognized f o r many years and more r e c e n t l y t h e i r r o l e as s t r u c t u r a l and f u n c t i o n a l components of c e l l s and membranes has been a s u b j e c t of d e t a i l e d i n v e s t i gation. Phospholipids have been used a s e m u l s i f i e r s, a s c r y s t a l modifiers, and a s a n t i o x i d a n t s i n various food a p p l i c a t i o n s. Phospholipids i n muscles have a number of p h y s i o l o g i c a l functions i n t h e l i v e animal but t h e i r importance i n t h e q u a l i t y of f r e s h and processed meats i s s t i l l r e l a t i v e l y ob s cure. I s o l a t i o n of Fhospholipids E x t r a c t i o n A major f a c t o r i n t h e i s o l a t i o n of phospholipids r e s i d e s i n t h e e x t r a c t i o n procedures. The phospholipids a r e bound t o p r o t e i n s i n a manner which d e f i e s e x t r a c t i o n by conventionally used f a t s o l v e n t s which e x t r a c t e s s e n t i a l l y o n l y t h e n e u t r a l l i q u i d s. Most e x t r a c t i o n methods f o r t o t a l l i p i d s follow t h e p r a c t i c e of Folch, e t a l. ( 6 ) or some v a r i a t i o n of t h i s procedure. This involves hoxogenization of t h e t i s s u e w i t h 2:lCHClz: MeOH and washing t h e e x t r a c t by a d d i t i o n t o it of 0.2 i t s volume of water o r appropriate s a l t s o l u t i o n. The r e s u l t i n g mixture s e p a r a t e s i n t o two phases upon standing, The lower phase i s t h e t o t a l l i p i d e x t r a c t. I n t h e washing procedure, t h e system of t i s s u e e x t r a c t p l u s water contains CHC13, MeOH, and water i n t h e proportions 8:4:3 (V:V) a s c r i t i c a l proport i o n s which must be kept constant. Variations on t h i s procedure have been employed f o r f i s h Bligh and Dyer (2) and muscle t i s s u e s Ostrander and Dugan (13). The a l c o h o l e f f e c t i v e l y r e l e a s e s t h e p r o t e i n and t h e chloroform t h e n provides t h e solvent f o r e f f e c t i v e removal of t h e l i p i d from t h e system. Separation Most methods of s e p a r a t i o n of phospholipids, e i t h e r a s a c l a s s or a s i n d i v i d u a l phospholipid components, depend on some means of s e l e c t i v e adsorption. Choudhury and Arnold ( 4 ) were able t o determine t h e n e u t r a l o i l content of vegetable o i l s a s follows: shake f o r 1 0 min. i n a 125 m l e r l e n meyer f l a s k 23 g crude o i l, 25 g s i l i c i c a c i d and 50 m l CHC13. A f t e r f i l t e r i n g through a s i n t e r e d g l a s s funnel under vacuum, t h e s i l i c i c a c i d i s washed with f i v e 50ml lots CHC13. The combined f i l t r a t e and washings a r e f r e e d from CHCIS on a water b a t h and t h e residue heated t o constant weight a t 105OC i n a vacuum oven or under PITz. The phospholipids a r e determined PY washing t h e s i l i c i c a c i d w i t h MeOH, evaporating t h e MeOH and weighing t h e residue. They found phospholipid content t o be 6.25$ i n soybean o i l, 5.83% i n corn o i l and 3.25% i n cottonseed o i l.
2 99. A number of investigators have applied this procedure to determination of phospholipids or to concentrating them prior to separation into individual components. Kuchmak and Dugan (11) reported that phospholipids from pork muscle were well separated in this manner but that some residual neutral fats remained with the phospholipids. Hornstein, et al. (9) made the same observation. They modified the polarity of the solvent and with a mixture of chloroformhexanediethyl ether (2:l:l) were able to effect a quantitative separation of phospholipids. Separation into individual phospholipids has been accomplished by silicic acid column chromatography and by thinlayer chromatography. Column chromatography with silicic acid seldom gives cleancut separation of components. The cephalins, phosphatidyl ethanolamine and phosphatidyl serine, frequently elute together and lecithin overlaps with lysolecithin and occasionally with sphingomyelin. Kuchmak and Dugan (12) used silicic acid and separated the cephalins on a silicic acidsilicate column described by Rouser, et al. (15). Rouser, et al. (16) established a lipid separation scheme based on DEAE Cellulose which permitted elution of lecithin, sphingomyelin, ceramide, cerebroside, lysolecithin, sterol esters and glycerides as a group. Phosphatidyl ethanolamine eluted as a separate fraction and phosphatidyl serine eluted with the gangliosides as shown in Table 1. Table 1. Elution of Lipids from DEAE Cellulose (Acetate Form) Solvent 1. Lecithin, sphingomyelin, ceramide, cerebroside, cholesterol, lysolecithin, sterol esters, and glycerides 2. Phosphatidyl ethanolamine 3, Water soluble nonlipids ( sugars, amino acids, purines, salt) 4. Uncharacterized components and free fatty acids 5. Phosphatidyl serine and ganglioside 6. Cerebroside sulfate, inositol phosphatide and cardiolipin Substance CHC13/MeOH 7/1 CHCl,/MeOH 7/3 MeOH CHC13/glacial CH3COOH 3/1 containing M CH3COOK Glacial CH3COOH CHCL/MeOH 4/1 containing 10 &/liter concentrated aqueous NH40H *From Rouser et al. (16) 7
3 100. They then separated the components of the first fraction from the DEAE Cellulose column on a Silicic AcidSilicateWater column as shown in Table 2, Table 2. Elution from a Silicic AcidSilicateWater Column* Solvent Sub stance CHC13 Cholesterol CHC13/MeOH, 19/1 Ceramide CHC13/MeOH, 4/ % H20 Cerebrosides CHC13/MeOH, 4/ % H20 Lecithin CHCl3/Me0H, 4/ % H20 Sphingomyelin MeOH + 2% H20 *From Rouser, et al. (16) Lysolecithin Hornstein et al. (10) separated beef and pork lipids into four fractions by silicic acid chromatography using successive 300ml portions of CHC13/MeOH 20/1, CHC13/MeOH 1/1, and MeOH. They reported that the first two fractions consisted mainly of neutral lipids, the third frac tion contained the cephalins, and the fourth contained lecithin and sphingomyelin. The range of components in beef and pork lipids are given in Table 3. Table 3, Lipid Lipids of Beef and Pork Phscle (%)* Beef Nonphosphorus 24 Phospholipid Cephalin 4045 Lec i thin 4045 Sphingomyelin 1015 Protein 510 *From Hornstein et, al. (10) Pork
4 101. Hidaka et al. (8) used the procedure of Hornstein et al. to separate the lipids of several muscles of Japanese Black Cattle. of their results are shown in Table 4. (10) Some Table 4. Percentage of Lipid Fractions in Total Lipids from Muscles of Japanese Black Cattle* Total Fraction 1 Fraction 2 Fraction 3 Denatured Muscle (iglyc ( Cephalins ) (Lecithins Proteins Lipid erides ) and Sphingomyelins ) Fore sha'nk Hind shank Tender Loin 100 8% Loin *From Hidaka, et al. (8) Kuchmak and Dugan (11) used the scheme shown in Table 5 for separating the lipids of pork muscle into 6 fractions Table 5. Fraction I I1 I11 IV V VI Scheme for Chromatographic Separation on Silicic Acid* Eluant Volume Components CHC13 2 Nonphospholipids CH3COC% 113 Principally nonphospholipids 10% MeOH in CHC13 1 Cerebrosides (?) 15% MeOH in CHC13 X m l 20% MeOH in CHC13 1 Cephalins 25% MeOH in CHCl3 Xml 35% MeOH in CHC13 4 Lecithins Me OH 2 Sphingomyelins *From Kuchmak and Dugan (11)
5 102. The phospholipids found in various muscles of the hog carcass are shown in Table 6. Table 6. Percentage of Each Phospholipid Type in the Phospholipids of Hog Muscle Tissue* phospholipid Belly Carcass Location Ha Loin ~. Rib Phosphatidyl ethanolamine Phosphatidyl serine Lecithin Sphingomyelin *From Kuchmak and Dugan (11) Lecithin and phosphatidyl ethanolamine are the dominant phospholipids and all phospholipids vary from muscle to muscle in the carcass. A technique applied recently in our laboratory uses a multibore column packed with silicic acid, This has given clean discrete separation of individual phospholipids. The apparent overlap of lecithin, obtained by us and others, with a long tailing of minute quantities of lysolecithin may be explained by the observation of Camejo (3) that lecithin in contact with methanol on certain silicic acid preparations may undergo limited hydrolysis and yield lysolecithin plus some free fatty acid and methyl esters. Phospholipid Effect on Meat Characteristics Composition effects The amount of phospholipid in total lipid of meats is small and the effect on meat characteristics must be derived from the strong contribution of unique characteristics of the phospholipid moieties.. The factors which are unique are the presence of esterified phosphoric acid, a nitrogenous moiety in most phospholipids, the relatively high unsaturation of the fatty acids, and the close association with proteins. The association with protein determines in large measure the difficulty encountered in extracting phospholipids. This binding prevents direct extraction with chloroform and even extends to freezedried meats. Giam and Dugan (7) found a marked difference in the fatty acid composition. of 'free' lipids, those which may be extracted by ordinary fat solvents, and 'bound' lipids, those which require treatment with methanol prior to or concurrent with the use of chloroform as extracting solvent. Representative data for pork, beef, and lamb are shown in Table 7.
6 103. Table 7. F a t t y Acid Composition of "Free" and " bund" Lipids of Freezedried Raw Pork, Lamb, and Beef of t o t a l f a t t y a c i d s ). * (4 Raw Pork Fatty acid Raw Lamb Raw Beef Free Bound Free Bound Free :l :l O :l : : : X 2.o :l Y O Z :1 *From Giam and Dugan ( 7 ) Bound
7 104. The d i f f e r e n c e s noted a r e p a r t i c u l a r l y marked f o r l i n o l e i c and arachidonic a c i d s, both of which a r e found i n e l e v a t e d concentrations i n phospholipids. Kuchmak and Dugan ( 1 2 ) examined t h e f a t t y a c i d composition and t h e d i s t r i b u t i o n of t h e f a t t y a c i d s i n t h e phospholipids from various pork muscles. Marked d i f f e r e n c e s i n composition were noted f o r t h e various carcass l o c a t i o n s. The f a t t y a c i d s of t h e phosphatidylethanolamine f r a c t i o n a r e shown i n Table 8. Table 8. F a t t y Acid Composition of Phosphatidylethanolamine from Porcine Muscles (Mole $)* Fatty Acid 1o:o 12:o 13:O a 14:O b 15:O 16:O 16:l 17:O 18:O 18:l 18:2 18:3 2O:l 21:o 20:4 22:o 22 :1 Yuscle Source Belly Ham Loin Ribs O e From Kuchmak and Dugan ( 1 2 ) E s p e c i a l l y marked variakions were noted i n t h e amounts of s t e a r i c, l i n o l e i c, and arachidonic a c i d s. The arachidonic a c i d content of t h e b e l l y muscle was more t h a n t h r e e times g r e a t e r t h a n t h a t of t h e ham muscle. Allen, e t a l. (1)determined t h e comparative l i p i d composition of t h r e e porcine muscles: t h e diaphragm, L. d o r s i, and Psoas major. I n e v a l u a t i n g t h e d i f f e r e n c e s between composition of n e u t r a l l i p i d s and of t o t a l l i p i d e x t r a c t s, t h e y r e l a t e d d i f f e r e n c e s i n s t e a r i c and o l e i c a c i d s t o an i n f e r r e d cephalin o r l e c i t h i n content. They noted f u r t h e r an apparent g r e a t e r u n s a t u r a t i o n i n nonneutral l i p i d s from psoas major and I
8 105. suggested that lipids fromthis muscle might become rancid more quickly than those of the other two muscles. Peng and Dugan (14)showed that the dark meat of chicken contained proportionally more linoleic acid and arachidonic acid in given phospholipids than were found in the same phospholipids of white meat. Oxidative and other quality effects Some of the quality factors related to phospholipids are only inferred while others may be directly attributed to the phospholipids. Hornstein,.et al. (10) observed strong fishy odors from heating of cephalins from pork or beef and a diminished fishy odor associated with an aroma suggestive of liver when the lecithins of pork or beef were heated. Both total lipid and phospholipid fractions from pork or beef became rancid quickly when exposed to air. They concluded that phospholipids possibly contributed to poor flavors in excessively lean meat. Marked darkening of the phospholipids accompanied the development of rancidity. Younathan and Watts (17) compared the development of rancidity in extracted fat with that in whole tissue from pork. They noted that TM values of the tissues were many factors greater than in extracted fat. When the lipids were examined, it was found that the TBA of neutral lipids was much less than that of a total lipid extract or of the fraction which they referred to as phospho or proteolipids as in Table 9. Table 9. Rancidity in Pork Lipid Fractions* Wt Lipid/g Tissue TBA Values/g Tissue Lipid Fraction Rancid Antioxidant Rancid Antioxidant Sample eated Sample Sample eated Sample g g Total Lipids Neutral fat, Phospho or Proteolipids, *From Younathan and Watts (17) Similar observations were made by Zipser, et al. investigation of lipids from oxidizing mullet. (18) an El Gharbawi and Dugan (5) studied the stability of nitrogenous compounds and lipids during storage of freezedried beef in cans with varying oxygennitrogen ratios. The fatty acid composition of the neutral lipid and the phospholipid fractions changed with oxidation during storage
9 106. according t o t h e oxygen content of t h e can atmosphere. The o x i d a t i o n of t h e t i s s u e l i p i d s appeared t o occur i n two s t a g e s w i t h t h e phospholipids oxidizing f i r s t. Loss of t h e unsaturated f a t t y a c i d s i n t h e phospholipids was more pronounced t h a n i n t h e n e u t r a l f a t. Associated w i t h t h e l i p i d changes were decreased s o l u b l e p r o t e i n and nonprotein nitrogen, decrease of f r e e amino groups and l o s s of rehydration capacity. The r e l a t i o n of composition of phospholipids t o changes i n t h e meat from which t h e s e a r e derived may be d i r e c t e d t o t h e observation of Kuchmak and Dugan ( 1 2 ) t h a t t h e l i n o l e i c a c i d content of l e c i t h i n from pork b e l l y muscle was markedly g r e a t e r t h a n t h e l i n o l e i c content of l e c i t h i n i n t h e o t h e r muscles studied. The l i n o l e i c content of phosphat i d y l ethanolamine from b e l l y muscle i s a l s o g r e a t e r t h a n t h a t i n t h e o t h e r muscles s t u d i e d b u t t h e most dramatic d i f f e r e n c e l i e s i n t h e arachidonic a c i d content of t h i s phospholipid. With t h e higher l e v e l of polyunsaturated f a t t y a c i d s i n t h e phospholipids of b e l l y muscle, it seems reasonable t o s p e c u l a t e t h a t t h e tendency t o s t a l i n g and r a n c i d i t y i n s l i c e d bacon may c o r r e l a t e q u i t e w e l l w i t h t h e s e compositional f a c t o r s. The r o l e of o t h e r f a c t o r s a r e not w e l l e s t a b l i s h e d a s y e t. Among t h e s e a r e t h e f u n c t i o n of t h e nitrogenous moiety as well a s t h a t of t h e phosphoric a c i d p o r t i o n of t h e molecule a s r e g u l a t o r s of o x i d a t i v e processes. The presence of a s u b s t a n t i a l q u a n t i t y of plasmalogen a s s o c i a t e d w i t h t h e comparable d i a c y l phosphoglyceride r a i s e s a number of i n t e r e s t i n g i s s u e s. Our c u r r e n t program i s concerned both with plasmalogens and w i t h o x i d a t i v e mechanisms of t h e phosphoglycerides. References 1. Allen, E., 36 (1967) R. G. Cassens, and R. W. Bray. 26, J. Animal Science, Camejo, German. J. Chromatog, 21, 6 (1966) 4. 30, 5. ElGharbawi, Mohamed I., and L. R. Dugan, Jr. J. Food Sci., 6. Folch, J., M. Lees, and G. H. SloaneStanley. 497 (1957) J. Biol. Chem., ( 1965 ) Giam, Irene, and L, R. Dugan, Jr. J. Food Sci., 2, , (1965) Hidaka, Toshiro, Mioko Endo, and Masaaki Kojima. Memoirs of t h e F a c u l t y of Agr., University of Miyazaki, 4, 2 1 (1965) 9. Hornstein, I., P. F. Crme, and J. R. Ruck. Anal. Chem., 39, 352 (1967)
10 Hornstein, I., P. F. Crove, and M. J. Heimberg. 581 (1961) 11. Kuchmak, M e and L. R. Dugan, Jr. 734 (1963) J. Am. O i l Chemists' SOC., 12e Kuchmak, M. and L. R, Dugan, Jr. 45 (1965) 13. Ostrander, Joyce, and L. R. Dugan, Jr. 39, 178 (1962) 40, J. Am. O i l Chemists' Soc., 42, 14. Peng, C. Y. and L. R e Dugan, J r. 533 (1965) J. Food Sci., 26, J. Am. O i l Chemists' SOC., J. Am. O i l Chemists' SOC., 42, 15 Rouser, G., J. O'Brien, and D. Heller. 38, 14 (1961) 16. Rouser, G., A. J. Barman, G. Kritchevsky, D. Heller, and J. S, O'Brien. J. Am. O i l Chemists' SOC., 38, 544 (1961) 17 Younathan, Margaret T., (1960) 18. Zipser, Marelynn, Jacqueline Dupont, and Betty M. Watts. Sci., 27, 135 (1962) J. Am. O i l Chemists' SOC., and Betty M. Watts. J. Food Sci., 25, 538 J. Food DR. CRAIG: Thank you D r. Dugan f o r a most i n t e r e s t i n g discussion of t h e phospholipids i n meat. We will hold t h e discussion of t h i s paper and t h e other two papers u n t i l t h e end of t h e program. The t i t l e of t h e i s "The I s o l a t i o n and second paper, t o be presented by D r. VanderbJal, Characterization of Pork S k e l e t a l Muscle Sarcolemma." I ' m happy t o present t o you D r. VanderWal t o present t h i s t o p i c t o you.
Classification, functions and structure
 Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Classification, functions and structure Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Nicolae Testemitanu" Lipids
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson
 Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Test Bank for Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5th Edition by Nelson Link download full: http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-forlehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-5th-edition-by-nelson/ Chapter
Consequently, lipoprotein fractions have been analyzed
 THE PHOSPHOLIPID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN SERUM LIPOPROTEIN FRACTIONS SEPARATED BY ULTRACENTRIFUGATION * BY GERALD B. PHILLIPS (From the Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, College of Physicians and
THE PHOSPHOLIPID COMPOSITION OF HUMAN SERUM LIPOPROTEIN FRACTIONS SEPARATED BY ULTRACENTRIFUGATION * BY GERALD B. PHILLIPS (From the Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, College of Physicians and
Lipids. Lipids. Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague
 Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
Lipids Jiří Jonák and Lenka Fialová Institute of Medical Biochemistry, 1st Medical Faculty of the Charles University, Prague Lipids 1. General introduction 2. Nomenclature of fatty acids 3. Degradation
The Elution Behaviors of Acidic Phospholipids on. Chromatography*
 J. Biochem., 69, 255-263 (1971) The Elution Behaviors of Acidic Phospholipids on Column Chromatography* Tei SHIMOJO, Hideo KANOH and Kokichi OHNO The Department of Biochemistry, Sapporo Medical College,
J. Biochem., 69, 255-263 (1971) The Elution Behaviors of Acidic Phospholipids on Column Chromatography* Tei SHIMOJO, Hideo KANOH and Kokichi OHNO The Department of Biochemistry, Sapporo Medical College,
The lipid composition of normal mouse liver*
 d. Lipid Research, April, 1962 Volume 3, Number 1 The lipid composition of normal mouse liver* GARY J. NELSON? Donner Laboratory of Biophysics and Medical Physics, University of California, Berkeley 4,
d. Lipid Research, April, 1962 Volume 3, Number 1 The lipid composition of normal mouse liver* GARY J. NELSON? Donner Laboratory of Biophysics and Medical Physics, University of California, Berkeley 4,
FATS & OILS GLOSSARY
 FATS & OILS GLOSSARY Antioxidant A substance that slows or interferes with the reaction of a fat or oil with oxygen. The addition of antioxidants to fats or foods containing them retard rancidity and increases
FATS & OILS GLOSSARY Antioxidant A substance that slows or interferes with the reaction of a fat or oil with oxygen. The addition of antioxidants to fats or foods containing them retard rancidity and increases
Chapter 11: Lipids. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Chapter 11: Lipids Voet & Voet: Pages 380-394 Slide 1 Lipids Lipids are distinguished by their high solubility in non polar solvents and low solubility in H2O Diverse group of compounds including Fats,
Biological role of lipids
 Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
Lipids Lipids Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. Extraction = the action of taking out
TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
 Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Link full download: https://testbankservice.com/download/testbank-for-lehninger-principles-of-biochemistry-6th-edition-bynelson TEST BANK FOR LEHNINGER PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY 6TH EDITION BY NELSON
Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush
 6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
6 Dr. Nafith Abu Tarboush June 26 th 2013 Noor Salem 1 Not corrected Review Lipids are composed of two main connected parts : o Alcohol Sphingosine Glycerol o Fatty Acids (3 in number) Saturated Long Chain
Chapter 20 Lipids. Organic and Biochem
 Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Lipid Chemistry. Presented By. Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair
 Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Lipid Chemistry Presented By Ayman Elsamanoudy Salwa Abo El-khair 4 Objectives: 1. By the end of this chapter the student should be able to: define lipids. describe the biological importance of lipids.
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION CLASSIFICATION OF LIPIDS PROPERTIES OF LIPIDS REACTIONS OF LIPIDS (CHEMICAL PROPERTIES) SOME QUANTITATIVE TESTS FOR LIPIDS CHEMISTRY AND PROPERTIES
II- Compound Lipids. 1- Phospholipids
 II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
II- ompound Lipids ompound (conjugated) lipids are lipids conjugated with other substances. They include: 1- Phospholipids formed of lipid, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous base. 2- Glycolipids, formed
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd
 ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
ANSC (NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Membrane Lipids and Sphingolipidsd I. Classes of membrane lipids A. Glycerolipids (quantitatively the most important of the three membrane lipids) B. Shingolipids
Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND. Bridgwater, England LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS. Fourth Edition. Invergowrie, Dundee, Scotland
 Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS Fourth Edition WILLIAM W.CHRISTIE MRS Lipid Analysis Unit, Scottish Crop Research Institute, Dundee, Scotland Invergowrie, and
Lipid Analysis ISOLATION, SEPARATION, IDENTIFICATION AND LIPIDOMIC ANALYSIS Fourth Edition WILLIAM W.CHRISTIE MRS Lipid Analysis Unit, Scottish Crop Research Institute, Dundee, Scotland Invergowrie, and
MCQS ON LIPIDS. Dr. RUCHIKA YADU
 MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature
 GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
GUTS Lecture Syllabus for Lipid Structure and Nomenclature For Questions or Assistance contact: Dr. Gwen Sancar, gsancar@ad.unc.edu Learning bjectives After completing the GUTS lecture and associated self-
THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL
 THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL Prepared at the 39th JECFA (1992), published in FNP 52 Add 1 (1992). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at the 55th JECFA (2000). An ADI of 0-3 mg/kg bw was established
THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL Prepared at the 39th JECFA (1992), published in FNP 52 Add 1 (1992). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at the 55th JECFA (2000). An ADI of 0-3 mg/kg bw was established
Ahmad O. Olimat. Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh. Dr.Mamoun
 10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
10 Ahmad O. Olimat Abdallah Al-Qawasmeh Mohammed Yousef Dr.Mamoun A QUICK RECAP Eicosanoids They are derived from Arachidonic acid, a fatty acid that contains 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. They
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids
 I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
I. Structure and Properties of Lipids Lipids: A diverse group of compounds characterized by their low solubility in water and a high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol. Nonpolar
IN THE FIRST PART (1) of this study of the effects of a
 Effects of a nutritional deficiency of unsaturated fats on the distributionof fatty acids in rat liver mitochondrial phospholipids RALPH M. JOHNSON and TAKERU IT0 Institute of Nutrition and Food Technology,
Effects of a nutritional deficiency of unsaturated fats on the distributionof fatty acids in rat liver mitochondrial phospholipids RALPH M. JOHNSON and TAKERU IT0 Institute of Nutrition and Food Technology,
SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE
 California Avocado Society 1968 Yearbook 52: 102-108 SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE Yoshio Kikuta Present address: Department of Botany, Faculty of Agriculture,
California Avocado Society 1968 Yearbook 52: 102-108 SEASONAL CHANGES OF AVOCADO LIPIDS DURING FRUIT DEVELOPMENT AND STORAGE Yoshio Kikuta Present address: Department of Botany, Faculty of Agriculture,
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Lipids Lipids are hydrophobic or amphiphilic insoluble in water soluble in organic solvents soluble in lipids Lipids are used as energy storage molecules structural components of membranes protective molecules
Total lipids and phospholipids of turkey tissues
 Retrospective Theses and Dissertations 1964 Total lipids and phospholipids of turkey tissues Socorro Olaivar Acosta Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/rtd
Retrospective Theses and Dissertations 1964 Total lipids and phospholipids of turkey tissues Socorro Olaivar Acosta Iowa State University Follow this and additional works at: http://lib.dr.iastate.edu/rtd
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS:
 LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
LIPIDS II: TRIACYLGLYCEROLS: How are they broken down? o Hydrolyzed into 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol o Physiologically in body: Enzyme called a LIPASE present in adipocytes and intestines o Saponification
Biochemistry. Classification of Lipids METABOLISM OF LIPIDS. Principal Investigator
 Paper : 05 Metabolism of Lipids Module: 04 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Content Reviewer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Suaib Luqman,
Paper : 05 Metabolism of Lipids Module: 04 Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Content Reviewer Dr. Sunil Kumar Khare, Professor, Department of Chemistry, IIT-Delhi Dr. Suaib Luqman,
Lipids. Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals. Storage Lipids: derivatives of fatty acids. 11/21/10
 1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
1 Lipids Lehninger 3 rd ed. Chapter 11 (For biosynthesis see Chapter 21) 2 Lipids: a Diverse group of chemicals Insolubility in water. Fats and oils: energy stores. Phospholipids and sterols: structural
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM. BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
PHOSPHOLIPIDS METABOLISM BY Dr. Walid Said Zaki Dr. Marwa Ali LECTURER OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY 1. State the definition and classification of Phospholipids. 2. Describe the general structure
THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL interacted with MONO- and DIGLYCERIDES of FATTY ACIDS
 THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL interacted with MONO- and DIGLYCERIDES of FATTY ACIDS Prepared at the 39th JECFA (1992), published in FNP 52 Add 1 (1992). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at
THERMALLY OXIDIZED SOYA BEAN OIL interacted with MONO- and DIGLYCERIDES of FATTY ACIDS Prepared at the 39th JECFA (1992), published in FNP 52 Add 1 (1992). Metals and arsenic specifications revised at
MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS
 December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
Lipids Analysis. Lipids
 Lipids Analysis Stephen Barnes 3 5 15 Lipids Lipids are mostly very hydrophobic Most are conjugates of fatty acids of a variety of chain lengths, which have different degrees of unsaturation, cis trans
Lipids Analysis Stephen Barnes 3 5 15 Lipids Lipids are mostly very hydrophobic Most are conjugates of fatty acids of a variety of chain lengths, which have different degrees of unsaturation, cis trans
Lecture 3 6/28/10. Membrane Lipids. Importance of Membranes. Categories of Lipids. Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7. ! Membranes are important in
 Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
Lecture 3 Lipids: Chapter 20 Sections 4-7! The most polar lipids are found in the membranes of cells and organelles! Why?! These lipids are amphipathic! Membranes are complex and have many components Membrane
 Title Spot Test Method Convenient in Column Chromatography for Det Author(s) Morita, Shigeru; Hanai, Tetsuya Citation Bulletin of the Institute for Chemi University (1975), 53(3): 279-283 Issue Date 1975-09-16
Title Spot Test Method Convenient in Column Chromatography for Det Author(s) Morita, Shigeru; Hanai, Tetsuya Citation Bulletin of the Institute for Chemi University (1975), 53(3): 279-283 Issue Date 1975-09-16
Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols
 Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids
 common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
common name hapter 28: Lipids In a slightly different order than in your textbook Fatty Acids shorthand notations #of : # of = #of, location of = line structure comments butyric acid 4:0 in butterfat lauric
Lipid Analysis. Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th Introduction to lipid structures
 Lipid Analysis Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th 2005 Introduction to lipid structures Fatty acids Acylglycerols Glycerophospholipids Sterols Strategies involved in lipid
Lipid Analysis Andréina Laffargue, IRD CRYMCEPT Montpellier workshop, October 17th 2005 Introduction to lipid structures Fatty acids Acylglycerols Glycerophospholipids Sterols Strategies involved in lipid
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY
 BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
BCH 3000 PRINCIPLES OF BIOCHEMISTRY (Semester 2-2012/13) 1 LIPID Learning outcome (Objectives) Function and distribution. Characteristics of fatty acids-structure and chemical properties. Saturated and
UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry. Natura-Brasil. EA Laboratory of Dermatological Research,
 Iuliana Popa 1, Noëlle Remoué 2 and Jacques Portoukalian 3 1 UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry 2 Natura-Brasil 3 EA 41 69 Laboratory of Dermatological Research, University of Lyon I, Faculty
Iuliana Popa 1, Noëlle Remoué 2 and Jacques Portoukalian 3 1 UMR 8612, Faculty of Pharmacy Chatenay-Malabry 2 Natura-Brasil 3 EA 41 69 Laboratory of Dermatological Research, University of Lyon I, Faculty
2.2 Properties of Water
 2.2 Properties of Water I. Water s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth. A. Life depends on hydrogen bonds in water. B. Water is a polar molecule. 1. Polar molecules have slightly charged regions
2.2 Properties of Water I. Water s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth. A. Life depends on hydrogen bonds in water. B. Water is a polar molecule. 1. Polar molecules have slightly charged regions
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry. General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4. Lipids
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
King Saud University College of Science Department of Biochemistry General Biochemistry-II (BCH 302) Chapter 4 Lipids Prepared by Dr. Farid Ataya http://fac.ksu.edu.sa/fataya http://faculty.ksu.edu.sa/75112
A THOROUGH KNOWLEDGE of normal human red cell. of red cell lipids in normal man. Characterization and quantification
 Characterization and quantification of red cell lipids in normal man PETER WAYS* and DONALD J. HANAHAN Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington SUMMARY Human
Characterization and quantification of red cell lipids in normal man PETER WAYS* and DONALD J. HANAHAN Departments of Biochemistry and Medicine, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington SUMMARY Human
CLASSIFICATION. The lipid composition of human plasma chylomicrons. * Present address: Fujikoshi Hospital, 20 Ishigane, Toyama
 The lipid composition of human plasma chylomicrons PETER WOOD, KUNITARO IMAICHI, * JOHN KNOWLES, GEORGE MICHAELS, and LAURANCE KINSELL Institute for Metabolic Research, Highland-Alameda County Hospital,
The lipid composition of human plasma chylomicrons PETER WOOD, KUNITARO IMAICHI, * JOHN KNOWLES, GEORGE MICHAELS, and LAURANCE KINSELL Institute for Metabolic Research, Highland-Alameda County Hospital,
PREPARATION OF LIPIDE EXTRACTS FROM BRAIN TISSUE*
 PREPARATION OF LIPIDE EXTRACTS FROM BRAIN TISSUE* JORDI FOLCH, I. ASCOLI, M. LEES,? J. A. MEATH,$ AND F. N. LEBARON (From the McLean Hospital Research Laboratories, Waverley, Massachusetts, and the Department
PREPARATION OF LIPIDE EXTRACTS FROM BRAIN TISSUE* JORDI FOLCH, I. ASCOLI, M. LEES,? J. A. MEATH,$ AND F. N. LEBARON (From the McLean Hospital Research Laboratories, Waverley, Massachusetts, and the Department
Ex : Butter contain large proportion of short chains of fatty acids, so it has high saponification number while margarine with more long fatty acids,
 Lec 2 1. Saponification number Definition : The number of m gms of KOH required to saponify the free and combined fatty acids in one gram of a given fat. Uses : The amount of alkali needed to saponify
Lec 2 1. Saponification number Definition : The number of m gms of KOH required to saponify the free and combined fatty acids in one gram of a given fat. Uses : The amount of alkali needed to saponify
Fatty Acid and Lipid Composition of the Brain
 European J. Biochem. 4 (1968) 340-344 Fatty Acid and Lipid Composition of the Brain of a Myelin Deficient Mutant, the Quaking Mouse N. A. BAUMANN, C. M. JACQUE, S. A. POLLET, and M. L. HARPIN Laboratoire
European J. Biochem. 4 (1968) 340-344 Fatty Acid and Lipid Composition of the Brain of a Myelin Deficient Mutant, the Quaking Mouse N. A. BAUMANN, C. M. JACQUE, S. A. POLLET, and M. L. HARPIN Laboratoire
Fatty acid esterification and chylomicron formation during fat absorption: nialc0lm WHYTE,t ARTHUR KARMEN, and DEWITT 8. GOODMAN$
 J. Lipid Research, July 19G3 Volume 4, Number 3 Fatty acid esterification and chylomicron formation during fat absorption: 2. Phospholipids* nialc0lm WHYTE,t ARTHUR KARMEN, and DEWITT 8. GOODMAN$ Laboratory
J. Lipid Research, July 19G3 Volume 4, Number 3 Fatty acid esterification and chylomicron formation during fat absorption: 2. Phospholipids* nialc0lm WHYTE,t ARTHUR KARMEN, and DEWITT 8. GOODMAN$ Laboratory
Total lipid and membrane lipid analysis of normal animal and human lenses
 Total lipid and membrane lipid analysis of normal animal and human lenses J. Stevens Andrews and Thomas Leonard-Martin Comparisons of lens fiber cell membrane isolation methods were made. Although membrane
Total lipid and membrane lipid analysis of normal animal and human lenses J. Stevens Andrews and Thomas Leonard-Martin Comparisons of lens fiber cell membrane isolation methods were made. Although membrane
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
Fatty Acid Methylation Kits
 Methyl esterification kit for fatty acids analysis Fatty Acid Methylation Kits Below are two methods for efficiently preparing fatty acid samples for GC analysis. Neither method requires high temperatures,
Methyl esterification kit for fatty acids analysis Fatty Acid Methylation Kits Below are two methods for efficiently preparing fatty acid samples for GC analysis. Neither method requires high temperatures,
Nutritive Value of Meat. ANSC 3404 Texas Tech University. Why Beef? American Heart Association
 Nutritive Value of Meat ANSC 3404 Texas Tech University Why Beef? American Heart Association 1 Issues People today are concerned about: Limiting dietary fat Cholesterol High Blood Pressure Getting the
Nutritive Value of Meat ANSC 3404 Texas Tech University Why Beef? American Heart Association 1 Issues People today are concerned about: Limiting dietary fat Cholesterol High Blood Pressure Getting the
Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example:
 Carboxylic acids LECTURE 3 Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example: Lipids: classification, structure and biological role. By/Arshed Abd
Carboxylic acids LECTURE 3 Carboxylic acids is а compound whose characteristic functional group is the carboxyl group -COOH, example: Lipids: classification, structure and biological role. By/Arshed Abd
Opinion on the safety assessment of phospholipds obtained from egg yolk as food produced using a new process
 EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL XXIV CONSUMER POLICY AND CONSUMER HEALTH PROTECTION Directorate B - Scientific opinions on health matters Unit B3 - Management of scientific committees II SCIENTIFIC
EUROPEAN COMMISSION DIRECTORATE-GENERAL XXIV CONSUMER POLICY AND CONSUMER HEALTH PROTECTION Directorate B - Scientific opinions on health matters Unit B3 - Management of scientific committees II SCIENTIFIC
Lipid and Fatty Acid Composition of Rabbit Meat as Affected by Gamma Irradiation
 Lipid and Fatty Acid Composition of Rabbit Meat as Affected by Gamma Irradiation Hesham M. Badr Atomic Energy Authority, Nuclear Research Center, Abou Zaabal, P.O. Box 13759 Cairo, Egypt. heshambadr_aea@yahoo.co.uk
Lipid and Fatty Acid Composition of Rabbit Meat as Affected by Gamma Irradiation Hesham M. Badr Atomic Energy Authority, Nuclear Research Center, Abou Zaabal, P.O. Box 13759 Cairo, Egypt. heshambadr_aea@yahoo.co.uk
Lipids. Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids.
 Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
Chapter 28 Lipids Polar bears have a large reserve of lipids. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison, and Susan Arena Course 28.1 Lipids:
OF FATTY LIVERS. XLII. PROTEIN AND THE DIETARY PRODUCTION. On a number of occasions however use of this diet has failed to produce in our
 XLII. PROTEIN AND THE DIETARY PRODUCTION OF FATTY LIVERS. BY HAROLD JOHN CHANNON AND HARRY WILKINSON. From the Department of Biochemistry, The University, Liverpool. (Received December 20th, 1934.) THE
XLII. PROTEIN AND THE DIETARY PRODUCTION OF FATTY LIVERS. BY HAROLD JOHN CHANNON AND HARRY WILKINSON. From the Department of Biochemistry, The University, Liverpool. (Received December 20th, 1934.) THE
FATTY ACID COMPONENT OF SENEGAL MANATEE FATS
 FATTY ACID COMPONENT OF SENEGAL MANATEE FATS SHINGO ITOH AND HIDEO TSUYUKI Departmeni of Food Engineering, College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine, Nikon Universiry, Tokyo. ABSTRACT The fats in cerviel,
FATTY ACID COMPONENT OF SENEGAL MANATEE FATS SHINGO ITOH AND HIDEO TSUYUKI Departmeni of Food Engineering, College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine, Nikon Universiry, Tokyo. ABSTRACT The fats in cerviel,
Functions of Lipids. - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g).
 Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology
 Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology Issued by THE NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF CANADA VOI,UME 37 AUGUST 1959 NUMBER 8 A RAPID METHOD OF TOTAL LIPID EXTRACTION AND PURIFICATION1 Abstract Lipid
Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Physiology Issued by THE NATIONAL RESEARCH COUNCIL OF CANADA VOI,UME 37 AUGUST 1959 NUMBER 8 A RAPID METHOD OF TOTAL LIPID EXTRACTION AND PURIFICATION1 Abstract Lipid
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*)
 NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
4. Determination of fat content (AOAC, 2000) Reagents
 94 ANALYTICAL METHODS 1. Determination of moisture content (AOAC, 2000) 1. Dry the empty dish and lid in the oven at 105 C for 3 h and transfer to desiccator to cool. Weigh the empty dish and lid. 2. Weigh
94 ANALYTICAL METHODS 1. Determination of moisture content (AOAC, 2000) 1. Dry the empty dish and lid in the oven at 105 C for 3 h and transfer to desiccator to cool. Weigh the empty dish and lid. 2. Weigh
' Present address: lnstituto de Investigaciones Bioquimicas, Universidad
 Quantitative release of fatty acids from lipids by a simple hydrolysis procedure Marta I. Aveldafio' and Lloyd A. Horrocks Department of Physiologzcal Chemistry, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
Quantitative release of fatty acids from lipids by a simple hydrolysis procedure Marta I. Aveldafio' and Lloyd A. Horrocks Department of Physiologzcal Chemistry, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
* Address requests for reprints to: Dr. Aaron J. Marcus, Hematology
 Lipid composition of subcellular particles of human blood platelets AARON J. MARCUS,* HARRIS L. ULLMAN, and LENORE B. SAFIER Hematology Section, New York Veterans Administration Hospital, New York 10010;
Lipid composition of subcellular particles of human blood platelets AARON J. MARCUS,* HARRIS L. ULLMAN, and LENORE B. SAFIER Hematology Section, New York Veterans Administration Hospital, New York 10010;
Lipid changes in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 658-663 B. P. HUGHES From the Muscular Dystrophy Research Laboratory, Institute of Neurology, The National Hospital, London SUMMARY Thin layer
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1972, 35, 658-663 B. P. HUGHES From the Muscular Dystrophy Research Laboratory, Institute of Neurology, The National Hospital, London SUMMARY Thin layer
Feeding Feedlot Steers Fish Oil Differentially Enhances the Fatty Acid Composition of Muscle Tissue 1
 Feeding Feedlot Steers Fish Oil Differentially Enhances the Fatty Acid Composition of Muscle Tissue 1 T.J. Wistuba 2,3, E.B. Kegley 2, J.K. Apple 2, and D.C. Rule 4 Story in Brief Inclusion of fish oil,
Feeding Feedlot Steers Fish Oil Differentially Enhances the Fatty Acid Composition of Muscle Tissue 1 T.J. Wistuba 2,3, E.B. Kegley 2, J.K. Apple 2, and D.C. Rule 4 Story in Brief Inclusion of fish oil,
Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review
 Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review 1.Know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds In order to complete outer shells in electrons bonds can be Ionic; one atom donates or receives electrons Covalent; atoms
Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review 1.Know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds In order to complete outer shells in electrons bonds can be Ionic; one atom donates or receives electrons Covalent; atoms
Phospholipids Metabolism
 Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush A heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds Formed mainly from alcohol & fatty acids combined together
Important reactions of lipids
 Taif University College of Medicine Preparatory Year Students Medical chemistry (2) Part II (Lipids) week 4 lectures 1435-36 Important reactions of lipids Lectures outlines Definition and importance of
Taif University College of Medicine Preparatory Year Students Medical chemistry (2) Part II (Lipids) week 4 lectures 1435-36 Important reactions of lipids Lectures outlines Definition and importance of
Dr. Jerry Shurson Department of Animal Science
 Dr. Jerry Shurson Department of Animal Science University of Minnesota Pigs are what they eat Diet fatty acid (FA) composition affects FA profile in pork fat FA composition varies among adipose tissue
Dr. Jerry Shurson Department of Animal Science University of Minnesota Pigs are what they eat Diet fatty acid (FA) composition affects FA profile in pork fat FA composition varies among adipose tissue
Lipids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8
 Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
Lipids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 8 Lipids Lipids are a heterogeneous class of naturally occurring organic compounds
15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries Vol. 34, No. 7,
 Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries Vol. 34, No. 7, 1968 633 Studies on the Discoloration of Red Fishes- X Enzyme Involved in the Discoloration of Carotenoid Pigments in Fish Skin
Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries Vol. 34, No. 7, 1968 633 Studies on the Discoloration of Red Fishes- X Enzyme Involved in the Discoloration of Carotenoid Pigments in Fish Skin
IN RECENT YEARS several systems of TLC for the separation. Separation of neutral glycosphingolipids and sulfatides by thin-layer chromatography
 Separation of neutral glycosphingolipids and sulfatides by thin-layer chromatography VLADIMIR P. SKIPSKI, ANSON F. SMOLOWE,* and MARION BARCLAY Division of Experimental Chemotherapy, Sloan-Kettering Institute
Separation of neutral glycosphingolipids and sulfatides by thin-layer chromatography VLADIMIR P. SKIPSKI, ANSON F. SMOLOWE,* and MARION BARCLAY Division of Experimental Chemotherapy, Sloan-Kettering Institute
Changes in Composition and Structure of Triacylglycerol of Adipose Tissue and Skin from Laying Hens as Influenced by Dietary Fats
 Changes in Composition and Structure of Triacylglycerol of Adipose Tissue and Skin from Laying Hens as Influenced by Dietary Fats Akihiro HIRATA*, Tetsuya MASUDA*, Teiji KIMURA* and Yoshiyuki OHTAKE* *
Changes in Composition and Structure of Triacylglycerol of Adipose Tissue and Skin from Laying Hens as Influenced by Dietary Fats Akihiro HIRATA*, Tetsuya MASUDA*, Teiji KIMURA* and Yoshiyuki OHTAKE* *
Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Influence of Fat Content and Composition on Malonaldehyde Concentration in Chicken Meat and Skin
 Influence of Fat Content and Composition on Malonaldehyde Concentration in Chicken Meat and Skin j. PIKUL Institute of Animal Products Technology, Agricultural University of Poznan, 60-624 Poznan, Wojska
Influence of Fat Content and Composition on Malonaldehyde Concentration in Chicken Meat and Skin j. PIKUL Institute of Animal Products Technology, Agricultural University of Poznan, 60-624 Poznan, Wojska
Classification of Lipids
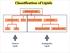 Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Classification of Lipids Neutral Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Amphipathic Lipids Most cell-membrane lipids are one of two main classes of amphipathic hydrolyzable lipids. Glycerophospholipids (phosphoglycerides):
Macromolecules. The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1.
 Macromolecules The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1. CARBOHYDRATES 1. LIPIDS 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS Carbon Compounds All compounds
Macromolecules The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1. CARBOHYDRATES 1. LIPIDS 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS Carbon Compounds All compounds
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 10 Lipids
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 10 Lipids CHAPTER 10 Lipids Key topics: Biological roles of lipids Structure and properties of storage lipids Structure and properties of membrane lipids Structure and properties
The Effect of Cooking on the Phospholipid Content of Lean Ground Beef
 University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 8-1966 The Effect of Cooking on the Phospholipid Content of Lean Ground Beef Kitty Lee
University of Tennessee, Knoxville Trace: Tennessee Research and Creative Exchange Masters Theses Graduate School 8-1966 The Effect of Cooking on the Phospholipid Content of Lean Ground Beef Kitty Lee
Phosphatidylcholine from Hen's Egg
 588 I959 The Fatty Acids of Phosphatidylethanolamine and Phosphatidylcholine from Hen's Egg By J. C. HAWKE Fats Research Laboratory, Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Wellington, New Zealand
588 I959 The Fatty Acids of Phosphatidylethanolamine and Phosphatidylcholine from Hen's Egg By J. C. HAWKE Fats Research Laboratory, Department of Scientific and Industrial Research, Wellington, New Zealand
Lipids and Biological Membranes
 Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
Lipids and Biological Membranes Lipids: Found in all living organisms Especially important as components of biological membranes Defined functionally, not structurally, as compounds that are totally or
FAT. Dr. Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology
 FAT Dr. Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology OBJECTIVES LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define what is lipid/fat
FAT Dr. Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology OBJECTIVES LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define what is lipid/fat
The HPLC Preparative Scale-Up of Soybean Phospholipids Application
 The HPLC Preparative Scale-Up of Soybean Phospholipids Application Food and Flavors Authors Cliff Woodward and Ron Majors Agilent Technologies, Inc. 285 Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 1988-161 USA Abstract
The HPLC Preparative Scale-Up of Soybean Phospholipids Application Food and Flavors Authors Cliff Woodward and Ron Majors Agilent Technologies, Inc. 285 Centerville Road Wilmington, DE 1988-161 USA Abstract
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012
 LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
LIPIDS Dr. Latifah Al-Oboudi 2012 The Lipid Family Triglycerides Phospholipids Sterols All types of lipids are: soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and ether, but not in water. Differ
Studies on blood platelet phospholipids*
 Volume 1 Studies on blood platelet phospholipids* AARON J. MARCUS, HARRS L. ULLMAN, and MORRS WOLFhfAN Hematology Section, New York Veterans Hospital, New York 10, N. Y., and the Department of Medicine,
Volume 1 Studies on blood platelet phospholipids* AARON J. MARCUS, HARRS L. ULLMAN, and MORRS WOLFhfAN Hematology Section, New York Veterans Hospital, New York 10, N. Y., and the Department of Medicine,
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS. Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry
 METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
METABOLISM OF ACYLGLYCEROLS AND SPHINGOLIPDS Ben S. Ashok MSc.,FAGE.,PhD., Dept. of Biochemistry STORAGE AND MEMBRANE LIPIDS STORAGE LIPIDS Mainly as triacylglycerols (triglycerides) in adipose cells Constitute
2. Simple lipids: Triacylglycerols and waxes are classified as simple lipids. The characteristics of each are described in the sections below.
 Paper 4: Biomolecules and their interactions Module 21: Classification of Lipids: simple and compound lipids, phospholipids, Cholesterol OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students
Paper 4: Biomolecules and their interactions Module 21: Classification of Lipids: simple and compound lipids, phospholipids, Cholesterol OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students
Biomolecules: lipids
 Biomolecules: lipids Organic biomolecules: lipids Organic amphiphilic compounds insoluble in water Easily extracted from animal and vegetal cells using apolar solvents Fundamental to build cell's shape
Biomolecules: lipids Organic biomolecules: lipids Organic amphiphilic compounds insoluble in water Easily extracted from animal and vegetal cells using apolar solvents Fundamental to build cell's shape
Agenda. Focus on Flavor. Sensory Characteristics 9/5/12. PorkBridge 2009 November 5 th Session Packer Perspective on Quality of Hogs
 2009-10 Grow-Finish Educational Series A world of knowledge brought directly to you Thank you for participating in PorkBridge 2009-10. To start the presentation, advance one slide by pressing enter or
2009-10 Grow-Finish Educational Series A world of knowledge brought directly to you Thank you for participating in PorkBridge 2009-10. To start the presentation, advance one slide by pressing enter or
January 31, Chemistry of Life. Carbohydrates. Lipids. Proteins. Biologically Important Macromolecules. Nucleic Acids
 Chemistry of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Biologically Important Macromolecules Nucleic Acids Polymers Polymers are large molecules of repeating sub units (building blocks) Individual Building Blocks......can
Chemistry of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Biologically Important Macromolecules Nucleic Acids Polymers Polymers are large molecules of repeating sub units (building blocks) Individual Building Blocks......can
