Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
|
|
|
- Gabriel Edwards
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2012 December 31, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh received $958,038 in formula funds for the grant award period January 1, 2009 through December 31, Accomplishments for the reporting period are described below. Research Project 1: Project Title and Purpose A Genetic Model of Congenital Obstructive Nephropathy - End-stage kidney disease costs over 15 billion dollars annually in the United States and represents a major cause of death and impaired quality of life. The long-term objective of this project is to gain a better understanding of the most common cause of kidney disease in children - a blockage in urine flow. Completion of the studies outlined in this proposal will help us design new diagnostic tests and treatment strategies for children and adults with kidney disease. Duration of Project 1/1/2009-9/15/2011 Summary of Research Completed This project ended during a prior state fiscal year. For additional information, please refer to the Commonwealth Universal Research Enhancement C.U.R.E. Annual Reports on the Department's Tobacco Settlement/Act 77 web page at Research Project 2: Project Title and Purpose Novel Mouse Model of Vesicoureteral Reflux and Dysfunctional Voiding Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) or backtracking of urine from the bladder back up into the kidneys, is the most common urinary tract birth defect. Reflux nephropathy or kidney injury associated with reflux is the 4 th leading cause of kidney failure in children. Reflux is also associated with dysfunctional voiding (DV) (abnormal bladder contractions) and patients with both conditions have a high risk for reflux nephropathy. Despite the association between reflux and voiding dysfunction, no one has found a genetic link. Our lab has developed a genetic mouse model that has very high rates of reflux, and also has evidence of voiding dysfunction (as well as evidence of long term injury resembling reflux nephropathy). Using this mouse, we can identify treatments for patients with VUR and DV to decrease the incidence of long term injury from reflux nephropathy. Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh 2008 Formula Grant Page 1
2 Duration of Project 10/19/ /31/2012 Project Overview Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR; backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureter) and dysfunctional voiding (DV) are associated with kidney scaring or reflux nephropathy, with the highest risks being in patients with both VUR and DV. Our laboratory has generated a unique genetic mouse model with both VUR and DV, called Fgfr2 St-/- (with deletion of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 in stroma around the Wolffian duct and ureter and in the bladder). Preliminary analyses of Fgfr2 St-/- mice reveal high VUR rates likely from abnormal insertion of the ureter into the bladder (from aberrant ureteric induction off the Wolffian duct) and from aberrant ureteral peristalsis. Fgfr2 St-/- mice have evidence of abnormal voiding, likely from aberrant bladder muscle contractions. Our hypothesis is that Fgfr2 St-/- mice represent a genetic model linking VUR and DV that pose a significant risk for reflux nephropathy. We will test the hypothesis with the following Aims: Aim 1: To determine roles of Fgfr2 in stroma during Wolffian duct/ureteric bud, ureter, and bladder development. Aim 2: To determine mechanisms by which Fgfr2 stromal deletion leads to VUR and ureteric, ureteral peristaltic, and voiding defects. Principal Investigator Carlton M. Bates, MD Associate Professor Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC One Children s Hospital Drive 4401 Penn Avenue Pittsburgh, PA Other Participating Researchers Kenneth Walker employed by Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh Expected Research Outcomes and Benefits At present, vesicoureteral reflux or backtracking of urine from the bladder back up into the kidneys, is the most common urinary tract birth defect. Reflux nephropathy or long term injury to the kidneys associated with reflux is the 4 th leading cause of kidney failure in children and a leading cause of increased blood pressure. There is a clear association between reflux and voiding dysfunction (not urinating frequently enough, abnormal bladder contractions) and those patients with both conditions are at a much higher risk for reflux nephropathy than those with either condition alone. Despite the association between reflux and voiding dysfunction, there has never been a genetic link described. We have a novel genetic mouse model that has very high rates of reflux and also has evidence of voiding dysfunction (as well as evidence of long term injury resembling reflux nephropathy). Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh 2008 Formula Grant Page 2
3 This gives us an opportunity to understand potential genetic links between these conditions. It also allows us to understand how these genetic abnormalities result in the combination of reflux and voiding dysfunction. Ultimately, we can learn insights into appropriate treatments for patients with these conditions to decrease the incidence of long term injury from reflux nephropathy. Summary of Research Completed The progress report will be divided according to the specific aims of the project: Specific Aim 1: To determine roles of Fgfr2 in stroma during Wolffian duct/ureteric bud, ureter, and bladder development. We had made significant progress in this Aim as noted on the previous progress report. Below is the new data obtained over the period covered by this report. Fgfr2 St-/- bladders have poor compliance, high pressures, decreased contractile forces and less ability to relax: We previously showed that Fgfr2 St-/- mice had dysfunctional voiding by void stain on paper (VSOP) assays. We then sought to more thoroughly interrogate bladder dysfunction in the mutants. Thus, we performed decerebrate cystometry in live animals, by infusing saline at 10ml/minute and noting bladder pressures and voiding responses over time. Compared to controls, mutants had higher baseline and threshold pressures and decreased intercontraction intervals (Figure 1). We then isolated bladder sheets, finding that mutants had attenuated relaxation responses to β 3 - adrenergic agonists vs. controls (not shown). In contrast, Fgfr2 St-/- bladders relaxed normally in response to forskolin, which increases camp levels as happens in response to adrenergic agonists; this suggests that Fgfr2 St-/- bladders maintain a partially contracted state. Also, the contractile force generated by Fgfr2 St-/- bladders was markedly attenuated with electrical field stimulation, cholinergic agonists (10 mm Carbachol), purinergic agonists (10 m - -methylene ATP) and KCl (120 mm) (Figure 1 and not shown). We stretched bladder sheets at 500mm intervals and plotted baseline (passive) tension and active force generated by electrical stimulation; Fgfr2 St-/- bladders had increased passive tension (poor compliance) and decreased active force (attenuated contractions) with increasing stretch vs. controls (Figure 1). Thus, 1 month old Fgfr2 St-/- bladders have poor compliance, high pressures and reduced contractile forces, likely secondary to an inability to relax normally. Fgfr2 St-/- mice have evidence of progressive chronic kidney disease: Given the constellation of lower urinary tract defects in Fgfr2 St-/- mice (detailed in this report and the previous report), we examined the mutants for signs of renal injury. At 1 month of age, ~75% of Fgfr2 St-/- mice (n=4) had mild to moderate hydronephrosis on H&E stained sections and renal ultrasound (US) without an obvious gender bias; there was no evidence of renal fibrosis on trichrome stained sections (not shown). By 6 months of age, 100% of the Fgfr2 St-/- mice (n=10) had moderate to severe hydronephrosis on H&E sections and US, without an obvious gender bias (Figure 2 and not shown). Trichrome staining shows that compared with controls, 6 month old Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh 2008 Formula Grant Page 3
4 Fgfr2 St-/- mice had fibrosis within glomeruli and the peritubular interstitium and in the deep medulla adjacent to the renal pelvis (Figure 2). Thus, with advancing age, Fgfr2 St-/- mice develop worsening hydronephrosis and renal fibrosis. We then examined serum and urinary biomarkers of chronic kidney disease. At 1 month, Fgfr2 St-/- mice have normal serum markers including blood urea nitrogen (BUN), phosphorous, bicarbonate, and potassium (not shown). By 6 months, however, both male and female Fgfr2 St-/- mice had high BUN and phosphorous levels compared to controls (Figure 3). Male mutants had lower bicarbonate levels and trends for increased potassium levels versus controls (Figure 3) (females have not yet been assayed). Also, 6 month male and female Fgfr2 St-/- mice have trends for increased 24 hour urine protein/creatinine ratios (n=4) (not shown). Thus, Fgfr2 St-/- mice have evidence of evolving chronic kidney disease based on serum biomarkers and proteinuria. The type of chronic kidney disease we are detecting appears to mimic the renal injury seen in patients with reflux nephropathy. Specific Aim 2: To determine mechanisms by which Fgfr2 stromal deletion leads to VUR and ureteric, ureteral peristaltic, and voiding defects. We have made progress in completing this Aim over the current reporting period. Fgfr2 St-/- embryonic bladders and ureters have evidence of increased hedgehog signaling: We previously showed that Bmp4 and Sprouty1 levels were decreased in E10.5 Fgfr2 St-/- urogenital ridges (and are likely downstream targets of Fgfr2 in E10.5 stroma that are driving the ureteric defects in the mutants). Since Fgfr2 is also expressed in ureter and bladder mesenchyme, we assessed E16.5 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders and ureters for signaling defects. Given critical roles of hedgehog (Hh) in the mesenchyme, we examined Hh activity. By in situ hybridization, Sonic hedgehog (Shh) expression appears normal in Fgfr2 St-/- bladder urothelium; however, Hh signaling readouts, Patched 1 and Bmp4, appear enhanced and expanded in the mesenchyme (Figure 4). We then confirmed similar Shh levels in E16.5 Fgfr2 St-/- and control bladders by real time PCR (qpcr); however, multiple Hh activity readouts including Patched 1, Gli1, hedgehog interacting protein (Hhip), and Bmp4 were (or trended to be) elevated by 45-70% vs. controls (Figure 5). Also, qpcr in E16.5 ureters revealed similar Shh levels, but increased levels of Hh readouts (Figure 5). Thus, E16.5 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders and ureters appear to have increased Hh activity, which could mispattern the muscle and/or lamina propria. Since Shh is unaltered, Fgfr2 likely represses factors that enhance Shh signaling and/or blocks expression of other ligands (e.g. Indian Hh). We then performed qpcr for factors that enhance Hh activity. E16.5 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders had increased Boc and trends for more Cdo (related to Boc), while Gas1 was unaltered (Figure 6). We saw similar patterns in E16.5 ureters (Figure 6). Thus, loss of Fgfr2 may increase factors such as Cdo and Boc that enhance Hh activity (Figure 6). Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh 2008 Formula Grant Page 4
5 P1 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders appear to have dysregulation of genes regulating proliferation/differentiation, muscle and connective tissue patterning, and receptors/channels: We then examined P1 bladders for changes in gene expression that may be mediating many of the physiological defects seen in Fgfr2 St-/- mice (Figure 1). Thus, we performed RNA-Seq on P1 Fgfr2 St-/- and cre negative control bladder mrna (n=3 per group). We made cdna libraries (Illumina) and performed 100 base single end sequencing (~20 million reads/sample) (Tufts Genomics Core). We then identified 98 differentially expressed genes in Fgfr2 St-/- bladders versus controls, using a high degree of stringency (false discovery rate < 0.2). Many of the top genes encoded for proteins that regulate proliferation/differentiation, muscle or connective tissue patterning, and channels or receptors (Table). We have begun validating differential expression of the genes by qpcr (Table, blue font). Although hedgehog signaling has dropped dramatically after E16.5, many of the apparently upregulated genes at P1 such as Nmyc and Sox9 are known hedgehog targets (Table); it is unclear whether this represents sustained expression in the absence of ongoing Hh signaling. Thus, despite overtly normal histology in P1 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders, we have begun identifying genes that may be driving functional defects. Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh 2008 Formula Grant Page 5
6 Figures and Tables: Figure 1: One month old Fgfr2 St-/- bladders have poor compliance and reduced force of contractions. a. Cystometry shows that Fgfr2 St-/- have high baseline and threshold pressures and shortened intercontraction intervals vs. controls (arrows=voiding). b. Electrical field stimulation in isolated bladder sheets shows that force generated is attenuated in mutants vs. controls. c. Contractions evoked by Carbachol are attenuated in mutants vs. controls. d. With increasing stretch, Fgfr2 St-/- bladders have increased passive tension (poor compliance) and decreased active force from electrical stimulation (attenuated contractions) vs. controls. Figure 2: Six month old Fgfr2 St-/- kidneys have hydronephrosis and fibrosis. a-d. H&E stained sections (a,c) and ultrasound images (b,d) show a normal control (a,b) and a Fgfr2 St-/- mouse with severe hydroneph-rosis (c,d) (p= papilla, *= pelvis). e-g. Trichrome stained sections show a normal control (e) including glomeruli (arrowheads) and a Fgfr2 St-/- kidney with blue staining indicating glomerular fibrosis (f, arrowheads), interstitial fibrosis (f, arrow) and peripelvic fibrosis (g) (p=pelvis) (insets in e and f show higher power views of glomeruli). Figure 3: Six month old Fgfr2 St-/- mice have serum biomarkers consistent with chronic kidney disease. a,b. Compared with controls, male and female Fgfr2 St-/- mice have increases in BUN (a) and phosphorous (b). c,d. Male Fgfr2 St-/- mice have decreased bicarbonate and trend for increased potassium vs. controls (*p<0.01). Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh 2008 Formula Grant Page 6
7 Figure 4: E16.5 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders have normal Shh but increased Ptc1 and Bmp4 expression: a,b. In situ reveals similar Shh levels in control and Fgfr2 St-/- urothelium. c-f. In situ shows enhanced and expanded Ptc1 and Bmp4 staining in submucosa of Fgfr2 St-/- mice (d,f) vs. controls (c,e) (see lines in c,d). all= 200x mag. Figure 5: Real time PCR reveals equivalent Shh but increased readouts of Hh activity in E16.5 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders and ureters: E16.5 bladders (a) and ureters (b) have similar Shh mrna but increases in Hh readouts in mutant (M) tissues vs. controls (C). n=3 per genotype. *p<0.05. Bladder Hhip p=0.06; Ureter Hhip p=0.09, Bmp4 p=0.08. Figure 6: qpcr shows likely increases in Boc and Cdo in E16.5 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders & ureters: a,b. E16.5 bladders (a) and ureters (b) have similar Gas1 levels but increased (or trends for) Cdo and Boc. n=3 per genotype. *p<0.05. Bladder Cdo p=0.06; Ureter Boc p=0.1. c. Proposed signaling with Fgfr2 loss. Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh 2008 Formula Grant Page 7
8 Table: Differential expression of genes in P1 Fgfr2 St-/- bladders relative to controls Proliferation/Differentiation Muscle/connective tissue patterning Channels/receptors Increased Decreased Increased Decreased Increased Decreased Nmyc, Gdf10, Gdf1, Osr2, Eya2, Fz10, Dkk2, Scx, Kif26b Tbx20, Klf9, Klf15, Rnf17, Prune2, Zbtb16 Mylpf, Actn2, Sox9, Col9a2/17a1/23a1/ 6a4, Adamts15/19, Ankrd1, Myl6b, Neb, Hdc, Emilin3 Myocardin, Sorbs1 Troponin I2/C1, Troponin I1, Dpp6, Clca3, Trpm5 Cholinergic receptor M2, Hcn1, Mrgprd Blue font = qpcr confirms differential expression Children s Hospital of Pittsburgh 2008 Formula Grant Page 8
Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant
 Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh received $958,038 in
Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh Annual Progress Report: 2008 Formula Grant Reporting Period July 1, 2011 June 30, 2012 Formula Grant Overview The Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh received $958,038 in
Formation of Urine: Formation of Urine
 The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
The Urinary outflow tract: monitors and regulates extra-cellular fluids excretes harmful substances in urine, including nitrogenous wastes (urea) returns useful substances to bloodstream maintain balance
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats
 Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Hydronephrosis. Nephrosis. Refers to the kidney
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
What is hydronephrosis? Hydro Nephrosis Refers to water or fluid Refers to the kidney A build-up of fluid (urine) in the kidney is the medical term for a build-up of urine in the kidney. As the urine builds
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests. Amelyn R.
 Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests Amelyn R. Rafael, MD 1 Functions of the Urinary Bladder 1. storage of urine 150 cc 1 st urge
Renal Physiology: Filling of the Urinary Bladder, Micturition, Physiologic Basis of some Renal Function Tests Amelyn R. Rafael, MD 1 Functions of the Urinary Bladder 1. storage of urine 150 cc 1 st urge
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
The Kidney Dissection (photos curtosy of Murray Jensen at UMN)
 CJ Shuster AP2 Lab Addenum Kidney Dissection 1 The Kidney Dissection (photos curtosy of Murray Jensen at UMN) BACKGROUND INFORMATION The human urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary
CJ Shuster AP2 Lab Addenum Kidney Dissection 1 The Kidney Dissection (photos curtosy of Murray Jensen at UMN) BACKGROUND INFORMATION The human urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, one urinary
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) New
 Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) New What is vesicoureteral reflux? Vesicoureteral reflux is the abnormal backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureter and up to the kidney. The majority of the time this
Vesicoureteral Reflux (VUR) New What is vesicoureteral reflux? Vesicoureteral reflux is the abnormal backflow of urine from the bladder into the ureter and up to the kidney. The majority of the time this
Prenatal Hydronephrosis
 Prenatal Hydronephrosis What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis is dilation of the kidney, specifically the renal pelvis (place where urine is stored after its production). This can be the result of an
Prenatal Hydronephrosis What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis is dilation of the kidney, specifically the renal pelvis (place where urine is stored after its production). This can be the result of an
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM
 AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
AP2, Lab 7 - THE URINARY SYSTEM I. SYSTEM COMPONENTS (Figs. 25.1 25.4) KIDNEYS Each kidney contains approx. 1,000,000 tubular NEPHRONS which produce FILTRATE from the plasma and then add to or take from
Physiologic Anatomy and Nervous Connections of the Bladder
 Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Micturition Objectives: 1. Review the anatomical organization of the urinary system from a physiological point of view. 2. Describe the micturition reflex. 3. Predict the lines of treatment of renal failure.
Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR)
 Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR) WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0876 Version: 5 Review date: June 2020 How does the urinary system work? The urinary system consists of the
Vesico Ureteric Reflux (VUR) WINSTON HELEN Author: Paediatric Department Document Number: STHK0876 Version: 5 Review date: June 2020 How does the urinary system work? The urinary system consists of the
CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT
 AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
AP BIOLOGY ANIMAL FORM & FUNCTION ACTIVITY #5 NAME DATE HOUR CONTROLLING THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT KIDNEY AND NEPHRON NEPHRON FUNCTIONS Animal Form & Function Activity #5 page 1 NEPHRON STRUCTURE NEPHRON
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux
 Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
Indications and effectiveness of the open surgery in vesicoureteral reflux Suzi DEMIRBAG, MD Department of Pediatric Surgery, Gulhane Military Medical Academy, Ankara, TURKEY Vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)
The Urinary System. Medical Assisting Third Edition. Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
The Urinary System PowerPoint presentation to accompany: Medical Assisting Third Edition Booth, Whicker, Wyman, Pugh, Thompson 30-2 Learning Outcomes 30.1 Describe the structure, location, and functions
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
hoofdstuk :07 Pagina ix Introduction
 hoofdstuk 00 08-03-2001 15:07 Pagina ix Introduction Incontinence at pediatric age is a problem that can harm the psychological and physical development of children. Starting in 1986 we have searched for
hoofdstuk 00 08-03-2001 15:07 Pagina ix Introduction Incontinence at pediatric age is a problem that can harm the psychological and physical development of children. Starting in 1986 we have searched for
Functions of the Urinary System
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes Acid-base balance in the blood
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
The Excretory System. Biology 20
 The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
The Excretory System Biology 20 Introduction Follow along on page 376 What dangers exist if your body is unable to regulate the fluid balance of your tissues? What challenged would the body have to respond
a) They are the most common cause of pediatric kidney failure. b) They are always symptomatic. c) They can be asymmetric.
 Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
Practice questions: 1. The paraxial mesoderm gives rise to somites. The structure of the somite a) is a loose mesenchymal sheet that will migrate toward the notochord. b) is an epithelial rosette with
Information for Patients
 Information for Patients Congenital Malformation in the Urinary Tract: Ureteral Duplication, Ureterocele, and Ectopic Ureter English Table of contents Ureteral Duplication... 3 Symptoms and Diagnosis...
Information for Patients Congenital Malformation in the Urinary Tract: Ureteral Duplication, Ureterocele, and Ectopic Ureter English Table of contents Ureteral Duplication... 3 Symptoms and Diagnosis...
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM
 DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
A. Correct! Flushing acids from the system will assist in re-establishing the acid-base equilibrium in the blood.
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 16: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following would solve a drop in blood ph? Question #01 (A) Decreased retention of acids. (B) Increased excretion
6/5/2010. Renal vein invasion & Capsule Penetration (T3a) Adrenal Gland involvement (T4 vs. M1) Beyond Gerota s Fascia? (?T4).
 GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
GU Cancer Staging: Updates and Challenging Areas 13 th Current Issues in Surgical Pathology San Francisco, CA June 5, 2010 Jeffry P. Simko, PhD, MD Associate Professor Departments of Urology and Anatomic
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Urinary System. BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Urinary System BSC 2086 A & P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Filter plasma, separate and eliminate wastes Functions Regulate blood volume and pressure Regulate osmolarity of body
Vesicoureteral Reflux: The Difficulty of Consensus OR Why Can t We All Just get Along?
 Vesicoureteral Reflux: The Difficulty of Consensus OR Why Can t We All Just get Along? J Brandt MD MPH Pediatric Nephrology, UNMSOM Family Practice Grand Rounds 2/14/2012 Why do we worry about VUR? 3
Vesicoureteral Reflux: The Difficulty of Consensus OR Why Can t We All Just get Along? J Brandt MD MPH Pediatric Nephrology, UNMSOM Family Practice Grand Rounds 2/14/2012 Why do we worry about VUR? 3
Objectives. Key Outlines:
 Objectives! Iden8fy and describe the Func8onal Anatomy of Urinary Bladder! Describe the mechanism of filling and emptying of the urinary bladder! Cystometrogram! Appreciate neurogenic control of the mechanism
Objectives! Iden8fy and describe the Func8onal Anatomy of Urinary Bladder! Describe the mechanism of filling and emptying of the urinary bladder! Cystometrogram! Appreciate neurogenic control of the mechanism
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SPRING 2016
 THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SPRING 2016 Ashley R. Jackson PhD Candidate Significance of Renal Urothelium During Development and Disease March 31, 2016 Graves 1167 1:00pm
THE OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES GRADUATE PROGRAM SPRING 2016 Ashley R. Jackson PhD Candidate Significance of Renal Urothelium During Development and Disease March 31, 2016 Graves 1167 1:00pm
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp , Chapter 19: pp ,
 P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
P215 Spring 2018: Renal Physiology Chapter 18: pp. 504-520, 525-527 Chapter 19: pp. 532-548, 553-560 I. Main Components of the Renal System 1. kidneys 2. ureters 3. urinary bladder 4. urethra 4 Major Functions
Neurogenic Bladder. Spina Bifida Education Day Conference SBA of Northeastern New York Albany, New York April 14, Eric Levey, M.D.
 Neurogenic Bladder Spina Bifida Education Day Conference SBA of Northeastern New York Albany, New York April 14, 2018 Eric Levey, M.D. Pediatrics & Neurodevelopmental Disabilities Chief Medical Officer,
Neurogenic Bladder Spina Bifida Education Day Conference SBA of Northeastern New York Albany, New York April 14, 2018 Eric Levey, M.D. Pediatrics & Neurodevelopmental Disabilities Chief Medical Officer,
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Development of the Urinary System. 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney Structures
 Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
Development of the Urinary System Excretory portion of urinary system derived from intermediate mesoderm Week 4: 1 st nephrons/renal corpuscles form Nephrotomes form and develop hollow lumens to form nephric
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Urinary System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 17 Part I. Clinical Applications
 Name: Urinary System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 17 Part I. Clinical Applications Lab Day/Time: 1 1. Mr. Bud Weiser is very drunk when he is brought to the emergency room after falling down the steps
Name: Urinary System Physiology Study Guide, Chapter 17 Part I. Clinical Applications Lab Day/Time: 1 1. Mr. Bud Weiser is very drunk when he is brought to the emergency room after falling down the steps
10. Diagnostic imaging for UTI
 10. Diagnostic imaging for UTI Key question: What is the most effective imaging test for the diagnosis of structural abnormalities of the urinary tract and/or kidney damage in children with UTI? Current
10. Diagnostic imaging for UTI Key question: What is the most effective imaging test for the diagnosis of structural abnormalities of the urinary tract and/or kidney damage in children with UTI? Current
Urinary System. Genitourinary System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 11. Overview 1/4/2013
 Genitourinary System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 11 Overview Urinary system Kidneys Ureter Bladder Nephron Male reproductive system Testes Accessory Structures Susie Turner, M.D. 71/3/13 Major homeostatic
Genitourinary System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 11 Overview Urinary system Kidneys Ureter Bladder Nephron Male reproductive system Testes Accessory Structures Susie Turner, M.D. 71/3/13 Major homeostatic
Urinary system. Lab-7
 Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
Urinary system Lab-7 Excretion: processes that remove wastes and excess materials from the body Urinary system (kidneys): excretes nitrogenous wastes, excess solutes, and water The Kidneys Regulate Water
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
Urinary System and Fluid Balance. Urine Production
 Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Urinary System and Fluid Balance Name Pd Date Urine Production The three processes critical to the formation of urine are filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Match these terms with the correct statement
Travelling down the tube: developmental biology of the ureter and urinary bladder
 Travelling down the tube: developmental biology of the ureter and urinary bladder Adrian S. Woolf Institute of Human Development University of Manchester Children s Hospital and University of Manchester,
Travelling down the tube: developmental biology of the ureter and urinary bladder Adrian S. Woolf Institute of Human Development University of Manchester Children s Hospital and University of Manchester,
microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease
 microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease January 2018 Safe Harbor Statement Statements contained in this presentation regarding matters that are not
microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease January 2018 Safe Harbor Statement Statements contained in this presentation regarding matters that are not
Journal Club. 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal
 Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Child and Family Information Material
 Endoscopic Treatment Child and Family Information Material Vesicoureteral What is endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)? In endoscopic treatment of VUR, the doctor uses a special viewing
Endoscopic Treatment Child and Family Information Material Vesicoureteral What is endoscopic treatment of vesicoureteral reflux (VUR)? In endoscopic treatment of VUR, the doctor uses a special viewing
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology
 Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Physiology - Problem Drill 17: The Kidneys and Nephronal Physiology Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem statement and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Obstructive Uropathy. PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO. Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta
 Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden
 Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Chapter 26: Urinary System By: Eddie Tribiana and Piers Frieden The urinary system is important because it performs vital excretory functions Takes blood from renal arteries into the kidney to filtrate
Bladder exstrophy and epispadias
 Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Bladder exstrophy and epispadias This leaflet explains about bladder exstrophy and epispadias and what to expect
Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Foundation Trust: Information for Families Bladder exstrophy and epispadias This leaflet explains about bladder exstrophy and epispadias and what to expect
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Supplemental Figure 1. Egr1 expression in adult Achilles tendons. (A,B) Achilles tendons were isolated from 2 month-old Egr1 +/- mice and stained for
 Supplemental Figure 1. Egr1 expression in adult Achilles tendons. (A,B) Achilles tendons were isolated from 2 month-old Egr1 +/- mice and stained for LacZ activity, which reflects Egr1 expression. (A)
Supplemental Figure 1. Egr1 expression in adult Achilles tendons. (A,B) Achilles tendons were isolated from 2 month-old Egr1 +/- mice and stained for LacZ activity, which reflects Egr1 expression. (A)
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
UNCOVERING THE ROLES OF TOLL-LIKE RECEPTOR 7 AND INTERFERON REGULATORY FACTOR 5 IN IMMUNE COMPLEX GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
 Name Email Barry Horne, Jr. bkhorne@bu.edu Institutional Affiliation Campus School Medical Campus Graduate Medical Sciences Division Department Graduate Program in Genetics and Genomics, Immunology Training
Name Email Barry Horne, Jr. bkhorne@bu.edu Institutional Affiliation Campus School Medical Campus Graduate Medical Sciences Division Department Graduate Program in Genetics and Genomics, Immunology Training
PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING. Dr A Brink
 PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING Dr A Brink Causes of hydronephrosis includes: Pelvi-ureteric obstruction Vesico-ureteric reflux Vesico-ureteric obstruction Posterior uretral valves Duplex kidneys Radiopharmaceutical
PAEDIATRIC RENAL IMAGING Dr A Brink Causes of hydronephrosis includes: Pelvi-ureteric obstruction Vesico-ureteric reflux Vesico-ureteric obstruction Posterior uretral valves Duplex kidneys Radiopharmaceutical
Urinary Tract Abnormalities
 Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
The Urinary System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 16 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Vesicoureteral reflux and reflux nephropathy
 Vesicoureteral reflux and reflux nephropathy This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis,
Vesicoureteral reflux and reflux nephropathy This infokid topic is for parents and carers about children s kidney conditions. Visit www.infokid.org.uk to find more topics about conditions, tests & diagnosis,
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Filtration Reabsorption Secretion Concentration
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Urinary System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 25 For this lab you will use parts
Supplemental Information. Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate. Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation. through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway
 Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Neuron, Volume 73 Supplemental Information Otic Mesenchyme Cells Regulate Spiral Ganglion Axon Fasciculation through a Pou3f4/EphA4 Signaling Pathway Thomas M. Coate, Steven Raft, Xiumei Zhao, Aimee K.
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Vertebrate Limb Patterning
 Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
Vertebrate Limb Patterning What makes limb patterning an interesting/useful developmental system How limbs develop Key events in limb development positioning and specification initiation of outgrowth establishment
TITLE: A PSCA Promoter Based Avian Retroviral Transgene Model of Normal and Malignant Prostate
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-03-1-0163 TITLE: A PSCA Promoter Based Avian Retroviral Transgene Model of Normal and Malignant Prostate PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Robert Reiter, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The
AD Award Number: DAMD17-03-1-0163 TITLE: A PSCA Promoter Based Avian Retroviral Transgene Model of Normal and Malignant Prostate PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Robert Reiter, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: The
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6
 BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
BIOL2030 Human A & P II -- Exam 6 Name: 1. The kidney functions in A. preventing blood loss. C. synthesis of vitamin E. E. making ADH. B. white blood cell production. D. excretion of metabolic wastes.
Kidneys and Homeostasis
 16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
16 The Urinary System The Urinary System OUTLINE: Eliminating Waste Components of the Urinary System Kidneys and Homeostasis Urination Urinary Tract Infections Eliminating Waste Excretion Elimination of
Active Hedgehog Signaling Regulates Renal Capsule Morphogenesis
 Active Hedgehog Signaling Regulates Renal Capsule Morphogenesis by Hovhannes Martirosyan A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Laboratory Medicine and
Active Hedgehog Signaling Regulates Renal Capsule Morphogenesis by Hovhannes Martirosyan A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science Laboratory Medicine and
The Urinary System. Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System Functions of the Urinary System Elimination of waste products Nitrogenous wastes Toxins Drugs Functions of the Urinary System Regulate aspects of homeostasis Water balance Electrolytes
The Urinary System 15PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations
 Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 23: The Urinary System, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function
 Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
Alterations of Renal and Urinary Tract Function Chapter 29 Urinary Tract Obstruction Urinary tract obstruction is an interference with the flow of urine at any site along the urinary tract The obstruction
WJEC. Kidney. Question
 WJEC Kidney Question 7 Examiner Arholwr yn unig (d) Humans can be affected by a condition known as multiple sclerosis (MS). In this condition T cells of the immune system attack and destroy the
WJEC Kidney Question 7 Examiner Arholwr yn unig (d) Humans can be affected by a condition known as multiple sclerosis (MS). In this condition T cells of the immune system attack and destroy the
Obstructive Nephropathy
 Obstructive Nephropathy Liza A. Lucero RN, FNP-C, MSN Renal Medicine Associates Conflicts No conflict of interests Obstructive Nephropathy Objectives Definition of Obstructive Nephropathy Causes Clinical
Obstructive Nephropathy Liza A. Lucero RN, FNP-C, MSN Renal Medicine Associates Conflicts No conflict of interests Obstructive Nephropathy Objectives Definition of Obstructive Nephropathy Causes Clinical
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
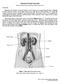 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS. DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010
 RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010 Alive patient RA + tracers Tc-99m(86%) + MAG 3 DMSA (DTPA) T½ = 6,5h Gamma camera ect. Radio-active
RADIO-NUCLIDE STUDIES FOR THE EVALUATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTIONS DR RIANA NEL NUCLEAR MEDICINE DEPT 27 Sept 2010 Alive patient RA + tracers Tc-99m(86%) + MAG 3 DMSA (DTPA) T½ = 6,5h Gamma camera ect. Radio-active
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Pelvioureteric junction obstruction of the lower collecting system associated with incomplete ureteral duplication: A case report
 Ped Urol Case Rep 2014;1(6):11-15 DOI:10.14534/PUCR.201468061 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Pelvioureteric
Ped Urol Case Rep 2014;1(6):11-15 DOI:10.14534/PUCR.201468061 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Pelvioureteric
INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS
 1 INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS The working-group consists of: Fin Biering-Sørensen representing the Executive Committee of The International
1 INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY DATA SETS URINARY TRACT IMAGING BASIC DATA SET - COMMENTS The working-group consists of: Fin Biering-Sørensen representing the Executive Committee of The International
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Acute Kidney Injury. I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS
 Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
Acute Kidney Injury I. David Weiner, M.D. Division of Nephrology, Hypertension and Transplantation University of Florida and NF/SGVHS 374-6102 David.Weiner@medicine.ufl.edu www.renallectures.com Concentration
