The Utility of MR Imaging Using the HASTE and True FISP Sequences in Diagnosing Bowel Obstruction 1
|
|
|
- Camron Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
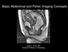
1 The Utility of MR Imaging Using the HASTE and True FISP Sequences in Diagnosing Bowel Obstruction 1 Eun Joo Yun, M.D. 1, 2, Tae Kyoung Kim, M.D. 1, 3, Byung Ihn Choi, M.D. Purpose: To determine the value of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) using HASTE (half- Fourier single-shot turbo spin-echo) and true FISP (fast imaging with steady-state precession and heavy T2-weighting) sequences in diagnosing bowel obstruction. Materials and Methods: Thirty-one consecutive patients in whom suspected bowel obstruction was revealed at plain abdominal radiography, barium study, and computed tomography (CT) were admitted during an eight-month period. Eighteen of 27 in whom bowel obstruction was confirmed underwent MRI using HASTE and true FISP sequences. Results: At MRI, bowel obstruction was diagnosed in all patients. Using the HASTE sequence, the site of obstruction was correctly identified in 16 patients(89%) and the cause of obstruction was correctly diagnosed in 15(83%). Using the true FISP sequence, the corresponding figures were 16(89%) and 16(89%). Of the 18 patients with confirmed bowel obstruction, 33%(6/18) showed better lesion conspicuity at true FISP, for 39%(7/18), conspicuity was equal at both sequences, 28%(5/18) showed better conspicuity at HASTE. Conclusion: MRI can be useful for evaluation the presence, site and cause of bowel obstruction. On comparing the findings of HASTE and true FISP sequences, no significant differences were observed. Index words : Intestines, obstruction Intestines, MR MRI has been widely applied in the evaluation of various abdominal diseases (1, 2), but its use for the evaluation of gastrointestinal disease has been slow to develop because of long acquisition times (resulting in increased motion artifacts, mostly from either respiration or peristalsis) and the unavailability of good MR contrast 1 Department of Radiology, Seoul National University College of Medicine 2 Department of Radiology, Hanllym University College of Medicine 3 Department of Radiology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine Received September 6, 2003 ; Accepted January 31, 2003 Address reprint requests to : Byung Ihn Choi, M.D., Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, 28 Yongon-dong, Chongno-gu, Seoul , Korea. Tel Fax choibi@radcom.snu.ac.kr 485 agents for the gastrointestinal tube (3, 4). As a result, only a small number of published studies have focused on the appearance of intestinal disease processes evaluated by MRI and there have been few reports concerning bowel obstruction (5 8). Several recent reports have described the use of fast MRI in small bowel disease, including small bowel obstruction (9 11). In this study, we investigated bowel obstruction using HASTE and true FISP sequences. Our purpose was to evaluate the efficacy of MRI using HASTE and true FISP sequences in demonstrating bowel obstruction, in identifying the sites involved, and in determining the cause of obstruction.
2 Materials and Methods Thirty-one consecutive patients in whom suspected bowel obstruction was revealed at plain abdominal radiography (n=18), barium study (n=7), and computed tomography (CT) (n=10), were admitted during an eightmonth period. In 26 of the 31, bowel obstruction was confirmed at surgery, and one case was confirmed at colonoscopic biopsy. Of these 27 with confirmed bowel obstruction, 18 underwent MRI using the HASTE and true FISP sequences, and these 18, in whom the respective conditions had been pathologically proven, comprised our series. The remaining nine, whose condition had been pathologically proven but who did not undergo MRI, were excluded from our study. Among the 18 patients [M:F=8:10; age range=25 93 (mean, 53) years], the common clinical symptoms were nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and distention. Thirteen patients had a history of prior surgery (gastrointestinal malignancy, =10; bowel perforation due to trauma or ulcer, =3). For MR examinations, a 1.0 Tesla scanner (Magnetom Impact Expert, Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) with a 15 mt/m gradient system and a body phased array coil was used. HASTE (repetition time [TR], infinite; echo time [TE], 87 ms; flip angle, 150 ; number of excitations, 1; matrix number, ; field of view [FOV], mm; slice thickness, 6 mm) and true FISP (TR, 7.6 ms; TE, 3.5 ms; flip angle, 80 ; number of excitations, 1; matrix number, ; FOV, mm; slice thickness, 6 mm) images were obtained during single breath-holds lasting an average of 19 seconds. Axial and coronal scans were obtained using both MRI sequences; fat suppression and cardiac or respiratory gating were not used. No medications for suppressing bowel peristalsis and contrast agent were given, and enteric contrast material or water were not ingested. The total examination time did not exceed 10 minutes. Two radiologists reviewed the images in terms of the presence, site and cause of bowel obstruction, comparing the image quality of the two MRI sequences and reaching their decisions consensually. Obstruction was diagnosed if a definite transition zone was observed, with dilated fluid and/or air-filled loops of small bowel proximal to the site of obstruction and collapsed loops of Fig. 1. A 33-year-old man who had total gastrectomy for gastric cancer with recurred tumor in transverse colon. Coronal true FISP MR image (TR/TE 7.6/3.5, FA 80 ) shows wall thickening of distal transverse colon (arrows) and dilated small bowel loops, suggesting malignant obstruction. Surgery revealed recurrence. 486 Fig. 2. A 47-year-old man who had subtotal gastrectomy for gastric cancer with small bowel obstruction due to postoperative adhesion. Coronal true FISP MR image shows multiple dilated, fluidfilled small bowel loops and an abrupt transition (arrow) of dilated and collapsed bowel loops. No mass lesions are seen around site of transition. It was confirmed by surgery.
3 small or large bowel distal to this site, and whether obstruction involved the proximal or distal small bowel, or the large bowel, was determined. Small and large bowel were differentiated according to their morphology and the central location of small bowel loops versus the peripheral position of the colon, best appreciated at coronal imaging (10). The cause of bowel obstruction was determined by evaluating the appearance of the obstruction site and the patient s past medical history. In these in whom gastrointestinal malignancy had necessitated surgery prior to MRI, post-operative adhesion or tumor recurrence was diagnosed on the basis of the following criteria: beak-like narrowing but the absence of a definite mass for post-operative adhesion, and an incriminating focal intraluminal mass or focal wall thickening of adjacent bowel for tumor recurrence (12). Intussusception was diagnosed if an intussuscepted segment and leading point were detected. Inflammatory bowel disease was diagnosed if mild diffuse bowel wall thickening was present, and colon cancer if a focal intraluminal mass or pronounced focal bowel wall thickening was observed. Results In all patients, MRI using the HASTE and true FISP sequences, demonstrated the existence of bowel obstruction. The obstruction site was correctly identified in 16 of 18 cases; the exception were two cases of distal small bowel obstruction. Obstruction occurred at the distal small bowel in 13 cases, the proximal small bowel in two, the ascending colon in two, and the transverse colon in one; its cause was tumor recurrence after surgery for gastrointestinal malignancy (Fig. 1) in seven cases, postoperative adhesion (Fig. 2) in six, intussusception (Fig. 3) in two, and colon cancer (Fig. 4), bezoar, and A B Fig. 3. A 43-year-old-woman with intussusception due to inflammatory polyp. A. Enteroclysis shows coil-spring appearance and filling defect in distal ileum. B. Axial true FISP MR image shows multilayered appearance of the dilated ileum, suggesting intussusception. C. Coronal true FISP MR image shows the polypoid mass in dilated distal ileum (arrow). The lesion was confirmed at surgery as a cause of small bowel obstruction. Pathology revealed inflammatory polyp. C 487
4 tuberculosis (Fig. 5) in one case each (Table 1). At HASTE sequencing, the site of obstruction was correctly identified in 16 patients(89%), and its cause in 15 patients(83%). For the true FISP sequence, the corresponding figures were 16(89%) and 16(89%) (Table 2). For both sequences, the two unidentified cases involved a recurrent tumor and postoperative adhesion. The cause of obstruction diagnosed only at true FISP was a bezoar in the small bowel. Of the 18 patients with bowel obstruction, 33%(6/18) showed better lesion conspicuity at true FISP. For 39% (7/18), conspicuity was the same at both sequences, and for 28%(5/18) it was better at HASTE (Table 3). Discussion The purpose of radiological imaging in patients with bowel obstruction includes the confirmation or exclusion of such obstruction, identification of the site involved, and assessment of the severity, and cause of the obstruction and whether strangulation or other complications have arisen. Conventionally, plain radiography, Table 2. Results of Presence, Site and Cause of Bowel Obstruction Using the HASTE and true FISP Sequences in 18 Patients Presence Site Cause HASTE 18/18 (100%) 16/18 (89%) 15/18 (83%) True FISP 18/18 (100%) 16/18 (89%) 16/18 (89%) Table 1. Site, Cause and MR Findings of Bowel Obstruction in 18 Patients No. Site Cause MR findings 01 Proximal small bowel Recurrent colon cancer Recurred mass 02 Distal small bowel Postoperative adhesion 03 Distal small bowel Recurred gastric cancer? 04 Distal small bowel Postoperative adhesion 05 Distal small bowel Recurred colon cancer Recurred mass 06 Distal small bowel Recurred colon cancer Omental cake 07 Distal small bowel Postoperative adhesion 08 Ascending colon Tuberculosis Thickened wall of terminal ileum 09 Distal small bowel Intussusception due to polyp Polypoid mass 10 Transverse colon Recurrent gastric cancer Recurred mass 11 Distal small bowel Postoperative adhesion 12 Distal small bowel Recurred colon cancer Irregular mass in pelvic cavity 13 Distal small bowel Postoperative adhesion 14 Ascending colon Primary colon cancer Thickened wall of ascending colon 15 Distal small bowel Recurred colon cancer Irregular soft tissue mass 16 Distal small bowel Postoperative adhesion 17 Distal small bowel Intussusception due to lymphoma Intussuscepted segment of bowel 18 Proximal small bowel Bezoar Foreign body on only True FISP *: abrupt transition of dilated and collapsed bowel loops without any mass Fig. 4. A 93-year-old-woman with small bowel obstruction due to primary ascending colon cancer. Coronal true FISP (A) and HASTE (B) (TR/TE 10.9/87, FA 150 ) MR images show dilated small bowel loops and markedly dilated proximal portion of ascending colon. Another scan shows focal wall thickening of distal portion of ascending colon. She refused surgery. This case was confirmed by colonoscopic biopsy. A B 488
5 barium studies and CT have been widely used (13). Plain film findings are thought to be diagnostic in about 50 60% of cases and equivocal in about 20 30% (14). One report showed that enteroclysis correctly predicted the presence of obstruction in 100% of cases and its absence in 88%; the level of obstruction in 89%, and its cause in 86%(15). When small bowel obstruction was classified as high or low grade; CT showed a sensitivity of 81% for high-grade and 48% for low-grade obstruction (16). Initially, T1-weighted SE imaging along with various types of contrast agent was used, but was limited by Table 3. Conspicuity of Lesions in 18 Bowel Obstructions Using the HASTE and true FISP Sequences Conspicuity Number (percentage) True FISP > HASTE 6/18 (33%) True FISP = HASTE 7/18 (39%) True FISP < HASTE 5/18 (28%) long imaging times, relatively poor image quality, and the expensive nature of the examination. The limitations of MRI in imaging of the bowel include long imaging times and poor spatial and contrast resolution; MR studies suffer from image degradation due to respiration-induced ghosting and peristaltic motion artifacts (12). The use of abdominal MRI has increased in recent years, aided by the availability of respiratory triggering and breath-hold sequencing, used to prevent motion artifacts, and the use of MRI with fast imaging sequences has recently been attempted. An alternative MRI technique is a fast T2-weighted sequence such as HASTE, the advantages of which include its very short imaging time, the fact that a contrast agent is not required, and its possible use in conjunction with barium studies. The value of MRI in patients with inflammatory bowel disease or small bowel tumors is well documented (17 19), and the use of new scanning sequences is likely to increase its use for the detection of processes involving A B Fig. 5. A 50-year-old man with obstruction of the terminal ileum due to tuberculosis. MR images (axial true FISP (A), HASTE (B), coronal true FISP (C), HASTE (D)) show concentric bowel wall thickening in the ileocecal area (arrow) and dilated small bowel. The lesion was confirmed at surgery as a cause of small bowel obstruction. Pathology revealed tuberculosis. C D 489
6 the gut wall and adjacent mesentery (3). In addition, the introduction of T2-weighted breath-hold sequencing has increased the usefulness of MRI in patients with acute bowel obstruction (10). In this study, HASTE and true FISP sequences were used as scanning modalities. The recent development of the former, a T2-weighted single-shot fast spin-echo pulse sequence known in full as the half-fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo sequence allows the acquisition of breathing-independent T2-weighted images in less than 1 second per section. Because of the short acquisition time per image, the HASTE sequence is not sensitive to patient movement or respiratory artifacts, making it suitable for use with uncooperative or pediatric patients. It is, furthermore, susceptibility insensitive (11, 19). True FISP displays fluid homogeneously, with a high signal-to-noise ratio, and permits high resolution regardless of the type of tissue. Motion, however, causes heavy signal loss. Gradient-echo sequences such as true FISP have a number of important advantages over spinecho sequences: 1, shorter measurement times; 2, increased signal-to-noise (SNR) and contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), with the same imaging time; 3, three-dimensional imaging; 4, better overall image quality and good anatomic demonstration of the small bowel on T2-like images; 5, fewer motion artifacts. Their disadvantages, however, include artifacts caused by magnetic susceptibility and the effects of field inhomogeneity (4, 20 22). MRI is similar to CT in that the images obtained demonstrate the overall topography of the abdomen. In addition to its lack of ionizing radiation, the inherent advantages of MRI over CT include its multiplanar imaging capability and high soft-tissue contrast; its multiplanar capability is also an important advantage. The lesion itself or the relationship between it and contiguous alimentary tract are better demonstrated on coronal or sagittal images (23 26). In diagnosing bowel obstruction, careful appraisal of MR images may reveal other abnormalities and reduce the number of differential diagnoses. However, the value of MRI findings for specific diagnosis is still to be determined. In patients with suspected bowel obstruction who are about to undergo surgery or are acutely ill, MRI may be the imaging technique of choice: because of the short imaging time and the fact that enteric contrast material is not needed, diagnostic study is possible. The ability of MRI to identify the cause of bowel obstruction could, furthermore, influence clinical management. As 490 in CT, the major advantage of MRI over contrast studies in evaluating bowel obstruction is its ability to demonstrate extraluminal abnormalities, a fact that is especially important in patients with malignant abdominal lesions (6, 8). In this study, MRI was able, in the majority of cases, to discriminate between malignant and benign obstruction in postoperative patients who had undergone surgery to resolve a gastrointestinal malignant tumor. MRI also correctly diagnosed intussusception, colon cancer, bezoar, and obstruction associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Subjective comparison indicated that HASTE and true FISP sequences showed the same diagnostic accuracy, and lesion conspicuity was also similar. True FISP imaging, however, more clearly demonstrates a lesion than does HASTE: with HASTE there is blurring in the phase-encoding direction, but on true FISP images, the bowel is surrounded by a sharp hypointense line (though this is a kind of artifact). Thus, the major advantage of the true FISP sequence is superior bowel delineation. Its disadvantages, however, include the variable signal intensity of intra-abdominal fat and the ferromagnetic artifact in patients with surgical clips. Because they show intra-abdominal fat as hyperintense, HASTE images provide better evaluation of extraluminal structures. In using MRI with HASTE and true FISP sequences, there are pitfalls and limitations. First, a dilated bowel can show either very high or very low signal intensity, depending on the nature of intraluminal fluid or gas. The presence of hypointense gas might on occasion be mistaken for a tumor, so careful image analysis is essential. In addition, MRI cannot indicate the possibility of bowel strangulation or intramural gas, or the presence of a small amount of pneumoperitoneum. As mentioned earlier, however, the clear advantages of MRI include its multiplanar capacity and the greater ease with which bowel loops are traced. This study suffers several limitations. First, the number of patients involved was extremely small; the accuracy of MRI in the evaluation of bowel obstruction should be tested in a larger population. Second, statistical analysis was not possible, and our findings thus have no application to clinical medicine. Third, although it is absolutely essential that MRI be compared with other widely appreciated and used imaging techniques, we have not correlated our results with these of other imaging studies.
7 In this report, we have shown that MRI using HASTE and true FISP sequences can provide images that permit assessment of the presence, site and cause of bowel obstruction. These techniques offer the advantages of multiplanar capacity, good spatial resolution, and the absence of ionizing radiation and barium-induced artifact. The short imaging time combined with the fact that no contrast material is used help reduce the cost of the procedure, which is likely to prove less expensive than previous MR techniques used to evaluate bowel obstruction. Our study has, we believe, highlighted the value of MRI in patients with suspected bowel obstruction and may also be useful in determining guidelines for MRI use in a given institution. In conclusion, MRI using HASTE and true FISP sequences can be useful in the evaluation of bowel obstruction. Further clinical trials and blind comparative study with CT may, however, be needed. References 1. Low RN, Sigeti JS. MR imaging of peritoneal disease: comparison of contrast-enhanced fast multiplanar spoiled gradient-recalled and spin-echo imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1994;163: Brink JA, Borrello JA. MR imaging of the biliary system. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 1995;3: Goldberg HI, Thoeni RF. MRI of the gastrointestinal tract. Radiol Clin North Am 1989;27: Gourtsoyiannis N, Papanikolaus N, Grammatikakis J, Maris T, Prassopoulos P. MR imaging of the small bowel with a true-fisp sequence after enteroclysis with water solution. Invest Radiol 2000; 35: Vlahos L, Gouliamos A, Athanasopoulou A, et al. A comparative study between Gd-DTPA and oral magnetic particles (OMP) as gastrointestinal (GI) contrast agents for MRI of the abdomen. Magn Reson Imaging 1994;12: Bagley AS, Semelka RC. Investigating bowel disease with ultrasound and MRI. Abdom Imaging 1994;19: Beall DP, Regan F. MRI of bowel obstruction using the HASTE sequence. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1996;20: Chou CK, Liu GC, Chen LT, Jaw TS. The use of MRI in bowel obstruction. Abdom Imaging 1993;18: Regan F, Cavaluzzi J, Nguyen B. Fast MR abdominal imaging using the HASTE sequence. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;170: Regan F, Beall DP, Bohlman ME, Khazan R, Sufi A, Schaefer DC. Fast MR imaging and the detection of small-bowel obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;170: Lee JK, Marcos HB, Semelka RC. MR imaging of the small bowel using the HASTE sequence. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1998;170: Semelka RC, Shoenut JP, Silverman R, Kroeker MA, Yaffe CS, Micflikier AB. Bowel disease: prospective comparison of CT and 1.5T pre- and postcontrast MR imaging with T1-weighted fat-suppressed breath-hold FLASH sequences. J Magn Res Imaging 1991; 1: Maglinte DD, Balthazar EJ, Kelvin FM, Megibow AJ. The role of radiology in the diagnosis of small-bowel obstruction. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1997;168: Mucha P Jr. Small intestinal obstruction. Surg Clin North Am 1987; 67: Shrake PD, Rex DK, Lappas JC, Maglinte DD. Radiographic evaluation of suspected small bowel obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol 1991;86: Maglinte DD, Gage SN, Harmon BH, et al. Obstruction of the small intestine: accuracy and role of CT in diagnosis. Radiology 1993;188: Shoenut JP, Semelka RC, Silverman R, Yaffe CS, Micflikier AB. Magnetic resonance imaging in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 1993;17: Shoenut JP, Semelka RC, Magro CM, Silverman R, Yaffe CS, Micflikier AB. Comparison of magnetic resonance imaging and endoscopy in distinguishing the type and severity of inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Gastroenterol 1994;19: Semelka RC, John G, Kelekis NL, Burdendy DA, Ascher SM. Small-bowel neoplastic disease: demonstration by MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 1996;6: Pavlidis J, Trierweiler R, Allis J, Groschel. Fast steady-state imaging: DESS, True FISP and CISS. Educational updates, SIEMENS, 1995; Deshpande VS, Shea SM, Laub G, Simonetti OP, Finn JP, Li D. 3D magnetization-prepared true-fisp: a new technique for imaging coronary arteries. Magn Reson Med 2001;46: Gourtsoyiannis N, Papanikolaus N, Grammatikakis J, Maris T, Prassopoulos P. MR enteroclysis protocol optimization: comparison between 3D FLASH with fat saturation after intravenous gadolinium injection and true FISP sequences. Eur J Radiol 2001; 11: Chou CK, Chen LT, Sheu RS, Wang ML, Jaw TS, Liu GC. MRI manifestations of gastrointestinal wall thickening. Abdom Imaging 1994;19: Chou CK, Liu GC, Chen LT, Jaw TS. Retrograde air insufflation in MRI: a technical note. Abdom Imaging 1993;18: Chou CK, Liu GC, Chen LT, Jaw TS. MRI manifestations of peritoneal carcinomatosis. Gastrointest Radiol 1992;17: Kim JH, Ha HK, Sohn MJ, et al. Usefulness of MR imaging for diseases of the small intestine: comparison with CT. Korean J Radiol 2000;1:
8 492
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
C. CT scan shows ascites and thin enhancing parietal peritoneum
 291 A B Fig. 1. A 55-year-old gastric cancer patient with peritoneal carcinomatosis. At surgery, there was large amount of ascites in peritoneal cavity and there were multiple small metastatic nodules
291 A B Fig. 1. A 55-year-old gastric cancer patient with peritoneal carcinomatosis. At surgery, there was large amount of ascites in peritoneal cavity and there were multiple small metastatic nodules
Non Contrast MRA. Mayil Krishnam. Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine
 Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Non Contrast MRA Mayil Krishnam Director, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Imaging University of California, Irvine No disclosures Non contrast MRA-Why? Limitations of CTA Radiation exposure Iodinated contrast
Fig. 1. Ileal and jejunal metastases from adenocarcinoma of the lung in 62-year-old male with a clinical history of bloody stool. A.
 507 A B Fig. 1. Ileal and jejunal metastases from adenocarcinoma of the lung in 62-year-old male with a clinical history of bloody stool. A. An intraluminal polypoid mass (arrow) is seen in the dilated
507 A B Fig. 1. Ileal and jejunal metastases from adenocarcinoma of the lung in 62-year-old male with a clinical history of bloody stool. A. An intraluminal polypoid mass (arrow) is seen in the dilated
Relationship Between Small Bowel Obstruction and Small Bowel Feces Sign: Four Cases Report
 Case Report Elmer Press Relationship Between Small Bowel Obstruction and Small Bowel Feces Sign: Four Cases Report Altintoprak Fatih a, e, Gunduz Yasemin b, Yalkin Omer c, Gundugdu Kemal c, Serbulent Gokhan
Case Report Elmer Press Relationship Between Small Bowel Obstruction and Small Bowel Feces Sign: Four Cases Report Altintoprak Fatih a, e, Gunduz Yasemin b, Yalkin Omer c, Gundugdu Kemal c, Serbulent Gokhan
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 09/17/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 38 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 09/17/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 38 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Application of Magnetic Resonance Images in Gastrointestinal Malignancies
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 269-275 269 Application of Magnetic Resonance Images in Gastrointestinal Malignancies SHENG-LAN YU 1 YUK-MING TSANG 1 PO-CHIN LIANG 1 HUNG-JUNG WANG 1 CHIEN-YAO HSU 1 TA-CHENG WEI
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 269-275 269 Application of Magnetic Resonance Images in Gastrointestinal Malignancies SHENG-LAN YU 1 YUK-MING TSANG 1 PO-CHIN LIANG 1 HUNG-JUNG WANG 1 CHIEN-YAO HSU 1 TA-CHENG WEI
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo
 Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
Functional Chest MRI in Children Hyun Woo Goo Department of Radiology and Research Institute of Radiology Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea No ionizing radiation
MRI of the Pancreas UNIT A18.1 A18.1.1
 MRI of the UNIT A18.1 MRI provides comprehensive information on the full range of pancreatic diseases. We employ a set protocol incorporating various types of sequences including transverse and coronal
MRI of the UNIT A18.1 MRI provides comprehensive information on the full range of pancreatic diseases. We employ a set protocol incorporating various types of sequences including transverse and coronal
Abdominal applications of DWI
 Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
Postgraduate course, SPR San Antonio (Texas), May 14-15, 2013 Abdominal applications of DWI Rutger A.J. Nievelstein Wilhelmina Children s s Hospital, Utrecht (NL) Outline What is DWI? How to perform? Challenges
CARDIAC MRI. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovascular Disease. Overview
 CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
CARDIAC MRI Dr Yang Faridah A. Aziz Department of Biomedical Imaging University of Malaya Medical Centre Cardiovascular Disease Diseases of the circulatory system, also called cardiovascular disease (CVD),
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA
 99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
99. MRA Principles and Carotid MRA As described in Chapter 12, time of flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is commonly utilized in the evaluation of the circle of Willis. TOF MRA allows depiction
Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver Metastases
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 10:165 169 (1999) Original Research Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 10:165 169 (1999) Original Research Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver
ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN. Carlos J. Sivit M.D.
 ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN Carlos J. Sivit M.D. ACUTE ABDOMEN Clinical condition characterized by severe abdominal pain developing over several hours ACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN Common childhood complaint
ACUTE ABDOMEN IN OLDER CHILDREN Carlos J. Sivit M.D. ACUTE ABDOMEN Clinical condition characterized by severe abdominal pain developing over several hours ACUTE ABDOMINAL PAIN Common childhood complaint
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings
 Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings Poster No.: C-1571 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Turturici, G. Gherarducci, F. Bianchi, R. Pascale, M. Tonerini,
Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings Poster No.: C-1571 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Turturici, G. Gherarducci, F. Bianchi, R. Pascale, M. Tonerini,
Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Magnetic Resonance Angiography 1 Magnetic Resonance Angiography exploits flow enhancement of GR sequences saturation of venous flow allows arterial visualization saturation of arterial flow allows venous
Usefulness of MR Imaging for Diseases of the Small Intestine: Comparison with CT
 Usefulness of MR Imaging for Diseases of the Small Intestine: Comparison with CT Ji-Hoon Kim, MD Hyun Kwon Ha, MD Min Jee Sohn, MD yung Suck Shin, MD Young Suk Lee, MD Soo Yoon Chung, MD Pyo Nyun Kim,
Usefulness of MR Imaging for Diseases of the Small Intestine: Comparison with CT Ji-Hoon Kim, MD Hyun Kwon Ha, MD Min Jee Sohn, MD yung Suck Shin, MD Young Suk Lee, MD Soo Yoon Chung, MD Pyo Nyun Kim,
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain
 Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Half-Fourier Acquisition Single-Shot Turbo Spin-Echo (HASTE) MR: Comparison with Fast Spin-Echo MR in Diseases of the Brain Mahesh R. Patel, Roman A. Klufas, Ronald A. Alberico, and Robert R. Edelman PURPOSE:
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts. David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology
 Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
Basic Abdominal and Pelvic Imaging Concepts David L. Smith, MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Basic Imaging Concepts Contrast Resolution vs Spacial Resolution Spacial Resolution......refers to the ability
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL
 SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy?
 January 2013 Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy? Johanna Sheu, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 Agenda Menu of tests Definition/anatomy/classification Pediatrics
January 2013 Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy? Johanna Sheu, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 Agenda Menu of tests Definition/anatomy/classification Pediatrics
3D high-resolution MR imaging can provide reliable information
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
children Crohn s disease in MR enterography for GI Complications Microscopy Characterization Primary sclerosing cholangitis Anorectal fistulae
 MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
MR enterography for Crohn s disease in children BOAZ KARMAZYN, MD PEDIATRIC RADIOLOGY ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR Characterization Crohn disease Idiopathic chronic transmural IBD Increasing incidence Age 7/100,000
Fat Suppression in the Abdomen
 Clinical How I do it? Fat Suppression in the Abdomen Wilhelm Horger Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany Introduction Due to the different chemical environment, hydrogen nuclei in - and in -tissue
Clinical How I do it? Fat Suppression in the Abdomen Wilhelm Horger Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany Introduction Due to the different chemical environment, hydrogen nuclei in - and in -tissue
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
6/23/2009. Inversion Recovery (IR) Techniques and Applications. Variations of IR Technique. STIR, FLAIR, TI and TI Null. Applications of IR
 The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
Rohini N. Nadgir 1 Jorge A. Soto 1 Klea Dendrinos 2 Brian C. Lucey 1 James M. Becker 3 Francis A. Farraye 2
 Nadgir et al. MRI of Complicated Pouchitis Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:W386 W391 0361 803X/06/1874 W386 American Roentgen Ray
Nadgir et al. MRI of Complicated Pouchitis Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations A C M E D E N T U R I C A L I M A G I N G AJR 2006; 187:W386 W391 0361 803X/06/1874 W386 American Roentgen Ray
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Effect of Adjusted Positioning on Gastric Distention and Fluid Distribution During CT Gastrography
 CT Gastrograph y Gastrointestinal Imaging Technical Innovation Se Hyung Kim 1 Jeong Min Lee 1,2 Joon Koo Han 1,2 Jae Young Lee 1,2 Han Kwang Yang 3 Hyuk-Joon Lee 3 Kyung-Sook Shin 4 Byung Ihn Choi 1,2
CT Gastrograph y Gastrointestinal Imaging Technical Innovation Se Hyung Kim 1 Jeong Min Lee 1,2 Joon Koo Han 1,2 Jae Young Lee 1,2 Han Kwang Yang 3 Hyuk-Joon Lee 3 Kyung-Sook Shin 4 Byung Ihn Choi 1,2
NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY
 A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction
 Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract - Small Bowel Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK,
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract - Small Bowel Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK,
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors
 CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
Comparison of 1.5 T Tesla and 3.0 T Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluating Local Extension of Endometrial Cancer
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 27 1, 21 28, March 2015 Original Comparison of 1.5 T Tesla and 3.0 T Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluating Local Extension of Endometrial Cancer Naomi YAGI, Masanori HIROSE,
Showa Univ J Med Sci 27 1, 21 28, March 2015 Original Comparison of 1.5 T Tesla and 3.0 T Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Evaluating Local Extension of Endometrial Cancer Naomi YAGI, Masanori HIROSE,
VIBE MRI for Evaluating the Normal and Abnormal Gastrointestinal Tract in Fetuses
 Inaoka et al. MRI of Fetal Gastrointestinal Tract Women s Imaging Clinical Observations 12_07_2063_Inaoka.fm 11/9/07 WOMEN S IMAGING Tsutomu Inaoka 1 Hiroyuki Sugimori 1 Yoshihito Sasaki 2 Koji Takahashi
Inaoka et al. MRI of Fetal Gastrointestinal Tract Women s Imaging Clinical Observations 12_07_2063_Inaoka.fm 11/9/07 WOMEN S IMAGING Tsutomu Inaoka 1 Hiroyuki Sugimori 1 Yoshihito Sasaki 2 Koji Takahashi
Index words : Bile duct radiography, technology Bile ducts MR Bile ducts surgery Liver, transplantation
 Hilar Branching Anatomy of Living Adult Liver Donors: Comparison of T2-MR Cholangiography and Contrast Enhanced T1-MR Cholangiography in Terms of Diagnostic Utility 1 Joon Seok Lim, M.D. 1, Myeong-Jin
Hilar Branching Anatomy of Living Adult Liver Donors: Comparison of T2-MR Cholangiography and Contrast Enhanced T1-MR Cholangiography in Terms of Diagnostic Utility 1 Joon Seok Lim, M.D. 1, Myeong-Jin
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 65. Benign Hepatic Masses
 65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
65. Benign Hepatic Masses Pulse sequences acquired for abdominal MRI typically consist of fast acquisition schemes such as single-shot turbo spin echo (i.e. HASTE) and gradient echo schemes such as FLASH
Usefulness of the Navigator-echo triggering Technique for Free-Breathing 3D MRCP
 Usefulness of the Navigator-echo triggering Technique for Free-Breathing 3D MRCP Poster No.: C-1257 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Matsunaga, G. Ogasawara, K. Fujii, T. Irie, T.
Usefulness of the Navigator-echo triggering Technique for Free-Breathing 3D MRCP Poster No.: C-1257 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Matsunaga, G. Ogasawara, K. Fujii, T. Irie, T.
Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction complicating chemotherapy in paediatric oncohaematological patients: clinical and imaging features
 The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), 377 381 Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction complicating chemotherapy in paediatric oncohaematological patients: clinical and imaging features 1 G E LEE, MD, 1
The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), 377 381 Acute colonic pseudo-obstruction complicating chemotherapy in paediatric oncohaematological patients: clinical and imaging features 1 G E LEE, MD, 1
Small Bowel Intussusception in an Adult due to Lipoma: a Rare Cause of Obstruction. Case report and Literature Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 1 Small Bowel Intussusception in an Adult due to Lipoma: a Rare Cause of Obstruction. Case report and Literature Review Yashpal, M Bansal, A Kudva
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 1 Small Bowel Intussusception in an Adult due to Lipoma: a Rare Cause of Obstruction. Case report and Literature Review Yashpal, M Bansal, A Kudva
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction
 Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK, Leeds/UK
Computed tomography (CT) imaging review of small bowel obstruction Poster No.: C-1602 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: A. Vousough, D. S. Prasad ; Aberdeen/UK, Leeds/UK
Utility of CT enterography in the evaluation of small bowel pathologies
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Varma RU et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1328-1332 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174190
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Varma RU et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Oct;4(5):1328-1332 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20174190
MR Findings in a Rare Case of Sclerosing Mesenteritis of the Mesocolon
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 21:632 636 (2005) Clinical Note MR Findings in a Rare Case of Sclerosing Mesenteritis of the Mesocolon Nadir Ghanem, MD,* Gregor Pache, MD, Thorsten Bley, MD, Elmar
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 21:632 636 (2005) Clinical Note MR Findings in a Rare Case of Sclerosing Mesenteritis of the Mesocolon Nadir Ghanem, MD,* Gregor Pache, MD, Thorsten Bley, MD, Elmar
Pseudo Washout Sign in High-Flow Hepatic Hemangioma on Gadoxetic Acid Contrast-Enhanced MRI Mimicking Hypervascular Tumor
 Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Doo et al. Pseudo Washout Sign on MRI of Hemangioma Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Kyung Won Doo 1 Chang Hee Lee Jae Woong Choi Jongmee Lee
Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Doo et al. Pseudo Washout Sign on MRI of Hemangioma Gastrointestinal Imaging Clinical Observations Kyung Won Doo 1 Chang Hee Lee Jae Woong Choi Jongmee Lee
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
MR coronary artery imaging with 3D motion adapted gating (MAG) in comparison to a standard prospective navigator technique
 Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (2005) 7, 793 797 Copyright D 2005 Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1097-6647 print / 1532-429X online DOI: 10.1080/10976640500287547 ANGIOGRAPHY MR coronary artery
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (2005) 7, 793 797 Copyright D 2005 Taylor & Francis Inc. ISSN: 1097-6647 print / 1532-429X online DOI: 10.1080/10976640500287547 ANGIOGRAPHY MR coronary artery
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment
 1 I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment II. Author Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Indiana University Department of Radiology Riley Hospital for Children 702 Barnhill Rd., Rm 1053b
1 I. Intussusception in Children: Diagnostic Imaging and Treatment II. Author Kimberly E. Applegate, MD, MS Indiana University Department of Radiology Riley Hospital for Children 702 Barnhill Rd., Rm 1053b
Localization of Gastrointestinal Bleeding by Cinematic 99m Tc Labeled Red Blood Cell Scan
 Localization of Gastrointestinal Bleeding by Cinematic 99m Tc Labeled Red Blood Cell Scan Chia-Shang Wu 1, Chang-Chung Lin 1, Nan-Jing Peng 1, 1 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Kaohsiung Veterans General
Localization of Gastrointestinal Bleeding by Cinematic 99m Tc Labeled Red Blood Cell Scan Chia-Shang Wu 1, Chang-Chung Lin 1, Nan-Jing Peng 1, 1 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Kaohsiung Veterans General
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Adult Celiac Disease: What Is the Role of MRI?
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 24:625 629 (2006) Original Research Adult Celiac Disease: What Is the Role of MRI? Ernesto Tomei, MD, 1 Richard C. Semelka MD, 2 * Larissa Braga, MD, PhD, 2 Andrea
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 24:625 629 (2006) Original Research Adult Celiac Disease: What Is the Role of MRI? Ernesto Tomei, MD, 1 Richard C. Semelka MD, 2 * Larissa Braga, MD, PhD, 2 Andrea
Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diffusion-Weighted Imaging of Prostate Cancer Ryota Shimofusa, MD,* Hajime Fujimoto, MD, Hajime Akamata, MD, Ken Motoori, MD,* Seiji Yamamoto, MD,* Takuya Ueda, MD,* and Hisao Ito, MD*
The adequate MR sequences for the detection of normal appendix in pregnant women
 The adequate MR sequences for the detection of normal appendix in pregnant women Poster No.: C-3310 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: J. W. Lee, Y. H. Jeon, J. Y. Hwang,
The adequate MR sequences for the detection of normal appendix in pregnant women Poster No.: C-3310 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: GI Tract Authors: J. W. Lee, Y. H. Jeon, J. Y. Hwang,
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results
 Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Case Reports: Tumor Detection by Diffusion-Weighted MRI and ADC-Mapping with Correlation to PET/CT Results Matthias Philipp Lichy, M.D.; Philip Aschoff, M.D.; Christina Pfannenberg, M.D.; Schlemmer Heinz-Peter,
Introduction and Definitions
 Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
How Much Tesla Is Too Much?
 How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
Ultrasonographic differentiation of bezoar from feces in small bowel obstruction
 Ultrasonographic differentiation of bezoar from feces in small bowel obstruction Kyung Hoon Lee 1, Hyun Young Han 1, Hee Jin Kim 1, Hee Kyung Kim 1, Moon Soo Lee 2 Departments of 1 Radiology and 2 Surgery,
Ultrasonographic differentiation of bezoar from feces in small bowel obstruction Kyung Hoon Lee 1, Hyun Young Han 1, Hee Jin Kim 1, Hee Kyung Kim 1, Moon Soo Lee 2 Departments of 1 Radiology and 2 Surgery,
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients
 128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
MR QA/QC for MRgRT. Rick Layman, PhD, DABR Department of Radiology July 13, 2015
 MR QA/QC for MRgRT Rick Layman, PhD, DABR Department of Radiology July 13, 2015 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute
MR QA/QC for MRgRT Rick Layman, PhD, DABR Department of Radiology July 13, 2015 The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute
INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis
 INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis DM Plata Ariza, MD; E Martínez Chamorro, MD; D Castaño Pardo, MD; M Arroyo López, MD; E Peghini Gavilanes,
INTRALUMINAL GAS IN NON-PERFORATED ACUTE APPENDICITIS: A predictor of gangrenous appendicitis DM Plata Ariza, MD; E Martínez Chamorro, MD; D Castaño Pardo, MD; M Arroyo López, MD; E Peghini Gavilanes,
The Value of Urgent Barium Enema and Computed Tomography in Acute Malignant Colonic Obstruction: Is Urgent Barium Enema Still Necessary?
 J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 105-110 The Value of Urgent Barium Enema and Computed Tomography in Acute Malignant Colonic Obstruction: Is Urgent Barium Enema Still Necessary? Chun-Chao Huang 1,2 Fei-Shih Yang
J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 105-110 The Value of Urgent Barium Enema and Computed Tomography in Acute Malignant Colonic Obstruction: Is Urgent Barium Enema Still Necessary? Chun-Chao Huang 1,2 Fei-Shih Yang
Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD
 Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD Name: Institution: Peter Draganov University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Overview Types of enteroscopy Enteroscopy equipment Enetoscopy do and don'ts
Deep Enteroscopy Methods to Diagnose Small Bowel IBD Name: Institution: Peter Draganov University of Florida, Gainesville, FL Overview Types of enteroscopy Enteroscopy equipment Enetoscopy do and don'ts
An evaluation of a superfast MRI sequence in the diagnosis of suspected acute appendicitis
 Brief Report An evaluation of a superfast MRI sequence in the diagnosis of suspected acute appendicitis Bin Zhu 1, Bing Zhang 1, Ming Li 1, Shifu Xi 2, Decai Yu 2, Yitao Ding 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Brief Report An evaluation of a superfast MRI sequence in the diagnosis of suspected acute appendicitis Bin Zhu 1, Bing Zhang 1, Ming Li 1, Shifu Xi 2, Decai Yu 2, Yitao Ding 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
 International Journal of Health Sciences, Qassim University, Vol. 8, No. 1 (January-March 2014) Case Report Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
International Journal of Health Sciences, Qassim University, Vol. 8, No. 1 (January-March 2014) Case Report Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt with Communicating Peritoneal & Subcutaneous Pseudocysts Formation
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP
 R.C. Chen, K.Y. Lin, J.M. Lii, et al MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP Ran-Chou Chen, 1,2 Kuang-Yang Lin, 3
R.C. Chen, K.Y. Lin, J.M. Lii, et al MR CHOLANGIOPANCREATOGRAPHY: PROSPECTIVE COMPARISON OF 3-DIMENSIONAL TURBO SPIN ECHO AND SINGLE-SHOT TURBO SPIN ECHO WITH ERCP Ran-Chou Chen, 1,2 Kuang-Yang Lin, 3
ACR MRI Accreditation Program. ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update. Educational Objectives. ACR accreditation. History. New Modular Program
 ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
ACR MRI Accreditation Program Update Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives Present requirements of the new
A free-breathing non-contrast-enhanced pulmonary magnetic resonance angiography at 3 Tesla
 Chinese Medical Journal 2009;122(18):2111-2116 2111 Original article A free-breathing non-contrast-enhanced pulmonary magnetic resonance angiography at 3 Tesla YANG Jian, WANG Wei, WANG Ya-rong, NIU Gang,
Chinese Medical Journal 2009;122(18):2111-2116 2111 Original article A free-breathing non-contrast-enhanced pulmonary magnetic resonance angiography at 3 Tesla YANG Jian, WANG Wei, WANG Ya-rong, NIU Gang,
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process
 ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
ACR MRI Accreditation: Medical Physicist Role in the Application Process Donna M. Reeve, MS, DABR, DABMP Department of Imaging Physics University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center Educational Objectives
Real-Time MRI of Joint Movement With TrueFISP
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 15:710 715 (2002) Technical Note Real-Time MRI of Joint Movement With TrueFISP Harald H. Quick, MSc, 1 * Mark E. Ladd, PhD, 1 Matthias Hoevel, MD, 2 Silke Bosk, RT,
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 15:710 715 (2002) Technical Note Real-Time MRI of Joint Movement With TrueFISP Harald H. Quick, MSc, 1 * Mark E. Ladd, PhD, 1 Matthias Hoevel, MD, 2 Silke Bosk, RT,
X-ray Corner. Imaging of the Small Bowel. Pantongrag-Brown L. Case 1. A 63-year-old man presented with abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
 THAI J 42 Imaging of the Small Bowel GASTROENTEROL 2015 X-ray Corner Imaging of the Small Bowel Pantongrag-Brown L Small bowel is the longest tubular organ in the body, about 18-22 feet. It is anchored
THAI J 42 Imaging of the Small Bowel GASTROENTEROL 2015 X-ray Corner Imaging of the Small Bowel Pantongrag-Brown L Small bowel is the longest tubular organ in the body, about 18-22 feet. It is anchored
Barium Studies of the Small Intestine
 Chin J Radiol 2004; 29: 309-314 309 Barium Studies of the Small Intestine JEN-HUEY CHIANG RHEUN-CHUAN LEE TSIU-SHAN TSENG YI-YOU CHIOU CHENG-YEN CHANG Department of Radiology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital
Chin J Radiol 2004; 29: 309-314 309 Barium Studies of the Small Intestine JEN-HUEY CHIANG RHEUN-CHUAN LEE TSIU-SHAN TSENG YI-YOU CHIOU CHENG-YEN CHANG Department of Radiology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success
 Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Vomiting in children: The good coordination between radiologists and pediatricians is the key to success C. Santos Montón 1, M. T. Garzon Guiteria 2, A. Hortal Benito-Sendín 1, K. El Karzazi 1, P. Sanchez
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Role of CT scan in evaluation and management of intestinal obstruction
 International Surgery Journal Baid G et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jul;4(7):2257-2261 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172777
International Surgery Journal Baid G et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Jul;4(7):2257-2261 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20172777
Imaging of Articular Cartilage
 Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Clinical Imaging of Articular Cartilage Imaging of Articular Cartilage Prof. Dr. K. Verstraete Ghent University Introduction : Articular Cartilage Histology and biochemical composition Review of Imaging
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Postoperative Chylothorax: the Use of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography and Thoracic Duct Embolization
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:182-186 Postoperative Chylothorax: the Use of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography and Thoracic Duct Embolization Chae Woon Lee, Hyun Jung Koo, Ji Hoon
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:182-186 Postoperative Chylothorax: the Use of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Lymphangiography and Thoracic Duct Embolization Chae Woon Lee, Hyun Jung Koo, Ji Hoon
Adult Intussusception
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 3, September 2005 Adult Intussusception Suhair Alsaad, MBCHB, CABS, FRCSI* Mariam Al-Muftah, MBCHB** Objectives: Adult intussusception is a rare entity. We present
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 27, No. 3, September 2005 Adult Intussusception Suhair Alsaad, MBCHB, CABS, FRCSI* Mariam Al-Muftah, MBCHB** Objectives: Adult intussusception is a rare entity. We present
Filiform polyposis of ulcerative colitis
 Filiform polyposis of ulcerative colitis Authors: Keisuke Yamada, Hironori Samura, Tatsuya Kinjo, Tetsu Kinjo, Akira Hokama, Jiro Fujita Article type: Clinical image Received: December 7, 2018. Accepted:
Filiform polyposis of ulcerative colitis Authors: Keisuke Yamada, Hironori Samura, Tatsuya Kinjo, Tetsu Kinjo, Akira Hokama, Jiro Fujita Article type: Clinical image Received: December 7, 2018. Accepted:
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update
 Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis
 The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
The British Journal of Radiology, 77 (2004), 792 799 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/95663370 E 2004 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review Pitfalls in the CT diagnosis of appendicitis 1 C D LEVINE, 2 O
Original Research. Jung Hoon Kim, MD, Tae Kyoung Kim, MD,* Hyo Won Eun, MD, Bong Soo Kim, MD, Moon-Gyu Lee, MD, Pyo Nyun Kim, MD, and Hyun Kwon Ha, MD
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:676 684 (2002) Original Research Preoperative Evaluation of Gallbladder Carcinoma: Efficacy of Combined Use of MR Imaging, MR Cholangiography, and Contrast-Enhanced
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 16:676 684 (2002) Original Research Preoperative Evaluation of Gallbladder Carcinoma: Efficacy of Combined Use of MR Imaging, MR Cholangiography, and Contrast-Enhanced
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
The mandibular condyle fracture is a common mandibular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
ORIGINAL RESEARCH P. Wang J. Yang Q. Yu MR Imaging Assessment of Temporomandibular Joint Soft Tissue Injuries in Dislocated and Nondislocated Mandibular Condylar Fractures BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Evaluation
