DISTRIBUTION OF PATHOGENIC NAEGLERIA SPP IN THAILAND
|
|
|
- Sara Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DISTRIBUTION OF PATHOGENIC NAEGLERIA SPP IN THAILAND Supathra Tiewcharoen and Virach Junnu Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine Hospital, Mahidol University, Bangkok 17, Thailand Abstract. Research concerning the distribution, isolation, viability, ultrastructure, morphology and immunogenicity of Naegleria fowleri has been increasing in Thailand during The distribution of the organism was carried out from 1985 to 1987 in Si Sa Ket and Ubon Rachathani Provinces, after the first fatal case was reported in Si Sa Ket. Since then in a 1998 survey of N. fowleri in stagnant water around industrial areas was carried out in Pathum Thani, Samut Prakan and Lopburi provinces. The results showed that 1% of pathogenic Naegleria belonged to species fowleri as characterized by morphology and the occurrence of pathogenesis in mice after nasal inoculation. In the same year, Nacapunchai et al (1999) determined the prevalence of amebae in aquatic habitat of human environments in five parts of Thailand during the summer. Fourteen percent of free living Naegleria spp were found in both soil and water resources. Recent studies of the ultrastructure, factors affecting the viability and SDS-PAGE electrophoretic patterns of 3 Thai strains of pathogenic Naegleria spp indicated their similarities in morphological characteristics of pathogenic reference control, Naegleria fowleri CDC VO 381. Additional study using a genetic approach to species criteria using allozyme electrophoresis had been conducted. INTRODUCTION The ameboflagellate Naegleria fowleri is a highly virulent organism. The first isolations of the organism were from patients with meningoencephalitis from several countries and continents. Many early attempts to isolate N. fowleri from environmental source failed. In the present survey Naegleria fowleri from water resources were successfully recovered and selective isolation showed the high temperature tolerance of the amebae. The viability on temperature, ph, chlorination, salinity, formalin, ultraviolet, drainage, rainfall, solar heat, etc, are important factors to explain the distribution of the organism in environmental and polluted resources. The information supported by SDS- PAGE electrophoresis and isoenzyme electrophoresis analysis aided in the identification of Naegleria spp in Thailand. Survey (Figs 1-4) The Naegleria is under the family Vahlkampfiidae. The classification of free-living amebae by Chang represents a continuation of the ideas of both Singh and Hanumiah (1979) and Page (1981) and is based on phylogenetic principles. Naegleria spp are distributed world-wide but the true incidence of human infection and prevalence is unknown. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) due to N. fowleri has existed for a number of years and most cases were diagnosed retrospectively (Beaver et al,1984). Victims for the most part are healthy young individuals with a recent history of contacting water with this amebae (Callicott, 1968). The disease affected males about three times more often than in females. This may be indicative of greater participation by male in waterrelated sports rather than sexual predisposition. About 13 cases of PAM have been reported world-wide due to N. fowleri (Abraham and Lawande, 1982; Lawande et al, 1979; Sugita et al, 1999). Of these 5 PAM cases were from the USA (Anderson et al, 1972), 16 cases reported from Czechoslovakia between 1962 to 1965 (Cerva et al, 1968) and 17 cases reported in Australia (Dorsch et al, 1983). The first case of Naegleria infection in Thailand was reported by Jariya et al in 1983 from Si Sa Ket Province. The second case was from Bangkok (Poungvarin and Jariya, 1991), the third and fourth case were from Trad Province (Somboonyosdech et al, 1987) and the fifth case was from Nakhon Pathom Province (Sirinavin et al, 1989). All of these patients died soon after infection. Luckily, the sixth case from Samut Prakan survived after treatment with amphotericin B and ketoconazole. (Poungvarin and Jariya, 1991). A few survivors were reported during The last case was a 38-year-old lorry driver with a history of auditory hallucination and impaired concentration associated with early morning headache, visual disturbance, seizure and signs of raised intracranial pressure. After he had swum in several of the hot springs which existed along his route especially in the area around Zhongshan, a town km north-west of Hong Kong. The first intervention slowed a right frontal abscess and pus drainage showed living N. fowleri. He was treated with amphotericin B 6 mg/day and rifampicin 46 mg/day, intravenous chloramphenical 1 g qid and surgery with decompressive occipital lobectomy (Angela et al, 1993). The outcome of psychological assessment revealed moderate disability. Since then, a 172 Vol 32 (Suppl 2) 1
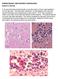
2 PATHOGENIC NAEGLERIA SPP IN THAILAND Fig 1- Trophozoite form in iron hematoxylin; Cytoplasm appears fine granular clear nucleus, dense central nucleolus and halo. (Mag 1,25) Fig 3- Cyst form in iron hematoxylin; Single cyst wall and typical nucleus of ameba were demonstrated. (Mag 1,25) Fig 2- Trophozoite form in iron hematoxylin; Living flagellate of Naegleria spp showing flagellum. (Mag 1,25) number of studies concerning the epidemiology were carried out during The distribution of Naegleria spp in Thailand both in tropical and subtropical areas have been studied. A survey for N. fowleri was carried out from 1985 to 1987 in Si Sa Ket and Ubon Rachathani Province (Jariya et al, 1988), after the first fatal cases was reported in Si Sa Ket. In 1998, a survey of N. fowleri in stagnant water around industrial area was done in Pathum Thani, Samut Prakan and Lopburi Province in order to detect the prevalence of Naegleria and the conditions which was most likely to be found. This research revealed that 1% of the Naegleria spp belonged to species fowleri as characterized by characteristic morphology and the occurrence of pathology in mice (Ratus ralus) after nasal inoculation (Jariya et al, 1997). This means that N. fowleri not only survives in natural waters but can also proliferate Fig 4- The histological studies revealed the large central karysome and halo around the nucleus of the organism. The amount of amebae were accumulated around perivascular space. (Mag 1,25) in thermal polluted water. (De Jonckheere et al, 1977). Nacapunchai et al (1999) determined the prevalence of amebae in aquatic habitat of human environments in five parts of Thailand during the summer of 1998, and reported that 14 % of free living Naegleri spp were found in both soil and water resources (Mascaro et al, 1989). Due to the fact that it can proliferate in surface water, local people can be easily infected just by swimming (Tyndall et al, 1989). Ultrastructures (Figs 5-1) The ultrastructure of pathogenic Thai strain was carried out (Mankalanond et al, 1999).The results revealed that the ultrastructure morphology from scanning electron microscope showed non-distinguish irregular outer surface and wrinkled membrane of Naegleria spp compared with reference control N. fowleri CDC VO381. It was also reported by transmission electron microscope that rough Vol 32 (Suppl 2) 1 173
3 Fig 5- Trophozoite form (SEM); Irregular outer surface and wrinkled membrane were demonstrated.(mag 3,) Fig 8- Trophozoite form (TEM); Vacuole (Unit membrane and contain electron-dense materials surrounded by whorl-like formations). Food and contractile vacuole were demonstrated. (Mag 3,) Fig 6- Trophozoite form (TEM); Rough endoplasmic reticulum appear as elongated tubular vesicles cover with ribosomes, nucleus, nucleolus. (Mag 1,) Fig 9- Trophozoite form (TEM); Nucleus, nuclear membrane was bounded by two clear electron dense. A few pores could be seen within the nuclear envelope. Nucleolus at the central portion of the nucleus appears dense. (Mag 26,) Fig 7- Trophozoite form (TEM); Dumb-bell shaped, cupshape and oval-shape mitochondria were demonstrated. (Mag 4,) Fig 1- Flagellate form (SEM); Pear shape and flagellum were seen. (Mag 3,) 174 Vol 32 (Suppl 2) 1
4 PATHOGENIC NAEGLERIA SPP IN THAILAND endoplasmic reticulum appeared as elongated tubular vesicles covered with ribosome and closely associate to mitochondria. Most impressive was the presence of many dum-bell shaped mitochondria. These were bound by two membranes separated by clear space, the outer membrane being thinner than the inner one. The cristae were thick, prominent and irregularly arranged. Cup shape and oval shape mitochondria were also found. Most numerous vacuoles were demonstrated, food and contractile vacuoles which were bound by a unit membrane and contains electron-dense material. The nuclear membrane was bounded by two clear electron dense. A few pores could be seen within the nuclear envelope and nucleolus at the central portion of the nucleus appeared dense. Factors affecting viability (Figs 11-16) Due to the fact that the amebae appears to multiply better during the hotter months of the year suggesting a seasonal pattern (Griffin, 1983; Nerad et al, 1983). These strains are rare and transient and there are many factors that stimulates growth. Supporting this knowledge, the viability of Naegleria spp was carried out in the same year (Tiewcharoen and Junnu, 1999a). We can concluded that Naegleria survives as the amebae form at -4 C to 5 C but optimal condition were 28 C. It does not survive if the ph was less than 5 or more than 12 and preferred fresh water to brackish in salty water higher than 2%. In addition, they were killed by chlorine concentration greater than.75 ppm and also in formalin at a concentration of greater than living amebae/ μl temperature (ßC) p<.5 Fig 11- The effect of temperature on Naegleria fowleri and pathogenic Naegleria spp. Trophozoites degenerated in hours at temperature -4 C. Pathoegenic Naegleria spp were killed at temperature greater than 5 C for 24 hours. 45 living amebae/ μl % salinity p<.5 Fig 12- The effect of salinity of Naegleria fowleri and pathogenic Naegleria spp. Trophozoites were destroyed in saline concentrations higher than 2%. Vol 32 (Suppl 2) 1 175
5 living amebae/ μl ppm p<.5 Fig 13- The effect of chlorine on Naegleria fowleri and pathogenic Naegleria spp. Chlorine concentrations greater than.75 ppm killed the amebae. 45 living amebae/ μl UV light distance (cm) p<.5 Fig 14- The effect of UV light distance on Naegleria folwleri and pathogenic Naegleria spp. The amebae were resistance to ultraviolet light. 7 living amebae/ μl % Formalin p<.5 Fig 15- The effect of formatlin on Naegleria fowleri and pathogenic Naegleria spp. All Naegleria spp were sensitive to formalin at concentrations greater than.5%. 176 Vol 32 (Suppl 2) 1
6 PATHOGENIC NAEGLERIA SPP IN THAILAND living amebae/ μl ph p<.5 Fig 16- The effect of ph on Naegleria fowleri and pathogenic Naegleria spp. The amoebae could not survive at a ph of less than 5 or more than 12. gel. All specific and non specific allozyme of pathogenic Naegleria Thai strain will be reported in next year. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work was partly supported by Research Grant No from the China Medical Board Fund, the Faculty of Medicine Hospital, Mahidol University, and by the Princess Mother s Medical Volunteer Foundation (PMMV). Our thanks are expressed to Dr Govinda S Visvesvara, Division of Parasitic Diseases, Centers for Disease and Prevention (CDC), Atlanta, Georgia USA for giving us the reference strain of Naegleria fowleri CDC VO381. Fig 17- Representative of proteins profiled extracted of Naegleria fowleri, pathogenic Naegleria spp; strain (Lane 1), strain (Lane 2), strain (Lane 3), CDC VO381 strain (Lane 4), M=Molecular weight markers..5%. However, all of the amoebae were resistant to ultraviolet light. Immunological studies (Fig 17) Recent studies carried out in 1999 on the molecular weight of pathogenic Thai strain Naegleria and the reference control strain N. fowleri by SDS-PAGE electrophoresis. The strains of pathogenic Naegleria isolated from fatal Thai patients were similar to N. fowleri and differed in a few distinct protein compounds (Tiewcharoen et al, 1999b). A genetic approach to species criteria using allozyme electrophoresis has also been conducted. The isoenzyme patterns were studied by using vertical slap gel electrophoresis on 7.5 % separating polyacrylamide REFERENCES Abraham SN, Lawande RV. Incidence of free-living amoebae in the nasal passage of local population in Zaria, Nigeria. J Trop Med Hyg 1982;85:217. Anderson K, Jamieson A, Jadine J B, Willaert E. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. Lancet 1972;4: Angela W, Richard K, Poon WS, Ng HK. Successful treatment of amoebic meningo-encephalitis in Chinese living in Hong Kong. Clin Neuro Neurosurg 1993;95: Beaver PC, Jung RC, Cupp EW. Clinical Parasitology, 9th ed. Philadelphia: Lee and Febiger, 1984: Callicott JH. Amoebic meningoencephalitis due to free living amoeba of the Hartmanella [Acanthamoeba] Naegleria groups. Am J Clin Pathol. 1968;49: Vol 32 (Suppl 2) 1 177
7 Cerva L, Novak K, Culbertson CG. An outbreak of acute fatal amoebic meningo-encephalitis. Am J Pathol 1968;88:436. De Jonckheere J, Van Dijck, Van de Voored H. The distribution of Naegleria fowleri in man-made thermal waters. Am J Trop Med Hyg 1977;26:1-15. Dorsch MM, Cameron AS, Robinson BS. The epidemiology and control of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis with particular reference to South Australia. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1983; 77:372. Griffin JL. The pathogenic amoeboflagellate Naegleria fowleri : Environmental isolation, competitor, ecologic, interactions and the flagellate-empty habitat hypothesis. J Protozoa 1983;3:43-9. Jariya P, Jaroomvasama N, Kunaratanapruk S, Lawhanuwat C, Pongchaikul P. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis: a first reported case in Thailand. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1983;14: Jariya P, Singprasert P, Lertlaituan P. Survey of amoeba in stagnant waters of the North - Eastern Thailand. J Parasitol Trop Med Assoc Thai 1988;11:4-6. Jariya P, Tiewcharoen S, Junnu V, Lertlaituan P, Suvithayasiri V. Survey of Naegleria fowleri the causative agent of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) in stagnant waters around factory area in Thailand. Hosp Gaz 1997;49: Lawande RV, Ogukanmi AE, Egler LJ. Prevalence of pathogenic free-living amoebae in Zaria, Nigeria. Am Trop Med Parasitol 1979;73:51. Mankalanond K, Tiewcharoen S, Junnu V. Ultrastructure of pathogenic Naegleria species isolated from three cases of primary meningoencephalitis infection from Thai patients. J Mahidol 1999;6:85-8. Mascaro ML, Mascaro MC, Osuna A, Perez MI, Gonzalez-Castro J. Study of Amoeboflagellate Isolated from the nasal mucosa of man. J Protozool 1986: Nacapunchai D, Lamom C, Ruangsittichai C, Sriwichai P. Isolation of free-living amoebae from soil and water resources in Thailand. J Trop Med Parasitol 1999;22:22-6. Nerad TA,Visvesvara G, Daggett PM. Chemically defined media for the cultivation of Naegleria pathogenic and high temperature tolerant species. J Protozoal 1983;3: Page FC. A light and electron-microscopical study of Protoacanthamoeba. g. (Amoebida, Acanthamoebidae). J Protozoal 1981;28:7. Poungvarin N, Jariya P. The fifth non-lethal case of primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis. J Med Assoc Thai 1991;74:112. Singh BN, Hanumiah V. Studies on pathogenic and nonpathogenic amoeba and the bearing of nuclear division and locomotive form and behavior on the classification of the order Amoebida. In 2 th Annual Conference of the AMI, Monograph #1, Association of Microbiologists of India Haryana Agricultural University, Hissar, Sirinavin S, Jariya P, Lertlaituan P, Chuahirun S, Pongkripetch M. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis in Thailand : report of a case and review literatures. J Med Assoc Thai 1989;72: Somboonyosdech S, Koeucharoen K, Pinkoew P. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis : A report of two cases in Trat Hospital. J Pediatr Soc Thai 1987;26:6-8. Sugita V, Fujii T, Hayashi I, Aoki T, et al. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis due to Naegleria fowleri : An autopsy case in Japan. Pathol Int 1999;49: Tiewcharoen S, Junnu V. Factors effecting the viability of pathogenic Naegleria species isolated from thai patients. J Trop Med Parasitol 1999a;22: Tiewcharoen S, Junnu V, Ongrotchanakun J. Protein pattern of crude extract of pathogenic Naegleria spp isolated from Thai patients by SDS-PAGE. J Trop Med Parasitol 1999b;22:46-9. Tyndall RL, Ironside KS, Metler PL, Tam EL, Hazes TC. Effect of therminal additions on the density and distribution of thermophilic amoebae and pathogenic Naegleria fowleri in a new create cooling lake. App Environ Microbiol 1989;55: Vol 32 (Suppl 2) 1
REVIEW PRIMARY AMEBIC MENINGOENCEPHALITIS AND NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: AN UPDATE
 REVIEW PRIMARY AMEBIC MENINGOENCEPHALITIS AND NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: AN UPDATE Virach Junnu 1, Supathra Tiewcharoen 1 and Jundee Rabablert 2 1 Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital,
REVIEW PRIMARY AMEBIC MENINGOENCEPHALITIS AND NAEGLERIA FOWLERI: AN UPDATE Virach Junnu 1, Supathra Tiewcharoen 1 and Jundee Rabablert 2 1 Department of Parasitology, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital,
Factors Affecting the Virulence of Naegleria fowleri for Mice
 Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 47(1), 1980, p. 129-134 Factors Affecting the Virulence of Naegleria fowleri for Mice R. M. HAGGERTY AND D. T. JOHN Department of Microbiology, MCV Station, Box 678, Commonwealth
Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 47(1), 1980, p. 129-134 Factors Affecting the Virulence of Naegleria fowleri for Mice R. M. HAGGERTY AND D. T. JOHN Department of Microbiology, MCV Station, Box 678, Commonwealth
FREE-LIVING PROTOZOA. PAM GAE; skin or lung lesions amebic keratitis; GAE; skin or lung lesions
 FREE-LIVING PROTOZOA Ameba Naegleria fowleri Acanthamoeba sp. Balamuthia mandrillaris Diseases PAM GAE; skin or lung lesions amebic keratitis; GAE; skin or lung lesions Naegleria fowleri ubiquitous in
FREE-LIVING PROTOZOA Ameba Naegleria fowleri Acanthamoeba sp. Balamuthia mandrillaris Diseases PAM GAE; skin or lung lesions amebic keratitis; GAE; skin or lung lesions Naegleria fowleri ubiquitous in
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 12 year-old male presented with a one-day history of fever and headache on the right side. Two days after admission, he developed a stiff neck
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 8 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 12 year-old male presented with a one-day history of fever and headache on the right side. Two days after admission, he developed a stiff neck
Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate. Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University
 Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Objectives After the lecture, students must know 1. General morphology of pathogenic
Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Objectives After the lecture, students must know 1. General morphology of pathogenic
Section 9: Amebic Meningitis/Encephalitis
 Section 9: Amebic Meningitis/Encephalitis BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. and Balamuthia are microscopic, free-living amebae (single-celled living organisms). Naegleria
Section 9: Amebic Meningitis/Encephalitis BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. and Balamuthia are microscopic, free-living amebae (single-celled living organisms). Naegleria
Pathogenic Free-Living Amebae
 Pathogenic Free-Living Amebae Naegleria fowleri primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) Acanthamoeba spp. granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE) granulomatous skin and lung lesions (primarily immunocompromised)
Pathogenic Free-Living Amebae Naegleria fowleri primary amebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) Acanthamoeba spp. granulomatous amebic encephalitis (GAE) granulomatous skin and lung lesions (primarily immunocompromised)
SPONTANEOUS GRANULOMATOUS AMEBIC ENCEPHALITIS : REPORT OF FOUR CASES FROM THAILAND
 SPONTANEOUS GRANULOMATOUS AMEBIC ENCEPHALITIS : REPORT OF FOUR CASES FROM THAILAND Tumtip Sangruchi 1, Augusto Julio Martinez 2, and Govinda S Visvesvara 3 1Department of Pathology, Siriraj Hospital Mahidol
SPONTANEOUS GRANULOMATOUS AMEBIC ENCEPHALITIS : REPORT OF FOUR CASES FROM THAILAND Tumtip Sangruchi 1, Augusto Julio Martinez 2, and Govinda S Visvesvara 3 1Department of Pathology, Siriraj Hospital Mahidol
Case Report Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis in an Iranian Infant
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 782854, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/782854 Case Report Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis in an Iranian Infant Zahra Movahedi, 1 Mohammad Reza Shokrollahi,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2012, Article ID 782854, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/782854 Case Report Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis in an Iranian Infant Zahra Movahedi, 1 Mohammad Reza Shokrollahi,
Infection of Blastocystis hominis in primary schoolchildren from Nakhon Pathom province, Thailand
 Tropical Biomedicine 23(1): 117 122 (2006) Infection of Blastocystis hominis in primary schoolchildren from Nakhon Pathom province, Thailand Rapeeporn Yaicharoen, Warunee Ngrenngarmlert, Nuttapong Wongjindanon,
Tropical Biomedicine 23(1): 117 122 (2006) Infection of Blastocystis hominis in primary schoolchildren from Nakhon Pathom province, Thailand Rapeeporn Yaicharoen, Warunee Ngrenngarmlert, Nuttapong Wongjindanon,
Granulomatous brain tumor caused by Acanthamoeba
 J Neurosurg64:505-509, 1986 Granulomatous brain tumor caused by Acanthamoeba Case report S. KWAME OFORI-KWAKYE, M.D., DAVID G. SIDEBOTTOM, M.D., JOSEPH HERBERT, M.D., EDWIN G. FISCHER, M.D., AND GOVINDA
J Neurosurg64:505-509, 1986 Granulomatous brain tumor caused by Acanthamoeba Case report S. KWAME OFORI-KWAKYE, M.D., DAVID G. SIDEBOTTOM, M.D., JOSEPH HERBERT, M.D., EDWIN G. FISCHER, M.D., AND GOVINDA
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
Growth Characteristics, Cytopathic Effect in Cell Culture, and
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 190, p. 61-6 0099-2240/0/04-061/0$02.00/0 Vol. 9, No. 4 Growth Characteristics, Cytopathic Effect in Cell Culture, and Virulence in Mice of 6 Type Strains Belonging
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Apr. 190, p. 61-6 0099-2240/0/04-061/0$02.00/0 Vol. 9, No. 4 Growth Characteristics, Cytopathic Effect in Cell Culture, and Virulence in Mice of 6 Type Strains Belonging
Cytology II Study of Cells
 Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Cytology II Study of Cells Biology 20 Cellular Basis of Life 1. Basic unit of Life 2. Composed of one or more cells 3. Arises from pre-existing cells Asexual (Mitosis)/Sexual (Meiosis) 4. Surrounded by
Cell Structure & Function. Source:
 Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Cell Structure & Function Source: http://koning.ecsu.ctstateu.edu/cell/cell.html Definition of Cell A cell is the smallest unit that is capable of performing life functions. http://web.jjay.cuny.edu/~acarpi/nsc/images/cell.gif
Parasitology. Lab. Amoeba
 Parasitology. Lab. Kingdom : Protista Subkingdom : Protozoa Phylum : Sacromastigophora Subphylum : Sarcodina Superclass : Rhizopoda Class : Lobosea Order : Amoebida Amoeba Protozoa Amoebae geneus Entamoeba
Parasitology. Lab. Kingdom : Protista Subkingdom : Protozoa Phylum : Sacromastigophora Subphylum : Sarcodina Superclass : Rhizopoda Class : Lobosea Order : Amoebida Amoeba Protozoa Amoebae geneus Entamoeba
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans:
 The parasite protozoa Phylum: Sarcomastigophora Sarcodina االميبات Amoebae Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans: 1. Entamoeba hartmanii, contain trophozoite and cyst 2. Entamoeba coli, cyst and trophozoite
The parasite protozoa Phylum: Sarcomastigophora Sarcodina االميبات Amoebae Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans: 1. Entamoeba hartmanii, contain trophozoite and cyst 2. Entamoeba coli, cyst and trophozoite
Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp.
 Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. 1 Protozoa-Simple classification Amoebapseudopodium(a)
Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. 1 Protozoa-Simple classification Amoebapseudopodium(a)
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp.
 Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Protozoa-Simple classification Amoeba- pseudopodium(a)
Protozoa: Introduction and classification Amoebae I. Pathogenic amoebae: Entamoeba histolytica, Naegleria fowleri, Acanthamoeba spp. Nimit Morakote, Ph.D. Protozoa-Simple classification Amoeba- pseudopodium(a)
Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases. (Amoebiasis)
 Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases (Amoebiasis) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University This document contains materials modified or
Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases (Amoebiasis) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University This document contains materials modified or
SCREENING OF ANTI-AMOEBIC ACTIVITY ON NAEGLERIA FOWLERI IN EXTRACTS OF THAI MEDICINAL PLANTS
 SCREENING OF ANTI-AMOEBIC ACTIVITY ON NAEGLERIA FOWLERI IN EXTRACTS OF THAI MEDICINAL PLANTS Tarmphong Luangboribun 1,2, Supathra Tiewcharoen 1, Jundee Rabablert 3, Prasert Auewarakul 2, Natchagorn Lumlerdkij
SCREENING OF ANTI-AMOEBIC ACTIVITY ON NAEGLERIA FOWLERI IN EXTRACTS OF THAI MEDICINAL PLANTS Tarmphong Luangboribun 1,2, Supathra Tiewcharoen 1, Jundee Rabablert 3, Prasert Auewarakul 2, Natchagorn Lumlerdkij
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Parasitic Diseases Protozoan and helminthic parasites are emerging as serious
The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells. The Microscopic World of Cells 9/21/2012
 Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Organisms are either: Single-celled, such as most prokaryotes and protists or Multicelled, such as plants, animals, and most fungi How do we study cells? Light microscopes can be used to explore the structures
Asian Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences and Biotechnology
 Research Article ISSN: 2349 7114 Asian Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences and Biotechnology Journal home page: www.ajrpsb.com ENTAMO ENTAMOEBA COLI AS STRONG PHAGOCYTIC PARASITIC ORGANISM Mosab
Research Article ISSN: 2349 7114 Asian Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences and Biotechnology Journal home page: www.ajrpsb.com ENTAMO ENTAMOEBA COLI AS STRONG PHAGOCYTIC PARASITIC ORGANISM Mosab
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Synergistic Activity of Azithromycin and Amphotericin B against Naegleria fowleri In ACCEPTED. Shannon M. Soltow* and George M.
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on October 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.00-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on October 00 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:./aac.00-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Unusual Presentation of Multiple Nerve Palsies with Granulomatous encephalitis Due to Acanthamoeba Species
 Human Parasitic Diseases Case report Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Unusual Presentation of Multiple Nerve Palsies with Granulomatous encephalitis
Human Parasitic Diseases Case report Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Unusual Presentation of Multiple Nerve Palsies with Granulomatous encephalitis
Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside the nucleus but within the cell membrane, includes the organelles, cytosol, and
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins Outer surface has oligosaccharides separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm
Chapter 7. (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell
 Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
Chapter 7 (7-1 and 7-2) A Tour of the Cell Microscopes as Windows to the World of Cells Cells were first described in 1665 by Robert Hooke. By the mid-1800s, the accumulation of scientific evidence led
CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND
 CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND Ampas Wisetmora *1,2, Duangduen Krailas 2, Choosak Nithikethkul 3,Wanchai Phatihattakorn 4, Opart Karnkawinpong 1, Thitima Wongsaroj
CONFIRMATION STATUS OF HELMINTHIASIS IN LOW RISK AREAS IN CENTRAL THAILAND Ampas Wisetmora *1,2, Duangduen Krailas 2, Choosak Nithikethkul 3,Wanchai Phatihattakorn 4, Opart Karnkawinpong 1, Thitima Wongsaroj
2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope. nucleus, nuclear envelope, nucleolus, ribosomes
 Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
Honors Biology Unit 2 Chapter 4 A TOUR OF THE CELL 1. light microscope 2. scanning electron microscope vs. transmission electron microscope 3. surface area to volume ratio 4. prokaryotic cell vs. animal
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes
 Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Review: Characteristics of Living Things Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3, Day 1 Notes 1. Made of 2. Require 3. (species) 4. Maintain 5. 6. to environment 7. 8. materials with surroundings (water,
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81
 Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
Cell Structure Text Ref Pg 4-7, 63-81 The Cellular Basis of Life Before people had a scientific explanation for where life came from, they believed in the theory of spontaneous generation, where organisms
Downloaded from:
 Phu, NH; Hoang Mai, NT; Nghia, HD; Chau, TT; Loc, PP; Thai, leh; Phuong, TM; Thai, CQ; Man, DN; Van Vinh Chau, N; Nga, TV; Campbell, J; Baker, S; Whitehorn, J (2013) Fatal consequences of freshwater pearl
Phu, NH; Hoang Mai, NT; Nghia, HD; Chau, TT; Loc, PP; Thai, leh; Phuong, TM; Thai, CQ; Man, DN; Van Vinh Chau, N; Nga, TV; Campbell, J; Baker, S; Whitehorn, J (2013) Fatal consequences of freshwater pearl
Case Study. Andrew L. Dunn, MD, 1 Tameika Reed, MT (ASCP), 2 Charlotte Stewart, MT (ASCP), 2 Rebecca A. Levy, MD 1,2 * ABSTRACT
 Naegleria fowleri That Induces Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis: Rapid Diagnosis and Rare Case of Survival in a 12-Year-Old Caucasian Girl Andrew L. Dunn, MD, 1 Tameika Reed, MT (ASCP), 2 Charlotte
Naegleria fowleri That Induces Primary Amoebic Meningoencephalitis: Rapid Diagnosis and Rare Case of Survival in a 12-Year-Old Caucasian Girl Andrew L. Dunn, MD, 1 Tameika Reed, MT (ASCP), 2 Charlotte
Plasma Membrane. comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings
 Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Cell Organelles Plasma Membrane comprised of a phospholipid bilayer and embedded proteins separates the cells s contents from its surroundings Cytosol the fluid Cytoplasm cell interior, everything outside
Unit 2:The Cell. Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology
 Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Unit 2:The Cell Section 3: Organelle Structure and Function Mrs. McNamara Biology Organelle-cell part that performs a specific function for the cell Most are surrounded by a membrane Each helps to maintain
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Lectures by Chris C. Romero, updated by Edward J. Zalisko PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fourth Edition Eric Simon, Jane Reece, and Jean Dickey Campbell
By: Brooke Sheppard
 By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
Induced encystment improves resistance to preservation and storage of Acanthamoeba castellanii
 Induced encystment improves resistance to preservation and storage of Acanthamoeba castellanii 141 S. J. CAMPBELL 1,P.R.INGRAM 2, C. W. ROBERTS 2 and F. L. HENRIQUEZ 1 * 1 School of Engineering and Science,
Induced encystment improves resistance to preservation and storage of Acanthamoeba castellanii 141 S. J. CAMPBELL 1,P.R.INGRAM 2, C. W. ROBERTS 2 and F. L. HENRIQUEZ 1 * 1 School of Engineering and Science,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles. 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells
 SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
SBI3U7 Cell Structure & Organelles 2.2 Prokaryotic Cells 2.3 Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus Prokaryotic Cells No membrane bound organelles Has a nucleus Eukaryotic Cells Membrane bound organelles Unicellular
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis
 Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
Chin J Radiol 2001; 26: 45-49 45 CASE REPORT Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings of Eosinophilic Meningoencephalitis Caused by Angiostrongyliasis TSYH-JYI HSIEH 1 GIN-CHUNG LIU 1 CHUAN-MIN YEN 2 YU-TING
Critical Masses. MIDG October 2015 Myra Hardy, Jeremy Carr, Tony He, Nigel Curtis
 Critical Masses MIDG October 2015 Myra Hardy, Jeremy Carr, Tony He, Nigel Curtis Case 2 16yo F 2 weeks focal seizures Intermittent left hemiparesis and sensory symptoms Headache PMHX: Asthma on Seretide
Critical Masses MIDG October 2015 Myra Hardy, Jeremy Carr, Tony He, Nigel Curtis Case 2 16yo F 2 weeks focal seizures Intermittent left hemiparesis and sensory symptoms Headache PMHX: Asthma on Seretide
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Cell Theory Cell Structure and Function Chapter 6 Pg. 94-124 What is a cell? The basic functional unit of all living things. The Cell Theory states All organisms are made of one or more cells. Cells are
Classification - Protozoa. Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba. Stools for O&P Examination. Stool Specimen. What to look for.
 Classification - Protozoa Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba Phylum Phylum Sarcomastigophora Sarcomastigophora Subkingdom Subkingdom Protozoa Protozoa Phylum Phylum Ciliophora Ciliophora Phylum Phylum Apicomplexa
Classification - Protozoa Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba Phylum Phylum Sarcomastigophora Sarcomastigophora Subkingdom Subkingdom Protozoa Protozoa Phylum Phylum Ciliophora Ciliophora Phylum Phylum Apicomplexa
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages :
 Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 4 - Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages
Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 4 - Genus : Chilomastix mesnili Considered to be a non-pathogen, it ' s resides in cecum and colon. The life cycle of this parasite have two stages
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Cell Parts Exam Study Guide
 Cell Parts Exam Study Guide Define these organelles: Cell wall- the definite boundary or wall of a plant cell that provides protection and structural support. Cell membrane- the outer layer that surrounds
Cell Parts Exam Study Guide Define these organelles: Cell wall- the definite boundary or wall of a plant cell that provides protection and structural support. Cell membrane- the outer layer that surrounds
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell
 Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
CNS parasitic infections. Jarmila Klieščiková, MD 1.LF UK
 CNS parasitic infections Jarmila Klieščiková, MD 1.LF UK Cosmopolite distribution Low prevalence Interference with underlying diseases (immunocompromised state) Treatment not always available Main pathogens
CNS parasitic infections Jarmila Klieščiková, MD 1.LF UK Cosmopolite distribution Low prevalence Interference with underlying diseases (immunocompromised state) Treatment not always available Main pathogens
Eukaryotic cell. Premedical IV Biology
 Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Eukaryotic cell Premedical IV Biology The size range of organisms Light microscopes visible light is passed through the specimen and glass lenses the resolution is limited by the wavelength of the visible
Chapter 3. Cell Structure
 Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
Chapter 3 Cell Structure Looking at Cells l The invention of microscopes allowed scientists to view cells for the first time l Scientists use the metric system to measure the size of cells l Metric Units
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Inner Life of Cell. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell Inner Life of Cell Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin
ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease
 ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Cell Organelles and their Functions. Chapter 4 Section 2
 Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Cell Organelles and their s Chapter 4 Section 2 1. Cell Membrane A phospholipid bilayer around the cell that contains proteins and other markers Separates the cell from its environment Secretes materials
Title. Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date DOI. Doc URL.
 Title PLASMACYTOID CELLS OF CANINE PERIPHERAL BLOOD IN ELE Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date 1970-09 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.18.3.125
Title PLASMACYTOID CELLS OF CANINE PERIPHERAL BLOOD IN ELE Author(s)SONODA, Mitsuo; KOBAYASHI, Kosaku CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 18(3): 125- Issue Date 1970-09 DOI 10.14943/jjvr.18.3.125
Household pin w/ bactera. Cell Structure and Function
 Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Household pin w/ bactera Cell Structure and Function Review Atoms have energy levels Electrons hang out in regions surrounding atomic nucleus First shell may hold two electrons (1 orbital) Second shell
Review from Biology A
 Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Chapter 4 Review from Biology A The Cell Theory All organisms are made of cells Cells come from pre-existing cells The cell is the simplest collection of matter that can live Scientists whose work you
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lectures by Edward J. Zalisko
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Campbell Essential Biology, Fifth Edition, and Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology, Fourth Edition Eric J. Simon, Jean L. Dickey, and Jane B.
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 4. Most cells are microscopic. Cells vary in size and shape
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Most cells are microscopic Cells vary in size and shape 10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Most cells are microscopic Cells vary in size and shape 10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm
Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials are separated from cytoplasm by nuclear membrane. Complex structure Also
 Dr. Gugale Pritesh Ramanlal M.Sc., Ph.D., B.Ed., D.M.L.T. Email id - pritesh.gugale09@gmail.com Contact numbernumber- 8446475310 Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials
Dr. Gugale Pritesh Ramanlal M.Sc., Ph.D., B.Ed., D.M.L.T. Email id - pritesh.gugale09@gmail.com Contact numbernumber- 8446475310 Eukaryotic cells are essentially two envelope systems. Nuclear materials
Unit A: Cells. Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell
 Unit A: Cells Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell Standards By the end of this unit you should be able to: Recognize and explain the function of each organelle Look at micrographs/diagrams/pictures and correctly
Unit A: Cells Ch. 4 A Tour of the Cell Standards By the end of this unit you should be able to: Recognize and explain the function of each organelle Look at micrographs/diagrams/pictures and correctly
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism
 Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Cell Anatomy Anatomy = the study of the structures and components of an organism -Types of Cells: 1) Prokaryotic = simple, primitive = no membrane bound nucleus, only a dense, nuclear area = single-celled
Arousal of a New, Life-Taking Threat to the World.. Naegleria Fowleri!!
 Original Article Arousal of a New, Life-Taking Threat to the World.. Naegleria Fowleri!! Somia Gul* and Umaima Alam Faculty of Pharmacy, Jinnah University for Women, Karachi, Pakistan ABSTRACT Address
Original Article Arousal of a New, Life-Taking Threat to the World.. Naegleria Fowleri!! Somia Gul* and Umaima Alam Faculty of Pharmacy, Jinnah University for Women, Karachi, Pakistan ABSTRACT Address
3. Which cell has the greater ratio of surface area to volume?
 Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Chapter 4 Worksheet A Tour of the Cell Exercise 1 Metric System Review/Size and Scale of Our World (4.1) Use the information in the two modules and the chart in Module 4.2 to complete the following table
Free living amoebae and human disease
 Free living amoebae and human disease Evan Bursle Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology Whitmore Street Taringa, Qld 4068, Australia Email: evanbursle@gmail.com Jennifer Robson Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology Whitmore
Free living amoebae and human disease Evan Bursle Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology Whitmore Street Taringa, Qld 4068, Australia Email: evanbursle@gmail.com Jennifer Robson Sullivan Nicolaides Pathology Whitmore
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Thursday, October 16 th
 Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Thursday, October 16 th Good morning. Those of you needing to take the Enzymes and Energy Quiz will start very soon. Students who took the quiz Wednesday: Please QUIETLY work on the chapter 6 reading guide.
Ch 3 Cell Structure 10/1/2008. Cells Under the Microscope. Natural laws limit cell size. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs.
 Ch 3 Cell Structure Cells Under the Microscope Electron microscopes have much higher magnifying and resolving powers than light microscopes. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs. Stolipher Cell size and shape
Ch 3 Cell Structure Cells Under the Microscope Electron microscopes have much higher magnifying and resolving powers than light microscopes. Biology Periods 2, 3, 4, & 6 Mrs. Stolipher Cell size and shape
TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS
 TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS Normal Flora. Normal flora consists of microorganisms that are normally and consistently found in or on the body in the absence of disease. Symbiosis. This is the close
TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS Normal Flora. Normal flora consists of microorganisms that are normally and consistently found in or on the body in the absence of disease. Symbiosis. This is the close
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
MONITORING THE THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY OF ANTIMALARIALS AGAINST UNCOMPLICATED FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND
 SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH MONITORING THE THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY OF ANTIMALARIALS AGAINST UNCOMPLICATED FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND C Rojanawatsirivej 1, S Vijaykadga 1, I Amklad 1, P Wilairatna
SOUTHEAST ASIAN J TROP MED PUBLIC HEALTH MONITORING THE THERAPEUTIC EFFICACY OF ANTIMALARIALS AGAINST UNCOMPLICATED FALCIPARUM MALARIA IN THAILAND C Rojanawatsirivej 1, S Vijaykadga 1, I Amklad 1, P Wilairatna
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates
 Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Section 7 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure (pages 174 181) Key Concept What are the functions of the major cell structures? Comparing a Cell to a Factory (page 174) 1. What is an organelle? 2. Label the structures
Fungal cell walls are rigid with less flexibility due to a combination of more sugar (more chitin) and protein flexibility.
 Cell Structure Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by yourself or in a group, answer the following questions about the Cell Structure material. This assignment is worth 40 points with the possible
Cell Structure Assignment Score. Name Sec.. Date. Working by yourself or in a group, answer the following questions about the Cell Structure material. This assignment is worth 40 points with the possible
Cell Structure. Present in animal cell. Present in plant cell. Organelle. Function. strength, resist pressure created when water enters
 Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Cell Structure Though eukaryotic cells contain many organelles, it is important to know which are in plant cells, which are in animal cells and what their functions are. Organelle Present in plant cell
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Learning Objectives. 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic Morphology 5. Name of diesease 6. Prevention and Control
 Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
Cell Structure and Function. Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages and 68-69
 Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Cell Structure and Function Biology 12 Unit 1 Cell Structure and Function Inquiry into Life pages 45 59 and 68-69 Assignments for this Unit Pick up the notes/worksheet for this unit and the project There
Structure and Function of Cells
 Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Structure and Function of Cells Learning Outcomes Explain the cell theory Explain why cell size is usually very small Describe the Fluid Mosaic Model of membranes Describe similarities and differences
Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell.
 Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
Section 3: Eukaryotic cells contain organelles that allow the specializations and the separation of functions within the cell. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What I Learned Essential Questions
THE PREVALENCE OF ENTEROBIUS VERMICULARIS AMONG PRIMARY SCHOOL STUDENTS IN SAMUT PRAKAN PROVINCE, THAILAND
 THE PREVALENCE OF ENTEROBIUS VERMICULARIS AMONG PRIMARY SCHOOL STUDENTS IN SAMUT PRAKAN PROVINCE, THAILAND C Nithikathkul 1, B Changsap 2, S Wannapinyosheep 2, C Poister 3 and P Boontan 2 Departments of
THE PREVALENCE OF ENTEROBIUS VERMICULARIS AMONG PRIMARY SCHOOL STUDENTS IN SAMUT PRAKAN PROVINCE, THAILAND C Nithikathkul 1, B Changsap 2, S Wannapinyosheep 2, C Poister 3 and P Boontan 2 Departments of
ULTRA STRUCTURE CHANGES OF DIOSGENIN-TREATED HUMAN MONOCYTE U937-DERIVED MACROPHAGES INDUCED BY NAEGLERIA FOWLERI LYSATE
 Effect of Diosgenin on Human Macrophages Induced by N. fowleri Lysate ULTRA STRUCTURE CHANGES OF DIOSGENIN-TREATED HUMAN MONOCYTE U937-DERIVED MACROPHAGES INDUCED BY NAEGLERIA FOWLERI LYSATE Supathra Tiewcharoen
Effect of Diosgenin on Human Macrophages Induced by N. fowleri Lysate ULTRA STRUCTURE CHANGES OF DIOSGENIN-TREATED HUMAN MONOCYTE U937-DERIVED MACROPHAGES INDUCED BY NAEGLERIA FOWLERI LYSATE Supathra Tiewcharoen
Objectives. To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles.
 Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
Cell Organelles 3.2 Objectives To determine the differences between plant and animal cells To discover the structure and function of cellular organelles. Basic Cellular Structures Cell membrane (cytoplasmic
