Role of Ultrasound in Acute Non Traumatic Abdominal Emergencies
|
|
|
- Horatio Craig
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINALARTICLE Role of Ultrasound in Acute Non Traumatic Abdominal Emergencies Kamlesh Gupta, Ramesh Chander, Arvinder Singh, Sohan Singh, Sandeep Singh Abstract The current study was undertaken to access the role of ultrasound in acute non traumatic abdominal emergencies, analysis of ultrasound findings and its correlation with clinical findings, laboratory and other radiological investigations along with operative findings, wherever possible and to determine the sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing various conditions. A total of patients included in this study underwent abdominal ultrasonography. Definite diagnosis was made in 87 cases (87%). The sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound in diagnosing acute appendicitis, perforation of a hollow viscus, intestinal obstruction and acute pancreatitis was around 86. 1% and 83.3%, 86.3% and 80%, 3.7% and 80%, 70% and 7% respectively. In a biliary conditions, ultrasound examination was highly sensitive. In diagnosing Hepatobiliary conditions ultrasonography is highly sensitive and highly specific. In diagnosing other conditions such as acute appendicitis, perforation, intestinal obstruction, acute pancreatitis and ureteric colic, ultrasonography have good overall sensitivity and specificity. Ultrasonography should be a part of routine surgical investigations as it guides in timely intervention in surgical cases. Key Words Acute Abdomen, Non Traumatic, Abdominal Emergencies, Ultrasonography Introduction Acute abdominal pain or better known as acute abdomen is defined as tremendous severe pain arising in the abdominal area and requires immediate care. There is a lack of consensus on the overall incidence of the acute abdomen in the developing world, likely as a result of the range of locations which fall into this category (e.g., Southeast Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Central America) in addition to various socioeconomic, dietary, cultural, and environmental differences. Many generalisations regarding acute abdomen are shared with those of developed nations, including acute appendicitis and intestinal obstruction, which account for up to 2 and 3% of all cases, respectively. Common causes of the acute abdomen based on quadrant are as follows (1). 1. Right Upper Quadrant - Cholecystitis, biliary colic, cholangitis, hepatitis, hepatic abscess, intestinal obstruction, peptic ulcer disease. 2. Left Upper Quadrant -gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, pancreatitis, splenomegaly, intestinal obstruction 3. Right Lower Quadrant-appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease, diverticulitis, mesenteric adenitis, intestinal obstruction, ectopic pregnancy, salpingitis, ovarian torsion, nephrolithiasis 4. Left Lower Quadrant - diverticulitis, intestinal obstruction, inflammatory bowel disease, ischemic colitis, ectopic pregnancy, salpingitis, ovarian torsion, nephrolithiasis. Imaging plays a very important role in planning the early treatment and management of these patients because clinical evaluation results can be inaccurate.thus the current study was undertsken to evaluate the use of ultrasonography in acute abdomen and to find out its sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis as well as to correlate it with surgical/histopathological results, if required. Material and Methods The present study comprised of patients presenting with acute non traumatic abdominal emergencies and subsequently subjected to USG examination after clinical examination. Patients with unstable vital signs, shock and trauma were specifically excluded from the study. The instrument used was ultrasound having a curvilinear probe of 3.MHz - MHz or linear high frequency probe 712MHz. Based on sonographic findings provisional From the Department of Radio-Diagnosis and Imaging, Govt. Medical College, Amritsar- (Punjab)-India Correspondence to : Dr. Ramesh Chander, Associate Professor, Department of Radio-Diagnosis and Imaging, GMC Amritsar-(Pb) India 172
2 diagnosis was made. The final diagnosis was made on the basis of operative findings/therapeutic response/ FNAC findings/histopathological/laboratory findings. The sonographic diagnosis was co-related to the surgical/ histopathological findings in appropriate cases. Results In our study, the most common age of presentation was between 21 to 30 years followed by 31 to 40 years with mean age of about 28 years (Table 1). There were 62 males and 38 females with a male to female ratio of 1.63:1 (Table 2). Most of the patients presented with acute abdominal pain lasting from a few hours to a few days along with features such as nausea / vomiting / fever / hematuria / rigidity / or guarding. The most common cause of pain abdomen in our study was acute appendicitis followed by GIT cases. Out of patients USG gave an accurate diagnosis in 87 cases (87%). On ultrasonography 31 cases were diagnosed as acute appendicitis, 1 cases were diagnosed as perforation of hollow viscus, 1 cases were diagnosed as intestinal obstruction, 7 cases were diagnosed as acute pancreatitis, 8 cases were diagnosed as acute cholecystitis, 1 case as choledocholithiasis, 4 cases as urolithiasis, 1 case as intussusception, 1 case as hemorrhagic ovarian cyst and in 13 cases, the conclusive diagnosis was not reached which can be contributed towards the limitation of the ultrasound. Based on final diagnosis after clinical / operative / histopathology findings and correlation, we had 36 cases of acute appendicitis, 22 cases of perforation of hollow viscus, cases of intestinal obstruction, 10 cases of acute pancreatitis, 8 cases of acute cholecystitis, 1 case of choledocholithiasis, 4 cases of urolithiasis, 2 cases of intussusception and 1 case of hemorrhagic ovarian cyst (Table 3). In present study, the sensitivity and specificity for ultrasound in diagnosing acute appendicitis, perforation of hollow viscus, intestinal obstruction and acute pancreatitis was around 86. 1% and 83.3%, 86.3% and 80%, 3.7% and 80%, 70% and 7% respectively. For acute cholecystitis, urolithiasis, choledocholithiasis and hemorrhagic ovarian cyst, the corresponding sensitivity of ultrasonic diagnosis was % respectively. In case of intussusception the sensitivity of ultrasonography was as low as 0%. These variations in sensitivity can be explained due to small sample size of some of the etiologies. Discussion USG diagnosis was compared with the final diagnosis based on laboratory values, radiological findings, and operative findings. Out of patients USG made a correct diagnosis 87 cases (87%). Ultrasound examination is highly accurate in diagnosing the exact cause of pain in patients presenting with acute abdominal conditions (2). Allemann et al (3) in his study described that in cases of patients with acute abdominal pain US improved the correct diagnostic rate from 348 (70%) to 414 (83%). In the same study, the diagnostic accuracy for acute appendicitis and biliary tract disease improved after US from 4 (2%) to 488 (8%) and from 463 (3%) to 40 (%), respectively; the corresponding sensitivities and specificities were 1% and % and 4% and %. In our study, ultrasound was misleading in 13 cases where the conclusive diagnosis could not be reached at using ultrasonography alone. In these cases, the accurate diagnosis was obtained either at surgery or by using adjuvant and /or higher modalities such as CT scan. Out of the 36 confirmed cases of acute appendicitis, the ultrasound was able to detect 31 cases. All of them showed the inflamed appendix consistent with non compressible, blind ending tubular structure (Fig.1). Ultrasonography could not identify cases, which were later on confirmed to be the cases of acute appendicitis on laparotomy. Out of these cases, 2 cases were of Fig 1. Inflammed Appendix is seen as a Non Compressible, Aperistaltic, Tubular Structure of Diamete Greater than 6 mm with a Blind end Arising from the Caecum Fig 2. Sonographic Appearance as Seen in Case of Perforated Appendix. A loculated Hypoechoic Collection is Present in Relation to the Terminal Ileum and Caecum 173
3 Table 1. Showing the Age Distribution in Cases of Non Traumatic Acute Abdominal Emergencies Age Group (years) No. of cases Percentage >60 Table.2 Showing Sex Distribution of the Study Cases Sex of the patients No. of patients Males Females Table.3 Showing Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain in Study Cases of Nontraumatic Acute Abdominal Emergencies Cause of Acute Pain Abdomen Acute Appendicitis Perforation of Hollow Viscus Intestinal Obstruction Acute Pancreatitis Acute Cholecystitis Urolithiasis Intussusception Choledocholithiasis Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst perforated appendix and in the remaining 3 cases, the appendix could not be visualised due to extensive bowel gas and patient's non-cooperation (Fig.2). The sensitivity and specificity for ultrasound diagnosis were 86. 1% and 83.3%, respectively. Pacharn P, et al (4) in their study described the sensitivity of sonography to be 81.1% (30 of 37); and specificity to be 87.8% (137 of 16). There were total 22 confirmed cases of perforation of hollow viscus. Most of the patients had fever and presented with a sharp and burning pain in the epigastrium and in the umbilical region. Out of these, 10 cases had rigidity and 12 had a fever at the time of presentation. The use of ultrasound could identify 1 out of 22 cases. Pneumoperitoneum was accurately identified in 18 out of 22 cases (Fig.3). Ultrasonography could not diagnosed 3 cases, which later on were confirmed on laprotomy to be a perforation of hollow viscus. 1 case was of perforation of malignant gastric ulcer and the remaining 2 cases were of distal ileal perforation, which were missed on ultrasonography. Ultrasound examination could accurately predict the location of perforation in 3 out 22 cases only. The sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis 174 No. Of Cases Percentage with ultrasound were 86.3% and 80% respectively. Braccini G, et al () described a sensitivity of 86% and a specificity of 83.% for the use of ultrasound in the diagnosis of perforation of hollow viscus. There were confirmed cases of intestinal obstruction. Most of the patients presented with a progressive vague abdominal discomfort with distention of abdomen. In the remaining, there was an abrupt onset with colicky pain and rapid deterioration. Ultrasound was accurate in the diagnosis of 1 out of cases in form of dilated, fluid filled aperistaltic bowel loops with coarse level intraluminal echoes (Fig 4). On follow up, 7 cases were operated after the clinical diagnosis of acute intestinal obstruction and on laprotomy these showed up as cases of mechanical obstruction-4 due to adhesions, 2 related to hernias and 1 due to caecal volvulus. In the remaining cases, only conservative treatment was done. In most of the cases of ileus in our series, the underlying cause could not be ascertained on ultrasonography. The sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis with ultrasound were 3.7% and 80% respectively. Schmutz GR,et al (6) evaluated the role of ultrasonography in the bowel obstruction and
4 Fig 3. Sonographic Appearance of Perforation. The Free Intraperitoneal Air Appears as Diffusely Echogenic Stripe with Dirty Posterior Shadowing. Fig 4. Small bowel obstruction. Multiple Dilated, Fluid Filled, Aperistaltic Bowel Loops are Present with a Caliber of Greater than 3. mm Fig. Sonographic Appearance of Acute Pancreatitis With Heterogenous Echotexture with Multiple Intrapancreatic Echopoor Areas Representing Fluid Collections. Fig 6. Sonographic Appearance of Acute Cholecystitis. Gall bladder Shows Multiple Calculi in its lumen along with Thickening and Edema of its wall. Fig 7. Ureterolithiasis. The Kidney shows Moderate Hydronephrotic changes. A well Defined Calculus with Distal Acoustic Shadowing at the Distal End of the Right Ureter Fig 8. Sonographic Appearance in Intussusception. A Well Defined, Round Bowel Mass with Concentric Bowel Layers and a Diameter of 4.3 cm with target/ Doughnut Appearance Fig. Sonographic Appearance in Choledocholithiasis. The Intrahepatic Biliary Radicals are Markedly Dilated Fig 10. Hemorrhagic Ovarian Cyst. A well Defined Heterogenous Cystic Lesion with Internal Echoes is shown in Relation to Right Adnexal reported a sensitivity of % with an overall accuracy of 81.3%. In the present study, we had 10 confirmed cases of acute pancreatitis. Most of the patients presented with a classic pain in the epigastrium radiating to the back with associated symptoms of nausea and vomiting. Out of these 10 cases, ultrasonography was accurate in 7 cases which showed bulky pancreas with irregular margins 17
5 and peripancreatic/intrapancreatic fluid or edema (Fig ). 3 cases that were not identified on ultrasonography, were of acute pancreatitis involving the tail region of the pancreas. It was due to the limitation of ultrasound and because of the extensive gas that the full length view of pancreas could not be obtained in these cases. In our series, the serum amylase levels in the patients with acute pancreatitis were elevated in 8 out of 10 cases. The sensitivity and specificity of diagnosis with ultrasound were 70% and 7% respectively. Wang SS,et al (7) found out the role of ultrasonography in acute pancreatitis and calculated a sensitivity of 71.8% and specificity of 8% for use of ultrasonography in acute pancreatitis. There were total 8 cases of acute cholecystitis in our series. Most of the patients were healthy middle aged females and presented with tenderness in right upper quadrant. Few of them had nausea and vomiting. All of these 8 cases were followed up and the diagnosis was confirmed post operatively. Plain X ray abdomen was done in all the cases,however only 1 case revealed multiple radiodense opacities in the right hypochondrium. Ultrasound abdomen showed calculus/calculi in gall bladder lumen with dense posterior acoustic shadowing. The walls of the GB were thickened and edematous (Fig 6). The sensitivity of diagnosis on ultrasound was %. Ralls PW, et al (8) found that the positive predictive value for the GB calculi combined with the positive sonographic Murphy's sign was 2.2% and when along with the GB wall thickening, it was.2%. There were total 4 cases of urolithiasis that presented with colicky pain in the abdomen consistent with non traumatic acute abdominal emergencies. 3 cases had acute pain in groin with nausea and vomiting where as 1 case presented with colicky loin pain. Ultrasonography accurately diagnosed the cause of pain by demonstrating the obstructing ureteric calculus with proximal hydroureteronephrosis in all 4 cases of urolithiasis (Fig 7). We obtained a sensitivity of % using ultrasound for diagnosing ureterolithiasis in a small sample. Park SJ, et al () found out that the overall sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound for detecting ureteric calculi was high, being 8.3% and % respectively. We had 2 confirmed cases of small bowel intussusception. Both cases presented with a rapid onset pain in the central part of the abdomen. 1 of them had fever, vomiting and blood in stools. Sonography showed a well defined round to oval lesion on transverse section with maintained gut signature. Central hypoechoic area with peripheral echogenicity giving doughnut sign. On longitudinal sections, there was herniation of a segment of a bowel loop into another segment giving telescope sign or trident sign (Fig 8) Out of these one case was accurately diagnosed with ultrasonography whereas the second case was not diagnosed on ultrasonography. The diagnosis was arrived at on higher modality (CT scan) in this case and confirmed on laprotomy. There was 1 case 176 of choledocholithiasis, which was accurately diagnosed by ultrasonography and later on confirmed by higher modalities and post- surgically. Ultrasound showed marked dilatation of intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary radicals with a calculus at its distal end (Fig ). This case presented with discoloration of skin and eyes due to jaundice along with fever and pain in the right side of the abdomen. The Liver function tests were highly elevated in this case. We had one case of hemorrhagic ovarian cyst in our series. The patient had a history of acute pelvic pain of short duration with tenderness in the lower abdomen. On ultrasonography,a well defined cystic lesion was seen in right adnexal region. Coarse level internal echoes with septations and layering was seen. Right ovary could not be seen separate from this mass. Left ovary and uterus were normal (Fig10). The clinical features are not always decisive and accurate about the diagnosis of acute abdominal pain. Patient management is improved by the use of ultrasonography. This also strengthens the decision to operate and improve overall efficiency of the surgical units. This was also shown by McGrath and Keeling (10) in their study. References Hardy A, Butler B, Crandall M. The Evaluation of the Acute Abdomen. Common Problems in Acute Care Surgery. Moore LJ, Turner KL, Todd SR (Eds.) Springer, New York.23; XVII.pp.27 Chhetri RK, Shrestha ML. A comparative study of preoperative with operative diagnosis in acute abdomen. Kathmandu Univ Med J 200; 3(2): Allemann F, Cassina P, Röthlin M, et al. Ultrasound scans done by surgeons for patients with acute abdominal pain: a prospective study. Eur J Surg 1; (10): Pacharn P, Ying J, Linam LE, et al. Sonography in the Evaluation of Acute Appendicitis. Are Negative Sonographic Findings Good Enough. J Ultrasound Med 20; 2:174-. Braccini G, Lamacchia M, Boraschi P, et al. Ultrasound versus plain film in the detection of pneumoperitoneum. Abdom Imaging 16; 21(): Schmutz GR, Benko A, Fournier L,et al. Small bowel obstruction: role and contribution of sonography. Eur Radiol 17; 7(7): Wang SS, Lin XZ, Tsai YT, et al. Clinical significance of ultrasonography, computed tomography, and biochemical tests in the rapid diagnosis of gallstone-related pancreatitis: a prospective study. J Pancreas 188; 3(2): Ralls PW, Colletti PM, Lapin SA, et al. Real-time sonography in suspected acute cholecystitis. Prospective evaluation of primary and secondary signs. Radiology 18; 1(3): Park SJ, Yi BH, Lee HK, et al. Evaluation of Patients With Suspected Ureteral Calculi Using Sonography as an Initial Diagnostic Tool. How Can We Improve Diagnostic Accuracy. J Ultrasound Med 2008; 27: McGrath FP, Keeling F. The role of early sonography in the management of the acute abdomen. Clin Radiol. 11;:172-4.
Comparative Study between Plain Radiography and Ultrasound Abdomen in Non Traumatic Surgical Acute Abdominal Conditions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Study between Plain Radiography and Ultrasound Abdomen in Non Traumatic Surgical Acute Sharma P 1, Sidharth 2, Singh BP 3, Singh D 3, Gupta A 4 1 Department of Radiology and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Study between Plain Radiography and Ultrasound Abdomen in Non Traumatic Surgical Acute Sharma P 1, Sidharth 2, Singh BP 3, Singh D 3, Gupta A 4 1 Department of Radiology and
Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Role of (Non Gynaecological Causes) Kaleem Ahmad 1, Rishav Kumar Jain 2, Ashok Yadav 3, Shilpa Vahikar 4 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, 2 Professor, Department
Original Research Article Role of (Non Gynaecological Causes) Kaleem Ahmad 1, Rishav Kumar Jain 2, Ashok Yadav 3, Shilpa Vahikar 4 1 Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, 2 Professor, Department
JMSCR Vol 3 Issue 11 Page November 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i11.52 Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Acute Abdomen
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v3i11.52 Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Acute Abdomen
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/163 Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen Madipeddi Venkanna 1, Doolam Srinivas 2, Budida
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/163 Clinical, Diagnostic, and Operative Correlation of Acute Abdomen Madipeddi Venkanna 1, Doolam Srinivas 2, Budida
SIMPLE GUIDE FOR SONOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF APPENDICITIS
 SIMPLE GUIDE FOR SONOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF APPENDICITIS A Case Study by Dr. Avni K P Skandhan, India (Consultant Radio Diagnosis, Malabar Institute of Medical Science, Malappuram, Kerala) Email: avniskandhan@gmail.com
SIMPLE GUIDE FOR SONOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF APPENDICITIS A Case Study by Dr. Avni K P Skandhan, India (Consultant Radio Diagnosis, Malabar Institute of Medical Science, Malappuram, Kerala) Email: avniskandhan@gmail.com
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
ACUTE ABDOMEN. Dr. M Asadi. Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS. Assistant Professor of General Surgery
 ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr. M Asadi Assistant Professor of General Surgery Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS Definition I. The term Acute Abdomen refers to signs & symptoms of abdominal pain and tenderness,
ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr. M Asadi Assistant Professor of General Surgery Surgical Oncology Research Center MUMS Definition I. The term Acute Abdomen refers to signs & symptoms of abdominal pain and tenderness,
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol
 FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學
 Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Abdominal radiology 腹部放射線學 台北醫學大學 - 市立萬芳醫院 留偉順 laowilson@hotmail.com The Normal Abdominal Series Chest Supine abdomen Erect abdomen Left lateral decubitus abdomen Learning objectives Understanding normal
Original Article INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS ABSTRACT
 Original Article Diagnostic value of Plain Abdominal Radiograph, Ultrasonography and Clinical impression of the surgeon in acute peritonitis. Ankit Shukla 1, Ramesh Bharti 2, Rajesh Chaudhary 1, Manjeet
Original Article Diagnostic value of Plain Abdominal Radiograph, Ultrasonography and Clinical impression of the surgeon in acute peritonitis. Ankit Shukla 1, Ramesh Bharti 2, Rajesh Chaudhary 1, Manjeet
Request Card Task ANSWERS
 Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases
 Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases Hsiu-Po Wang Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University Hospital Real-time ultrasound has become a standard
Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases Hsiu-Po Wang Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University Hospital Real-time ultrasound has become a standard
Acute Pancreatitis: Role of Imaging Modalities
 International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2015, Vol 2, No.9,109-114. 109 Available online at http://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Abstract Acute Pancreatitis: Role
International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies (IJIMS), 2015, Vol 2, No.9,109-114. 109 Available online at http://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Abstract Acute Pancreatitis: Role
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes
 Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Intestinal Obstruction Clinical Presentation & Causes V Chidambaram-Nathan Consultant Transplant and General Surgeon Sheffield Kidney Institute Northern General Hospital Intestinal Obstruction One of the
Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento
 Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento https://www.google.com/search?sa=g&hl=en&q=public+disclosure&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:caqsigeahwelekju2aqaaawlelcmpwgaygpgcamskpib_1qnza7ai
Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento https://www.google.com/search?sa=g&hl=en&q=public+disclosure&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:caqsigeahwelekju2aqaaawlelcmpwgaygpgcamskpib_1qnza7ai
Retrospective study analyzing the data on non-traumatic abdominal emergency surgeries done tertiary care hospital, Chennai
 Original Research Article Retrospective study analyzing the data on non-traumatic abdominal emergency surgeries done tertiary care hospital, Chennai S. Vijayalakshmi 1, Sriramchristopher M 2* 1 Associate
Original Research Article Retrospective study analyzing the data on non-traumatic abdominal emergency surgeries done tertiary care hospital, Chennai S. Vijayalakshmi 1, Sriramchristopher M 2* 1 Associate
Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC
 Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC Gastrointestinal Emergencies is 7% of the CEN A. Acute abdomen B. Bleeding C. Cholecystitis D. Cirrhosis E. Diverticulitis
Gastrointestinal Emergencies CEN REVIEW 2017 MARY RALEY, BSN, RN, CEN, TCRN, TNSCC Gastrointestinal Emergencies is 7% of the CEN A. Acute abdomen B. Bleeding C. Cholecystitis D. Cirrhosis E. Diverticulitis
Adult Intussusception
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 3, September 2005 Adult Intussusception Suhair Alsaad, MBCHB, CABS, FRCSI* Mariam Al-Muftah, MBCHB** Objectives: Adult intussusception is a rare entity. We present
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 3, September 2005 Adult Intussusception Suhair Alsaad, MBCHB, CABS, FRCSI* Mariam Al-Muftah, MBCHB** Objectives: Adult intussusception is a rare entity. We present
Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 32 Gastroenterology General Pathophysiology General Risk Factors for GI emergencies: Excessive Consumption Excessive Smoking Increased Ingestion of Caustic Substances Poor Bowel Habits
Abdominal Ultrasound. Diane Hallinen, MD. Bloodroot
 Abdominal Ultrasound Diane Hallinen, MD Bloodroot Abdominal Ultrasound Vasculature Hepatobiliary Spleen Kidney Bladder Bowel Where to put the probe? Vasculature We are going to talk about Celiac Trunk
Abdominal Ultrasound Diane Hallinen, MD Bloodroot Abdominal Ultrasound Vasculature Hepatobiliary Spleen Kidney Bladder Bowel Where to put the probe? Vasculature We are going to talk about Celiac Trunk
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
A comprehensive study on acute non-traumatic abdominal emergencies
 International Surgery Journal Malviya A et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jul;4(7):2297-2302 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172785
International Surgery Journal Malviya A et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jul;4(7):2297-2302 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172785
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines. Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination
 Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination Approved by Council Feb 2018 Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination Approved by Council Feb 2018 Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to
Gastrointestinal & Genitourinary Emergencies. Lesson Goal. Learning Objectives 9/10/2012
 Gastrointestinal & Genitourinary Emergencies Lesson Goal Recognize, assess & provide care to patients with abdominal cavity injuries Learning Objectives Discuss different causes of nontraumatic abdominal
Gastrointestinal & Genitourinary Emergencies Lesson Goal Recognize, assess & provide care to patients with abdominal cavity injuries Learning Objectives Discuss different causes of nontraumatic abdominal
DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH IN NON TRAUMATIC CAUSES OF ACUTE ABDOMEN
 30 Original article DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH IN NON TRAUMATIC CAUSES OF ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr Deepak Rajput ( Associate Professor ) Dr Aashaka Patel ( Resident ) Radio diagnosis Department,
30 Original article DIAGNOSTIC VALUE OF PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH IN NON TRAUMATIC CAUSES OF ACUTE ABDOMEN Dr Deepak Rajput ( Associate Professor ) Dr Aashaka Patel ( Resident ) Radio diagnosis Department,
The role of abdominal X-rays in the investigation of suspected acute appendicitis
 Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 2(11) pp. 1216-1220, November 2011 Available online@ http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2011 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 2(11) pp. 1216-1220, November 2011 Available online@ http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2011 International Research Journals Full Length Research
Evaluation of the of the sensitivity, accuracy and positive predictive value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of Appendicitis.
 West African Journal of Ultrasound Vol 17 Number 2 (2016) Evaluation of the of the sensitivity, accuracy and positive predictive value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of Appendicitis. 1 2 3 Oguntola
West African Journal of Ultrasound Vol 17 Number 2 (2016) Evaluation of the of the sensitivity, accuracy and positive predictive value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of Appendicitis. 1 2 3 Oguntola
Ultrasound of: Appendicitis Intussusception Pyloric Stenosis
 Ultrasound of: Appendicitis Intussusception Pyloric Stenosis Andrew Phelps MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Radiology UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital No Disclosures Take Home Message Appendicitis occurs
Ultrasound of: Appendicitis Intussusception Pyloric Stenosis Andrew Phelps MD Assistant Professor Pediatric Radiology UCSF Benioff Children s Hospital No Disclosures Take Home Message Appendicitis occurs
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno. Objectives. Why?
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
ROLE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF ASCITES Ramesh Chander 1, Kamlesh Gupta 2, Arvinder Singh 3, V. K. Rampal 4, Mohit Khandelwal 5
 ROLE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF ASCITES Ramesh Chander 1, Kamlesh Gupta 2, Arvinder Singh 3, V. K. Rampal 4, Mohit Khandelwal 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ramesh Chander, Kamlesh Gupta, Arvinder
ROLE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF ASCITES Ramesh Chander 1, Kamlesh Gupta 2, Arvinder Singh 3, V. K. Rampal 4, Mohit Khandelwal 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ramesh Chander, Kamlesh Gupta, Arvinder
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Introduction and Definitions
 Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Surgical Education Series
 Surgical Education Series The Acute Abdomen Ahmad kachooei, MD MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Surgery Department of Surgery University of Qom Outline Definitions What causes an acute abdomen
Surgical Education Series The Acute Abdomen Ahmad kachooei, MD MPH Assistant Professor Division of General Surgery Department of Surgery University of Qom Outline Definitions What causes an acute abdomen
Sonographic Appearances of Common Gut Pathology in Paediatric Patients: Comparison with Plain Abdominal Radiography
 3668 Radiographer Text 1/4/04 2:57 PM Page 11 The Radiographer vol. 51: 11-17 Sonographic Appearances of Common Gut Pathology in Paediatric Patients: Comparison with Plain Abdominal Radiography Lino Piotto
3668 Radiographer Text 1/4/04 2:57 PM Page 11 The Radiographer vol. 51: 11-17 Sonographic Appearances of Common Gut Pathology in Paediatric Patients: Comparison with Plain Abdominal Radiography Lino Piotto
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Objectives. Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology. RUQ: Normal Anatomy. Emergency Ultrasound: Gallbladder Location
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update
 Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research 11/16/2017. Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument 11/16/2017
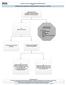 Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
USMLE and COMLEX II. CE / CK Review. General Surgery. 1. Northwestern Medical Review
 USMLE and COMLEX II CE / CK Review General Surgery 1. Northwestern Medical Review Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan 2014-2015 Acute Abdomen 1. Your patient
USMLE and COMLEX II CE / CK Review General Surgery 1. Northwestern Medical Review Northwestern Medical Review www.northwesternmedicalreview.com Lansing, Michigan 2014-2015 Acute Abdomen 1. Your patient
Research Article. Key Words: USG, MDCT, non-traumatic, acute, abdomen INTRODUCTION
 International Journal of Medical Science and Clinical Inventions 4(2): 2684-2688, 2017 DOI:10.18535/ijmsci/ v4i2.09 ICV 2015: 52.82 e-issn: 2348-991X, p-issn: 2454-9576 2017, IJMSCI Research Article Comparative
International Journal of Medical Science and Clinical Inventions 4(2): 2684-2688, 2017 DOI:10.18535/ijmsci/ v4i2.09 ICV 2015: 52.82 e-issn: 2348-991X, p-issn: 2454-9576 2017, IJMSCI Research Article Comparative
DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS
 DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS YASHODAMMAL 70 YRS OD LADY had C/o diffuse lower abdominal pain 20 days h/o blood in stools 4 days h/o vomiting 2 days h/o burning micturation
DR JAIKISHOR JOTHIRAJ MD POST GRADUATE DEPT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS YASHODAMMAL 70 YRS OD LADY had C/o diffuse lower abdominal pain 20 days h/o blood in stools 4 days h/o vomiting 2 days h/o burning micturation
Radiological Investigations of Abdominal Trauma
 76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
Abdominal & scrotal pain
 Abdominal & scrotal pain Junior Teach Emergency Department 1 Created by SR Bruijns 03/11/2010 Objectives Understanding of, and emergency management of Acute abdominal pain Undifferentiated abdominal pain
Abdominal & scrotal pain Junior Teach Emergency Department 1 Created by SR Bruijns 03/11/2010 Objectives Understanding of, and emergency management of Acute abdominal pain Undifferentiated abdominal pain
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 4 2013 Article 6 Case report: Intussusception of the colon through a colostomy: A rare presentation of colonic intussusception. Dr. Nora Trabulsi Dr.
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 4 2013 Article 6 Case report: Intussusception of the colon through a colostomy: A rare presentation of colonic intussusception. Dr. Nora Trabulsi Dr.
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings
 August 2011 Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings Omar Pardesi, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient LD: History & Physical HPI: 28 y.o. female presents with diffuse abdominal
August 2011 Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings Omar Pardesi, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient LD: History & Physical HPI: 28 y.o. female presents with diffuse abdominal
Always keep it in the differential
 Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently
 Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Clinical Application and Value of Ultrasound in Diagnosis of. Acute Abdomen A Single Center Experience
 Original Paper Research in Health Science ISSN 2470-6205 (Print) ISSN 2470-6213 (Online) Vol. 3, No. 1, 2018 www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/rhs Clinical Application and Value of Ultrasound in Diagnosis
Original Paper Research in Health Science ISSN 2470-6205 (Print) ISSN 2470-6213 (Online) Vol. 3, No. 1, 2018 www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/rhs Clinical Application and Value of Ultrasound in Diagnosis
Introduction to Evidence Based Medicine:
 Introduction to Evidence Based Medicine: General Abdominal Examination o Inspection Cullen s sign and Grey Turner s sign are indications of intraperitoneal or retroperitoneal hemorrhage. Traditionally,
Introduction to Evidence Based Medicine: General Abdominal Examination o Inspection Cullen s sign and Grey Turner s sign are indications of intraperitoneal or retroperitoneal hemorrhage. Traditionally,
THE ACUTE ABDOMEN: A COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF CLINICAL, RADIOLOGICAL AND OPERATIVE FINDINGS
 wjpmr, 2018,4(6), 183-189 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.639 Abhinav et al. Research Article WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL ISSN 2455-3301 AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.wjpmr.com WJPMR THE ACUTE ABDOMEN: A COMPARATIVE
wjpmr, 2018,4(6), 183-189 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.639 Abhinav et al. Research Article WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL ISSN 2455-3301 AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.wjpmr.com WJPMR THE ACUTE ABDOMEN: A COMPARATIVE
General Surgery Service
 General Surgery Service Patient Care Goals and Objectives Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric assessed for a) Obesity surgery b) Treatment of i) Adenocarcinoma of the stomach ii) GIST iii) Carcinoid 2) Optimize
General Surgery Service Patient Care Goals and Objectives Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric assessed for a) Obesity surgery b) Treatment of i) Adenocarcinoma of the stomach ii) GIST iii) Carcinoid 2) Optimize
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum. Elective Student S. C.
 Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Paediatric surgical emergencies. Mani Thyagarajan BWCH
 Paediatric surgical emergencies Mani Thyagarajan BWCH General points Always discuss Call consultant for help ASAP CT scan is a bad modality in paediatrics Ultrasound? Intussusception? Renal colic? UTI
Paediatric surgical emergencies Mani Thyagarajan BWCH General points Always discuss Call consultant for help ASAP CT scan is a bad modality in paediatrics Ultrasound? Intussusception? Renal colic? UTI
Abdominal Pain. Luke Donnelly, MD Emergency Medicine
 Abdominal Pain Luke Donnelly, MD Emergency Medicine Objectives Approach to abdominal pain Evaluation Critical diagnoses and treatments Abdominal Pain Most Common ER Complaint Broad Differential Can often
Abdominal Pain Luke Donnelly, MD Emergency Medicine Objectives Approach to abdominal pain Evaluation Critical diagnoses and treatments Abdominal Pain Most Common ER Complaint Broad Differential Can often
Imaging of common diseases of hepatobiliary and GI system
 Imaging of common diseases of hepatobiliary and GI system Natthaporn Tanpowpong, M.D. Diagnostic radiology Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University Normal plain radiograph A = Common bile duct
Imaging of common diseases of hepatobiliary and GI system Natthaporn Tanpowpong, M.D. Diagnostic radiology Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University Normal plain radiograph A = Common bile duct
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/12/2012. Chapter 29. Nontraumatic Abdominal Injuries
 Chapter 29 Nontraumatic Abdominal Injuries Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with nontraumatic abdominal pain Learning Objectives
Chapter 29 Nontraumatic Abdominal Injuries Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with nontraumatic abdominal pain Learning Objectives
Appendicitis. I. Background & Significance: Algorithm Definitions 1. CASE
 I. Background & Significance: Appendicitis Appendicitis is one of the most common acquired surgical conditions of childhood. Diagnosis of appendicitis remains difficult. Much work has been done on validation
I. Background & Significance: Appendicitis Appendicitis is one of the most common acquired surgical conditions of childhood. Diagnosis of appendicitis remains difficult. Much work has been done on validation
Abdominal Imaging. Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings
 Abdom Imaging 27:47 50 (2002) DOI: 10.1007/s00261-001-0048-1 Abdominal Imaging Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 2002 Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings K. Konno, 1 H. Ishida, 1 M. Sato, 1 H.
Abdom Imaging 27:47 50 (2002) DOI: 10.1007/s00261-001-0048-1 Abdominal Imaging Springer-Verlag New York Inc. 2002 Gallbladder perforation: color Doppler findings K. Konno, 1 H. Ishida, 1 M. Sato, 1 H.
Table 0: Description of Grading System for Anatomic Severity of Disease in Emergency. Local disease confined to the organ with minimal abnormality
 Table 0: of Grading System for Anatomic Severity of Disease in Emergency Local disease confined to the organ with minimal Local disease confined to the organ with severe Local extension Table 1: Universal
Table 0: of Grading System for Anatomic Severity of Disease in Emergency Local disease confined to the organ with minimal Local disease confined to the organ with severe Local extension Table 1: Universal
Intraperitoneal cysts in infancy and childhood An overview and sonographic differentiation
 Intraperitoneal cysts in infancy and childhood An overview and sonographic differentiation M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Intraperitoneal cysts
Intraperitoneal cysts in infancy and childhood An overview and sonographic differentiation M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Intraperitoneal cysts
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Chapter 24 - Abdominal_Emergencies
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 24.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 13, 15, 18, 20 22 24.2 Describe the location, structure, and function of the organs in the abdominal
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 24.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. 13, 15, 18, 20 22 24.2 Describe the location, structure, and function of the organs in the abdominal
SASKATCHEWAN REGISTERED NURSES ASSOCIATION. RNs WITH ADDITIONAL AUTHORIZED PRACTICE CLINICAL DECISION TOOL AUGUST 2017
 DEFINITION Cholelithiasis Presence of gall stones in the biliary tract. Biliary Colic Right upper quadrant pain due to obstruction of a bile duct by a gallstone. Cholecystitis Inflammation of the gallbladder
DEFINITION Cholelithiasis Presence of gall stones in the biliary tract. Biliary Colic Right upper quadrant pain due to obstruction of a bile duct by a gallstone. Cholecystitis Inflammation of the gallbladder
Gallstone ileus:diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma
 Saurabh et al. 1 CASE SERIES OPEN ACCESS Gallstone ileus:diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma Shireesh Saurabh, Andrew Camerota, Jeffrey Zavotsky ABSTRACT Introduction: Gallstone ileus is a rare complication
Saurabh et al. 1 CASE SERIES OPEN ACCESS Gallstone ileus:diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma Shireesh Saurabh, Andrew Camerota, Jeffrey Zavotsky ABSTRACT Introduction: Gallstone ileus is a rare complication
Complicated Meckel`s diverticulum; to be considered as a differential diagnosis in the acute abdominal pain. Ultrasound and MDCT imaging finding
 Complicated Meckel`s diverticulum; to be considered as a differential diagnosis in the acute abdominal pain. Ultrasound and MDCT imaging finding Poster No.: C-0174 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational
Complicated Meckel`s diverticulum; to be considered as a differential diagnosis in the acute abdominal pain. Ultrasound and MDCT imaging finding Poster No.: C-0174 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational
Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen
 Prof. András Palkó MD, PhD Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen Faculty of General Medicine University of Szeged Hungary 1 Definition Sudden onset of severe symptoms requiring emergency
Prof. András Palkó MD, PhD Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen Faculty of General Medicine University of Szeged Hungary 1 Definition Sudden onset of severe symptoms requiring emergency
Causes of abdominal pain Doctors in the ED spend lots of time and money diagnosing abdominal pain. They still often do not know the exact cause
 1 2 3 What's Going On in There? EMS and Abdominal Pain Kevin McFarlane BSN,RN,CEN,CPEN,EMT Southwest Emergency Education and Consulting What is going on in there Acute Abdomen Sudden onset of pain within
1 2 3 What's Going On in There? EMS and Abdominal Pain Kevin McFarlane BSN,RN,CEN,CPEN,EMT Southwest Emergency Education and Consulting What is going on in there Acute Abdomen Sudden onset of pain within
A Comparative Ultrasound and Plain Abdominal X-Ray: Evaluation of Non-Classical Clinical Cases of Appendicitis
 A Comparative Ultrasound and Plain Abdominal X-Ray: Evaluation of Non-Classical Clinical Cases of Appendicitis Dorothy Makanjuola, FRCR; Qasim Al-Qasabi, FRCS; Tajuddin Malabarey, FRCR From the Departments
A Comparative Ultrasound and Plain Abdominal X-Ray: Evaluation of Non-Classical Clinical Cases of Appendicitis Dorothy Makanjuola, FRCR; Qasim Al-Qasabi, FRCS; Tajuddin Malabarey, FRCR From the Departments
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery
 12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
No Disclosures. Approach to Abdominal Radiographs
 Approach to Abdominal Radiographs Tapas K. Tejura, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology Keck Medical Center of USC tapas.tejura@med.usc.edu No Disclosures 34-year-old male with acute abdominal
Approach to Abdominal Radiographs Tapas K. Tejura, M.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology Keck Medical Center of USC tapas.tejura@med.usc.edu No Disclosures 34-year-old male with acute abdominal
2. Blunt abdominal Trauma
 Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases. Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT)
 Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Interesting Pediatric ultrasound cases Presented by: Falguni Patel (RDMS, RVT) Role of ultrasound to rule out Appendicitis Overview: Ultrasound is relatively inexpensive, safe and quick solution to rule
Pelvic Pain? Cause Beyond the Ovary
 Pelvic Pain? Cause Beyond the Ovary Catherine Kirkpatrick Consultant Sonographer United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust Aims Consider not all pelvic pain is ovary or uterus related Explore some non gynae
Pelvic Pain? Cause Beyond the Ovary Catherine Kirkpatrick Consultant Sonographer United Lincolnshire Hospitals Trust Aims Consider not all pelvic pain is ovary or uterus related Explore some non gynae
Pictorial review of bowel ultrasound: Common and unsuspected pathologies
 Pictorial review of bowel ultrasound: Common and unsuspected pathologies Poster No.: C-1668 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Law, A. Ali, G. Hutchison; Bolton/UK Keywords: Ultrasound-Colour
Pictorial review of bowel ultrasound: Common and unsuspected pathologies Poster No.: C-1668 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Law, A. Ali, G. Hutchison; Bolton/UK Keywords: Ultrasound-Colour
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology
 American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
Plain Radiographs in Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain. Plain Radiographs in Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain
 Jake Block, MD Associate Professor Associate Vice-Chairman for Clinical Operations Director, Musculoskeletal and Emergency Radiology Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Vanderbilt University
Jake Block, MD Associate Professor Associate Vice-Chairman for Clinical Operations Director, Musculoskeletal and Emergency Radiology Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Vanderbilt University
Appendicitis USG vs CT
 Appendicitis USG vs CT Dr Sateesh Kumar Kailasam MBBS Dip EM (RCGP, UK) MRCEM (UK) Group Head Maxcure Group of Hospitals National Treasurer Society for Emergency Medicine India (SEMI) My Talk includes
Appendicitis USG vs CT Dr Sateesh Kumar Kailasam MBBS Dip EM (RCGP, UK) MRCEM (UK) Group Head Maxcure Group of Hospitals National Treasurer Society for Emergency Medicine India (SEMI) My Talk includes
Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions
 Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions Miah MAY Introduction In our day to day practice we have to face many of the acute abdominal conditions. As we know acute abdomen
Role of radiology and imaging in the daignosis of acute abdominal conditions Miah MAY Introduction In our day to day practice we have to face many of the acute abdominal conditions. As we know acute abdomen
GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT
 GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Author: Dr Linda Jewes, Consultant Microbiologist Date Amended: December 2016 Approved by Committee/Group: Drugs & Therapeutics
GASTRO-INTESTINAL TRACT INFECTIONS - ANTIMICROBIAL MANAGEMENT Name & Title Of Author: Dr Linda Jewes, Consultant Microbiologist Date Amended: December 2016 Approved by Committee/Group: Drugs & Therapeutics
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Ultrasound evaluation of patients with acute abdominal pain in the emergency department
 Ultrasound evaluation of patients with acute abdominal pain in the emergency department Poster No.: C-2584 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. A. Falticeanu, A.-M. Alecsa-Lupu,
Ultrasound evaluation of patients with acute abdominal pain in the emergency department Poster No.: C-2584 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit A. A. Falticeanu, A.-M. Alecsa-Lupu,
Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy?
 January 2013 Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy? Johanna Sheu, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 Agenda Menu of tests Definition/anatomy/classification Pediatrics
January 2013 Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy? Johanna Sheu, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 Agenda Menu of tests Definition/anatomy/classification Pediatrics
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Gastroenterology. Certification Examination Blueprint. Purpose of the exam
 Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Gastroenterology Certification Examination Blueprint Purpose of the exam The exam is designed to evaluate the knowledge, diagnostic reasoning, and clinical judgment skills expected of the certified gastroenterologist
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation
 Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation
 Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Acute pelvic pain in female patient: Clinical and Radiological evaluation Poster No.: C-0909 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit N. Ramesh 1, T. Simelane 2 ; 1 Portlaoise/IE,
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction
 Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract - Small Bowel Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK,
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract - Small Bowel Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK,
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis
 1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
: Abdominal Emergencies
 INTRODUCTION Abdominal complaints are very common in emergency medicine. The specific cause of the abdominal pain can very rarely be determined in the pre-hospital environment, however performing a good
INTRODUCTION Abdominal complaints are very common in emergency medicine. The specific cause of the abdominal pain can very rarely be determined in the pre-hospital environment, however performing a good
