FUNCTIONAL CONDITION OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND RELATIONSHIP WITH A PHYSICAL WORKING CAPACITY OF ATHLETES FOOTBALL PLAYERS
|
|
|
- Leslie Lynch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 wjpmr, 2018,4(12), SJIF Impact Factor: Makhmudov et al. Research Article WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN WJPMR FUNCTIONAL CONDITION OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND RELATIONSHIP WITH A PHYSICAL WORKING CAPACITY OF ATHLETES FOOTBALL PLAYERS Iskandar Mavlyanov 1, Dilshodbek Makhmudov 2 * and Sardor Parpiev 3 1 Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Deputy Director of the Republican Scientific-Research Centre of Sports Medicine, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. 2 PhD Student, MD, Department of Functional Diagnostics, the Republican Scientific-Research Centre of Sports Medicine, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. 3 MD, Department of Functional Diagnostics, the Republican Scientific-Research Centre of Sports Medicine, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. *Corresponding Author: Dilshodbek Makhmudov PhD Student, MD, Department of Functional Diagnostics, the Republican Scientific-Research Centre of Sports Medicine, Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Article Received on 28/09/2018 Article Revised on 19/10/2018 Article Accepted on 09/11/2018 ABSTRACT In this article it was investigated the indicators of the functional state of the respiratory system in athletes-players. It is considered that excessive physical activity places increased demands on the oxygen supply of the body, particularly, respiratory system. It was studied functional state of the respiratory system, taking into account the degree of physical performance of an athlete. The study was carried out at 300 football players. Age of football players ranged from 18 to 25 years. Athletes, football, depending on the degree of physical performance were divided into the following groups: with high, above average, average, below average and low performance. The results of the conducted studies of the respiratory function in athletes-football players compared with the performance of the respiratory function in the control group shows a clear difference. The FVC index in the studied football players alone is 17.4% higher than in the control group. Therefore, in football players, there is a relatively quick response from the respiratory system to physical activity. This is apparently due to the training of the respiratory system, which promotes an accurate and adequate fit of the level of pulmonary ventilation to the metabolic needs of the athlete's body during normal activities and the associated energy costs. Respiratory system in athletes-football players, like other functional-metabolic systems of the body, is being rebuilt in the process of adaptation to ever-increasing physical exertion and acquires a more economical use of reserve resources to compensate for energy costs and ensure normal life activity body athlete. KEYWORDS: Respiratory function; athletes; football players; forced expiratory volume in 1 second, forced vital capacity; lung capacity; EVC; IVC. INTRODUCTION It is known that the respiratory system plays a strategic role in ensuring the supply of oxygen to working muscles and in removing carbon dioxide from the body, [1] which allows the body to maintain gas homeostasis not only under extreme conditions, but also under conditions of high physical exertion. Low functional activity of this system significantly affects the physical and mental performance, reducing the body's resistance to harmful factors and psycho-emotional stress. [2,3] Therefore, the study of this issue is very relevant for professional athletes involved in various sports, with different motor load. Of particular importance is this issue in those sports that place increased demands on aerobic capabilities. [4] These sports include football. In connection with the above, we have studied the indicators of the functional state of the respiratory system in athletes-players. Considering that excessive physical activity places increased demands on the oxygen supply of the body, in particular, the respiratory system, we have studied the functional state of the respiratory system, taking into account the degree of physical performance of an athlete. The purpose of the study: the study and evaluation of indicators of respiratory function in athletes, football, depending on their physical performance and playing roles. MATERIALS AND METHODS The study was carried out at 300 football players. Age of football players ranged from 18 to 25 years. Athletes, football, depending on the degree of physical performance were divided into the following groups: with high, above average, average, below average and 11
2 low performance. Considering that the athletes-soccer players during the game in the field perform different physical activity tasks by us in each group on physical performance, they are still divided according to the game role into goalkeepers, defenders, midfielders and forwards. The function of external respiration was studied in athletes at rest on a spirometer BTL-08 Spiro. As indicators of respiratory function, forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), forced expiratory flow at 75%, 50% and 25% vital capacity of the lungs (MOC75, MOC50, MOC25), lungs capacity (LC), vital capacity of the lungs on the inhale and exhale (EVC, IVC), maximum ventilation of the lungs (MVL). Evaluation of physical performance was performed by conducting an ECG study before and after individually calculated load. The controls were indicators of the function of external respiration of 19 healthy volunteers, students of the medical institute, of corresponding ages. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION The results of the conducted studies of the respiratory function (RF) in athletes-football players compared with the performance of the respiratory function in the control group shows a clear difference. The FVC index in the studied football players alone is 17.4% higher than in the control group. Therefore, in football players, there is a relatively quick response from the respiratory system to physical activity. This is apparently due to the training of the respiratory system, which promotes an accurate and adequate fit of the level of pulmonary ventilation to the metabolic needs of the athlete's body during normal activities and the associated energy costs. [4,5] The study of a different respiratory system index in athletes-football players - FEV1, measured in relative rest conditions, shows that its value exceeds the control value by 18.0%. This indicates a relatively high ability of the respiratory muscles in the examined athletes to exhale for the first second. The study of the indicators of the forced flow in the studied athletes depending on the specific proportion of the forced vital capacity of the lungs also indicates the presence of a certain difference between the control groups. At that, the value of МОС75 exceeds the values of control by 24%, МОС50 - by 15% and МОС25 - by 18%, respectively. Consequently, in football players, there is a relatively high potential of the bronchial tree in meeting the body s need for oxygen. Since, as a rule, MOC75, it characterizes the speed of the air flow through the small bronchi, MOC50 - according to the middle bronchi, and MOC25 - according to the main bronchi and trachea. At the same time, the most pronounced difference in the value of MOC75 compared to MOC50 and MOC25, apparently, indicates a comparatively higher adaptation of the terminal bronchi to the functional loads of the athlete-football player compared to other departments of the airways. We also studied the vital capacity indicators of the lungs during inhalation and expiration (EVC, IVC) in the studied football players. And here there is a higher value of the vital capacity of the lungs both during inhalation and in exhalation. The value of the latter exceeds those in the control group by 31.4% and 13.7%, respectively. Consequently, according to these indicators, the respiratory systems of athletes have higher capabilities than non-professional sportsmen. Indeed, a comparative study of the value of the indicator of MVL in the football players studied shows that the value of the latter for the sportsmen exceeds that of the control group by 27.5%. It follows from this that the respiratory system of the athlete-football player was rebuilt in the direction of the growth of the inhaled air volume due to the constant physical exertion associated with the training process. Since the respiratory system is one of the leading vegetative component of the athlete's organism adaptation to ever-increasing physical loads, increasing its function and often becomes a link limiting the intensity and duration of the development of adaptive reactions of the body. Moreover, the aerobic performance of the body, physical performance, endurance and skill of an athlete [3,6] largely depend on the adequate response of the respiratory system to physical activity (training effect). Based on the fact that the intensity of the respiratory function is ultimately associated with physical performance, we have measured the respiratory function, taking into account the degree of physical performance of the studied football players. The results of the studies are presented in Figure 1A, 1B. As can be seen from the data presented, 10.33% of football players' performance was assessed as high, 10.66% - above average, 40.66% - average, 20.33% - below average and 18.0% - low. Therefore, among the studied athletes, football players with high degrees of physical performance were only 1/3 of the athletes. The bulk of the athletes were athletes with an average degree of physical performance. Analysis of the results of the study of respiratory function indicators, depending on the specified degrees of physical performance, shows that the value of FVC in athletes with low physical performance is lower by 23.8% compared to athletes with high performance, by 25.7% compared to with higher average working capacity, by 21.4% compared with average working capacity, by 15.2% compared with lower average working capacity. Studying the value of another indicator of RF FEV1 also shows that football players with low physical performance are lower compared to high, above average, average and below average performance levels by 20.8%, 23.3%, 19.6% and 14.4% respectively. A similar picture occurs with respect to 12
3 other indicators of respiratory function, in particular, PEV, MOCaver, MOC25, MOC50, MOC75, LC, MVL, EVC and IVC (Fig. 1). Consequently, as physical performance decreases in parallel, the value of the studied parameters related to the respiratory system function decreases as well. It is quite clear that the lower the physical activity and performance, the less the body needs energy substrates, oxygen and, accordingly, respiratory function. Fig. 1: Indicators of respiratory function in football players, depending on the degree of physical activity. It should be noted that the role of each player on the field during the game requires different tactical, technical and physical performance. In this regard, it was of particular interest to us to study the indicators of lung function, depending on the role of a football player. As was shown above, the RF indicators were studied depending on the role played in each group of players, depending on their degree of physical performance. The analysis revealed that goalkeepers among football players were 9.67%, defenders %, midfielders % and forwards % of all sportsmen studied. At the same time, the proportion of goalkeepers among footballers with high, above average, average, below average and low physical performance turned out to be almost the same and amounted to 9.67%, 9.37%, 9.01%, 8.19% and 12, 96%. Therefore, goalkeepers are relatively more common among footballers with low physical performance and less often among footballers with average and below average physical performance. 13
4 Defenders, depending on the degree of performance, were distributed as follows: among footballers, high performance %, above average %, average %, below average %, low %, respectively. Therefore, the defenders are relatively more common among footballers with medium and below average physical performance and less often among footballers with high physical performance. Among footballers with high performance, midfielders and strikers accounted for 38.7% and 22.58%, among footballers with higher average performance % and 31.25%, among footballers with average performance % and %, among football players with lower average working capacity % and 19.67%, among football players with low working capacity % and 24.37%, respectively. Consequently, in the groups studied, midfielders and forwards are also represented almost equally, although their share is slightly higher among footballers with higher physical performance and the prevalence of the share of midfielders is traced compared to forwards. To analyze the dependence of the RF of football players on their gaming lines, 3 groups were singled out according to the degree of physical working capacity, in particular, groups with high, medium and low working capacity. The results of studies of this dependence in goalkeeper footballers are presented in Fig.2. Fig. 2: Indicators of respiratory function in football players goalkeepers, depending on the degree of physical activity (Note: * -Р <0.05). As can be seen from the presented data, the value of FVC in football players with a low degree of efficiency is lower compared to those of average and high efficiency by 18.9% and 43.2%, respectively. Similar shifts take place with respect to the values of FEV1, PEF and LC (Fig. 2A). The value of the speed indices of the respiratory system as MOC (MOCaver, MOC75, MOC50, and MOC25) in players with a given role, as can be seen from Fig. 2B, indicates the absence of a clear dependence on the degree of physical performance of the players. The results of studies on the dependence of the function of the respiratory system on the physical performance of players playing defense are shown in Fig. 3A, 3B. Fig. 3: Indicators of respiratory function in football players defenders, depending on the degree of physical activity (Note: *-Р <0.05). 14
5 As can be seen from the data presented, there is a definite relationship between the performance of respiratory function and the degree of efficiency. At the same time, the value of such RF indicators as FVC, FEV1, PEF, LC are noticeably higher in defenders with high and medium performance as compared to low performance. Thus, the value of the indicated RF parameters in football defenders with low performance compared with the average performance becomes lower by 100.0%, 97.1%, 59.1% and 86.5%, respectively FVC, FEV1, PEF and LC. An almost similar picture takes place in relation to other indicators of respiratory function (Fig. 3B). The study of this issue in football midfielders, as can be seen from Fig. 4A, 4B, shows that football players with an average degree of efficiency have the highest values of respiratory function. At the same time, the value of RC in football players with an average working capacity is higher than with a high working capacity by 18.4% and compared to a low working capacity by 52.6%, respectively. The ratio of FEV1, PEF and LC values also shows an identical picture (Fig. 4A). At the same time, the study of the speed parameters of lung function, as can be seen from the data presented in Figure 4B, indicates the presence of a slightly different relationship. At the same time, if the MOCaver value does not have a difference in the degree of working capacity, the MOC75 value increases as the degree of physical working capacity decreases, and the MOC50 value, on the contrary, increases. Fig. 4: Indicators of respiratory function in football midfielders, depending on the degree of physical activity (Note: * -Р <0.05). The results of studies on the dependence of the function of the respiratory system on the physical performance of players playing defense are shown in Fig. 5A, 5B. Fig. 5: Indicators of respiratory function in football players forwards, depending on the degree of physical activity (Note: * -Р <0.05). 15
6 As can be seen from the presented data, among the football players attacking the studied indicators of the functional state of the respiratory system is directly dependent on the degree of physical performance. The lower the degree of physical performance, the lower the value of the studied parameters of respiratory function. This pattern is clearly seen both in relation to the biomechanical and velocity indicators of the functional state of the respiratory system. CONCLUSION Thus, the conducted research indicates that the respiratory system in athletes-football players, like other functional-metabolic systems of the body, is being rebuilt in the process of adaptation to ever-increasing physical exertion and acquires a more economical use of reserve resources to compensate for energy costs and ensure normal life activity body athlete. The respiratory system, increasing the power and endurance of the respiratory muscles, contributes to an increase in the volume of inhaled air relative to the functional residual capacity of the lungs and, ultimately, an increase in the body's aerobic performance. REFERENCES 1. Butova O.A., Masalov S.V. The functional state of the respiratory system of athletes with different training activity // Bulletin of RUFN, 2008; 7: S ; 2. Aghadzhanyan N.A., Marachev A.G., Bobkov G.A. Ecological human physiology. - M.: Publishing firm "KRUK", 1998; Vorfolomeeva L., Smirnova Z. Individual assessment of the state of the external respiration system of qualified skiers-racers at the stage of preparation for the highest achievements // Olympic and professional sport., 2014; 1(25): С.65-68; 4. Safonov V.A., Tarasova N.N. nervous regulation of respiration // Human physiology, 2006; 32(4): C.64-76; 5. Breslav I.S., Nozdrachev A.D. Regulation of respiration: the vice and behavioral components // Successes of physiological sciences, 2007; 38(2): Vanyushin Yu.S. Indicators of external respiration and gas exchange in athletes of different sports / Yu.S.Vanyushin // Growing organism: adaptation to physical and mental stress: rep. symposium and sc. Seminar for young scientists and teachers. - Kazan, 1996; Guba V.P., Lexakov A.V., Antipov A.V. Integral training of football players. Moscow, 2010;
AN INTEGRAL ESTIMATION OF THE FUNCTIONAL STATUS OF THE EXTERNAL RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS OF QUALIFIED FUTSAL PLAYERS
 Journal of Physical Education & Health, 2014, vol. 3 (5), 37-41 AN INTEGRAL ESTIMATION OF THE FUNCTIONAL STATUS OF THE EXTERNAL RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS OF QUALIFIED FUTSAL PLAYERS V. P. Guba 1, S. L. Skorovich
Journal of Physical Education & Health, 2014, vol. 3 (5), 37-41 AN INTEGRAL ESTIMATION OF THE FUNCTIONAL STATUS OF THE EXTERNAL RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS OF QUALIFIED FUTSAL PLAYERS V. P. Guba 1, S. L. Skorovich
#8 - Respiratory System
 Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Ch 16 A and P Lecture Notes.notebook May 03, 2017
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology
 Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Year 10 Physical Education LC1 Medium Term Plan
 Year 10 Physical Education LC1 Medium Term Plan Overarching challenge question Exam board links Line of enquiry s Home learning How can the cardio-respiratory system aid the human body in physical activity
Year 10 Physical Education LC1 Medium Term Plan Overarching challenge question Exam board links Line of enquiry s Home learning How can the cardio-respiratory system aid the human body in physical activity
Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology
 Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology University of Utah Center for Emergency Programs and The Utah Asthma Program Incidence, Impact and Goals of Asthma Management Prevalence, Morbidity
Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology University of Utah Center for Emergency Programs and The Utah Asthma Program Incidence, Impact and Goals of Asthma Management Prevalence, Morbidity
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
Performance Enhancement. Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance
 Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. Name the 3 parts of a neuron and their function: a. b. c. 2. What is
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. Name the 3 parts of a neuron and their function: a. b. c. 2. What is
Chapter 3. Pulmonary Function Study Assessments. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 3 Pulmonary Function Study Assessments 1 Introduction Pulmonary function studies are used to: Evaluate pulmonary causes of dyspnea Differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disorders
Chapter 3 Pulmonary Function Study Assessments 1 Introduction Pulmonary function studies are used to: Evaluate pulmonary causes of dyspnea Differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disorders
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Breathing and pulmonary function
 EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Analysis of Lung Function
 Computer 21 Spirometry is a valuable tool for analyzing the flow rate of air passing into and out of the lungs. Flow rates vary over the course of a respiratory cycle (a single inspiration followed by
Computer 21 Spirometry is a valuable tool for analyzing the flow rate of air passing into and out of the lungs. Flow rates vary over the course of a respiratory cycle (a single inspiration followed by
ABSTRACT OF THE DOCTORAL THESIS BY CHEPEA I. ION BOGDAN THESIS ADVISER: PHD PROFESSOR DORINA ORŢĂNESCU TITLE OF THE THESIS:
 ABSTRACT OF THE DOCTORAL THESIS BY CHEPEA I. ION BOGDAN THESIS ADVISER: PHD PROFESSOR DORINA ORŢĂNESCU TITLE OF THE THESIS: OPTIMIZATION OF HANDBALL JUNIOR PLAYERS PERFORMANCE CAPACITY BY APPLYING OPERATIONAL
ABSTRACT OF THE DOCTORAL THESIS BY CHEPEA I. ION BOGDAN THESIS ADVISER: PHD PROFESSOR DORINA ORŢĂNESCU TITLE OF THE THESIS: OPTIMIZATION OF HANDBALL JUNIOR PLAYERS PERFORMANCE CAPACITY BY APPLYING OPERATIONAL
PED1. General Certificate of Education January 2009 Advanced Subsidiary Examination. SPORT AND PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1
 General Certificate of Education January 2009 Advanced Subsidiary Examination SPORT AND PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 PED1 Friday 16 January 2009 1.30 pm to 3.00 pm For this paper you must have: a 12-page
General Certificate of Education January 2009 Advanced Subsidiary Examination SPORT AND PHYSICAL EDUCATION Unit 1 PED1 Friday 16 January 2009 1.30 pm to 3.00 pm For this paper you must have: a 12-page
St Ninian s High School. Physical Education
 St Ninian s High School Physical Education S4 National 5 Football Contents Cycle of Analysis 2 Factors Impacting on Performance 3 Types of Fitness 4 Methods of Training 8 Principle of Training 11 Programme
St Ninian s High School Physical Education S4 National 5 Football Contents Cycle of Analysis 2 Factors Impacting on Performance 3 Types of Fitness 4 Methods of Training 8 Principle of Training 11 Programme
Montgomery County Public Schools Grade 6 Physical Education Curriculum Framework
 Montgomery County Public Schools Grade 6 Physical Education Curriculum Framework Standard I: Exercise Physiology Students will demonstrate the ability to use scientific principles to design and participate
Montgomery County Public Schools Grade 6 Physical Education Curriculum Framework Standard I: Exercise Physiology Students will demonstrate the ability to use scientific principles to design and participate
S O C C E R F I T - F A C T S
 S O C C E R F I T N E S S I N C. V O L U M E 4, I S S U E 1 : F E B R U A R Y 1 5, 2 0 1 2 S P E E D E N D U R A N C E T R A I N I N G T H E K E Y T O A S U C C E S S F U L T R A I N I N G C A M P I N
S O C C E R F I T N E S S I N C. V O L U M E 4, I S S U E 1 : F E B R U A R Y 1 5, 2 0 1 2 S P E E D E N D U R A N C E T R A I N I N G T H E K E Y T O A S U C C E S S F U L T R A I N I N G C A M P I N
Effects of Physical Activity and Sleep Quality in Prevention of Asthma
 Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology Advances Effects of Physical Activity and Sleep Quality in Prevention of Asthma Tartibian B., Yaghoobnezhad F. and Abdollahzadeh N. J Phys Pharm Adv 2014, 4(5): 356-359
Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology Advances Effects of Physical Activity and Sleep Quality in Prevention of Asthma Tartibian B., Yaghoobnezhad F. and Abdollahzadeh N. J Phys Pharm Adv 2014, 4(5): 356-359
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests
 6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
ASSESSMENT OF PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES OF BADMINTON PLAYERS
 ASSESSMENT OF PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES OF BADMINTON PLAYERS Mr. Manoj Singh Rana Asstt. Prof., L.N.U.P.E, Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India msrana@gmail.com ABSTRACT The purpose of this study is to analysis
ASSESSMENT OF PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES OF BADMINTON PLAYERS Mr. Manoj Singh Rana Asstt. Prof., L.N.U.P.E, Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh, India msrana@gmail.com ABSTRACT The purpose of this study is to analysis
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems
 Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems Learning Objectives 1. State the parts of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and give the functions of each part. 2. Identify the parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Systems Learning Objectives 1. State the parts of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems and give the functions of each part. 2. Identify the parts of the cardiovascular
INFLUENCE OF ANTISECRETORY THERAPY ON THE COURSE OF BRONCHIAL
 INFLUENCE OF ANTISECRETORY THERAPY ON THE COURSE OF BRONCHIAL ASTHMA COMBINED WITH GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE Z. Z. Saatov, E. H. Dusmuhamedova, G. N. Sobirova Republican specialized scientific and
INFLUENCE OF ANTISECRETORY THERAPY ON THE COURSE OF BRONCHIAL ASTHMA COMBINED WITH GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE Z. Z. Saatov, E. H. Dusmuhamedova, G. N. Sobirova Republican specialized scientific and
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY
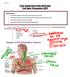 Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Playing, Practice, Training How can we do it all? Presenter: Karla Thompson Director of Soccer Operations Arizona Fury Soccer Club
 Playing, Practice, Training How can we do it all? Presenter: Karla Thompson Director of Soccer Operations Arizona Fury Soccer Club Karla Thompson Director of Soccer Operations USSF B License National Youth
Playing, Practice, Training How can we do it all? Presenter: Karla Thompson Director of Soccer Operations Arizona Fury Soccer Club Karla Thompson Director of Soccer Operations USSF B License National Youth
**Department of Physiology, K. G 's Medical College Lucknow, tbalrampur Hospital, Lucknow
 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1998; 42 (3) : 412-416 PULMONARY FUNCTIONS IN INDIAN SPORTSMEN PLAYING DIFFERENT SPORTS PRATEEK KUMAR MEHROTRA*, NARSINGH VARMA**, SUNITA TIWARI** AND PRABHAT KUMARt *G. S. V.
Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 1998; 42 (3) : 412-416 PULMONARY FUNCTIONS IN INDIAN SPORTSMEN PLAYING DIFFERENT SPORTS PRATEEK KUMAR MEHROTRA*, NARSINGH VARMA**, SUNITA TIWARI** AND PRABHAT KUMARt *G. S. V.
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Respiratory System Mechanics
 M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD
 COPD DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD Confirm Diagnosis Presence and history of symptoms: Shortness of breath Cough
COPD DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT CHECKLIST Anyone who smokes and/or has shortness of breath and sputum production could have COPD Confirm Diagnosis Presence and history of symptoms: Shortness of breath Cough
Paper No. : 09 Physiology and Sports Anthropology Module : 10 Variation in respiratory Function with Environment. Development Team
 Paper No. : 09 Physiology and Sports Module : 10 Development Team Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator Prof. Anup Kumar Kapoor Department of, University of Delhi Dr Rashmi Sinha IGNOU, Delhi Content
Paper No. : 09 Physiology and Sports Module : 10 Development Team Principal Investigator Paper Coordinator Prof. Anup Kumar Kapoor Department of, University of Delhi Dr Rashmi Sinha IGNOU, Delhi Content
PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT)
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT) Objectives: By the end of the present lab, students should be able to: 1. Record lung volumes and capacities and compare them with those of a typical person of the same gender,
PULMONARY FUNCTION TEST(PFT) Objectives: By the end of the present lab, students should be able to: 1. Record lung volumes and capacities and compare them with those of a typical person of the same gender,
3. Which statement is false about anatomical dead space?
 Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Respiratory MCQs 1. Which of these statements is correct? a. Regular bronchioles are the most distal part of the respiratory tract to contain glands. b. Larynx do contain significant amounts of smooth
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
SPORT AND COACHING PRINCIPLES
 VOCATIONAL WJEC Level 1/2 Vocational Award in SPORT AND COACHING PRINCIPLES REGULATED BY OFQUAL DESIGNATED BY QUALIFICATIONS WALES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS - EXTERNAL Teaching from 2018 For award from
VOCATIONAL WJEC Level 1/2 Vocational Award in SPORT AND COACHING PRINCIPLES REGULATED BY OFQUAL DESIGNATED BY QUALIFICATIONS WALES SAMPLE ASSESSMENT MATERIALS - EXTERNAL Teaching from 2018 For award from
SPIROMETRY TECHNIQUE. Jim Reid New Zealand
 Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Jim Reid New Zealand The Basics Jim Reid Spirometry measures airflow and lung volumes, and is the preferred lung function test in COPD. By measuring reversibility of obstruction, it is also diagnostic
Effect of different intensities of aerobic training on vital capacity of middle aged obese men
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 8 (August-2014) pp. 85-90 www.ijcrar.com Effect of different intensities of aerobic training on vital capacity of middle aged obese men M.Muralikrishna and P.V. Shelvam*
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 8 (August-2014) pp. 85-90 www.ijcrar.com Effect of different intensities of aerobic training on vital capacity of middle aged obese men M.Muralikrishna and P.V. Shelvam*
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
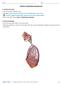 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Our Lungs, Our Air, Our Health
 UNIT 5 Our Lungs, Our Air, Our Health The Health Effects of Air Pollution ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION The first part of this activity introduces students to the human respiratory system. Using provided posters
UNIT 5 Our Lungs, Our Air, Our Health The Health Effects of Air Pollution ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION The first part of this activity introduces students to the human respiratory system. Using provided posters
QATs. VCE Physical Education SCHOOL-ASSESSED COURSEWORK UNIT 3 OUTCOME 2. Introduction. Quality Assessment Tasks
 QATs Quality Assessment s Introduction UNIT 3 OUTCOME 2 VCE Physical Education SCHOOL-ASSESSED COURSEWORK Outcome 2 Use data collected in practical activities to analyse how the major body and energy systems
QATs Quality Assessment s Introduction UNIT 3 OUTCOME 2 VCE Physical Education SCHOOL-ASSESSED COURSEWORK Outcome 2 Use data collected in practical activities to analyse how the major body and energy systems
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
FITNESS TRAINING WITH THE BALL FOR YOUNG SOCCER PLAYERS
 FITNESS TRAINING WITH THE BALL FOR YOUNG SOCCER PLAYERS Do you think it is important to use a fitness method based on soccer? Do players who train fitness with the ball increase their soccer performance?
FITNESS TRAINING WITH THE BALL FOR YOUNG SOCCER PLAYERS Do you think it is important to use a fitness method based on soccer? Do players who train fitness with the ball increase their soccer performance?
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS
 Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Chapter 8. Bellringer. Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System
 Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Bellringer Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Objectives Trace the path of blood through the
Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Bellringer Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Objectives Trace the path of blood through the
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements
 Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Spirometry and Flow Volume Measurements Standards & Guidelines December 1998 To serve the public and guide the medical profession Revision Dates: December 1998 Approval Date: June 1998 Originating Committee:
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:
 Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF FOUR WEEKS OF PRANAYAMA TECHNIQUE ON LUNG FUNCTION TEST OF NORMAL VOLUNTEERS Amit Mujumdar 1, Sudarshan Hande
Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 TO STUDY THE EFFECT OF FOUR WEEKS OF PRANAYAMA TECHNIQUE ON LUNG FUNCTION TEST OF NORMAL VOLUNTEERS Amit Mujumdar 1, Sudarshan Hande
A Comparative Study on Vital Capacity of Different Level Kabaddi Players
 A Comparative Study on Vital Capacity of Different Level Kabaddi Players Dr. Daudayal Yadav*, Dr. Jaswant Singh** and Ms. Anita Chaudhary*** * Assistant Professor, Department of Physical Education, C.C.S.
A Comparative Study on Vital Capacity of Different Level Kabaddi Players Dr. Daudayal Yadav*, Dr. Jaswant Singh** and Ms. Anita Chaudhary*** * Assistant Professor, Department of Physical Education, C.C.S.
Chapter 9. Producing Data: Experiments. BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1
 Chapter 9 Producing Data: Experiments BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1 How Data are Obtained Observational Study Observes individuals and measures variables of interest but does not attempt to influence the responses
Chapter 9 Producing Data: Experiments BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1 How Data are Obtained Observational Study Observes individuals and measures variables of interest but does not attempt to influence the responses
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
The Effect of using Ballistic Training on Some Physical Variables and on the Skill of High Jump Shooting among Handball Juniors
 1 The Effect of using Ballistic Training on Some Physical Variables and on the Skill of High Jump Shooting among Handball Juniors * Dr/ Amr Sayed Hassan INTRODUCTION: The most important objective of sports
1 The Effect of using Ballistic Training on Some Physical Variables and on the Skill of High Jump Shooting among Handball Juniors * Dr/ Amr Sayed Hassan INTRODUCTION: The most important objective of sports
#7 - Respiratory System
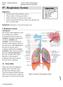 #7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
#7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology
 Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
Lab 4: Respiratory Physiology and Pathophysiology This exercise is completed as an in class activity and including the time for the PhysioEx 9.0 demonstration this activity requires ~ 1 hour to complete
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
Functional State of the Respiratory System in Patients with Abdominal Sepsis
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. III, Issue 2/ May 2015 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Functional State of the Respiratory System in Patients with Abdominal
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. III, Issue 2/ May 2015 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Functional State of the Respiratory System in Patients with Abdominal
Comparison of lung diffusing capacity in young elite athletes and their counterparts
 Pulmonol. 2018;24(4):219-223 www.journalpulmonology.org BRIEF COMMUNICATION Comparison of lung diffusing capacity in young elite athletes and their counterparts B. Lazovic a,f,, M. Zlatkovic-Svenda b,f,
Pulmonol. 2018;24(4):219-223 www.journalpulmonology.org BRIEF COMMUNICATION Comparison of lung diffusing capacity in young elite athletes and their counterparts B. Lazovic a,f,, M. Zlatkovic-Svenda b,f,
SPIROMETRY METHOD. COR-MAN IN / EN Issue A, Rev INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark
 SPIROMETRY METHOD COR-MAN-0000-006-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
SPIROMETRY METHOD COR-MAN-0000-006-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
Exercise 7: Respiratory System Mechanics: Activity 1: Measuring Respiratory Volumes and Calculating Capacities Lab Report
 Exercise 7: Respiratory System Mechanics: Activity 1: Measuring Respiratory Volumes and Calculating Capacities Lab Report Pre-lab Quiz Results You scored 100% by answering 5 out of 5 questions correctly.
Exercise 7: Respiratory System Mechanics: Activity 1: Measuring Respiratory Volumes and Calculating Capacities Lab Report Pre-lab Quiz Results You scored 100% by answering 5 out of 5 questions correctly.
FUNCTIONAL READINESS LEVEL INCREASE DURING COMPETITIVE PERIOD IN FEMALE FOOTBALL FOR STUDENTS
 UDC 796.015 DOI 10.14526/01_1111_16 FUNCTIONAL READINESS LEVEL INCREASE DURING COMPETITIVE PERIOD IN FEMALE FOOTBALL FOR STUDENTS Naboychenko E.S. candidate of economic sciences, associate professor Samoylov
UDC 796.015 DOI 10.14526/01_1111_16 FUNCTIONAL READINESS LEVEL INCREASE DURING COMPETITIVE PERIOD IN FEMALE FOOTBALL FOR STUDENTS Naboychenko E.S. candidate of economic sciences, associate professor Samoylov
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
Chapter 9. Producing Data: Experiments. BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1
 Chapter 9 Producing Data: Experiments BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1 Experiment versus Observational Study Both typically have the goal of detecting a relationship between the explanatory and response variables.
Chapter 9 Producing Data: Experiments BPS - 5th Ed. Chapter 9 1 Experiment versus Observational Study Both typically have the goal of detecting a relationship between the explanatory and response variables.
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory Diagnostic Procedures 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Bell Work Complete cost of smoking exercise. We will go over this together! (Don t worry)!
Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory Diagnostic Procedures 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Bell Work Complete cost of smoking exercise. We will go over this together! (Don t worry)!
DESIGN, ANALYSIS AND IMPLEMENTATION OF SPIROMETER
 DESIGN, ANALYSIS AND IMPLEMENTATION OF SPIROMETER Asmita Parve Mokal1, Dr. M.J. Sheikh2, Bipin D. Mokal3 1M Tech Student, Department of Mechanical Engg, B.D.C.O.E., Sevagram 442102 2Prof and HOD, Department
DESIGN, ANALYSIS AND IMPLEMENTATION OF SPIROMETER Asmita Parve Mokal1, Dr. M.J. Sheikh2, Bipin D. Mokal3 1M Tech Student, Department of Mechanical Engg, B.D.C.O.E., Sevagram 442102 2Prof and HOD, Department
Guidance. Name and describe the 4 types of guidance. What are the key features of each of the types of guidance?
 Skill What components make up skill? Describe a motor skill Explain what a skilled performer is What are the main characteristics of skilful movement? Classification What is a continuum? Describe a closed
Skill What components make up skill? Describe a motor skill Explain what a skilled performer is What are the main characteristics of skilful movement? Classification What is a continuum? Describe a closed
of sports performance
 Credit value: 10 Unit 11 Analysis of sports performance 11 Analysis of sports performance Coaches and athletes need to know how movement and physiology affect performance. There is also increasing awareness
Credit value: 10 Unit 11 Analysis of sports performance 11 Analysis of sports performance Coaches and athletes need to know how movement and physiology affect performance. There is also increasing awareness
UNIT 3 PACKET NAME: HOUR: DATE: NO: Chapter 11: Movement and Coordination SKELETAL SYSTEM UNIT 3 CHAPTER 11, CHAPTER 12, FETIG /STRYCZEK
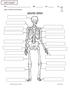 UNIT 3 PACKET NAME: HOUR: DATE: NO: 1 Chapter 11: Movement and Coordination SKELETAL SYSTEM 2 Functions of the Skeletal System The human body has bones. Label the parts of the bone. Below give the function
UNIT 3 PACKET NAME: HOUR: DATE: NO: 1 Chapter 11: Movement and Coordination SKELETAL SYSTEM 2 Functions of the Skeletal System The human body has bones. Label the parts of the bone. Below give the function
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
sphere A diameter / cm 1 3 (i) The student calculated the surface area: volume ratio of sphere B as 2:1.
 1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
1. A student investigated how the surface area of a single-celled organism is related to its volume. The student used two spheres, A and B, as models of two organisms. The surface area and volume of each
EFFECTS OF BADMINTON SPECIFIC CIRCUIT TRAINING ON SELECTED PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES OF BADMINTON PLAYERS AUTHOR
 PP: 85-98 R. Paper 12 V2/I -I/ Design: Experimental Received on Aug 2015 - Reviewed on Sept 2015 EFFECTS OF BADMINTON SPECIFIC CIRCUIT TRAINING ON SELECTED PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES OF BADMINTON PLAYERS
PP: 85-98 R. Paper 12 V2/I -I/ Design: Experimental Received on Aug 2015 - Reviewed on Sept 2015 EFFECTS OF BADMINTON SPECIFIC CIRCUIT TRAINING ON SELECTED PHYSIOLOGICAL VARIABLES OF BADMINTON PLAYERS
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet
 Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration And Circulation Reinforcement Worksheet Name: Sec: Date: Q1. MCQs. 1) Which type of blood vessels carries blood away from the heart? a) Veins b) Arteries c) Capillaries
THE EFFECTS OF REDUCED GAMES FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE QUALITY OF SPEED IN THE YOUNG ALGERIANS FOOTBALLERS
 European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1286323 Volume 4 Issue 7 2018 HE EFFECS OF REDUCED
European Journal of Physical Education and Sport Science ISSN: 2501-1235 ISSN-L: 2501-1235 Available on-line at: www.oapub.org/edu doi: 10.5281/zenodo.1286323 Volume 4 Issue 7 2018 HE EFFECS OF REDUCED
Vertical jump performance and anaerobic ATP resynthesis
 PDHPE Student Activities Comes to Life Energy Systems and Athlete Performance Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is required to perform any form of muscular contraction. Muscle cells only store enough ATP to
PDHPE Student Activities Comes to Life Energy Systems and Athlete Performance Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) is required to perform any form of muscular contraction. Muscle cells only store enough ATP to
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
What do pulmonary function tests tell you?
 Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
Pulmonary Function Testing Michael Wert, MD Assistant Professor Clinical Department of Internal Medicine Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical
10.1 The Pulmonary-Circulatory System
 pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
Content Indica c tion Lung v olumes e & Lung Indica c tions i n c paci c ties
 Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Spirometry Content Indication Indications in occupational medicine Contraindications Confounding factors Complications Type of spirometer Lung volumes & Lung capacities Spirometric values Hygiene &
Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number.
 Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY. A. Definition of Spirometry
 UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
UNIT TWO: OVERVIEW OF SPIROMETRY A. Definition of Spirometry Spirometry is a medical screening test that measures various aspects of breathing and lung function. It is performed by using a spirometer,
VCERT PE Final Test Revision
 VCERT PE Final Test Revision Skeletal System This one is known as the Condyloid Joint Definition: The point at which two or more bones meet to produce movement. Slightly Moveable Joints- spine Fix Joints-
VCERT PE Final Test Revision Skeletal System This one is known as the Condyloid Joint Definition: The point at which two or more bones meet to produce movement. Slightly Moveable Joints- spine Fix Joints-
Comparing the effect of physical activity on pulmonary function of Kerman s professional endurance runners and non-athletes
 International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 5 (12): 1552-1556 Science Explorer Publications Comparing the effect of physical
International Research Journal of Applied and Basic Sciences 2013 Available online at www.irjabs.com ISSN 2251-838X / Vol, 5 (12): 1552-1556 Science Explorer Publications Comparing the effect of physical
YOGIC BREATHING Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System
 YOGIC BREATHING Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System BREATHING Breath in, breath out. As long as you keep doing this you will never die! Breathing is an involuntary process. However unlike
YOGIC BREATHING Anatomy and Physiology of the Respiratory System BREATHING Breath in, breath out. As long as you keep doing this you will never die! Breathing is an involuntary process. However unlike
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
SSEH1103 Health, Physiology & Nutrition Lecture Notes
 SSEH1103 Health, Physiology & Nutrition Lecture Notes Lecture One: Health, Wellness and Physical Fitness 1. Define: a. health b. wellness c. fitness 2. Wellness: a. 6 dimensions 3. Fitness: a. role of
SSEH1103 Health, Physiology & Nutrition Lecture Notes Lecture One: Health, Wellness and Physical Fitness 1. Define: a. health b. wellness c. fitness 2. Wellness: a. 6 dimensions 3. Fitness: a. role of
Personal Career. Super Compensation-Theory 2 3 Exercise, recovery and nutrition. Circadian ( biological clock ) rhythm.
 Personal Career 0 "Exercise, nutrition and recovery; to super compensation in practice nowadays among young athletes - new aspects". Harri Hakkarainen MD, MSc ( sport physiology, - biomechanics and coaching
Personal Career 0 "Exercise, nutrition and recovery; to super compensation in practice nowadays among young athletes - new aspects". Harri Hakkarainen MD, MSc ( sport physiology, - biomechanics and coaching
BASIC AND SPECIAL PHYSICAL PREPARATION OF TOP TABLE TENNIS PLAYERS
 BASIC AND SPECIAL PHYSICAL PREPARATION OF TOP TABLE TENNIS PLAYERS Prof. Zoran Djokic coach of Yugoslav National Team. Faculty of Physical Education and Sport University - Novi Sad - Yugoslavia 1 Introduction
BASIC AND SPECIAL PHYSICAL PREPARATION OF TOP TABLE TENNIS PLAYERS Prof. Zoran Djokic coach of Yugoslav National Team. Faculty of Physical Education and Sport University - Novi Sad - Yugoslavia 1 Introduction
Chapter 10 Review [K/U] [T/I] [C] [A]
![Chapter 10 Review [K/U] [T/I] [C] [A] Chapter 10 Review [K/U] [T/I] [C] [A]](/thumbs/77/75865209.jpg) Chapter 10 Review [T/I] [C] [A] Knowledge For each question, select the best answer from the four alternatives. 1. Cells cannot carry out basic life functions without having a continuous supply of which
Chapter 10 Review [T/I] [C] [A] Knowledge For each question, select the best answer from the four alternatives. 1. Cells cannot carry out basic life functions without having a continuous supply of which
I. PHILOSOPHY AND GOALS
 I. PHILOSOPHY AND GOALS PHILOSOPHY Physical Education Philosophy The Belén Jesuit Physical Education Department's philosophy is concerned with developing the students' total physical and mental well being
I. PHILOSOPHY AND GOALS PHILOSOPHY Physical Education Philosophy The Belén Jesuit Physical Education Department's philosophy is concerned with developing the students' total physical and mental well being
RESPIRATION AND SLEEP AT HIGH ALTITUDE
 MANO Pulmonologist-Intensivis Director of ICU and Sleep Dis Evangelism Ath RESPIRATION AND SLEEP AT HIGH ALTITUDE 2 nd Advanced Course in Mountain Medicine MAY 25-27 OLYMPUS MOUNTAIN Respiration Breathing
MANO Pulmonologist-Intensivis Director of ICU and Sleep Dis Evangelism Ath RESPIRATION AND SLEEP AT HIGH ALTITUDE 2 nd Advanced Course in Mountain Medicine MAY 25-27 OLYMPUS MOUNTAIN Respiration Breathing
