BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1):
|
|
|
- Blanche Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1): DOI: /bst Knocking down TCF8 inhibits high glucose- and angiotensin IIinduced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in podocytes Changhuan Bai 1,2, Shumei Liang 3, Yunshan Wang 4, Bo Jiao 1, * 1 Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shandong University, Ji'nan, Shandong, China; 2 Department of Pharmacy, The Second People's Hospital of Liaocheng, Liaocheng, Shandong, China; 3 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Ji'nan, Shandong, China; 4 Weihai International Biotechnology Research and Development Center, Shandong University, Weihai, Shandong, China. Summary Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a physiological phenomenon in mammalian embryogenesis by which epithelial cells become mesenchymal stem cells. Studies have indicated that an inappropriate EMT plays a key role in a variety of pathogenic processes such as embryonic development and tumor metastasis. Moreover, recent studies have indicated EMT also plays an important role in renal fibrosis. In the current study, glucose and angiotensin II promoted EMT in podocytes as well as changes in the cellular morphology of podocytes. A high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II also promoted podocyte movement and migration. Moreover, a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II promoted TCF8 expression. Inhibiting TCF8 expression with sirna reversed EMT in podocytes in the presence of a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin. Inhibiting TCF8 expression also reversed changes in cellular morphology and podocyte movement and migration. Therefore, glucose and angiotensin II may promote EMT in podocytes via TCF8. Keywords: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT), podocyte, glucose, angiotensin II, TCF8 1. Introduction In the kidneys, podocytes are attached to the outside of the glomerular basement membrane. The glomerular basement membrane plays an important role in maintaining the normal structure and function of the glomerulus via the actin cytoskeleton of podocytes and specific expression of protein molecules (1). Nephrin, WT1, and synaptopodin are phenotypic markers of mature podocytes (2). Podocytes have long processes that interdigitate and that are separated by very narrow spaces (30-40 nm) that are bridged by a membrane called the slit diaphragm (3). This diaphragm allows water and small solute molecules to pass through but it filters Released online in J-STAGE as advance publication January 22, *Address correspondence to: Dr. Bo Jiao, Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Shandong University, 44 West Culture Road, Ji'nan, Shandong, China. jiaob@sdu.edu.cn out plasma proteins and other macromolecules, and this property is the main determinant of the permeability of the renal glomerular filtration barrier (1). Therefore, podocytes play an important role in protecting the integrity of the glomerular filtration barrier, adjusting the ultrafiltration coefficient, and maintaining the normal structure of the glomerular basement membrane (4). Ultrastructural changes in podocytes and reduced expression of associated molecules is closely related to renal impairment and can lead to glomerulosclerosis and renal interstitial fibrosis (5). The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is a process by which polarized epithelial cells undergo numerous biochemical changes to obtain a mesenchymal cell phenotype (6). EMT is also involved in tumor migration and invasion (7). Podocytes are epithelial cells, so when they are affected by different conditions (such as TGF-β, a high concentration of glucose, doxorubicin, or some other stimuli), EMT may occur (8-10). When EMT occurs, epithelial phenotypic markers such as E-cadherin, P-cadherin, nephrin, podocalyxin, and synaptopodin are downregulated, and mesenchymal phenotypic markers
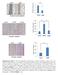
2 78 BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1): such as desmin, FSP-1, MMP-9, ILK, fibronectin, vimentin, α-sma, collagen I, and snail are upregulated (11). EMT is considered to be the key factor for an impaired kidney producing myofibroblasts in renal fibrosis, which may lead to renal interstitial fibrosis (12). Podocytes, which are also known as glomerular visceral epithelial cells, are cells affected by different types of injury. EMT in podocytes will result in damage to the glomerular filtration barrier and proteinuria; in severe cases, it may lead to podocyte detachment from the glomerular basement membrane and apoptosis, causing a decrease in the number of podocytes, thereby aggravating proteinuria and glomerular sclerosis (13,14). EMT in podocytes is a key starting point for studying the mechanisms by which proteinuria and renal fibrosis develop (15). The aim of the current study was to examine EMT in podocytes in the presence of a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II. This study examined the effects of a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II on EMT and the expression of TCF8 in podocytes. This study also examined the effects of downregulating TCF8 on EMT in podocytes. 2. Materials and Methods 2.1. Cell culture and reagents The podocyte line used in this study was donated by Prof. Ding Jie (Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China). E-cadherin, α-catenin, N-cadherin, vimentin, TCF8, and β-actin antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (Beverly, MA, USA) qrt-pcr Total RNA was extracted from cell lines using the TRIZOL reagent (Invitrogen). Reverse transcription (RT) was performed using the Thermoscript RT System (Invitrogen). Hotstart PCR conditions were as follows: 45 s at 94 C, 30 s at 55 C, and 1 min at 72 C for cycles (for TCF8) or 26 cycles (for glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)). The primers used in the study were: TCF8: sense 5'-GCACAACCAAGTGCAGAAGA-3' and antisense 5'-CATT TGCAGATTGAGGCTGA-3'; GAPDH: sense 5'-TGCCTCCTGCACCACCAACT-3' and antisense 5'-CCCGTTCAGCTCAGGGATGA-3' Plasmid construction and transfection For TCF8 RNA interference, control and TCF8 shrna plasmids (#1: CCGGGCTGCCAATAAGCAAACGAT TCTCGAGAATCGTTTGCTTATTGGCAGCTTTTT; #2: CCGGGCTGTTGTTCTGCCAACAGTTCTCGA GAACTGTTGGCAGAACAACAGCTTTTT; #3: CC GGCGGCGCAATAACGTTACAAATCTCGAGATT TGTAACGTTATTGCGCCGTTTTT) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Biotechnology (Sigma-Aldrich, CA, USA) and were used to transfect podocytes to establish a cell line with knocked-down TCF8. The transfection efficiency of TCF8 was verified with Western blotting and quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qrt-pcr) analyses Western blot assay Equal amounts of protein were separated using SDS polyacrylamide gels and were electrotransferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (Millipore, Bedford, MA, USA). The membranes were immunoblotted overnight at 4 C with primary antibodies, followed by their respective secondary antibodies. β-actin was used as the loading control Cell invasion and motility assay Cell invasion was measured in Matrigel (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA)-coated Transwell inserts (6.5 mm, Costar, NY, USA) containing polycarbonate filters with 8-μm pores as previously described. The inserts were coated with 50 μl of 1 mg/ml Matrigel matrix in accordance with the manufacturer's recommendations cells in 200 μl of serum-free medium were plated in the upper chamber, and 600 μl of medium with 10% fatal bovine serum was added to the lower well. After incubation for 24 h, top cells were removed and bottom cells were counted. Cells that migrated to the lower surface of the membrane were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and stained with 0.5% crystal violet. For each membrane, five random fields were counted at 10 magnification. The mean was calculated and data were expressed as the mean ± S.D. from three independent experiments done in triplicate. Motility assays were similar to invasion assays with Matrigel except that the Transwell inserts were not coated with Matrigel. 3. Results 3.1. A high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II promoted EMT in podocytes Previous studies reported that a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II may promote EMT in kidney epithelial cells (16,17). The current study examined whether those substances would have the same effect on podocytes. Podocytes were treated with 0, 10, 20, and 30 mm of glucose. As shown in Figures 1A and 1B, the expression of the epithelial marker molecules E-cadherin and α-catenin decreased with an increase in the glucose concentration. As shown in Figures 1C and 1D, the expression of the mesenchymal marker molecules N-cadherin and vimentin increased with an increase in the glucose concentration. Podocytes were then treated
3 BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1): Figure 1. A high concentration of glucose inhibited the expression of epithelial biomarkers (E-cadherin and α-catenin) and promoted the expression of mesenchymal biomarkers (N-cadherin and vimentin) in podocytes. (A) Podocytes were incubated with 0-30 mm of glucose for 24 h and the expression of E-cadherin was measured with Western blotting. (B) Podocytes were incubated with 0-30 mm of glucose for 24 h and the expression of α-catenin was measured with Western blotting. (C) Podocytes were incubated with 0-30 mm of glucose for 24 h and the expression of N-cadherin was measured with Western blotting. (D) Podocytes were incubated with 0-30 mm of glucose for 24 h and the expression of vimentin was measured with Western blotting. Figure 2. Angiotensin II inhibited the expression of epithelial biomarkers (E-cadherin and α-catenin) and promoted the expression of mesenchymal biomarkers (N-cadherin and vimentin) in podocytes. (A) Podocytes were incubated with 0-9 μm of angiotensin II for 24 h and the expression of E-cadherin was measured with Western blotting. (B) Podocytes were incubated with 0-9 μm of angiotensin II for 24 h and the expression of α-catenin was measured with Western blotting. (C) Podocytes were incubated with 0-9 μm of angiotensin II for 24 h and the expression of N-cadherin was measured with Western blotting. (D) Podocytes were incubated with 0-9 μm of angiotensin II for 24 h and the expression of vimentin was measured with Western blotting. with 0, 3, 6, and 9 μm of angiotensin II. As shown in Figures 2A and 2B, the expression of the epithelial marker molecules E-cadherin and α-catenin decreased with an increase in the angiotensin II concentration. As shown in Figures 2C and 2D, the expression of the mesenchymal marker molecules N-cadherin and vimentin increased with an increase in the angiotensin II concentration. Results indicated that a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II promoted EMT in podocytes A high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II changed podocyte morphology and promoted podocyte migration and invasion The current study examined the effects of a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin on podocytes. As shown in Figures 3A and 3B, podocytes displayed morphological changes when stimulated with 30 mm of glucose or 9 μm of angiotensin II. As shown in Figures 3C-3F, a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin promoted podocyte cell migration and invasion. The number of migrating and invading podocytes in the presence of 30 mm of glucose or 9 μm of angiotensin II was about twice that in the presence of 0 mm of glucose or angiotensin II A high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II promoted TCF8 expression TCF8 is a transcription factor that plays an important role in EMT (6). The current study examined whether a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II affects TCF8. Podocytes were treated with 0, 10, 20, and 30 mm of glucose. As shown in Figure 4A, the expression of TCF8 increased with an increase in the glucose concentration. Podocytes were then treated with 0, 3, 6, and 9 μm of angiotensin II. As shown in Figure 4B, the expression of TCF8 increased with an increase in the angiotensin II concentration. Results indicated that a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II promoted TCF8 expression. TCF8 expression was
4 80 BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1): Figure 3. A high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II promoted changes in the cell morphology of podocytes as well as podocyte migration and invasion. (A) Changes in the cell morphology of podocytes in the presence of 0 and 30 mm of glucose. (B) Changes in the cell morphology of podocytes in the presence of 0 and 9 μm of angiotensin II. (C) The migration of podocytes in the presence of 0 and 30 mm of glucose was measured with a transwell assay. (D) The migration of podocytes in the presence of 0 and 9 μm of angiotensin II was measured with a transwell assay. (E) Invasion by podocytes in the presence of 0 and 30 mm of glucose was measured with a Matrigel assay. (F) Invasion by podocytes in the presence of 0 and 9 μm of angiotensin II was measured with a Matrigel assay. suppressed using antisense RNA. Three TCF8 antisense RNA sequences were transfected into podocytes. As shown in Figures 4C and 4D, TCF8 expression was down-regulated according to Western blotting and qrtpcr Silencing TCF8 reversed EMT that was induced with a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II As shown in Figures 5A and 5B, the expression of the epithelial marker molecules E-cadherin and α-catenin
5 BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1): Figure 4. A high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II promoted the expression of TCF8 in podocytes. (A) Podocytes were incubated with 0-30 mm of glucose for 24 h and TCF8 expression was measured with Western blotting. (B) Podocytes were incubated with 0-9 μm of angiotensin II for 24 h and TCF8 expression was measured with Western blotting. (C) Expression of TCF8 protein after three TCF8 antisense RNA sequences were transfected into podocytes was assayed using Western blotting. (D) Expression of TCF8 mrna after three TCF8 antisense RNA sequences were transfected into podocytes was assayed using qrt- PCR. Figure 5. Silencing TCF8 expression in podocytes reversed expression of EMT biomarkers induced with glucose and angiotensin II. (A) Podocytes with silenced TCF8 were incubated with 0 or 30 mm of glucose for 24 h and expression of the epithelial biomarkers E-cadherin and α-catenin was measured with Western blotting. (B) Podocytes with silenced TCF8 were incubated with 0 or 9 μm of angiotensin II for 24 h and expression of the epithelial biomarkers E-cadherin and α-catenin expression was measured with Western blotting. (C) Podocytes with silenced TCF8 were incubated with 0 or 30 mm of glucose for 24 h and expression of the mesenchymal biomarkers N-cadherin and vimentin was measured with Western blotting. (D) Podocytes with silenced TCF8 were incubated with 0 or 9 μm of angiotensin II for 24 h and expression of the mesenchymal biomarkers N-cadherin and vimentin was measured with Western blotting.
6 82 BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1): decreased with an increase in the glucose or angiotensin II concentration, but this phenomenon was reversed in podocytes with silenced TCF8. As shown in Figures 5C and 5D, the expression of the mesenchymal marker molecules N-cadherin and vimentin increased with an increase in the glucose or angiotensin II concentration, Figure 6. Silencing TCF8 expression reversed changes in the cell morphology of podocytes and podocyte migration and invasion induced with a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II. (A) Normal podocytes and changes in in the cell morphology of podocytes with silenced TCF8 in the presence of 0 and 30 mm of glucose. (B) Normal podocytes and changes in the cell morphology of podocytes with silenced TCF8 in the presence of 0 and 9 μm of angiotensin II. (C) Migration of normal podocytes and podocytes with silenced TCF8 in the presence of 0 and 30 mm of glucose. (D) Migration of normal podocytes and podocytes with silenced TCF8 in the presence of 0 and 9 μm of angiotensin II. (E) Invasion by normal podocytes and podocytes with silenced TCF8 in the presence of 0 and 30 mm of glucose. (F) Invasion by normal podocytes and podocytes with silenced TCF8 in the presence of 0 and 9 μm of angiotensin II.
7 BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1): but this phenomenon was reversed in podocytes with silenced TCF8. Results indicated that silencing TCF8 reversed EMT that was induced with a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II Silencing TCF8 reversed changes in podocyte morphology and podocyte migration and invasion induced with a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II As shown in Figures 6A and 6B, morphological changes induced with a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II were reversed in podocytes with silenced TCF8. As shown in Figures 6C and 6D, a higher rate of cell migration was induced with a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II, but this phenomenon was reversed in podocytes with silenced TCF8. As shown in Figures 6E and 6F, a higher rate of cell invasion was induced with a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II, but this phenomenon was reversed in podocytes with silenced TCF8. In conclusion, silencing TCF8 reversed changes in podocyte morphology and podocyte migration and invasion induced with a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II. 4. Discussion Podocyte injury is a key factor for proteinuria in some kidney diseases (2). Proteinuria was assumed to be the result of podocyte depletion due to apoptosis (2). However, a recent study has indicated that the podocyte count did not change significantly when microalbuminuria was evident in diabetic rats (18). In addition, podocyte detachment and apoptosis lag far behind the onset of proteinuria. Whether initial podocyte injury leads to the onset of proteinuria is uncertain (3). Emerging evidence has indicated that podocytes can undergo EMT when exposed to specific pathological conditions, and this may explain the onset of proteinuria. A study has described the phenotypic and morphological changes in diseased podocytes as an EMT (19). Mounting evidence has revealed that glucose and angiotensin II are two key mediators associated with progressive renal injury in chronic kidney disease, and specifically in hypertensive and diabetic nephropathy (in which progressive renal fibrosis is a major determinant of clinical outcomes) (16). The current study characterized the role of TCF8 in EMT in podocytes. EMT markers were detected in the presence of a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II. Results indicated that a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II promoted EMT in podocytes, and results also indicated that a high concentration of glucose and angiotensin II caused changes in podocyte morphology and they promoted podocyte migration and invasion. Moreover, results indicated that TCF8 is significantly overexpressed in the presence of a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II. Silencing TCF8 reversed EMT in podocytes and changes in podocyte morphology, and it also reversed the increase in podocyte migration and invasion. Collectively, these findings are the first to suggest that TCF8 is involved in EMT in podocytes. Recent studies have indicated that EMTs are not limited to renal epithelial cells but that EMTs also occur in endothelial cells and podocytes (20). EMT in podocytes may be reversible before podocytes decrease and die off. Podocytes may have biological characteristics causing an EMT under pathological conditions, and an EMT could conceivably result. Podocytes may undergo some changes such as cell detachment, apoptosis, and an EMT when subjected to a harmful stimulus, and the severity and duration of those changes may depend on the specific injury. However, there are numerous unknowns regarding the mechanism of EMT in podocytes and how an EMT in podocytes leads to glomerular disease. TCF8, also known as ZEB1 or δ EF1, is located on the short arm of human chromosome 10 (21). TCF8 is characterized by a homeodomain flanked by two zinc finger domains, and TCF8 encodes 1108 amino acids. An important molecular event in EMT is the downregulation of E-cadherin. TCF8 can bind with E-cadherin promoter and inhibit the expression of E-cadherin. TCF8 has been found to be closely related to EMT in tumors, but its role in EMT in podocytes has yet to be elucidated. In conclusion, the current results revealed that TCF8 was generally overexpressed in podocytes in the presence of a high concentration of glucose or angiotensin II and that TCF8 was involved in EMT. These results indicate that TCF8 plays a key role in promoted EMT in podocytes and that TCF8 may be an effective novel therapeutic target for the management of glomerular disease. References 1. May CJ, Saleem M, Welsh GI. Podocyte dedifferentiation: A specialized process for a specialized cell. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014; 5: Ilatovskaya DV, Levchenko V, Lowing A, Shuyskiy LS, Palygin O, Staruschenko A. Podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy: Implications of angiotensin II-dependent activation of TRPC channels. Sci Rep. 2015; 5: Harindhanavudhi T, Parks A, Mauer M, Caramori ML. Podocyte structural parameters do not predict progression to diabetic nephropathy in normoalbuminuric type 1 diabetic patients. Am J Nephrol. 2015; 41: Du M, Wang Q, Li W, Ma X, Wu L, Guo F, Zhao S, Huang F, Wang H, Qin G. Overexpression of FOXO1 ameliorates the podocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by high glucose in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 471: Liu Y. New insights into epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;
8 84 BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1): : Wang Y, Wen M, Kwon Y, et al. CUL4A induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes cancer metastasis by regulating ZEB1 expression. Cancer Res. 2014; 74: Ding Y, Li X, Hong D, Jiang L, He Y, Fang H. Silence of MACC1 decreases cell migration and invasion in human malignant melanoma through inhibiting the EMT. Biosci Trends. 2016; 5: Kumar PA, Welsh GI, Raghu G, Menon RK, Saleem MA, Reddy GB. Carboxymethyl lysine induces EMT in podocytes through transcription factor ZEB2: Implications for podocyte depletion and proteinuria in diabetes mellitus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2016; 590: Zhao L, Wang X, Sun L, Nie H, Liu X, Chen Z, Guan G. Critical role of serum response factor in podocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition of diabetic nephropathy. Diab Vasc Dis Res. 2016; 13: Dai H, Zhang Y, Yuan L, Wu J, Ma L, Shi H. CTGF mediates high-glucose induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through activation of beta-catenin in podocytes. Ren Fail. 2016; 16: Sun LN, Chen ZX, Liu XC, Liu HY, Guan GJ, Liu G. Curcumin ameliorates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of podocytes in vivo and in vitro via regulating caveolin-1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014; 68: Chen T, Zheng LY, Xiao W, Gui D, Wang X, Wang N. Emodin ameliorates high glucose induced-podocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition in-vitro and in-vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35: Li G, Li CX, Xia M, Ritter JK, Gehr TW, Boini K, Li PL. Enhanced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition associated with lysosome dysfunction in podocytes: Role of p62/ Sequestosome 1 as a signaling hub. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015; 35: Zhang C, Xia M, Boini KM, Li CX, Abais JM, Li XX, Laperle LA, Li PL. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in podocytes mediated by activation of NADPH oxidase in hyperhomocysteinemia. Pflugers Arch. 2011; 462: Jung E, Kim J, Ho Kim S, Kim S, Cho MH. Gemigliptin improves renal function and attenuates podocyte injury in mice with diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015; 761: Yang F, Huang XR, Chung AC, Hou CC, Lai KN, Lan HY. Essential role for Smad3 in angiotensin II-induced tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Pathol. 2010; 221: Tang R, Yang C, Tao JL, You YK, An N, Li SM, Wu HL, Liu HF. Epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation of renal tubular epithelial cells induced by urinary proteins requires the activation of PKC-alpha and betai isozymes. Cell Biol Int. 2011; 35: Jha JC, Thallas-Bonke V, Banal C, Gray SP, Chow BS, Ramm G, Quaggin SE, Cooper ME, Schmidt HH, Jandeleit-Dahm KA. Podocyte-specific Nox4 deletion affords renoprotection in a mouse model of diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia. 2016; 59: Loeffler I, Wolf G. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Nephropathy: Fact or Fiction? Cells. 2015; 4: Ziyadeh FN, Wolf G. Pathogenesis of the podocytopathy and proteinuria in diabetic glomerulopathy. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2008; 4: Zhan HX, Wang Y, Li C, Xu JW, Zhou B, Zhu JK, Han HF, Wang L, Wang YS, Hu SY. LincRNA-ROR promotes invasion, metastasis and tumor growth in pancreatic cancer through activating ZEB1 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2016; 374: (Received November 29, 2016; Revised December 27, 2016; Accepted December 31, 2016)
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS
 Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS Proteinuria is a major healthcare problem that affects several hundred million people worldwide. Proteinuria is a cardinal
Podocyte Biology and clinical applications Dr. F. Ahmadi Professor Of Nephrology TUMS Proteinuria is a major healthcare problem that affects several hundred million people worldwide. Proteinuria is a cardinal
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4654-4660 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0048142 Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4654-4660 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0048142 Original Article Increased LincRNA ROR is association with poor prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients
3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES
 How to Cite this article: Podocyte Injury in Glomerular Diseases - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES Mirjana Sabljar Matovinović Podocytes are injured in diabetic
How to Cite this article: Podocyte Injury in Glomerular Diseases - ejifcc 20/01 2009 http://www.ifcc.org 3. PODOCYTE INJURY IN GLOMERULAR DISEASES Mirjana Sabljar Matovinović Podocytes are injured in diabetic
cells ISSN
 Cells 2015, 4, 631-652; doi:10.3390/cells4040631 Review OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Nephropathy: Fact or Fiction? Ivonne
Cells 2015, 4, 631-652; doi:10.3390/cells4040631 Review OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Nephropathy: Fact or Fiction? Ivonne
MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer J.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer J.-X.
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
GLI-1 facilitates the EMT induced by TGF-β1 in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 6809-6815 GLI-1 facilitates the EMT induced by TGF-β1 in gastric cancer M. LIANG 1, X.-C. LIU 1, T. LIU 2, W.-J. LI 3, J.-G. XIANG 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 6809-6815 GLI-1 facilitates the EMT induced by TGF-β1 in gastric cancer M. LIANG 1, X.-C. LIU 1, T. LIU 2, W.-J. LI 3, J.-G. XIANG 1,
Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
Astragaloside IV ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced
 Astragaloside IV ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis implicating regulation of energy metabolism Xu-Guang Jiang 1,2,, Kai Sun 1,3,4,5,, Yu-Ying Liu 1,4,5, Li Yan 1,4,5,
Astragaloside IV ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis implicating regulation of energy metabolism Xu-Guang Jiang 1,2,, Kai Sun 1,3,4,5,, Yu-Ying Liu 1,4,5, Li Yan 1,4,5,
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing SOX4
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity
 Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
Gallic acid prevents isoproterenol-induced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis through regulation of JNK2 signaling and Smad3 binding activity Yuhee Ryu 1,+, Li Jin 1,2+, Hae Jin Kee 1,, Zhe Hao Piao 3, Jae
IL-37 suppresses migration and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells through inhibition of HIF-1α induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8179-8185 IL-37 suppresses migration and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells through inhibition of HIF-1α induced epithelial-mesenchymal
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8179-8185 IL-37 suppresses migration and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells through inhibition of HIF-1α induced epithelial-mesenchymal
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation
 Repository of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin (Germany) http://edoc.mdc-berlin.de/14009/ The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Published in final
Repository of the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin (Germany) http://edoc.mdc-berlin.de/14009/ The Ebf1 knockout mouse and glomerular maturation Schmidt-Ott, K.M. Published in final
TGF-β1 promotes cells invasion and migration by inducing epithelial mesenchymal transformation in oral squamous cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2137-2144 TGF-β1 promotes cells invasion and migration by inducing epithelial mesenchymal transformation in oral squamous cell carcinoma
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2137-2144 TGF-β1 promotes cells invasion and migration by inducing epithelial mesenchymal transformation in oral squamous cell carcinoma
The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4039-4044 The diagnostic value of determination of serum GOLPH3 associated with CA125, CA19.9 in patients with ovarian cancer H.-Y. FAN
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Role for integrin-linked kinase in mediating tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrogenesis
 Role for integrin-linked kinase in mediating tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrogenesis Yingjian Li, Junwei Yang, Chunsun Dai, Chuanyue Wu, and Youhua Liu Department
Role for integrin-linked kinase in mediating tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial fibrogenesis Yingjian Li, Junwei Yang, Chunsun Dai, Chuanyue Wu, and Youhua Liu Department
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy
 MINI REVIEW Zemin Cao, Mark E Cooper* ABSTRACT As the increasing prevalence of diabetes reaches epidemic proportions worldwide, diabetic nephropathy and associated end-stage renal failure will be an unavoidable
MINI REVIEW Zemin Cao, Mark E Cooper* ABSTRACT As the increasing prevalence of diabetes reaches epidemic proportions worldwide, diabetic nephropathy and associated end-stage renal failure will be an unavoidable
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 14: , 2016
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 14: 1771-1784, 2016 GSK 3β inhibitor attenuates urinary albumin excretion in type 2 diabetic db/db mice, and delays epithelial to mesenchymal transition in mouse kidneys and
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 14: 1771-1784, 2016 GSK 3β inhibitor attenuates urinary albumin excretion in type 2 diabetic db/db mice, and delays epithelial to mesenchymal transition in mouse kidneys and
BioScience Trends. 2016; 10(4):
 Original Article 258 Silence of MACC1 decreases cell migration and invasion in human malignant melanoma through inhibiting the EMT Yingguo Ding*, Xiaomin Li, Dongsheng Hong, Li Jiang, Yong He, Hong Fang
Original Article 258 Silence of MACC1 decreases cell migration and invasion in human malignant melanoma through inhibiting the EMT Yingguo Ding*, Xiaomin Li, Dongsheng Hong, Li Jiang, Yong He, Hong Fang
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
Expression of lncrna TCONS_ in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5655-5660 Expression of lncrna TCONS_00027978 in hepatocellular carcinoma and its influence on prognosis and survival Q. CHEN 1, G.-D.
Down-regulation of mir-23a inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by up-regulation of SnoN
 Human Cell (2018) 31:22 32 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-017-0180-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Down-regulation of mir-23a inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by up-regulation of SnoN Haiping
Human Cell (2018) 31:22 32 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-017-0180-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Down-regulation of mir-23a inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by up-regulation of SnoN Haiping
Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 82-86 Prognostic significance of overexpressed long non-coding RNA TUG1 in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma P.-Q. WANG, Y.-X.
Original Article Long non-coding RNA PANDAR overexpression serves as a poor prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(5):2728-2734 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0073509 Original Article Long non-coding RNA PANDAR overexpression serves as a poor prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2018;11(5):2728-2734 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0073509 Original Article Long non-coding RNA PANDAR overexpression serves as a poor prognostic biomarker in oral squamous cell
Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus entry
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s
 Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s The basic facts about proteinuria and FSGS A primer on proteinuria Endothelium and glycocalyx Podocytes Pathology
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s The basic facts about proteinuria and FSGS A primer on proteinuria Endothelium and glycocalyx Podocytes Pathology
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Effect of lncrna LET on proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 1609-1614 Effect of lncrna LET on proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells G. KONG 1, X.-J. QI 2, J.-F. WANG 3 1 Department of
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 1609-1614 Effect of lncrna LET on proliferation and invasion of osteosarcoma cells G. KONG 1, X.-J. QI 2, J.-F. WANG 3 1 Department of
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Wen-Shuang Wang 1,2, Xing-Sheng Yang 2, Min Xia 1, Hai-Yang Jiang 1, Jian-Qing Hou 1 * Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.9.4435 RESEARCH ARTICLE Silencing of Twist Expression by RNA Interference Suppresses Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition, Invasion, and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.9.4435 RESEARCH ARTICLE Silencing of Twist Expression by RNA Interference Suppresses Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition, Invasion, and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Title: Intermedin attenuates renal fibrosis by induction of heme oxygenase-1 in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction
 Author's response to reviews Title: Intermedin attenuates renal fibrosis by induction of heme oxygenase-1 in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction Authors: Xi Qiao (qiaoxi7347@126.com) Lihua Wang (lihuawang236@126.com)
Author's response to reviews Title: Intermedin attenuates renal fibrosis by induction of heme oxygenase-1 in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction Authors: Xi Qiao (qiaoxi7347@126.com) Lihua Wang (lihuawang236@126.com)
MicroRNA-124 suppresses Slug-mediated lung cancer metastasis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 3802-3811 MicroRNA-124 suppresses Slug-mediated lung cancer metastasis Z. CUI, Y. HU Medical Oncology Department I, General Hospital,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 3802-3811 MicroRNA-124 suppresses Slug-mediated lung cancer metastasis Z. CUI, Y. HU Medical Oncology Department I, General Hospital,
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
LncRNA LET function as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer development
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 6002-6007 LncRNA LET function as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer development C.-X. ZHOU, X. WANG, N. YANG, S.-K. XUE, W.-C. LI, P.-P.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 6002-6007 LncRNA LET function as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer development C.-X. ZHOU, X. WANG, N. YANG, S.-K. XUE, W.-C. LI, P.-P.
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Molecular signaling cascade of mirnas in causing Diabetes Nephropathy
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(8) Molecular signaling cascade of mirnas in causing Diabetes Nephropathy Dyave Gowda Padmashree & Narayanaswamy Ramachra Swamy* Department of Biochemistry, Central
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(8) Molecular signaling cascade of mirnas in causing Diabetes Nephropathy Dyave Gowda Padmashree & Narayanaswamy Ramachra Swamy* Department of Biochemistry, Central
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or
 Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Hypoxia promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inducing Twist1 expression
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3061-3068 Hypoxia promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inducing Twist1 expression X.-D. ZHANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3061-3068 Hypoxia promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inducing Twist1 expression X.-D. ZHANG
Role of Acid Sphingomyelinase Knockout Mice in Protection Against Hyperhomocystenimia Induced Glomerular Injury
 Role of Acid Sphingomyelinase Knockout Mice in Protection Against Hyperhomocystenimia Induced Glomerular Injury Sophie S. Yuth Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Virginia
Role of Acid Sphingomyelinase Knockout Mice in Protection Against Hyperhomocystenimia Induced Glomerular Injury Sophie S. Yuth Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Virginia
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Long non-coding RNA Loc is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3808-3812 Long non-coding RNA Loc344887 is a potential prognostic biomarker in non-small cell lung cancer B. WU 1, X.-J. ZHANG 2, X.-G.
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Information. Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like. Behaviors in Mice by Modulating. Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation
 Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Neuron, Volume 100 Supplemental Information Menin Deficiency Leads to Depressive-like Behaviors in Mice by Modulating Astrocyte-Mediated Neuroinflammation Lige Leng, Kai Zhuang, Zeyue Liu, Changquan Huang,
Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8624-8629 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma H.-X. AN 1, B. XU 2, Q. WANG 3, Y.-S.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8624-8629 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG6 predicts poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma H.-X. AN 1, B. XU 2, Q. WANG 3, Y.-S.
LncRNA GHET1 predicts a poor prognosis of the patients with non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 2328-2333 LncRNA GHET1 predicts a poor prognosis of the patients with non-small cell lung cancer Q.-M. SHEN 1,2, H.-Y. WANG 1,2, S. XU
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 2328-2333 LncRNA GHET1 predicts a poor prognosis of the patients with non-small cell lung cancer Q.-M. SHEN 1,2, H.-Y. WANG 1,2, S. XU
LncRNA NKILA suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and migration by inactivating PI3K/Akt pathway
 Original Article LncRNA NKILA suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and migration by inactivating PIK/Akt pathway Jian Huang #, Lingfeng Zhao #, Wei Chen #, Jian Duan 4, Dibesh Shrestha, Ruize Zhou,
Original Article LncRNA NKILA suppresses colon cancer cell proliferation and migration by inactivating PIK/Akt pathway Jian Huang #, Lingfeng Zhao #, Wei Chen #, Jian Duan 4, Dibesh Shrestha, Ruize Zhou,
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
LncRNA RGMB-AS1 is activated by E2F1 and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 1979-1986 LncRNA RGMB-AS1 is activated by E2F1 and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma Z. ZHANG 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 1979-1986 LncRNA RGMB-AS1 is activated by E2F1 and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma Z. ZHANG 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 498-503 Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma J.-J. WEN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 498-503 Analysis of circulating long non-coding RNA UCA1 as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of osteosarcoma J.-J. WEN
Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention
 REVIEW J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1 12, 2004 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention YOUHUA LIU Division of Cellular
REVIEW J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1 12, 2004 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention YOUHUA LIU Division of Cellular
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt
 Supplementary Information CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt Jae Hyang Lim, Hirofumi Jono, Kensei Komatsu, Chang-Hoon Woo, Jiyun Lee, Masanori Miyata,
Supplementary Information CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt Jae Hyang Lim, Hirofumi Jono, Kensei Komatsu, Chang-Hoon Woo, Jiyun Lee, Masanori Miyata,
Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 2353-2359 Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer K. HUANG, W.-S. FAN, X.-Y. FU, Y.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019; 23: 2353-2359 Long noncoding RNA DARS-AS1 acts as an oncogene by targeting mir-532-3p in ovarian cancer K. HUANG, W.-S. FAN, X.-Y. FU, Y.-L.
Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(4):4241-4246 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0012296 Original Article Tissue expression level of lncrna UCA1 is a prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer Hong Jiang,
Original Article Differential microrna expression in the serum of patients with nephrotic syndrome and clinical correlation analysis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):7282-7286 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008575 Original Article Differential microrna expression in the serum of patients with nephrotic syndrome and clinical correlation
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):7282-7286 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008575 Original Article Differential microrna expression in the serum of patients with nephrotic syndrome and clinical correlation
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
http / /cjbmb. bjmu. edu. cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology A431 . Western aza-dC FUT4-siRNA
 ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
ISSN 1007-7626 CN 11-3870 / Q http / /cjbmb bjmu edu cn Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2015 8 31 8 836 ~ 842 DOI 10 13865 /j cnki cjbmb 2015 08 09 FUT4-siRNA 5-aza-dC 1 3 * 1 1 3
Blockade of Wnt/ -Catenin Signaling by Paricalcitol Ameliorates Proteinuria and Kidney Injury
 BASIC RESEARCH www.jasn.org Blockade of Wnt/ -Catenin Signaling by Paricalcitol Ameliorates Proteinuria and Kidney Injury Weichun He, Young Sun Kang, Chunsun Dai, and Youhua Liu Department of Pathology,
BASIC RESEARCH www.jasn.org Blockade of Wnt/ -Catenin Signaling by Paricalcitol Ameliorates Proteinuria and Kidney Injury Weichun He, Young Sun Kang, Chunsun Dai, and Youhua Liu Department of Pathology,
Original Article LncRNA HOXD-AS1 promotes melanoma cell proliferation and invasion by suppressing RUNX3 expression
 Am J Cancer Res 2017;7(12):2526-2535 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0064925 Original Article LncRNA HOXD-AS1 promotes melanoma cell proliferation and invasion by suppressing RUNX3 expression Hailin Zhang,
Am J Cancer Res 2017;7(12):2526-2535 www.ajcr.us /ISSN:2156-6976/ajcr0064925 Original Article LncRNA HOXD-AS1 promotes melanoma cell proliferation and invasion by suppressing RUNX3 expression Hailin Zhang,
Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA BCAR4 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma, and promotes cell invasion and metastasis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 4445-4451 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA BCAR4 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma, and promotes cell invasion
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 4445-4451 Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA BCAR4 predicts a poor prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma, and promotes cell invasion
Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8749-8754 Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer X.-M. LIU 1, B. YANG 2,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 8749-8754 Increased long noncoding RNA LINP1 expression and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer X.-M. LIU 1, B. YANG 2,
Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells *
 Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
Journal of Animal and Feed Sciences, 16, Suppl. 2, 2007, 325 329 Effects of methionine-containing dipeptides on α s1 casein expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells * H.H. Wu 1, J.Y. Yang 1,2, K.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one. of the most common diseases found in the population.
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
Genetic Testing of Children with Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome
 The 5 th Global Congress For Consensus in Pediatrics & Child Health Genetic Testing of Children with Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome Fang Wang Peking University First Hospital Nephrotic Syndrome (NS)
The 5 th Global Congress For Consensus in Pediatrics & Child Health Genetic Testing of Children with Steroid Resistant Nephrotic Syndrome Fang Wang Peking University First Hospital Nephrotic Syndrome (NS)
Influence of tacrolimus on podocyte injury inducted by angiotensin II
 568520JRA0010.1177/1470320314568520Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone SystemShengyou et al. research-article2015 Original Article Influence of tacrolimus on podocyte injury inducted by angiotensin
568520JRA0010.1177/1470320314568520Journal of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone SystemShengyou et al. research-article2015 Original Article Influence of tacrolimus on podocyte injury inducted by angiotensin
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 functions as a tumor promoter in colorectal cancer by regulating EMT and Notch signaling pathway
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3586-3591 Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 functions as a tumor promoter in colorectal cancer by regulating EMT and Notch signaling pathway
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3586-3591 Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 functions as a tumor promoter in colorectal cancer by regulating EMT and Notch signaling pathway
PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype to promote glioblastoma migration and invasion
 Xu et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:158 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0841-0 RESEARCH PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype
Xu et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:158 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0841-0 RESEARCH PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Mohammad Husain Department of Biotechnology, Jamia Millia Islamia New Delhi
 Role of Vitamin D receptor (VDR) in HIV induced tubular injury Mohammad Husain Department of Biotechnology, Jamia Millia Islamia New Delhi 07/10/2015 INTRODUCTION Vitamin D is technically not a Vitamin;
Role of Vitamin D receptor (VDR) in HIV induced tubular injury Mohammad Husain Department of Biotechnology, Jamia Millia Islamia New Delhi 07/10/2015 INTRODUCTION Vitamin D is technically not a Vitamin;
Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4298-4303 Association between downexpression of mir-1301 and poor prognosis in patients with glioma Q.-L. BAI, C.-W. HU, X.-R. WANG, G.-F.
Original Article USP43 promotes tumorigenesis through regulating cell cycle and EMT in breast cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(11):11014-11021 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0037554 Original Article USP43 promotes tumorigenesis through regulating cell cycle and EMT in breast cancer Fei Lin 1*,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(11):11014-11021 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0037554 Original Article USP43 promotes tumorigenesis through regulating cell cycle and EMT in breast cancer Fei Lin 1*,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
