Renin Inhibitors: Novel Agents for Renoprotection or a Better Angiotensin Receptor Blocker for Blood Pressure Lowering?
|
|
|
- George Patrick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Renin Inhibitors: Novel Agents for Renoprotection or a Better Angiotensin Receptor Blocker for Blood Pressure Lowering? Eduardo Pimenta, MD a, *, Suzanne Oparil, MD b KEYWORDS Hypertension Renin inhibitors Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) is an important modulator of blood pressure (BP) and volume regulation in both normotensive and hypertensive persons. 1 The development of pharmacologic antagonists to its various components has proved useful in the treatment of hypertension and related target-organ damage. Renin, which is synthesized and released predominately from the juxtaglomerular granular epithelioid cells in the kidney, catalyzes the formation of angiotensin (Ang) I from angiotensinogen. Ang I, in turn, is processed by angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and other proteases to form Ang II (Fig. 1). Renin is required for the production of Ang I and II. Renin is synthesized as a preprohormone that contains a signal peptide that leads the inactive molecule to the exterior of the cell. 2 Prorenin is rendered enzymatically active by both proteolytic and nonproteolytic processes. Proteolytic activation occurs via the actual removal of the pro-peptide chain. Most proteolytic activation of prorenin occurs within the juxtaglomerular cells. 3 Nonproteolytic activation is a 2-step process that allows prorenin that has been secreted from the juxtaglomerular cells into the circulation to acquire enzymatic activity without removal of the prosegment. While both prorenin and active renin are secreted from the juxtaglomerular cells into the circulation, prorenin is the predominant circulating form, accounting for approximately 90% of total renin in normal human plasma and for an even greater portion of the total in diabetic patients. 4 6 The major physiologic and pathophysiologic effects of the RAAS are mediated by the octapeptide Ang II. Ang II has a variety of biological actions that lead to hypertension and related target organ damage. It is a potent vasoconstrictor and Dr. Pimenta has no conflicts. Dr. Oparil has received grants-in-aid from Abbott Laboratories, Astra Zeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers-Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Forest Laboratories, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Merck & Co, Pfizer, Sankyo, Sanofi-Aventis, and Schering-Plough; and has served as a consultant for Bristol Myers-Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Merck & Co, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi Aventis, and The Salt Institute. a Department of Hypertension and Nephrology, Dante Pazzanese Institute of Cardiology, Av. Dr. Dante Pazzanese, 500, Sao Paulo, SP, Brazil, b Vascular Biology and Hypertension Program, University of Alabama at Birmingham, th Street South, ZRB 1034, Birmingham, AL , USA * Corresponding author. address: espimenta@hotmail.com (E. Pimenta). Cardiol Clin 26 (2008) doi: /j.ccl /08/$ see front matter ª 2008 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. cardiology.theclinics.com
2 528 Pimenta & Oparil PRORENIN RENIN RENIN RECEPTOR AT1 RECEPTOR ANGIOTENSINOGEN ANG I ANG II ACE CHYMASE AT2 RECEPTOR Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; Ang, angiotensin; AT1, angiotensin II type 1 receptor; AT2, angiotensin II type 2 receptor. stimulates sodium retention directly via renal vascular and tubular effects and indirectly by increasing aldosterone synthesis and release, thirst, and antidiuretic hormone release. Ang II also increases sympathetic outflow from the brain and norepinephrine release from peripheral sympathetic nerve terminals. In addition, Ang II is a potent growth hormone and mitogen, inducing both cell hyperplasia and hypertrophy. Importantly, Ang II inhibits renin release via a feedback mechanism that tends to stabilize BP in the normal range in normotensive individuals. The actions of Ang II can be antagonized by blocking Ang II at the AT1 receptor site or by reducing the generation of Ang II. b-blockers (BB) inhibit the b-adrenergic receptor-mediated release of renin from the kidney, thus reducing plasma renin activity (PRA). 7,8 However, renin secretion from the juxtaglomerular cells is also regulated by chloride transport across the renal macula densa cells. Ang II receptor activity and renal perfusion pressure play important roles in renin release as well. b-adrenergic blockade alone can therefore only partially decrease the secretion of renin and reduce the generation of Ang II. ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) lower BP and prevent target organ damage and cardiovascular disease events by blocking the RAAS. ACE inhibitors were first developed as an unintended consequence of the search for an explanation for the drop in BP induced by the venom of a pit viper. 9 The discovery in the venom of the snake Bothrops jararaca of a peptide that blocked kininase II led to the synthesis of the ACE inhibitors. 10,11 ACE inhibitors are potent orally active inhibitors of the enzyme that converts the inactive decapeptide Ang I into the active octapeptide Ang II. Although ACE inhibitors decrease Ang II generation, they stimulate PRA by blocking feedback inhibition of renin release (Table 1). ARBs are selective antagonists of the AT1 receptor of Ang II that also stimulate PRA via blockade of Ang II mediated feedback inhibition of renin release. More recently, aliskiren, the first in a new class of orally effective direct renin inhibitors (DRIs) was approved for the treatment of hypertension. In this review, we discuss the history of the development of DRIs and available data regarding the effects of DRIs in the treatment of hypertension and related target organ damage. HISTORY Renin was discovered in 1898 by Tigerstedt and Bergman 12 with the observation that extracts of renal tissues increase BP. Since then numerous attempts have been made to inhibit renin and thus lower BP. The concept of renin inhibition for managing hypertension by blocking the RAAS pathway at its point of activation is very attractive since the renin-angiotensinogen reaction is the first and rate-limiting step in the synthesis of Ang II. It has been postulated that blocking the RAAS by inhibiting the catalytic action of renin directly would be potentially more efficacious in treating hypertension and associated with fewer adverse Table 1 Effects of antihypertensive agents on targets of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system pathway Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Renin Concentration Plasma Renin Activity Direct renin inhibitors Y Y [ Y Angiotensin receptor [ [ [ [ blockers Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors [ Y [ [ [ increased; Ydecreased. Data from Staessen JA, Li Y, Richart T. Oral renin inhibitors. Lancet 2006;368: ; with permission.
3 Renin Inhibitors 529 effects than blocking downstream components of the RAAS. 13 While the concept of inhibiting renin directly is appealing, the development of effective orally active DRIs has been technically challenging. First, preclinical studies of DRIs designed for human use must be performed in primates, such as marmosets, or in transgenic models expressing both human renin and angiotensinogen genes, because of the species specificity of the reninangiotensinogen reaction. 14 The sequence of renin differs greatly among species, such that human renin will not cleave heterologous angiotensinogen and inhibitors designed for human renin will not inhibit the activity of heterologous renin. Second, the reagents used in the first attempts to inhibit human renin, renin antibodies, and synthetic analogs of the prosegment of prorenin, proved unsatisfactory for a variety of reasons. 15,16 These proteins had short half lives when administered parenterally, were inactive when administered orally, and led to immunologic complications such as the development of autoantibodies. Accordingly, developmental efforts shifted toward a search for effective small molecule renin inhibitors. The first successful small molecule inhibitor of renin was pepstatin, an aspartyl protease inhibitor. 17 While pepstatin successfully inhibited renin in vitro, it had a variety of disadvantages, including lack of selectivity for renin and poor solubility in water. Structural derivatives of pepstatin increased its solubility and selectivity for renin, but none of these compounds was ever used clinically because of low efficacy in vivo, lack of oral bioavailability, and high cost of synthesis The first clinical experience with a selective renin inhibitor was obtained with the angiotensinogen analog renin inhibitor peptide (RIP). 21 Although RIP effectively reduced BP during intravenous administration in humans, it was abandoned because of evidence of a direct cardiodepressant effect unrelated to the renin inhibition. Subsequent efforts to develop small molecule renin inhibitors were directed toward synthesizing peptide analogs of the N-terminal amino acid sequence of angiotensinogen that contained amino acid substitutions at the renin cleavage site (scissile bond). These peptide inhibitors had limited potency (micromolar range) and were replaced with noncleavable analogs that had the advantages of greater potency (nanomolar range) and oral bioavailability. 13 Some of those peptidelike analogs, eg, remikiren, enalkiren, and zankiren, reduced PRA and increased plasma renin concentration after oral administration in humans, indicating renin inhibition However, these drugs had a weak BP lowering effect when administered orally. 25,26 Oral administration of remikiren and parenteral infusion of enalkiren in healthy saltrestricted volunteers did not lower BP or alter heart rate, but did evoke dose-dependent decreases in PRA, Ang I, and Ang II that were rapidly reversed after termination of the treatments. 27,28 Highdose intravenous boluses of enalkiren did reduce BP in hypertensive patients when salt-depleted, while heart rate remained unchanged. 29 A comparison of placebo, enalaprilat (1.25 mg intravenously), and enalkiren (0.03 to 1.00 mg/kg intravenously) in hypertensive patients pretreated with hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) to activate the RAAS showed that enalkiren produced decreases in systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP) that were statistically significant compared with placebo but less robust than seen with enalaprilat. 30 Similarly, both orally and intravenously administered remikiren (Ro ) produced significant decreases in SBP, PRA, and circulating Ang II in hypertensive subjects. 31 Oral administration of another compound, CGP-38560A, was compared with captopril, at what were considered to be maximal doses: 0.25 mg/kg of the renin inhibitor and 50 mg of captopril. 32 BP decreased markedly after captopril (15.3 mm Hg), but not after renin inhibitor (6.4 mm Hg) administration. The peptidomimetic renin inhibitors failed as antihypertensive medications because of their large molecular size and lipophilicity, which resulted in poor intestinal absorption and considerable first-pass hepatic metabolism, significantly limiting oral bioavailability. 23 In addition, their short duration of action and weak BP-lowering activity, as well as the successful marketing of ACE inhibitors and ARBs in the 1980s and 1990s contributed to the failure of the first-generation DRIs. 33 ALISKIREN is a low molecular weight (MW 552, free base) nonpeptidic renin inhibitor that consists of a substituted octanamide (Fig. 2). The extended peptide-like backbone that characterized earlier peptidomimetic renin inhibitors was eliminated. The addition of various alkylether aromatic side chains promoted interaction with the S3sp subpocket of the active site of renin and dramatically enhanced the affinity of aliskiren for renin and its selectivity over other aspartic peptidases. Retrosynthesis analysis was used to simplify the synthetic process and reduce the high cost of manufacture. 13, the only orally active renin inhibitor approved for the treatment of hypertension in humans, is a competitive transition state analog
4 530 Pimenta & Oparil Fig. 2. Representation of the 3-dimensional structure of aliskiren. (From Gradman AH, Kad R. Renin inhibition in hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008; 51:519 28; with permission.) and selective inhibitor of human renin. It has a therapeutic potential similar to that of other antagonists of the RAAS. 34 In humans, the plasma concentration of aliskiren increases dose-dependently after oral administration in doses of 40 to 640 mg/ day, peaking after 3 to 6 hours. 35 The average plasma half-life is 23.7 hours, ranging from 20 to 45 hours, making aliskiren suitable for once-daily administration (Table 2). The oral bioavailability of aliskiren in humans is limited (2.7%). 35 is 47% to 51% protein bound and the steady-state plasma concentration is reached after 5 to 8 days of treatment. The main elimination route of aliskiren is via biliary excretion as unmetabolized drug. 35 is more potent and selective for human renin than the other orally active DRIs, ie, remikiren and enalkiren. is not metabolized by cytochrome P450, and thus has low potential for significant interactions with other drugs, eg, warfarin, lovastatin, digoxin, valsartan, amlodipine, metformin, celecoxib, atenolol, atorvastatin, ramipril, and HCTZ effectively blocks the RAAS. In a double-blind cross-over study in 18 healthy volunteers receiving a low-sodium diet, the effects of four oral doses of aliskiren (40, 80, 160, and 640 mg/day) compared with placebo and the ACE inhibitor enalapril (20 mg) on components of RAAS were evaluated. 35 reduced PRA in a dosedependent manner after both a single oral dose and 8 days of repeated once-daily dosing. The highest doses of aliskiren reduced Ang II levels by a maximum of 89% and 75% on days 1 and 8, respectively, compared with placebo, and aliskiren R 80 mg/day decreased plasma and urinary aldosterone levels by 40% and 50%, respectively. Enalapril reduced Ang II levels similarly to aliskiren, but also increased PRA 15-fold. The hormonal effects of dual RAAS blockade with aliskiren and the ARB valsartan were evaluated in 12 mildly sodium-depleted normotensive individuals in a double-blind crossover-designed study. 40 Participants received aliskiren 300 mg, valsartan 160 mg, a combination of aliskiren 150 mg plus valsartan 80 mg, or placebo. Valsartan monotherapy increased PRA, Ang I, and Ang II, while PRA, Ang I, and Ang II levels with combination therapy were similar to placebo, indicating that the addition of aliskiren to valsartan eliminates the compensatory increase in PRA and Ang caused by ARBs. RENOPROTECTIVE EFFECTS OF ALISKIREN Renoprotective effects of aliskiren have been demonstrated in double transgenic rats (dtgr) that express genes for both human renin and angiotensinogen. has been compared with valsartan in preventing target-organ damage in dtgr. Matched 6-week-old dtgr received either no treatment, low-dose or high-dose aliskiren, or low-dose or high-dose valsartan. 14 Untreated dtgr showed severe hypertension, albuminuria, and increased serum creatinine by week 7, with a 100% mortality rate by week 9. In Table 2 Pharmacokinetic properties of oral renin inhibitors Bioavailability, % IC 50, nmol/l Plasma Half Life, h (SD) (7.6) CGP < Enalkiren NA (0.4) Remilkiren < (4.1) Zankiren NA 1.1 NA IC 50 is the concentration needed for 50% inhibition of human renin. NA indicates data not available. Data from Staessen JA, Li Y, Richart T. Oral renin inhibitors. Lancet 2006;368: ; with permission.
5 Renin Inhibitors 531 contrast, both doses of aliskiren and high-dose valsartan lowered BP, reduced albuminuria and creatinine levels, and resulted in 100% survival at week 9. Treatment with aliskiren and high-dose valsartan also reduced left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH), and the magnitude of the aliskiren effect was somewhat dose-dependent. Other animal studies showed that aliskiren protects the kidney by reducing renal inflammation and albuminuria. Administration of aliskiren or losartan to dtgr and control Sprague-Dawley rats reduced albuminuria and complement activation. 41 In another study performed in a rat model of advanced diabetic nephropathy, aliskiren reduced albuminuria and other markers of renal damage, including expression of transforming growth factor (TGF)-b and collagens III and IV. 42 When aliskiren was compared with ACE inhibitors or ARBs in these models, the renal and cardiac protective effects were approximately equal. 14,42 also reduces albuminuria in humans. A study of 15 patients with type 2 diabetes and elevated urinary albumin/creatinine ratio (UACR > 30 mg g 1 ) examined the effects on SBP and UACR of treatment with aliskiren 300 mg once daily and furosemide in a stable dose for 28 days, followed by a 4-week withdrawal period. 43 Both 24-hour SBP assessed by ambulatory BP monitoring and UACR decreased significantly with aliskiren. UACR decreased significantly (17%) in the first 2 to 4 days of treatment and reached a maximum reduction of 44% at the end of the treatment period (Fig. 3). UACR decreased progressively throughout the treatment period, whereas the 24-hour BP did not fall further after day 7. Five of the 15 patients had greater than 50% reduction in albuminuria at the end of treatment compared with baseline; 11 of the 15 had greater than 25% reduction, and 13 had greater than 10% reduction. During posttreatment washout, UACR remained significantly below baseline for 12 days. ALISKIREN IN THE TREATMENT OF HUMAN HYPERTENSION, both as monotherapy and in combination with other agents, has been evaluated extensively in hypertensive patients. monotherapy has a dose-dependent antihypertensive effect that is significantly greater than placebo. In a randomized double-blind study, 652 patients with mild to moderate hypertension defined as DBP R 95 and <110 mm Hg, were assigned to receive placebo, irbesartan 150 mg, or once-daily doses of aliskiren (150, 300, or 600 mg) for 8 weeks after a 2-week placebo run-in period. 44 Once-daily oral treatment with each of the three doses of aliskiren significantly decreased mean sitting SBP and DBP compared with placebo (Fig. 4). No additional BP reduction was obtained with aliskiren 600 mg. After 8 weeks of treatment, 21% and 50% (P <.05) of patients assigned to placebo and aliskiren 300 mg, respectively, achieved BP control defined as BP lower than 140/90 mm Hg. In another randomized, double-blind, placebocontrolled trial, 672 hypertensive patients (mean sitting DBP 95 to 109 mm Hg) received placebo or aliskiren 150, 300, or 600 mg once daily. 45 After 8 weeks, aliskiren 150, 300, and 600 mg significantly reduced mean sitting BP (systolic/diastolic) by 13.0/10.3, 14.7/11.1, and 15.8/12.5 mm Hg from baseline, respectively, versus 3.8/4.9 mm Hg with placebo (all P <.0001 for SBP and DBP). significantly reduced mean 24-hour ambulatory BP and its BP-lowering effect persisted for up to 2 weeks after treatment withdrawal. 150, 300, and 600 mg reduced PRA (geometric Fig. 3. Urinary albumin/creatinine ratio in diabetic patients with microor macroalbuminuria treated with aliskiren for 28 days followed by 28 days washout. (From Persson F, Rossing P, Schjoedt KJ, et al. Time course of the antiproteinuric and antihypertensive effects of direct renin inhibition in type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int 2008;73(12): ; with permission).
6 532 Pimenta & Oparil Trough Sitting DBP Reduction (mm Hg) Placebo 150 mg * 300 mg 600 mg ** ** Fig. 4. Blood pressure reduction achieved with aliskiren compared with placebo. SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure. *P <.01 compared with placebo; **P <.0001 compared with placebo Placebo 150 mg 300 mg 600 mg Trough Sitting SBP Reduction (mm Hg) * -16 ** ** mean change from baseline) by 79.5%, 81.1%, and 75.0%, respectively, whereas PRA increased by 19.5% from baseline in the placebo group. treatment resulted in dose-dependent increases from baseline in renin concentration. was well tolerated; overall adverse event rates were 40.1%, 46.7%, and 52.4% with aliskiren 150, 300, and 600 mg, respectively, compared with 43.0% with placebo. A pooled analysis that included 8481 patients who participated in double-blind trials and received aliskiren monotherapy or placebo for 8 to 12 weeks showed that once-daily aliskiren, 150 or 300 mg, produced reductions in mean trough sitting DBP of 10.1 and 11.8 mm Hg, respectively, compared with 6.2 mm Hg for placebo (P <.0001). 46 Trough SBP was lowered by 12.5 and 15.2 mm Hg, compared with 5.9 mm Hg for placebo (P <.0001). There were no statistically significant differences in the magnitude of BP reduction in men versus women or in patients younger versus older than 65 years. monotherapy has been compared with representatives of several different classes of antihypertensive medications and has been shown to produce comparable or greater reductions in BP. For example, in a double-blind study, 842 patients with hypertension (mean sitting DBP 95 to 109 mm Hg) were randomized to aliskiren 150 mg or the ACE inhibitor ramipril 5 mg. 47 Dose titration (to aliskiren 300 mg/ramipril 10 mg) and subsequent addition of hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg, titrated to 25 mg if required) were permitted at weeks 6, 12, 18, and 21 for inadequate BP control. The active treatment period was completed by 81.6% of patients. At week 26, aliskiren-based therapy produced greater mean reductions in SBP (17.9 versus 15.2 mm Hg, P ) and DBP (13.2 versus 12.0 mm Hg, P 5.025) and higher rates of SBP control (<140 mmhg; 72.5% versus 64.1%, P ) compared with ramipril-based therapy. During withdrawal, BP increased more rapidly after stopping ramipril-based than aliskiren-based therapy.
7 Renin Inhibitors 533 When used in combination with a thiazide diuretic, aliskiren is more effective than either monotherapy in reducing BP. In an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, 2776 patients with mean sitting DBP 95 to 109 mm Hg were randomized to receive once-daily treatment with aliskiren (75, 150, or 300 mg), hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) (6.25, 12.5, or 25 mg), the combination of aliskiren and HCTZ, or placebo, in a factorial design. 48 Combination treatment was superior to both component monotherapies in reducing BP (maximum SBP/DBP reduction of 21.2/14.3 mm Hg from baseline with aliskiren/hctz 300/25 mg), and resulted in a higher responder rate (patients with DBP < 90 mm Hg and/or R10 mm Hg reduction) and a better control rate (patients achieving SBP/DBP < 140/90 mm Hg) than either monotherapy. monotherapy reduced PRA by up to 65% from baseline and when HCTZ was combined with aliskiren, decreases in PRA of 46.1% to 63.5% were observed. Dual RAAS inhibition with maximum recommended doses of the DRI aliskiren and the ARB valsartan has shown greater antihypertensive efficacy than monotherapy with either agent. In a doubleblind study, 1797 patients with hypertension (mean sitting DBP 95 to 109 mm Hg and 8-hour daytime ambulatory DBP R 90 mm Hg) were randomly assigned to receive once-daily aliskiren 150 mg, valsartan 160 mg, a combination of aliskiren 150 mg and valsartan 160 mg, or placebo for 4 weeks, followed by forced titration to maximum recommended doses for another 4 weeks. 49 At week 8, the mean sitting SBP was lowered from baseline by 17.2, 12.8, 13.0, and 4.6 mm Hg, respectively, and mean sitting DBP was lowered from baseline by 12.2, 9.7, 9.0, and 4.1 mm Hg, respectively, with the combination of aliskiren 300 mg and valsartan 320 mg, valsartan 320 mg monotherapy, aliskiren 300 mg monotherapy, and placebo (P <.0001 combination compared with placebo or either monotherapy) (Fig. 5). The proportion of patients achieving a successful response to treatment at week 8 was significantly higher with the combination of aliskiren and valsartan (66%) than with aliskiren alone (53%; P ) or valsartan alone (55%; P 5.001). Valsartan monotherapy produced significantly greater increases in PRA from baseline than did placebo (160% versus 18%; P ). By contrast, aliskiren alone significantly reduced PRA by 73% (P <.0001 versus placebo), while the combination of aliskiren and valsartan led to a 44% reduction in PRA (P <.0001 versus placebo). The combination of aliskiren and valsartan provided significantly greater reductions in plasma aldosterone concentration from baseline at week 8 than did placebo ( 31% versus 17%; P <.0001). Valsartan alone also reduced aldosterone concentration ( 25%; P versus placebo), while aliskiren monotherapy had no significant effect on aldosterone concentration. The rates of adverse events and laboratory abnormalities were similar in all groups. Some have hypothesized that reactive renin secretion may limit the effectiveness of DRIs. 50 Although aliskiren suppresses PRA, it causes major reactive increases in plasma renin concentration. If the system is at all leaky, allowing even a small percentage of the excess prorenin generated during DRI treatment to be activated, the antihypertensive effect of the DRI may be offset, limiting its utility as an antihypertensive agent. Further study and additional clinical experience with aliskiren and other DRIs, as they become available, are needed to validate or refute this hypothesis. Blood Pressure Reduction (mm Hg) * Systolic * * * Diastolic * Fig. 5. Effect of study treatments on mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure. *P <.0001 compared with placebo; yp <.0001 compared with aliskiren/ valsartan combination * /valsartan Valsartan placebo
8 534 Pimenta & Oparil SUMMARY Introduction of the DRI aliskiren has opened doors for newer possibilities in antihypertensive therapy. has antihypertensive efficacy comparable to other classes of antihypertensive medications, including diuretics, ACEinhibitors, ARBs, and calcium channel blockers and with a tolerability and safety profile similar to placebo. It also has additive antihypertensive effects when combined with these other drug classes. Preliminary studies of the effects of aliskiren on target organ damage demonstrate comparable or greater efficacy compared with other RAAS antagonists. Results of clinical outcome trials are needed to establish the role of this novel class of antihypertensive medication in the therapeutic armamentarium. REFERENCES 1. Pimenta E, Oparil S. Etiology and pathogenesis of systemic hypertension. In: Crawford MH, DiMarco JP, Paulus WJ, editors. Cardiology, 3rd edition. London: Mosby, in press. 2. Danser AH, Denium J. Renin, pro-renin and putative (Pro)renin receptor. Hypertension 2005;46: Reudelhuber TL, Ramla D, Chiu L, et al. Proteolytic processing of human pro-renin in renal and nonrenal tissues. Kidney Int 1994;46: Danser AH, Derkx FH, Schalekamp MA, et al. Determinants of interindividual variation of renin and pro-renin concentrations: evidence for a sexual dimorphism of (pro)renin levels in humans. J Hypertens 1998;16: Luetscher JA, Kraemer FB, Wilson DM, et al. Increased plasma inactive renin in diabetes mellitus. A marker of microvascular complication. N Engl J Med 1985;312: Price DA, Porter LE, Gordon M, et al. The paradox of the low-renin state in diabetic nephropaty. J Am Soc Nephrol 1999;10: Bühler FR, Laragh JH, Vaughan ED, et al. Antihypertensive action of propranolol: specific anti-renin responses in high and normal renin forms of essential, renal, renovascular and malignant hypertension. Am J Cardiol 1973;32: Michelakis AM, McAllister RG. The effect of chronic adrenergic receptor blockade on plasma renin activity in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1972;34: Ondetti MA. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science 1977;196: Ferreira SH. A bradykinin-potentiating factor present in the venom of Bothrops jararaca. Br J Pharmacol 1965;24: Ferreira SH, Greene X. Isolation of bradykininpotentiating peptides from Bothrops jararaca venom. Biochemistry 1970;9: Tigerstedt R, Bergman PG. Niere und Kreislauf. Skand Arch Physiol 1898;8: Gradman AH, Kad R. Renin inhibition in hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;51: Pils B, Shagdarsuren E, Wellner M, et al., a human renin inhibitor, ameliorates cardiac and renal damage in double-transgenic rats. Hypertension 2005;46: Azizi M, Webb R, Nussberger J, et al. Renin inhibition with aliskiren: where are we now, and where are we going? J Hypertens 2006;24: Michel JB, Galen FX, Guettier C, et al. Immunological approach to blockade of the renin-substrate reaction. J Hypertens 1989;7:S Gross F, Lazar J, Orth H. Inhbition of the reninangiotensinogen reaction by pepstatin. Science 1972;175: Evin G, Gardes J, Kreft C, et al. Soluble pepstatins: a new approach to blockade in vivo of the renin angiotensin system. Clin Sci 1978;55:167s 71s. 19. Eid M, Evin G, Castro B, et al. New renin inhibitors homologous with pepstatin. Biochem J 1981;197: Boger J, Lohr NS, Ulm EH, et al. Novel renin inhibitors containing the amino acid statine. Nature 1983;303: Zusman RM, Burton J, Christensen D, et al. Hemodynamic effects of a competitive renin in inhibitory peptide in humans. Evidence for multiple mechanisms of action. Trans Assoc Am Physicians 1983; 96: Macfayden RJ, Jones CR, Doig JK, et al. Responses to an orally active renin inhibitor, remikiren (Ro ), after controlled salt depletion in humans. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1995;25: Rongen GA, Lenders JW, Smits P, et al. Clinical pharamacokinetics and efficacy of renin inhibitors. Clin Pharmacokinet 1995;29: Himmelmann A, Bergbrant A, Svensson A, et al. Remikiren (Ro ) an orally active renin inhibitor in essential hypertension. Effects on blood pressure and the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Am J Hypertens 1996;9: Ménard J, Boger RS, Moyse DM, et al. Dosedependent effects of the renin inhibitor zankiren HCl after a single oral dose in mildly sodium-depleted normotensive subjects. Circulation 1995;91: Rongen GA, Lenders JW, Kleinbloesem CH, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of the renin inhibitor Ro in patients with hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1993;54: Camenzind E, Nussberger J, Juillerat L, et al. Effect of the renin response during renin inhibition: oral Ro in normal humans. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1991;18:
9 Renin Inhibitors Delabays A, Nussberger J, Porchet M, et al. Hemodynamic and humoral effects of the new renin inhibitior enalkiren in normal humans. Hypertension 1989; 13: Weber MA, Neutel JM, Essinger I, et al. Assessment of renin dependency of hypertension with a dipeptide renin inhibitor. Circulation 1990;81: Neutel JM, Luther RR, Boger RS, et al. Immediate blood pressure effects of the renin inhibitor enalkiren and the ACE inhibitor enalaprilat. Am Heart J 1991; 122: Van den Meiracker AH, Admiraal PJ, Man in t Veld AJ, et al. Prolonged blood pressure reduction by orally active renin inhibitor RO in essential hypertension. Br Med J 1990;301: Jeunemaitre X, Menard J, Nussberger J, et al. Plasma angiotensin, renin and blood pressure during acute renin inhibition by GCP A in hypertensive patients. Am J Hypertens 1989;2: Staessen JA, Li Y, Richart T. Oral renin inhibitors. Lancet 2006;368: Nussberger J. Renin inhibitors. In: Oparil S, Weber MA, editors. Hypertension: a companion to Brenner and Rector s the kidney, 2nd edition. Philadelphia: Elsevier; p Nussberger J, Wuerzner J, Jensen C, et al. Angiotensin II supression in humans by the orally active renin inhibitor aliskiren (SPP100). Comparison with enalapril. Hypertension 2002;39:e1 e Dieterle W, Corynen S, Vaidyanathan S, et al. Effect of the oral renin inhibitor aliskiren on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of a single dose of warfarin in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2004;58: Dieterle W, Corynen S, Vaidyanathan S, et al. Pharmacokinetic interactions of the oral renin inhibitor aliskiren with lovastatin, atenolol, celecoxib and cimetidine. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005;43: Dieterich H, Kemp C, Vaidyanathan S, et al. Pharmacokinetic interaction of the oral renin inhibitor aliskiren with hydrochlorothiazide in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2006;79:P12 [abstract]. 39. Dieterich H, Kemp C, Vaidyanathan S, et al., the first in a new class or orally effective renin inhibitors, has no clinically significant drug interactions with digoxin in healthy volunteers. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2006;79:P64 [abstract]. 40. Azizi M, Ménard J, Bissery A, et al. Pharmacologic demonstration of the synergistic effects of a combination of the renin inhibitor aliskiren and the AT1 receptor antagonist valsartan on the angiotensin IIrenin feedback interruption. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004;15: Shagdarsuren E, Wellner M, Braesen JH, et al. Complement activation in angiotensin II-induced organ damage. Circ Res 2005;97: Kelly DJ, Zhang Y, Moe G, et al., a novel renin inhibitor, is renoprotective in a model of advanced diabetic nephropaty in rats. Diabetologia 2007;50: Persson F, Rossing P, Schjoedt KJ, et al. Time course of the antiproteinuric and antihypertensive effects of direct renin inhibition in type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int 2008;73(12): Gradman AH, Schmieder RE, Lins RL, et al., a novel orally effective rennin inhibitor, provides dose-dependent antihypertensive efficacy and placebo-like tolerability in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2005;111: Oh BH, Mitchell J, Herron JR, et al., an oral rennin inhibitor, provides dose-dependent efficacy and sustained 24-h blood pressure control in patients with hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49: Dahlöf B, Anderson DR, Arora V, et al., a direct renin inhibitor, provides antihypertensive efficacy and excellent tolerability independent of age or gender in patients with hypertension. J Clin Hypertens 2007;9:A157 [abstract]. 47. Andersen K, Weinberger MH, Egan B, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of aliskiren, an oral direct renin inhibitor, and ramipril in hypertension: a 6-month, randomized, double-blind trial. J Hypertens 2008;26: Villamil A, Chysant SG, Calhoun D, et al. Renin inhibition with aliskiren provides additive antihypertensive efficacy when used in combination with hydrochlorothiazide. J Hypertens 2007;25: Oparil S, Yarows SA, Patel S, et al. Efficacy and safety of combined use of aliskiren and valsartan in patients with hypertension: a randomized double-blind trial. Lancet 2007;370: Sealey JE, Laragh JH., the first renin inhibitor for treating hypertension: reactive renin secretion may limit its effectiveness. Am J Hypertens 2007;20:
Introduction. Kristina Allikmets REVIEW
 REVIEW Aliskiren an orally active renin inhibitor. Review of pharmacology, pharmacodynamics, kinetics, and clinical potential in the treatment of hypertension Kristina Allikmets Department of Drug Development
REVIEW Aliskiren an orally active renin inhibitor. Review of pharmacology, pharmacodynamics, kinetics, and clinical potential in the treatment of hypertension Kristina Allikmets Department of Drug Development
Renin inhibition with aliskiren in hypertension: focus on aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy
 REVIEW Renin inhibition with aliskiren in hypertension: focus on aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy Kalathil K Sureshkumar Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Allegheny General Hospital,
REVIEW Renin inhibition with aliskiren in hypertension: focus on aliskiren/hydrochlorothiazide combination therapy Kalathil K Sureshkumar Division of Nephrology and Hypertension, Allegheny General Hospital,
The renin-angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is
 James L. Pool, MD Abstract Background: Despite the availability of many effective, well-tolerated drugs, a significant proportion of treated hypertensive patients still have uncontrolled high blood pressure
James L. Pool, MD Abstract Background: Despite the availability of many effective, well-tolerated drugs, a significant proportion of treated hypertensive patients still have uncontrolled high blood pressure
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM
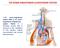 THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN-ALDOSTERONE SYSTEM The renin angiotensin system (RAS) or the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) is a hormone system that is involved in the regulation of the plasma sodium
Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets.
 Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets. Pr. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Consultation Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois Lausanne, Switzerland Introduction of new antihypertensive
Where are we with RAS blockade? New Targets. Pr. M. Burnier Service of Nephrology and Hypertension Consultation Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois Lausanne, Switzerland Introduction of new antihypertensive
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment GUIDELINES
 ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
ACE Inhibitor and Angiotensin II Antagonist Combination Treatment Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level
Aliskiren for the Treatment of Hypertension: An Update
 Clinical Medicine: Therapeutics R e v i e w Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Aliskiren for the Treatment of Hypertension: An Update S Lam 1,
Clinical Medicine: Therapeutics R e v i e w Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Aliskiren for the Treatment of Hypertension: An Update S Lam 1,
The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor
 The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Yong-Jin Kim, MD Seoul National University Hospital Human and Economic Costs of Hypertension
The Road to Renin System Optimization: Renin Inhibitor A New Perspective on the Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) Yong-Jin Kim, MD Seoul National University Hospital Human and Economic Costs of Hypertension
Is there a need of new RAAS blockers in diabetic hypertension?
 Is there a need of new RAAS blockers in diabetic hypertension? Dr. Dominik N. Müller First World Congress on Controversies in Obesity, Diabetes and Hypertension Berlin October 2006 Renin-Angiotensin System
Is there a need of new RAAS blockers in diabetic hypertension? Dr. Dominik N. Müller First World Congress on Controversies in Obesity, Diabetes and Hypertension Berlin October 2006 Renin-Angiotensin System
Disclosure of Relationships
 Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
Disclosure of Relationships Over the past 12 months Dr Ruilope has served as Consultant and Speakers Bureau member of Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, Daiichi-Sankyo, Menarini, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, Relypsa, Servier
The renin inhibitor aliskiren (Tekturna
 AJH 2007; 20:587 597 Aliskiren, the First Renin Inhibitor for Treating Hypertension: Reactive Renin Secretion May Limit Its Effectiveness Jean E. Sealey and John H. Laragh A review of six clinical trials
AJH 2007; 20:587 597 Aliskiren, the First Renin Inhibitor for Treating Hypertension: Reactive Renin Secretion May Limit Its Effectiveness Jean E. Sealey and John H. Laragh A review of six clinical trials
Amlodipine/olmesartan (Azor ) is indicated for the treatment of hypertension, alone or in combination with other antihypertensive medications.
 Page 1 of 8 Policies Repository Policy Title Policy Number Oral Antihypertensive Agents FS.CLIN.9 Application of Pharmacy Policy is determined by benefits and contracts. Benefits may vary based on product
Page 1 of 8 Policies Repository Policy Title Policy Number Oral Antihypertensive Agents FS.CLIN.9 Application of Pharmacy Policy is determined by benefits and contracts. Benefits may vary based on product
By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat
 What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan compared with other antihypertensive drugs
 (2002) 16 (Suppl 2), S24 S28 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh compared with other antihypertensive drugs University Clinic Bonn, Department of Internal
(2002) 16 (Suppl 2), S24 S28 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh compared with other antihypertensive drugs University Clinic Bonn, Department of Internal
Hypertension Management and End Organ Protection: Focus on Aliskiren
 REVIEW Hypertension Management and End Organ Protection: Focus on Toshio Imanishi, Hiroto Tsujioka and Takashi Akasaka Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Wakayama Medical University. 811-1, Kimiidera,
REVIEW Hypertension Management and End Organ Protection: Focus on Toshio Imanishi, Hiroto Tsujioka and Takashi Akasaka Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Wakayama Medical University. 811-1, Kimiidera,
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Aldosterone synthase inhibitors. John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow
 Aldosterone synthase inhibitors John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow Inhibition of aldosterone synthesis is hypothesized to be of benefit to patients with cardiovascular
Aldosterone synthase inhibitors John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow Inhibition of aldosterone synthesis is hypothesized to be of benefit to patients with cardiovascular
Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone
 Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Tomas Berl Key words: angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, combination therapy, direct renin inhibitor,
Renal protection by inhibition of the renin-angiotensinaldosterone system Tomas Berl Key words: angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, combination therapy, direct renin inhibitor,
New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients. Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland
 New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland Diabetes and nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is the most common
New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy patients Prof. M. Burnier, Service of Nephrology and Hypertension CHUV, Lausanne, Switzerland Diabetes and nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is the most common
Effect of aliskiren on proteinuria in non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a double-blind, crossover, randomised, controlled trial
 Int Urol Nephrol (2012) 44:1763 1770 DOI 10.1007/s11255-011-0110-z NEPHROLOGY ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of aliskiren on proteinuria in non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a double-blind, crossover, randomised,
Int Urol Nephrol (2012) 44:1763 1770 DOI 10.1007/s11255-011-0110-z NEPHROLOGY ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of aliskiren on proteinuria in non-diabetic chronic kidney disease: a double-blind, crossover, randomised,
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
The hypertensive effects of the renin-angiotensin
 Comparison of Telmisartan vs. Valsartan in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Hypertension Using Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring George Bakris, MD A prospective, randomized, open-label, blinded end-point
Comparison of Telmisartan vs. Valsartan in the Treatment of Mild to Moderate Hypertension Using Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring George Bakris, MD A prospective, randomized, open-label, blinded end-point
Strategies in Cardiovascular Disease and Respiratory Disease
 Strategies in Cardiovascular Disease and Respiratory Disease Drug Discovery and Medicinal Chemistry The Renin-Angiotensin Pathway Dr Anna Barnard - Spring 2017 Course Overview Lecture 1: Overview of the
Strategies in Cardiovascular Disease and Respiratory Disease Drug Discovery and Medicinal Chemistry The Renin-Angiotensin Pathway Dr Anna Barnard - Spring 2017 Course Overview Lecture 1: Overview of the
Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker. Disclosure
 Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker Rameshkumar Raman M.D Endocrine Associates of The Quad Cities Disclosure Speaker bureau Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Merck, Solvay
Hypertension Management Focus on new RAAS blocker Rameshkumar Raman M.D Endocrine Associates of The Quad Cities Disclosure Speaker bureau Abbott, Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Takeda, Merck, Solvay
Hypertension Update 2009
 Hypertension Update 2009 New Drugs, New Goals, New Approaches, New Lessons from Clinical Trials Timothy C Fagan, MD, FACP Professor Emeritus University of Arizona New Drugs Direct Renin Inhibitors Endothelin
Hypertension Update 2009 New Drugs, New Goals, New Approaches, New Lessons from Clinical Trials Timothy C Fagan, MD, FACP Professor Emeritus University of Arizona New Drugs Direct Renin Inhibitors Endothelin
Managing hypertension: a question of STRATHE
 (2005) 19, S3 S7 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Managing hypertension: a question of STRATHE Department of Cardiovascular Disease,
(2005) 19, S3 S7 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Managing hypertension: a question of STRATHE Department of Cardiovascular Disease,
Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction
 Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Cardio-Metabolic Franchise Entresto Development of sacubitril/valsartan (LCZ696) for the treatment of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction Randy L Webb, PhD Rutgers Workshop October 21, 2016 Heart
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR.
 ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
ANGIOTENSIN II RECEPTOR BLOCKERS: MORE THAN THE ALTERNATIVE PRESENTATION BY: PATRICK HO, USC PHARM D. CANDIDATE OF 2017 MENTOR: DR. CRAIG STERN, PHARMD, MBA, RPH, FASCP, FASHP, FICA, FLMI, FAMCP RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management. Investor Webcast June 2018
 Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management Investor Webcast June 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
Phase 3 investigation of aprocitentan for resistant hypertension management Investor Webcast June 2018 The following information contains certain forward-looking statements, relating to the company s business,
EPLERENONE (INSPRA ) THE FIRST SELECTIVE ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST FOR THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 Volume 18, Issue 6 March 2003 EPLERENONE (INSPRA ) THE FIRST SELECTIVE ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST FOR THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Eun-Jeong Kim, Pharm.D. Candidate Introduction Approximately 50
Volume 18, Issue 6 March 2003 EPLERENONE (INSPRA ) THE FIRST SELECTIVE ALDOSTERONE RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST FOR THE TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Eun-Jeong Kim, Pharm.D. Candidate Introduction Approximately 50
High-dose monotherapy vs low-dose combination therapy of calcium channel blockers and angiotensin receptor blockers in mild to moderate hypertension
 (2005) 19, 491 496 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-dose monotherapy vs low-dose combination therapy of calcium channel blockers
(2005) 19, 491 496 & 2005 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/05 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE High-dose monotherapy vs low-dose combination therapy of calcium channel blockers
Cedars Sinai Diabetes. Michael A. Weber
 Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Cedars Sinai Diabetes Michael A. Weber Speaker Disclosures I disclose that I am a Consultant for: Ablative Solutions, Boston Scientific, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Forest, Medtronics, Novartis, ReCor
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L
 Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
Amlodipine plus Lisinopril Tablets AMLOPRES-L COMPOSITION AMLOPRES-L Each uncoated tablet contains: Amlodipine besylate equivalent to Amlodipine 5 mg and Lisinopril USP equivalent to Lisinopril (anhydrous)
effects of angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor to cardiovascular and renal disease. Because of the detrimental effects associated
 Olmesartan Medoxomil for Hypertension: A Clinical Review Daryl Norwood, PharmD, Evans Branch III, PharmD, Bridget Smith, MD, and Marlon Honeywell, PharmD ABSTRACT Olmesartan medoxomil is the latest angiotensin
Olmesartan Medoxomil for Hypertension: A Clinical Review Daryl Norwood, PharmD, Evans Branch III, PharmD, Bridget Smith, MD, and Marlon Honeywell, PharmD ABSTRACT Olmesartan medoxomil is the latest angiotensin
Which antihypertensives are more effective in reducing diastolic hypertension versus systolic hypertension? May 24, 2017
 Which antihypertensives are more effective in reducing diastolic hypertension versus systolic hypertension? May 24, 2017 The most important reason for treating hypertension in primary care is to prevent
Which antihypertensives are more effective in reducing diastolic hypertension versus systolic hypertension? May 24, 2017 The most important reason for treating hypertension in primary care is to prevent
in patients with diabetes, nephropathy and/or chronic kidney disease Summary of recommendations July 2017
 Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Renal Association clinical guidelines: Hypertension management and reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy
Association of British Clinical Diabetologists (ABCD) and Renal Association clinical guidelines: Hypertension management and reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with diabetes, nephropathy
HTN: 80 mg once daily 23,f 80 mg once daily 23,f Hypertension 40, 80 mg $82.66 (80 mg once daily) HTN: 8-32 mg daily in one or two divided doses 1
 Detail-Document #260301 This Detail-Document accompanies the related article published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER March 2010 ~ Volume 26 ~ Number 260301 Comparison of Angiotensin Receptor
Detail-Document #260301 This Detail-Document accompanies the related article published in PHARMACIST S LETTER / PRESCRIBER S LETTER March 2010 ~ Volume 26 ~ Number 260301 Comparison of Angiotensin Receptor
Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
European Heart Journal Supplements (2004) 6 (Supplement H), H37 H42 Preventing the cardiovascular complications of hypertension Peter Trenkwalder* Department of Internal Medicine, Starnberg Hospital, Ludwig
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8. Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital
 Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
Clinical Updates in the Treatment of Hypertension JNC 7 vs. JNC 8 Lauren Thomas, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident South Pointe Hospital Objectives Review the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC
A systematic review and meta-analysis of aliskiren and angiotension receptor blockers in the management of essential hypertension
 Article A systematic review and meta-analysis of aliskiren and angiotension receptor blockers in the management of essential hypertension Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin- Aldosterone System 12(2) 102
Article A systematic review and meta-analysis of aliskiren and angiotension receptor blockers in the management of essential hypertension Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin- Aldosterone System 12(2) 102
VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION Dr Catherine BESEME Paris 6 th December 2005 6 th International Congress of Bangladesh Society of Medicine Hypertension is a risk factor at the source, with
VALUE OF ACEI IN THE MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION Dr Catherine BESEME Paris 6 th December 2005 6 th International Congress of Bangladesh Society of Medicine Hypertension is a risk factor at the source, with
HYPERTENSION IN CKD. LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
The control of hypertension in the. Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy REPORTS
 REPORTS Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy By Richard V. Milani, MD Abstract Elevated blood pressure, particularly systolic blood
REPORTS Reaching for Aggressive Blood Pressure Goals: Role of Angiotensin Receptor Blockade in Combination Therapy By Richard V. Milani, MD Abstract Elevated blood pressure, particularly systolic blood
By Edward Wassef, RPh, PharmD
 CE Free OBJECTIVES Continuing Education Lesson Upon successfully completing this lesson, the pharmacist will be able to: 1. discuss the importance of controlling hypertension. 2. describe the current Canadian
CE Free OBJECTIVES Continuing Education Lesson Upon successfully completing this lesson, the pharmacist will be able to: 1. discuss the importance of controlling hypertension. 2. describe the current Canadian
Reducing proteinuria
 Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillin Reducing proteinuria GUIDELINES a. The beneficial effect of treatment regimens that include angiotensinconverting enzyme inhibitors
Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), Renin Inhibitors, and Combinations Step Therapy Program Summary
 OBJECTIVE The intent of the Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), Renin Inhibitors, and Combinations Step Therapy (ST) program is to encourage use of cost-effective generic products - ACEIs, ACEI
OBJECTIVE The intent of the Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists (ARBs), Renin Inhibitors, and Combinations Step Therapy (ST) program is to encourage use of cost-effective generic products - ACEIs, ACEI
Efficacy and safety of Olmesartan,Losartan, Valsartan, and Irbesartan in the Control of Essential Hypertension
 Efficacy and safety of Olmesartan,Losartan, Valsartan, and Irbesartan in the Control of Essential Hypertension Done by :Meznah zaid Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate Princess Nora Bint Abdul Rahman University
Efficacy and safety of Olmesartan,Losartan, Valsartan, and Irbesartan in the Control of Essential Hypertension Done by :Meznah zaid Al-mutairi Pharm.D Candidate Princess Nora Bint Abdul Rahman University
Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London
 Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email:
Combination therapy Giuseppe M.C. Rosano, MD, PhD, MSc, FESC, FHFA St George s Hospitals NHS Trust University of London KCS Congress: Impact through collaboration CONTACT: Tel. +254 735 833 803 Email:
Direct renin inhibitors: the dawn of a new era, or just a variation on a theme?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: 2435 2439 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfm363 Advance Access publication 7 June 2007 Editorial Review Direct renin inhibitors: the dawn of a new era, or just a variation on a theme?
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2007) 22: 2435 2439 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfm363 Advance Access publication 7 June 2007 Editorial Review Direct renin inhibitors: the dawn of a new era, or just a variation on a theme?
ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA
 ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA Type I IDDM is characterized by The abrupt onset of symptoms Insulinopenia
ROLE OF ANGIOTENSIN CONVERTING ENZYME INHIBITORS AND ANGIOTENSIN RECEPTOR BLOCKERS IN TYPE I DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY DR.NASIM MUSA Type I IDDM is characterized by The abrupt onset of symptoms Insulinopenia
heart failure John McMurray University of Glasgow.
 A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
A to Z of RAAS blockade in heart failure John McMurray BHF Cardiovascular Research Centre University of Glasgow. RAAS inhibition in CHF ACE inhibition in patients with low LVEF CHF CONSENSUS Enalapril
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone. in chronic heart failure
 Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
Optimal blockade of the Renin- Angiotensin-Aldosterone Aldosterone- (RAA)-System in chronic heart failure Jan Östergren Department of Medicine Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm, Sweden Key Issues
Hypertension Update Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital
 Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
Hypertension Update 2008 Warwick Jaffe Interventional Cardiologist Ascot Hospital Definition of Hypertension Continuous variable At some point the risk becomes high enough to justify treatment Treatment
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension William C. Cushman, MD, FAHA, FACP, FASH Chief, Preventive Medicine, Veterans Affairs Medical Center Professor, Preventive Medicine, Medicine, and Physiology University of Tennessee
Diabetes and Hypertension William C. Cushman, MD, FAHA, FACP, FASH Chief, Preventive Medicine, Veterans Affairs Medical Center Professor, Preventive Medicine, Medicine, and Physiology University of Tennessee
Amlodipine/Valsartan (Exforge ) Changing the Landscape of BP Management
 Amlodipine/Valsartan (Exforge ) Changing the Landscape of BP Management Bum-Kee Hong Yongdong Severance Hospital Yonsei University College of Medicine Rationale for Multiple-Mechanism Therapy Inadequacy
Amlodipine/Valsartan (Exforge ) Changing the Landscape of BP Management Bum-Kee Hong Yongdong Severance Hospital Yonsei University College of Medicine Rationale for Multiple-Mechanism Therapy Inadequacy
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Irbesartan (Aprovel) for prevention of cardiovascular complications in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation
 Irbesartan (Aprovel) for prevention of cardiovascular complications in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of
Irbesartan (Aprovel) for prevention of cardiovascular complications in patients with persistent atrial fibrillation August 2008 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN
 AZEARLY Tablets Each Tablet Contains Azilsartan 20/40/80 mg PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN Generic name: Azilsartan Chemical name: 2-Ethoxy-1-{[2'-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-
AZEARLY Tablets Each Tablet Contains Azilsartan 20/40/80 mg PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN Generic name: Azilsartan Chemical name: 2-Ethoxy-1-{[2'-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-
ABSTRACT ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Joel Neutel Ali Shojaee Jen-Fue Maa. Adv Ther (2012) 29(6): DOI /s z
 Adv Ther (212) 29(6):58 523. DOI 1.17/s12325-12-3-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH Efficacy of Amlodipine/Olmesartan ± Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients Uncontrolled on Prior Calcium Channel Blocker or Angiotensin II
Adv Ther (212) 29(6):58 523. DOI 1.17/s12325-12-3-z ORIGINAL RESEARCH Efficacy of Amlodipine/Olmesartan ± Hydrochlorothiazide in Patients Uncontrolled on Prior Calcium Channel Blocker or Angiotensin II
Valsartan Amlodipine HCT Combination: Control To Goal. Dr. Sameh Shaheen M.B.B.Ch, MSc, MD, FESC, FSCAI. Prof of cardiology Ain Shams University
 Valsartan Amlodipine HCT Combination: Control To Goal Dr. Sameh Shaheen M.B.B.Ch, MSc, MD, FESC, FSCAI Prof of cardiology Ain Shams University Sonesta Hotel Cairo Egypt December 4 th 5 th ; 213 Hypertension
Valsartan Amlodipine HCT Combination: Control To Goal Dr. Sameh Shaheen M.B.B.Ch, MSc, MD, FESC, FSCAI Prof of cardiology Ain Shams University Sonesta Hotel Cairo Egypt December 4 th 5 th ; 213 Hypertension
Hypertension is a persistent elevation of B.P. above the normal level. Approximately 1 billion people have hypertension
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com STUDY OF LEVEL IN ESSENTIAL HYPERTENSION Krithika Mohanraj 1 *, Dr.R.Rajeswari 2 Bharath University, Chennai.
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com STUDY OF LEVEL IN ESSENTIAL HYPERTENSION Krithika Mohanraj 1 *, Dr.R.Rajeswari 2 Bharath University, Chennai.
Hypertension in Geriatrics. Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist 10 September 2016
 Hypertension in Geriatrics Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist 10 September 2016 Annual mortality (%) Cardiovascular Mortality Rates are Higher among Dialysis Patients 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 25-34
Hypertension in Geriatrics Dr. Allen Liu Consultant Nephrologist 10 September 2016 Annual mortality (%) Cardiovascular Mortality Rates are Higher among Dialysis Patients 100 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 25-34
Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly: Addressing an Unmet Need
 REVIEW Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly: Addressing an Unmet Need Daniel A. Duprez, MD, PhD Cardiovascular Division, Medical School, University of Minnesota, Minn. ABSTRACT Systolic hypertension is
REVIEW Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly: Addressing an Unmet Need Daniel A. Duprez, MD, PhD Cardiovascular Division, Medical School, University of Minnesota, Minn. ABSTRACT Systolic hypertension is
How clinically important are the results of the large trials in hypertension?
 How clinically important are the results of the large trials in hypertension? Stéphane LAURENT, MD, PhD, FESC Pharmacology Department and PARCC / INSERM U970 Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Université
How clinically important are the results of the large trials in hypertension? Stéphane LAURENT, MD, PhD, FESC Pharmacology Department and PARCC / INSERM U970 Hôpital Européen Georges Pompidou, Université
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy. MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan
 Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
Prevention And Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy MOH Clinical Practice Guidelines 3/2006 Dr Stephen Chew Tec Huan Prevention Tight glucose control reduces the development of diabetic nephropathy Progression
AT 1 -receptor blockers: differences that matter
 (2002) 16, S9 S16 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh AT 1 -receptor blockers: differences that matter Division of Cardiovascular Diseases, The Western
(2002) 16, S9 S16 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh AT 1 -receptor blockers: differences that matter Division of Cardiovascular Diseases, The Western
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 27 May 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 27 May 2009 RASILEZ HCT 150 mg/12.5 mg, film-coated tablets B/30 (CIP code: 392 151-6) RASILEZ HCT 150 mg/25 mg, film-coated
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 27 May 2009 RASILEZ HCT 150 mg/12.5 mg, film-coated tablets B/30 (CIP code: 392 151-6) RASILEZ HCT 150 mg/25 mg, film-coated
Original Paper. ID: 7805
 Original Paper The Efficacy and Safety of Initial Use of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide Fixed-Dose Combination in Hypertensive Patients With and Without High Cardiovascular Risk Matthew R. Weir, MD; 1
Original Paper The Efficacy and Safety of Initial Use of Irbesartan/Hydrochlorothiazide Fixed-Dose Combination in Hypertensive Patients With and Without High Cardiovascular Risk Matthew R. Weir, MD; 1
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives
 Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillian GUIDELINES a. Regimens that include angiotensin-converting enzyme
Blood Pressure Control role of specific antihypertensives Date written: May 2005 Final submission: October 2005 Author: Adrian Gillian GUIDELINES a. Regimens that include angiotensin-converting enzyme
Review. Rationale for the use of multiple blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system in specific patient populations
 Rationale for the use of multiple blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system in specific patient populations Review Blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) have an established
Rationale for the use of multiple blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system in specific patient populations Review Blockers of the renin angiotensin aldosterone system (RAAS) have an established
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Antihypertensive Medications Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Antihypertensive Medications Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Antihypertensive Medications Page 1 of 10 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Antihypertensive Medications Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization
Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?
 Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?,FACA,FICA,MASH,FVBWG,MISCP CONSULTANT OF CARDIOLOGY DIRECTOR OF PORT-FOUAD HOSPITAL CCU Consideration of antihypertensive agents
Metabolic Consequences of Anti Hypertensives: Is It Clinically Important?,FACA,FICA,MASH,FVBWG,MISCP CONSULTANT OF CARDIOLOGY DIRECTOR OF PORT-FOUAD HOSPITAL CCU Consideration of antihypertensive agents
Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race
 Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race Allison Helmer, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy July 22, 2017 DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT
Hypertension Update Clinical Controversies Regarding Age and Race Allison Helmer, PharmD, BCACP Assistant Clinical Professor Auburn University Harrison School of Pharmacy July 22, 2017 DISCLOSURE/CONFLICT
Byvalson. (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow
 Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
DRUG UTILIZATION PATTERNS OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVES IN VARIOUS WARDS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN TAMILNADU
 Original Article DRUG UTILIZATION PATTERNS OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVES IN VARIOUS WARDS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN TAMILNADU V.Gowri 1, K.Punnagai, K.Vijaybabu 3, Dr.Darling Chellathai 4 1 Assistant Professor
Original Article DRUG UTILIZATION PATTERNS OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVES IN VARIOUS WARDS IN A TERTIARY CARE HOSPITAL IN TAMILNADU V.Gowri 1, K.Punnagai, K.Vijaybabu 3, Dr.Darling Chellathai 4 1 Assistant Professor
The retinal renin-angiotensin system: implications for therapy in diabetic retinopathy
 (2002) 16, S42 S46 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh : implications for therapy in diabetic retinopathy AK Sjølie 1 and N Chaturvedi 2 1 Department
(2002) 16, S42 S46 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh : implications for therapy in diabetic retinopathy AK Sjølie 1 and N Chaturvedi 2 1 Department
In patients with severe hypertension, the shortterm
 Review Paper The Risks and Benefits of Initial Irbesartan Hydrochlorothiazide Combination Therapy in Patients With Severe Hypertension Pablo Lapuerta, MD; 1 * Stanley Franklin, MD 2 The impact of delays
Review Paper The Risks and Benefits of Initial Irbesartan Hydrochlorothiazide Combination Therapy in Patients With Severe Hypertension Pablo Lapuerta, MD; 1 * Stanley Franklin, MD 2 The impact of delays
Jared Moore, MD, FACP
 Hypertension 101 Jared Moore, MD, FACP Assistant Program Director, Internal Medicine Residency Clinical Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine Division of General Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner
Hypertension 101 Jared Moore, MD, FACP Assistant Program Director, Internal Medicine Residency Clinical Assistant Professor of Internal Medicine Division of General Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Hypertension Guidelines: Are We Pressured to Change? Oregon Cardiovascular Symposium Portland, Oregon June 6, Financial Disclosures
 Hypertension Guidelines: Are We Pressured to Change? Oregon Cardiovascular Symposium Portland, Oregon June 6, 2015 William C. Cushman, MD Professor, Preventive Medicine, Medicine, and Physiology University
Hypertension Guidelines: Are We Pressured to Change? Oregon Cardiovascular Symposium Portland, Oregon June 6, 2015 William C. Cushman, MD Professor, Preventive Medicine, Medicine, and Physiology University
Nephrology. Safety and Tolerability of High-Dose Angiotensin Receptor Blocker Therapy in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Pilot Study
 American Journal of Nephrology Original Report: Patient-Oriented, Translational Research Am J Nephrol 2004;24:340 345 DOI: 10.1159/000078950 Received: March 8, 2004 Accepted: April 5, 2004 Published online:
American Journal of Nephrology Original Report: Patient-Oriented, Translational Research Am J Nephrol 2004;24:340 345 DOI: 10.1159/000078950 Received: March 8, 2004 Accepted: April 5, 2004 Published online:
First line treatment of primary hypertension
 First line treatment of primary hypertension Dr. Vijaya Musini Assistant Professor, Dept. Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics Manager, Drug Assessment Working Group Therapeutics Initiative Editor,
First line treatment of primary hypertension Dr. Vijaya Musini Assistant Professor, Dept. Anesthesiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics Manager, Drug Assessment Working Group Therapeutics Initiative Editor,
Clinical cases with Coversyl 10 mg
 Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg For upgraded benefits in hypertension A Editorial This brochure, Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg for upgraded benefits in hypertension, illustrates a variety of hypertensive
Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg For upgraded benefits in hypertension A Editorial This brochure, Clinical cases Coversyl 10 mg for upgraded benefits in hypertension, illustrates a variety of hypertensive
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 7 January 2009
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 7 January 2009 LERCAPRESS 10 mg/10 mg, film-coated tablets Pack of 30 (CIP code: 385 953-3) Pack of 90 (CIP code:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 7 January 2009 LERCAPRESS 10 mg/10 mg, film-coated tablets Pack of 30 (CIP code: 385 953-3) Pack of 90 (CIP code:
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE. Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota
 SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
Are all Antihypertensives the same?
 Are all Antihypertensives the same? Athanasios J. Manolis MD, FACC, FESC, FAHA Director of Cardiology Dept, Asklepeion General Hospital, Athens Greece. Adj. Ass. Professor, Hypertension Section, Boston
Are all Antihypertensives the same? Athanasios J. Manolis MD, FACC, FESC, FAHA Director of Cardiology Dept, Asklepeion General Hospital, Athens Greece. Adj. Ass. Professor, Hypertension Section, Boston
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone
 Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Drugs acting on the reninangiotensin-aldosterone system John McMurray Eugene Braunwald Scholar in Cardiovascular Diseases, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston & Visiting Professor, Harvard Medical School
Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated
 CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY: PHYSICIAN UPDATE Manipulation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Michael M. Givertz, MD Since the initial description of angiotensin II mediated hypertension 40 years ago, basic and clinical
Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC
 Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC Seung Woo Park, MD Samsung Medical Center BP Control Rates in Asia BP controlled BP uncontrolled 24.3% 36.6% 19% Turkey
Rationale for the use of Single Pill Combination (SPC) and Asian data of ARB/CCB SPC Seung Woo Park, MD Samsung Medical Center BP Control Rates in Asia BP controlled BP uncontrolled 24.3% 36.6% 19% Turkey
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. S Oparil 1, SG Chrysant 2, M Melino 3, J Lee 3, S Karki 3 and R Heyrman 3 1. Introduction
 (2010) 24, 831 838 & 2010 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-9240/10 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term efficacy of a combination of amlodipine and olmesartan medoxomil±hydrochlorothiazide
(2010) 24, 831 838 & 2010 Macmillan Publishers Limited All rights reserved 0950-9240/10 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term efficacy of a combination of amlodipine and olmesartan medoxomil±hydrochlorothiazide
Hypertension Management: A Moving Target
 9:45 :30am Hypertension Management: A Moving Target SPEAKER Karol Watson, MD, PhD, FACC Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Karol E. Watson,
9:45 :30am Hypertension Management: A Moving Target SPEAKER Karol Watson, MD, PhD, FACC Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Karol E. Watson,
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy
 Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Hypertension and diabetic nephropathy Elisabeth R. Mathiesen Professor, Chief Physician, Dr sci Dep. Of Endocrinology Rigshospitalet, University of Copenhagen Denmark Hypertension Brain Eye Heart Kidney
Telmisartan Pritor Tablets
 Telmisartan Pritor Tablets QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Telmisartan (Pritor TM ) 40 mg Tablet: Each tablet contains 40 mg Telmisartan. Telmisartan (Pritor TM ) 80 mg Tablet: Each tablet contains
Telmisartan Pritor Tablets QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Telmisartan (Pritor TM ) 40 mg Tablet: Each tablet contains 40 mg Telmisartan. Telmisartan (Pritor TM ) 80 mg Tablet: Each tablet contains
Anti-hypertensive agents
 Anti-hypertensive agents Dr. Pran Kishore Deb Assistant Professor, Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Faculty of Pharmacy, Philadelphia University-Jordan Email: pdeb@philadelphia.edu.jo Anti-hypertensive
Anti-hypertensive agents Dr. Pran Kishore Deb Assistant Professor, Pharmaceutical Medicinal Chemistry Faculty of Pharmacy, Philadelphia University-Jordan Email: pdeb@philadelphia.edu.jo Anti-hypertensive
New Trials. Iain Squire. Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leicester. Chair, BSH
 New Trials Iain Squire Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leicester Chair, BSH BSH Heart Failure Day for Revalidation and Training 2017 Presentation title: New Trials Speaker: Iain Squire
New Trials Iain Squire Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine University of Leicester Chair, BSH BSH Heart Failure Day for Revalidation and Training 2017 Presentation title: New Trials Speaker: Iain Squire
COMPOSITION. A film coated tablet contains. Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan
 Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg COMPOSITION A film coated tablet contains Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg PHARMACOLOGICAL
Rotazar (Film coated tablets) Irbesartan Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg COMPOSITION A film coated tablet contains Active ingredient: irbesartan 75 mg, 150 mg or 300 mg. Rotazar 75 mg, 150 mg, 300 mg PHARMACOLOGICAL
MICARDIS Composition Pharmacological properties Pharmacokinetics
 MICARDIS Boehringer (Tablet) Composition 1 tablet contains 40 or 80 mg [1,1 -biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid, 4 -[(1,4 dime-thyl- 2 -propyl[2,6-bi-1h-benzimidazole]-1 -yl)methyl] (= telmisartan) Excipients:
MICARDIS Boehringer (Tablet) Composition 1 tablet contains 40 or 80 mg [1,1 -biphenyl]-2-carboxylic acid, 4 -[(1,4 dime-thyl- 2 -propyl[2,6-bi-1h-benzimidazole]-1 -yl)methyl] (= telmisartan) Excipients:
See Important Reminder at the end of this policy for important regulatory and legal information.
 Clinical Policy: Olmesartan/Amlodipine (Azor), Olmesartan/Amlodipine/ HCTZ (Tribenzor) Reference Number: CP.CPA.XX Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 08.18 Line of Business: Commercial See Important
Clinical Policy: Olmesartan/Amlodipine (Azor), Olmesartan/Amlodipine/ HCTZ (Tribenzor) Reference Number: CP.CPA.XX Effective Date: 11.16.16 Last Review Date: 08.18 Line of Business: Commercial See Important
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australians with Renal Impairment. Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy GUIDELINES
 Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
Specific effects of calcium channel blockers in diabetic nephropathy Date written: September 2004 Final submission: September 2005 Author: Kathy Nicholls GUIDELINES a. Non-dihydropyridine calcium channel
