Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review
|
|
|
- Maud Cain
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact: Rajdda@radiology.ufl.edu College of Medicine - University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, United States. Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to disclose
2 Outline 1. Simulation-SIM as assessment tool 2. Clinical and Neuroradiolgical findings of Non- Accidental Trauma (NAT) 3. Pitfalls Congenital infections Birth related injuries e.g. subdural tentorial hematomas 4. Search pattern to prevent observational errors 5. Assertive guidelines to call NAT to avoid cognitive errors 6. Recommended imaging plan for a follow up
3 Background Computer aided simulation (SIM) was developed and designed to test residents for readiness for call 8 hour simulation of 65 emergent & critical care cases of varying degrees of difficulty, including normal studies using full DICOM image sets SIM was taken by 127 first (R1) & second (R2) year residents from 16 USA radiology training programs
4 Results 75% of the residents either called the study normal (observational error) or gave an incorrect diagnosis (cognitive error) No significant difference between R1 and R2 residents with an average scores of 17 versus 25% respectively Conclusion: Significant observational and cognitive gap exists in detecting and differentiating NAT from other disease entities
5 Brain: Axial loading injury - Skull fracture High impact trauma - Skull base fracture & brain injury Penetrating trauma Shaking Injury - Diffuse axonal injury & SDH Shearing injury Venous tethering Asphyxiation/Hypoxic brain injury Long term sequelae - Global atrophy Spine Neuro NAT Manifestations Axial loading injury - Vertebral compression fracture Spinal cord injury
6 1 2 SIM Case % of the residents failed to make the diagnosis indicating the need to revisit the radiology of NAT Fig 1 - Extensive scalp hematoma (white arrows) with associated skull fracture (red arrows) Fig 2 - Right sided posterior rib fractures (yellow arrows), better identified on zooming (Fig 3) and changing windows (Fig 4)
7 Traditional Radiology Teaching of Neuro NAT Prominent extra-axial spaces (between purple arrows) predispose for extra-axial bleeding after getting shaken. Repetitive shaking leads to mixed age of extra-axial blood products (white arrows). Larger subdural hemorrhage (SDH) (white arrows) is an uncommon spontaneous event in infants. Other types of blood collections include: subpial (yellow arrow) & intradural (pink arrow) hemorrhage and subdural hygromas (purple arrows)
8 Fig 1 & 2 - Axial loaded skull fracture (red arrows) 1 Traditional Radiology Teaching of Neuro NAT 2 Typical transverse fracture of the temporal bone (red arrows) 3 4 Axial CT (Fig 3) shows transverse oriented fracture (pink arrow) with its complete extent better demonstrated with on the 3D reformation (Fig 4)
9 A complete review of the additional findings in NAT Cervical Spine/Cord Injury Most commonly from a shaking/ whiplash type mechanism May damage the lower brainstem and upper cervical cord Could present as apnea and hypoxia. Subdural and epidural cord hematomas, cord contusion and ligamentous rupture Cervical spine MRI must be performed if there is any clinical suspicion of shaking-type injury
10 Spinal Trauma Long segment spinal cord edema Axial loaded associated spinal column injury 1 2 Sagittal (Fig 1) & axial (Fig 2) T2 images reveal spinal cord edema extending from the foramen magnum to C7 level (red arrows) Lateral lumbar spine X-ray shows typical compression deformity of a vertebral body (white arrow) Teaching point: Cervical spine CT without bony injury is clearly underestimates the extent of cord injury
11 Shaking Injury Diffuse Axonal Injury preferentially affects Gray-white matter junctions Corpus callosum & basal ganglia Dorsolateral aspect of the pons & upper brainstem Shearing Injury causes Disruption of delicate cortical bridging veins as they leave the cortex to enter the dural venous sinuses, most commonly the superior sagittal sinus Subdural hematomas & hygromas
12 DWI Multiple areas of restricted diffusion along the right tentorial incisura, in the mesial right temporal lobe, right temporal pole, anterior frontal lobes bilaterally and adjacent to the cribriform plate (red arrows) Teaching Point: Diffuse axonal injury from shaking is usually multifocal and most often affects the gray-white matter junction, the corpus callosum, basal ganglia and the dorsolateral pons & upper brainstem
13 P1 Perforator (Shear) Injury DAI in a 2-Month-Old with History of SDH Teaching Point: Diffuse axonal injury is often subtle requiring special attention to SWI and DWI sequences P1 perforator distribution edema: a shear effect not a post herniation effect (yellow arrow) Figs 1 & 2 show a focus of microhemorrhage (white arrow) in the right frontal convexity and a left frontal acute SDH (red arrows) with foci of acute restriction in the left frontal lobe (yellow arrows) in Fig 3 &4
14 3-Month-Old with Seizures and Periorbital Bruising Figs 1 & 2 show dilated subarachnoid spaces (red arrows) with bridging veins (orange arrows) separating the subdural hygroma (pink arrow) from diffuse brain atrophy Post-contrasted T1 images (Figs 3 & 4) reveal extensive subdural enhancement with pial irritation suggestive of mixed age subdural & subarachnoid hemorrhage (white arrows) Teaching Point: Patients with diffuse atrophy from repetitive trauma may require contrast to differential acute from chronic injury
15 Hypoxic Ischemic Injury & Strangulation Asphyxiation/Hypoxic brain injury Strangulation Smothering Apnea associated w/ brain stem stretch injuries in infants Affects Whole brain if severe High ATP utilization zones if less severe
16 Hypoxic Ischemic Injury & Strangulation Hypoxic ischemic injury (HIE) Spares the basal ganglia, thalami brainstem and cerebellum Strangulation May affect unilateral watershed territory due to extrinsic compression of carotid artery Hemorrhagic laminar necrosis may occur 7-10 days after initial insult Must perform MRA to assess for vascular injury
17 10 Month Old with Seizures Fig 1shows bilateral, frontal SDH (red arrows) with parafalcine extension (white arrow) and focal areas of diffusion restriction in the subcortical white matter in the right MCA/ACA watershed zone (yellow arrows in Figs 2 & 3) Teaching Point: Strangulation often presents unilaterally and should trigger MRA of the neck to assess for vascular injury
18 Diffuse Brain Swelling (Dysautoregulation vs Hypoxia) 1 2 Initial CT scan (Fig 1) read as Normal. Follow up CT 24 hours later (Fig 2) reveals loss of grey white matter differentiation, diffuse hypodensity of the white matter and complete effacement of the sulci consistent with diffuse cerebral edema. Teaching Point: Causes of diffuse cerebral swelling include Diffuse primary injury (e.g. DAI) and metabolic derangement
19 11-Month-Old with Trauma Figs 1&2 show a large subgaleal hematoma (orange arrow) & upward transtentorial herniation (red arrow) due to diffuse edema causing effacement of the prepontine cisterns (yellow arrow) and diffuse sulcal effacement (pink arrows) Teaching Point: Serial imaging & comparisons to priors, if available, are critical for identification of early signs of diffuse edema / brain injury
20 Direct Impact Trauma High likelihood of skull fracture, best seen on 3D reconstruction Cortical contusion Focal parenchymal contusions & lacerations near scalp hematoma or fracture Traumatic SDH & subarachnoid hemorrhage tend to stem from direct disruption of vessels at fracture site
21 Unresponsive & Apneic Child Initial CT Axial, non-contrasted CT images reveal diffuse interhemispheric and tentorial SDH (red arrows) and developing subdural hygromas (yellow arrows) with no overt skull fractures or soft tissue hematoma
22 1 Unresponsive & Apneic Child Follow up MRI T1 (Fig 1 & 3) and FLAIR (Fig 2) show acute SDH (red arrows) superior to the transverse sinuses with significant enlargement of the panhemispheric subdural fluid collections (yellow arrows), as compared to the initial CT with minimal blood foci on T2* gradient imaging (white arrows in Fig 4)
23 Stabbing/Penetrating Trauma Similar potential findings as direct impact trauma Other complications include Intracerebral hematoma Posttraumatic aneurysm Carotid-cavernous fistula Arterial occlusion or venous thrombosis CSF leakage CT is recommended due to possible retained metallic foreign bodies
24 30-Day-Old with Trauma Coronal (Fig 1) and axial (Figs 2 & 3) CT images show hyperdensities in the subarachnoid spaces (red arrows) likely related to subcortical venous stasis and acute SDH & subarachnoid hemorrhage along the vertex. This is associated with diffuse loss of gray-white differentiation (yellow arrows) & effacement of the ventricles and sulci Teaching Point: Even when imaging clearly shows diffuse cerebral edema & HIE with its poor prognosis complete documentation of findings (e.g. fractures) is still needed for medical legal purposes.
25 3-Month-Old with Right Parietal Trauma Initial CT Fig 1shows extensive right facial & scalp hematoma (red arrows) with comminuted and displaced right parietal bone fracture (yellow arrows in Fig 2) and a small subjacent hemorrhagic contusion and edema (white arrow in Fig 3). This wedge-shaped defect in the pariental lobe in association with high energy impact is concerning for entrapped brain tissue in the adjacent fracture fragments.
26 3-Month-Old with Right Parietal Trauma MRI follow up 3 days later T1 and DWI images confirm the posttraumatic wedge-shaped defect extending from the right parietal cortex to the right ventricular trigone (red arrows) with a focus of entrapped brain tissue at the fracture site (yellow arrow) and small volume extra axial blood (white arrow) on the T2* gradient sequence Teaching Point: High velocity direct impact trauma tends to have a more focal distribution
27 Vertex tethering / laceration Linear blood in subcortical location on CT is consistent with brain laceration (red arrow) Widespread cortical & subcortical brain lacerations (yellow arrows) on DWI
28 31 Month-Old Boy after Fall Initial CT Fig 1 & 3 reveal a slightly depressed occipital bone fracture extending into the right temporal bone (red arrows). Fig 2 shows a small right cerebellar hemorrhage (yellow arrows) and a possible infarct (pink arrow). Fig 4 demonstrates right parietal occipital brain laceration (white arrow) subjacent to the skull fracture.
29 31 Month-Old Boy after Fall Follow up MRI Fig 1 & 2 illustrate increased conspicuity of the brain laceration (red arrows) with a new focus of diffusion restriction in the anterior temporal pole (yellow arrow). Fig 3 reveals more extensive right cerebellar hemorrhage (pink arrow) than indicated on the initial CT Teaching Point: CT may underestimate the extent of hemorrhage, as well as more subtle injuries away from the impact site
30 Long-Term Sequelae Metabolic insults lead to global atrophy, most commonly following diffuse cerebral edema (if the patient survives) Unexplained macrocephaly related to chronic subdural effusions (red arrows) producing an increased cranial volume Unexplained atrophy (pink arrows) & acute parafalcine SDH (yellow arrows)
31 1 2 Axial CT post NAT(Fig 1 & 2) shows decreased basal ganglia density (red arrows) & sulcal effacement (yellow arrows) related to hypoxic effects (confirmed at autopsy). In addition, there is a focal acute cortical hemorrhage (orange arrow) Initial DWI Brain stem injury apparent at 10 days follow up MR Initial DWI sequence shows few scattered foci of restricted diffusion (red arrows) with subtle involvement of the pons (yellow arrows) that becomes markedly more apparent on the follow up DWI 10 days later Alive at this time Dying at this time
32 Patient 1-HSV Infection Simulating NAT Patient 2- Birth Related SDH Simulating NAT Pitfalls in the diagnosis of NAT: Patient 1 - Mutlifocal areas of diffusion restriction (red arrows) consistent with DAI in this patient with suspicion for NAT that were proven to be caused HSV infection. Patient 2 Tentorial SDH (yellow arrows) was seen on a MRI done for postnatal HIE in this premature infant which should not be interpreted as NAT on follow up MRI
33 Importance of Follow up: Fatal sequelae of NAT Teaching Point: Routine follow up CTs are required n unresponsive patients in whom the clinical signs and symptoms are unreliable to detect the fatal complications. 5 6 Initial non contrast CT (Fig 1) shows a subdural catheter in the left parietal region in this unresponsive patient with known NAT. CT done 2 days later (Figs 2-4) reveal a large left MCA infarct (yellow arrows) with uncal herniation (orange arrow) Non contrast CT performed 9 days after the initial CT (Fig 5 & 6) shows hemorrhagic transformation of the left MCA infarct (white arrows).
34 Proposed Imaging Protocol by Jaspan et al. Suspected NAT CT Day 0 Days 1-2 Continued follow-up, as indicated Skull radiographs and Cranial US CT If neurologic symptoms & normal/equivocal CT Days 3-4 MRI: T1, T2, FLAIR and DWI T2*GRE or SWI Suspected Vascular Injury MRA At 10 days If intracranial abnormalities
35 Conclusions Traditional outlook for NAT in Neuroradiology Subdural collections in different stages Multiple fractures of skull; Mutiple Wormian bones/sutural diastases; Classic transverse fracture of the temporal bone Additional findings which all the Neuroradiologists need to look for are- Axial loading injury and spinal cord injury in spine In brain a range of injury pattern- DAI,Shearing injury, hypoxic injury, P1 perforator injury, delayed manifestations like large arterial territorial stroke, venous tethering and laceration
36 References Bradford, R., et al(2013). Serial neuroimaging in infants with abusive head trauma: Timing abusive injuries - Clinical article. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. Dwek, J. R. (2011). The radiographic approach to child abuse. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research. Fernando, S., et al (2008). Neuroimaging of nonaccidental head trauma: Pitfalls and controversies. Pediatric Radiology. Foerster, B.R. et al. Neuroimaging Evaluation of Non-Accidental Head Trauma with Correlation to Clinical Outcomes: A Review of 57 Cases. The Journal of pediatrics (2009). Hsieh, K. L.-C., et al (2015). Revisiting neuroimaging of abusive head trauma in infants and young children. AJR. Kemp, A. M., et al (2011). Neuroimaging: what neuroradiological features distinguish abusive from non-abusive head trauma? A systematic review. Archives of Disease in Childhood. Tung, G., et al (2006). Comparison of accidental and nonaccidental traumatic head injury in children on noncontrast computed tomography. Pediatrics. Lonergan, G. J., et al( 2003). From the Archives of the AFIP. Child Abuse: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation RadioGraphics. Piteau, S. J., et all(2012). Clinical and Radiographic Characteristics Associated With Abusive and Nonabusive Head Trauma: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics.
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Classical CNS Disease Patterns
 Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Classical CNS Disease Patterns Inflammatory Traumatic In response to the trauma of having his head bashed in GM would have experienced some of these features. NOT TWO LITTLE PEENY WEENY I CM LACERATIONS.
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of
 L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of Radiology RSNA Annual Meeting 2016 Trainee call readiness
L M Thornton, MD; L Lanier, MD; C L Sistrom, MD; D Rajderkar, MD; A Mancuso, MD; IM Schmalfuss, MD University of Florida, Gainesville Department of Radiology RSNA Annual Meeting 2016 Trainee call readiness
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
Causes: 2. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage A. Saccular (berry) aneurysm - Is the most frequent cause of clinically significant subarachnoid hemorrhage is rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm. B. Vascular malformation
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
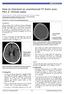 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma.
 Neuroimaging of vascular/secondary secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma. Andrès Server Alonso Department of Neuroradiology Division of Radiology Ullevål University Hospital Oslo, Norway. Guidelines
Neuroimaging of vascular/secondary secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma. Andrès Server Alonso Department of Neuroradiology Division of Radiology Ullevål University Hospital Oslo, Norway. Guidelines
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA and Subarachnoid Hemorrhage By: Shifaa AlQa qa Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Causes: Rupture of a saccular (berry) aneurysm Vascular malformation Trauma Hematologic disturbances
Neuropathology Of Head Trauma. Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center
 Neuropathology Of Head Trauma Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center Nothing to disclose Disclosure Introduction 500,000 cases/year of serious head injury
Neuropathology Of Head Trauma Mary E. Case, M.D. Professor of Pathology St. Louis University Health Sciences Center Nothing to disclose Disclosure Introduction 500,000 cases/year of serious head injury
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 3 Bleeds and hemorrhages K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
CT - Brain Examination
 CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
CT - Brain Examination Submitted by: Felemban 1 CT - Brain Examination The clinical indication of CT brain are: a) Chronic cases (e.g. headache - tumor - abscess) b) ER cases (e.g. trauma - RTA - child
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management
 Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Intracranial spontaneous hemorrhage mechanisms, imaging and management Dora Zlatareva Department of Diagnostic Imaging Medical University, Sofia, Bulgaria Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) ICH 15% of strokes
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
 Revisited imaging findings and pathophysiology of abusive head trauma with emphasis on diffusionweighted imaging (eede-219) I. Elhelf *, R. Oral, T. Sato, A. Capizzano, Y. Sato, M. Amarneh, T. Sasaki,
Revisited imaging findings and pathophysiology of abusive head trauma with emphasis on diffusionweighted imaging (eede-219) I. Elhelf *, R. Oral, T. Sato, A. Capizzano, Y. Sato, M. Amarneh, T. Sasaki,
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE
 THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
Meninges and Ventricles
 Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Meninges and Ventricles Irene Yu, class of 2019 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Describe the meningeal layers, the dural infolds, and the spaces they create. Name the contents of the subarachnoid space. Describe the
Head trauma - interpreting CT scans
 Head trauma - interpreting CT scans Poster No.: C-2075 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. Rihtar; Zagreb/HR Keywords: Trauma, Hemorrhage, Edema, Diagnostic procedure, CT, Neuroradiology
Head trauma - interpreting CT scans Poster No.: C-2075 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. Rihtar; Zagreb/HR Keywords: Trauma, Hemorrhage, Edema, Diagnostic procedure, CT, Neuroradiology
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know. 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012
 Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Recurrent Subdural Hematomas in Benign Macrocrania of Infancy
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Medical & Clinical DOI: 10.21767/2471-299X.100032 Recurrent Subdural Hematomas in Benign Macrocrania of Infancy Ademar Lucas Junior São Camilo Diagnostic
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Medical & Clinical DOI: 10.21767/2471-299X.100032 Recurrent Subdural Hematomas in Benign Macrocrania of Infancy Ademar Lucas Junior São Camilo Diagnostic
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE
 THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
THE ROLE OF IMAGING IN DIAGNOSIS OF SUBDURAL HEMATOMA: REVIEW ARTICLE * Dr. Sumendra Raj Pandey, Prof. Dr. Liu Pei WU, Dr. Sohan Kumar Sah, Dr. Lalu Yadav, Md. Sadam Husen Haque and Rajan KR. Chaurasiya
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma
 Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma Rebecca Girardet Associate Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Child Protection Pediatrics McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center
Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma Rebecca Girardet Associate Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Child Protection Pediatrics McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center
Pathological reaction to disease
 Chapter1 Pathological reaction to disease Normal anatomy Figures 1.1 1.6 2 4 Brain swelling and internal herniation Figures 1.7 1.15 5 9 Epilepsy Figures 1.16 1.18 9 10 Cerebellar atrophy Figures 1.19
Chapter1 Pathological reaction to disease Normal anatomy Figures 1.1 1.6 2 4 Brain swelling and internal herniation Figures 1.7 1.15 5 9 Epilepsy Figures 1.16 1.18 9 10 Cerebellar atrophy Figures 1.19
The clinical scenario in this patient has been well reviewed by expert witnesses.
 September 29, 2014 Michael J. Cronkright, Esq. Kronzek & Cronkight, PLLC 420 S. Waverly Road, Suite 100 Lansing, MI 48917 Re: Preliminary Report on Naomi Burns Dear Mr. Cronkright, I have reviewed all
September 29, 2014 Michael J. Cronkright, Esq. Kronzek & Cronkight, PLLC 420 S. Waverly Road, Suite 100 Lansing, MI 48917 Re: Preliminary Report on Naomi Burns Dear Mr. Cronkright, I have reviewed all
STROKE - IMAGING. Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli.
 STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
STROKE - IMAGING Dr RAJASEKHAR REDDY 2nd Yr P.G. RADIODIAGNOSIS KIMS,Narkatpalli. STROKE Describes a clinical event that consists of sudden onset of neurological symptoms Types Infarction - occlusion of
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Cerebral Vascular Diseases. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Cerebral Vascular Diseases Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD Outline I. Stroke statistics II. Cerebral circulation III. Clinical symptoms of stroke IV. Pathogenesis of cerebral infarcts (Stroke) 1. Ischemic - Thrombotic
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists.
 Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage
 July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
July 2013 A Guide to the Radiologic Evaluation of Extra-Axial Hemorrhage John Dickson, Harvard Medical School Year III Agenda 1. Define extra-axial hemorrhage and introduce its subtypes 2. Review coup
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4
 NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4 Strokes and infarcts K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
NEURORADIOLOGY DIL part 4 Strokes and infarcts K. Agyem MD, G. Hall MD, D. Palathinkal MD, Alexandre Menard March/April 2015 OVERVIEW Introduction to Neuroimaging - DIL part 1 Basic Brain Anatomy - DIL
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment
 Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Diagnosis and Treatment John W. Engstrom MD, Philip R. Weinstein MD, and William P. Dillon M.D. University of California, San Francisco Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN. Scalp, Skull. Anatomically Based Differentials. Skull Normal Variants. Scalp Mass, Child.
 Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN
 Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN History of Marshall scale Proposed by Marshall, et al in 1991 to classify head
Marshall Scale for Head Trauma Mark C. Oswood, MD PhD Department of Radiology Hennepin County Medical Center, Minneapolis, MN History of Marshall scale Proposed by Marshall, et al in 1991 to classify head
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
What Are We Going to Do? Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy. Hydrocephalus and Effects of Interruption of CSF Flow. Tube Blockage Doctrine
 Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
Fourth Year Meds Clinical Neuroanatomy Ventricles, CSF, Brain Swelling etc. David A. Ramsay, Neuropathologist, LHSC What Are We Going to Do? Hydrocephalus and some effects of the interruption of CSF flow
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES
 TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries
 Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
PA SYLLABUS. Syllabus for students of the FACULTY OF MEDICINE No.2
 Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Marc Norman, Ph.D. - Do Not Use without Permission 1. Cerebrovascular Accidents. Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry
 Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Cerebrovascular Accidents Marc Norman, Ph.D. Department of Psychiatry Neuropsychiatry and Behavioral Medicine Neuropsychology Clinical Training Seminar 1 5 http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/images/ency/fullsize/18009.jpg
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes
 Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
North Oaks Trauma Symposium Friday, November 3, 2017
 Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
Traumatic Intracranial Hemorrhage Aaron C. Sigler, DO, MS Neurosurgery Tulane Neurosciences None Disclosures Overview Anatomy Epidural hematoma Subdural hematoma Cerebral contusions Outline Traumatic ICH
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
Stroke School for Internists Part 1
 Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
Stroke School for Internists Part 1 November 4, 2017 Dr. Albert Jin Dr. Gurpreet Jaswal Disclosures I receive a stipend for my role as Medical Director of the Stroke Network of SEO I have no commercial
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]
![[(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD] [(PHY-3a) Initials of MD reviewing films] [(PHY-3b) Initials of 2 nd opinion MD]](/thumbs/89/98619893.jpg) 2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
2015 PHYSICIAN SIGN-OFF (1) STUDY NO (PHY-1) CASE, PER PHYSICIAN REVIEW 1=yes 2=no [strictly meets case definition] (PHY-1a) CASE, IN PHYSICIAN S OPINION 1=yes 2=no (PHY-2) (PHY-3) [based on all available
Acute Ischaemic Stroke
 Acute Ischaemic Stroke CT or MR SCA READIG FORM SCA ID: DATE OF READIG: SCA QUALIT: Good Moderate Poor Comment: READER ID: TPE OF SCA: CT: Without contrast: With contrast: MR: Diffusion: Perfusion ote
Acute Ischaemic Stroke CT or MR SCA READIG FORM SCA ID: DATE OF READIG: SCA QUALIT: Good Moderate Poor Comment: READER ID: TPE OF SCA: CT: Without contrast: With contrast: MR: Diffusion: Perfusion ote
MRI Imaging of GP Medicare Eligible Conditions
 MRI Imaging of GP Medicare Eligible Conditions By Dr. Andrew Stuart Radiologist Sydney Adventist Hospital 0562/SAH/1112/SAH Learning Objectives Indications for GP referred Medicare eligible MRI scans MRI
MRI Imaging of GP Medicare Eligible Conditions By Dr. Andrew Stuart Radiologist Sydney Adventist Hospital 0562/SAH/1112/SAH Learning Objectives Indications for GP referred Medicare eligible MRI scans MRI
Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma
 July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
July, 2005 Imaging of Acute Cerebral Trauma Louis Rivera, Harvard Medical School, Year III 46 y/o Female s/p Trauma - Unrestrained? MVC requiring Med Flight - Facial bruising/swelling - DEEP COMA - SEIZURES
Traumatic Brain Injury TBI Presented by Bill Masten
 1 2 Cerebrum two hemispheres and four lobes. Cerebellum (little brain) coordinates the back and forth ballet of motion. It judges the timing of every movement precisely. Brainstem coordinates the bodies
1 2 Cerebrum two hemispheres and four lobes. Cerebellum (little brain) coordinates the back and forth ballet of motion. It judges the timing of every movement precisely. Brainstem coordinates the bodies
Traumatic brain injuries are caused by external mechanical forces such as: - Falls - Transport-related accidents - Assault
 PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
PP2231 Brain injury Cerebrum consists of frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes Diencephalon consists of thalamus, hypothalamus Cerbellum Brain stem consists of midbrain, pons, medulla Central
Radiological investigations
 Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Paravertebral calcification as a potential indicator for nonaccidental trauma
 Paravertebral calcification as a potential indicator for nonaccidental trauma Katsuaki Kojima 1*, Jennifer Nimtz 1, Steven W Martin 1, Stephen R Guertin 1, Ellen C Cavenagh 2 1. Department of Pediatrics
Paravertebral calcification as a potential indicator for nonaccidental trauma Katsuaki Kojima 1*, Jennifer Nimtz 1, Steven W Martin 1, Stephen R Guertin 1, Ellen C Cavenagh 2 1. Department of Pediatrics
Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms
 Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms P. Ellen Grant MD Associate Professor of Radiology, HMS Director, Center for Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging & Developmental Science Children s
Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms P. Ellen Grant MD Associate Professor of Radiology, HMS Director, Center for Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging & Developmental Science Children s
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Insults to the Term Brain
 Insults to the Term Brain Monica Epelman, MD mepelman@nemours.org Literature comparing US and MR has deficiencies Retrospective studies Long time interval between US and MR exams in the same patient
Insults to the Term Brain Monica Epelman, MD mepelman@nemours.org Literature comparing US and MR has deficiencies Retrospective studies Long time interval between US and MR exams in the same patient
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019. Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students,2019 Dr Heyam Awad Lecture 2: Disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CASE 1. Female 21 years old DOL: November 28, 2016
 CASE 1 Female 21 years old DOL: November 28, 2016 Injuries and Sequelae: GCS: 4 / 15 and coma for 3 weeks Multifocal intracranial hemorrhage at right thalamus and left frontal and temporal lobe Diffuse
CASE 1 Female 21 years old DOL: November 28, 2016 Injuries and Sequelae: GCS: 4 / 15 and coma for 3 weeks Multifocal intracranial hemorrhage at right thalamus and left frontal and temporal lobe Diffuse
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
Blood Supply of the CNS
 Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
Blood Supply of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the four arteries supplying the CNS. Follow up each artery to its destination. Describe the circle of Willis and its branches. Discuss the principle
CEREBRAL INFARCTION AS NEUROSURGICAL POST OPERATIVE COMPLICATION : SERIAL CASES
 CEREBRAL INFARCTION AS NEUROSURGICAL POST OPERATIVE COMPLICATION : SERIAL CASES Oleh Ferry Wijanarko, dr, Sp BS DR Agus Turchan, dr, Sp BS BEDAH SARAF SOLO Secretariat : Neurosurgery Subdivision Dr Moewardi
CEREBRAL INFARCTION AS NEUROSURGICAL POST OPERATIVE COMPLICATION : SERIAL CASES Oleh Ferry Wijanarko, dr, Sp BS DR Agus Turchan, dr, Sp BS BEDAH SARAF SOLO Secretariat : Neurosurgery Subdivision Dr Moewardi
Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
It has been demonstrated that postmortem MDCT, or virtual
 Published April 5, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2966 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.B. Smith G.E. Lattin Jr P. Berran H.T. Harcke Common and Expected Postmortem CT Observations Involving the Brain: Mimics of Antemortem
Published April 5, 2012 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2966 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.B. Smith G.E. Lattin Jr P. Berran H.T. Harcke Common and Expected Postmortem CT Observations Involving the Brain: Mimics of Antemortem
Tips and tricks for detecting diffuse axonal injury on CT and MR neuroimaging
 Tips and tricks for detecting diffuse axonal injury on CT and MR neuroimaging Poster No.: C-3080 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Marinkic, D. Zadravec ; Zagreb/HR, Zageb/HR Keywords:
Tips and tricks for detecting diffuse axonal injury on CT and MR neuroimaging Poster No.: C-3080 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Marinkic, D. Zadravec ; Zagreb/HR, Zageb/HR Keywords:
Case Conference: Neuroradiology. Case 1: Tumor Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures
 Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Case Conference: Neuroradiology Case 1: 22yo F w/ HA and prior Seizures David E. Rex, MD, PhD Stanford University Hospital Department of Radiology Case 1: Tumor Most likely gangiloglioma, oligodendroglioma,
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings. Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD
 Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Typical idiopathic intracranial hypertension Optic nerve appearance and brain MRI findings Jonathan A. Micieli, MD Valérie Biousse, MD A 24 year old African American woman is referred for bilateral optic
Acute stroke imaging
 Acute stroke imaging Aims Imaging modalities and differences Why image acute stroke Clinical correlation to imaging appearance What is stroke Classic definition: acute focal injury to the central nervous
Acute stroke imaging Aims Imaging modalities and differences Why image acute stroke Clinical correlation to imaging appearance What is stroke Classic definition: acute focal injury to the central nervous
Traumatic Brain Injuries
 Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
Traumatic Brain Injuries Scott P. Sherry, MS, PA-C, FCCM Assistant Professor Department of Surgery Division of Trauma, Critical Care and Acute Care Surgery DISCLOSURES Nothing to disclose Discussion of
Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous structures - Significant thoracic inj
 PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
Unit #3: Dry Lab A. David A. Morton, Ph.D.
 Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
Unit #3: Dry Lab A David A. Morton, Ph.D. Skull Intracranial Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Epidural Hematoma Pg. 26 Skull Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subdural Hematoma Pg. 26 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Pg. 26 Subarachnoid
